Molecular Profiling of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus-Associated Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Cutaneous Melanoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Samples
2.2. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.3. DNA Isolation
2.4. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Molecular Detection
2.5. BRAF StripAssay
2.6. Next-Generation Sequencing
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Presentations
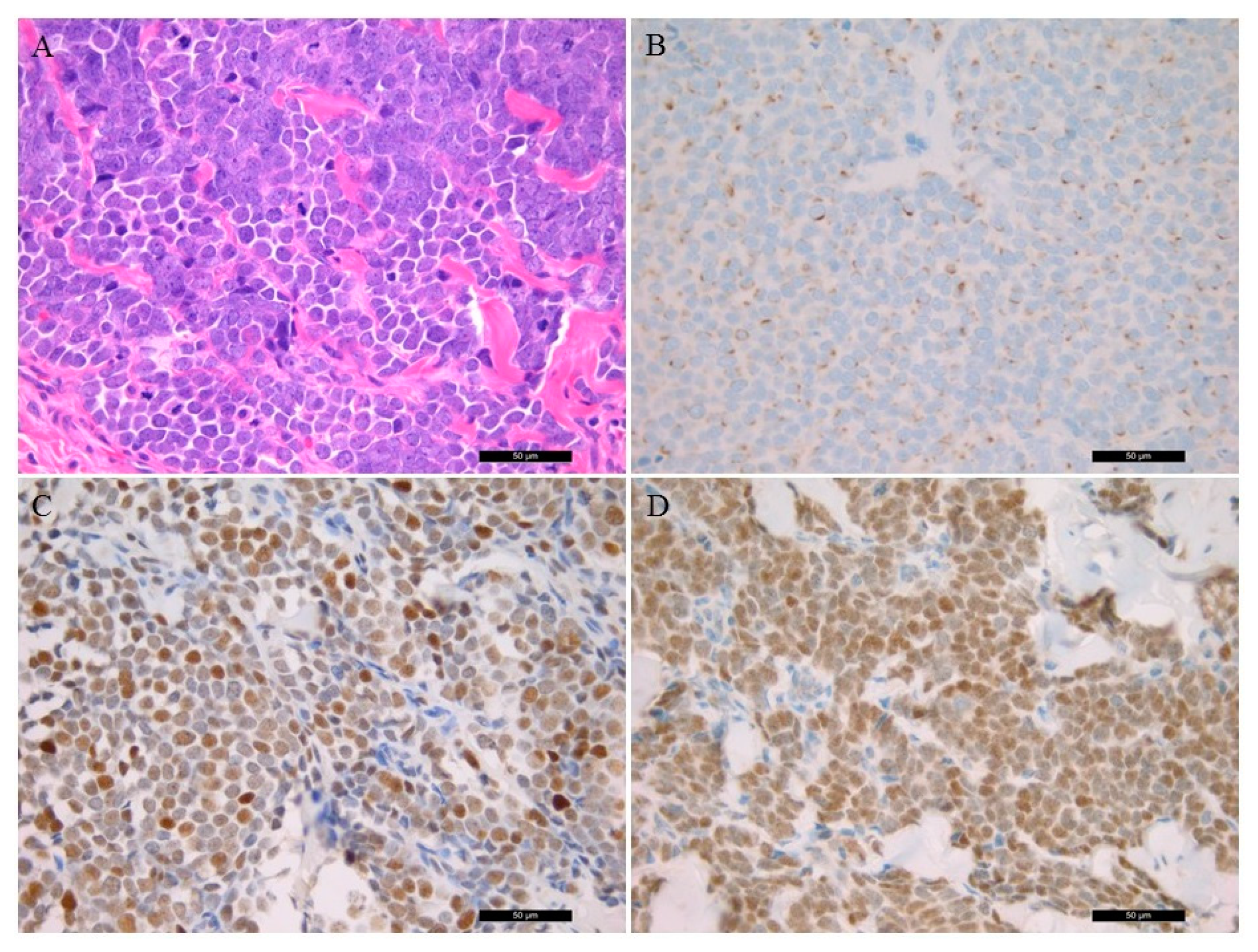
3.2. Histological Features Including Immunohistochemistry
3.3. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Detection
3.4. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Amplification in Melanoma Samples
3.5. NGS-Based Mutation Profiling
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harms, K.L.; Healy, M.A.; Nghiem, P.; Sober, A.J.; Johnson, T.M.; Bichakjian, C.K.; Wong, S.L. Analysis of Prognostic Factors from 9387 Merkel Cell Carcinoma Cases Forms the Basis for the New 8th Edition AJCC Staging System. Ann. Surg Oncol. 2016, 23, 3564–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, P.W. Update on Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Lab. Med. 2017, 37, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coggshall, K.; Tello, T.L.; North, J.P.; Yu, S.S. Merkel Cell Carcinoma: An Update and Review: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Staging. J. Am. Acad Derm. 2018, 78, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agelli, M.; Clegg, L.X.; Becker, J.C.; Rollison, D.E. The Etiology and Epidemiology of Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2010, 34, 14–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, T.L.; Dennis, S.; Kachare, S.D.; Vohra, N.A.; Wong, J.H.; Zervos, E.E. Dramatic Increase in the Incidence and Mortality from Merkel Cell Carcinoma in the United States. Am. Surg. 2015, 81, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tetzlaff, M.T.; Harms, P.W. Danger Is Only Skin Deep: Aggressive Epidermal Carcinomas. An Overview of the Diagnosis, Demographics, Molecular-Genetics, Staging, Prognostic Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Advances in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Shuda, M.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S. Clonal Integration of a Polyomavirus in Human Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Science 2008, 319, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshiri, A.S.; Doumani, R.; Yelistratova, L.; Blom, A.; Lachance, K.; Shinohara, M.M.; Delaney, M.; Chang, O.; McArdle, S.; Thomas, H.; et al. Polyomavirus-Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A More Aggressive Subtype Based on Analysis of 282 Cases Using Multimodal Tumor Virus Detection. J. Investig. Derm. 2017, 137, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andea, A.A.; Patel, R.; Ponnazhagan, S.; Kumar, S.; DeVilliers, P.; Jhala, D.; Eltoum, I.E.; Siegal, G.P. Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Correlation of KIT Expression with Survival and Evaluation of KIT Gene Mutational Status. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, V.; Song, Y.; Santamaria-Barria, J.A.; Cosper, A.K.; Lam, Q.; Faber, A.C.; Boland, G.M.; Yeap, B.Y.; Bergethon, K.; Scialabba, V.L.; et al. Activation of PI3K Signaling in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuromi, T.; Matsushita, M.; Iwasaki, T.; Nonaka, D.; Kuwamoto, S.; Nagata, K.; Kato, M.; Akizuki, G.; Kitamura, Y.; Hayashi, K. Association of Expression of the Hedgehog Signal with Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Infection and Prognosis of Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 69, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.Q.; Waldeck, K.; Vergara, I.A.; Schröder, J.; Madore, J.; Wilmott, J.S.; Colebatch, A.J.; De Paoli-Iseppi, R.; Li, J.; Lupat, R.; et al. UV-Associated Mutations Underlie the Etiology of MCV-Negative Merkel Cell Carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 5228–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, G.; Walradt, T.; Markarov, V.; Blom, A.; Riaz, N.; Doumani, R.; Stafstrom, K.; Moshiri, A.; Yelistratova, L.; Levinsohn, J.; et al. Mutational Landscape of MCPyV-Positive and MCPyV-Negative Merkel Cell Carcinomas with Implications for Immunotherapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3403–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harms, P.W.; Harms, K.L.; Moore, P.S.; DeCaprio, J.A.; Nghiem, P.; Wong, M.K.K.; Brownell, I.; International Workshop on Merkel Cell Carcinoma Research (IWMCC) Working Group. The Biology and Treatment of Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Current Understanding and Research Priorities. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, E.; Kiss, M.; Szabó, K.; Kemény, L. Detection of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus DNA in Merkel Cell Carcinomas. Br. J. Derm. 2009, 161, 930–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirikanjanapong, S.; Melamed, J.; Patel, R.R. Intraepidermal and Dermal Merkel Cell Carcinoma with Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Situ: A Case Report with Review of Literature. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2010, 37, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuda, M.; Arora, R.; Kwun, H.J.; Feng, H.; Sarid, R.; Fernández-Figueras, M.-T.; Tolstov, Y.; Gjoerup, O.; Mansukhani, M.M.; Swerdlow, S.H.; et al. Human Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Infection I. MCV T Antigen Expression in Merkel Cell Carcinoma, Lymphoid Tissues and Lymphoid Tumors. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.S.; Choi, Y.-L.; Choi, J.-S.; Roh, J.H.; Pyon, J.K.; Woo, K.-J.; Lee, E.H.; Jang, K.-T.; Han, J.; Park, C.-S.; et al. Detection of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus in Merkel Cell Carcinomas and Small Cell Carcinomas by PCR and Immunohistochemistry. Histol. Histopathol. 2011, 26, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitz, M.; Stieler, K.; Grundhoff, A.; Moll, I.; Brandner, J.M.; Fischer, N. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Detection in Merkel Cell Cancer Tumors in Northern Germany Using PCR and Protein Expression. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux-Kozal, V.; Lévêque, N.; Brodard, V.; Lesage, C.; Dudez, O.; Makeieff, M.; Kanagaratnam, L.; Diebold, M.-D. Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Histopathologic and Prognostic Features According to the Immunohistochemical Expression of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Large T Antigen Correlated with Viral Load. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swick, B.L.; Srikantha, R.; Messingham, K.N. Specific Analysis of KIT and PDGFR-Alpha Expression and Mutational Status in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2013, 40, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Figueras, M.T.; Puig, L.; Musulen, E.; Gilaberte, M.; Ferrándiz, C.; Lerma, E.; Ariza, A. Prognostic Significance of P27Kip1, P45Skp2 and Ki67 Expression Profiles in Merkel Cell Carcinoma, Extracutaneous Small Cell Carcinoma, and Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Histopathology 2005, 46, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, S.A.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; Pattanaprichakul, P.; Fox, P.; Torres-Cabala, C.A.; Bassett, R.L.; Prieto, V.G.; Richards, H.W.; Curry, J.L. Detection of Mitotic Figures and G2+ Tumor Nuclei with Histone Markers Correlates with Worse Overall Survival in Patients with Merkel Cell Carcinoma. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2014, 41, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, D.L.; Frieling, G.W. Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Review and Update on Current Concepts. Diagn. Histopathol. 2016, 22, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwun, H.J.; Shuda, M.; Feng, H.; Camacho, C.J.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Controls Viral Replication and Oncoprotein Expression by Targeting the Cellular Ubiquitin Ligase SCFFbw7. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, K.L.; Lazo de la Vega, L.; Hovelson, D.H.; Rahrig, S.; Cani, A.K.; Liu, C.-J.; Fullen, D.R.; Wang, M.; Andea, A.A.; Bichakjian, C.K.; et al. Molecular Profiling of Multiple Primary Merkel Cell Carcinoma to Distinguish Genetically Distinct Tumors From Clonally Related Metastases. JAMA Derm. 2017, 153, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrama, D.; Peitsch, W.K.; Zapatka, M.; Kneitz, H.; Houben, R.; Eib, S.; Haferkamp, S.; Moore, P.S.; Shuda, M.; Thompson, J.F.; et al. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Status Is Not Associated with Clinical Course of Merkel Cell Carcinoma. J. Investig. Derm. 2011, 131, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knepper, T.C.; Montesion, M.; Russell, J.S.; Sokol, E.S.; Frampton, G.M.; Miller, V.A.; Albacker, L.A.; McLeod, H.L.; Eroglu, Z.; Khushalani, N.I.; et al. The Genomic Landscape of Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Clinicogenomic Biomarkers of Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5961–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koburger, I.; Meckbach, D.; Metzler, G.; Fauser, U.; Garbe, C.; Bauer, J. Absence of Merkel Cell Polyoma Virus in Cutaneous Melanoma. Exp. Derm. 2011, 20, 78–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmbold, P.; Lahtz, C.; Herpel, E.; Schnabel, P.A.; Dammann, R.H. Frequent Hypermethylation of RASSF1A Tumour Suppressor Gene Promoter and Presence of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 2207–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katano, H.; Ito, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Sato, Y.; Tsuji, T.; Matsuo, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Sata, T. Detection of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus in Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Kaposi’s Sarcoma. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1951–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworkin, A.M.; Tseng, S.Y.; Allain, D.C.; Iwenofu, O.H.; Peters, S.B.; Toland, A.E. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Immunocompetent Individuals. J. Investig. Derm. 2009, 129, 2868–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassem, A.; Technau, K.; Kurz, A.K.; Pantulu, D.; Löning, M.; Kayser, G.; Stickeler, E.; Weyers, W.; Diaz, C.; Werner, M.; et al. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Sequences Are Frequently Detected in Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer of Immunosuppressed Patients. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csoboz, B.; Rasheed, K.; Sveinbjørnsson, B.; Moens, U. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus and Non-Merkel Cell Carcinomas: Guilty or Circumstantial Evidence? APMIS 2020, 128, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiman, A.; Kikuchi, H.; Scocchia, D.; Smith, P.; Tsang, Y.W.; Snead, D.; Cree, I.A. Validation of an NGS Mutation Detection Panel for Melanoma. BMC Cancer 2017, 17, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.-L.; Zhou, L.; Sadri, N. Comparison of Targeted next Generation Sequencing (NGS) versus Isolated BRAF V600E Analysis in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. Virchows Arch. 2018, 473, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, I.; Simi, L.; Salvianti, F.; Castiglione, F.; Sonnati, G.; Pinzani, P. Analytical Evaluation of an NGS Testing Method for Routine Molecular Diagnostics on Melanoma Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tumor-Derived DNA. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Patient | Gender | Age (years) | Location | Size (cm) | Depth (cm) | Treatment | Metastasis | Survival (Month) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 89 | left knee | 4 | 1 | excision and chemotherapy | n.a. | 7 |
| 2 | M | 80 | right face | 1.5 | 0.9 | excision | lost follow-up | |
| 3 | M | 88 | right chest | 2.2 | 0.5 | excision | lost follow-up | |
| 4 | F | 68 | left shoulder | 1.1 | 0.7 | neoadjuvant chemotherapy | axillary lymph node | 24 |
| 5 | M | 83 | right thigh | 2.4 | 2.2 | excision | lost follow-up | |
| 6 | M | 76 | right 3rd finger | 1 | 6.7 | excision | n.a. | 9 |
| 7 | F | 85 | right face | 1.4 | 1.6 | radiotherapy | lost follow-up | |
| 8 | F | 63 | right gluteus | 2 | 0.4 | radiotherapy | n.a. | 6 |
| 9 | M | 68 | right forearm | 6 | 1 | excision | lymp node | 3 |
| Cases | Lymphocyte Infiltration | Ki-67 (%) | Cytokeratin 20 | Synaptophysin | Chromogranin A | Thyroid Transcription Factor 1 | p53 | MCPyV IHC | LT1 PCR | LT3 PCR | VP1 PCR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | low | 60 | + | + | + | - | diffuse + | + | - | + | + |
| 2 | low | 60 | + | + | + | - | patchy + | + | - | + | + |
| 3 | low | 50 | + | + | - | - | diffuse + | - | - | - | + |
| 4 | low | 60 | dot-like | marked | marked | - | - | diffuse + | - | + | - |
| 5 | low | 80 | dot-like | marked | focal | - | weakly + | - | - | - | - |
| 6 | moderate | 70 | dot-like | marked | marked | - | - | patchy + | - | + | - |
| 7 | low | 60 | dot-like | dot-like | dot-like | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 8 | moderate | 70 | dot-like | + | patchy + | - | diffuse + | - | - | + | - |
| 9 | low | 60 | dot-like | dot-like | dot like | - | patchy + | diffuse + | - | + | + |
| Scheme | Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Nucleotide Change | Amino Acid Change | Variant Allele Frequency (%) | Clinical Sgnificance | COSMIC ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 (+) | RB1 | retinoblastoma 1 | c.2033A>T | p.His678Leu | 48 | no data available | - |
| S2 (+) | STK11 | serine/threonine kinase 11 | c.1062C>G | p.Phe354Leu | 54.55 | neutral | COSM21360 |
| S3 (+) | EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor | c.2137G>A | p.Glu713Lys | 30.25 | no data available | - |
| FBXW7 | F-box/WD repeat-containing protein 7 | c.1031C>T | p.Ser344Phe | 89.3 | COSM1177864 | ||
| TP53 | tumor protein P53 | c.832C>T | p.Pro278Ser | 92.4 | pathogenic | COSM10939 | |
| S4 (+) | CTNNB1 | catenin beta-1 | c.59C>T | p.Ala20Val | 9 | pathogenic | COSM5702 |
| S5 (-) | CDKN2A | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A | c.442G>A | p.Ala148Thr | 50 | neutral | COSM3774362 |
| FGFR1 | fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | c.2181-6C>T | - | 48.6 | no data available | - | |
| S6 (+) | ABL1 | tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 | c.740A>G | p.Lys247Arg | 42.1 | benign | - |
| FOXL2 | forkhead box protein L2 | c.536C>G | p.Ala179Gly | 65.3 | benign | COSM4600643 | |
| HNF1A | hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 A | c.864del | p.Pro291GlnfsTer51 | 7.5 | pathogenic | COSM935974 | |
| S7 (-) | no mutation detected | ||||||
| S8 (+) | JAK3 | Janus kinase 3 | c.2164G>A | p.Val722Ile | 42.5 | neutral | COSM34213 |
| S9 (+) | TP53 | tumor protein P53 | c.-28-4G>A | - | 4.5 | no data available | - |
| M1 (+) | BRAF | serine/threonine kinase BRAF | c.1799_1800delinsAA | p.Val600Glu | 40 | pathogenic | COSM475 |
| PIK3CA | phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate 3-kinase | c.1031T>C | p.Val344Ala | 13.4 | pathogenic | COSM86951 | |
| STK11 | serine/threonine kinase 11 | c.1211C>T | p.Ser404Phe | 35.1 | no data available | - | |
| M2 (+) | BRAF | serine/threonine kinase BRAF | c.1799T>A | p.Val600Glu | 22.2 | pathogenic | COSM476 |
| CDKN2A | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A | c.169dup | p.Ala57GlyfsTer63 | 20.6 | pathogenic | COSM110662 | |
| SMAD4 | mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4 | c.122A>G | p.Glu41Gly | 5.7 | no data available | - | |
| M3 (+) | BRAF | serine/threonine kinase BRAF | c.1799T>A | p.Val600Glu | 15.4 | pathogenic | COSM476 |
| APC | adenomatous polyposis coli | c.3949G>C | p.Glu1317Gln | 50 | pathogenic | COSM19099 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mokánszki, A.; Méhes, G.; Csoma, S.L.; Kollár, S.; Chang Chien, Y.-C. Molecular Profiling of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus-Associated Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Cutaneous Melanoma. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020212
Mokánszki A, Méhes G, Csoma SL, Kollár S, Chang Chien Y-C. Molecular Profiling of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus-Associated Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Cutaneous Melanoma. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(2):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020212
Chicago/Turabian StyleMokánszki, Attila, Gábor Méhes, Szilvia Lilla Csoma, Sándor Kollár, and Yi-Che Chang Chien. 2021. "Molecular Profiling of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus-Associated Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Cutaneous Melanoma" Diagnostics 11, no. 2: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020212
APA StyleMokánszki, A., Méhes, G., Csoma, S. L., Kollár, S., & Chang Chien, Y.-C. (2021). Molecular Profiling of Merkel Cell Polyomavirus-Associated Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Cutaneous Melanoma. Diagnostics, 11(2), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020212






