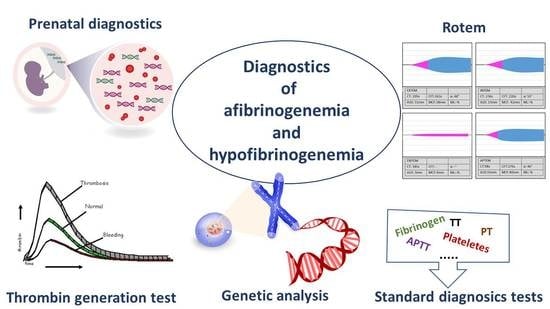
Congenital Afibrinogenemia and Hypofibrinogenemia: Laboratory and Genetic Testing in Rare Bleeding Disorders with Life-Threatening Clinical Manifestations and Challenging Management
Abstract
:1. Classification and Terminology of Congenital Fibrinogen Disorders
2. Structure and Function of Fibrinogen
3. Epidemiology and Clinical Features
4. Laboratory Assays
5. Genetics of Afibrinogenemia and Hypofibrinogenemia
6. Genetic Diagnosis and Antenatal Diagnosis
7. Treatment
Management of Thrombotic Complications
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simurda, T.; Brunclikova, M.; Asselta, R.; Caccia, S.; Zolkova, J.; Kolkova, Z.; Loderer, D.; Skornova, I.; Hudecek, J.; Lasabova, Z.; et al. Genetic Variants in the FGB and FGG Genes Mapping in the Beta and Gamma Nodules of the Fibrinogen Molecule in Congenital Quantitative Fibrinogen Disorders Associated with a Thrombotic Phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moerloose, P.; Casini, A.; Neerman-Arbez, M. Congenital Fibrinogen Disorders: An Update. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2013, 39, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mumford, A.D.; Ackroyd, S.; Alikhan, R.; Bowles, L.; Chowdary, P.; Grainger, J.; Mainwaring, J.; Mathias, M.; O′Connell, N.; BCSH Committee. Guideline for the diagnosis and management of the rare coagulation disorders: A United Kingdom Haemophilia Centre Doctors′ Organization guideline on behalf of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 167, 304–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyvandi, F.; Di Michele, D.; Bolton-Maggs, P.H.; Lee, C.A.; Tripodi, A.; Srivastava, A. Classification of rare bleeding disorders (RBDs) based on the association between coagulant factor activity andclinical bleeding severity. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 1938–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziomalos, K.; Vakalopoulou, S.; Perifanis, V.; Garipidou, V. Treatment of congenital fibrinogen deficiency: Overview and recent findings. Vasc. Heal. Risk Manag. 2009, 5, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vakalopoulou, S.; Rizopoulou, D.; Zafiriadou, E.; Perifanis, V.; Tziomalos, K.; Lefkou, E.; Hill, M.; Dolan, G.; Garipidou, V. Management of acute bleeding in a patient with congenital afibrinogenaemia. Haemophilia 2006, 12, 676–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, A.; Undas, A.; Palla, R.; Thachil, J.; De Moerloose, P.; Subcommittee on Factor XIII and Fibrinogen. Diagnosis and classification of congenital fibrinogen disorders: Communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 1887–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moerloose, P.; Neerman-Arbez, M.; Casini, A. Clinical Features and Management of Congenital Fibrinogen Deficiencies. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2016, 42, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snahnicanova, Z.; Loderer, D.; Sokol, J.; Stasko, J.; Lasabova, Z.; Kubisz, P.; Simurda, T. Fibrinogen Martin: A Novel Mutation in FGB (Gln180Stop) Causing Congenital Afibrinogenemia. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2016, 42, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simurda, T.; Stanciakova, L.; Stasko, J.; Dobrotova, M.; Kubisz, P. Yes or no for secondary prophylaxis in afibrinogenemia? Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2015, 26, 978–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, M.A.; Işik, B.; Patiroglu, T.; Karakukcu, M.; Mutlu, F.T.; Yilmaz, E.; Unal, E. A case of congenital afibrinogenemia complicated with thromboembolic events that required repeated amputations. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2015, 26, 354–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simurda, T.; Casini, A.; Stasko, J.; Hudecek, J.; Skornova, I.; Vilar, R.; Neerman-Arbez, M.; Kubisz, P. Perioperative management of a severe congenital hypofibrinogenemia with thrombotic phenotype. Thromb. Res. 2020, 188, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asselta, R.; Paraboschi, E.M.; Duga, S. Hereditary Hypofibrinogenemia with Hepatic Storage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, D.; de Moerloose, P.; Batorova, A.; Lazur, J.; Palumbo, L.; Neerman-Arbez, M. Hypofibrinogenaemia caused by a novel FGG missense mutation (W253C) in the gamma chain globular domain impairing fibrinogen secretion. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollman, J.M.; Pandi, L.; Sawaya, M.R.; Riley, M.; Doolittle, R.F. Crystal structure of human fibrinogen. Biochemistry 2009, 4, 3877–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kadiry, A.E.-H.; Merhi, Y. The Role of the Proteasome in Platelet Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neerman-Arbez, M.; De Moerloose, P.; Casini, A. Laboratory and Genetic Investigation of Mutations Accounting for Congenital Fibrinogen Disorders. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2016, 42, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiscia, G.L.; Margaglione, M. Human Fibrinogen: Molecular and Genetic Aspects of Congenital Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simurda, T.; Caccia, S.; Asselta, R.; Zolkova, J.; Stasko, J.; Skornova, I.; Snahnicanova, Z.; Loderer, D.; Lasabova, Z.; Kubisz, P. Congenital hypofibrinogenemia associated with a novel heterozygous nonsense mutation in the globular C-terminal domain of the γ-chain (p.Glu275Stop). J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2019, 50, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neerman-Arbez, M.; Casini, A. Clinical Consequences and Molecular Bases of Low Fibrinogen Levels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mackie, I.J.; Kitchen, S.; Machin, S.J.; Lowe, G.D.O. Haemostasis and Thrombosis Task Force of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Guidelines on fibrinogen assays. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 121, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skornova, I.; Simurda, T.; Stasko, J.; Horvath, D.; Zolkova, J.; Holly, P.; Brunclikova, M.; Samos, M.; Bolek, T.; Schnierer, M.; et al. Use of Fibrinogen Determination Methods in Differential Diagnosis of Hypofibrinogenemia and Dysfibrinogenemia. Clin. Lab. 2021, 67, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simurda, T.; Zolkova, J.; Snahnicanova, Z.; Loderer, D.; Skornova, I.; Sokol, J.; Hudecek, J.; Stasko, J.; Lasabova, Z.; Kubisz, P. Identification of Two Novel Fibrinogen Bβ Chain Mutations in Two Slovak Families with Quantitative Fibrinogen Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asselta, R.; Duga, S.; Tenchini, M.L. The molecular basis of quantitative fibrinogen disorders. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 2115–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilar, R.; Fish, R.J.; Casini, A.; Neerman-Arbez, M. Fibrin(ogen) in human disease: Both friend and foe. Haematologica 2020, 105, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luyendyk, J.P.; Schoenecker, J.G.; Flick, M.J. The multifaceted role of fibrinogen in tissue injury and inflammation. Blood 2019, 133, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korte, W.; Poon, M.C.; Iorio, A.; Makris, M. Thrombosis in Inherited Fibrinogen Disorders. Transfus. Med. Hemotherapy 2017, 44, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palla, R.; Peyvandi, F.; Shapiro, A.D. Rare bleeding disorders: Diagnosis and treatment. Blood 2015, 125, 2052–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyvandi, F.; Palla, R.; Menegatti, M.; Siboni, S.M.; Halimeh, S.; Faeser, B.; Pergantou, H.; Platokouki, H.; Giangrande, P.; Peerlinck, K.; et al. Coagulation factor activity and clinical bleeding severity in rare bleeding disorders: Results from the European Network of Rare Bleeding Disorders. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Report on the WFH Annual Global Survey 2019. Available online: https://elearning.wfh.org/resource/report-on-the-annual-global-survey-2019/pdf-1714.pdf (accessed on 11 June 2021).
- Mannucci, P.M.; Duga, S.; Peyvandi, F. Recessively inherited coagulation disorders. Blood 2004, 104, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naz, A.; Biswas, A.; Khan, T.N.; Goodeve, A.; Ahmed, N.; Saqlain, N.; Ahmed, S.; Ujjan, I.D.; Shamsi, T.S.; Oldenburg, J. Identification of novel mutations in congenital afibrinogenemia patients and molecular modeling of missense mutations in Pakistani population. Thromb. J. 2017, 15, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lissitchkov, T.; Madan, B.; Djambas Khayat, C.; Zozulya, N.; Ross, C.; Karimi, M.; Kavakli, K.; De Angulo, G.R.; Almomen, A.; Subramanian, K.; et al. Fibrinogen concentrate for treatment of bleeding and surgical prophylaxis in congenital fibrinogen deficiency patients. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peyvandi, F. Epidemiology and treatment of congenital fibrinogen deficiency. Thromb. Res. 2012, 130, S7–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, A.; von Mackensen, S.; Santoro, C.; Djambas Khayat, C.; Belhani, M.; Ross, C.; Dorgalaleh, A.; Naz, A.; Ünal, E.; Abdelwahab, M.; et al. Clinical phenotype, fibrinogen supplementation, and health-related quality of life in patients with afibrinogenemia. Blood 2021, 137, 3127–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraboschi, E.M.; Duga, S.; Asselta, R. Fibrinogen as a Pleiotropic Protein Causing Human Diseases: The Mutational Burden of Aα, Bβ, and γ Chains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peyvandi, F.; Haertel, S.; Knaub, S.; Mannucci, P.; Mancuso, G. Incidence of bleeding symptoms in 100 patients with inherited afibrinogenaemia or hypofibrinogenaemia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1634–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaman, Y.; Isguder, R.; Demirag, B.; Agin, H.; Ozek, G.; Tatl, B.G.; Albudak, E.; Berksoy, E. Spontaneous epidural and subdural hematoma in a child with afibrinogenemia and postoperative management. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2014, 25, 398–400. [Google Scholar]
- Casini, A.; de Moerloose, P. Can the phenotype of inherited fibrinogen disorders be predicted? Haemophilia 2016, 22, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubisz, P.; Dobrotova, M.; Necas, L.; Stasko, J.; Simurda, T. Perioperative Coagulation Management in a Patient with Congenital Afibrinogenemia during Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2016, 42, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Özdemir, Ö.; Sarı, M.E.; Kurt, A.; Şen, E.; Atalay, C.R. Recurrent massive haemoperitoneum associated with ruptured corpus luteum in women with congenital afibrinogenemia; case report. Turk. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 11, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Merchan, E.C. Surgical wound healing in bleeding disorders. Haemophilia 2012, 18, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casini, A.; Brungs, T.; Lavenu-Bombled, C.; Vilar, R.; Neerman-Arbez, M.; De Moerloose, P. Genetics, diagnosis and clinical features of congenital hypodysfibrinogenemia: A systematic literature review and report of a novel mutation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soares, A.W.; Maia, M.; Santo, J.E.; Costa, A.P.; Pereira, A.; Catarino, C. Hypofibrinogenemia: A case od spontaneous bleeding and central venous thrombosis in the same lifetime. EJCRIM 2020, 7, 1424. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, X.; Teng, Y. Women with Congenital Hypofibrinogenemia/Afibrinogenemia: From Birth to Death. Clin. Appl. Thromb. 2020, 26, 1076029620912819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Saez, A. Occurrence of Thrombosis in Rare Bleeding Disorders. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2013, 39, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, S.; Reddy, B.; Nagesh, C.; Srinivas, B.; Manjunath, C. Recurrent myocardial infarction in a case of congenital Afibrinogenemia. Hear. Views 2014, 15, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukaddam, A.; Patil, R.; Jadli, A.; Chandrakala, S.; Ghosh, K.; Shetty, S. Paradoxical Bleeding and Thrombosis in a Patient with Afibrinogenemia and Fibrinogen Mumbai Mutation. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 143, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Moerloose, P.; Boehlen, F.; Neerman-Arbez, M. Fibrinogen and the risk of thrombosis. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2010, 36, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselta, R.; Platè, M.; Robusto, M.; Borhany, M.; Guella, I.; Soldà, G.; Afrasiabi, A.; Menegatti, M.; Tahir, S.; Peyvandi, F.; et al. Clinical and molecular characterisation of 21 patients affected by quantitative fibrinogen deficiency. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 113, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teresa, S.M.; Marta, M.; Emiliano, D.B.; Mariangela, F.; Raffaele, P.; Ezio, Z. Thrombosis of abdominal aorta in congenital afibrinogenaemia: Case report and review of literature. Haemophilia 2015, 21, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B.; Chen, N.; Sun, G.; Guo, X. Congenital fibrinogen disorders with repeated thrombosis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2020, 49, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.S.; Dimichele, D.M. Rare inherited disorders of fibrinogen. Haemophilia 2008, 14, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casini, A. From Routine to Research Laboratory: Strategies for the Diagnosis of Congenital Fibrinogen Disorders. Hamostaseologie 2020, 40, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton-Maggs, P.H.B.; Perry, D.J.; Chalmers, E.A.; Parapia, L.A.; Wilde, J.T.; Williams, M.D.; Collins, P.W.; Kitchen, S.; Dolan, G.; Mumford, A.D. The rare coagulation disorders—Review with guidelines for management from the United Kingdom Haemophilia Centre Doctors′ Organisation. Haemophilia 2004, 10, 593–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simurda, T.; Vilar, R.; Zolkova, J.; Ceznerova, E.; Kolkova, Z.; Loderer, D.; Neerman-Arbez, M.; Casini, A.; Brunclikova, M.; Skornova, I.; et al. A Novel Nonsense Mutation in FGB (c.1421G>A; p.Trp474Ter) in the Beta Chain of Fibrinogen Causing Hypofibrinogenemia with Bleeding Phenotype. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miesbach, W.; Schenk, J.; Alesci, S.; Lindhoff-Last, E. Comparison of the fibrinogen Clauss assay and the fibrinogen PT derived method in patients with dysfibrinogenemia. Thromb. Res. 2010, 126, e428–e433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Luo, M.; Yan, J.; Liao, L.; Zhou, W.; Deng, X.; Deng, D.; Cheng, P.; Lin, F. Combined use of Clauss and prothrombin time-derived methods for determining fibrinogen concentrations: Screening for congenital dysfibrinogenemia. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2017, 32, e22322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simurda, T.; Zolkova, J.; Kolkova, Z.; Loderer, D.; Dobrotova, M.; Skornova, I.; Brunclíkova, M.; Grendar, M.; Lasabova, Z.; Stasko, J.; et al. Comparison of clinical phenotype with genetic and laboratory results in 31 patients with congenital dysfibrinogenemia in northern Slovakia. Int. J. Hematol. 2020, 111, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krammer, B.; Anders, O.; Nagel, H.R.; Burstein, C.; Steiner, M. Screening of dysfibrinogenaemia using the fibrinogen function versus antigen concentration ratio. Thromb. Res. 1994, 76, 577–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.R.; Escobar, M.A. Less common congenital disorders of hemostasis. In Consultative Hemostasis and Thrombosis; Kitchens, C.S., Alving, B.M., Kessler, C.M., Eds.; W.B. Saunders Co: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002; pp. 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, J.H.; Goodnough, L.T. How I use fibrinogen replacement therapy in acquired bleeding. Blood 2015, 125, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bornikova, L.; Peyvandi, F.; Allen, G.; Bernstein, J.; Manco-Johnson, M.J. Fibrinogen replacement therapy for congenital fibrinogen deficiency. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2011, 9, 1687–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogami, K. The utility of thromboelastography in inherited and acquired bleeding disorders. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 174, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalina, U.; Stöhr, H.-A.; Bickhard, H.; Knaub, S.; Siboni, S.M.; Mannucci, P.M.; Peyvandi, F. Rotational thromboelastography for monitoring of fibrinogen concentrate therapy in fibrinogen deficiency. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2008, 19, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.T.; Nascimento, B.; Beckett, A. Thromboelastography and Thromboelastometry in Assessment of Fibrinogen Deficiency and Prediction for Transfusion Requirement: A Descriptive Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 7020539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunakanan, S.; Akaraborworn, O.; Sangthong, B.; Thongkhao, K. Correlation between Maximum Clot Firmness in FIBTEM and Fibrinogen Level in Critical Trauma Patients. Crit. Care Res. Pr. 2019, 2019, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Vries, J.J.; Veen, C.S.B.; Snoek, C.J.M.; Kruip, M.J.H.A.; de Maat, M.P.M. FIBTEM clot firmness parameters correlate well with the fibrinogen concentration measured by the Clauss assay in patients and healthy subjects. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2020, 80, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.; Rangarajan, S.; Karimi, M.; Toogeh, G.; Apte, S.; Lissitchkov, T.; Acharya, S.; Manco-Johnson, M.J.; Srivastava, A.; Brand, B.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, clot strength and safety of a new fibrinogen concentrate: Randomized comparison with active control in congenital fibrinogen deficiency. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyvandi, F. Results of an international, multicentre pharmacokinetic trial in congenital fibrinogen deficiency. Thromb. Res. 2009, 124, S9–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treliński, J.; Pachniewska, K.; Matczak, J.; Robak, M.; Chojnowski, K. Assessment of Selected ROTEM Parameters, Kinetics of Fibrinogen Polymerization and Plasmin Amidolytic Activity in Patients with Congenital Fibrinogen Defects. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 25, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duarte, R.C.F.; Ferreira, C.N.; Rios, D.R.A.; dos Reis, H.J.; Carvalho, M.D.G. Thrombin generation assays for global evaluation of the hemostatic system: Perspectives and limitations. Rev. Bras. de Hematol. e Hemoter. 2017, 39, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrier, C.; Shima, M.; Hoffman, M. The central role of thrombin in bleeding disorders. Blood. Rev. 2019, 38, 100582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripodi, A. Thrombin Generation Assay and Its Application in the Clinical Laboratory. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szanto, T.; Lassila, R.; Lemponen, M.; Lehtinen, E.; Neerman-Arbez, M.; Casini, A. Whole Blood Thromboelastometry by ROTEM and Thrombin Generation by Genesia According to the Genotype and Clinical Phenotype in Congenital Fibrinogen Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casini, A.; Neerman-Arbez, M.; de Moerloose, P. Heterogeneity of congenital afibrinogenemia, from epidemiology to clinical consequences and management. Blood Rev. 2020, 48, 100793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, A.; Blondon, M.; Tintillier, V.; Goodyer, M.; Sezgin, M.E.; Gunes, A.M.; Hanss, M.; de Moerloose, P.; Neerman-Arbez, M. Mutational Epidemiology of Congenital Fibrinogen Disorders. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 118, 1867–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simeoni, I.; Stephens, J.C.; Hu, F.; Deevi, S.V.; Megy, K.; Bariana, T.K.; Lentaigne, C.; Schulman, S.; Sivapalaratnam, S.; Vries, M.J.; et al. A high-throughput sequencing test for diagnosing inherited bleeding, thrombotic, and platelet disorders. Blood 2016, 127, 2791–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Downes, K.; Megy, K.; Duarte, D.; Vries, M.; Gebhart, J.; Hofer, S.; Shamardina, O.; Deevi, S.V.V.; Stephens, J.; Mapeta, R.; et al. Diagnostic high-throughput sequencing of 2396 patients with bleeding, thrombotic, and platelet disorders. Blood 2019, 134, 2082–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moret, A.; Zúñiga, Á.; Ibáñez, M.; Cid, A.R.; Haya, S.; Ferrando, F.; Blanquer, A.; Cervera, J.; Bonanad, S. Clinical and molecular characterization by next generation sequencing of Spanish patients affected by congenital deficiencies of fibrinogen. Thromb. Res. 2019, 180, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bor, M.V.; Feddersen, S.; Pedersen, I.S.; Sidelmann, J.J.; Kristensen, S.R. Dysfibrinogenemia-Potential Impact of Genotype on Thrombosis or Bleeding. Semin. Thromb. Hemost 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibian, S.; Shams, M.; Naderi, M.; Dorgalaleh, A. Prenatal diagnosis in rare bleeding disorders-An unresolved issue? Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2018, 4, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neerman-Arbez, M.; Vu, D.; Abu-Libdeh, B.; Bouchardy, I.; Morris, M.A. Prenatal diagnosis for congenital afibrinogenemia caused by a novel nonsense mutation in the FGB gene in a Palestinian family. Blood 2003, 101, 3492–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Callum, J.; Farkouh, M.E.; Scales, D.C.; Heddle, N.M.; Crowther, M.; Rao, V.; Hucke, H.; Carroll, J.; Grewal, D.; Brar, S.; et al. Effect of Fibrinogen Concentrate vs Cryoprecipitate on Blood Component Transfusion After Cardiac Surgery: The FIBRES Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2019, 322, 1966–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, B.; Goodnough, L.T.; Levy, J.H. Cryoprecipitate therapy. Br. J. Anaesth. 2014, 113, 922–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ross, C.R.; Subramanian, S.; Navarro-Puerto, J.; Subramanian, K.; Kalappanavar, N.K.; Khayat, C.D.; Acharya, S.S.; Peyvandi, F.; Rucker, K.; Liang, W.; et al. Pharmacokinetics, surrogate efficacy and safety evaluations of a new human plasma-derived fibrinogen concentrate (FIB Grifols) in adult patients with congenital afibrinogenemia. Thromb. Res. 2021, 199, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casini, A.; de Moerloose, P. Fibrinogen concentrates in hereditary fibrinogen disorders: Past, present and future. Haemophilia 2020, 26, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margaglione, M.; Vecchione, G.; Cappucci, F.; Macarini, L.; D′Andrea, G.; Di Matteo, C.; Grandone, E. Venous thrombosis in afibrinogenemia: A successful use of rivaroxaban. Haemophilia 2015, 21, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaman, G. Prophylaxis of bleeding episodes and surgical interventions in patients with rare inherited coagulation disorders. Blood. Transf. 2008, 6, S39–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Type and Subtypes Quantitative Fibrinogen Disorders | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Afibrinogenemia | |
| A. Afibrinogenemia | Afibrinogenemia and bleeding phenotype or asymptomatic individuals |
| B. Afibrinogenemia with a thrombotic phenotype | Afibrinogenemia and thrombotic phenotype |
| Hypofibrinogenemia | |
| A. Severe hypofibrinogenemia | Functional fibrinogen level ˂0.5 g/L |
| B. Moderate hypofibrinogenemia | Functional fibrinogen level between 0.5–0.9 g/L |
| C. Mild hypofibrinogenemia | Functional fibrinogen level between 1.0 g/L and lower limit of normal level |
| D. Hypofibrinogenemia with fibrinogen storage disease | Congenital hypofibrinogenemia with histologically proven accumulation of fibrin in hepatocytes |
| Diagnostic Procedures | Afibrinogenemia | Hypofibrinogenemia |
|---|---|---|
| Prothrombin time (PT) | extremely prolonged | prolonged/normal—depending on fibrinogen levels |
| Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) | extremely prolonged | prolonged/normal—depending on fibrinogen levels |
| Thrombin time (TT) | extremely prolonged | prolonged/normal—depending on fibrinogen levels |
| Reptilase time (RT) | extremely prolonged | prolonged/normal—depending on fibrinogen levels |
| Fibrinogen activity (FBG: F (Clauss)) | undetectable | proportional decrease |
| Fibrinogen antigen (FBG: Ag) | undetectable | proportional decrease |
| PT-derived fibrinogen assay | undetectable | decrease, proportional to fibrinogen levels |
| Genotype (FGA, FGB, FGG genes) | ||
| Global hemostasis tests (research laboratories) | ||
| Number of Mutations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Mutation Type | FGA | FGB | FGG |
| Missense | 54 | 55 | 100 |
| Nonsense | 25 | 12 | 4 |
| Splicing | 11 | 7 | 9 |
| Regulatory | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Small deletions | 28 | 8 | 15 |
| Small insertions | 11 | 2 | 0 |
| Small indels | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Gross deletions | 5 | 1 | 1 |
| Gross insertions/duplications | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Complex rearrangements | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Total (public HGMD repository) | 142 | 90 | 131 |
| (169) | (107) | (153) | |
| Number of Mutations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Disease/Phenotype | FGA | FGB | FGG |
| Afibrinogenemia | 55 | 24 | 14 |
| Dysfibrinogenemia | 38 | 17 | 50 |
| Renal amyloidosis | 14 | 0 | 0 |
| Hypofibrinogenemia | 13 | 30 | 41 |
| Fibrinogen variant | 4 | 3 | 7 |
| Susceptibility to venous thromboembolism | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Decreased fibrinogen levels? | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| Decreased fibrinogen levels | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Hypodysfibrinogenemia | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| Afibrinogenaemia? | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| Afibrinogenemia/hypofibrinogenemia | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Afibrinogenemia with recurrent venous thromboembolism | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Amyloidosis, Ostertag-type | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Deep vein thrombosis? | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Dysfibrinogenemia? | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Hemorrhages | 1 | 3 | 0 |
| Association with increased post-stroke mortality | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Menorrhagia | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Thrombosis | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Venous thromboembolism? | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Association with cerebral infarction | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Epistaxis | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Hypofibrinogenaemia? | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Association with increased clot stiffness | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Increased plasma fibrinogen levels | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Thrombotic tendency | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Protection against venous thromboembolism | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Increased risk for deep venous thrombosis | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Hypofibrinogenaemia with hepatic storage | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Total (public HGMD repository) | 142 | 90 | 131 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simurda, T.; Asselta, R.; Zolkova, J.; Brunclikova, M.; Dobrotova, M.; Kolkova, Z.; Loderer, D.; Skornova, I.; Hudecek, J.; Lasabova, Z.; et al. Congenital Afibrinogenemia and Hypofibrinogenemia: Laboratory and Genetic Testing in Rare Bleeding Disorders with Life-Threatening Clinical Manifestations and Challenging Management. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112140
Simurda T, Asselta R, Zolkova J, Brunclikova M, Dobrotova M, Kolkova Z, Loderer D, Skornova I, Hudecek J, Lasabova Z, et al. Congenital Afibrinogenemia and Hypofibrinogenemia: Laboratory and Genetic Testing in Rare Bleeding Disorders with Life-Threatening Clinical Manifestations and Challenging Management. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(11):2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112140
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimurda, Tomas, Rosanna Asselta, Jana Zolkova, Monika Brunclikova, Miroslava Dobrotova, Zuzana Kolkova, Dusan Loderer, Ingrid Skornova, Jan Hudecek, Zora Lasabova, and et al. 2021. "Congenital Afibrinogenemia and Hypofibrinogenemia: Laboratory and Genetic Testing in Rare Bleeding Disorders with Life-Threatening Clinical Manifestations and Challenging Management" Diagnostics 11, no. 11: 2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112140
APA StyleSimurda, T., Asselta, R., Zolkova, J., Brunclikova, M., Dobrotova, M., Kolkova, Z., Loderer, D., Skornova, I., Hudecek, J., Lasabova, Z., Stasko, J., & Kubisz, P. (2021). Congenital Afibrinogenemia and Hypofibrinogenemia: Laboratory and Genetic Testing in Rare Bleeding Disorders with Life-Threatening Clinical Manifestations and Challenging Management. Diagnostics, 11(11), 2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112140