Machine Learning Consensus Clustering Approach for Hospitalized Patients with Dysmagnesemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Data Collection
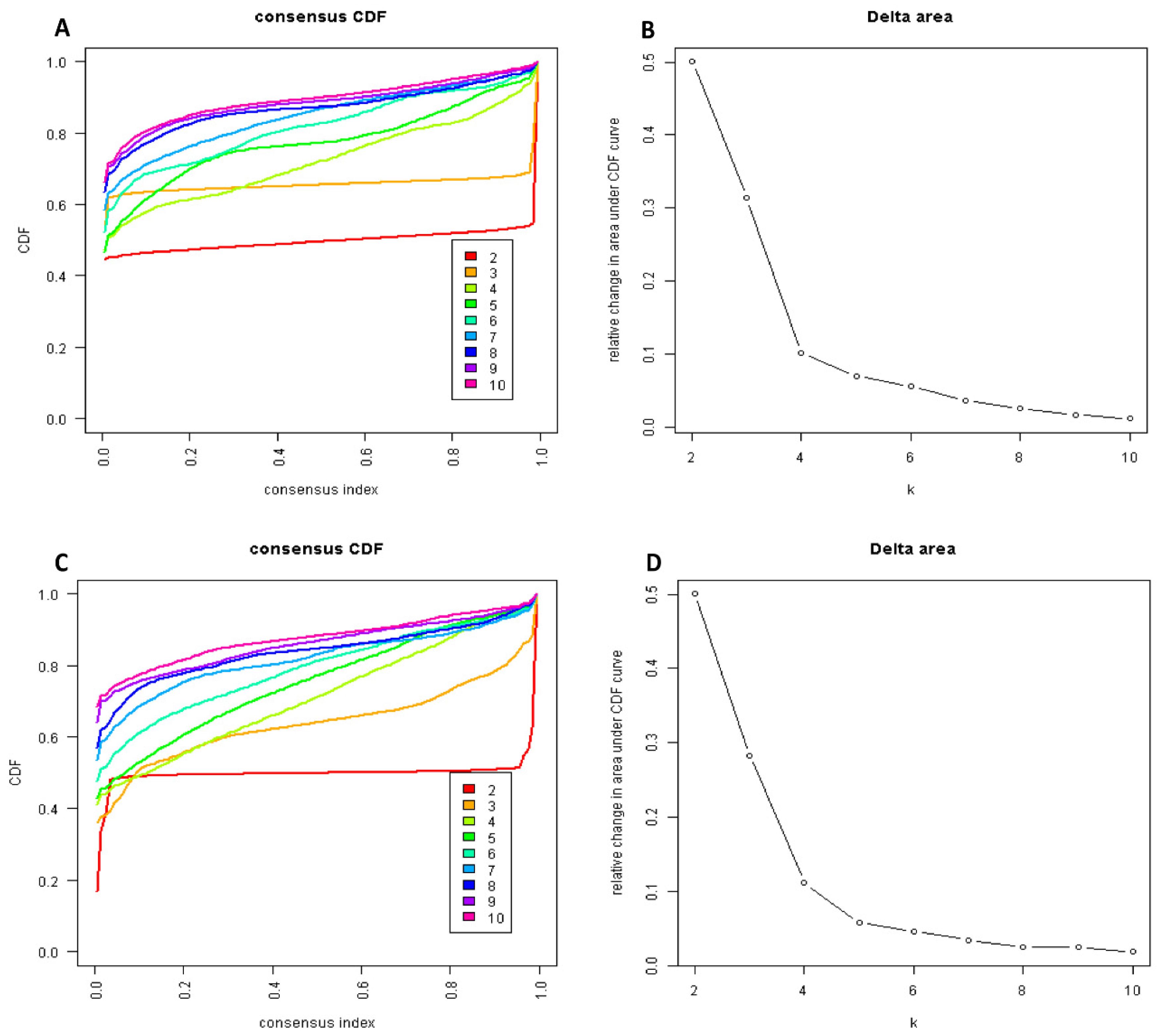
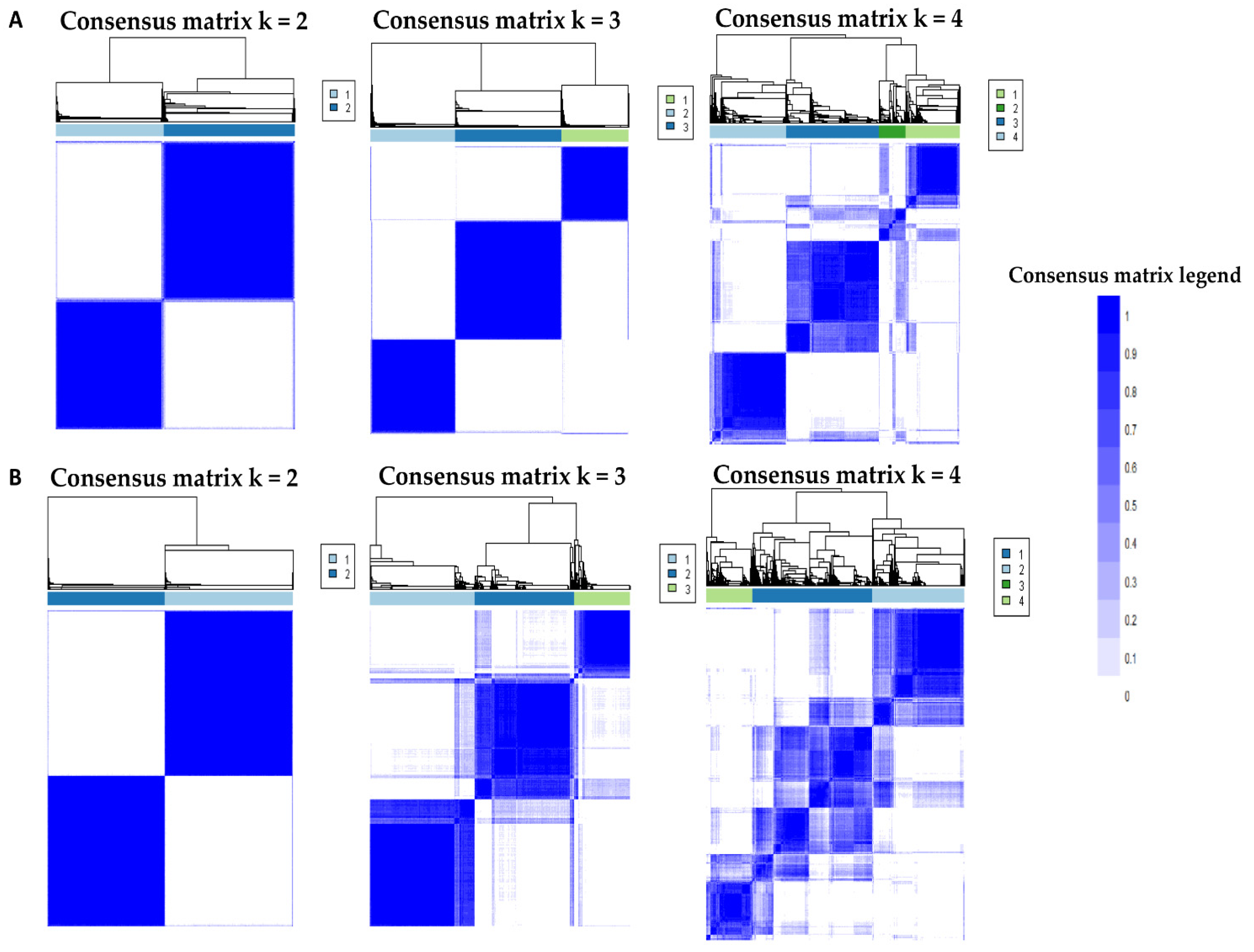
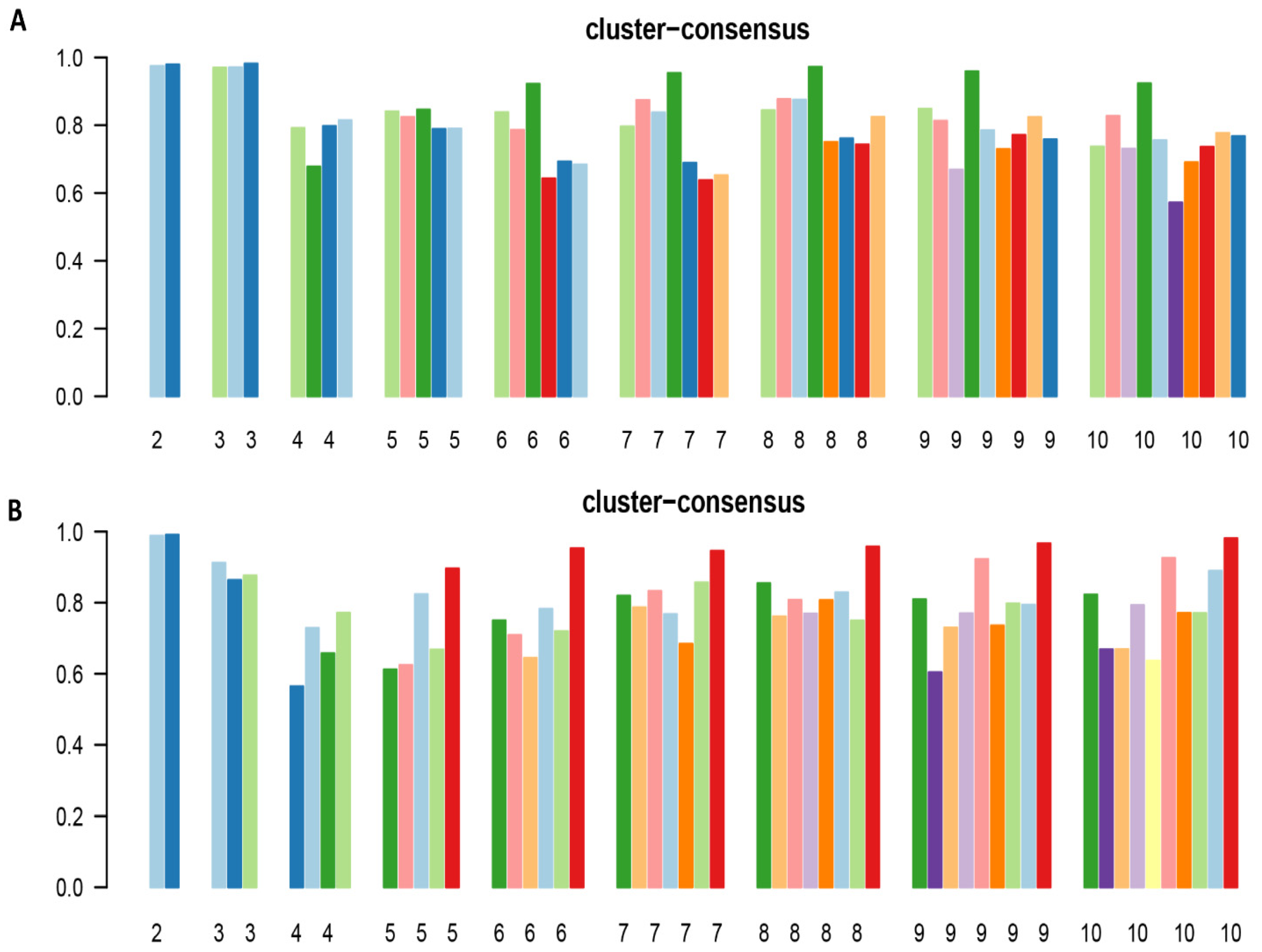
2.3. Cluster Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
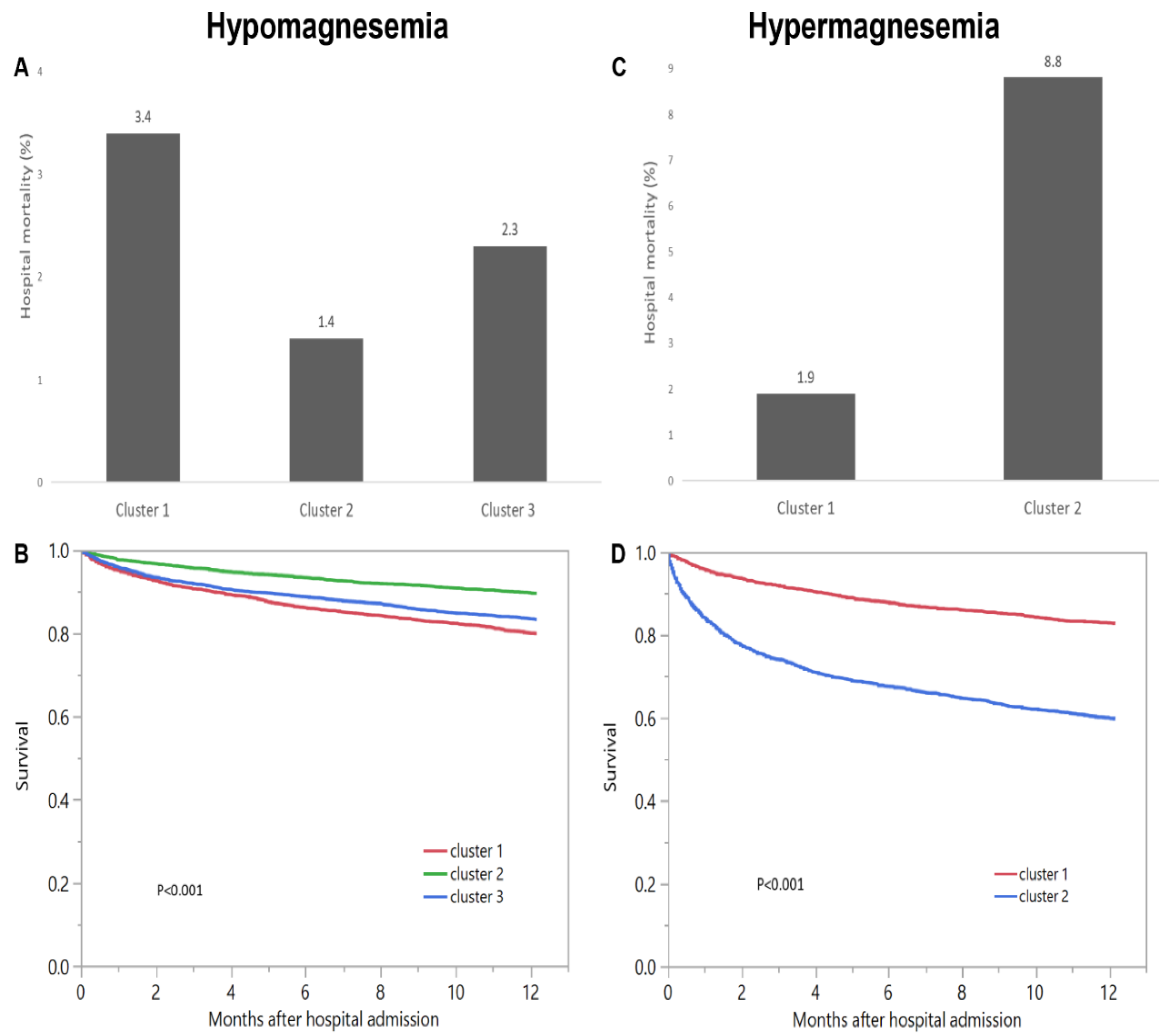
3.1. Hypomagnesemia Cohort
3.2. Hypermagnesemia Cohort
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACEI | angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors |
| AG | anion gap |
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| ARB | angiotensin receptor blockers |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CDF | cumulative distribution function |
| CHF | congestive heart failure |
| CI | confidence interval |
| Cl | chloride |
| CM | consensus matrix; |
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CVA | cerebrovascular accident |
| DM | diabetes mellitus |
| eGFR | estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| EMR | electronic medical record |
| ESKD | end stage kidney disease |
| GI | gastrointestinal |
| Hb | hemoglobin |
| HCO3 | bicarbonate |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| ID | infectious disease |
| K | potassium |
| MI | myocardial infarction |
| ML | machine learning |
| Na | sodium |
| OR | odds ratio |
| PAC | proportion of ambiguously clustered pairs |
| PVD | peripheral vascular disease |
| RS | respiratory system |
| SID | strong ion difference |
References
- Glasdam, S.M.; Glasdam, S.; Peters, G.H. The Importance of Magnesium in the Human Body: A Systematic Literature Review. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2016, 73, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheungpasitporn, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Kittanamongkolchai, W.; Srivali, N.; Edmonds, P.J.; Ungprasert, P.; O’Corragain, O.A.; Korpaisarn, S.; Erickson, S.B. Proton pump inhibitors linked to hypomagnesemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Ren. Fail. 2015, 37, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheungpasitporn, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Mao, M.A.; Srivali, N.; Ungprasert, P.; Varothai, N.; Sanguankeo, A.; Kittanamongkolchai, W.; Erickson, S.B. Hypomagnesaemia linked to depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Intern. Med. J. 2015, 45, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Jin, F.; Hao, Y.; Li, H.; Tang, T.; Wang, H.; Yan, W.; Dai, K. Magnesium and the risk of cardiovascular events: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Baaij, J.H.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Magnesium in man: Implications for health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheungpasitporn, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Harindhanavudhi, T.; Edmonds, P.J.; Erickson, S.B. Hypomagnesemia linked to new-onset diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocr. Res. 2016, 41, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiroli, D.; Marraccini, C.; Zanetti, E.; Ragazzi, M.; Gianoncelli, A.; Quartieri, E.; Gasparini, E.; Iotti, S.; Baricchi, R.; Merolle, L. Imbalance of Mg Homeostasis as a Potential Biomarker in Colon Cancer. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheungpasitporn, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Qian, Q. Dysmagnesemia in Hospitalized Patients: Prevalence and Prognostic Importance. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, E.T.; Rude, R.K.; Singer, F.R.; Shaw, S.T., Jr. A high prevalence of hypomagnesemia and hypermagnesemia in hospitalized patients. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1983, 79, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Erickson, S.B. Admission hypomagnesemia linked to septic shock in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Ren. Fail. 2015, 37, 1518–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malinowska, J.; Małecka, M.; Ciepiela, O. Variations in Magnesium Concentration Are Associated with Increased Mortality: Study in an Unselected Population of Hospitalized Patients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheungpasitporn, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Chewcharat, A.; Petnak, T.; Mao, M.A.; Davis, P.W.; Bathini, T.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Qureshi, F.; Erickson, S.B. Hospital-Acquired Dysmagnesemia and In-Hospital Mortality. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, D.G.; Lindner, G.; Ahmad, S.S.; Sauter, T.; Wolzt, M.; Leichtle, A.B.; Fiedler, G.M.; Exadaktylos, A.K.; Fuhrmann, V. Hypermagnesemia is a strong independent risk factor for mortality in critically ill patients: Results from a cross-sectional study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 26, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheungpasitporn, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Bathini, T.; Hansrivijit, P.; Vaitla, P.; Medaura, J.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Chewcharat, A.; Mao, M.A.; Erickson, S.B. Impact of admission serum magnesium levels on long-term mortality in hospitalized patients. Hosp. Pract. (1995) 2020, 48, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Hansrivijit, P.; Petnak, T.; Mao, M.A.; Bathini, T.; Duriseti, P.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Qureshi, F.; Erickson, S.B.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Impact of serum magnesium levels at hospital discharge and one-year mortality. Postgrad. Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheungpasitporn, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Erickson, S.B. Admission hypomagnesemia and hypermagnesemia increase the risk of acute kidney injury. Ren. Fail. 2015, 37, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Srivali, N.; Erickson, S.B. Admission serum magnesium levels and the risk of acute respiratory failure. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2015, 69, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naksuk, N.; Hu, T.; Krittanawong, C.; Thongprayoon, C.; Sharma, S.; Park, J.Y.; Rosenbaum, A.N.; Gaba, P.; Killu, A.M.; Sugrue, A.M.; et al. Association of Serum Magnesium on Mortality in Patients Admitted to the Intensive Cardiac Care Unit. Am. J. Med. 2017, 130, 229.e213–229.e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheungpasitporn, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Ungprasert, P.; Wijarnpreecha, K.; Mao, M.A.; Aeddula, N.R.; Kaewput, W.; Bathini, T.; Kroner, P.T. Hepatitis A hospitalizations among kidney transplant recipients in the United States: Nationwide inpatient sample 2005-2014. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 32, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Ketteler, M. Magnesium basics. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, i3–i14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Kaewput, W.; Kovvuru, K.; Hansrivijit, P.; Kanduri, S.R.; Bathini, T.; Chewcharat, A.; Leeaphorn, N.; Gonzalez-Suarez, M.L.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Promises of Big Data and Artificial Intelligence in Nephrology and Transplantation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacEachern, S.J.; Forkert, N.D. Machine learning for precision medicine. Genome 2021, 64, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viton, F.; Elbattah, M.; Guérin, J.-L.; Dequen, G. Multi-channel ConvNet Approach to Predict the Risk of in-Hospital Mortality for ICU Patients. In Proceedings of the DeLTA, 1 November 2021; pp. 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Bo, L.; Xu, Z.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Wen, P.; Wan, X.; Yang, T.; Deng, X.; Bian, J. An explainable machine learning algorithm for risk factor analysis of in-hospital mortality in sepsis survivors with ICU readmission. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 2021, 204, 106040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malyugin, B.; Sakhnov, S.; Izmailova, S.; Boiko, E.; Pozdeyeva, N.; Axenova, L.; Axenov, K.; Titov, A.; Terentyeva, A.; Zakaraiia, T.; et al. Keratoconus Diagnostic and Treatment Algorithms Based on Machine-Learning Methods. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Chen, Z.; Shang, Q.; Ma, C.; Chen, X.; Xiao, E. A Promising and Challenging Approach: Radiologists’ Perspective on Deep Learning and Artificial Intelligence for Fighting COVID-19. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Gutiérrez, F.; Kennedy, J.I.; Cooksey, R.; Atkinson, M.; Choy, E.; Brophy, S.; Huo, L.; Zhou, S.M. Mining Primary Care Electronic Health Records for Automatic Disease Phenotyping: A Transparent Machine Learning Framework. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Jeong, E.; Kim, H.; Pyun, H.W.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, Y.; Jin, S.; Hong, D.; Lee, D.W.; et al. Machine Learning-Based Three-Month Outcome Prediction in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Single Cerebrovascular-Specialty Hospital Study in South Korea. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdaca, G.; Caprioli, S.; Tonacci, A.; Billeci, L.; Greco, M.; Negrini, S.; Cittadini, G.; Zentilin, P.; Ventura Spagnolo, E.; Gangemi, S. A Machine Learning Application to Predict Early Lung Involvement in Scleroderma: A Feasibility Evaluation. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedyalkova, M.; Madurga, S.; Simeonov, V. Combinatorial K-Means Clustering as a Machine Learning Tool Applied to Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedyalkova, M.; Barazorda-Ccahuana, H.L.; Sârbu, C.; Madurga, S.; Simeonov, V. Fuzzy partitioning of clinical data for DMT2 patients. J. Environ. Sci. Health A Tox. Hazard. Subst. Environ. Eng. 2020, 55, 1450–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachmann, M.; Rippen, E.; Schuster, T.; Xhepa, E.; von Scheidt, M.; Pellegrini, C.; Trenkwalder, T.; Rheude, T.; Stundl, A.; Thalmann, R.; et al. Subphenotyping of Patients With Aortic Stenosis by Unsupervised Agglomerative Clustering of Echocardiographic and Hemodynamic Data. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2021, 14, 2127–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.E.; Baskaran, L.; Lee, B.C.; Pandey, M.K.; Goebel, B.; Lee, S.E.; Sung, J.M.; Andreini, D.; Al-Mallah, M.H.; Budoff, M.J.; et al. Differential progression of coronary atherosclerosis according to plaque composition: A cluster analysis of PARADIGM registry data. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkerson, M.D.; Hayes, D.N. ConsensusClusterPlus: A class discovery tool with confidence assessments and item tracking. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1572–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Mao, M.A.; Keddis, M.T.; Kattah, A.G.; Chong, G.Y.; Pattharanitima, P.; Nissaisorakarn, V.; Garg, A.K.; Erickson, S.B.; Dillon, J.J.; et al. Hypernatremia subgroups among hospitalized patients by machine learning consensus clustering with different patient survival. J. Nephrol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Dumancas, C.Y.; Nissaisorakarn, V.; Keddis, M.T.; Kattah, A.G.; Pattharanitima, P.; Petnak, T.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Garovic, V.D.; Mao, M.A.; et al. Machine Learning Consensus Clustering Approach for Hospitalized Patients with Phosphate Derangements. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Shen, J.; Hong, W.; Zhou, W.; Xiang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, C.; Luo, S. Risk stratification of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients using machine learning based on lipid profiles. Lipids Health Dis. 2021, 20, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monti, S.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.; Golub, T. Consensus clustering: A resampling-based method for class discovery and visualization of gene expression microarray data. Mach. Learn. 2003, 52, 91–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Șenbabaoğlu, Y.; Michailidis, G.; Li, J.Z. Critical limitations of consensus clustering in class discovery. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stekhoven, D.J.; Bühlmann, P. MissForest—Non-parametric missing value imputation for mixed-type data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alyousef, A.A.; Nihtyanova, S.; Denton, C.; Bosoni, P.; Bellazzi, R.; Tucker, A. Nearest Consensus Clustering Classification to Identify Subclasses and Predict Disease. J. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2018, 2, 402–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Therneau, T.M.; Atkinson, E.J.; Tafti, A.P.; Zhang, N.; Amin, S.; Limper, A.H.; Khosla, S.; Liu, H. Unsupervised machine learning for the discovery of latent disease clusters and patient subgroups using electronic health records. J. Biomed. Inform. 2020, 102, 103364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huijgen, H.J.; Soesan, M.; Sanders, R.; Mairuhu, W.M.; Kesecioglu, J.; Sanders, G.T. Magnesium levels in critically ill patients. What should we measure? Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2000, 114, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaloga, G.P. Interpretation of the serum magnesium level. Chest 1989, 95, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaloga, G.P.; Wilkens, R.; Tourville, J.; Wood, D.; Klyme, D.M. A simple method for determining physiologically active calcium and magnesium concentrations in critically ill patients. Crit. Care Med. 1987, 15, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Alawi, A.M.; Majoni, S.W.; Falhammar, H. Magnesium and Human Health: Perspectives and Research Directions. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 9041694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pham, P.C.; Pham, P.A.; Pham, S.V.; Pham, P.T.; Pham, P.M.; Pham, P.T. Hypomagnesemia: A clinical perspective. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc. Dis. 2014, 7, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thongprayoon, C.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Hansrivijit, P.; Thirunavukkarasu, S.; Chewcharat, A.; Medaura, J.; Mao, M.A.; Kashani, K.B. Association of serum magnesium level change with in-hospital mortality. BMJ Evid. Based Med. 2020, 25, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gile, J.J.; Lopez, C.L.; Ruan, G.J.; Hathcock, M.A.; Abeykoon, J.P.; Heimgartner, J.R.; Baumann, N.A.; McMahon, M.M.; Micallef, I.N.; Johnston, P.B.; et al. Hypomagnesemia at the time of autologous stem cell transplantation for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is associated with an increased risk of failure. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limaye, C.S.; Londhey, V.A.; Nadkart, M.Y.; Borges, N.E. Hypomagnesemia in critically ill medical patients. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2011, 59, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, P.; Lv, Q.; Lai, T.; Xu, F. Does Hypomagnesemia Impact on the Outcome of Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Shock 2017, 47, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, M.; Honarmand, A. Admission hypomagnesemia--impact on mortality or morbidity in critically ill patients. Middle East. J. Anaesthesiol. 2007, 19, 645–660. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Del Gobbo, L.C.; Imamura, F.; Wu, J.H.; de Oliveira Otto, M.C.; Chiuve, S.E.; Mozaffarian, D. Circulating and dietary magnesium and risk of cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.; Bideau, R.; Valdes, R., Jr.; Elin, R.J. Acute hypermagnesemia and respiratory arrest following infusion of MgSO4 for tocolysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 1999, 285, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhari, S.R.; Siriki, R.; Teran, F.J.; Batuman, V. Fatal Hypermagnesemia Due to Laxative Use. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 355, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Laecke, S. Hypomagnesemia and hypermagnesemia. Acta Clin. Belg. 2019, 74, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Patient Characteristics | Hypomagnesemia Cohort (n = 13,320) | Hypermagnesemia Cohort (n = 4671) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | Cluster 3 | p-Value | Cluster 1 | Cluster 2 | p-Value | |
| (n = 3446) | (n = 4351) | (n = 5523) | (n = 2445) | (n = 2226) | |||
| Age (years) | 66.0 ± 13.5 | 48.2 ± 15.9 | 67.9 ± 13.4 | <0.001 | 59.5 ± 17.4 | 71.9 ± 14.6 | <0.001 |
| Male sex | 1458 (42) | 1848 (42) | 2987 (54) | <0.001 | 1444 (59) | 1399 (63) | 0.008 |
| Race | <0.001 | 0.72 | |||||
| -White | 3208 (93) | 3810 (88) | 5196 (94) | 2198 (90) | 2016 (91) | ||
| -Black | 40 (1) | 109 (3) | 64 (1) | 53 (2) | 43 (2) | ||
| -Others | 198 (6) | 432 (10) | 263 (5) | 194 (8) | 167 (8) | ||
| Principal diagnosis | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||
| -Cardiovascular | 408 (12) | 443 (10) | 1084 (20) | 863 (35) | 718 (32) | ||
| -Endocrine/metabolic | 133 (4) | 136 (3) | 218 (4) | 83 (3) | 126 (6) | ||
| -Gastrointestinal | 433 (13) | 829 (19) | 466 (8) | 247 (10) | 231 (10) | ||
| -Genitourinary | 184 (5) | 94 (2) | 332 (6) | 16 (0.7) | 335 (15) | ||
| -Hematology/oncology | 1163 (34) | 1082 (25) | 1632 (30) | 283 (12) | 157 (7) | ||
| -Infectious disease | 334 (10) | 226 (5) | 159 (3) | 67 (3) | 141 (6) | ||
| -Respiratory | 131 (4) | 85 (2) | 254 (5) | 152 (6) | 139 (6) | ||
| -Injury/poisoning | 363 (11) | 828 (19) | 649 (12) | 293 (12) | 187 (8) | ||
| -Other | 297 (9) | 628 (14) | 729 (13) | 441 (18) | 192 (9) | ||
| Charlson Comorbidity Score | 3.4 ± 3.0 | 1.3 ± 1.9 | 2.7 ± 2.6 | <0.001 | 1.4 ± 1.9 | 3.2 ± 2.8 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidities | |||||||
| -Hypertension | 2400 (70) | 944 (22) | 4101 (74) | <0.001 | 1088 (44) | 1621 (73) | <0.001 |
| -Diabetes mellitus | 1169 (34) | 455 (10) | 1835 (33) | <0.001 | 282 (12) | 862 (39) | <0.001 |
| -Coronary artery disease | 788 (23) | 190 (4) | 1493 (27) | <0.001 | 451 (18) | 933 (42) | <0.001 |
| -Congestive heart failure | 215 (6) | 67 (2) | 398 (7) | <0.001 | 203 (8) | 614 (28) | <0.001 |
| -Peripheral vascular disease | 170 (5) | 50 (1) | 256 (5) | <0.001 | 49 (2) | 204 (9) | <0.001 |
| -Stroke | 240 (7) | 96 (2) | 547 (10) | <0.001 | 164 (7) | 312 (14) | <0.001 |
| -End-stage kidney disease | 278 (8) | 38 (1) | 458 (8) | <0.001 | 19 (0.8) | 270 (12) | <0.001 |
| -Dementia | 36 (1) | 14 (0.3) | 80 (1) | <0.001 | 26 (1) | 79 (4) | <0.001 |
| -COPD | 410 (12) | 136 (3) | 676 (12) | <0.001 | 232 (9) | 393 (18) | <0.001 |
| -Cirrhosis | 178 (5) | 132 (3) | 187 (3) | <0.001 | 58 (2) | 132 (6) | <0.001 |
| -Cancer | 1699 (49) | 1087 (25) | 2071 (37) | <0.001 | 414 (17) | 597 (27) | <0.001 |
| -Leukemia/lymphoma | 142 (4) | 123 (3) | 293 (5) | <0.001 | 117 (5) | 90 (4) | 0.22 |
| Alcohol use | 234 (7) | 393 (9) | 213 (4) | <0.001 | 162 (7) | 107 (5) | 0.008 |
| Laboratory test | |||||||
| -eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 67 ± 29 | 101 ± 23 | 63 ± 26 | <0.001 | 81 ± 25 | 28 ± 16 | <0.001 |
| -Potassium (mEq/L) | 3.9 ± 0.6 | 3.9 ± 0.5 | 4.3 ± 0.6 | <0.001 | 4.2 ± 0.6 | 4.8 ± 0.9 | <0.001 |
| -Magnesium (mg/dL) | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | <0.001 | 2.6 ± 0.4 | 2.7 ± 0.4 | <0.001 |
| -Albumin (g/dL) | 3.2 ± 0.5 | 3.1 ± 0.5 | 3.7 ± 0.4 | <0.001 | 3.8 ± 0.4 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | <0.001 |
| -Total calcium (mg/dL) | 8.3 ± 0.8 | 8.2 ± 0.6 | 9.2 ± 0.7 | <0.001 | 9.3 ± 0.6 | 9.0 ± 0.8 | <0.001 |
| -Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 3.7 ± 1.0 | 3.5 ± 0.8 | 3.8 ± 0.9 | <0.001 | 3.7 ± 0.7 | 5.0 ± 1.8 | <0.001 |
| Medication | |||||||
| -ACEI/ARB | 1629 (47) | 557 (13) | 3047 (55) | <0.001 | 789 (32) | 1172 (53) | <0.001 |
| -Diuretics | 1524 (44) | 699 (16) | 2602 (47) | <0.001 | 1007 (41) | 1150 (70) | <0.001 |
| Acute kidney injury | 830 (24) | 179 (4) | 1431 (26) | <0.001 | 156 (6) | 1947 (87) | <0.001 |
| Hospital Mortality | OR (95% CI) | 1-Year Mortality | HR (95% CI) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (a) Hypomagnesemia cohort | ||||
| Cluster 1 | 3.4% | 2.45 (1.79–3.35) | 20.1% | 2.04 (1.79–2.32) |
| Cluster 2 | 1.4% | 1 (ref) | 10.5% | 1 (ref) |
| Cluster 3 | 2.3% | 1.63 (1.20–2.22) | 16.8% | 1.68 (1.49–1.90) |
| (b) Hypermagnesemia cohort | ||||
| Cluster 1 | 1.9% | 1 (ref) | 17.3% | 1 (ref) |
| Cluster 2 | 8.8% | 5.04 (3.63–6.98) | 40.3% | 2.85 (2.51–3.24) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thongprayoon, C.; Sy-Go, J.P.T.; Nissaisorakarn, V.; Dumancas, C.Y.; Keddis, M.T.; Kattah, A.G.; Pattharanitima, P.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Mao, M.A.; Qureshi, F.; et al. Machine Learning Consensus Clustering Approach for Hospitalized Patients with Dysmagnesemia. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112119
Thongprayoon C, Sy-Go JPT, Nissaisorakarn V, Dumancas CY, Keddis MT, Kattah AG, Pattharanitima P, Vallabhajosyula S, Mao MA, Qureshi F, et al. Machine Learning Consensus Clustering Approach for Hospitalized Patients with Dysmagnesemia. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(11):2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112119
Chicago/Turabian StyleThongprayoon, Charat, Janina Paula T. Sy-Go, Voravech Nissaisorakarn, Carissa Y. Dumancas, Mira T. Keddis, Andrea G. Kattah, Pattharawin Pattharanitima, Saraschandra Vallabhajosyula, Michael A. Mao, Fawad Qureshi, and et al. 2021. "Machine Learning Consensus Clustering Approach for Hospitalized Patients with Dysmagnesemia" Diagnostics 11, no. 11: 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112119
APA StyleThongprayoon, C., Sy-Go, J. P. T., Nissaisorakarn, V., Dumancas, C. Y., Keddis, M. T., Kattah, A. G., Pattharanitima, P., Vallabhajosyula, S., Mao, M. A., Qureshi, F., Garovic, V. D., Dillon, J. J., Erickson, S. B., & Cheungpasitporn, W. (2021). Machine Learning Consensus Clustering Approach for Hospitalized Patients with Dysmagnesemia. Diagnostics, 11(11), 2119. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11112119









