Assessing PD-L1 Expression Level via Preoperative MRI in HCC Based on Integrating Deep Learning and Radiomics Features
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Detection of PD-L1 Expression Status
2.3. Image Acquisition and Tumor Segmentation
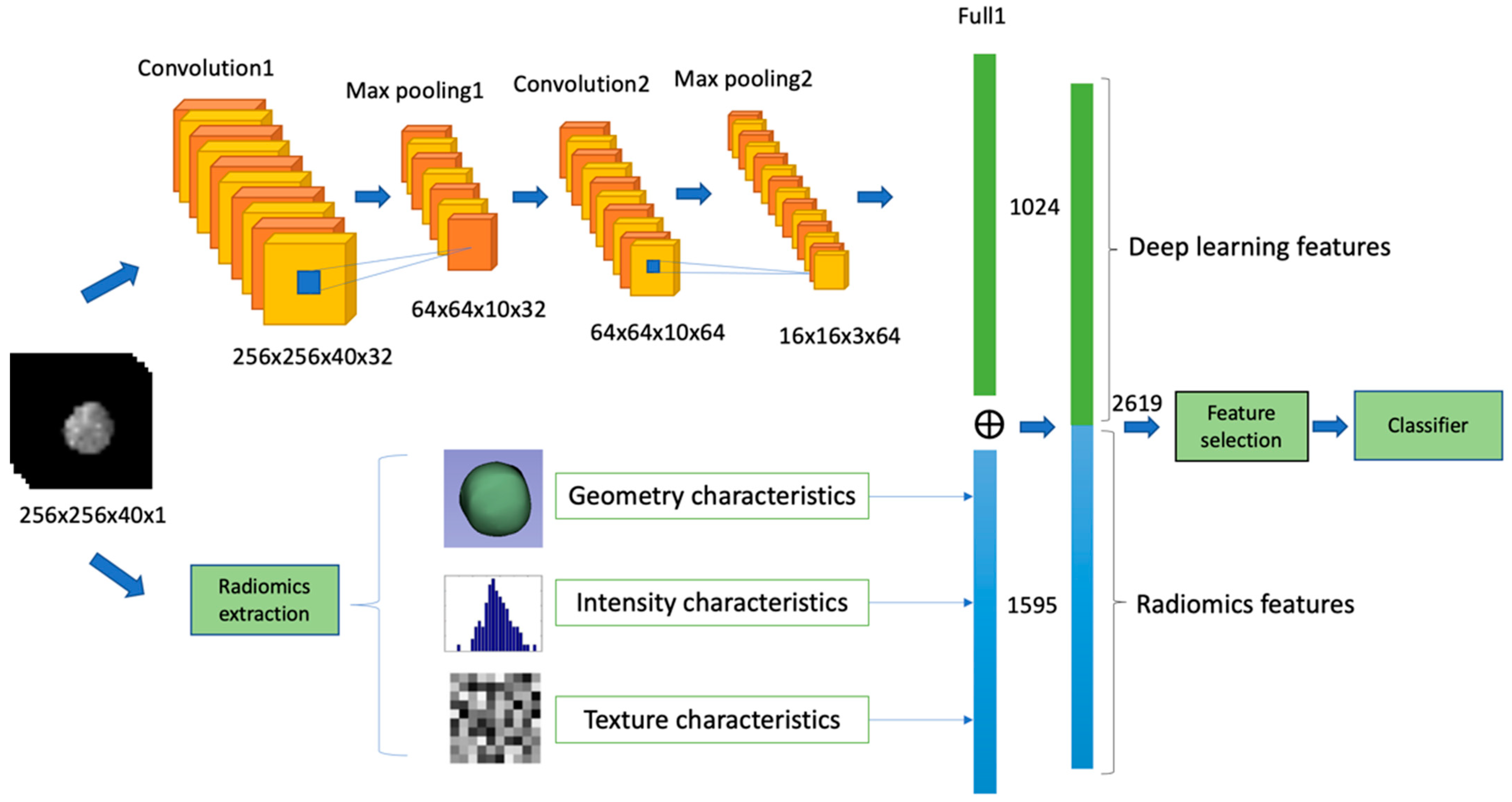
2.4. Feature Extraction
2.4.1. Radiomics Features (RsF)
2.4.2. Deep Learning Features (DLF)
2.4.3. Integrated Features (RsF+DLF)
2.5. Feature Selection and Classifier Modeling
2.6. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Patient Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Comparison of Different Classifiers
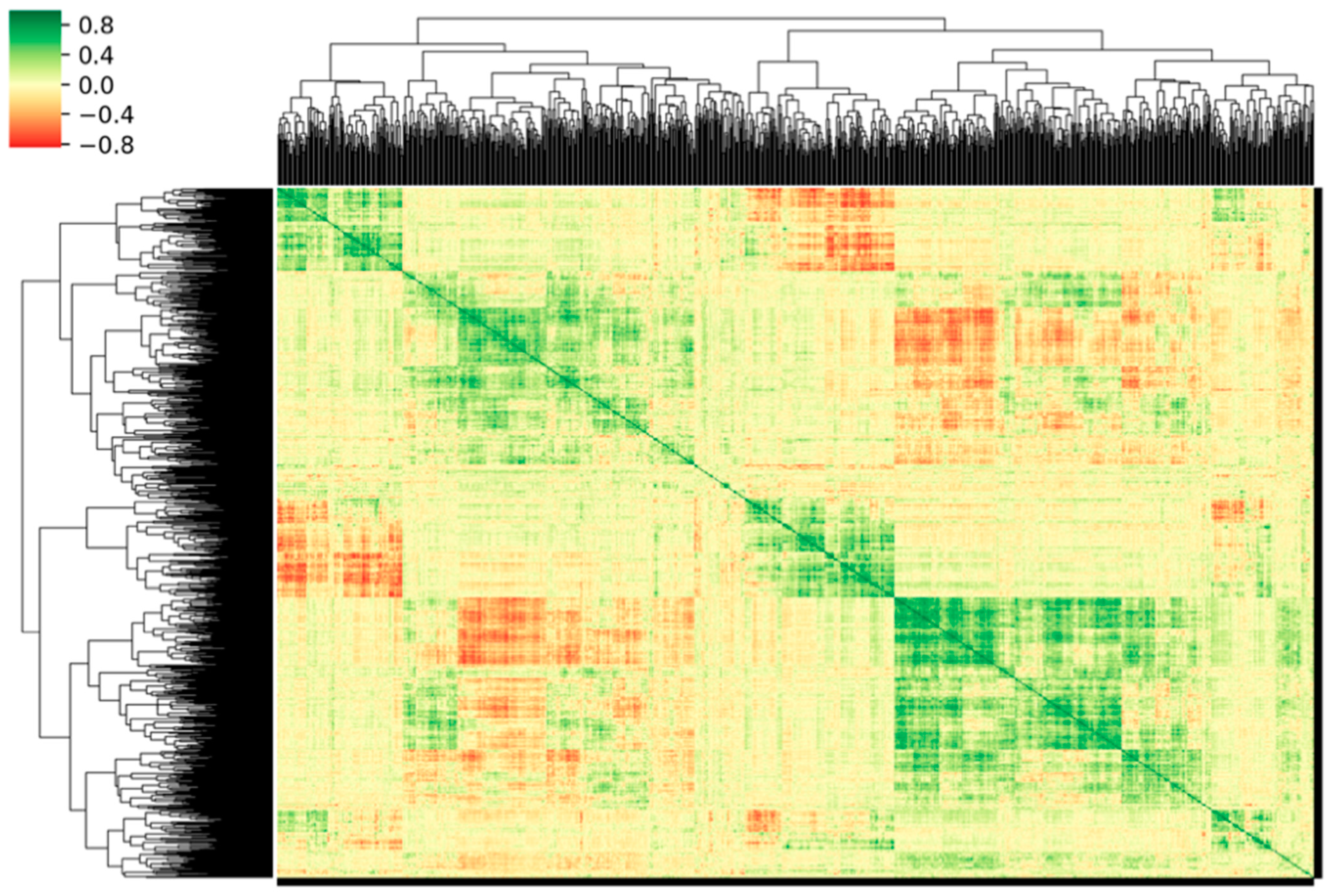
3.3. Feature Selection and Signature Building
3.4. Prediction for PD-L1 Expression Level
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ozakyol, A. Global Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC Epidemiology). J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2017, 48, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migden, M.R.; Rischin, D.; Schmults, C.D.; Guminski, A.; Hauschild, A.; Lewis, K.D.; Chung, C.H.; Hernandez-Aya, L.; Lim, A.M.; Chang, A.L.S.; et al. PD-1 blockade with cemiplimab in advanced cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowell, D.; Morris, L.G.T.; Grigg, C.M.; Weber, J.K.; Samstein, R.M.; Makarov, V.; Kuo, F.; Kendall, S.M.; Requena, D.; Riaz, N.; et al. Patient HLA class I genotype influences cancer response to checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Science 2018, 359, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmid, P.; Rugo, H.S.; Adams, S.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Iwata, H.; Diéras, V.; Henschel, V.; Molinero, L.; Chui, S.Y.; et al. Atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel as first-line treatment for unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (IMpassion130): Updated efficacy results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kee, D.; McArthur, G. Immunotherapy of melanoma. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 43, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansell, S.M.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Maloney, D.G. Immunotherapy in lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khanna, P.; Blais, N.; Gaudreau, P.-O.; Corrales-Rodriguez, L. Immunotherapy Comes of Age in Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2016, 18, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruger, S.; Ilmer, M.; Kobold, S.; Cadilha, B.L.; Endres, S.; Ormanns, S.; Schuebbe, G.; Renz, B.W.; D’Haese, J.G.; Schloesser, H.; et al. Advances in cancer immunotherapy 2019—Latest trends. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mak, D.W.; Li, S.; Minchom, A. Challenging the recalcitrant disease—Developing molecularly driven treatments for small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 119, 132–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachandran, V.P.; Beatty, G.L.; Dougan, S.K. Broadening the impact of immunotherapy to pancreatic cancer: Challenges and opportunities. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 2056–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1–positive non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robert, C.; Ribas, A.; Schachter, J.; Arance, A.; Grob, J.J.; Mortier, L.; Daud, A.; Carlino, M.S.; McNeil, C.; Lotem, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Ipilimumab in advanced melanoma (KEYNOTE-006): Post-hoc 5-year results from an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.; Gilhodes, J.; Maerevoet, M.; Herbaux, C.; Morschhauser, F.; Brice, P.; Garciaz, S.; Borel, C.; Ysebaert, L.; Obéric, L.; et al. Efficacy of chemotherapy or chemo-anti-PD-1 combination after failed anti-PD-1 therapy for relapsed and refractory hodgkin lymphoma: A series from lysa centers. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Edeline, J.; Cattan, S.; Ogasawara, S.; Palmer, D.H.; Verslype, C.; Zagonel, V.; Fartoux, L.; Vogel, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab (pembro) in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): KEYNOTE-224 update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; Meng, X.; Kong, L.; Yu, J. Progress and challenges of predictive biomarkers of anti PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy: A systematic review. Cancer Lett. 2018, 414, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer–immune set point. Nature 2017, 541, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanmamed, M.F.; Chen, L. A paradigm shift in cancer immunotherapy: From enhancement to normalization. Cell 2018, 175, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, H.; Jung, W.; Kim, A.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, W.B.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, B.H. Expression and prognostic significance of programmed death protein 1 and programmed death ligand-1, and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated molecule-4 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Apmis 2017, 125, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Yuan, F.; Qi, F.; Sun, J.; Rao, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, P.; Fang, T.; Yang, B.; Xia, J. Expression and clinical significance of LAG-3, FGL1, PD-L1 and CD8+ T cells in hepatocellular carcinoma using multiplex quantitative analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semaan, A.; Dietrich, D.; Bergheim, D.; Dietrich, J.; Kalff, J.C.; Branchi, V.; Matthaei, H.; Kristiansen, G.; Fischer, H.-P.; Goltz, D. CXCL12 expression and PD-L1 expression serve as prognostic biomarkers in HCC and are induced by hypoxia. Virchows Arch. 2017, 470, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Q.; Li, M.; Xu, W.; Pang, K.; Guo, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z. Clinical benefits of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatol. Int. 2020, 14, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Gao, X.-S.; Xiong, W.; Guo, W.; Han, L.; Bai, Y.; Peng, C.; Cui, M.; Xie, M. Increased programmed death ligand-1 expression predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 4805–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.-L.; Zhang, S.-W.; Chao, X.; Wang, C.-H.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.-K.; Wen, Y.-L.; Yun, J.-P.; Luo, R.-Z. Coexpression of CMTM6 and PD-L1 as a predictor of poor prognosis in macrotrabecular-massive hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Cheng, X.; Sun, S.; Zhou, J. Transcriptional activation of PD-L1 by Sox2 contributes to the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3061–3067. [Google Scholar]
- Takada, K.; Okamoto, T.; Shoji, F.; Shimokawa, M.; Akamine, T.; Takamori, S.; Katsura, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Fujishita, T.; Toyokawa, G.; et al. Clinical Significance of PD-L1 Protein Expression in Surgically Resected Primary Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1879–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crinò, L.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non–small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Cobo, M.; Schenker, M.; Zurawski, B.; Menezes, J.; Richardet, E.; Bennouna, J.; Felip, E.; Juan-Vidal, O.; et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab combined with two cycles of chemotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 9LA): An international, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmeyer, A.; Barlesi, F.; Waterkamp, D.; Park, K.; Ciardiello, F.; Von Pawel, J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Hida, T.; Kowalski, D.M.; Dols, M.C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): A phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tray, N.; Weber, J.; Adams, S. Predictive Biomarkers for Checkpoint Immunotherapy: Current Status and Challenges for Clinical Application. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trebeschi, S.; Drago, S.G.; Birkbak, N.J.; Kurilova, I.; Cǎlin, A.M.; Delli Pizzi, A.; Lalezari, F.; Lambregts, D.M.J.; Rohaan, M.W.; Parmar, C.; et al. Predicting response to cancer immunotherapy using noninvasive radiomic biomarkers. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shien, K.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.A.; Wistuba, I.I. Predictive biomarkers of response to PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors in non–small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2016, 99, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemlina, G.; Ikeda, S.; Kurzrock, R. The biology of Hepatocellular carcinoma: Implications for genomic and immune therapies. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.H.; Kim, J.; Joung, J.-G.; Cha, H.; Park, W.-Y.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.-J.; Parl, K.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, K.-H.; et al. Correlations between metabolic texture features, genetic heterogeneity, and mutation burden in patients with lung cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewski, M.R.; Gillies, R.R. The biological meaning of radiomic features. Radiology 2021, 298, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, K.; Qian, Z.; Wang, K.; Fan, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T. MRI features can predict EGFR expression in lower grade gliomas: A voxel-based radiomic analysis. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyen, M. Radiogenomic imaging-linking diagnostic imaging and molecular diagnostics. World J. Radiol. 2014, 6, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Tan, H.; Gao, F.; Hai, J.; Ning, P.; Chen, J.; Zhu, S.; Wang, M.; Dou, S.; Shi, D. Predicting the grade of hepatocellular carcinoma based on non-contrast-enhanced MRI radiomics signature. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 2802–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, J.; He, D.; Li, M.; Yin, H.; Tian, S.; Zhang, H.; Song, B. Development and validation of magnetic resonance imaging-based radiomics models for preoperative prediction of microsatellite instability in rectal cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, G.O.; Park, S.-H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Park, N.J.-Y.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, S.-W.; Hong, D.G.; Park, J.Y.; Han, H.S. Predicting Model for Tumor Budding Status using Radiomics Features of 18F-PET/CT and in Cervical Cancer. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-H.; Long, L.-H.; Cui, Y.; Jia, A.Y.; Zhu, X.-G.; Wang, H.-Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhan, C.-M.; Wang, Z.-H.; Wang, W.-H. Mri-Based radiomics model for preoperative prediction of 5-year survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valentinuzzi, D.; Vrankar, M.; Boc, N.; Ahac, V.; Zupancic, Z.; Unk, M.; Skalic, K.; Zagar, I.; Studen, A.; Simoncic, U.; et al. [18F]FDG PET immunotherapy radiomics signature (iRADIOMICS) predicts response of non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with pembrolizumab. Radiol. Oncol. 2020, 54, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borhani, A.A.; Yuri, R.C.; Velichko, Y.S.; Hectors, S.; Taouli, B.; Lewis, S. Radiomics of hepatocellular carcinoma: Promising roles in patient selection, prediction, and assessment of treatment response. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 46, 674–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Xue, H.; Wang, L.; Jing, R.; Chen, S.; Che, F.; Heng, X.; Xue, F.; et al. An MRI-based radiomics signature as a pretreatment noninvasive predictor of overall survival and chemotherapeutic benefits in lower-grade gliomas. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inge, L.J.; Dennis, E. Development and applications of computer image analysis algorithms for scoring of PD-L1 immunohistochemistry. Immuno Oncol. Technol. 2020, 6, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hectors, S.J.; Lewis, S.; Besa, C.; King, M.; Said, D.; Putra, J.; Ward, S.; Higashi, T.; Thung, S.; Yao, S.; et al. MRI radiomics features predict immuno-oncological characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 3759–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Limkin, E.J.; Vakalopoulou, M.; Dercle, L.; Champiat, S.; Han, S.R.; Verlingue, L.; Brandao, V.; Lancia, A.; Ammari, S.; et al. A radiomics approach to assess tumour-infiltrating CD8 cells and response to anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy: An imaging biomarker, retrospective multicohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1180–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, F.; Shi, Y.; Song, B. Machine learning: An approach to preoperatively predict PD-1/PD-L1 expression and outcome in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma using MRI biomarkers. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e000910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Mu, L.; Zhou, J.; Tang, W.; Zhang, L.; Xie, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, J. Imaging features of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging for evaluation of tumor-infiltrating CD8 cells and PD-L1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Qiu, Q.; Dai, H.; Feng, A.; Xing, L. Pretreatment CT-Based Radiomics Signature as a Potential Imaging Biomarker for Predicting the Expression of PD-L1 and CD8+TILs in ESCC. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 12003–12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Liao, M.; Xu, L.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, K.; Song, B.; Zeng, Y. Preoperative Radiomic Approach to Evaluate Tumor-Infiltrating CD8+ T Cells in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Using Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 4537–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tustison, N.; Brian, J.; Avants, J.; Cook, P.A.; Zheng, Y.; Egan, A.; Yushkevich, P.A.; Gee, J. N4ITK: Improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1310–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nyúl, L.; Jayaram, G.; Udupa, K.; Zhang, X. New variants of a method of MRI scale standardization. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2000, 19, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Griethuysen, J.J.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hara, K.; Saito, D.; Shouno, H. Analysis of function of rectified linear unit used in deep learning. In 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN); IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, M.; Barham, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; Ghemawat, S.; Irving, G.; Isard, M.; et al. Tensorflow: A system for large-scale machine learning. In Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation OSDI, Savannah, GA, USA, 2–4 November 2016; pp. 265–283. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Benesty, J.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Cohen, I. Pearson correlation coefficient. In Noise Reduction in Speech Processing; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Fehr, D.; HVeeraraghavan, H.; Wibmer, A.; Gondo, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Vargas, H.A.; Sala, E.; Hricak, H.; Deasy, J.O. Automatic classification of prostate cancer Gleason scores from multiparametric magnetic resonance images. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6265–E6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larozza, A.; Moratal, D.; Paredes-Sánchez, A.; Soria-Olivas, E.; Chust, M.L.; Arribas, L.A.; Arana, E. Support vector machine classification of brain metastasis and radiation necrosis based on texture analysis in MRI. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 42, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Ai, J.; Deng, Y.; Guan, X.; Johnson, D.R.; Ang, C.Y.; Zhang, C.; Perkins, E.J. Identification of biomarkers that distinguish chemical contaminants based on gene expression profiles. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ota, K.; Oishi, N.; Ito, K.; Fukuyama, H. A comparison of three brain atlases for MCI prediction. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 221, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.-W.; Lin, C.-J. Feature ranking using linear SVM. In Proceedings of the Workshop on the Causation and Prediction Challenge, WCCI 2008, Hong Kong, China, 1–6 June 2008; pp. 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Mladenić, D.; Brank, J.; Grobelnik, M.; Milic-Frayling, N. Feature selection using linear classifier weights: Interaction with classification models. In Proceedings of the 27th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Sheffield, UK, 25–29 July 2004; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zweig, M.H.; Campbell, G. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) plots: A fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin. Chem. 1993, 39, 561–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizal, R.A.; Gulo, S.; Della, O.; Sihombing, C.; Napitupulu, A.B.M.; Gultom, A.Y.; Siagian, T.J. Analisis Gray Level Co-Occurrence Matrix (Glcm) Dalam Mengenali Citra Ekspresi Wajah. J. Mantik 2019, 3, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Nanni, L.; Brahnam, S.; Ghidoni, S.; Menegatti, E.; Barrier, T. Different Approaches for Extracting Information from the Co-Occurrence Matrix. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Quackenbush, J.; Lambin, P.; Bussink, J.; Mak, R.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Exploratory Study to Identify Radiomics Classifiers for Lung Cancer Histology. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mumtaz, W.; Xia, L.; Yasin, M.A.M.; Ali, S.S.A.; Malik, A.S. A wavelet-based technique to predict treatment outcome for major depressive disorder. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; He, L.; Chen, X.; Pan, D.; Ma, Z.; Liang, C.; Tian, J.; Liang, C. Radiomics Signature: A Potential Biomarker for the Prediction of Disease-Free Survival in Early-Stage (I or II) Non—Small Cell Lung Cancer. Radiology 2016, 281, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Layers | Parameter Setting |
| Conv 3D-1 | size = 5 × 5 × 5; stride = 1; zero-padded |
| Relu-1 | Alpha = 0.2 |
| Max Pool 3D-1 | size = 4 × 4 × 4; stride = 4; zero-padded |
| Conv 3D-2 | size = 5 × 5 × 5; stride = 1; zero-padded |
| Relu-2 | Alpha = 0.2 |
| Max Pool 3D-2 | size = 4 × 4 × 4; stride = 4; zero-padded |
| Fully connected-1 | |
| Flat-1 | |
| Relu-3 | Alpha = 0.2 |
| Dropout-1 | p = 0.5 |
| Fully connected-2 | |
| SoftMax |
| VariablesS | High-Expression (PD-L1 50%) | Low-Expression (PD-L1 50%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 55.20 11.05 | 54.48 12.70 | 0.077 |
| Sex | 0.369 | ||
| Male | 26 (86.7%) | 58 (79.5%) | |
| Female | 4 (13.3%) | 15 (20.5%) | |
| HBV_DNA | 0.224 | ||
| Positive | 13 (43.0%) | 17 (23.3%) | |
| Negative | 17 (57.0%) | 56 (76.7%) | |
| HBs | 0.182 | ||
| Positive | 25 (83.3%) | 51 (69.9%) | |
| Negative | 5 (16.7%) | 22 (30.1%) | |
| AFP(ng/mL) | 0.260 | ||
| 20 | 11 (36.7%) | 24 (32.9%) | |
| 20 | 19 (63.3%) | 49 (67.1%) | |
| Maximal tumor diameter | 0.903 | ||
| 5 | 19 (63.3%) | 41 (56.2%) | |
| 5 | 11 (36.7%) | 32 (43.8%) | |
| CEA | 2.61 ± 1.48 | 2.56 ± 1.53 | 0.427 |
| TBIL | 13.99 ± 5.28 | 13.28 ± 5.71 | 0.962 |
| Model | Accuracy | AUC | Negative Predictive | Positive Predictive | Sensitivity | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVM | 0.786 | 0.758 | 0.859 | 0.625 | 0.667 | 0.836 |
| AE | 0.708 | 0.677 | 0.794 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.794 |
| LR-Lasso | 0.553 | 0.675 | 0.885 | 0.382 | 0.866 | 0.424 |
| Decision Tree | 0.737 | 0.678 | 0.810 | 0.551 | 0.533 | 0.821 |
| Random Forest | 0.737 | 0.706 | 0.819 | 0.548 | 0.566 | 0.808 |
| LDA | 0.747 | 0.724 | 0.873 | 0.551 | 0.733 | 0.753 |
| Features | High-Expression | Low-Expression | Coefficient | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
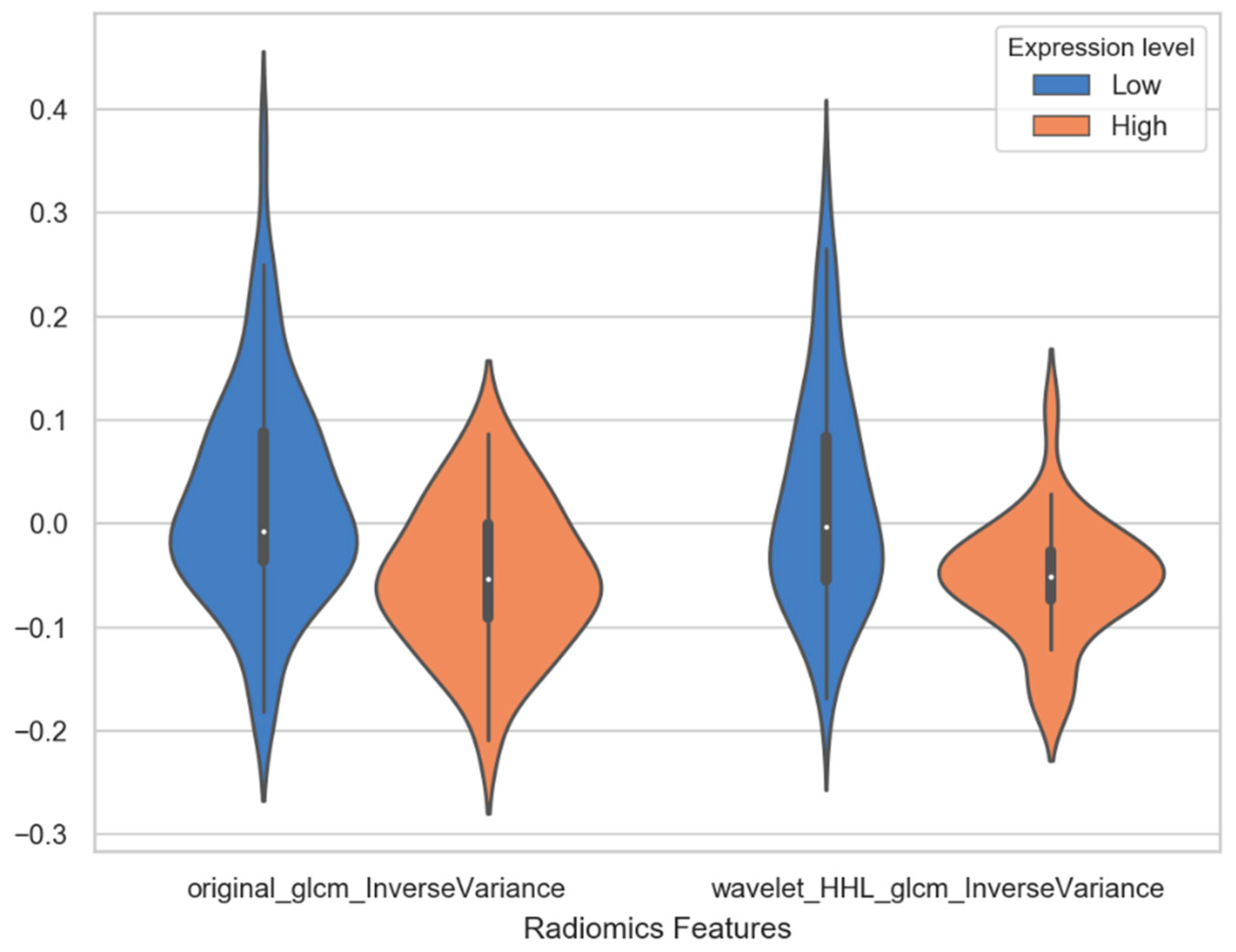
| original_glcm_InverseVariance | −0.05 ± 0.07 | 0.02 ± 0.10 | −0.995 | 0.001 |
| wavelet_HHL_firstorder_Mean | 0.03 ± 0.12 | −0.01 ± 0.08 | 0.742 | 0.286 |
| wavelet_HHL_glcm_InverseVariance | −0.05 ± 0.06 | 0.02 ± 0.10 | −0.748 | 0.001 |
| gradient_ngtdm_Contrast | 0.01 ± 0.07 | 0.00 ± 0.11 | −0.714 | 0.064 |
| squareroot_glcm_ClusterTendency | 0.02 ± 0.12 | −0.01 ± 0.09 | 0.819 | 0.234 |
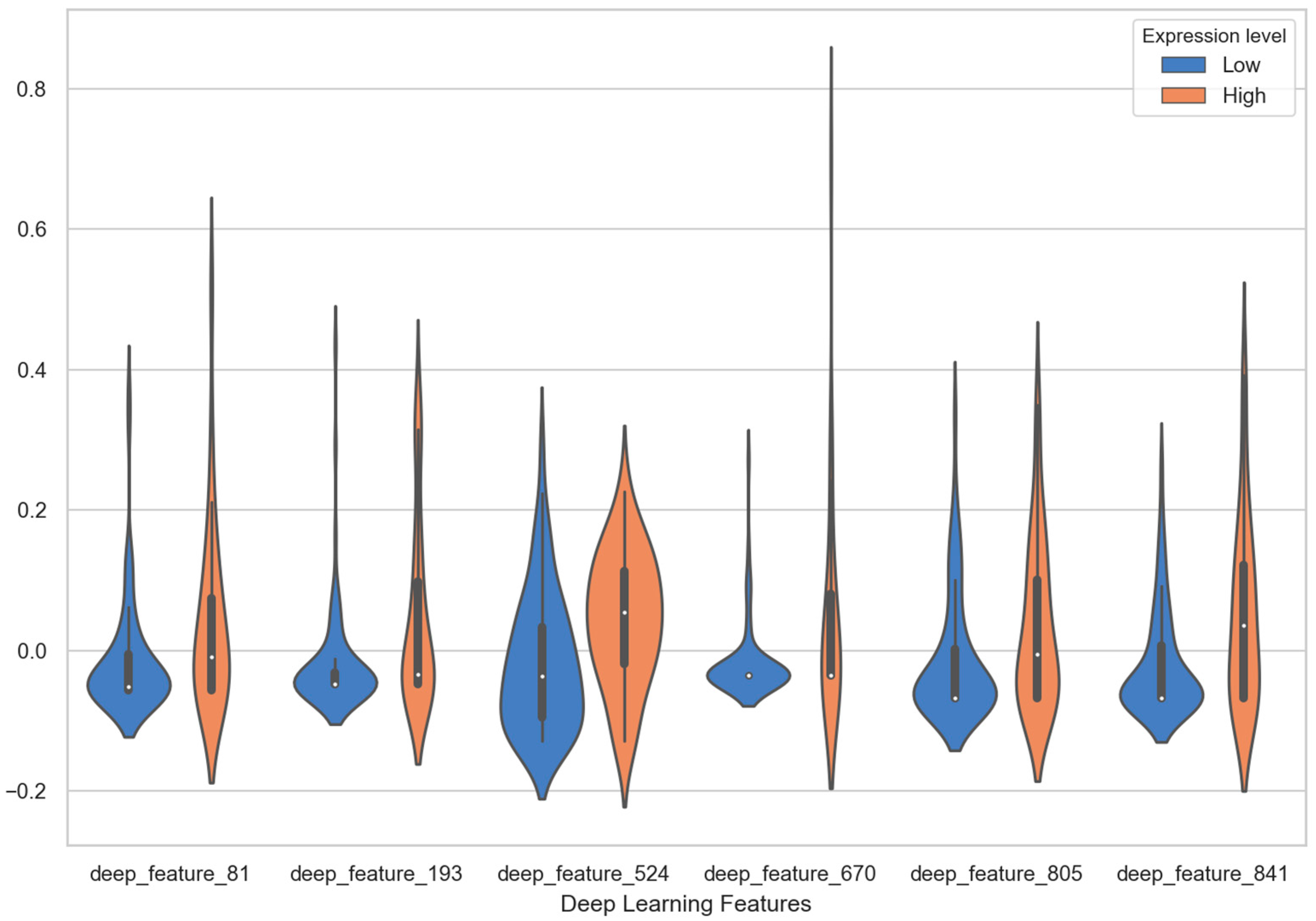
| deep_feature_81 | 0.04 ± 0.13 | −0.02 ± 0.08 | 1.116 | 0.028 |
| deep_feature_193 | 0.04 ± 0.13 | −0.02 ± 0.08 | 1.005 | 0.012 |
| deep_feature_486 | −0.02 ± 0.10 | 0.01 ± 0.10 | −0.841 | 0.310 |
| deep_feature_524 | 0.04 ± 0.09 | −0.02 ± 0.10 | 1.064 | 0.003 |
| deep_feature_629 | −0.02 ± 0.07 | 0.01 ± 0.11 | −0.953 | 0.278 |
| deep_feature_670 | 0.04 ± 0.16 | −0.02 ± 0.05 | 1.461 | 0.019 |
| deep_feature_805 | 0.03 ± 0.12 | −0.01 ± 0.09 | 1.240 | 0.031 |
| deep_feature_841 | 0.05 ± 0.13 | −0.02 ± 0.07 | 1.142 | 0.006 |
| deep_feature_889 | 0.03 ± 0.15 | −0.01 ± 0.06 | 0.813 | 0.503 |
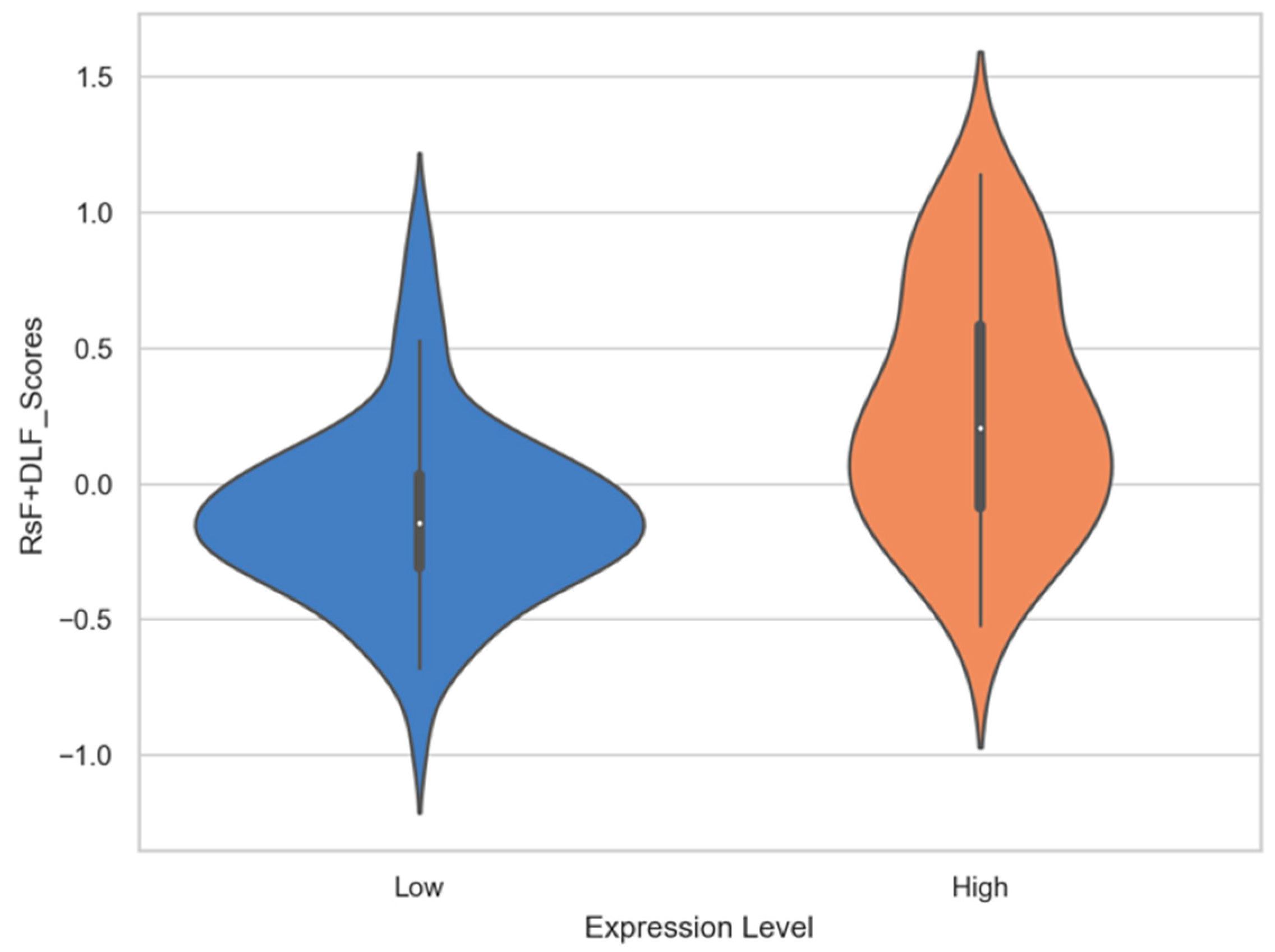
| RsF+DLF _Score | 0.27 ± 0.44 | −0.11 ± 0.33 | None | 2.502 × 10−9 |
| Model | AUC | Accuracy | f1-Score | Specificity | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RsF | 0.794 ± 0.035 | 0.766 ± 0.094 | 0.494 ± 0.212 | 0.916 ± 0.077 | 0.687 ± 0.301 | 0.400 ± 0.190 |
| DLF | 0.852 ± 0.043 | 0.854 ± 0.050 | 0.703 ± 0.131 | 0.947 ± 0.087 | 0.892 ± 0.166 | 0.633 ± 0.217 |
| RsF+DLF | 0.897 ± 0.084 | 0.887 ± 0.041 | 0.764 ± 0.106 | 0.981 ± 0.029 | 0.948 ± 0.076 | 0.660 ± 0.167 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Y.; Komolafe, T.E.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, G.; Chen, T.; Zhou, B.; Yang, X. Assessing PD-L1 Expression Level via Preoperative MRI in HCC Based on Integrating Deep Learning and Radiomics Features. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101875
Tian Y, Komolafe TE, Zheng J, Zhou G, Chen T, Zhou B, Yang X. Assessing PD-L1 Expression Level via Preoperative MRI in HCC Based on Integrating Deep Learning and Radiomics Features. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(10):1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101875
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Yuchi, Temitope Emmanuel Komolafe, Jian Zheng, Guofeng Zhou, Tao Chen, Bo Zhou, and Xiaodong Yang. 2021. "Assessing PD-L1 Expression Level via Preoperative MRI in HCC Based on Integrating Deep Learning and Radiomics Features" Diagnostics 11, no. 10: 1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101875
APA StyleTian, Y., Komolafe, T. E., Zheng, J., Zhou, G., Chen, T., Zhou, B., & Yang, X. (2021). Assessing PD-L1 Expression Level via Preoperative MRI in HCC Based on Integrating Deep Learning and Radiomics Features. Diagnostics, 11(10), 1875. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101875





