Nucleic Acid-Based Diagnostic Tests for the Detection SARS-CoV-2: An Update
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Genomic Architecture and Key Virulence Factors of SARS-CoV-2
3. FDA-EUA NATs for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2
4. Specimen Collection
5. Preparation of Specimen for NATs
5.1. Spin Column Method
5.2. Magnetic Particle-Based Method
5.3. Other Specimen Processing Procedures
6. Controls for NATs
7. Real-Time RT-PCR
7.1. Multiplexed Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Pathogens
7.2. Automated Sample-to-Result and Point-of-Care Systems
8. End-Point RT-PCR
8.2. Enzyme-Based Colorimetric Detection
8.3. Fluorescence Detection
8.3.1. Capillary Electrophoresis
8.3.2. Digital Multiplexing Technologies
8.3.3. HDPCR Technology
8.4. Electrochemical Detection
8.5. MALDI-TOF Detection
9. qSTAR
10. RT-Digital PCR
11. Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification
11.1. RT-Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP)
11.1.1. Fluorescence Detection
11.1.2. Colorimetric Detection
11.1.3. Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)-Based Detection
11.2. NEAR
11.3. OMEGA Amplification
11.4. TMA
12. Sanger Sequencing
13. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
13.1. Illumina Sequencing by Synthesis (SBS) Technology
13.2. Oxford Nanopore Sequencing Technology
14. Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Reference Panel Results
15. Future Perspectives and Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Pneumonia of Unknown Cause—China. Available online: https://www.who.int/csr/don/05-january-2020-pneumonia-of-unkown-cause-china/en/ (accessed on 31 August 2020).
- World Health Organization. Novel Coronavirus—China. Available online: https://www.who.int/csr/don/12-january-2020-novel-coronavirus-china/en/ (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- World Health Organization. Molecular Assays to Diagnose COVID-19: Summary Table of Available Protocols. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/molecular-assays-to-diagnose-covid-19-summary-table-of-available-protocols (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC 2019-nCoV Real-Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel (CDC). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/134922/download (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Specific Primers and Probes for Detection 2019 Novel Coronavirus. Available online: http://ivdc.chinacdc.cn/kyjz/202001/t20200121_211337.html (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- Corman, V.M.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Drosten, C.; Landt, O.; Koopmans, M.; Zambon, M.; Peiris, M. Diagnostic Detection of 2019-nCoV by Real-Time RT-PCR; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update—27 October 2020; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gouel-Cheron, A.; Couffignal, C.; Elmaleh, Y.; Kantor, E.; Montravers, P. Preliminary observations of anaesthesia ventilators use for prolonged mechanical ventilation in intensive care unit patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain Med. 2020, 39, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salathe, M.; Althaus, C.L.; Neher, R.; Stringhini, S.; Hodcroft, E.; Fellay, J.; Zwahlen, M.; Senti, G.; Battegay, M.; Wilder-Smith, A.; et al. COVID-19 epidemic in Switzerland: On the importance of testing, contact tracing and isolation. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2020, 150, w20225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, K.O.; Li, K.K.; Chan, H.H.H.; Yi, Y.Y.; Tang, A.; Wei, W.I.; Wong, S.Y.S. Community Responses during Early Phase of COVID-19 Epidemic, Hong Kong. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics. FIND Evaluation Update: SARS-COV-2 Molecular Diagnostics; Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Escalante, S. Accelerating regulation in response to COVID-19. Bull. World Health Organ 2020, 98, 514–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. List of Stringent Regulatory Authorities (SRAs). Available online: https://www.who.int/medicines/regulation/sras/en/#:~:text=The%20concept%20of%20a%20stringent,international%20regulatory%20and%20procurement%20community (accessed on 27 August 2020).
- Ravi, N.; Cortade, D.L.; Ng, E.; Wang, S.X. Diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2 detection: A comprehensive review of the FDA-EUA COVID-19 testing landscape. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 165, 112454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, J.J.; Rossi, D. Oligonucleotides and the COVID-19 pandemic: A perspective. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2020, 30, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Wong, G.; Shi, W.; Liu, J.; Lai, A.C.K.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.; Bi, Y.; Gao, G.F. Epidemiology, genetic recombination, and pathogenesis of coronaviruses. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Virus Taxonomy: 2019 Release. Available online: https://talk.ictvonline.org/taxonomy/ (accessed on 3 September 2020).
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Lam, C.S.; Lau, C.C.; Tsang, A.K.; Lau, J.H.; Bai, R.; Teng, J.L.; Tsang, C.C.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery of seven novel Mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascella, M.; Rajnik, M.; Cuomo, A.; Dulebohn, S.C.; Di Napoli, R. Features, Evaluation and Treatment Coronavirus (COVID-19). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, D. Emerging coronaviruses: Genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 418–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, J.A.; Olson, A.N.; Neupane, K.; Munshi, S.; San Emeterio, J.; Pollack, L.; Woodside, M.T.; Dinman, J.D. Structural and functional conservation of the programmed −1 ribosomal frameshift signal of SARS coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 10741–10748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Peng, Y.; Huang, B.; Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Niu, P.; Meng, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome composition and divergence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) originating in China. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.X.; Fung, T.S.; Chong, K.K.; Shukla, A.; Hilgenfeld, R. Accessory proteins of SARS-CoV and other coronaviruses. Antiviral Res. 2014, 109, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, B.W.; Kiss, G.; Kunding, A.H.; Bhella, D.; Baksh, M.F.; Connelly, S.; Droese, B.; Klaus, J.P.; Makino, S.; Sawicki, S.G.; et al. A structural analysis of M protein in coronavirus assembly and morphology. J. Struct. Biol. 2011, 174, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmik, D.; Nandi, R.; Jagadeesan, R.; Kumar, N.; Prakash, A.; Kumar, D. Identification of potential inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 by targeting proteins responsible for envelope formation and virion assembly using docking based virtual screening, and pharmacokinetics approaches. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 84, 104451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vennema, H.; Godeke, G.J.; Rossen, J.W.; Voorhout, W.F.; Horzinek, M.C.; Opstelten, D.J.; Rottier, P.J. Nucleocapsid-independent assembly of coronavirus-like particles by co-expression of viral envelope protein genes. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2020–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.; Lin, P.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Lee, S.P.; Chao, Y.C. Assembly of human severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like particles. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 318, 833–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortola, E.; Roy, P. Efficient assembly and release of SARS coronavirus-like particles by a heterologous expression system. FEBS Lett. 2004, 576, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeDiego, M.L.; Álvarez, E.; Almazán, F.; Rejas, M.T.; Lamirande, E.; Roberts, A.; Shieh, W.-J.; Zaki, S.R.; Subbarao, K.; Enjuanes, L. A severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus that lacks the E gene is attenuated in vitro and in vivo. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, Z.Y.; Kong, W.P.; Nabel, G.J. Generation of synthetic severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus pseudoparticles: Implications for assembly and vaccine production. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 12557–12565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millet, J.K.; Whittaker, G.R. Host cell proteases: Critical determinants of coronavirus tropism and pathogenesis. Virus Res. 2015, 202, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchdoerfer, R.N.; Cottrell, C.A.; Wang, N.; Pallesen, J.; Yassine, H.M.; Turner, H.L.; Corbett, K.S.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S.; Ward, A.B. Pre-fusion structure of a human coronavirus spike protein. Nature 2016, 531, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Niu, S.; Song, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Qiao, C.; Hu, Y.; Yuen, K.-Y.; et al. Structural and functional basis of SARS-CoV-2 entry by using human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 894–904.e899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrapp, D.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Goldsmith, J.A.; Hsieh, C.L.; Abiona, O.; Graham, B.S.; McLellan, J.S. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science 2020, 367, 1260–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lee, K.H.; Steinhauer, D.A.; Stevens, D.J.; Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C. Structure of the hemagglutinin precursor cleavage site, a determinant of influenza pathogenicity and the origin of the labile conformation. Cell 1998, 95, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauer, D.A. Role of hemagglutinin cleavage for the pathogenicity of influenza virus. Virology 1999, 258, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobel, A.G.; Benton, D.J.; Xu, P.; Roustan, C.; Martin, S.R.; Rosenthal, P.B.; Skehel, J.J.; Gamblin, S.J. SARS-CoV-2 and bat RaTG13 spike glycoprotein structures inform on virus evolution and furin-cleavage effects. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Chen, K.; Zou, J.; Han, P.; Hao, J.; Han, Z. Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamming, I.; Timens, W.; Bulthuis, M.L.; Lely, A.T.; Navis, G.; van Goor, H. Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis. J. Pathol. 2004, 203, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Liu, G.; Ma, H.; Zhao, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Mohammed, A.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Y.; Xie, J.; et al. Biochemical characterization of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 527, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Li, K.; Liang, J.; Wang, L.; Du, L.; Jiang, S. Current development of COVID-19 diagnostics, vaccines and therapeutics. Microbes Infect. 2020, 22, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.Q.; Xiao, H.; Tam, J.P.; Liu, D.X. Sumoylation of the nucleocapsid protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 2387–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surjit, M.; Liu, B.; Chow, V.T.; Lal, S.K. The nucleocapsid protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus inhibits the activity of cyclin-cyclin-dependent kinase complex and blocks S phase progression in mammalian cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 10669–10681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, Y.; Ulasli, M.; Schepers, H.; Mauthe, M.; V’Kovski, P.; Kriegenburg, F.; Thiel, V.; de Haan, C.A.M.; Reggiori, F. Nucleocapsid protein recruitment to replication-rranscription complexes plays a crucial role in coronaviral life cycle. J. Virol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zúñiga, S.; Cruz, J.L.G.; Sola, I.; Mateos-Gómez, P.A.; Palacio, L.; Enjuanes, L. Coronavirus nucleocapsid protein facilitates template switching and is required for efficient transcription. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schelle, B.; Karl, N.; Ludewig, B.; Siddell, S.G.; Thiel, V. Selective replication of coronavirus genomes that express nucleocapsid protein. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 6620–6630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, R.; Van Zyl, M.; Fielding, B.C. The coronavirus nucleocapsid is a multifunctional protein. Viruses 2014, 6, 2991–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralinski, L.E.; Menachery, V.D. Return of the coronavirus: 2019-nCoV. Viruses 2020, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterer, G.W. Diagnosing viral and atypical pathogens in the setting of community-acquired pneumonia. Clin. Chest Med. 2017, 38, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim Laboratory Biosafety Guidelines for Handling and Processing Specimens Associated with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/lab-biosafety-guidelines.html (accessed on 11 September 2020).
- Gavin, P.J.; Thomson, R.B. Review of rapid diagnostic tests for influenza. Clin. Appl. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 4, 151–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Laboratory Testing for Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) in Suspected Human Cases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Overview of Testing for SARS-CoV-2; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2020.
- Somerville, L.K.; Ratnamohan, V.M.; Dwyer, D.E.; Kok, J. Molecular diagnosis of respiratory viruses. Pathology 2015, 47, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. In Vitro Diagnostics EUAs. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-emergency-use-authorizations-medical-devices/vitro-diagnostics-euas (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim Guidelines for Collecting, Handling, and Testing Clinical Specimens for COVID-19. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/guidelines-clinical-specimens.html (accessed on 13 September 2020).
- Faoagali, J. ‘Swabs’ then and now: Cotton to flocked nylon. Microbiol. Aust. 2010, 31, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biomeme. Biomeme SARS-CoV-2 Real-Time RT-PCR Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141052/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Jiangsu CoWin Biotech. Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Fast Nucleic Acid Detection Kit (PCR-Fluorescence Probing). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/140425/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Sansure BioTech. Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Nucleic Acid Diagnostic Kit (PCR-Fluorescence Probing). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/137651/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Fluidigm. Advanta Dx SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141541/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Yale School of Public Health. SalivaDirect. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141192/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Quidel. Lyra Direct SARS-CoV-2 Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/138178/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- dba SpectronRX. Hymon SARS-CoV-2 Test Kit. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/138530/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- BillionToOne. qSanger-COVID-19 Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141935/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- LumiraDx. LumiraDx SARS-CoV-2 RNA STAR Complete. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/143062/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Detectachem. MobileDetect Bio BCC19 (MD-Bio BCC19) Test Kit. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141791/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Bustin, S.A.; Mueller, R. Real-time reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) and its potential use in clinical diagnosis. Clin. Sci. 2005, 109, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heid, C.A.; Stevens, J.; Livak, K.J.; Williams, P.M. Real time quantitative PCR. Genome Res. 1996, 6, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, D. Quantification using real-time PCR technology: Applications and limitations. Trends Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Influenza SARS-CoV-2 (Flu SC2) Multiplex Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/139743/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Roche Molecular Systems. Cobas SARS-CoV-2 & Influenza A/B. 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141887/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Cepheid. Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2/Flu/RSV. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/142437/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Qiagen. QIAstat-Dx Respiratory SARS-CoV-2 Panel. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/136571/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- BioFire Diagnostics. BioFire Respiratory Panel 2.1 (RP2.1). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/137583/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Lin, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Guo, J.; Guo, Y.; Dai, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cai, Y.; et al. Co-infections of SARS-CoV-2 with multiple common respiratory pathogens in infected patients. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 606–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.; Hirsch, J.S.; Narasimhan, M.; Crawford, J.M.; McGinn, T.; Davidson, K.W.; Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area. JAMA 2020, 323, 2052–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Quinn, J.; Pinsky, B.; Shah, N.H.; Brown, I. Rates of co-infection between SARS-CoV-2 and other respiratory pathogens. JAMA 2020, 323, 2085–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttner, B.D.; Catho, G.; Pano-Pardo, J.R.; Pulcini, C.; Schouten, J. COVID-19: Don’t neglect antimicrobial stewardship principles! Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 808–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ge, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhao, K.; Chen, Y.; Wu, B.; Zhu, F.; Zhu, B.; Cui, L. Co-infection with respiratory pathogens among COVID-2019 cases. Virus Res. 2020, 285, 198005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, X.; Fan, X.G. Bacterial and fungal infections in COVID-19 patients: A matter of concern. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2020, 41, 1124–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.-C.; Wang, C.-Y.; Hsueh, P.-R. Co-infections among patients with COVID-19: The need for combination therapy with non-anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents? J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cepheid. Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/136314/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Roche Molecular Systems. cobas SARS-CoV-2 & Influenza A/B Nucleic Acid Test for Use on the Cobas Liat System. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/142193/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- BioFire Diagnostics. BioFire Respiratory Panel 2.1-EZ (RP2.1-EZ). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/142696/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Mesa Biotech. Accula SARS-Cov-2 Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/136355/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Merck Millipore. Rapid Lateral Flow Test Strips: Considerations for Product Development; EMD Millipore Corporation: Billerica, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- GeneMatrix. NeoPlex COVID-19 Detection Kit. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/138100/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Access Bio. CareStart COVID-19 MDx RT-PCR. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/139832/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Rheonix. Rheonix COVID-19 MDx Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/137489/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Visby Medical. Visby Medical COVID-19. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/142228/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- BioMérieux. SARS-COV-2 R-GENE. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/137742/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- BioFire Defense. BioFire COVID-19 Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/136353/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- DxTerity Diagnostics. DxTerity SARS-CoV-2 RT PCR CE Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141669/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Alimetrix. Alimetrix SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/142592/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- PlexBio. IntelliPlex SARS-CoV-2 Detection Kit. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/139527/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Applied BioCode. BioCode SARS-CoV-2 Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/139049/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- ChromaCode. HDPCR SARS-CoV-2 Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/138786/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Gordon, M.J.; Huang, X.; Pentoney, S.L., Jr.; Zare, R.N. Capillary electrophoresis. Science 1988, 242, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GenMark Diagnostics. ePlex SARS-CoV-2 Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/136282/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- GenMark Diagnostics. ePlex Respiratory Pathogen Panel 2. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/142905/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Ethos Laboratories. Ethos Laboratories SARS-CoV-2 MALDI-TOF Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/140780/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- National Jewish Health. SARS-CoV-2 MassArray Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/142548/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Agena Bioscience. MassARRAY SARS-CoV-2 Panel. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/143334/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- LumiraDx. LumiraDx SARS-CoV-2 RNA STAR. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141057/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Gnomegen. Gnomegen COVID-19 RT-Digital PCR Detection Kit. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/136738/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Bio-Rad Laboratories. Bio-Rad SARS-CoV-2 ddPCR Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/137579/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- PreciGenome. FastPlex Triplex SARS-CoV-2 Detection Kit (RT-Digital PCR). Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/139523/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Abbott Diagnostics. ID NOW COVID-19. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/136525/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Cue Health. Cue COVID-19 Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/138826/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Liu, J.; Nian, Q.-G.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.-F.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Zhu, S.-Y.; Zhu, Q.-Y.; Qin, E.D.; et al. Development of reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for rapid detection of novel avian influenza A (H7N9) virus. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahony, J.; Chong, S.; Bulir, D.; Ruyter, A.; Mwawasi, K.; Waltho, D. Development of a sensitive loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay that provides specimen-to-result diagnosis of respiratory syncytial virus infection in 30 min. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Song, Q.; Zhu, R.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, F.; Deng, J.; Qian, Y. Identification of human metapneumovirus genotypes A and B from clinical specimens by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 196, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyrc, K.; Milewska, A.; Potempa, J. Development of loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for detection of human coronavirus-NL63. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 175, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirato, K.; Yano, T.; Senba, S.; Akachi, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Nishinaka, T.; Notomi, T.; Matsuyama, S. Detection of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus using reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP). Virol. J. 2014, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notomi, T.; Mori, Y.; Tomita, N.; Kanda, H. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): Principle, features, and future prospects. J. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parida, M.; Sannarangaiah, S.; Dash, P.K.; Rao, P.V.; Morita, K. Loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A new generation of innovative gene amplification technique; perspectives in clinical diagnosis of infectious diseases. Rev. Med. Virol. 2008, 18, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seasun Biomaterials. AQ-TOP COVID-19 Rapid Detection Kit. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/138307/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Seasun Biomaterials. AQ-TOP COVID-19 Rapid Detection Kit PLUS. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/142800/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Pro-Lab Diagnostics. Pro-AmpRT SARS-CoV-2 Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141149/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Color Genomics. Color Genomics SARS-CoV-2 RT-LAMP Diagnostic Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/138249/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Sherlock BioSciences. Sherlock CRISPR SARS-CoV-2 Kit. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/137746/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- UCSF Health Clinical Laboratories. SARS-CoV-2 RNA DETECTR Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/139937/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Mammoth Biosciences. SARS-CoV-2 DETECTR Reagent Kit. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141765/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Kellner, M.J.; Koob, J.G.; Gootenberg, J.S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Zhang, F. SHERLOCK: Nucleic acid detection with CRISPR nucleases. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2986–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, Y.P.; Othman, S.; Lau, Y.L.; Radu, S.; Chee, H.Y. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A versatile technique for detection of micro-organisms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 626–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qian, C.; Wu, H.; Qian, W.; Wang, R.; Wu, J. Technical aspects of nicking enzyme assisted amplification. Analyst 2018, 143, 1444–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atila BioSystems. iAMP COVID-19 Detection Kit. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/136870/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, R.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Y. Omega Amplification. 2017. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/WO2017205510A1/en (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Hologic. Aptima SARS-CoV-2 Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/138096/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Singleton, P. Nucleic acid amplification II: NASBA, TMA, SDA. In DNA Methods in Clinical Microbiology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 126–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplar Healthcare. Poplar SARS-CoV-2 TMA Pooling Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/140792/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Quest Diagnostics Infectious Disease. Quest Diagnostics HA SARS-CoV-2 Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/140239/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- PrivaPath Diagnostics. LetsGetChecked Coronavirus (COVID-19) Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/138406/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Beijing Wantai Biological Pharmacy. Wantai SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Kit. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141997/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- RTA Laboratories Biological Products Pharmaceutical and Machinery Industry. Diagnovital SARS-CoV-2 Real-Time PCR Kit. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/138928/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Kchouk, M.; Gibrat, J.; Elloumi, M. Generations of sequencing technologies: From first to next generation. Biol. Med. 2017, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illumina. Illumina COVIDSeq Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/138776/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- ARTIC Network. SARS-CoV-2. Available online: https://artic.network/ncov-2019 (accessed on 13 November 2020).
- Guardant Health. Guardant-19. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141487/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- University of California. UCLA SwabSeq COVID-19 Diagnostic Platform. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/142805/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Helix. Helix COVID-19 NGS Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/140917/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Clear Labs. Clear Dx SARS-CoV-2 Test. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/142418/download (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Ambardar, S.; Gupta, R.; Trakroo, D.; Lal, R.; Vakhlu, J. High throughput sequencing: An overview of sequencing chemistry. Indian J. Microbiol. 2016, 56, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. SARS-CoV-2 Reference Panel Comparative Data. 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/sars-cov-2-reference-panel-comparative-data (accessed on 2 November 2020).
- Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics. SARS-CoV-2 Diagnostic Pipeline. Available online: https://www.finddx.org/covid-19/pipeline/?section=molecular-assays#diag_tab (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- Cowling, B.J.; Leung, G.M. Epidemiological research priorities for public health control of the ongoing global novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) outbreak. Eur. Surveill. 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GlobeNewswire. QuantuMDx Launches Rapid, Sensitive SARS-CoV-2 Test. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2020/05/01/2025959/0/en/QuantuMDx-Launches-Rapid-Sensitive-SARS-CoV-2-Test.html (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- Scope Fluidics. SARS-CoV-2. Available online: http://pcrone.com/products/sars-cov-2/ (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- Binx Health. Sherlock Biosciences and Binx Health Announce Global Partnership to Develop First CRISPR-Based Point-of-Care Test for COVID-19. Available online: https://mybinxhealth.com/news/sherlock-biosciences-binx-health-partnership-crispr-poc-covid-19/ (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- Genedrive. Point-of-Care Solution to Detect SARS-CoV-2 Virus in Saliva. Available online: http://www.genedriveplc.com/press-releases/gdr_-_poc_update_(22.10.20).pdf (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- Spartan Bioscience. SPARTAN COVID-19 TEST. Available online: https://www.spartanbio.com/products/medical/covid-19/ (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- National Institutes of Health. Rapid Acceleration of Diagnostics (RADx). Available online: https://www.nih.gov/research-training/medical-research-initiatives/radx/funding#radx-tech-atp-funded (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- Bosch. PCR-Test for SARS-CoV-2. Available online: https://www.bosch-vivalytic.com/en/product/vivalytic-tests/pcr-test-for-sars-cov-2/ (accessed on 12 November 2020).
- DnaNudge. CovidNudge Test. Available online: https://www.dnanudge.com/v6/uploads/files/covid-docs/CovidNudge-IFU-4.1a-October-2020.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- Diagnostics for the Real World. SAMBA II SARS-CoV-2 Test. Available online: https://drw-ltd.com/samba-ii-sars-cov-2-test.html (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- OptiGene. COVID-19_Direct Plus RT-LAMP KIT-500 Kit. Available online: http://www.optigene.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/IFU_DirectPlus_v1.0-1.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- Caspr Biotech. Innovative Solutions for SARS-CoV-2 Testing. Available online: https://caspr.bio/pdf/Brochure.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- Molbio Diagnostics. Truenat SARS CoV-2. Available online: https://www.molbiodiagnostics.com/uploads/product_download/20200610.165040~Truenat-SARS-CoV-2-packinsert-VER-03.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- Mobidiag. A Complete Solution for Rapid Molecular Diagnostics of Coronavirus Infection. Available online: https://mobidiag.com/products/coronavirus/#Novodiag-COVID-19 (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- GeneReach Biotechnology. POCKIT™ Central SARS-CoV-2 (orf 1ab) Premix Reagent. Available online: https://www.genereach.com/index.php?func=product&action=add_item&item_no=209 (accessed on 7 November 2020).
- Samson, R.; Navale, G.R.; Dharne, M.S. Biosensors: Frontiers in rapid detection of COVID-19. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
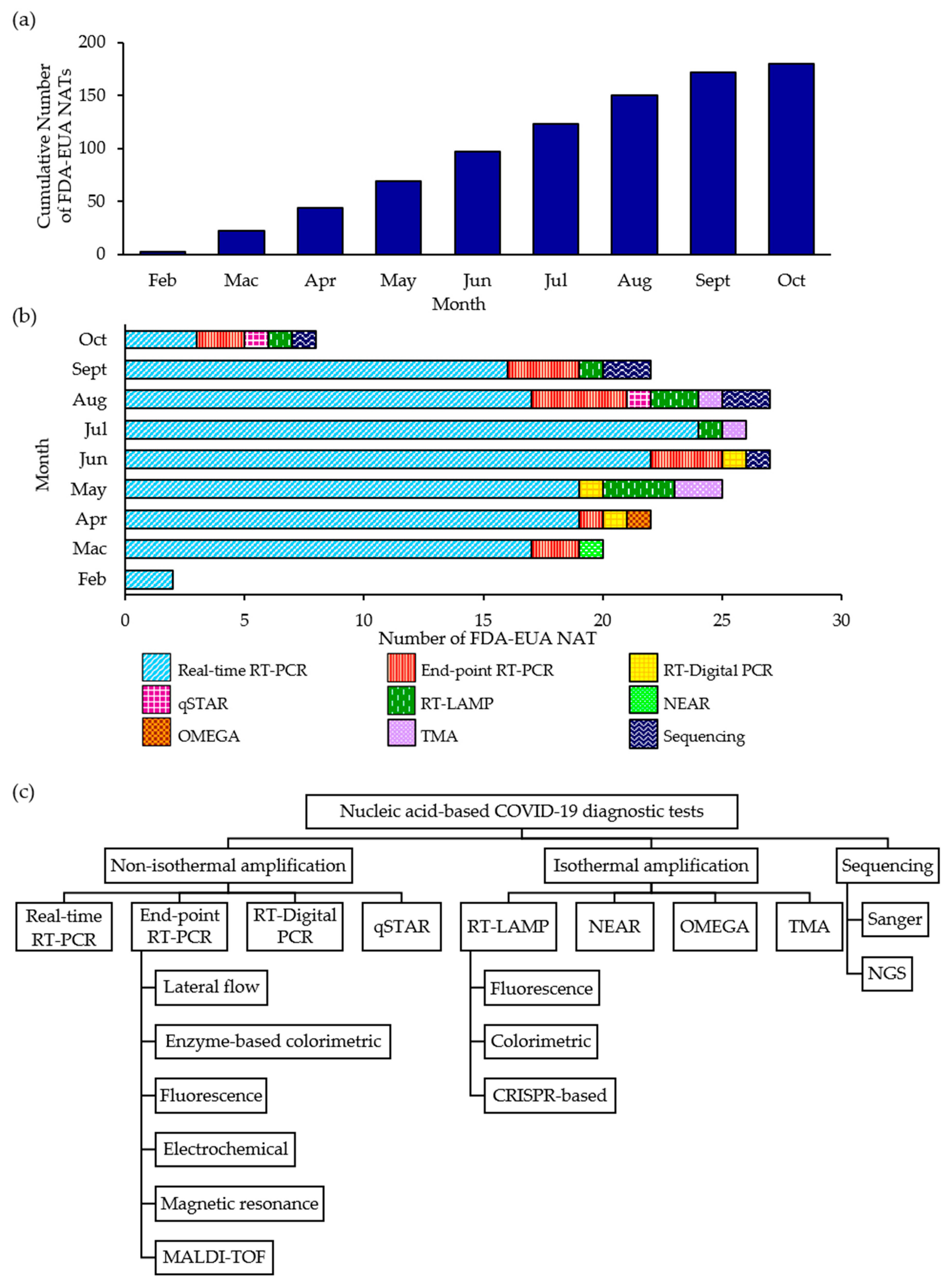
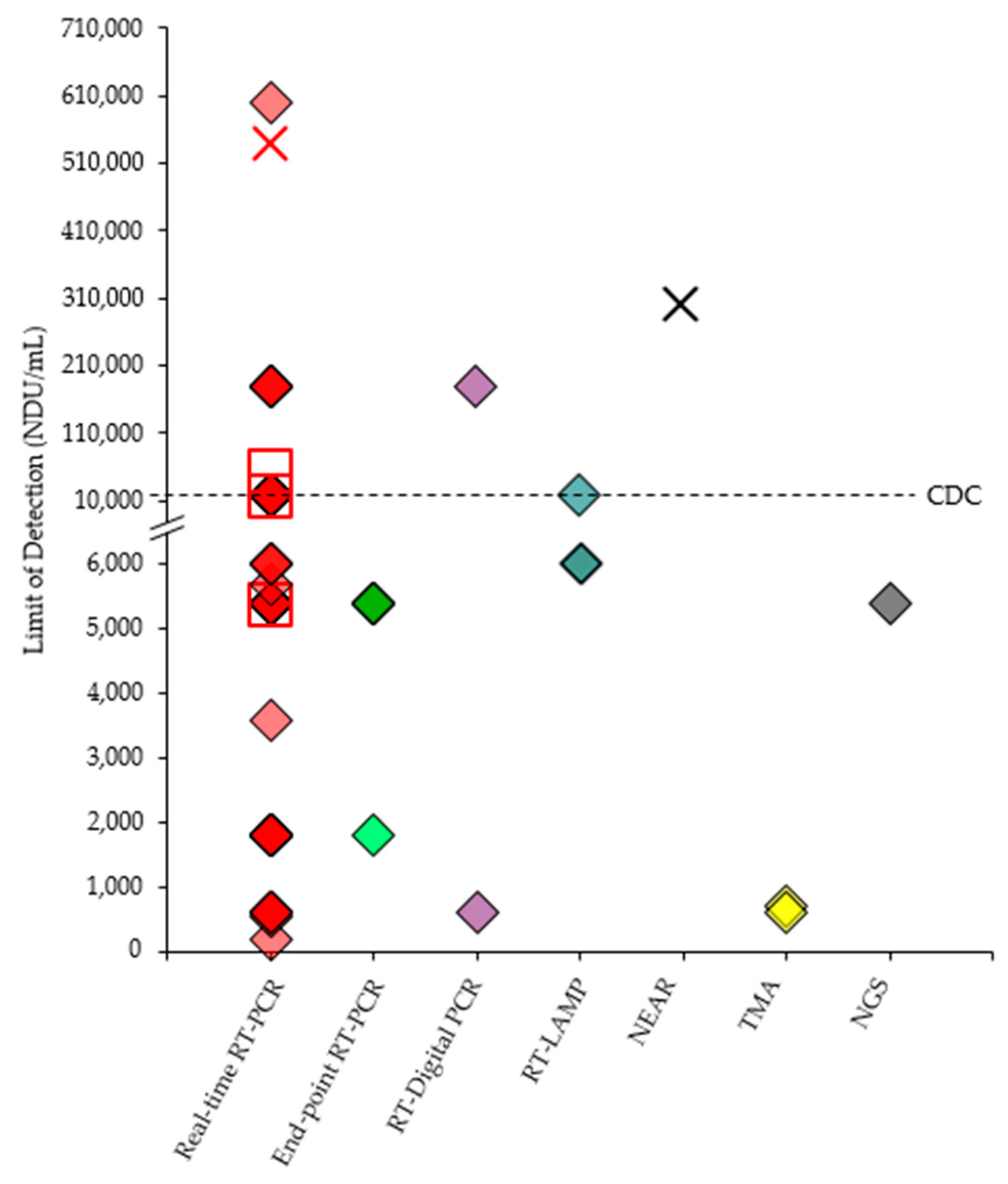
| Developer | Name of the Test | Authorized Setting | Targeted Gene(s) of SARS-CoV-2 | Limit of Detection (LoD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real-Time RT-PCR * | ||||
| Beijing Wantai Biological Pharmacy Enterprise Co., Ltd. | Wantai SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Kit | H | Orf1ab, N | 50 copies/mL |
| Fluidigm Corporation | Advanta Dx SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Assay | H | N1, N2 | 6.25 GE/µL |
| Yale School of Public Health, Department of Epidemiology of Microbial Diseases | SalivaDirect | H | N1 | 6 copies/µL |
| Biomeme, Inc. | Biomeme SARS-CoV-2 Real-Time RT-PCR Test | H | Orf1ab, S | 1.8 GE/µL |
| Jiangsu CoWin Biotech Co., Ltd. | Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Fast Nucleic Acid Detection Kit (PCR-Fluorescence Probing) | H | Orf1ab, N | 300 copies/mL |
| Access Bio, Inc. | CareStart COVID-19 MDx RT-PCR | H | N, RdRp | 10 copies/reaction |
| Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) | Influenza SARS-CoV-2 (Flu SC2) Multiplex Assay | H | N | 1.01 × 10−2 TCID50/mL (TaqPath 1-step Multiplex); 5.06 × 10−2 TCID50/mL (Ultraplex 1-step ToughMix) |
| RTA Laboratories Biological Products Pharmaceutical and Machinery Industry | Diagnovital SARS-CoV-2 Real-Time PCR Kit | H | E, RdRp | 38 copies/mL |
| dba SpectronRX | Hymon SARS-CoV-2 Test Kit | H | E, N | 5 copies/µL |
| Quidel Corporation | Lyra Direct SARS-CoV-2 Assay | H | pp1ab | 1.28 × 104 GE/mL |
| GeneMatrix, Inc. | NeoPlex COVID-19 Detection Kit | H | N, RdRp | 50 copies/reaction |
| BioMérieux SA | SARS-COV-2 R-GENE | H | PCR1: N, RdRp PCR2: E | 380 GC/mL |
| Sansure BioTech Inc. | Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Nucleic Acid Diagnostic Kit (PCR-Fluorescence Probing) | H | Orf1ab, N | 200 copies/mL |
| Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. | TaqPath COVID-19 Combo Kit | H | Orf1ab, S, N | 10 GCE/reaction |
| Wadsworth Center, NYSDOH | New York SARS-CoV-2 Real-time Reverse Transcriptase (RT)-PCR Diagnostic Panel | H | N1, N2 | 25 GC/reaction |
| Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) | CDC 2019-Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV) Real-Time RT-PCR Diagnostic Panel | H | N1, N2 | 100 RNA copies/µL (Qiagen DSP); 100.5 RNA copies/µL (Qiagen EZ1) |
| Real-time RT-PCR for Use on Automated Sample-to-result System | ||||
| BioFire Diagnostics, LLC | BioFire Respiratory Panel 2.1-EZ (RP2.1-EZ) | H, M, W | S, M | 5 × 102 copies/mL |
| Cepheid | Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2/Flu/RSV | H, M, W | E, N2 | 131 copies/mL |
| Roche Molecular Systems, Inc. | cobas SARS-CoV-2 & Influenza A/B Nucleic Acid Test for use on the cobas Liat System | H, M, W | Orf1a/b, E | 12 copies/mL |
| Roche Molecular Systems, Inc. | cobas SARS-CoV-2 & Influenza A/B | H, M | Orf1a/b, E | 0.12 TCID50/mL |
| BayCare Laboratories, LLC | BayCare SARS-CoV-2 RT PCR Assay | H | ORF1, E | 0.007 TCID50/mL |
| Kaiser Permanente Mid-Atlantic States | KPMAS COVID-19 Test | H | Orf1ab, E | 0.007 TCID50/mL (Orf1ab); 0.004 TCID50/mL (E) |
| University of California San Diego Health | UCSD RC SARS-CoV-2 Assay | H | Orf1ab, E | 0.007 TCID50/mL (Orf1ab); 0.004 TCID50/mL (E) |
| Quest Diagnostics Infectious Disease, Inc. | Quest Diagnostics PF SARS-CoV-2 Assay | H | 2 regions of Orf1ab | 1 × 10−2 TCID50/mL |
| Quest Diagnostics Infectious Disease, Inc. | Quest Diagnostics RC SARS-CoV-2 Assay | H | Orf1ab, E | 0.007 TCID50/mL (Orf1ab); 0.004 TCID50/mL (E) |
| Omnipathology Solutions Medical Corporation | Omni COVID-19 Assay by RT-PCR | H | N1, N2 | 1.23 copies/µL |
| Abbott Molecular Inc. | Alinity m SARS-CoV-2 assay | H, M | N, RdRp | 100 virus copies/mL |
| BioFire Diagnostics, LLC | BioFire Respiratory Panel 2.1 (RP2.1) | H, M | S, M | 5.0 × 102 copies/mL |
| Becton, Dickinson & Company (BD) | BD SARS-CoV-2Reagents for BD MAX System | H, M | N1, N2 | 40 GE/mL |
| Luminex Corporation | ARIES SARS-CoV-2 Assay | H, M | Orf1ab, N | 3.33 × 102 GCE/mL |
| Becton, Dickinson & Company (BD) | BioGX SARS-CoV-2 Reagents for BD MAX™ System | H, M | N1, N2 | 40 GE/mL |
| QIAGEN GmbH | QIAstat-Dx Respiratory SARS-CoV-2 Panel | H, M | Orf1b, E | 500 copies/mL |
| NeuMoDx Molecular, Inc. | NeuMoDx SARS-CoV-2 Assay | H, M | N, Nsp2 | 150 copies/mL |
| BioFire Defense, LLC | BioFire COVID-19 Test | H, M | 2 regions of Orf1ab, Orf8 | 3.3 × 102 GC/mL |
| Cepheid | Xpert Xpress SARS-CoV-2 | H, M, W | E, N2 | 0.02 PFU/mL |
| DiaSorin Molecular LLC | Simplex COVID-19 Direct | H, M | Orf1ab, S | 500 copies/mL |
| Abbott Diagnostics Scarborough, Inc. | Abbott RealTime SARS-CoV-2 | H | N, RdRp | 100 virus copies/mL |
| Hologic, Inc. | Panther Fusion SARS-CoV-2 Assay | H | 2 regions of Orf1ab | 1 × 10−2 TCID50/mL |
| Roche Molecular Systems, Inc. | cobas SARS-CoV-2 | H, M | Orf1ab, E | 0.007 TCID50/mL (Orf1ab); 0.004 TCID50/mL (E) |
| End-point RT-PCR with Lateral Flow Detection | ||||
| Mesa Biotech Inc. | Accula SARS-CoV-2 Test | H, M, W | N | 200 copies/reaction |
| End-point RT-PCR with Enzyme-based Colorimetric Detection | ||||
| Visby Medical, Inc. | Visby Medical COVID-19 | H, M | N | 1112 GC/mL |
| Rheonix, Inc. | Rheonix COVID-19 MDx Assay | H | N1 | 625 GE/mL |
| End-point RT-PCR with Fluorescence Detection | ||||
| Alimetrix, Inc. | Alimetrix SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Assay | H | Orf1ab, N1, N2 | 250 copies/mL (Zymo Research Quick-DNA/RNA Viral MagBead Extraction); 1000 copies/mL (Qiagen QIAamp 96 Virus QIAcube HT Kit) |
| DxTerity Diagnostics, Inc. | DxTerity SARS-CoV-2 RT PCR CE Test | H | Orf1ab, E, N | 50 copies/mL |
| QDx Pathology Services | QDX SARS-CoV-2 Assay | H | N1, N2 | 1000 copies/mL (Applied Biosystems 7500 Fast and the Applied Biosystems Quant Studio 7 systems), 250 copies/mL (Applied Biosystems Quant Studio 12K system) |
| PlexBio Co., Ltd. | IntelliPlex SARS-CoV-2 Detection Kit | H | E, N, RdRp | 140 copies/mL |
| Applied BioCode, Inc. | BioCode SARS-CoV-2 Assay | H | 2 regions in N gene | 1.72 × 10−2 TCID50/mL |
| ChromaCode Inc. | HDPCR SARS-CoV-2 Assay | H | N1, N2 | 1000 copies/mL (Applied Biosystems 7500 Fast and the Applied Biosystems Quant Studio 7 systems), 250 copies/mL (Applied Biosystems Quant Studio 12K system) |
| End-point RT-PCR with Electrochemical Detection | ||||
| GenMark Diagnostics, Inc. | ePlex Respiratory Pathogen Panel 2 | H, M | NR | 250 GC/mL |
| GenMark Diagnostics, Inc. | ePlexSARS-CoV-2 Test | H, M | NR | 750 GC/mL |
| End-point RT-PCR with Magnetic Resonance Detection | ||||
| T2 Biosystems, Inc. | T2SARS-CoV-2 Panel | H, M | NR | 2000 GE/mL |
| End-point RT-PCR with MALDI-TOF Detection | ||||
| Agena Bioscience, Inc. | MassARRAY SARS-CoV-2 Panel | H | Orf1ab, N1, N2, N3, ORF1 | 2.5 copies/μL |
| National Jewish Health | SARS-CoV-2 MassArray Test | H | Orf1ab, N1, N2, N3, ORF1 | 0.69 copies/µL |
| Ethos Laboratories | Ethos Laboratories SARS-CoV-2 MALDI-TOF Assay | H | Orf1ab, N1, N2, N3, ORF1 | 1 TCID50/mL |
| RT-Digital PCR | ||||
| PreciGenome LLC | FastPlex Triplex SARS-CoV-2 detection kit (RT-Digital PCR) | H | Orf1ab, N | 571.4 copies/mL |
| Gnomegen LLC | Gnomegen COVID-19 RT-Digital PCR Detection Kit | H | N1, N2 | 8 GC/reaction |
| Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc | Bio-Rad SARS-CoV-2 ddPCR Test | H | N1, N2 | 150 copies/mL |
| qSTAR | ||||
| LumiraDx UK Ltd. | LumiraDx SARS-CoV-2 RNA STAR Complete | H | Orf1a | 7500 copies/mL |
| LumiraDx UK Ltd. | LumiraDx SARS-CoV-2 RNA STAR | H | Orf1a | 500 copies/mL |
| Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification | ||||
| Cue Health Inc. | Cue COVID-19 Test | H, M, W | N | 1.3 GC/µL |
| RT-LAMP with Fluorescence Detection | ||||
| Seasun Biomaterials, Inc. | AQ-TOP COVID-19 Rapid Detection Kit PLUS | H | Orf1ab, N | 1 copy/µL |
| Pro-Lab Diagnostics | Pro-AmpRT SARS-CoV-2 Test | H | Orf1ab | 125 GE/swab |
| Seasun Biomaterials, Inc. | AQ-TOP COVID-19 Rapid Detection Kit | H | Orf1ab | 7 copies/µL |
| RT-LAMP with Colorimetric Detection | ||||
| Detectachem Inc. | MobileDetect Bio BCC19 (MD-Bio BCC19) Test Kit | H, M | E, N | 75 copies/µL |
| Color Genomics, Inc. | Color Genomics SARS-CoV-2 RT-LAMP Diagnostic Assay | H | Orf1ab, E, N | 0.75 copies/µL |
| RT-LAMP with CRISPR-based Detection | ||||
| Mammoth Biosciences, Inc. | SARS-CoV-2 DETECTR Reagent Kit | H | N | 20 copies/µL |
| UCSF Health Clinical Laboratories, UCSF Clinical Labs at China Basin | SARS-CoV-2 RNA DETECTR Assay | H | N | 20 copies/µL |
| Sherlock BioSciences, Inc. | Sherlock CRISPR SARS-CoV-2 Kit | H | Orf1ab, N | 6.75 copies/µL (Orf1ab); 1.35 copies/µL (N) |
| NEAR | ||||
| Abbott Diagnostics Scarborough, Inc. | ID NOW COVID-19 | H, M, W | RdRp | 125 GE/mL |
| OMEGA Amplification | ||||
| Atila BioSystems, Inc. | iAMP COVID-19 Detection Kit | H | Orf1ab, N | 10 copies/μL |
| TMA | ||||
| Poplar Healthcare | Poplar SARS-CoV-2 TMA Pooling assay | H | 2 regions of Orf1ab | 83 copies/mL |
| Quest Diagnostics Infectious Disease, Inc. | Quest Diagnostics HA SARS-CoV-2 Assay | H | 2 regions of Orf1ab | 83 copies/mL |
| PrivaPath Diagnostics, Inc. | LetsGetChecked Coronavirus (COVID-19) Test | H | 2 regions of Orf1ab | 83 copies/mL |
| Hologic, Inc. | Aptima SARS-CoV-2 assay | H | 2 regions of Orf1ab | 83 copies/mL |
| Sanger Sequencing | ||||
| BillionToOne, Inc. | qSanger-COVID-19 Assay | H | N | 3200 copies/mL |
| NGS | ||||
| University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) | UCLA SwabSeq COVID-19 Diagnostic Platform | H | S2 | 250 GCE/mL |
| Clear Labs, Inc. | Clear Dx SARS-CoV-2 Test | H | 21 target genes | 2000 copies/mL |
| Guardant Health, Inc. | Guardant-19 | H | N1 | 125 copies/mL |
| Helix OpCo LLC (dba Helix) | Helix COVID-19 NGS Test | H | S | 125 GCE/mL |
| Illumina, Inc. | Illumina COVIDSeq Test | H | 98 target genes | 1000 copies/mL |
| Developer | Name of Test | Technology | Specimen Indicated for Testing | Time to Result | Limit of Detection | Target Gene | Status | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DnaNudge Ltd. | CovidNudge Test | RT-PCR | NP swab or sputum | 90 min | 250 viral copies/swab | N1, N2, N3, RdRp1, RdRp2, E | CE-IVD | [160] |
| Diagnostics for the Real World Ltd. | SAMBA II SARS-CoV-2 Test | Isothermal amplification, lateral flow | Throat and nose swabs | <90 min | 250 copies/mL | Orf1ab, N | CE-IVD | [161] |
| OptiGene Ltd. | COVID-19_Direct Plus RT-LAMP KIT-500 kit | RT-LAMP | OP/NP swab dilutions and saliva samples | <20 min | 103 copies/mL | NR | CE-IVD | [162] |
| Caspr Biotech | Caspr Lyo-CRISPR SARS-CoV-2 Kit (FAM) Direct Sample | RT-LAMP, CRISPR | NP/OP and nasal swabs | <60 min | 25 copies/μL | 2 regions in N, Orf1ab | N/A | [163] |
| Molbio Diagnostics Pvt Ltd. | Truenat SARS CoV-2 | Chip-based Real-Time RT-PCR | OP and NP swabs | 35 min | 407 genome copies/mL | RdRp | India CDSCO | [164] |
| Mobidiag | Novodiag COVID-19 | RT-PCR | NP swab | 1 h 20 min | NR | Orf1ab, N | CE-IVD | [165] |
| GeneReach Biotechnology Corp | POCKIT Central SARS-CoV-2 (Orf1ab) Premix Reagent | Insulated Isothermal PCR (iiPCR) technology | OP swab | 85 min | NR | Orf1ab | CE-IVD | [166] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, C.Y.; Chan, K.G.; Yean, C.Y.; Ang, G.Y. Nucleic Acid-Based Diagnostic Tests for the Detection SARS-CoV-2: An Update. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010053
Yu CY, Chan KG, Yean CY, Ang GY. Nucleic Acid-Based Diagnostic Tests for the Detection SARS-CoV-2: An Update. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(1):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010053
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Choo Yee, Kok Gan Chan, Chan Yean Yean, and Geik Yong Ang. 2021. "Nucleic Acid-Based Diagnostic Tests for the Detection SARS-CoV-2: An Update" Diagnostics 11, no. 1: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010053
APA StyleYu, C. Y., Chan, K. G., Yean, C. Y., & Ang, G. Y. (2021). Nucleic Acid-Based Diagnostic Tests for the Detection SARS-CoV-2: An Update. Diagnostics, 11(1), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010053







