Brain Resources: How Semantic Cueing Works in Mild Cognitive Impairment due to Alzheimer’s Disease (MCI-AD)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Controls
2.3. Neuropsychological Evaluation
2.4. FDG-PET Acquisition
2.5. Image Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Structural Connectivity
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Neuropsychological Tests
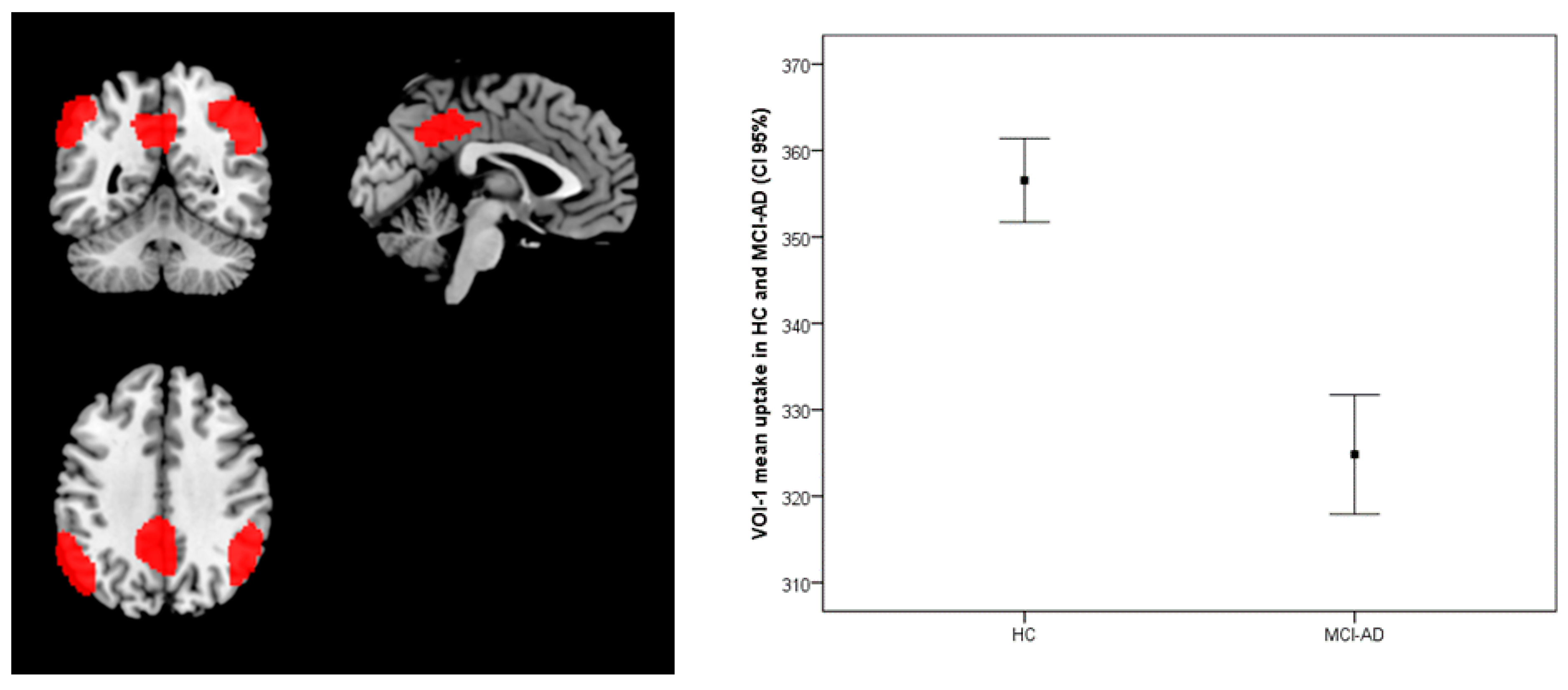
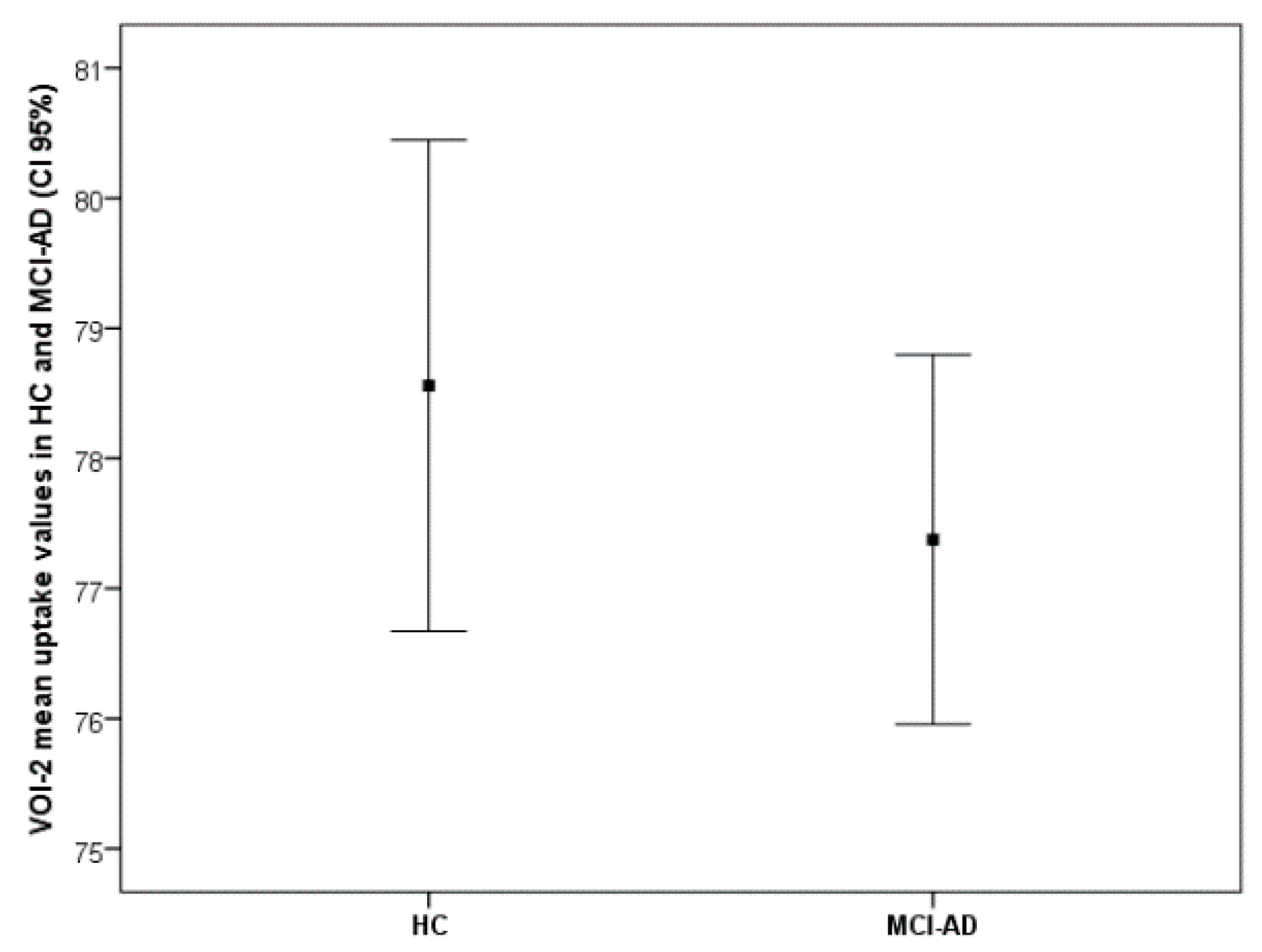
3.2. FDG-PET
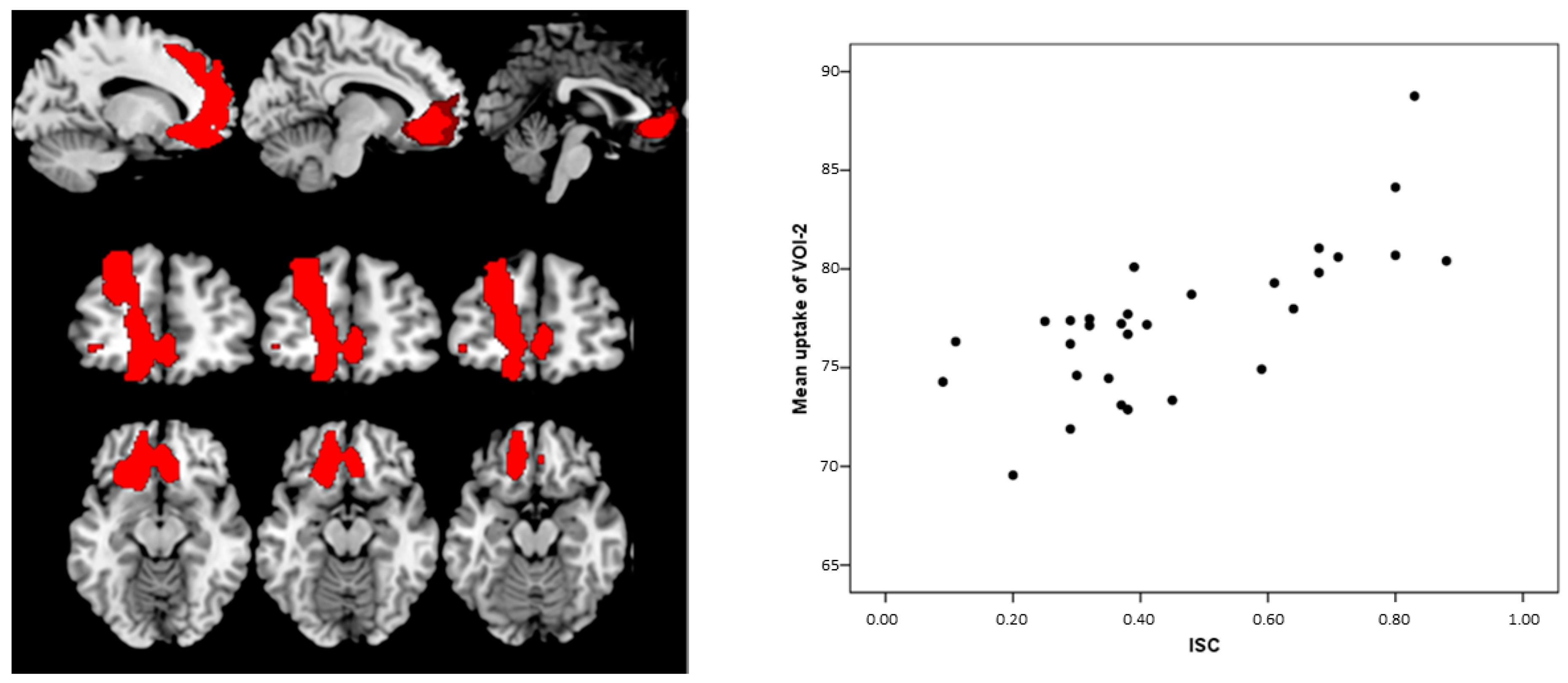
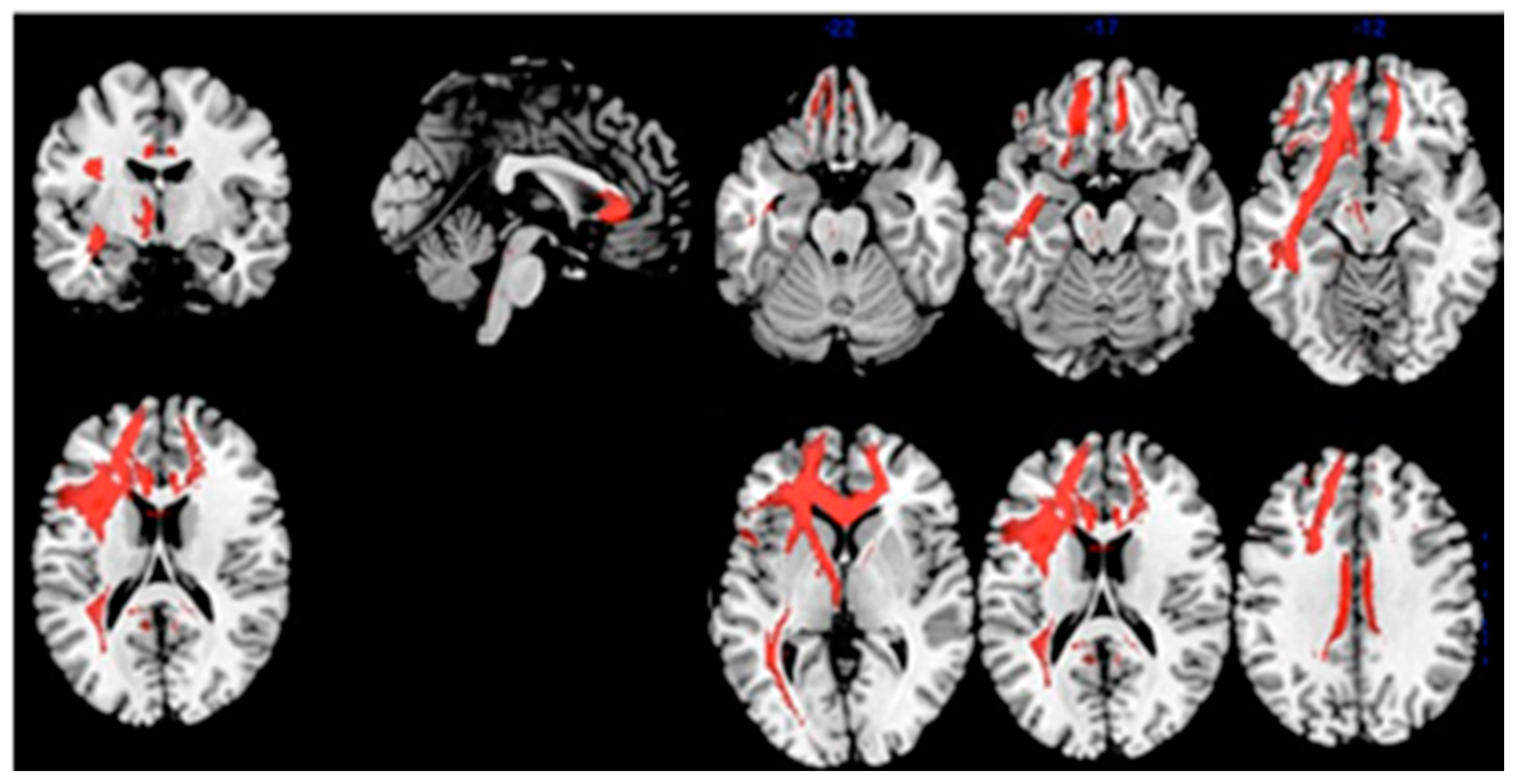
3.3. Structural Connectivity
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albert, M.S.; DeKosky, S.T.; Dickson, D.; Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Fox, N.C.; Gamst, A.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.J.; Petersen, R.C.; et al. The Diagnosis of Mild Cognitive Impairment due to Alzheimer’s Disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association Workgroups on Diagnostic Guidelines for Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grober, E.; Veroff, A.E.; Lipton, R.B. Temporal unfolding of declining episodic memory on the Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test in the predementia phase of Alzheimer’s disease: Implications for clinical trials. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 10, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Jacova, C.; Hampel, H.; Molinuevo, J.L.; Blennow, K. Advancing research diagnostic criteria for Alzheimer’s disease: The IWG-2 criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Bak, T.; Caffarra, P.; Caltagirone, C.; Ceccaldi, M.; Collette, F.; Crutch, S.J.; Della Sala, S.; Démonet, J.-F.; Dubois, B.; et al. The need for harmonisation and innovation of neuropsychological assessment in neurodegenerative dementias in Europe: Consensus document of the Joint Program for Neurodegenerative Diseases Working Group. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarazin, M.; Berr, C.; De Rotrou, J.; Fabrigoule, C.; Pasquier, F.; Legrain, S.; Michel, B.; Puel, M.; Volteau, M.; Touchon, J.; et al. Amnestic syndrome of the medial temporal type identifies prodromal AD: A longitudinal study. Neurology 2007, 69, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlesimo, G.A.; Monaco, M.; Fadda, L.; Serra, L.; Marra, C.; Caltagirone, C.; Bruni, A.C.; Curcio, S.; Bozzali, M.; Carlesimo, G.A. Influence of controlled encoding and retrieval facilitation on memory performance in patients with different profiles of mild cognitive impairment. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 938–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, G.; Vanacore, N.; Vetrano, D.L.; Priori, A.; Rizzuto, D.; Mayer, F.; Maggiore, L.; Ghiretti, R.; Cucumo, V.; Mariani, C.; et al. Free and cued selective reminding test predicts progression to Alzheimer’s disease in people with mild cognitive impairment. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 39, 1867–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, B.; Albert, M.L. Amnestic MCI or prodromal Alzheimer’s disease? Lancet Neurol. 2004, 3, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Jacova, C.; Dekosky, S.T.; Barberger-Gateau, P.; Cummings, J. Research criteria for the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: Revising the NINCDS-ADRDA criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, B.; Feldman, H.H.; Jacova, C.; Cummings, J.L.; Dekosky, S.T.; Barberger-Gateau, P. Revising the definition of Alzheimer’s disease: A new lexicon. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tounsi, H.; Deweer, B.; Ergis, A.-M.; Van Der Linden, M.; Pillon, B.; Michon, A.; Dubois, B. Sensitivity to Semantic Cuing: An Index of Episodic Memory Dysfunction in Early Alzheimer Disease. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 1999, 13, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koric, L.; Ranjeva, J.-P.; Felician, O.; Guye, M.; De Anna, F.; Soulier, E.; Didic, M.; Ceccaldi, M. Cued Recall Measure Predicts the Progression of Gray Matter Atrophy in Patients with Amnesic Mild Cognitive Impairment. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2013, 36, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teichmann, M.; Epelbaum, S.; Samri, D.; Levy Nogueira, M.; Michon, A.; Hampel, H. Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test-accuracy for the differential diagnosis of Alzheimer’s and neurodegenerative diseases: A large-scale biomarker-characterized monocenter cohort study (ClinAD). Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquier, F.; Grymonprez, L.; Lebert, F.; Van der Linden, M. Memory impairment differs in frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurocase 2001, 7, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemos, R.; Duro, D.; Simoes, M.R.; Santana, I. The free and cued selective reminding test distinguishes frontotemporal dementia from Alzheimer’s disease. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2014, 29, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffarra, P.; Ghetti, C.; Ruffini, L.; Spallazzi, M.; Spotti, A.; Barocco, F.; Guzzo, C.; Marchi, M.; Gardini, S. Brain Metabolism Correlates of The Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test in Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 51, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epelbaum, S.; Bouteloup, V.; Mangin, J.F.; La Corte, V.; Migliaccio, R.; Bertin, H.; Habert, M.O.; Fischer, C.; Azouani, C.; Fillon, L.; et al. Neural correlates of episodic memory in the Memento cohort. Alzheimer’s Dementia Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2018, 4, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girtler, N.; De Carli, F.; Amore, M.; Arnaldi, D.; Bosia, L.E.; Bruzzaniti, C.; Cappa, S.F.; Cocito, L.; Colazzo, G.; Ghio, L.; et al. A normative study of the Italian printed word version of the free and cued selective reminding test. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 36, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlund, L.-O.; Barkhof, F.; Fazekas, F.; Bronge, L.; Augustin, M.; Sjogren, M.; Wallin, A.; Ader, H.; Leys, D.; Pantoni, L.; et al. A New Rating Scale for Age-Related White Matter Changes Applicable to MRI and CT. Stroke 2001, 32, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, F.; Mazzei, D.; Dessi, B.; Morbelli, S.; Brugnolo, A.; Barbieri, P.; Girtler, N.; Sambuceti, G.; Rodriguez, G.; Pagani, M. Unawareness of Memory Deficit in Amnestic MCI: FDG-PET Findings. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 22, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrone, A.; Asenbaum, S.; Borght, T.V.; Booij, J.; Nobili, F.; Någren, K.; Darcourt, J.; Kapucu, Ö.L.; Tatsch, K.; Bartenstein, P.; et al. EANM procedure guidelines for PET brain imaging using [18F]FDG, version 2. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 36, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gispert, J.D.; Pascau, J.; Reig, S.; Martínez-Lázaro, R.; Molina, V.; García-Barreno, P.; Desco, M. Influence of the normalization template on the outcome of statistical parametric mapping of PET scans. NeuroImage 2003, 19, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Rosa, P.A.; Cerami, C.; Gallivanone, F.; Prestia, A.; Caroli, A.; Castiglioni, I. A standardized [18F]-FDG-PET template for spatial normalization in statistical parametric mapping of dementia. Neuroinformatics 2014, 12, 575–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedges, L.V. Theory for Glass’s Estimator of Effect Size and Related Estimators. J. Educ. Stat. 1981, 6, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choen, J. Statistica Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Foulon, C.; Cerliani, L.; Kinkingnéhun, S.; Levy, R.; Rosso, C.; Urbanski, M.; Volle, E.; De Schotten, M.T. Advanced lesion symptom mapping analyses and implementation as BCBtoolkit. GigaScience 2018, 7, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojkova, K.; Volle, E.; Urbanski, M.; Humbert, F.; Dell’Acqua, F.; De Schotten, M.T. Atlasing the frontal lobe connections and their variability due to age and education: A spherical deconvolution tractography study. Brain Struct. Funct. 2016, 221, 1751–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.D.; Schacter, D.L.; Rotte, M.; Koutstaal, W.; Maril, A.; Dale, A.M.; Rosen, B.R.; Buckner, R.L. Building Memories: Remembering and Forgetting of Verbal Experiences as Predicted by Brain Activity. Science 1998, 281, 1188–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugdahl, K.; Lundervold, A.; Ersland, L.; Smievoll, A.I.; Sundberg, H.; Barndon, R. Left frontal activation during a semantic categorization task: An fMRI-study. Int. J. Neurosci. 1999, 99, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Cabeza, R.; Ciaramelli, E.; Olson, I.R.; Moscovitch, M. The parietal cortex and episodic memory: An attentional account. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Zvi, S.; Soroker, N.; Levy, D.A. Parietal lesion effects on cued recall following pair associate learning. Neuropsychologia 2015, 73, 176–194. [Google Scholar]
- Rajtmajer, S.M.; Roy, A.; Albert, R.; Molenaar, P.C.; Hillary, F.G. A voxelwise approach to determine consensus regions-of-interest for the study of brain network plasticity. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Woodcock, E.A.; White, R.; Diwadkar, V.A. The dorsal prefrontal and dorsal anterior cingulate cortices exert complementary network signatures during encoding and retrieval in associative memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 290, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, S.J.; Spengler, S.; Simons, J.S.; Steele, J.D.; Lawrie, S.M.; Frith, C.D.; Burgess, P.W. Functional Specialization within Rostral Prefrontal Cortex (Area 10): A Meta-analysis. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2006, 18, 932–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minoshima, S.; Giordani, B.; Berent, S.; Frey, K.A.; Foster, N.L.; Kuhl, D.E. Metabolic reduction in the posterior cingulate cortex in very early Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 1997, 42, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morbelli, S.; Piccardo, A.; Villavecchia, G.; Dessi, B.; Brugnolo, A.; Piccini, A.; Caroli, A.; Frisoni, G.; Rodriguez, G.; Nobili, F. Mapping brain morphological and functional conversion patterns in amnestic MCI: A voxel-based MRI and FDG-PET study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 37, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| HC (No. 17 ) (Mean ± sd) | MCI-AD ( No. 30) (Mean ± sd) | t-Test Values | p-Values | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y) | 66.5 ± 11.1 | 74.7 ± 5.7 | −2.841 | 0.010 |
| Education (y) | 11.5 ± 4.2 | 9.6 ± 4.6 | 1.455 | 0.154 |
| Gender M/F | 7/10 | 7/23 | / | / |
| MMSE | 28.4 ± 1.14 | 24.8 ± 3.3 | 4.232 | 0.001 |
| Tmt A | 55.9 ± 34.6 | 87.2 ± 43.5 | −2.702 | 0.010 |
| Tmt B | 108.8 ± 93.9 | 232.7±129.4 | - * | - |
| Symbol Digit | 37.8 ± 16.0 | 20.6 ± 8.2 | 4.136 | 0.001 |
| Stroop C | 42.0 ± 10.9 | 31.5 ± 10.3 | 3.222 | 0.003 |
| Stroop CW | 19.4 ± 9.7 | 10.4 ± 5.3 | 3.533 | 0.002 |
| Digit span | 6.1 ± 0.8 | 5.6 ± 0.9 | 1.934 | 0.171 |
| Corsi | 4.8 ± 1.1 | 3.9 ± 0.7 | 1.433 | 0.061 |
| Babcock test | 13.6 ± 3.9 | 4.6 ± 2.4 | 8.532 | 0.001 |
| CDT | 13.9 ± 1.6 | 11.2 ± 4.4 | 3.107 | 0.003 |
| CP | 10.1 ± 1.3 | 8.6 ± 2.0 | 2.936 | 0.005 |
| CPE | 68.2 ± 2.2 | 64.6 ± 5.8 | 3.042 | 0.004 |
| FVF | 36.2 ± 9.7 | 25.0 ± 9.1 | 3.832 | 0.001 |
| SVF | 42.9 ± 13.3 | 25.8 ± 8.1 | 4.818 | 0.001 |
| GDS | 3.4 ± 3.1 | 4.6 ± 3.7 | −1.207 | ns. |
| ADL | 6.0 ± 0 | 5.8 ± 0.57 | 1.278 | ns. |
| IADL | 8.0 ± 0 | 6.7 ± 1.5 | 4.306 | 0.001 |
| CDR | 0 ± 0 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | −7.077 | 0.001 |
| FCSRT | HC (No.17) | MCI-AD (No. 30) | t-Test Value | p Value | Effect Size | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCSRT-IFR | 25.0 ± 7.2 | 9.1 ± 6.0 | 7.731 | 0.001 | 1.528 | 0.951 |
| FCSRT-ITR | 46.1 ± 2.2 | 26.1 ± 10.5 | 10.024 | 0.001 | 2.344 | 0.988 |
| FCSRT-ISC | 0.93 ± 0.08 | 0.45 ± 0.22 | 10.764 | 0.001 | 2.899 | 0.978 |
| FCSRT-RP | 15.9 ± 0.3 | 13.4 ± 2.5 | 5.199 | 0.001 | 1.244 | 0.878 |
| FCSRT-DFR | 11.1 ± 2.6 | 2.7 ± 3.2 | 9.818 | 0.001 | 2.799 | 0.959 |
| FCSRT-TDR | 15.6 ± 0.63 | 8.5 ± 4.4 | 0.662 | 0.001 | 1.376 | 0.972 |
| Statistic | Cluster Level | Voxel Level | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster Extent | FWE-Corr. p Value | Cortical Region | Z Score of Maximum | Talairach Coordinates | Cortical Region | BA | |
| Comparison: Brain metabolism HC vs. MCI-AD | 2191 | 0.000 | L Parietal | 5.47 | −48, −68, 52 | Inf. Parietal Lobule | 39 |
| 2189 | 0.000 | R Parietal | 5.05 | 48, −54, 44 | Inf. Parietal Lobule | 40 | |
| 1458 | 0.000 | L Parietal | 4.85 | −12, −46, 38 | Precuneus | 31 | |
| 1295 | 0.001 | L Temporal | 4.22 | −72, −26, 4 | Middle Temp gy. | 21 | |
| Correlation: Index of Sensitivity of Cueing (ISC)–brain metabolism in MCI-AD | 2481 | 0.002 | L Frontal | 4.96 | −14, 44, 0 | Anterior Cingulate | 32 |
| L Frontal | 4.45 | −22, 44, 28 | Sup. Front. Gy. | 9 | |||
| L Frontal | 4.38 | −18, 52, 18 | Sup. Front. Gy. | 10 | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brugnolo, A.; Girtler, N.; Doglione, E.; Orso, B.; Massa, F.; Donegani, M.I.; Bauckneht, M.; Morbelli, S.; Arnaldi, D.; Nobili, F.; et al. Brain Resources: How Semantic Cueing Works in Mild Cognitive Impairment due to Alzheimer’s Disease (MCI-AD). Diagnostics 2021, 11, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010108
Brugnolo A, Girtler N, Doglione E, Orso B, Massa F, Donegani MI, Bauckneht M, Morbelli S, Arnaldi D, Nobili F, et al. Brain Resources: How Semantic Cueing Works in Mild Cognitive Impairment due to Alzheimer’s Disease (MCI-AD). Diagnostics. 2021; 11(1):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010108
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrugnolo, Andrea, Nicola Girtler, Elisa Doglione, Beatrice Orso, Federico Massa, Maria Isabella Donegani, Matteo Bauckneht, Silvia Morbelli, Dario Arnaldi, Flavio Nobili, and et al. 2021. "Brain Resources: How Semantic Cueing Works in Mild Cognitive Impairment due to Alzheimer’s Disease (MCI-AD)" Diagnostics 11, no. 1: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010108
APA StyleBrugnolo, A., Girtler, N., Doglione, E., Orso, B., Massa, F., Donegani, M. I., Bauckneht, M., Morbelli, S., Arnaldi, D., Nobili, F., & Pardini, M. (2021). Brain Resources: How Semantic Cueing Works in Mild Cognitive Impairment due to Alzheimer’s Disease (MCI-AD). Diagnostics, 11(1), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11010108








