Evaluation of Nuclear Cataract with Smartphone-Attachable Slit-Lamp Device
Abstract
1. Introduction
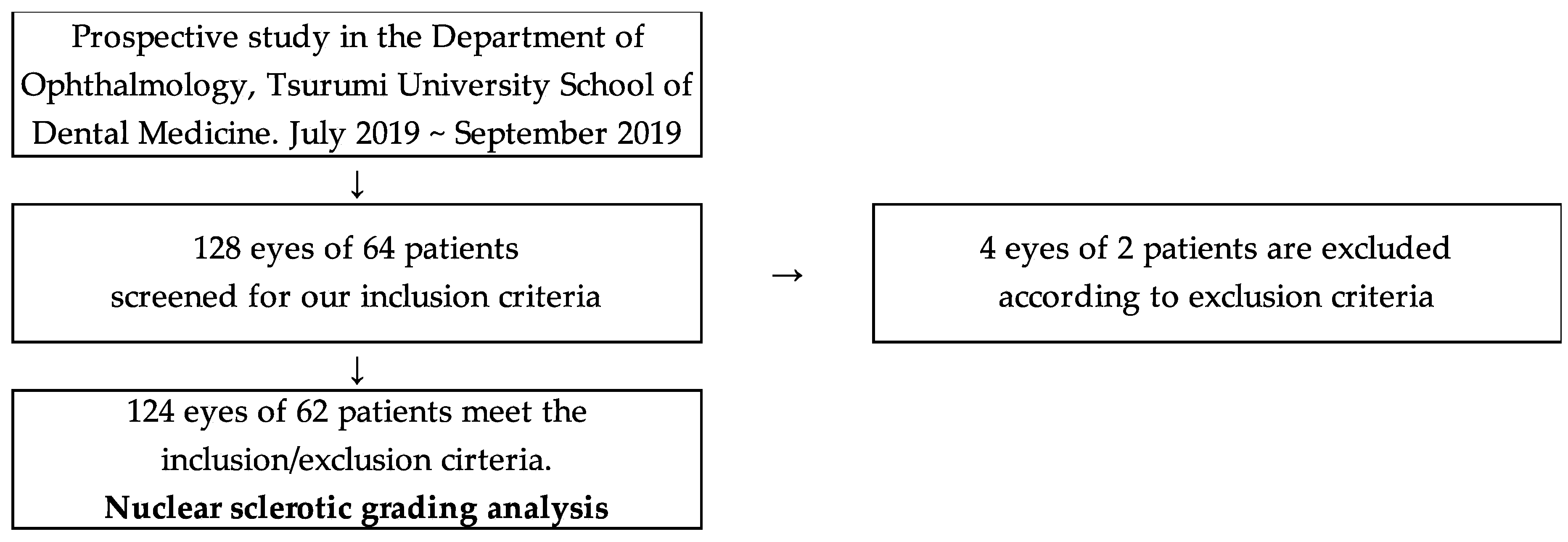
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
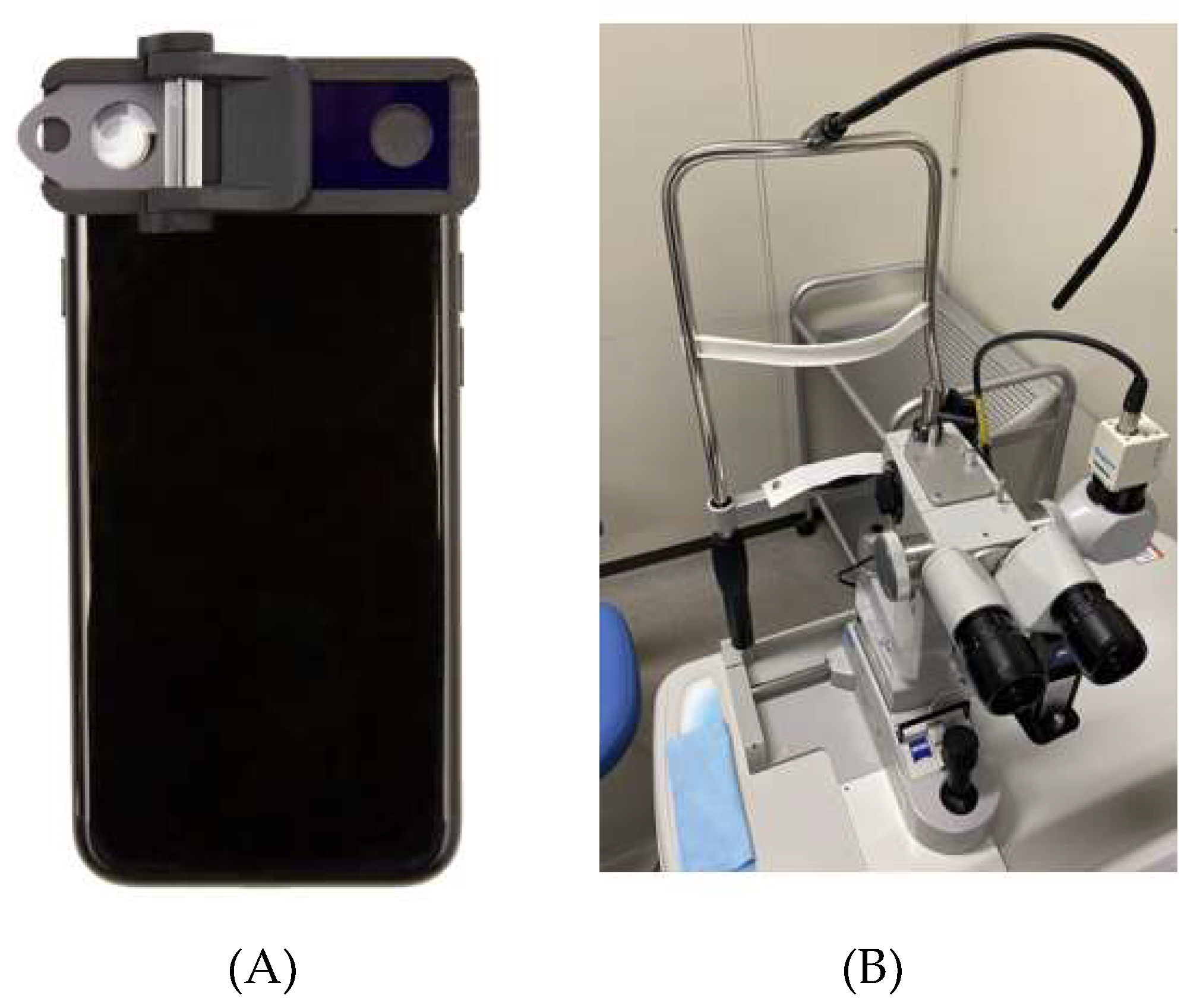
2.2. Conventional Non-Portable Slit-Lamp Microscope and SEC Examination
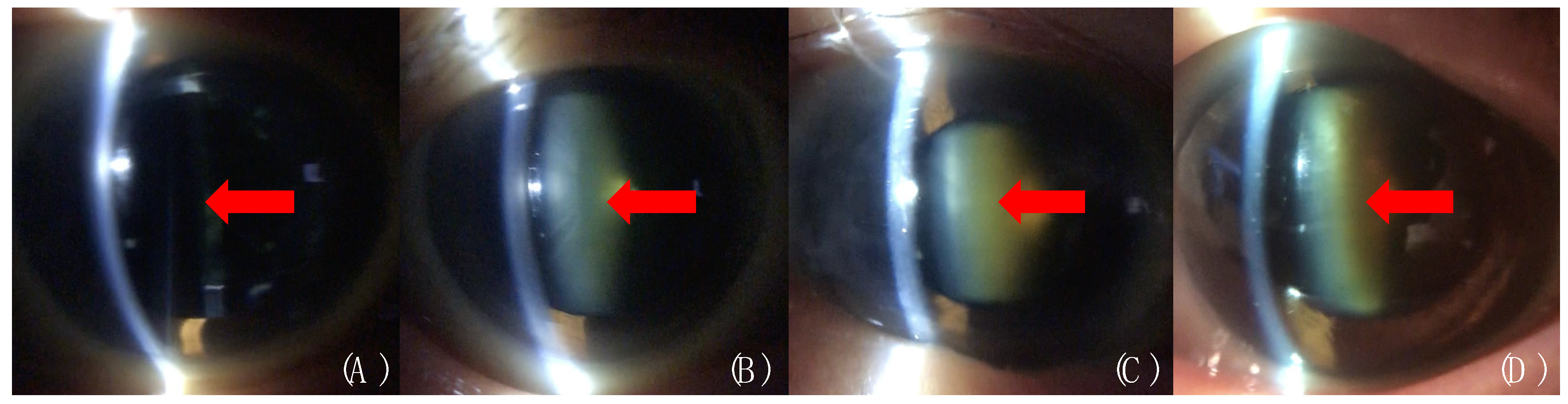
2.3. Cataract Evaluation by the Conventional Slit-Lamp Microscope and the SEC
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics of the Subjects
3.2. Correlation of Cataract Grading Evaluation by the Two Devices
3.3. Reproducibility of the Cataract Grading Evaluated by the Two Devices
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASC | anterior subcapsular cataract |
| BCVA | best corrected visual acuity |
| CI | confidence intervals |
| LOCS III | Lens Opacities Classification System III |
| logMAR | logarithm of the minimal angle of resolution |
| NUC | nuclear cataract |
| PSC | posterior subcapsular cataract |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SEC | Smart Eye Camera |
Appendix A
References
- Friedenwald, J.S. Clinical studies in slit-lamp ophthalmoscopy. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1929, 1, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, G.W.; Safir, A. The slit lamp: History, principles, and practice. In Clinical Opthalmology; Duane, T.D., Ed.; Harper & Row: New York, NY, USA, 1981; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Bourne, R.R.A.; Flaxman, S.R.; Braithwaite, T.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Das, A.; Jonas, J.B.; Keeffe, J.; Kempen, J.H.; Leasher, J.; Limburg, H.; et al. Magnitude, temporal trends, and projections of the global prevalence of blindness and distance and near vision impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e888–e897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaxman, S.R.; Bourne, R.R.A.; Resnikoff, S.; Ackland, P.; Braithwaite, T.; Cicinelli, M.V.; Das, A.; Jonas, J.B.; Keeffe, J.; Kempen, J.H.; et al. Global causes of blindness and distance vision impairment 1990–2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2017, 5, e1221–e1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.A.; Bron, A.J.; Ayliffe, W.; Sparrow, J.; Hill, A.R. The objective assessment of cataract. Eye 1987, 1, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, C.M.; Afshari, N.A. The global state of cataract blindness. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 28, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramke, J.; Evans, J.R.; Gilbert, C.E. Reducing inequity of cataract blindness and vision impairment is a global priority, but where is the evidence? Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 102, 1179–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, E.; Ogawa, Y.; Yazu, H.; Aketa, N.; Yang, F.; Yamane, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawakami, Y.; Tsubota, K. Smart Eye Camera: An innovative technique to evaluate tear film breakup time in a murine dry eye disease model. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nema, H.V.; Nema, N. Diagnostic Procedures in Ophthalmology; Alpha Science International Ltd: Oxford, United Kingdom, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Thylefors, B.; Chylack, L.T., Jr.; Konyama, K.; Sasaki, K.; Sperduto, R.; Taylor, H.R.; West, S.; WHO Cataract Grading Group. A simplified cataract grading system. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2002, 9, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundel, H.L.; Polansky, M. Measurement of observer agreement. Radiology 2003, 228, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.Z.; Tan, C.W. Smartphone Imaging in Ophthalmology: A Comparison with Traditional Methods on the Reproducibility and Usability for Anterior Segment Imaging. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2016, 45, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dubbs, S.B.; Blosser, K.M.; Richardson, A.C. A smartphone, a slit lamp, and an ophthalmology consult. Clin. Case Rep. 2019, 7, 2004–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadpour, M.; Mohammadpour, L.; Hassanzad, M. Smartphone Assisted Slit Lamp Free Anterior Segment Imaging: A novel technique in teleophthalmology. Cont. Lens Anterior Eye 2016, 39, 80–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiong, H.S.; Fang, J.L.; Wilson, G. Tele-manufactured affordable smartphone anterior segment microscope. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2016, 99, 580–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winn, B.; Whitaker, D.; Elliott, D.B.; Phillips, N.J. Factors affecting light-adapted pupil size in normal human subjects. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 1132–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Mort, R.L.; Ramaesh, T.; Kleinjan, D.A.; Morley, S.D.; West, J.D. Mosaic analysis of stem cell function and wound healing in the mouse corneal epithelium. BMC Dev. Biol. 2009, 9, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maa, A.Y.; Wojciechowski, B.; Hunt, K.J.; Dismuke, C.; Shyu, J.; Janjua, R.; Lu, X.; Medert, C.M.; Lynch, M.G. Early Experience with Technology-Based Eye Care Services (TECS): A Novel Ophthalmologic Telemedicine Initiative. Ophthalmology 2017, 124, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, M.B.; Silva, P.S.; Cavallerano, J.D.; Aiello, L.P. Clinical Components of Telemedicine Programs for Diabetic Retinopathy. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2016, 16, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, B.E.; Klein, R.; Linton, K.L.; Magli, Y.L.; Neider, M.W. Assessment of cataracts from photographs in the Beaver Dam Eye Study. Ophthalmology 1990, 97, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastawrous, A.; Mathenge, W.; Nkurikiye, J.; Wing, K.; Rono, H.; Gichangi, M.; Weiss, H.A.; Macleod, D.; Foster, A.; Burton, M.; et al. Incidence of Visually Impairing Cataracts Among Older Adults in Kenya. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e196354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chikamoto, N.; Fujitsu, Y.; Kimura, K.; Nishida, T.; Araki, T. Device for cataract analysis: Development and relevance to cataract surgery. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2010, 36, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cases | 64 | |
| Male/Female | 30/34 | |
| Age | 73.95 ± 9.28 | |
| Eyes | 128 | |
| Phakia | 110 | |
| Pseudophakia | 14 | |
| Lack of data | 4 | |
| Nuclear Sclerotic grading | ||
| Conventional/SEC | 1.84 ± 0.82/1.92 ± 0.82 | 0.47 * |
| SEC | ||
| Examination time, seconds | 30.38 ± 6.27 | |
| File size, MB | 85.96 ± 18.61 |
| Eye | n | R | p Value * | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | 62 | 0.926 | < 0.001 | 0.881 | 0.955 |
| L | 62 | 0.836 | < 0.001 | 0.743 | 0.898 |
| Total | 124 | 0.871 | < 0.001 | 0.821 | 0.907 |
| Smart Eye Camera | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional microscope | Grade | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2 | 5 | 78 | 2 | |
| 3 | 0 | 5 | 16 | |
| p Value | < 0.001 | |||
| Weighted kappa 95%CI | 0.807 | |||
| 0.798–0.816 | ||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yazu, H.; Shimizu, E.; Okuyama, S.; Katahira, T.; Aketa, N.; Yokoiwa, R.; Sato, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Fujishima, H. Evaluation of Nuclear Cataract with Smartphone-Attachable Slit-Lamp Device. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10080576
Yazu H, Shimizu E, Okuyama S, Katahira T, Aketa N, Yokoiwa R, Sato Y, Ogawa Y, Fujishima H. Evaluation of Nuclear Cataract with Smartphone-Attachable Slit-Lamp Device. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(8):576. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10080576
Chicago/Turabian StyleYazu, Hiroyuki, Eisuke Shimizu, Sho Okuyama, Takuya Katahira, Naohiko Aketa, Ryota Yokoiwa, Yasunori Sato, Yoko Ogawa, and Hiroshi Fujishima. 2020. "Evaluation of Nuclear Cataract with Smartphone-Attachable Slit-Lamp Device" Diagnostics 10, no. 8: 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10080576
APA StyleYazu, H., Shimizu, E., Okuyama, S., Katahira, T., Aketa, N., Yokoiwa, R., Sato, Y., Ogawa, Y., & Fujishima, H. (2020). Evaluation of Nuclear Cataract with Smartphone-Attachable Slit-Lamp Device. Diagnostics, 10(8), 576. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10080576






