Microorganism Response to Stressed Terrestrial Environments: A Raman Spectroscopic Perspective of Extremophilic Life Strategies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- the commonality of Raman spectral signatures between various sites and extreme environments;
- the factors which affect the recording of Raman spectral signatures from the extremophilic colonization of terrestrial sites;
- the definition of Raman data for evidence of extinct or extant life in the geological record.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Technical Considerations of the Use of Raman Spectroscopy for the Study of Extremophiles
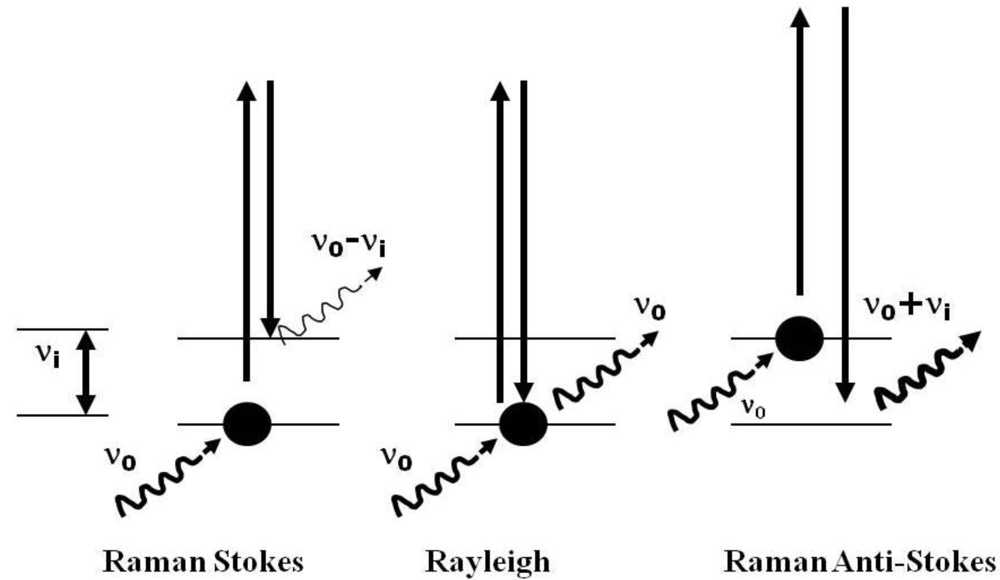
2.2. Analysis of the Data
| Specimen | Origin/Climate | Environmental Conditions | End | Chas | Epi | Sand | MR | Mag | Dol | Mar | Gyp | Salt | Apl | Fum | LB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANT1 [58] | Antarctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| ANT2 [58] | Antarctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| ANT5 [58] | Antarctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| EN1 [58] | Antarctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| EN2 [58] | Antarctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| RW [58] | Antarctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SP1A [59] | Arctic | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP1B [59] | Arctic | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP1C [59] | Tropical | Primary colonization | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP2A [60] | Arctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SP2B [60] | Arctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SP2C [60] | Arctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SP2D [60] | Arctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SP2E [60] | Arctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SP3A [61] | Antarctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SP3B [61] | Antarctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SP4A [62] | Hot desert | Primary colonization | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP4B [62] | Hot desert | Primary colonization | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP5A [63] | Antarctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SP5B [63] | Antarctic | Exposed mats | |||||||||||||
| SP6A [64] | X | X | |||||||||||||
| SP7A [65] | Arctic | Halotrophic | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP7B [65] | Arctic | Halotrophic | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP8A [66] | Antarctic | Sediments | |||||||||||||
| SP9A [67] | Arctic | High temperature/ Biofilm | |||||||||||||
| SP10A [68] | Arctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SP10B [68] | Arctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SP11A [69] | Hot desert | Halotrophic/ Natron | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP12A [70] | Hot desert | Halotrophic/ Halite | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP12B [70] | Hot desert | Halotrophic/ Halite | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP12C [70] | Hot desert | Halotrophic/ Halite | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP12D [70] | Hot desert | Halotrophic/ Halite | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP13A [71] | Antarctic | Snow algae | |||||||||||||
| SP13B [71] | Antarctic | Snow algae | |||||||||||||
| SP14A [72] | Antarctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SP14B [72] | Antarctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SP14C [72] | Antarctic | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SP15A [73] | Hot desert | Halotrophic | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP15B [73] | Hot desert | Halotrophic | X | X | X | ||||||||||
| SP15C [73] | Hot desert | Halotrophic/bact mats | |||||||||||||
| SP16A [74] | Antarctic | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP17A [75] | Deep see vents/mats | ||||||||||||||
| SP18A [76] | Hot desert | Halotrophic | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP18B [76] | Hot desert | Halotrophic | X | X | |||||||||||
| SP18C [76] | Hot desert | Halotrophic | X | X |
| ANT1 | ANT2 | ANT5 | EN1 | EN2 | RW | SP1A | SP1B | SP1C | SP2A | SP2B | SP2C | SP2D | SP2E | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| One carotenoid | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| Two or more carotenoids | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| Scytonemin | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| C-Phycocyanin | X | |||||||||||||
| Compound 1 | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| Compound 2 | X | |||||||||||||
| Calcium oxalate monohydrate Whewellite | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| Calcium oxalate dihydrate Weddellite | X | |||||||||||||
| Hematite | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Limonite/goethite | X | |||||||||||||
| Calcite | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Hydrocerussite | X | |||||||||||||
| Gypsum | X | |||||||||||||
| Pyrophyllite | X | |||||||||||||
| Rutile | X? | X? | ||||||||||||
| SP3A | SP3B | SP4A | SP4B | SP5A | SP5B | SP6A | SP7A | SP7B | SP8A | SP9A | SP10A | SP10B | SP11A | |
| Chlorophyll | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| One carotenoid | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| Two or more carotenoids | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| Scytonemin | X | X | X | X | ||||||||||
| C-Phycocyanin | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Atranorin or parietin | X | |||||||||||||
| Cholesterol | X | |||||||||||||
| Parietien | X | |||||||||||||
| Compound 3 | X | |||||||||||||
| Calcium oxalate monohydrate Whewellite | X | |||||||||||||
| Hematite | X | |||||||||||||
| Calcite | X | |||||||||||||
| Aragonite | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Quartz | X | |||||||||||||
| Realgar | X | |||||||||||||
| SP12A | SP12B | SP12C | SP12D | SP13A | SP13B | SP14A | SP14B | SP14C | SP15A | SP15B | SP15C | SP16A | SP17A | |
| Chlorophyll | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| One carotenoid | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| Two or more carotenoids | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Scytonemin | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| C-Phycocyanin | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Atranorin | X | |||||||||||||
| Phycobiliprotein | X | |||||||||||||
| Proteins | X | |||||||||||||
| Cellulose | X | |||||||||||||
| Compound 4 | X | |||||||||||||
| Compound 5 | X | |||||||||||||
| Compound 6 | X | |||||||||||||
| Compound 7 | X | |||||||||||||
| Compound 8 | X | |||||||||||||
| Calcium oxalate monohydrate Whewellite | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| Calcium oxalate dihydrate Weddellite | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Calcite | X | |||||||||||||
| SP18A | SP18B | SP18C | ||||||||||||
| Chlorophyll | X | |||||||||||||
| Scytonemin | X | |||||||||||||
| C-Phycocyanin | ||||||||||||||
| Compound 9 | X |
| COMPOUNDS | RAMAN SIGNATURES |
|---|---|
| Chlorophyll | 1326, 1285, 987, 916, 755, 744, 516 |
| Carotenoids | 1550–1500, 1145–1160, 990–1015 |
| Scytonemin | 1591, 1553, 1432, 1381, 1321, 1170, 984, 752, 675, 574 |
| C-Phycocyanin | 1638, 1582, 1463, 1369, 1272, 815 |
| Atranorin or parietin (antraquinone) | 1630, 963 |
| Cholesterol | 1445, 1437, 875, 539 |
| Atranorin | 1666, 1658, 1303, 1294, 1266, 588 |
| Parietien | 1671, 1613, 1553, 1387, 1370, 1277, 1255, 926, 458 |
| Phycobiliprotein | 1638, 1586, 1468, 1369, 1281, 1236, 1049, 665 |
| Proteins | 1659 (amide I)1240-1290 (amideIII) |
| Cellulose | 1380,1292 |
| Compound 1 chlorophyll-like | 1637, 1568, 1480, 1407, 1343, 1320, 789, 688, 554, 499 |
| Compound 2 | 1449, 1342, 952, 834, 748, 680, 595, 438, 257, 173 |
| Compound 3 | 1468, 1439, 948, 884 |
| Compound 4 | 1531, 1452, 1342, 1143, 748, 681 |
| Compound 5 (aliphatic) | 940 |
| Compound 6 (aromatic) | 1005 |
| Compound 7 aromatic polyphenolic compound | 1442, 1629, 1757 |
| Compound 8 | 1544, 1500, 1436, 1356, 1316, 1306, 1154 |
| Compound 9 | 1690, 1645, 1520, 1441, 1250 |
| Calcium oxalate monohydrate (whewellite) | 1490, 1463, 896, 504 |
| Calcium oxalate dihydrate (weddellite) | 1475, 910, 506 |
| Hematite | 610, 405, 292, 223 |
| Limonite/goethite | 555, 395, 299, 203 |
| Calcite | 1086, 713, 282, 156 |
| Aragonite | 1086, 708, 203, 156 |
| Hydrocerussite | 1051, 681, 412 |
| Gypsum | 1132, 1008, 679, 618, 492, 413 |
| Pyrophyllite | 813, 705, 353, 259, 214, 195, 171 |
| Rutile | 609, 442 |
| Quartz | 463, 205, 128 |
| Realgar | 342, 220, 192, 182 |
3. Conclusions
References and Notes
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Farwell, D.W.; Seaward, M.R.D.; Giacobini, C. Preliminary Raman Microscopic Analyses of a Lichen Encrustation Involved in the Biodeterioration of Renaissance Frescoes in Central Italy. Int. Biodeterior. 1991, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Holder, J.M.; Russell, N.C.; Wynn-Williams, D.D. Spectroscopy of Biological Molecules: Modern Trends; Carmona, P., Navarro, R., Hernanz, A., Eds.; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 509–510. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Russell, N.C.; Wynn-Williams, D.D. FT-Raman Spectroscopic and Scanning Electron Microscopic Study of Cryptoendolithic Lichens from Antarctica. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1997, 28, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Farwell, D.W.; Seaward, M.R.D. Raman Spectra of Oxalates in Lichen Encrustations on Renaissance Frescoes. Spectrochim. Acta 1991, 47, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Farwell, D.W.; Jenkins, R.; Seaward, M.R.D. Vibrational Raman Spectroscopic Studies of Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate and Dihydrate in Lichen Encrustations on Renaissance Frescoes. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1992, 23, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Seaward, M.R.D. Raman Spectroscopy and Lichen Biodeterioration Spectrosc. Eur. 1993, 5, 16–20. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Edwards, K.A.E.; Farwell, D.W.; Lewis, I.R.; Seaward, M.R.D. An Approach to Stone and Fresco Lichen Biodeterioration through FT-Raman Microscopic Investigation of Thallus-Substratum Encrustations. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1994, 25, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Seaward, M.R.D. Biodeterioration and Biodegradation 9; Bousher, A., Chandra, M., Edyvean, R., Eds.; Institute of Chemical Engineers Publication, Hobbs Printers: Totton, Hampshire, UK, 1995; pp. 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Holder, J.M.; Wynn-Williams, D.D. Comparative FT-Raman Spectroscopy of Xanthoria. Lichen-Substratum Systems from Temperate and Antarctic Habitats. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1947–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn-Williams, D.D.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Garcia-Pichel, F. Functional Biomolecules of Antarctic Stromatolitic and Endolithic Cyanobacterial Communities. Eur. J. Phycol. 1999, 34, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Garcia-Pichel, F.; Newton, E.M.; Wynn-Williams, D.D. Vibrational Raman Spectroscopic Study of Scytonemin, the UV-Protective Cyanobacterial Pigment. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2000, 56, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holder, J.M.; Wynn-Williams, D.D.; Rull Perez, F.; Edwards, H.G.M. Raman Spectroscopy of Pigments and Oxalates In Situ within Epilithic Lichens: Acarospora from the Antarctic and Mediterranean. New Phytol. 2000, 145, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Wynn-Williams, D.D.; Newton, E.M.; Coombes, S.J. Molecular Structural studies of Lichen Substances I: Parietin and Emodin. J. Mol. Struct. 2003, 648, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Newton, E.M.; Wynn-Williams, D.D. Molecular Structural Studies of Lichen Substances II: Atranorin, Gyrophoric Acid, Fumarprotocetraric Acid, Rhizocarpic Acid, Calycin, Pulvinic Dilactone and Usnic Acid. J. Mol. Struct. 2003, 651, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, C.P.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Jehlicka, J. Understanding the application of Raman spectroscopy to the detection of traces of life. Astrobiology 2010, 10, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenabeele, P.; Jehlicka, J.; Vitec, P.; Edwards, H.G.M. On the definition of Raman spectroscopic detection limits for the analyses of biomarkers in solid matrices. Planet. Space Sci. 2012, 62, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Wynn-Williams, D.D.; Little, S.J.; de Oliveira, L.F.C.; Cockell, C.S.; Ellis-Evans, J.C. Stratified Response to Environmental Stress in a Polar Lichen Characterised with FT-Raman Microscopic Analysis. Spectrochim. Acta Part. A 2004, 60, 2029–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Newton, E.M.; Wynn-Williams, D.D.; Lewis-Smith, R.I. Nondestructive Analysis of Pigments and other Organic Compounds in Lichens Using Fourier-Transform Raman Spectroscopy: A Study of Antarctic Epilithic Lichens. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2003, 59, 2301–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, J.; Palma, R.L.; Loyd, D.H.; Farwell, D.W.; Edwards, H.G.M. Analysis of the Rock Accretions in the Lower Pecos Region of Southwest Texas. Geoarchaeology 1995, 10, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaward, M.R.D.; Edwards, H.G.M. Lichen-Substratum Interface Studies with Particular Reference to Raman Microscopic Analysis. I. The Deterioration of Works of Art by Dirina Massiliensis forma Sorediata. Cryptogam. Bot. 1995, 5, 282–287. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Rull Perez, F. Lichen Biodeterioration of the Convento de la Peregrina, Sahagun, Spain. Biospectroscopy 1999, 5, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, S.E.J.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Seaward, M.R.D. Lichen Biodeterioration of Ecclesiastical Monuments in Northern Spain. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2004, 60, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar]
- Wynn-Williams, D.D.; Edwards, H.G.M. Proximal Analysis of Regolith Habitats and Protective Biomolecules In situ by Laser Raman Spectroscopy: Overview of Terrestrial Antarctic Habitats and Mars Analogs. Icarus 2000, 144, 486–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn-Williams, D.D.; Edwards, H.G.M. Antarctic Eco-Systems as Models for Extra-Terrestrial Surface Habitats. Planet. Space Sci. 2000, 48, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn-Williams, D.D.; Edwards, H.G.M. Astrobiology: The Quest for the Conditions of Life; Horneck, G., Baumstark-Khan, C., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2002; pp. 245–260. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Newton, E.M.; Wynn-Williams, D.D.; Dickensheets, D.; Schoen, C.; Crowder, C. Laser Wavelength Selection for Raman Spectroscopy of Microbial Pigments in situ in Antarctic Desert Ecosystem Analogues of Former Habitats on Mars. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2003, 1, 333–348. [Google Scholar]
- Ellery, A.; Kolb, C.; Lammer, H.; Parnell, J.; Edwards, H.; Richter, L.; Patel, M.; Romstedt, J.; Dickensheets, D.; Steele, A. Astrobiological Instrumentation for Mars—The Only Way is Down! Int. J. Astrobiol. 2003, 1, 365–380. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Newton, E.M.; Dickensheets, D.L.; Wynn-Williams, D.D. Raman Spectroscopic Detection of Biomolecular Markers from Antarctic Materials: Evaluation for Putative Martian Habitats. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2003, 59, 2277–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M. Raman Spectroscopic Protocol for the Molecular Recognition of Key Biomarkers in Astrobiological Exploration. Orig. Life Evol. Biospheres 2004, 34, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellery, A.; Wynn-Williams, D.D.; Parnell, J.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Dickensheets, D. The Role of Raman Spectroscopy as an Astrobiological Tool in the Exploration of Mars. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2004, 35, 441–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, J.R.; Nakamoto, K.; Brown, C.W. Introductory Raman Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Academy Press: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Canganella, F.; Wiegel, J. Extremophiles: From abyssal to terrestrial ecosystems and possibly beyond. Naturwissenschaften 2011, 98, 253–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Yu1, B. Geomicrobiological processes in extreme environments: A review. Episodes 2007, 30, 202–216. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, S. Extremophiles: Developments of their special functions and potential resources. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2002, 94, 518–525. [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild, L.J.; Mancinelli, R.L. Life in extreme environments. Nature 2001, 409, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedmann, E.I. Endolithic microorganisms in the Antarctic cold desert. Science 1982, 4536, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, H. Mineral-microbe interactions: A review. Front. Earth. Sci. China 2010, 4, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, P.C.; Rogers, J.R.; Choi, W.J.; Hiebert, F.K. Silicates, silicate weathering and microbial ecology. Geomicrobiol. J. 2001, 18, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J.R.; Bennett, P.C. Mineral stimulation of subsurface microorganisms: Release of limiting nutrients from silicates. Chem. Geol. 2004, 203, 91–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breier, J.A.; White, S.N.; German, C.R. Mineral-microbe interactions in deep-sea hydrothermal systems: A challenge for Raman spectroscopy. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2010, 368, 3067–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmel, D.; Maurin, L.C.; Mansont, J.L. Raman microspectrometry sulfur detection and characterization in the marine ectosymbiotic nematode Eubostrichus dianae (Desmodoridae, Stilbonematidae). Biol. Cell. 2009, 101, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oger, P.M.; Daniel, I.; Picard, A. In situ Raman and X-ray spectroscopies to monitor microbial activities under high hydrostatic pressure. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2010, 1189, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Dartnell, L.R.; Page, K.; Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Wright, G.; Munshi, T.; Scowen, I.J.; Ward, J.M.; Edwards, H.G.M. Destruction of Raman biosignatures by ionising radiation and the implications for life detection on Mars. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Vandenabeele, P.; Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Carter, E.A.; Rull Perez, F.; Hargreaves, M. The Rio Tinto Mars analogue site: An extremophilic Raman spectroscopic study. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2007, 68, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESA Robotic Exploration of Mars. Available online: http://exploration.esa.int/science-e/www/object/index.cfm?fobjectid=46048/ (accessed on 27 November 2012).
- Goodwin, J.R.; Hafner, L.M.; Fredericks, P.M. Raman spectroscopic study of the heterogeneity of microcolonies of a pigmented bacterium. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2006, 37, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehlicka, J.; Oren, A.; Vitek, P. Use of Raman spectroscopy for the identification of compatible solutes in halophilic bacteria. Extremophiles 2012, 16, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisk, M.R.; Storrie-Lombardi, M.C.; Douglas, S.; Popa, R.; McDonald, G.; di Meo-Savoie, C. Evidence of biological activity in Hawaiian subsurface basalts. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2003, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Cockell, C.S.; Clasteren, P.V.; Mosselmans, J.F.W.; Franchi, I.A.; Gilmour, I.; Kelly, L.; Olsson-Francis, K.; Johnson, D. Microbial endolithic colonization and the geological environment in young seafloor basalts. Chem. Geol. 2010, 279, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, D.F.; Pappalardo, R.T.; Anderson, M.S.; Grasby, S.E.; Mielke, R.E.; Wrigth, K.E.; Templeton, A.S. Biosignature detection at an Arctic analog to Europa. Astrobiology 2012, 12, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockell, C.S.; Osinki, G.R.; Banerjee, N.R.; Howard, K.T.; Gilmour, I.; Watson, J.S. The microbe-mineral environment and gypsum neogenesis in a weathered polar evaporite. Geobiology 2010, 8, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efrima, S.; Zeiri, L. Understanding SERS of Bacteria. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2008, 40, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiri, L.; Efrima, S. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of bacteria: The effect of excitation wavelength and chemical modification of the colloidal milieu. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2005, 36, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Su, L.; Shen, A.; Maternyc, A.; Hua, J. Application of surface-enhanced Raman scattering in cell analysis. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2011, 42, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, S.A.; Wilson, R.; Cooper, J.M.; Parnell, J. The use of surface-enhanced Raman scattering for detecting molecular evidence of life in rocks, sediments and sedimentary deposits. Astrobiology 2010, 10, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laucks, M.L.; Sengupta, A.; Jungle, K.; Davis, E.J.; Swanson, B.D. Comparison of psychro-active Arctic marine bacteria and common mesophillic bacteria using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2005, 59, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.; Monaghan, P.; Bowden, S.A.; Parnell, J.; Cooper, J.M. Surface-enhanced Raman signatures of pigmentation of cyanobacteria from within geological samples in a spectroscopic-microfluidic flow cell. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 7036–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Cockell, C.S. Raman spectroscopy of endoliths from Antarctic cold desert environments. Analyst 2005, 130, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Edwards, H.G.M. Raman spectroscopy in Astrobiology. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 384, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Benning, L.G. AMASE 2004 team. Raman spectroscopic analysis of Arctic nodules: Relevance to the astrobiological exploration of Mars. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 2927–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Wynn-Williams, D.D. FT-Raman spectroscopic analysis of an Antarctic endolith. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2003, 1, 349–355. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Moody, C.D.; Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Mancinelli, R. Raman spectroscopy of desert varnishes and their rock substrata. J. Raman Spectrosci. 2004, 35, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Moody, C.D.; Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Wynn-Williams, D.D. Raman spectroscopic detection of key biomarkers of cyanobacterial and lichens symbiosis in extreme Antarctic habitats: Evaluation for Mars lander missions. Icarus 2005, 174, 560–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Moody, C.D.; Newton, E.M.; Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Russell, M.J. Raman spectroscopic analysis of cyanobacterial colonization of hydromagnesite, a putative martian extremophile. Icarus 2005, 175, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Parnell, J.; Cockell, C.S.; Lee, P. Raman spectroscopic analysis of cyanobacterial gypsum halotrophs and relevance for sulfate deposits on Mars. Analyst 2005, 130, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, C.D.; Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Hodgson, D.A.; Doran, P.T.; Bishop, J.L. Biogeological Raman spectroscopic studies of Antarctic lacustrine sediments. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2005, 61, 2413–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Worland, M.R. Comparative evaluation of Raman spectroscopy at different wavelengths for extremophile exemplars. Orig. Life Evol. Biospheres 2005, 35, 489–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Benning, L.G. Raman spectroscopic and scanning electron microscopic analysis of a novel biological colonisation of volcanic rocks. Icarus 2006, 184, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Currie, K.J.; Ali, H.R.H.; Jorge-Villar, S.E.; David, A.R.; Denton, J. Raman spectroscopy of natron: Shedding light on ancient Egyptian mummification. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 388, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitek, P.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Jehlicka, J.; Ascaso, C.; de los Rios, A.; Vallea, S.; Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Davila, A.F.; Wierzchos, J. Microbial colonization of halite from the hyper-arid Atacama desert studied by Raman spectroscopy. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. 2010, 368, 3205–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Oliveira, L.F.C.; Cockell, C.S.; Ellis-Evans, J.C.; Wynn-Williams, D.D. Raman spectroscopy of senescing snow algae: Pigmentation changes in an Antarctic cold desert extremophile. Int. J. Astrobiol. 2004, 3, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, N.C.; Edwards, H.G.M.; Wynn-Williams, D.D. FT-Raman spectroscopic analysis of endolithic communities from Beacon sandstone in Victoria Land, Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 1998, 10, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Mohsin, M.A.; Sadooni, F.N.; Hassan, N.F.; Munshi, T. Life in the Sabkha: Raman spectroscopy of halotrophic extremophiles of relevance to planetary exploration. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Pullan, D.; Hargreaves, M.D.; Hofmann, B.A.; Westall, F. Morphological biosignatures from relict fossilised sedimentary geological specimens: A Raman spectroscopic study. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2007, 38, 1325–1361. [Google Scholar]
- White, S.N.; Dunk, R.M.; Peltzer, E.T.; Freeman, J.J.; Brewer, P.G. In situ Raman analyses of deep-sea hydrothermal and cold seep systems (Gorda Ridge and Hydrate Ridge). Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Edwards, H.G.M.; Sadooni, F.; Vitek, P.; Jehlicka, J. Raman spectroscopy of the Dukhan sabkha: Identification of geological and biogeological molecules in an extreme environment. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 2012, 368, 3099–3107. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.A.; Onstott, T.C. Follow the Water: Steve Squyres and the Mars Exploration Rovers. J. Franklin Inst. 2011, 348, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, V.R. Water and the Martian landscape. Nature 2001, 412, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squyres, S.W.; Kasting, J.F. Early Mars: How warm and how wet? Science 1994, 265, 744–749. [Google Scholar]
- Niles, P.B.; Catling, D.C.; Berger, G.; Chassefière, E.; Ehlmann, B.L.; Michalski, J.R.; Morris, R.; Ruff, S.W.; Sutter, B. Geochemistry of carbonates on Mars: Implications for climate history and nature of aqueous environments. Space Sci. Rev. 2013, 174, 301–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, V.E.; Castro, H.V.; Edwards, H.G.; de Oliveira, L.F.C. Carotenes and carotenoids in natural biological samples: A Raman spectroscopic analysis. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2010, 41, 642–650. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jorge-Villar, S.E.; Edwards, H.G.M. Microorganism Response to Stressed Terrestrial Environments: A Raman Spectroscopic Perspective of Extremophilic Life Strategies. Life 2013, 3, 276-294. https://doi.org/10.3390/life3010276
Jorge-Villar SE, Edwards HGM. Microorganism Response to Stressed Terrestrial Environments: A Raman Spectroscopic Perspective of Extremophilic Life Strategies. Life. 2013; 3(1):276-294. https://doi.org/10.3390/life3010276
Chicago/Turabian StyleJorge-Villar, Susana E., and Howell G.M. Edwards. 2013. "Microorganism Response to Stressed Terrestrial Environments: A Raman Spectroscopic Perspective of Extremophilic Life Strategies" Life 3, no. 1: 276-294. https://doi.org/10.3390/life3010276
APA StyleJorge-Villar, S. E., & Edwards, H. G. M. (2013). Microorganism Response to Stressed Terrestrial Environments: A Raman Spectroscopic Perspective of Extremophilic Life Strategies. Life, 3(1), 276-294. https://doi.org/10.3390/life3010276





