Chemogenetic Modulation of Electroacupuncture Analgesia in a Mouse Intermittent Cold Stress-Induced Fibromyalgia Model by Activating Cerebellum Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Expression and Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals
2.2. Modeling Fibromyalgia
2.3. Electroacupuncture
2.4. Mechanical and Thermal Nociception Tests
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Immunofluorescence
2.7. CB1 Receptor Agonist and Antagonist Administration
2.8. Chemogenetic Operation
2.9. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
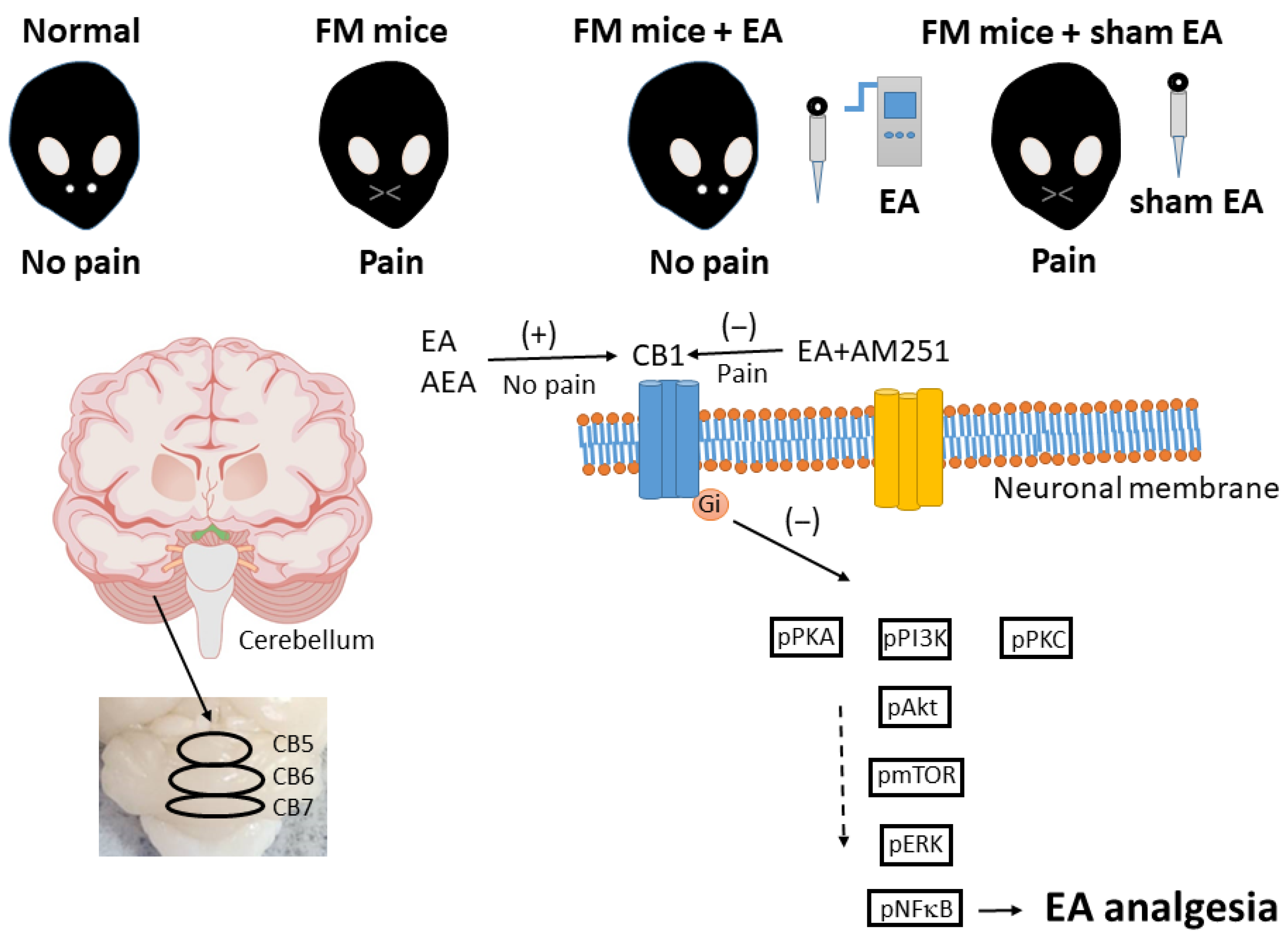
3.1. Attenuation of Intermittent Cold Stress-Induced Fibromyalgia-like Pain by Electroacupuncture
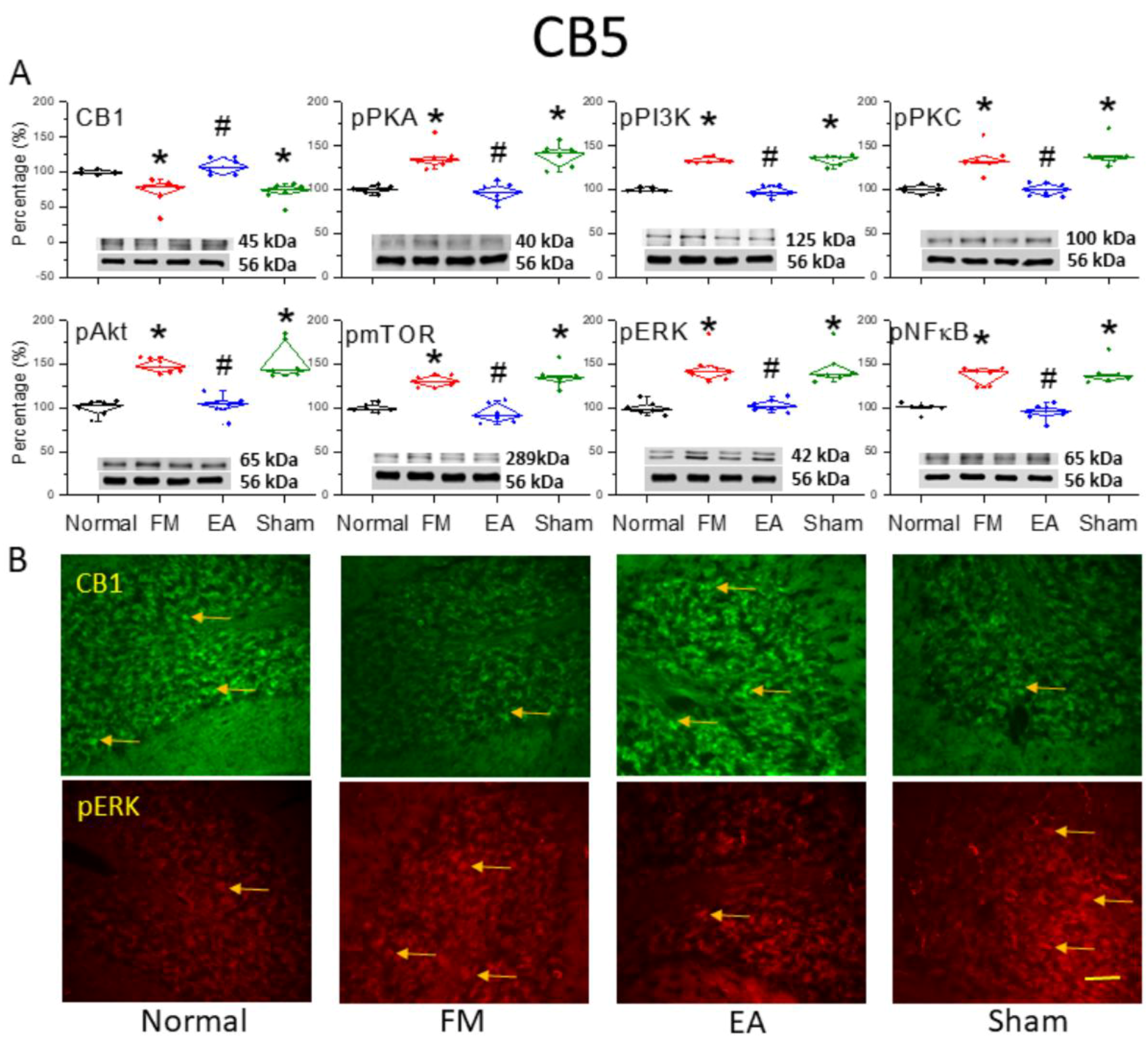
3.2. Reduced Expression of CB1 and Enhanced Activation of Pain-Related Signaling Factors in the Cerebellar C5 Region of FM-Model Mice Were Reversed by 2 Hz EA
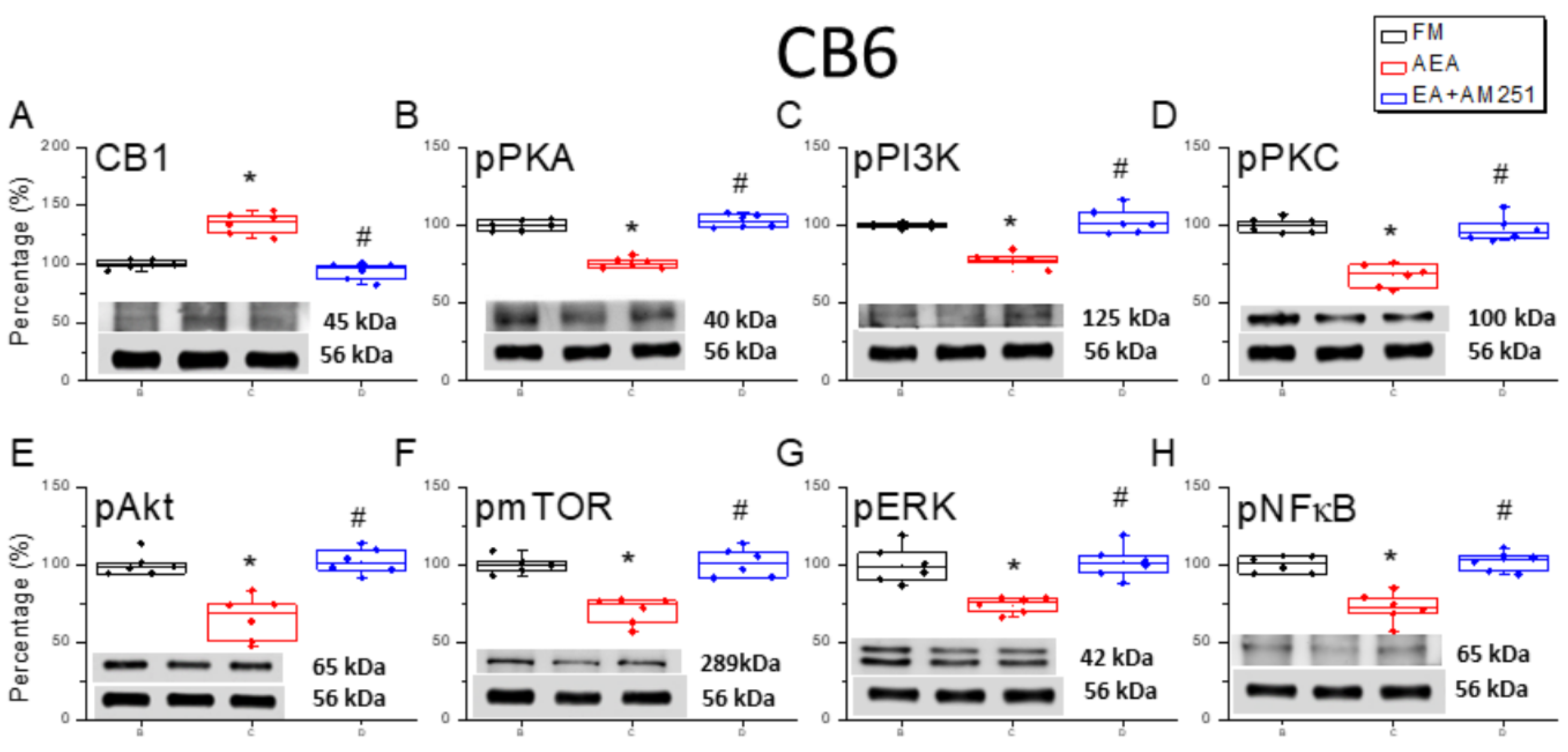
3.3. Reversal of CB1 Receptor Downregulation and ERK Upregulation in the Cerebellar CB6 Region by 2 Hz EA
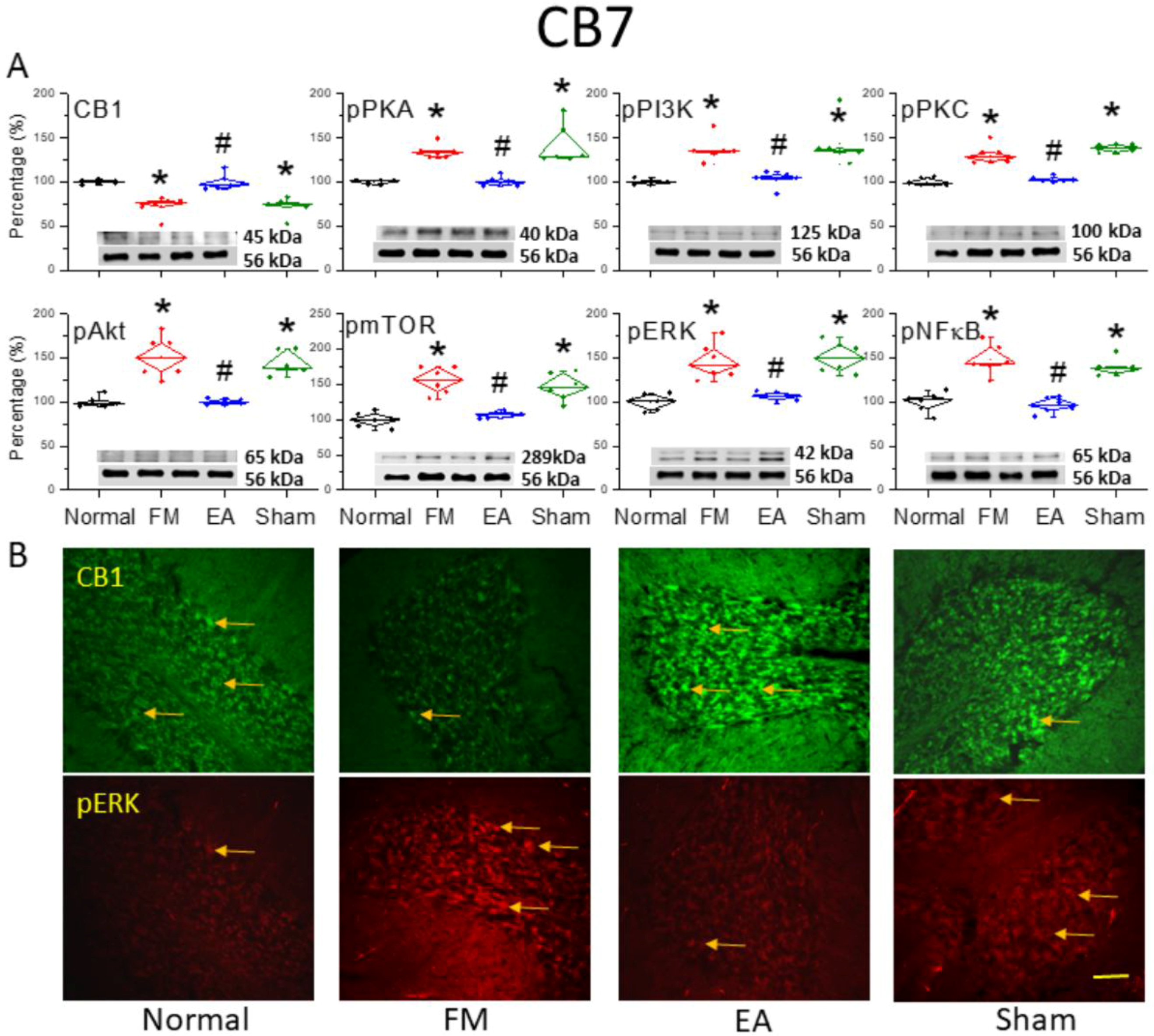
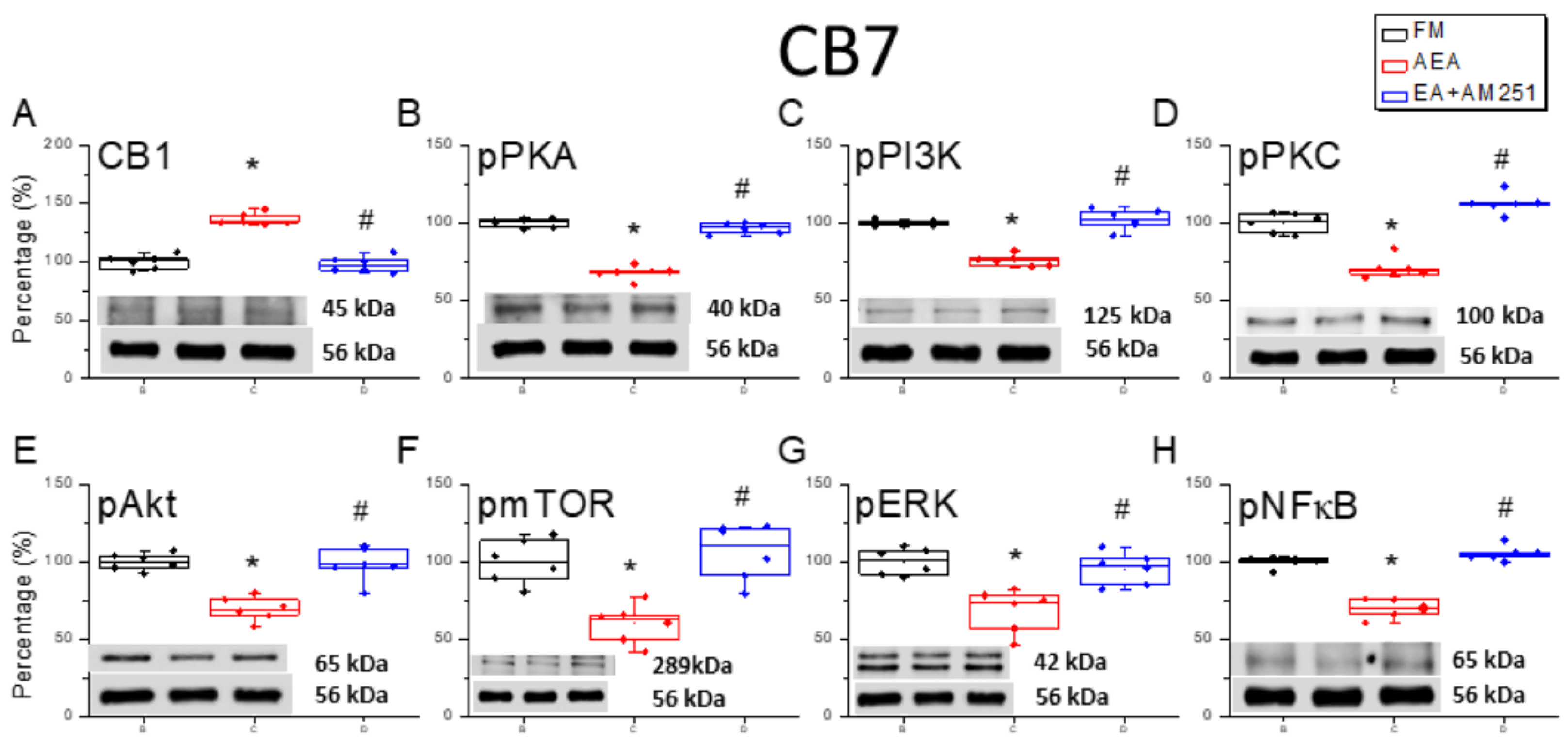
3.4. Reversal of CB1 Receptor Downregulation and Pain-Associated Kinase Upregulation by 2 Hz EA in the Cerebellar CB7 Region
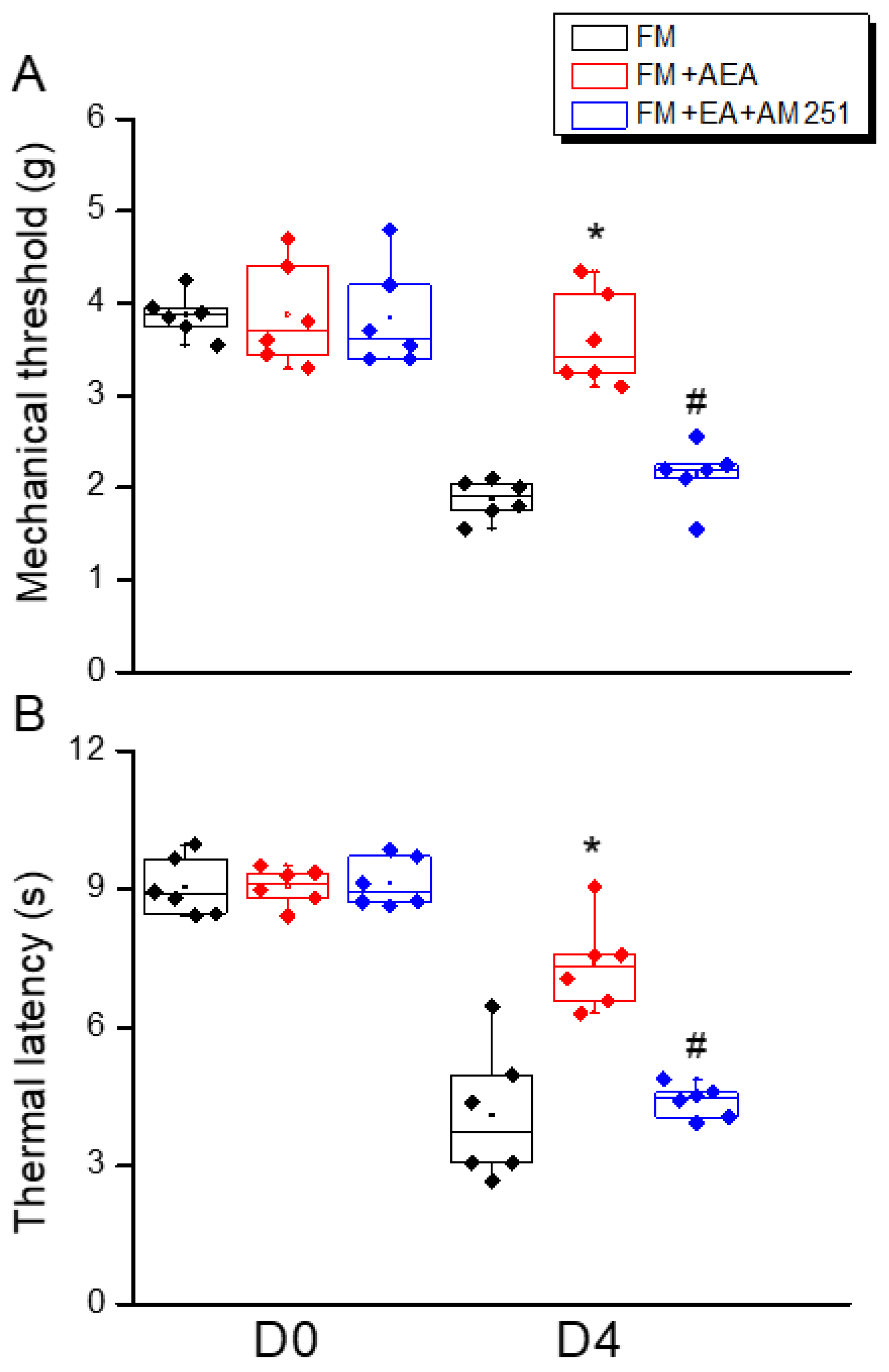
3.5. ICV Injection of a CB1 Agonist Reversed ICS-Induced Hyperalgesia While a CB1 Antagonist Blocked the Analgesic Effect of 2 Hz EA
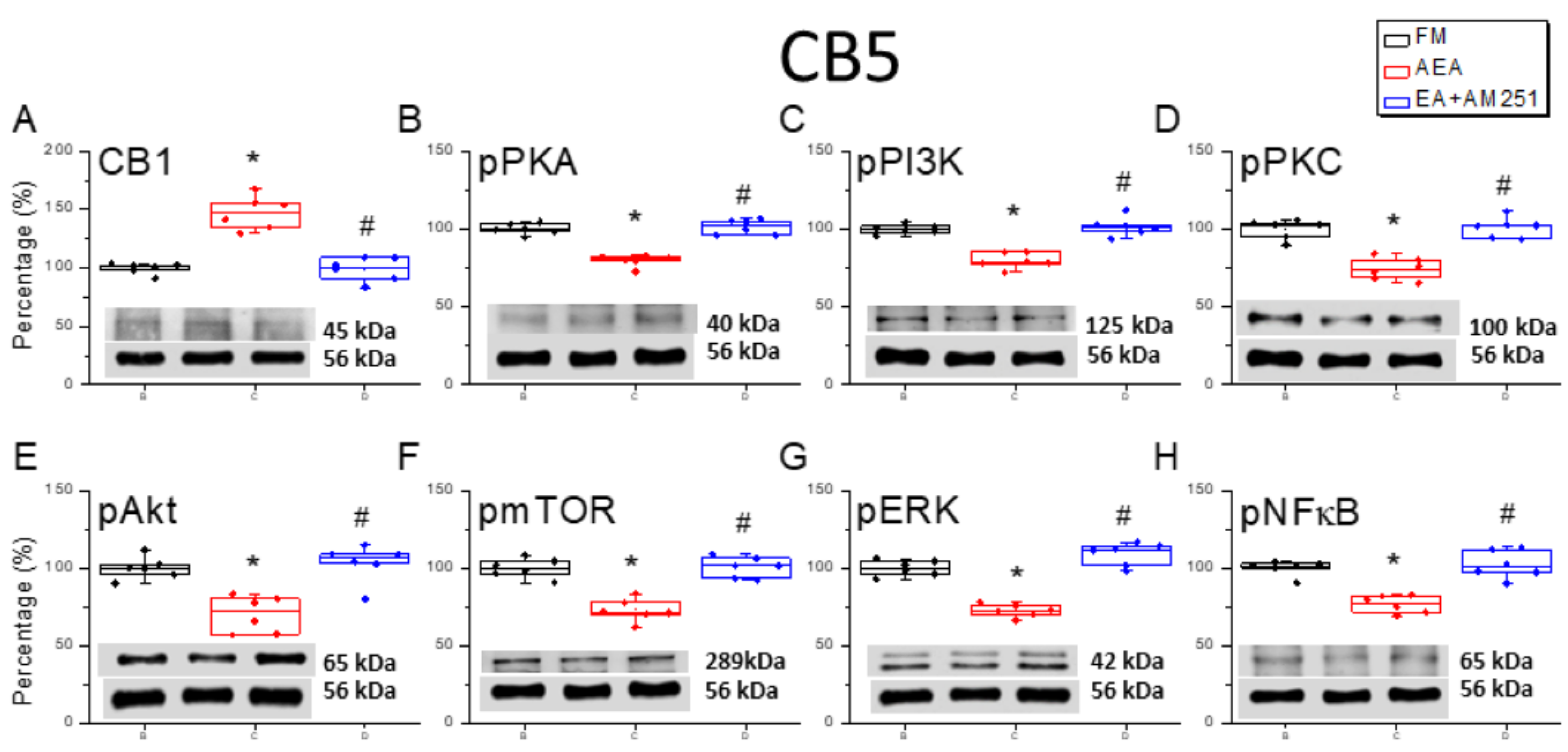
3.6. ICV Injection of a CB1 Agonist Reversed ICS-Induced Downregulation of CB1 Receptor and Upregulation of Nociceptive Signaling Factors in All Three Cerebellar Regions
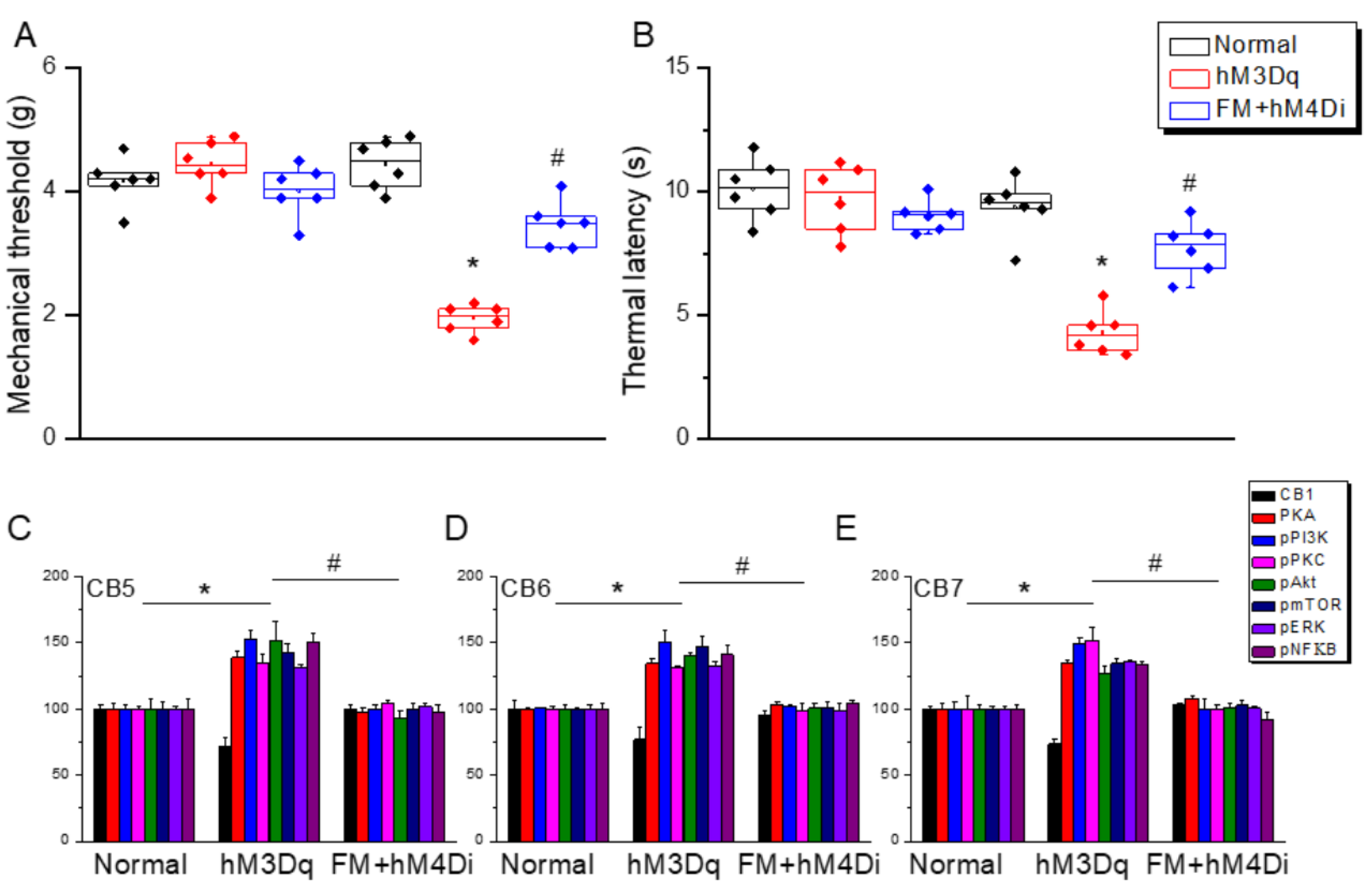
3.7. Chemogenetic Stimulation at Paraventricular Nucleus Induced Fibromyalgia and ICS-Induced Fibromyalgia Was Further Diminished by Chemogenetics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
5.1. Main Findings and Their Implications
5.2. Study Strengths and Limitations
5.3. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andres-Rodriguez, L.; Borras, X.; Feliu-Soler, A.; Perez-Aranda, A.; Angarita-Osorio, N.; Moreno-Peral, P.; Montero-Marin, J.; García-Campayo, J.; Carvalho, A.F.; Maes, M.; et al. Peripheral immune aberrations in fibromyalgia: A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocyigit, B.F.; Akyol, A. Fibromyalgia syndrome: Epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment. Reumatologia 2022, 60, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dailey, D.L.; Vance, C.G.T.; Rakel, B.A.; Zimmerman, M.B.; Embree, J.; Merriwether, E.N.; Geasland, K.M.; Chimenti, R.; Williams, J.M.; Golchha, M.; et al. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation Reduces Movement-Evoked Pain and Fatigue: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagy, I.; Bar-Lev Schleider, L.; Abu-Shakra, M.; Novack, V. Safety and Efficacy of Medical Cannabis in Fibromyalgia. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, D.S.; Forsberg, A.; Sandstrom, A.; Bergan, C.; Kadetoff, D.; Protsenko, E.; Lampa, J.; Lee, Y.C.; Höglund, C.O.; Catana, C.; et al. Brain glial activation in fibromyalgia—A multi-site positron emission tomography investigation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 75, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyorfi, M.; Rupp, A.; Abd-Elsayed, A. Fibromyalgia Pathophysiology. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanton, S.; Sandstrom, A.; Tour, J.; Kadetoff, D.; Schalling, M.; Jensen, K.B.; Sitnikov, R.; Ellerbrock, I.; Kosek, E. The translocator protein gene is associated with endogenous pain modulation and the balance between glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid in fibromyalgia and healthy subjects: A multimodal neuroimaging study. Pain 2022, 163, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfgren, M.; Sandstrom, A.; Bileviciute-Ljungar, I.; Mannerkorpi, K.; Gerdle, B.; Ernberg, M.; Fransson, P.; Kosek, E. The effects of a 15-week physical exercise intervention on pain modulation in fibromyalgia: Increased pain-related processing within the cortico-striatal- occipital networks, but no improvement of exercise-induced hypoalgesia. Neurobiol. Pain 2023, 13, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, M.S.; Nass, S.R.; Gabella, K.M.; Kinsey, S.G. The endocannabinoid system modulates stress, emotionality, and inflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 42, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecha, M.; Feliu, A.; Carrillo-Salinas, F.J.; Rueda-Zubiaurre, A.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; de Sola, R.G.; Guaza, C. Endocannabinoids drive the acquisition of an alternative phenotype in microglia. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 49, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, D.A.; Yudowski, G.A. Cannabinoid Receptors in the Central Nervous System: Their Signaling and Roles in Disease. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2016, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Lopez-Alcalde, J.; Zhang, L.; Siebenhuner, A.R.; Witt, C.M.; Barth, J. Acupuncture for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 12504–12517. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, B.; Erwood, K.; Ncomanzi, S.; Fischer, V.; O’Brien, D.; Lee, A. Management strategies for adult patients with dental anxiety in the dental clinic: A systematic review. Aust. Dent. J. 2022, 67 (Suppl. 1), S3–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, W.; Ge, J.; Liu, S. The immunomodulatory mechanisms for acupuncture practice. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1147718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, I.H.; Liao, H.Y.; Cheng, C.M.; Yen, C.M.; Lin, Y.W. Paper-Based Detection Device for Microenvironment Examination: Measuring Neurotransmitters and Cytokines in the Mice Acupoint. Cells 2022, 11, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.W.; Chou, A.I.W.; Su, H.; Su, K.P. Transient receptor potential V1 (TRPV1) modulates the therapeutic effects for comorbidity of pain and depression: The common molecular implication for electroacupuncture and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.Y.; Hsieh, C.L.; Huang, C.P.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture Attenuates CFA-induced Inflammatory Pain by suppressing Nav1.8 through S100B, TRPV1, Opioid, and Adenosine Pathways in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.Y.; Hsieh, C.L.; Huang, C.P.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture Attenuates Induction of Inflammatory Pain by Regulating Opioid and Adenosine Pathways in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Zhou, T. Effect of Acupuncture on Pain, Fatigue, Sleep, Physical Function, Stiffness, Well-Being, and Safety in Fibromyalgia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pain Res. 2022, 15, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, M.; Beci, G.; Salaffi, F. Acupuncture for Fibromyalgia: An Open-Label Pragmatic Study on Effects on Disease Severity, Neuropathic Pain Features, and Pain Catastrophizing. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2020, 2020, 9869250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, M.D.; Bobinski, F.; Sato, K.L.; Kolker, S.J.; Sluka, K.A.; Santos, A.R. IL-10 cytokine released from M2 macrophages is crucial for analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of acupuncture in a model of inflammatory muscle pain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 51, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.C.; Lu, K.Q.; Xiao, R.; Tang, W.C.; Wang, F. The Role of p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase-Mediated F-Actin in the Acupuncture-Induced Mitigation of Inflammatory Pain in Arthritic Rats. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghowsi, M.; Qalekhani, F.; Farzaei, M.H.; Mahmudii, F.; Yousofvand, N.; Joshi, T. Inflammation, oxidative stress, insulin resistance, and hypertension as mediators for adverse effects of obesity on the brain: A review. Biomedicine 2021, 11, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, G.X.; Tu, J.F.; Yang, J.W.; Ren, M.M.; Liu, J.L.; Lee, C.K.; Zhou, H.; Wang, Z.Y.; et al. Acupuncture Modulation of Chronic Neuropathic Pain and Its Association with Brain Functional Properties. J. Pain 2024, 25, 104645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Ha, I.H.; Park, H.J. The analgesic effect of acupuncture in neuropathic pain: Regulatory mechanisms of DNA methylation in the brain. Pain Rep. 2024, 9, e1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, M.; Zhang, Q.; Si, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, H.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, D.; Fang, Y. The role of purinergic signaling in acupuncture-mediated relief of neuropathic and inflammatory pain. In Purinergic Signalling; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.W.; Cheng, S.W.; Liu, W.C.; Zailani, H.; Wu, S.K.; Hung, M.C.; Su, K.P. Chemogenetic targeting TRPV1 in obesity-induced depression: Unveiling therapeutic potential of eicosapentaenoic acid and acupuncture. Brain Behav. Immun. 2025, 123, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyori, M.; Nagai, J.; Nakazawa, T.; Ueda, H. Absence of morphine analgesia and its underlying descending serotonergic activation in an experimental mouse model of fibromyalgia. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 472, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, D.T.N.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture Mitigates TRPV1 Overexpression in the Central Nervous System Associated with Fibromyalgia in Mice. Life 2024, 14, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forogh, B.; Haqiqatshenas, H.; Ahadi, T.; Ebadi, S.; Alishahi, V.; Sajadi, S. Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) versus transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in the management of patients with fibromyalgia: A randomized controlled trial. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2021, 51, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Erridge, S.; Holvey, C.; Coomber, R.; Usmani, A.; Sajad, M.; Guru, R.; Holden, W.; Rucker, J.J.; Platt, M.; et al. Assessment of clinical outcomes in patients with fibromyalgia: Analysis from the UK Medical Cannabis Registry. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miro, E.; Martinez, M.P.; Sanchez, A.I.; Caliz, R. Clinical Manifestations of Trauma Exposure in Fibromyalgia: The Role of Anxiety in the Association Between Posttraumatic Stress Symptoms and Fibromyalgia Status. J. Trauma. Stress 2020, 33, 1082–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazza, M. Medical cannabis for the treatment of fibromyalgia syndrome: A retrospective, open-label case series. J. Cannabis Res. 2021, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas-Yague, E.; Martinez-Pozas, O.; Gozalo-Pascual, R.; Munoz Blanco, E.; Lopez Panos, R.; Jimenez-Ortega, L.; Cuenca-Zaldívar, J.N.; Sánchez Romero, E.A. Comparative effectiveness of Maitland Spinal Mobilization versus myofascial techniques on pain and symptom severity in women with Fibromyalgia syndrome: A quasi-randomized clinical trial with 3-month follow up. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2024, 73, 103160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Pozas, O.; Sanchez-Romero, E.A.; Beltran-Alacreu, H.; Arribas-Romano, A.; Cuenca-Martinez, F.; Villafane, J.H.; Fernández-Carnero, J. Effects of Orthopedic Manual Therapy on Pain Sensitization in Patients with Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain: An Umbrella Review With Meta-Meta-analysis. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2023, 102, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Fukaya, M.; Maejima, T.; Yoshida, T.; Miura, E.; Watanabe, M.; Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Kano, M. The CB1 cannabinoid receptor is the major cannabinoid receptor at excitatory presynaptic sites in the hippocampus and cerebellum. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 2991–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donvito, G.; Nass, S.R.; Wilkerson, J.L.; Curry, Z.A.; Schurman, L.D.; Kinsey, S.G.; Lichtman, A.H. The Endogenous Cannabinoid System: A Budding Source of Targets for Treating Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain. Neuropsychopharmacology 2018, 43, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanton, S.; Menezes, J.; Krock, E.; Sandstrom, A.; Tour, J.; Sandor, K.; Jurczak, A.; Hunt, M.; Baharpoor, A.; Kadetoff, D. Anti-satellite glia cell IgG antibodies in fibromyalgia patients are related to symptom severity and to metabolite concentrations in thalamus and rostral anterior cingulate cortex. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 114, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsiao, I.-H.; Lin, M.-C.; Hsu, H.-C.; Chae, Y.; Su, Y.-K.; Lin, Y.-W. Chemogenetic Modulation of Electroacupuncture Analgesia in a Mouse Intermittent Cold Stress-Induced Fibromyalgia Model by Activating Cerebellum Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Expression and Signaling. Life 2025, 15, 1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091458
Hsiao I-H, Lin M-C, Hsu H-C, Chae Y, Su Y-K, Lin Y-W. Chemogenetic Modulation of Electroacupuncture Analgesia in a Mouse Intermittent Cold Stress-Induced Fibromyalgia Model by Activating Cerebellum Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Expression and Signaling. Life. 2025; 15(9):1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091458
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsiao, I-Han, Ming-Chia Lin, Hsin-Cheng Hsu, Younbyoung Chae, Yi-Kai Su, and Yi-Wen Lin. 2025. "Chemogenetic Modulation of Electroacupuncture Analgesia in a Mouse Intermittent Cold Stress-Induced Fibromyalgia Model by Activating Cerebellum Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Expression and Signaling" Life 15, no. 9: 1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091458
APA StyleHsiao, I.-H., Lin, M.-C., Hsu, H.-C., Chae, Y., Su, Y.-K., & Lin, Y.-W. (2025). Chemogenetic Modulation of Electroacupuncture Analgesia in a Mouse Intermittent Cold Stress-Induced Fibromyalgia Model by Activating Cerebellum Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Expression and Signaling. Life, 15(9), 1458. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091458







