Bioenergetic Model of Retrotransposon Activity in Cancer Cells
Abstract
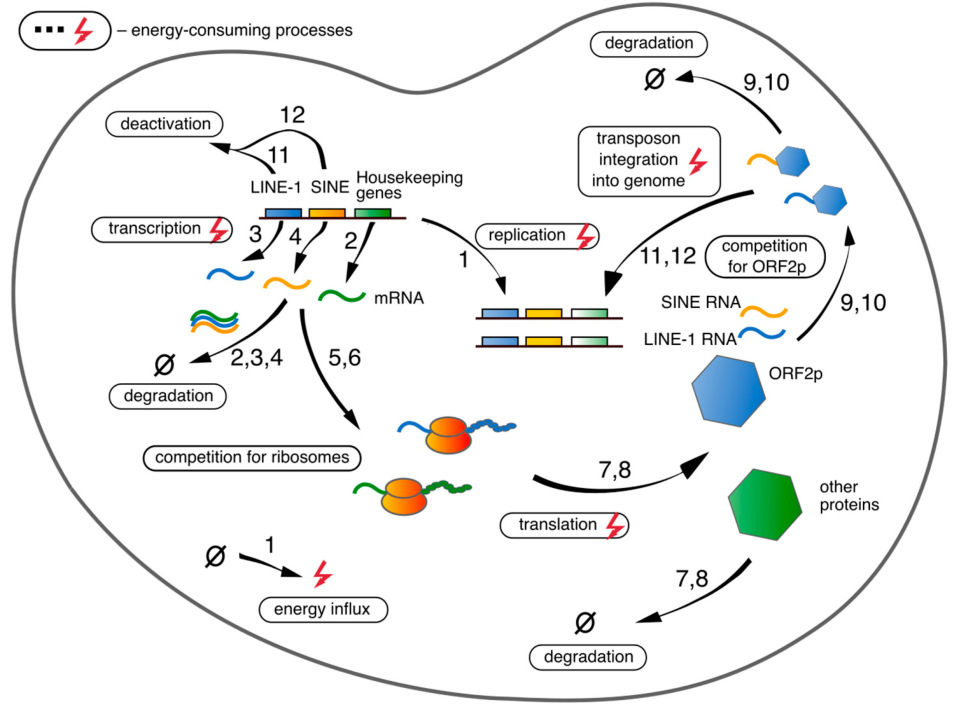
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Equations
2.2. Reaction Rates
2.2.1. Transcription
2.2.2. mRNA-Ribosome Complex Formation
2.2.3. Translation and L1′S mRNA-ORF2p Complex Formation
2.2.4. Alu’s mRNA-ORF2p Complex Formation
2.2.5. Integration of New RTE Copies into Genome
2.2.6. Energy Costs for DNA Replication
2.2.7. Degradation
2.3. Parameter Values
| Designation | Description | Value | Unit | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ng | human genome size | 3.08 × 109 | bp | BNID 101484 |
| Q | number of housekeeping genes | 3804 | m.p.c. | [26] |
| A0 | ATP influx rate | 1.31 × 1010 | m.p.c./min | BNID 110879 1 |
| τ | HeLa cell cycle duration | 1320 | min | BNID 109393 |
| Nq | median protein length for HeLa cells | 431 | aa | [27] |
| NQ | median gene length for HeLa cells | 1300 | bp | [27] 2 |
| NL | L1 length | 6000 | bp | [28] |
| NS | Alu length | 300 | bp | [29] |
| Naa | number of ATP molecules for adding one aa | 5 | – | [30] |
| Nnt | number of ATP molecules for adding one nucleotide | 15 | – | [30] |
| χmaxL | single-nucleotide incorporation rate for L1 insertion | 840 | 1/min | [31] 3 |
| χmaxS | single-nucleotide incorporation rate for Alu insertion | 840 | 1/min | [31] 3 |
| KχL | Michaelis constant of ATP consumption kinetics in L1 insertion | 1.1 × 107 | m.p.c. | [31] 4 |
| KχS | Michaelis constant of ATP consumption kinetics in Alu insertion | 1.1 × 107 | m.p.c. | [31] 4 |
| KL | L1′s mRNA–ORF1p association constant | 2.24 × 10−3 | 1/m.p.c. | [32] 5 |
| wq | maximum transcription rate per housekeeping gene | 4.64 | 1/min | BNID 111721 6 |
| wL | maximum transcription rate per L1 | 1 | 1/min | BNID 111721 6 |
| wS | maximum transcription rate per Alu | 20 | 1/min | BNID 111721 6 |
| θq | Michaelis constant of ATP consumption kinetics in housekeeping gene transcription | 3.8 × 109 | m.p.c. | BNID 111027 7 |
| θL | Michaelis constant of ATP consumption kinetics in L1 transcription | 3.8 × 109 | m.p.c. | BNID 111027 7 |
| θS | Michaelis constant of ATP consumption kinetics in Alu transcription | 3.8 × 109 | m.p.c. | BNID 111027 7 |
| γmaxq | maximum translation rate proteins of housekeeping genes | 300 | aa/min | BNID 104598 |
| γmaxL | maximum translation rate for L1′s protein | 300 | aa/min | BNID 104598 |
| Kγq | Michaelis constant of ATP consumption kinetics in housekeeping gene translation | 25,900 | m.p.c. | [33] |
| KγL | Michaelis constant of ATP consumption kinetics in L1 translation | 25,900 | m.p.c. | [33] |
| kbq | housekeeping gene’s mRNA–ribosome binding rate constant | 5 × 10−8 | 1/min | * |
| kbL | L1′s mRNA–ribosome binding rate constant | 5 × 10−8 | 1/min | * |
| kuq | housekeeping gene’s mRNA–ribosome unbinding rate constant | 0.01 | 1/min | * |
| kuL | L1′s mRNA–ribosome unbinding rate constant | 0.01 | 1/min | * |
| ksubS | rate constant of mL-to-mS substitution in mRNA–ORF2p complex | 5 × 10−8 | 1/min | * |
| ksubL | rate constant of mS-to-mL substitution in mRNA–ORF2p complex | 5 × 10−6 | 1/min | * |
| rtot | total number of ribosomes | 9.5 × 106 | m.p.c. | BNID 107347 |
| λa | ATP degradation rate constant | 1.47 | 1/min | * |
| dmq | degradation rate constant for housekeeping gene’s mRNAs | 1.15 × 10−3 | 1/min | BNID 104747 |
| dcq | degradation rate constant for cq complex | 1.55 × 10−3 | 1/min | * |
| dq | degradation rate constant for housekeeping gene’s proteins | 5.67 × 10−4 | 1/min | BNID 112253 |
| dmL | degradation rate constant for L1′s mRNAs | 1.15 × 10−3 | 1/min | BNID 104747 |
| dmS | degradation rate constant for Alu’s mRNAs | 1.15 × 10−3 | 1/min | BNID 104747 |
| dcL | degradation rate constant for cL complex | 1.55 × 10−3 | 1/min | * |
| dO1 | ORF1p degradation rate constant | 5.67 × 10−4 | 1/min | BNID 112253 |
| dbL | degradation rate constant for bL complex | 5.67 × 10−4 | 1/min | BNID 112253 |
| dbS | degradation rate constant for bS complex | 5.67 × 10−4 | 1/min | BNID 112253 |
| λL | L1 deactivation rate constant | 0.37 | 1/min | * |
| λS | Alu deactivation rate constant | 1.18 | 1/min | * |
| Vcell | cell volume | 3700 | μm3 | BNID 105879 |
| awt | number of ATP molecules in HeLa cell | 5.33 × 109 | m.p.c. | BNID 104449 |
| Lwt | number of active L1 in human genome | 1064 | m.p.c. | UCSC Genome Browser |
| Swt | number of active Alu in human genome | 13,243 | m.p.c. | UCSC Genome Browser |
2.4. Numerical Solution and Parameter Optimizaion
3. Results
3.1. Energy Reduction Under Fixed Parameter Values
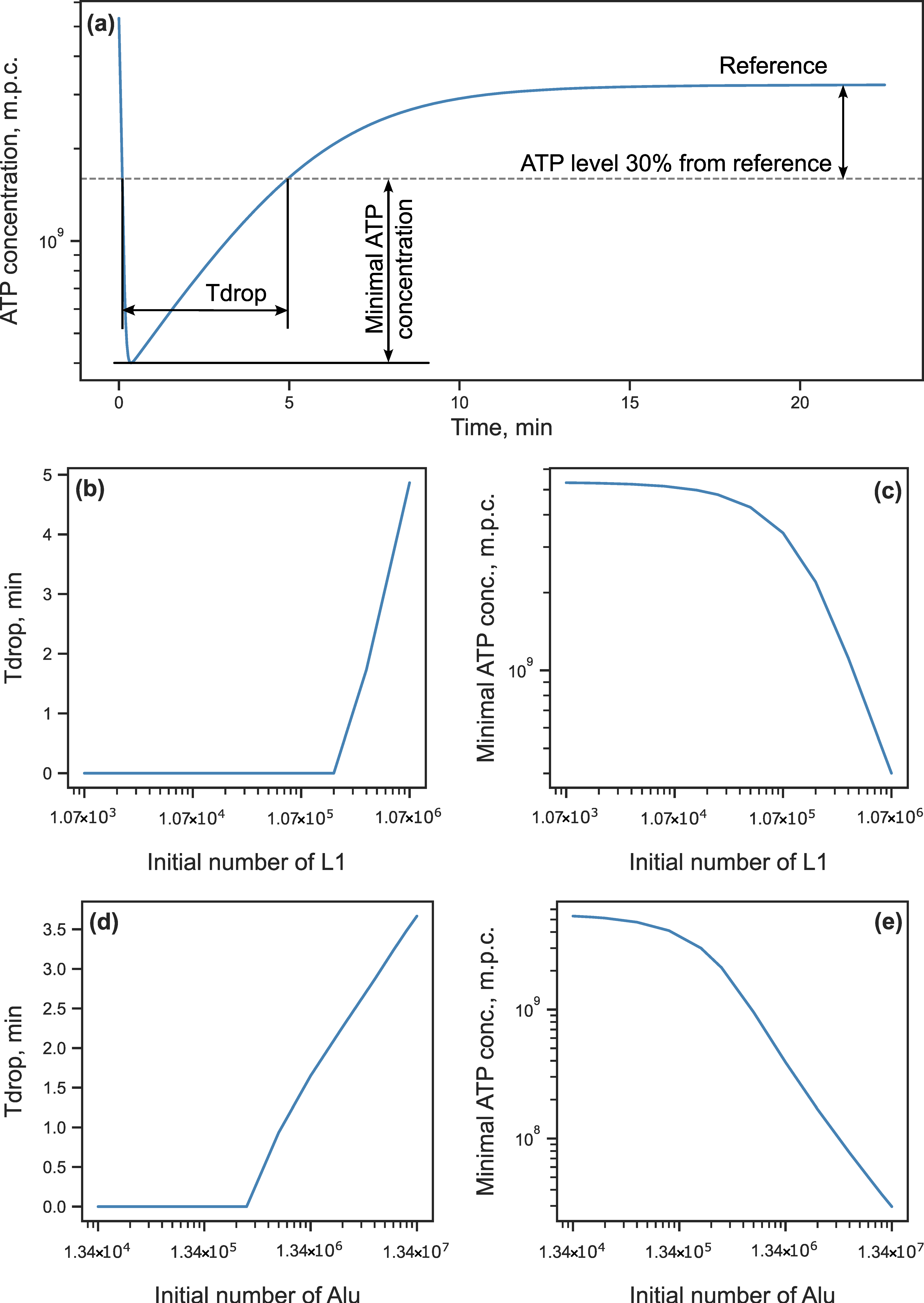
3.2. Energy Reduction Under Perturbed Parameter Values
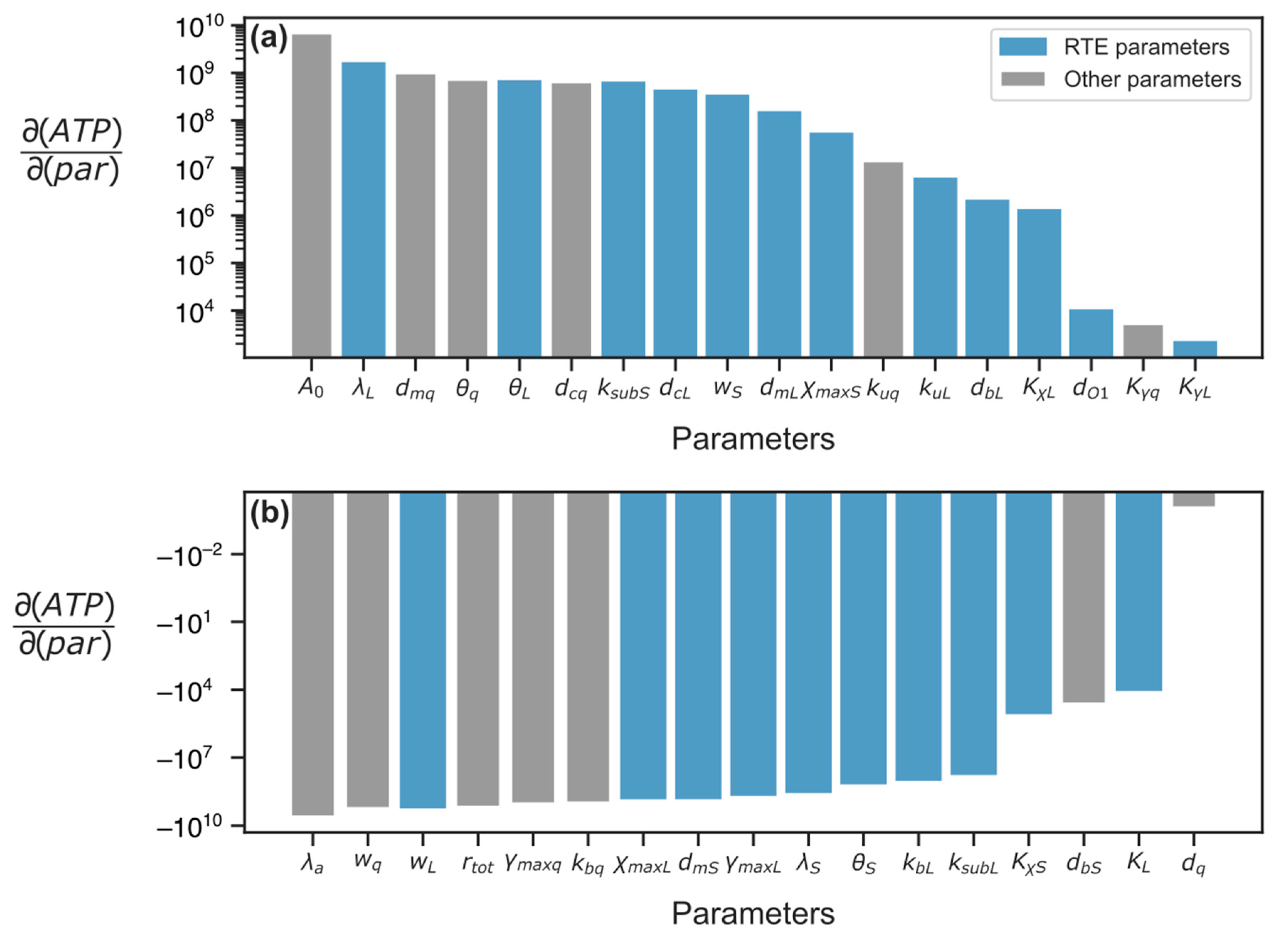
3.2.1. Parameter Sensitivity Analysis
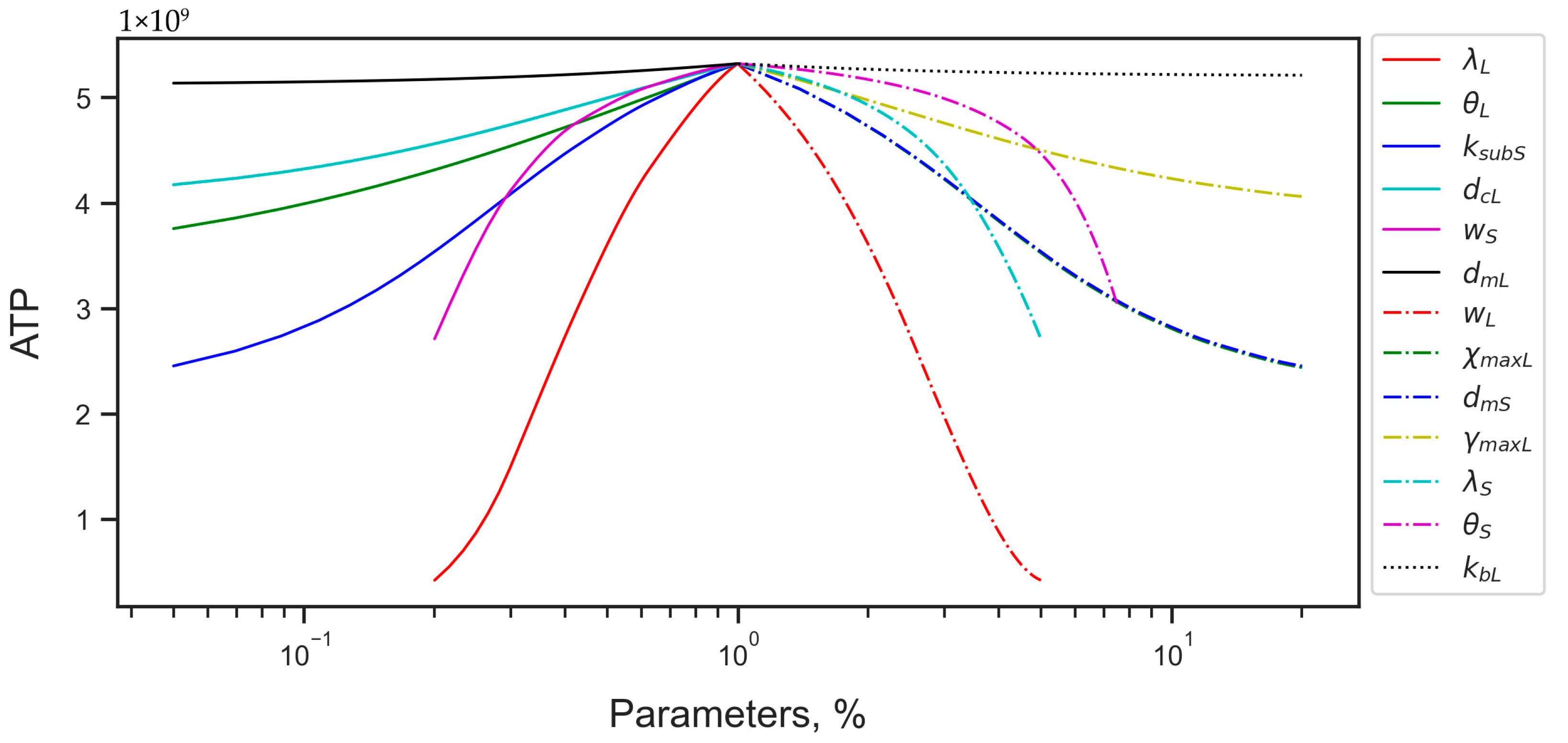
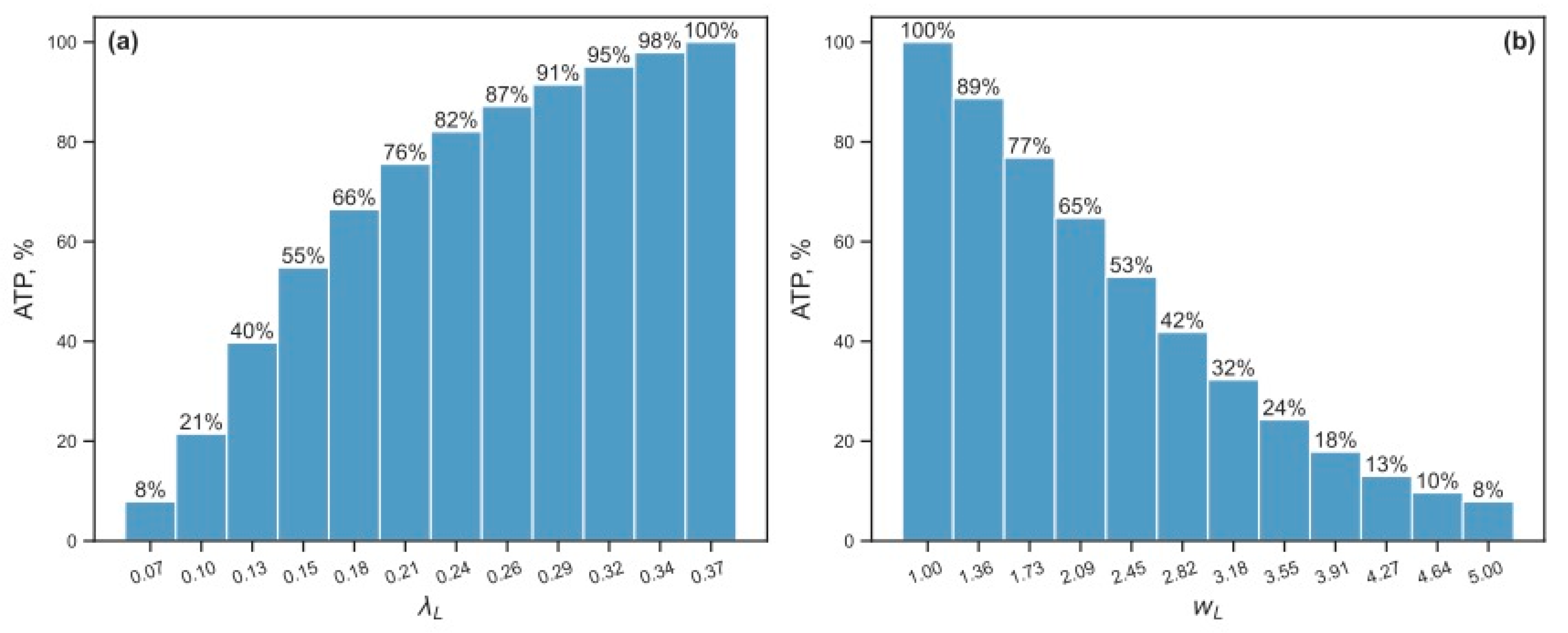
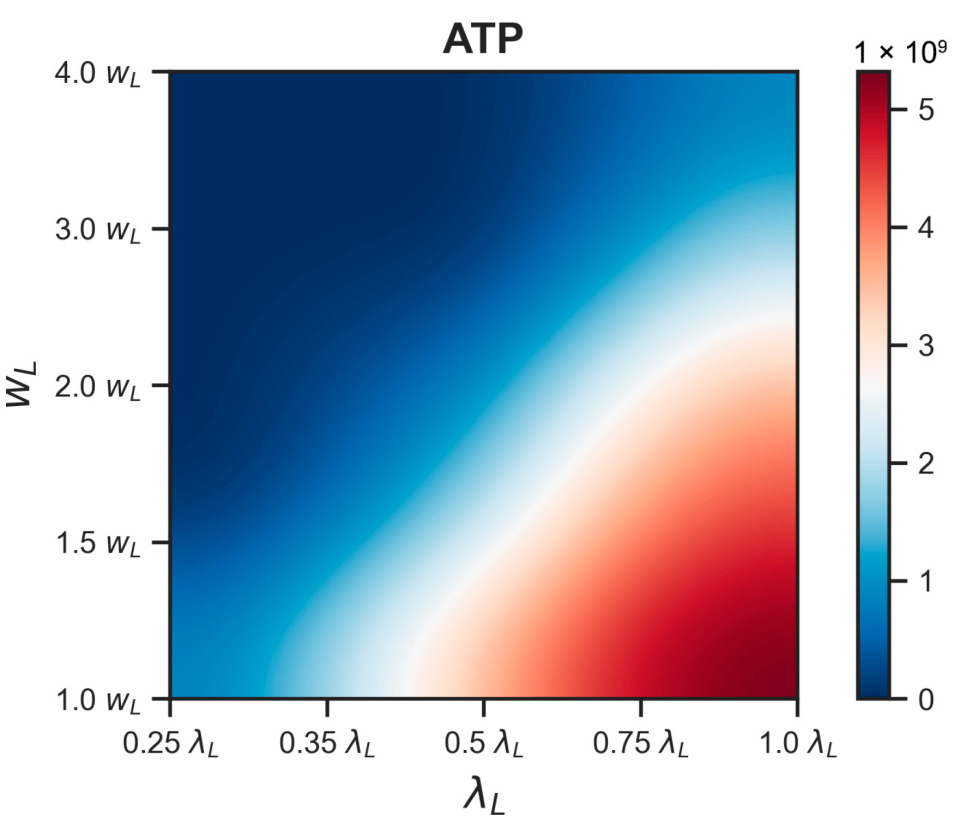
3.2.2. Energy Reduction and Redistribution Among the Processes Under Perturbations of RTE-Associated Parameter Values
4. Discussion
Model Limitations and Possible Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kazazian, H.H. Mobile Elements: Drivers of Genome Evolution. Science 2004, 303, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, R.E.; Bennett, E.A.; Iskow, R.C.; Devine, S.E. Which Transposable Elements Are Active in the Human Genome? Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassiotis, G.; Stoye, J.P. Immune Responses to Endogenous Retroelements: Taking the Bad with the Good. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbarbary, R.A.; Lucas, B.A.; Maquat, L.E. Retrotransposons as Regulators of Gene Expression. Science 2016, 351, aac7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, C.R.; Garcia-Perez, J.L.; Badge, R.M.; Moran, J.V. LINE-1 Elements in Structural Variation and Disease. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2011, 12, 187–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Goldenfeld, N. Stochastic Predator-Prey Dynamics of Transposons in the Human Genome. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 208101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, K.H. Our Conflict with Transposable Elements and Its Implications for Human Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2020, 15, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, C.A.; De Carvalho, D.D. Reactivation of Endogenous Retroelements in Cancer Development and Therapy. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2020, 4, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, R.K.; Ramakrishna, W. Transposons: Unexpected Players in Cancer. Gene 2022, 808, 145975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonova, K.I.; Brodsky, L.; Lipchick, B.; Pal, M.; Novototskaya, L.; Chenchik, A.A.; Sen, G.C.; Komarova, E.A.; Gudkov, A.V. P53 Cooperates with DNA Methylation and a Suicidal Interferon Response to Maintain Epigenetic Silencing of Repeats and Noncoding RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E89–E98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappinelli, K.B.; Strissel, P.L.; Desrichard, A.; Li, H.; Henke, C.; Akman, B.; Hein, A.; Rote, N.S.; Cope, L.M.; Snyder, A.; et al. Inhibiting DNA Methylation Causes an Interferon Response in Cancer via dsRNA Including Endogenous Retroviruses. Cell 2015, 162, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulois, D.; Loo Yau, H.; Singhania, R.; Wang, Y.; Danesh, A.; Shen, S.Y.; Han, H.; Liang, G.; Jones, P.A.; Pugh, T.J.; et al. DNA-Demethylating Agents Target Colorectal Cancer Cells by Inducing Viral Mimicry by Endogenous Transcripts. Cell 2015, 162, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishak, C.A.; Classon, M.; De Carvalho, D.D. Deregulation of Retroelements as an Emerging Therapeutic Opportunity in Cancer. Trends Cancer 2018, 4, 583–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Oreskovic, E.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, Q.; Gilman, A.; Lin, Y.S.; He, J.; Zheng, Z.; Lu, J.Y.; Lee, J.; et al. Transposon-Triggered Innate Immune Response Confers Cancer Resistance to the Blind Mole Rat. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 1219–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haoudi, A.; Semmes, O.J.; Mason, J.M.; Cannon, R.E. Retrotransposition-Competent Human LINE-1 Induces Apoptosis in Cancer Cells With Intact P53. BioMed Res. Int. 2004, 2004, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgnaoui, S.M.; Gosden, R.G.; Semmes, O.J.; Haoudi, A. Human LINE-1 Retrotransposon Induces DNA Damage and Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2006, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Heiden, M.G.; Cantley, L.C.; Thompson, C.B. Understanding the Warburg Effect: The Metabolic Requirements of Cell Proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasperski, A.; Kasperska, R. Bioenergetics of Life, Disease and Death Phenomena. Theory Biosci. 2018, 137, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Tsujimoto, Y. Intracellular ATP Levels Determine Cell Death Fate by Apoptosis or Necrosis. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar]
- Lieberthal, W.; Menza, S.A.; Levine, J.S. Graded ATP Depletion Can Cause Necrosis or Apoptosis of Cultured Mouse Proximal Tubular Cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 1998, 274, F315–F327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skulachev, V.P. Bioenergetic Aspects of Apoptosis, Necrosis and Mitoptosis. Apoptosis 2006, 11, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januszyk, K.; Li, P.W.-L.; Villareal, V.; Branciforte, D.; Wu, H.; Xie, Y.; Feigon, J.; Loo, J.A.; Martin, S.L.; Clubb, R.T. Identification and Solution Structure of a Highly Conserved C-Terminal Domain within ORF1p Required for Retrotransposition of Long Interspersed Nuclear Element-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 24893–24904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milo, R.; Jorgensen, P.; Moran, U.; Weber, G.; Springer, M. BioNumbers—The Database of Key Numbers in Molecular and Cell Biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, D750–D753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, G.; Barber, G.P.; Benet-Pages, A.; Casper, J.; Clawson, H.; Diekhans, M.; Fischer, C.; Gonzalez, J.N.; Hinrichs, A.S.; Lee, C.M.; et al. The UCSC Genome Browser Database: 2025 Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1243–D1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg, E.; Levanon, E.Y. Human Housekeeping Genes, Revisited. Trends Genet. 2013, 29, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milo, R.; Phillips, R. Cell Biology by the Numbers; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-317-23069-4. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, A.F.; Schmeckpeper, B.J.; Abdelrazik, M.; Comey, C.T.; O’Hara, B.; Rossiter, J.P.; Cooley, T.; Heath, P.; Smith, K.D.; Margolet, L. Origin of the Human L1 Elements: Proposed Progenitor Genes Deduced from a Consensus DNA Sequence. Genomics 1987, 1, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batzer, M.A.; Deininger, P.L. Alu Repeats and Human Genomic Diversity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.; Kondev, J.; Theriot, J.; Garcia, H. Physical Biology of the Cell, 2nd ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 978-0-429-16883-3. [Google Scholar]
- Reardon, J.E. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Reverse Transcriptase: Steady-State and Pre-Steady-State Kinetics of Nucleotide Incorporation. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 4473–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.; Yin, J. Quantitative Intracellular Kinetics of HIV Type 1. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 1999, 15, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiße, A.Y.; Oyarzún, D.A.; Danos, V.; Swain, P.S. Mechanistic Links between Cellular Trade-Offs, Gene Expression, and Growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1038–E1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, M.; Marinov, G.K. The Bioenergetic Costs of a Gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15690–15695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, P.; Terradot, G.; Danos, V.; Weiße, A.Y. Sources, Propagation and Consequences of Stochasticity in Cellular Growth. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlesworth, B.; Charlesworth, D. The Population Dynamics of Transposable Elements. Genet. Res. 1983, 42, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzic, A.L.; Deceliere, G. Models of the Population Genetics of Transposable Elements. Genet. Res. 2005, 85, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouzic, A.L.; Capy, P. Population Genetics Models of Competition Between Transposable Element Subfamilies. Genetics 2006, 174, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranzo, J.; Gómez, M.J.; de Saro, F.J.L.; Manrubia, S. Large-Scale Genomic Analysis Suggests a Neutral Punctuated Dynamics of Transposable Elements in Bacterial Genomes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banuelos, M.; Sindi, S. Modeling Transposable Element Dynamics with Fragmentation Equations. Math. Biosci. 2018, 302, 46–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Ferrer, A.; Nguyen, A.; Glémin, S.; Deragon, J.-M.; Panaud, O.; Gourbière, S. The Ecology of the Genome and the Dynamics of the Biological Dark Matter. J. Theor. Biol. 2021, 518, 110641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, S.; Gursky, V.V.; Samsonova, M.; Kanapin, A.; Samsonova, A. Stochastic Effects in Retrotransposon Dynamics Revealed by Modeling under Competition for Cellular Resources. Life 2021, 11, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyov, A.; Behr, J.M.; Hoyos, D.; Banks, E.; Drong, A.W.; Zhong, J.Z.; Garcia-Rivera, E.; McKerrow, W.; Chu, C.; Zaller, D.M.; et al. Mechanism-Guided Quantification of LINE-1 Reveals P53 Regulation of Both Retrotransposition and Transcription. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2023.05.11.539471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostertag, E.M.; Prak, E.T.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Moran, J.V.; Kazazian, H.H. Determination of L1 Retrotransposition Kinetics in Cultured Cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Tam, O.H.; Paniagua, E.; Hammell, M. TEtranscripts: A Package for Including Transposable Elements in Differential Expression Analysis of RNA-Seq Datasets. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3593–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, J.V.; Holmes, S.E.; Naas, T.P.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Boeke, J.D.; Kazazian, H.H. High Frequency Retrotransposition in Cultured Mammalian Cells. Cell 1996, 87, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, J.B.; Kopera, H.C.; Liu, Y.; Garcia-Canadas, M.; Catalina, P.; Leone, P.E.; Sanchez, L.; Kitzman, J.O.; Kidd, J.M.; Garcia-Perez, J.L.; et al. Variable Patterns of Retrotransposition in Different HeLa Strains Provide Mechanistic Insights into SINE RNA Mobilization Processes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, 7761–7779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Ahmad, S.F.; Xu, J. Regulation and Function of Transposable Elements in Cancer Genomes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penzkofer, T.; Dandekar, T.; Zemojtel, T. L1Base: From Functional Annotation to Prediction of Active LINE-1 Elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D498–D500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kines, K.J.; Sokolowski, M.; deHaro, D.L.; Christian, C.M.; Baddoo, M.; Smither, M.E.; Belancio, V.P. The Endonuclease Domain of the LINE-1 ORF2 Protein Can Tolerate Multiple Mutations. Mob. DNA 2016, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, A.L.; Kõks, S. Retrotransposition-Competent L1s Are Increased in the Genomes of Individuals with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2025, 250, 10575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazazian, H.H.; Moran, J.V. Mobile DNA in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belancio, V.P.; Roy-Engel, A.M.; Pochampally, R.R.; Deininger, P. Somatic Expression of LINE-1 Elements in Human Tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 3909–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, B.; Jones, A.E.; Caillet, C.J.; Das, S.; Royer, S.K.; Abrams, J.M. P53 Directly Represses Human LINE1 Transposons. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, P.; Kumar, A.; Parida, A.S.; De, A.K.; Bhadke, G.; Khatua, S.; Tiwari, B. P53-Mediated Regulation of LINE1 Retrotransposon-Derived R-Loops. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 301, 108200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovyov, A.; Behr, J.M.; Hoyos, D.; Banks, E.; Drong, A.W.; Thornlow, B.; Zhong, J.Z.; Garcia-Rivera, E.; McKerrow, W.; Chu, C.; et al. Pan-Cancer Multi-Omic Model of LINE-1 Activity Reveals Locus Heterogeneity of Retrotransposition Efficiency. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mita, P.; Sun, X.; Fenyö, D.; Kahler, D.J.; Li, D.; Agmon, N.; Wudzinska, A.; Keegan, S.; Bader, J.S.; Yun, C.; et al. BRCA1 and S Phase DNA Repair Pathways Restrict LINE-1 Retrotransposition in Human Cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watterson, A.; Coelho, M.A. Cancer Immune Evasion through KRAS and PD-L1 and Potential Therapeutic Interventions. Cell Commun. Signal 2023, 21, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
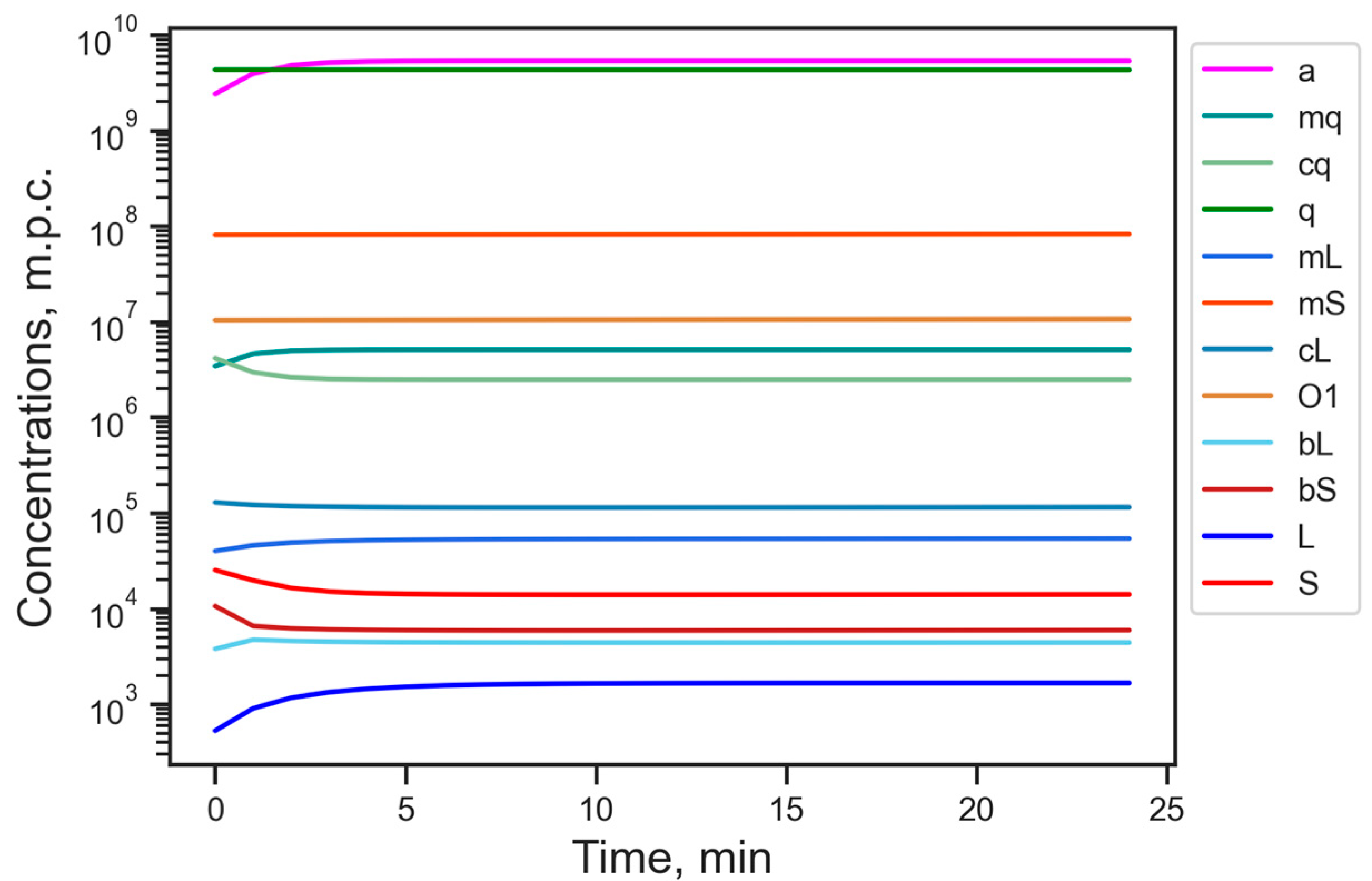
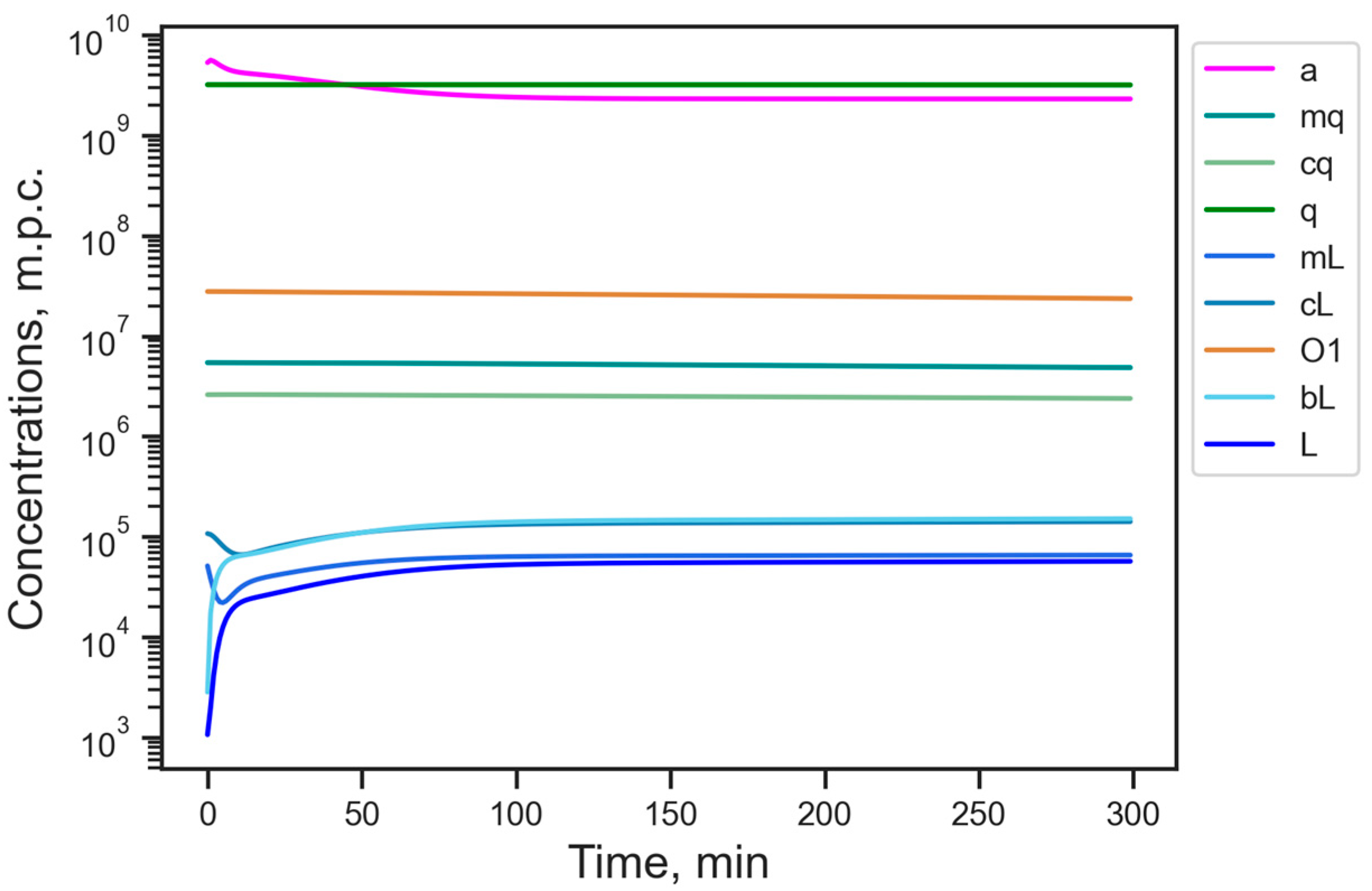

| Designation | Dynamical Variable | Stationary Value, m.p.c. |
|---|---|---|
| a | amount of available energy (ATP level) | 5.32 × 109 |
| mq | mRNA of housekeeping genes | 5.44 × 106 |
| cq | complex of mq with ribosomes | 2.61 × 106 |
| q | protein translated from cq | 3.20 × 109 |
| mL | mRNA of L1 | 5.13 × 104 |
| mS | mRNA of SINE | 1.22 × 108 |
| cL | complex of mL with ribosomes | 1.8 × 105 |
| O1 | ORF1p protein translated from cL | 2.78 × 107 |
| bL | complex of ORF2p proteins with mL | 2.83 × 103 |
| bS | complex of ORF2p proteins with mS | 5.64 × 103 |
| L | number of L1 in genome | 1.07 × 103 |
| S | number of Alu in genome | 1.34 × 104 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pavlov, S.; Duk, M.; Gursky, V.V.; Samsonova, M.; Kanapin, A.; Samsonova, A. Bioenergetic Model of Retrotransposon Activity in Cancer Cells. Life 2025, 15, 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091338
Pavlov S, Duk M, Gursky VV, Samsonova M, Kanapin A, Samsonova A. Bioenergetic Model of Retrotransposon Activity in Cancer Cells. Life. 2025; 15(9):1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091338
Chicago/Turabian StylePavlov, Sergei, Maria Duk, Vitaly V. Gursky, Maria Samsonova, Alexander Kanapin, and Anastasia Samsonova. 2025. "Bioenergetic Model of Retrotransposon Activity in Cancer Cells" Life 15, no. 9: 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091338
APA StylePavlov, S., Duk, M., Gursky, V. V., Samsonova, M., Kanapin, A., & Samsonova, A. (2025). Bioenergetic Model of Retrotransposon Activity in Cancer Cells. Life, 15(9), 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15091338








