Proteomics Analysis of Plasma Biomarker of Cognitive Frailty in Elders Who Locally Reside in Chiang Mai Province of Thailand
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Plasma Sample Collection and Protein Preparation
2.3. Two-Dimensional Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis or 2-DE
2.4. In-Gel Tryptic Digestion
2.5. Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis for Protein Identification
2.7. ELISA for Plasma Fibrinogen Gamma Chain (FGG)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data of Participants
3.2. 2-DE of Human Plasma Samples
3.3. Protein Identification
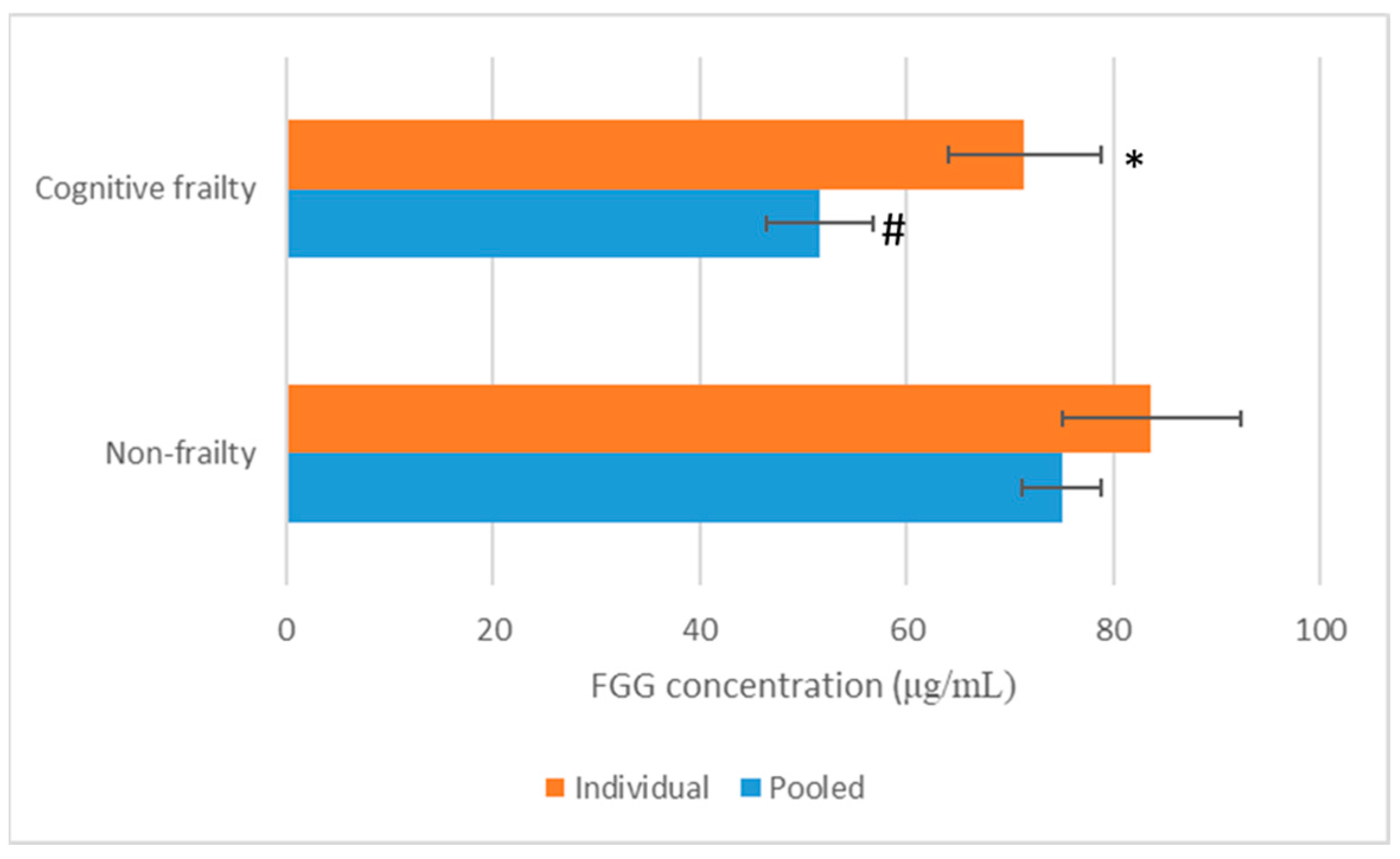
3.4. Validation of FGG in Human Plasma by ELISA Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MCI | Mild cognitive impairment |
| MoCA-B | The Montreal Cognitive Assessment-Basic |
| FGG | Fibrinogen gamma chain |
References
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Ageing 2015; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 1–149. Available online: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/publications/pdf/ageing/WPA2015_Report.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Medical Department. Manual Screening Assessment for Seniors; Veterans’ Affairs Office Printing Synthesis Organization: Bangkok, Thailand, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cesari, M.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; Lauretani, F.; Onder, G.; Bandinelli, S.; Maraldi, C.; Guralnik, J.M.; Pahor, M.; Ferrucci, L. Frailty syndrome and skeletal muscle: Results from the Invecchiare in Chianti study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, L.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Walston, J.; Newman, A.B.; Hirsch, C.; Gottdiener, J.; Seeman, T.; Tracy, R.; Kop, W.J.; Burke, G.; et al. Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype. J. Gerontol. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M146–M157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwood, K.; Song, X.; MacKnight, C.; Bergman, H.; Hogan, D.B.; McDowell, I.; Mitnitski, A. A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people. CMAJ. 2005, 173, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Promotion and Development of the Elderly. The Elderly Thailand; S Plus Media Ltd.: Nonthaburi, Thailand, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Collard, R.M.; Boter, H.; Schoevers, R.A.; Oude Voshaar, R.C. Prevalence of frailty in community-dwelling older persons: A systematic review. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 1487–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, A.; Young, J.; Iliffe, S.; Olde Rikkert, M.; Rockwood, K. Frailty in elderly people. Lancet 2013, 381, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchman, A.S.; Bennett, D.A. Cognitive frailty. J. Nutr. Health Aging. 2013, 17, 738–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, H.; Makizako, H.; Doi, T.; Yoshida, D.; Tsutsumimoto, K.; Anan, Y.; Uemura, K.; Ito, T.; Lee, S.; Park, H.; et al. Combined prevalence of frailty and mild cognitive impairment in a population of elderly Japanese people. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2013, 14, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chye, L.; Wei, K.; Nyunt, M.S.Z.; Gao, Q.; Wee, S.L.; Ng, T.P. Strong relationship between malnutrition and cognitive frailty in the Singapore Longitudinal Ageing Studies (SLAS-1 and SLAS-2). J. Prev. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 5, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roppolo, M.; Mulasso, A.; Rabaglietti, E. Cognitive frailty in Italian community-dwelling older adults: Prevalence rate and its association with disability. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2016, 21, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Nyunt, M.S.Z.; Gao, Q.; Feng, L.; Lee, T.S.; Tsoi, T.; Chong, M.S.; Lim, W.S.; Collinson, S.; Yap, P.; et al. Physical frailty, cognitive impairment, and the risk of neurocognitive disorder in the Singapore Longitudinal Ageing Studies. J. Gerontol. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 72, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solfrizzi, V.; Scafato, E.; Seripa, D.; Lozupone, M.; Imbimbo, B.; D’Amato, A.; Tortelli, R.; Schilardi, A.; Galluzzo, L.; Gandin, C.; et al. Reversible cognitive frailty, dementia, and all-cause mortality: The Italian Longitudinal Study on Aging. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 89.e1–89.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Awata, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Kojima, N.; Osuka, Y.; Motokawa, K.; Sakuma, N.; Inagaki, H.; Edahiro, A.; Hosoi, E.; et al. Cognitive frailty in community-dwelling older Japanese people: Prevalence and its association with falls. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2019, 19, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdeldin, S.; Enany, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zureena, Z.; Lokamani, I.; Yaoita, E.; Yamamoto, T. Basics and recent advances of two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Clin. Proteom. 2014, 11, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seesen, M.; Sirikul, W.; Ruangsuriya, J.; Griffiths, J.; Siviroj, P. Cognitive frailty in Thai community-dwelling elderly: Prevalence and its association with malnutrition. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.T.; Sriyam, S.; Sinchaikul, S.; Tsai, H.Y.; Phutrakul, S.; Chen, S.-T. Proteomics Characterization of Haptoglobin Alpha-2 Subunit in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Serum and Various Human Materials. J. Proteomics Bioinform. 2013, 6, 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Havlis, J.; Thomas, H.; Sebela, M.; Shevchenko, A. Fast-response proteomics by accelerated in-gel digestion of proteins. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simurda, T.; Brunclikova, M.; Asselta, R.; Caccia, S.; Zolkova, J.; Kolkova, Z.; Loderer, D.; Skornova, I.; Hudecek, J.; Lasabova, Z.; et al. Genetic variants in the FGB and FGG genes mapping in the beta and gamma nodules of the fibrinogen molecule in congenital quantitative fibrinogen disorders associated with a thrombotic phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, K.; Zhang, X.P.; Medved, L.; Takada, Y. Specific binding of integrin αvβ3 to the fibrinogen γ and αE chain C-terminal domains. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 5872–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, K.; Erickson, H.P.; Ikeda, Y.; Takada, Y. Identification of amino acid sequences in fibrinogen γ-chain and tenascin-C C-terminal domains critical for binding to integrin αvβ3. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 16891–16898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Gong, B.; Wang, P.; Huang, H.; Luo, L.; Liu, F. Novel prognostic biomarkers of gastric cancer based on gene expression microarray: COL12A1, GSTA3, FGA and FGG. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3727–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bae, J.H.; Yang, W.-H.; et al. Fibrinogen alpha chain knockout promotes tumor growth and metastasis through integrin–AKT signaling pathway in lung cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.H.; Wang, J.N.; Xiao, L.F.; Yan, M.; Chen, S.P.; Wang, L.; Yang, K. Elevated serum FGG levels prognosticate and promote the disease progression in prostate cancer. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 651647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyman, G.H.; Khorana, A.A. Cancer, clots and consensus: New understanding of an old problem. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 4821–4826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.Y.; Tian, T.; Zhu, H.Y.; Liang, J.H.; Wu, W.; Cao, L.; Lu, R.-N.; Wang, L.; Li, J.-Y.; Xu, W. Hyperfibrinogenemia is a poor prognostic factor in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 1841–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B.; Wang, C. Prognostic significance of combined fibrinogen concentration and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 2018, 15, 88–96. [Google Scholar]
- Shiose, S.; Hata, Y.; Noda, Y.; Sassa, Y.; Takeda, A.; Yoshikawa, H.; Fujisawa, K.; Kubota, T.; Ishibashi, T. Fibrinogen stimulates in vitro angiogenesis by choroidal endothelial cells via autocrine VEGF. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2004, 242, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, G.N.; Rosenfeldt, L.; Frederick, M.; Miller, W.; Waltz, D.; Kombrinck, K.; McElhinney, K.E.; Flick, M.J.; Monia, B.P.; Revenko, A.S.; et al. Colon cancer growth and dissemination relies upon thrombin, stromal PAR-1, and fibrinogen. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4235–4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.J. Evolutionary changes to transthyretin: Evolution of transthyretin biosynthesis. FEBS J. 2009, 276, 5342–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisel, J.W. Fibrinogen and fibrin. Adv. Protein Chem. 2005, 70, 247–299. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, D.H. Pathophysiologic roles of the fibrinogen gamma chain. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2004, 11, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosesson, M.W. Fibrinogen and fibrin structure and functions. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1894–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaosmanoglu, O.; Banerjee, S.; Sivas, H. Identification of biomarkers associated with partial epithelial to mesenchymal transition in the secretome of slug over-expressing hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell. Oncol. 2018, 41, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repetto, O.; De Re, V. Coagulation and fibrinolysis in gastric cancer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1404, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, Z.; Zeng, G.; Xie, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, N.; Wang, G. Clinical significance of urinary plasminogen and fibrinogen gamma chain as novel potential diagnostic markers for non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 502, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, J.E.; López-Fernández, H.; Diniz, M.S.; Baltazar, P.M.; Pinheiro, L.C.; da Silva, F.C.; Carrascal, M.; Videira, P.; Santos, H.M.; Capelo, J.L. Dithiothreitol-based protein equalization technology to unravel biomarkers for bladder cancer. Talanta 2018, 180, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doolittle, R.F. Searching for differences between fibrinogen and fibrin that affect the initiation of fibrinolysis. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Agents Med. Chem. 2008, 6, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosesson, M.W. Antithrombin I. Inhibition of thrombin generation in plasma by fibrin formation. Thromb. Haemost. 2003, 89, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosesson, M.W. Update on antithrombin I (fibrin). Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 98, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, K.; Arai, S.; Taira, C.; Sugano, M.; Honda, T.; Okumura, N. A novel frameshift mutation in the fibrinogen γC terminal region, FGG c.1169_1170delAT, leading to hypofibrinogenemia. Thromb. Res. 2017, 159, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Chen, W.N.; Liu, L.L.; Lin, W.S.; Jiao, B.Y.; Wu, Y.L.; Lin, J.; Lin, X. Hepatitis B spliced protein (HBSP) generated by a spliced hepatitis B virus RNA participates in abnormality of fibrin formation and functions by binding to fibrinogen γ chain. J. Med. Virol. 2010, 82, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.J.; Chen, Y.J.; Zuo, D.; Xiao, M.M.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, N.; Chen, R.-B. Quantitative proteomic analysis for high-throughput screening of differential glycoproteins in hepatocellular carcinoma serum. Cancer Biol. Med. 2015, 12, 246–254. [Google Scholar]
- Davalieva, K.; Kiprijanovska, S.; Maleva Kostovska, I.; Stavridis, S.; Stankov, O.; Komina, S.; Petrusevska, G.; Polenakovic, M. Comparative proteomics analysis of urine reveals down-regulation of acute phase response signaling and LXR/RXR activation pathways in prostate cancer. Proteomes 2018, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumura, D.; Kloepper, J.; Amoozgar, Z.; Duda, D.G.; Jain, R.K. Enhancing cancer immunotherapy using antiangiogenics: Opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloomston, M.; Zhou, J.X.; Rosemurgy, A.S.; Frankel, W.; Muro-Cacho, C.A.; Yeatman, T.J. Fibrinogen gamma overexpression in pancreatic cancer identified by large-scale proteomic analysis of serum samples. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2592–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Song, X.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, N.; Wei, L.; Chung, K.; Adcock, I.M.; Ling, C.; et al. Integrated analysis reveals lung fibrinogen gamma chain as a biomarker for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1765–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Wang, M.; Zhoa, M.; Ni, W.; Zhang, M. Discovery of fibrinogen γ-chain as a potential urinary biomarker for renal interstitial fibrosis in IgA nephropathy. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, V.; Gupta, A.; Bajpai, S.; Singhal, S.; Dey, A.B.; Dey, S. Serum proteomic approach for differentiation of frail and non-frail elderly. Adv. Gerontol. 2021, 11, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Liao, C.-C.; Huang, C.-H.; Tung, Y.-T.; Chang, H.-C.; Hsu, M.-C.; Huang, C.-C. Proteomics analysis to identify and characterize the biomarkers and physical activities of non-frail and frail older adults. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, N.; Venugopalan, G.; Pradhan, R.; Ambastha, A.; Upadhyay, A.D.; Dwivedi, S.; Dey, A.B.; Dey, S. Exploration of novel anti-oxidant protein sestrin in frailty syndrome in elderly. Aging Dis. 2018, 9, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoki, S.; Sachdev, P.S. Advances in biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease and vascular cognitive impairment and dementia: Current status and clinical implications. Vas-Cog J. 2025, 11, 26–35. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Liao, L.; Liu, Q.; Ma, R.; He, X.; Du, X.; Sha, D. Blood biomarkers for vascular cognitive impairment based on neuronal function: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2025, 16, 1496711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
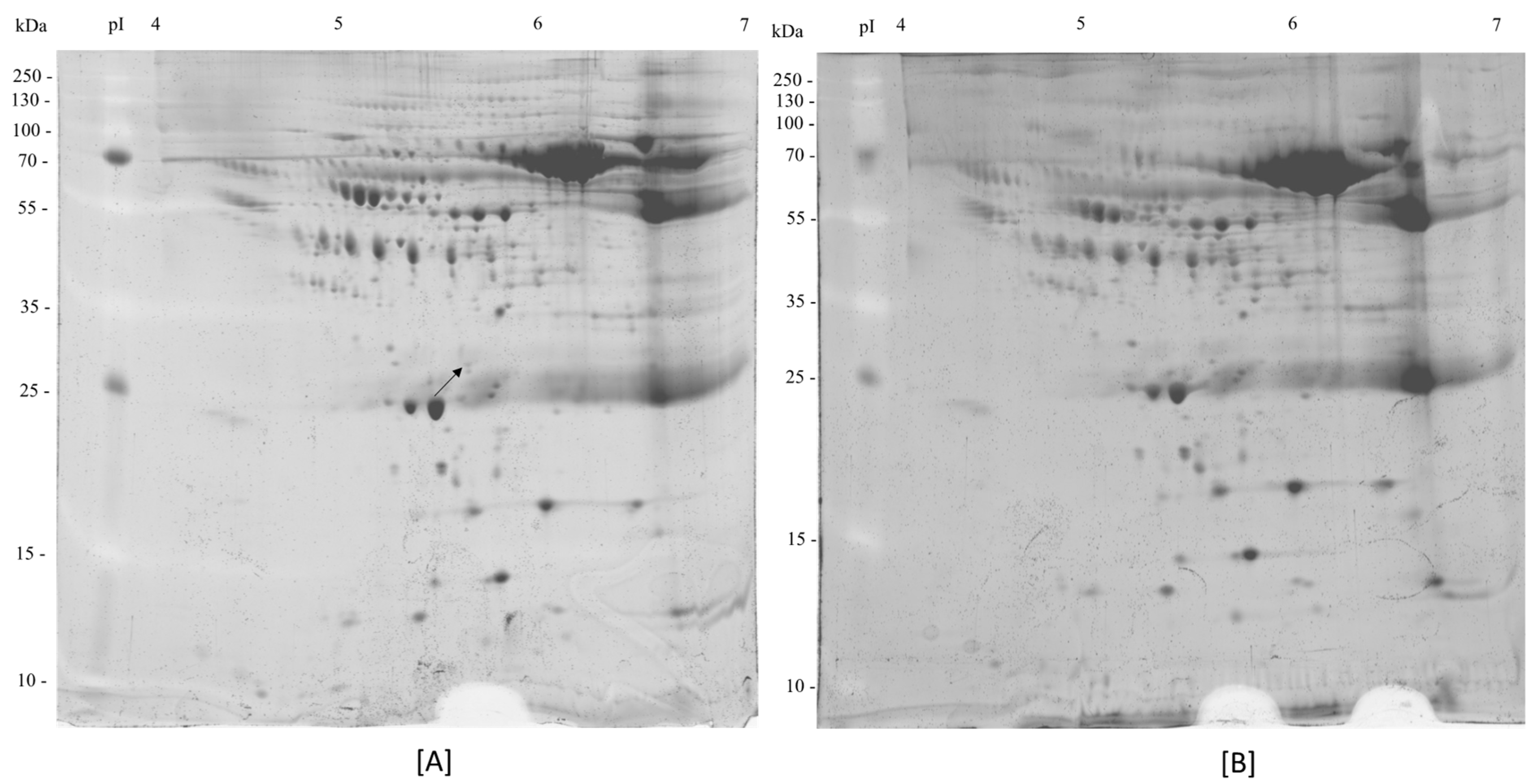
| Parameters | Non-Frailty (n = 9) | Cognitive Frailty (n = 9) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 72.33 ± 5.34 | 69.67 ± 4.42 | 0.299 |
| Weight (kg) | 55.61 ± 8.92 | 60.06 ± 12.88 | 0.367 |
| Height (cm) | 157.22 ± 7.08 | 162.00 ± 8.46 | 0.293 |
| Actual MoCA score (points) | 19.11 ± 3.72 | 21.11 ± 2.93 | 0.067 |
| Sex (male/female) | 3/6 | 5/4 | - |
| Educational level (Grade 1–3/Grade 4–6/High school or over) | 6/1/2 | 8/0/1 | - |
| Protein Spot | Protein Name | Accession No.a | Spot Location | Theoretical MW (kDa) | %Cov (95) | pI | Peptides Matched (95%) | Fold Change (FC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upregulation in non-frail | ||||||||
| 1 | Fibrinogen gamma chain | P02679 | Non-frail | 51.5 | 4.194 | 5.60 | 2 | >2 |
| Protein Identification Number | Protein Name (Gene) | Biological Roles | Biological Categories |
|---|---|---|---|
| P02679 | Fibrinogen γ chain (FGG) | Many biological roles are suggested as follows:
| Immune system, regulation, transport and homeostasis, coagulation, fibrinolysis, response, cell and ECM organization, protein metabolism |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aobchey, P.; Chaiyawat, P.; Seesen, M.; Ruangsuriya, J. Proteomics Analysis of Plasma Biomarker of Cognitive Frailty in Elders Who Locally Reside in Chiang Mai Province of Thailand. Life 2025, 15, 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081330
Aobchey P, Chaiyawat P, Seesen M, Ruangsuriya J. Proteomics Analysis of Plasma Biomarker of Cognitive Frailty in Elders Who Locally Reside in Chiang Mai Province of Thailand. Life. 2025; 15(8):1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081330
Chicago/Turabian StyleAobchey, Paitoon, Parunya Chaiyawat, Mathuramat Seesen, and Jetsada Ruangsuriya. 2025. "Proteomics Analysis of Plasma Biomarker of Cognitive Frailty in Elders Who Locally Reside in Chiang Mai Province of Thailand" Life 15, no. 8: 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081330
APA StyleAobchey, P., Chaiyawat, P., Seesen, M., & Ruangsuriya, J. (2025). Proteomics Analysis of Plasma Biomarker of Cognitive Frailty in Elders Who Locally Reside in Chiang Mai Province of Thailand. Life, 15(8), 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081330






