Encephalitis: Predictive Role of Clinical and Diagnostic Data on Outcome—A Monocentric Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
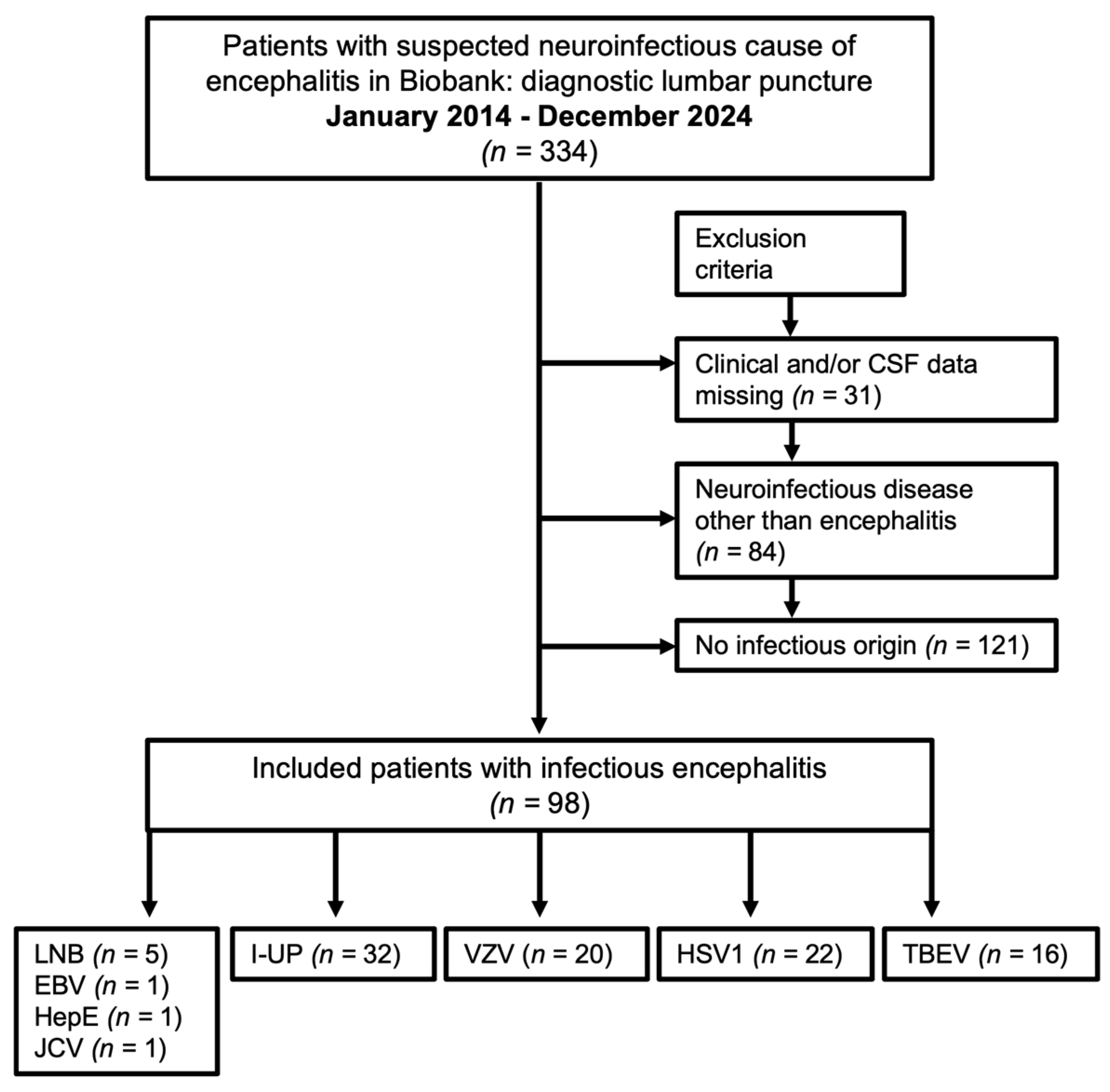
2.1. Patient Selection Process
2.2. Clinical and Demographic Parameters
2.3. CSF Analysis
2.4. Direct and Indirect Pathogen Detection
2.5. Intracellular and Surface Autoantibodies
2.6. CSF-CXCL13
2.7. MRI Examination
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Clinical and Diagnostic Data
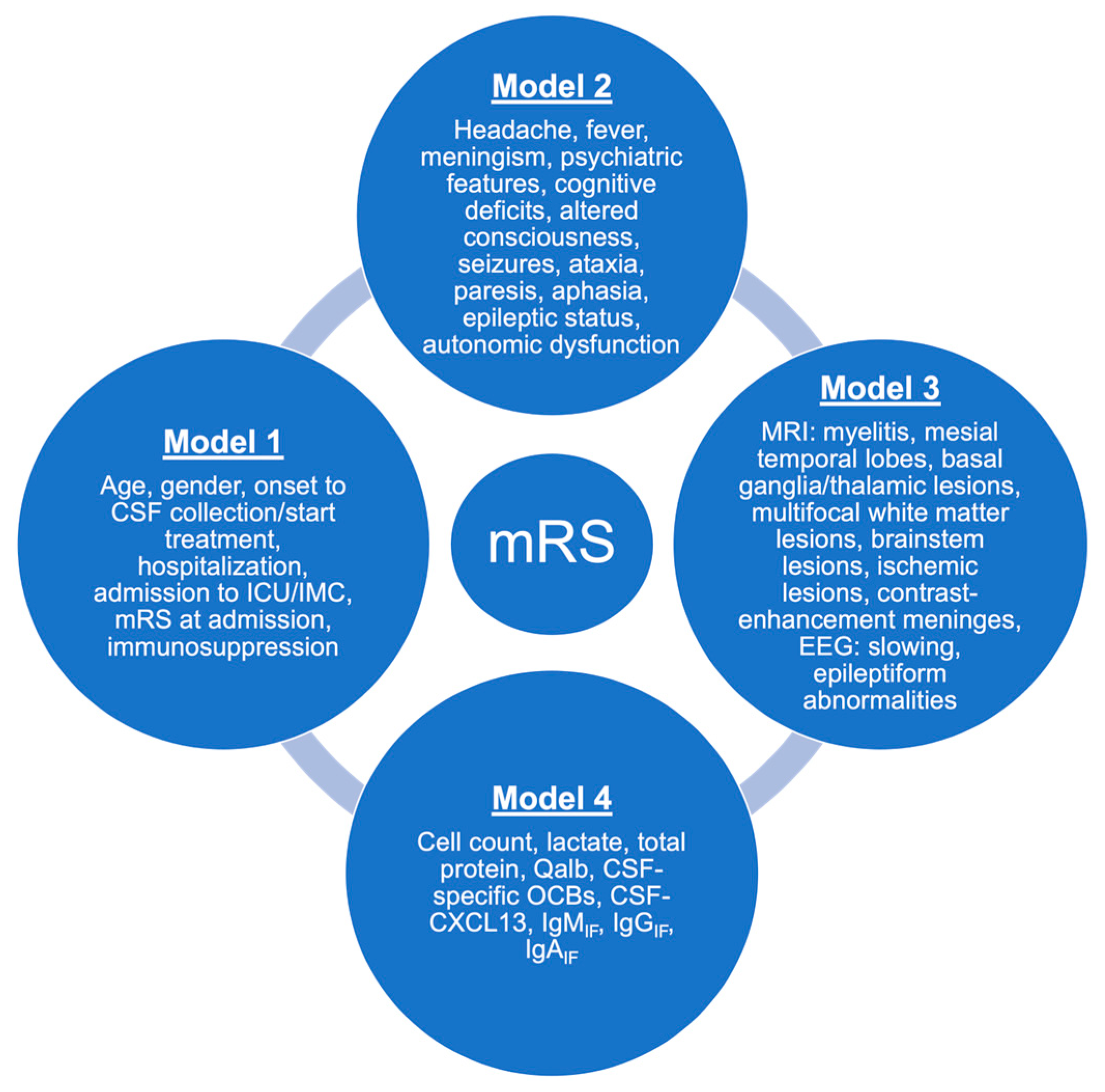
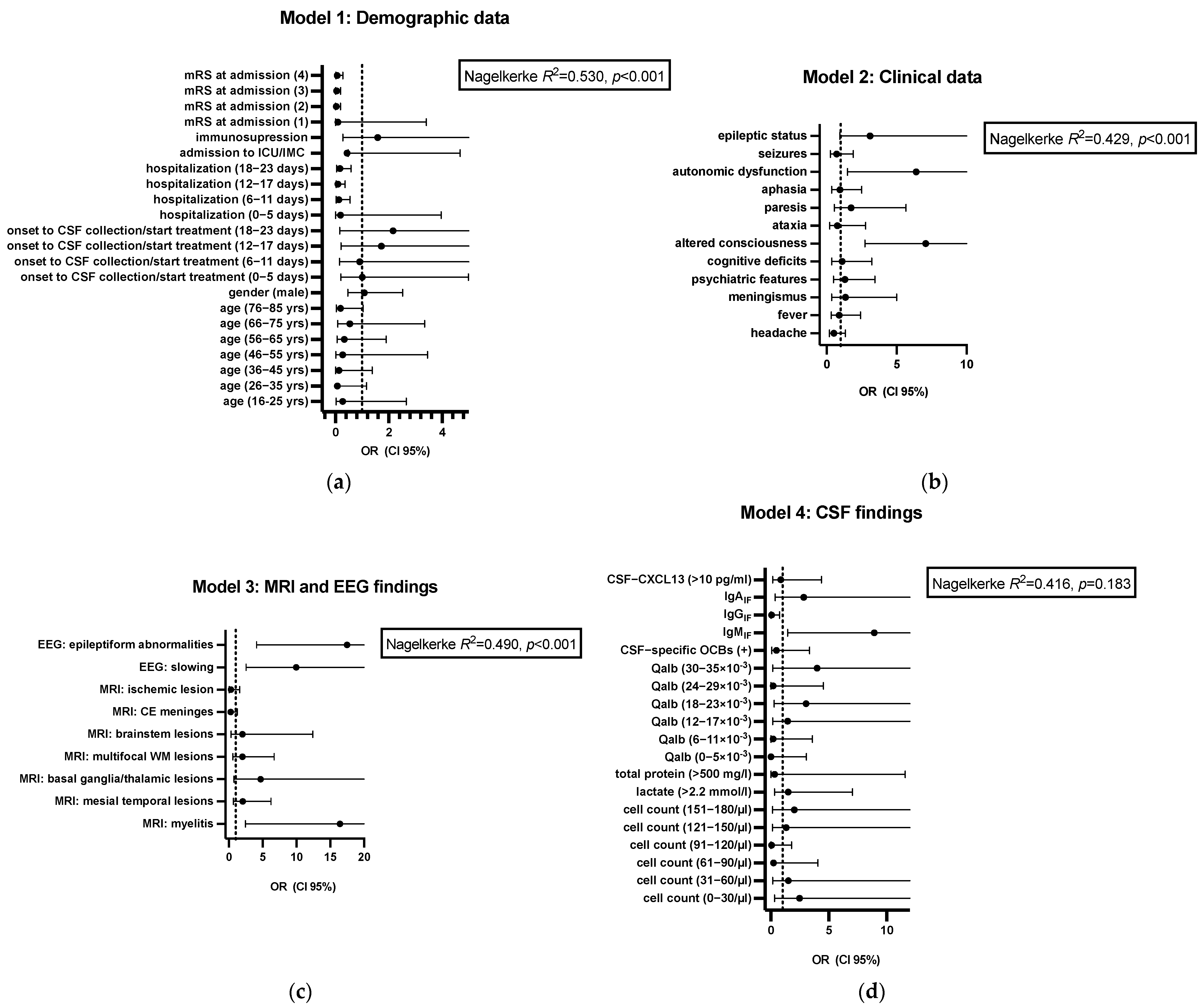
3.3. Predictors for Outcome
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- George, B.P.; Schneider, E.B.; Venkatesan, A.; Chaturvedi, V. Encephalitis hospitalization rates and inpatient mortality in the United States, 2000–2010. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyler, K.L. Emerging viral infections of the central nervous system: Part 1. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 939–948. [Google Scholar]
- Glaser, C.A.; Honarmand, S.; Anderson, L.J.; Schnurr, D.P.; Forghani, B.; Cossen, C.K.; Schuster, F.L.; Christie, L.J.; Tureen, J.H. Beyond viruses: Clinical profiles and etiologies associated with encephalitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 1565–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granerod, J.; Cunningham, R.; Zuckerman, M.; Mutton, K.; Davies, N.W.S.; Walsh, A.L.; Ward, K.N.; Hilton, D.A.; Ambrose, H.E.; Clewley, J.P.; et al. Causality in acute encephalitis: Defining aetiologies. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 783–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, P.G.E.; Quan, P.-L.; Lipkin, W.I. Viral Encephalitis of Unknown Cause: Current Perspective and Recent Advances. Viruses 2017, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoian, A.; Bajko, Z.; Stoian, M.; Cioflinc, R.A.; Niculescu, R.; Arbănași, E.M.; Russu, E.; Botoncea, M.; Bălașa, R. The Occurrence of Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis in SARS-CoV-2 Infection/Vaccination: Our Experience and a Systematic Review of the Literature. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvam, K.A.; Stahl, J.-P.; Chow, F.C.; Soldatos, A.; Tattevin, P.; Sejvar, J.; Mailles, A. Outcome and Sequelae of Infectious Encephalitis. J. Clin. Neurol. 2024, 20, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, A.; Tunkel, A.R.; Bloch, K.C.; Lauring, A.S.; Sejvar, J.; Bitnun, A.; Stahl, J.P.; Mailles, A.; Drebot, M.; Rupprecht, C.E.; et al. Case definitions, diagnostic algorithms, and priorities in encephalitis: Consensus statement of the international encephalitis consortium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1114–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanek, G.; Fingerle, V.; Hunfeld, K.-P.; Jaulhac, B.; Kaiser, R.; Krause, A.; Kristoferitsch, W.; O’Connell, S.; Ornstein, K.; Strle, F.; et al. Lyme borreliosis: Clinical case definitions for diagnosis and management in Europe. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erhart, D.K.; Klose, V.; Schäper, T.; Tumani, H.; Senel, M. CXCL13 in Cerebrospinal Fluid: Clinical Value in a Large Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumani, H.; Petereit, H.F.; Gerritzen, A.; Gross, C.C.; Huss, A.; Isenmann, S.; Jesse, S.; Khalil, M.; Lewczuk, P.; Lewerenz, J.; et al. S1 guidelines “lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid analysis” (abridged and translated version). Neurol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiber, H. Flow rate of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)—A concept common to normal blood-CSF barrier function and to dysfunction in neurological diseases. J. Neurol. Sci. 1994, 122, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiber, H.; Ungefehr, S.; Jacobi, C. The intrathecal, polyspecific and oligoclonal immune response in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 1998, 4, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiber, H. Cerebrospinal fluid--physiology, analysis and interpretation of protein patterns for diagnosis of neurological diseases. Mult. Scler. 1998, 4, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mader, S.; Gredler, V.; Schanda, K.; Rostasy, K.; Dujmovic, I.; Pfaller, K.; Lutterotti, A.; Jarius, S.; Di Pauli, F.; Kuenz, B.; et al. Complement activating antibodies to myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in neuromyelitis optica and related disorders. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lix, L.M.; Keselman, J.C.; Keselman, H.J. Consequences of assumption violations revisited: A quantitative review of alternatives to the one-way analysis of variance F test. Rev. Educ. Res. 1996, 66, 579–619. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, Y.; Luo, W.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Xu, Z. Predictors of mortality and poor outcome for patients with severe infectious encephalitis in the intensive care unit: A cross-sectional study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2024, 24, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, A.; Michael, B.D.; Probasco, J.C.; Geocadin, R.G.; Solomon, T. Acute encephalitis in immunocompetent adults. Lancet 2019, 393, 702–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupila, L.; Vuorinen, T.; Vainionpää, R.; Hukkanen, V.; Marttila, R.J.; Kotilainen, P. Etiology of aseptic meningitis and encephalitis in an adult population. Neurology 2006, 66, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.D.; Fugate, J.E.; Rabinstein, A.A. The spectrum of acute encephalitis: Causes, management, and predictors of outcome. Neurology 2015, 84, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdem, H.; Cag, Y.; Ozturk-Engin, D.; Defres, S.; Kaya, S.; Larsen, L.; Poljak, M.; Barsic, B.; Argemi, X.; Sørensen, S.M.; et al. Results of a multinational study suggest the need for rapid diagnosis and early antiviral treatment at the onset of herpetic meningoencephalitis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 3084–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, J.; Mani, V.; Bhoi, S.; Misra, U. Spectrum and outcome of acute infectious encephalitis/encephalopathy in an intensive care unit from India. QJM 2017, 110, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, N.; Anderson, N.E.; Croxson, M.C.; Powell, K.F. Herpes simplex encephalitis treated with acyclovir: Diagnosis and long term outcome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1997, 63, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, A.; Bergström, T.; Lindh, M.; Namvar, L.; Studahl, M. Varicella-zoster virus CNS disease—Viral load, clinical manifestations and sequels. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 46, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellner, J.; Trinka, E. Seizures and epilepsy in herpes simplex virus encephalitis: Current concepts and future directions of pathogenesis and management. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 2019–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, K.T.; Motta, M.; Asemota, A.O.; Kirsch, H.L.; Benavides, D.R.; Schneider, E.B.; McArthur, J.C.; Geocadin, R.G.; Venkatesan, A. Predictors of outcome in acute encephalitis. Neurology 2013, 81, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailles, A.; De Broucker, T.; Costanzo, P.; Martinez-Almoyna, L.; Vaillant, V.; Stahl, J.-P.; on behalf of the Steering Committee and Investigators Group. Long-term outcome of patients presenting with acute infectious encephalitis of various causes in France. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagrán-García, M.; Farina, A.; Campetella, L.; Arzalluz-Luque, J.; Honnorat, J. Autonomic nervous system involvement in autoimmune encephalitis and paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. Rev. Neurol. 2024, 180, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, X.; Tang, Y.; Wu, J. Clinical Study of Autonomic Dysfunction in Patients with Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 609750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ENCEPHALITICA Study Group; Jaquet, P.; de Montmollin, E.; Dupuis, C.; Sazio, C.; Conrad, M.; Susset, V.; Demeret, S.; Tadie, J.M.; Argaud, L.; et al. Functional outcomes in adult patients with herpes simplex encephalitis admitted to the ICU: A multicenter cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 2019, 45, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarton, B.; Jaquet, P.; Belkacemi, D.; de Montmollin, E.; Bonneville, F.; Sazio, C.; Frérou, A.; Conrad, M.; Daubin, D.; Chabanne, R.; et al. Assessment of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Changes and Functional Outcomes Among Adults With Severe Herpes Simplex Encephalitis. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2114328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.-J.; Lee, P.-I.; Huang, L.-M.; Chen, C.-J.; Chen, C.-L.; Lee, W.-T. The correlation between neurological evaluations and neurological outcome in acute encephalitis: A hospital-based study. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2007, 11, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, U.; Kalita, J. Seizures in encephalitis: Predictors and outcome. Seizure 2009, 18, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quist-Paulsen, E.; Kran, A.-M.B.; Lindland, E.S.; Ellefsen, K.; Sandvik, L.; Dunlop, O.; Ormaasen, V. To what extent can clinical characteristics be used to distinguish encephalitis from encephalopathy of other causes? Results from a prospective observational study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrose, H.E.; Granerod, J.; Clewley, J.P.; Davies, N.W.S.; Keir, G.; Cunningham, R.; Zuckerman, M.; Mutton, K.J.; Ward, K.N.; Ijaz, S.; et al. Diagnostic strategy used to establish etiologies of encephalitis in a prospective cohort of patients in England. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3576–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granerod, J.; Ambrose, H.E.; Davies, N.W.S.; Clewley, J.P.; Walsh, A.L.; Morgan, D.; Cunningham, R.; Zuckerman, M.; Mutton, K.J.; Solomon, T.; et al. Causes of encephalitis and differences in their clinical presentations in England: A multicentre, population-based prospective study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleri, G.; Libanore, V.; Corcione, S.; De Rosa, F.G.; Caramello, P. A retrospective study of viral central nervous system infections: Relationship amongst aetiology, clinical course and outcome. Infection 2017, 45, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, H.-L.; Lee, E.M.; Sung, H.; Kang, J.K.; Lee, S.-A.; Choi, S.-H. Clinical features, outcomes, and cerebrospinal fluid findings in adult patients with central nervous system (CNS) infections caused by varicella-zoster virus: Comparison with enterovirus CNS infections. J. Med. Virol. 2014, 86, 2049–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewpoowat, Q.; Salazar, L.; Aguilera, E.; Wootton, S.H.; Hasbun, R. Herpes simplex and varicella zoster CNS infections: Clinical presentations, treatments and outcomes. Infection 2016, 44, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrer, C.; Otto, F.; Pilz, G.; Haschke-Becher, E.; Trinka, E.; Hitzl, W.; Wipfler, P.; Harrer, A. The CXCL13/CXCR5-chemokine axis in neuroinflammation: Evidence of CXCR5+CD4 T cell recruitment to CSF. Fluids Barriers CNS 2021, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupprecht, T.A.; Kirschning, C.J.; Popp, B.; Kastenbauer, S.; Fingerle, V.; Pfister, H.-W.; Koedel, U. Borrelia garinii induces CXCL13 production in human monocytes through Toll-like receptor 2. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 4351–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimori, J.; Nakashima, I.; Kuroda, H.; Fujihara, K.; Aoki, M. Cerebrospinal fluid CXCL13 is a prognostic marker for aseptic meningitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 273, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilz, G.; Wipfler, P.; Otto, F.; Hitzl, W.; Afazel, S.; Haschke-Becher, E.; Trinka, E.; Harrer, A. Cerebrospinal fluid CXLC13 indicates disease course in neuroinfection: An observational study. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Burgel, N.D.; Bakels, F.; Kroes, A.C.M.; van Dam, A.P. Discriminating Lyme neuroborreliosis from other neuroinflammatory diseases by levels of CXCL13 in cerebrospinal fluid. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 2027–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudtzen, F.C.; Nilsson, A.C.; Hovius, J.W.; Skarphedinsson, S. The predictive value of CXCL13 in suspected Lyme neuroborreliosis: A retrospective cross-sectional study. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 39, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senel, M.; Rupprecht, T.A.; Tumani, H.; Pfister, H.W.; Ludolph, A.C.; Brettschneider, J. The chemokine CXCL13 in acute neuroborreliosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czupryna, P.; Grygorczuk, S.; Siemieniako-Werszko, A.; Okrzeja, J.; Dunaj-Małyszko, J.; Adamczuk, J.; Pancewicz, S.; Zajkowska, J.; Narejko, K.; Oklińska, J.; et al. Anti-Tick-Bourne Encephalitis IgM Intrathecal Synthesis as a Prediction Marker in Tick-Borne Encephalitis Patients. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemieniako-Werszko, A.; Czupryna, P.; Moniuszko-Malinowska, A.; Dunaj-Małyszko, J.; Pancewicz, S.; Grygorczuk, S.; Zajkowska, J. Anti-TBE Intrathecal Synthesis as a Prediction Marker in TBE Patients. Pathogens 2022, 11, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avirutnan, P.; Mehlhop, E.; Diamond, M.S. Complement and its role in protection and pathogenesis of flavivirus infections. Vaccine 2008, 26 (Suppl. S8), I100–I107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, C.E.; Studahl, M.; Bergström, T. Acute and prolonged complement activation in the central nervous system during herpes simplex encephalitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2016, 295–296, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | Patients with Encephalitis (n = 98) |
|---|---|
| Age [years], M (±SD) | 64.13 (±18.85) |
| Gender (male/female) | 56.1%/43.9% (55/43) |
| Herpesviridae ● HSV1 (n) ● VZV (n) TBEV (n) HepE (n) JCV (n) EBV (n) LNB (n) I-UP (n) | 22.4% (22) 20.4% (20) 16.3% (16) 1.0% (1) 1.0% (1) 1.0% (1) 5.1% (5) 32.7% (32) |
| Onset to CSF collection/start treatment [days], M (±SD) | 18.63 (±75.24) |
| Hospitalization [days], M (±SD) | 23.10 (±16.23) |
| Immunosuppression (n) | 8.2% (8) |
| Admission to ICU/IMC (n) | 42.9% (42) |
| mRS at admission ● 1(n) ● 2(n) ● 3(n) ● 4(n) ● 5(n) | 2.0% (2) 19.4% (19) 24.5% (24) 36.7% (36) 17.3% (17) |
| Variables | OR (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Age (26–35 yrs) | 0.07 (0.005–1.17) | 0.064 |
| Age (36–45 yrs) | 0.14 (0.01–1.38) | 0.092 |
| Age (76–85 yrs) | 0.19 (0.03–1.03) | 0.055 |
| Hospitalization (6–11 days) | 0.13 (0.03–0.55) | 0.006 |
| Hospitalization (12–17 days) | 0.10 (0.03–0.36) | <0.001 |
| Hospitalization (18–23 days) | 0.17 (0.05–0.58) | 0.005 |
| mRS at admission (2) | 0.03 (0.005–0.19) | <0.001 |
| mRS at admission (3) | 0.04 (0.01–0.19) | <0.001 |
| mRS at admission (4) | 0.07 (0.02–0.28) | <0.001 |
| Altered consciousness | 7.08 (2.73–18.32) | <0.001 |
| Autonomic dysfunction | 6.39 (1.50–27.30) | 0.012 |
| MRI: myelitis | 16.44 (2.43–111.39) | 0.004 |
| MRI: basal ganglia/thalamic lesions | 4.70 (0.76–29.22) | 0.097 |
| EEG: slowing | 9.97 (2.54–39.10) | <0.001 |
| Epileptic status | 3.10 (0.93–10.34) | 0.065 |
| EEG: epileptiform abnormalities | 17.49 (4.12–74.44) | <0.001 |
| IgMIF | 8.93 (1.44–55.15) | 0.018 |
| IgGIF | 0.05 (0.003–0.75) | 0.030 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Erhart, D.K.; Balz, L.T.; Tumani, H. Encephalitis: Predictive Role of Clinical and Diagnostic Data on Outcome—A Monocentric Study. Life 2025, 15, 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081313
Erhart DK, Balz LT, Tumani H. Encephalitis: Predictive Role of Clinical and Diagnostic Data on Outcome—A Monocentric Study. Life. 2025; 15(8):1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081313
Chicago/Turabian StyleErhart, Deborah K., Luisa T. Balz, and Hayrettin Tumani. 2025. "Encephalitis: Predictive Role of Clinical and Diagnostic Data on Outcome—A Monocentric Study" Life 15, no. 8: 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081313
APA StyleErhart, D. K., Balz, L. T., & Tumani, H. (2025). Encephalitis: Predictive Role of Clinical and Diagnostic Data on Outcome—A Monocentric Study. Life, 15(8), 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081313







