Clinical Outcomes of Oral Anticoagulation in Elderly East Asian Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Single-Center Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Clinical Outcomes and Definitions
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
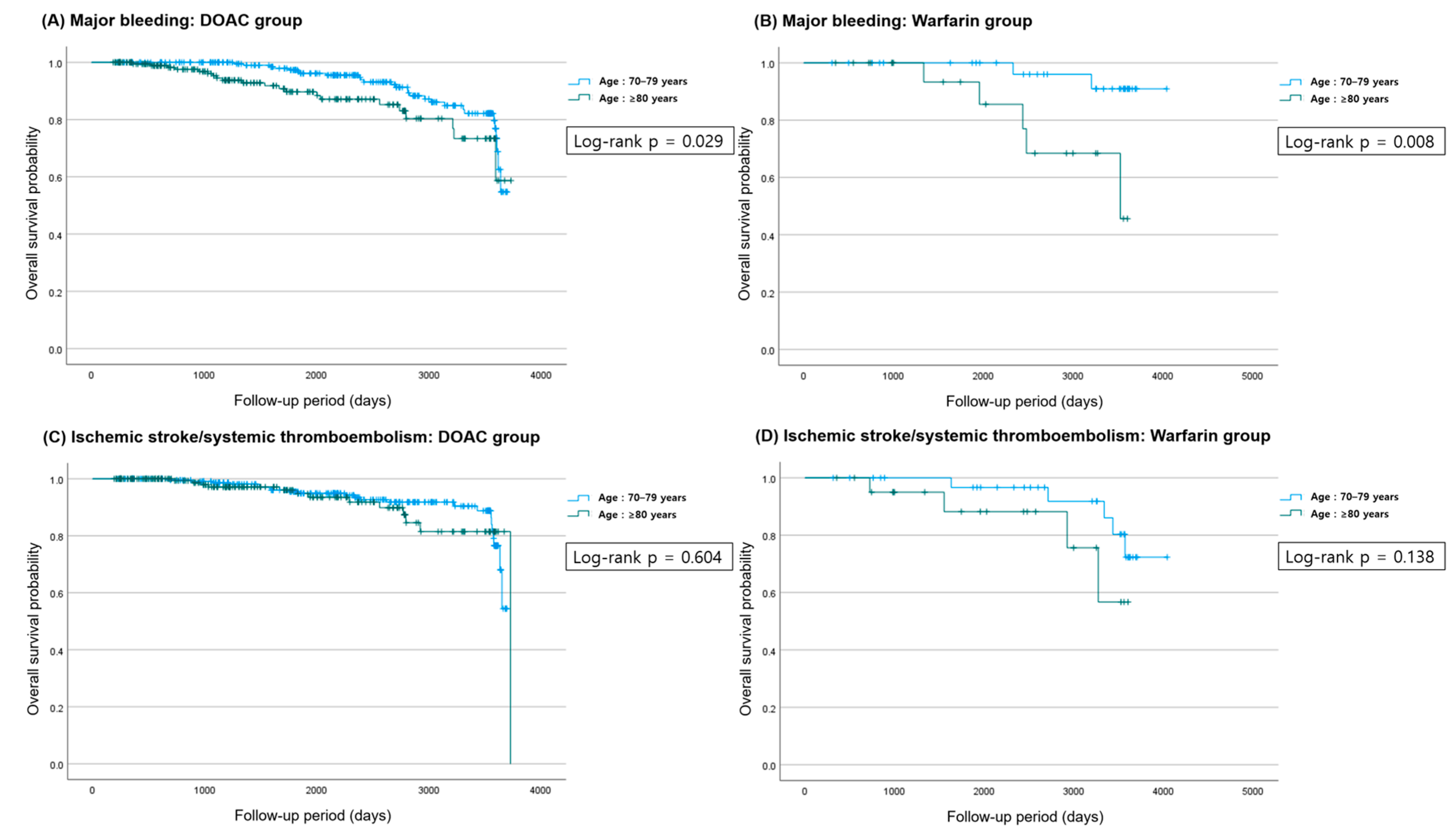
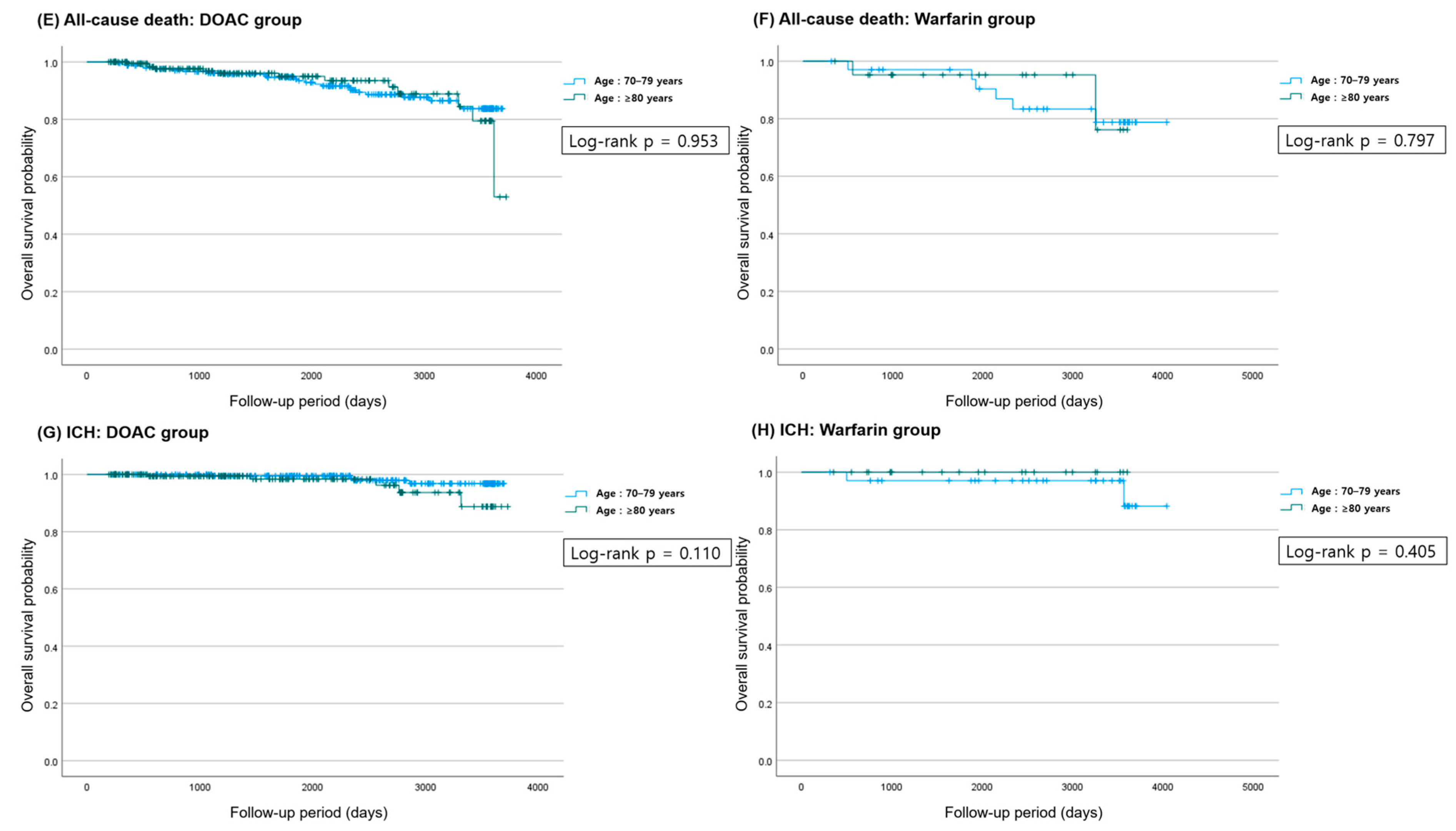
3.2. Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Rienstra, M.; Bunting, K.V.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Caso, V.; Crijns, H.; De Potter, T.J.R.; Dwight, J.; Guasti, L.; Hanke, T.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3314–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joglar, J.A.; Chung, M.K.; Armbruster, A.L.; Benjamin, E.J.; Chyou, J.Y.; Cronin, E.M.; Deswal, A.; Eckhardt, L.L.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Gopinathannair, R.; et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Atrial Fibrillation: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 109–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P.A.; Abbott, R.D.; Kannel, W.B. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: The Framingham Study. Stroke 1991, 22, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oancea, A.F.; Jigoranu, R.A.; Morariu, P.C.; Miftode, R.S.; Trandabat, B.A.; Iov, D.E.; Cojocaru, E.; Costache, I.I.; Baroi, L.G.; Timofte, D.V.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation and Chronic Coronary Ischemia: A Challenging Vicious Circle. Life 2023, 13, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreotti, F.; Geisler, T.; Collet, J.P.; Gigante, B.; Gorog, D.A.; Halvorsen, S.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Morais, J.; Navarese, E.P.; Patrono, C.; et al. Acute, periprocedural and longterm antithrombotic therapy in older adults: 2022 Update by the ESC Working Group on Thrombosis. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 262–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lip, G.Y.; Frison, L.; Halperin, J.L.; Lane, D.A. Comparative validation of a novel risk score for predicting bleeding risk in anticoagulated patients with atrial fibrillation: The HAS-BLED (Hypertension, Abnormal Renal/Liver Function, Stroke, Bleeding History or Predisposition, Labile INR, Elderly, Drugs/Alcohol Concomitantly) score. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Scharf, R.E. Thrombocytopenia and Hemostatic Changes in Acute and Chronic Liver Disease: Pathophysiology, Clinical and Laboratory Features, and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalgaard, F.; Xu, H.; Matsouaka, R.A.; Russo, A.M.; Curtis, A.B.; Rasmussen, P.V.; Ruwald, M.H.; Fonarow, G.C.; Lowenstern, A.; Hansen, M.L.; et al. Management of Atrial Fibrillation in Older Patients by Morbidity Burden: Insights From Get With The Guidelines-Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e017024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.J.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Yusuf, S.; Eikelboom, J.; Oldgren, J.; Parekh, A.; Pogue, J.; Reilly, P.A.; Themeles, E.; Varrone, J.; et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, R.P.; Ruff, C.T.; Braunwald, E.; Murphy, S.A.; Wiviott, S.D.; Halperin, J.L.; Waldo, A.L.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Weitz, J.I.; Spinar, J.; et al. Edoxaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2093–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.B.; Alexander, J.H.; McMurray, J.J.; Lopes, R.D.; Hylek, E.M.; Hanna, M.; Al-Khalidi, H.R.; Ansell, J.; Atar, D.; Avezum, A.; et al. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Garg, J.; Pan, G.; Singer, D.E.; Hacke, W.; Breithardt, G.; Halperin, J.L.; Hankey, G.J.; Piccini, J.P.; et al. Rivaroxaban versus warfarin in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, T.F.; Chiang, C.E.; Liao, J.N.; Chen, T.J.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Chen, S.A. Comparing the Effectiveness and Safety of Nonvitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants and Warfarin in Elderly Asian Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Chest 2020, 157, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, Y.; Hamatani, Y.; Esato, M.; Chun, Y.H.; Tsuji, H.; Wada, H.; Hasegawa, K.; Abe, M.; Lip, G.Y.H.; Akao, M. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes in Extreme Elderly (Age >/= 85 Years) Japanese Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: The Fushimi AF Registry. Chest 2016, 149, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.S.; Ahn, J.H.; Tantry, U.S.; Gurbel, P.A.; Jeong, Y.H. Should Antithrombotic Treatment Strategies in East Asians Differ from Caucasians? Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 16, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.H. “East asian paradox”: Challenge for the current antiplatelet strategy of “one-guideline-fits-all races” in acute coronary syndrome. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2014, 16, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.K.; Tantry, U.S.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; Jeong, M.H.; Park, S.J.; Kim, M.H.; Lim, D.S.; Shin, E.S.; Park, D.W.; Huo, Y.; et al. The East Asian Paradox: An Updated Position Statement on the Challenges to the Current Antithrombotic Strategy in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 121, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, S.; Zhu, J.; Liu, L.; Oh, B.H.; Wojdyla, D.M.; Aylward, P.; Bahit, M.C.; Gersh, B.J.; Hanna, M.; Horowitz, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of apixaban compared with warfarin for stroke prevention in patients with atrial fibrillation from East Asia: A subanalysis of the Apixaban for Reduction in Stroke and Other Thromboembolic Events in Atrial Fibrillation (ARISTOTLE) Trial. Am. Heart J. 2014, 168, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Tanahashi, N.; Momomura, S.; Uchiyama, S.; Goto, S.; Izumi, T.; Koretsune, Y.; Kajikawa, M.; Kato, M.; et al. Rivaroxaban vs. warfarin in Japanese patients with atrial fibrillation-the J-ROCKET AF study. Circ. J. 2012, 76, 2104–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Koretsune, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, S.A.; Chung, N.; Shimada, Y.J.; Kimura, T.; Miyazaki, K.; Abe, K.; Mercuri, M.; et al. Edoxaban vs. Warfarin in East Asian Patients With Atrial Fibrillation—An ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 Subanalysis. Circ. J. 2016, 80, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, M.J.; Choi, E.K.; Han, K.D.; Lee, S.R.; Lim, W.H.; Oh, S.; Lip, G.Y.H. Effectiveness and Safety of Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants in Asian Patients With Atrial Fibrillation. Stroke 2017, 48, 3040–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, M.; Connolly, S.J.; Zhu, J.; Liu, L.S.; Lau, C.P.; Pais, P.; Xavier, D.; Kim, S.S.; Omar, R.; Dans, A.L.; et al. Dabigatran versus warfarin: Effects on ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes and bleeding in Asians and non-Asians with atrial fibrillation. Stroke 2013, 44, 1891–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.S.; Hu, D.Y.; Oomman, A.; Tan, R.S.; Patel, M.R.; Singer, D.E.; Breithardt, G.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Becker, R.C.; Califf, R.; et al. Rivaroxaban for stroke prevention in East Asian patients from the ROCKET AF trial. Stroke 2014, 45, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaatz, S.; Ahmad, D.; Spyropoulos, A.C.; Schulman, S. Definition of clinically relevant non-major bleeding in studies of anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation and venous thromboembolic disease in non-surgical patients: Communication from the SSC of the ISTH. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohsaka, S.; Katada, J.; Saito, K.; Terayama, Y. Safety and effectiveness of apixaban in comparison to warfarin in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation: A propensity-matched analysis from Japanese administrative claims data. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2018, 34, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Park, H.W.; Lee, N.; Hyun, D.Y.; Won, J.; Oh, S.S.; Park, H.J.; Kim, Y.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, M.C.; et al. Optimal dose of dabigatran for the prevention of thromboembolism with minimal bleeding risk in Korean patients with atrial fibrillation. Europace 2017, 19, iv1–iv9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Lip, G.Y.; Lin, S.J.; Chiang, C.E. Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulants for Stroke Prevention in Asian Patients With Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation: Meta-Analysis. Stroke 2015, 46, 2555–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, A.P.; Lindhardsen, J.; Lip, G.Y.; Gislason, G.H.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Olesen, J.B. Female sex as a risk factor for stroke in atrial fibrillation: A nationwide cohort study. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 1745–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, V.C.; Wu, M.; Aboyans, V.; Chang, S.H.; Chen, S.W.; Chen, M.C.; Wang, C.L.; Hsieh, I.C.; Chu, P.H.; Lin, Y.S. Female sex as a risk factor for ischaemic stroke varies with age in patients with atrial fibrillation. Heart 2020, 106, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; Matsumoto, N.; Tachibana, E.; Kuronuma, K.; Oiwa, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Kojima, T.; Hanada, S.; Nomoto, K.; et al. Current use of direct oral anticoagulants for atrial fibrillation in Japan: Findings from the SAKURA AF Registry. J. Arrhythm. 2017, 33, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.; Lane, D.A. Bleeding risk assessment in atrial fibrillation: Observations on the use and misuse of bleeding risk scores. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 1711–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilke, T.; Bauer, S.; Mueller, S.; Kohlmann, T.; Bauersachs, R. Patient Preferences for Oral Anticoagulation Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Literature Review. Patient 2017, 10, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| DOAC | Warfarin | p-Value | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age 70–79 (n = 242) | Age ≥ 80 (n = 203) | Age 70–79 (n = 35) | Age ≥ 80 (n = 22) | Age 70–79 vs. Age ≥ 80 (DOAC Group) | Age 70–79 vs. Age ≥ 80 (Warfarin Group) | |
| Age | 75.9 ± 2.5 | 83.4 ± 3.1 | 75.5 ± 2.6 | 83.1 ± 2.9 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Sex (male) | 120 (49.6) | 76 (37.4) | 10 (28.6) | 6 (27.3) | 0.010 | 0.915 |
| BMI | 25.3 ± 9.7 | 24.1 ± 3.9 | 24.9 ± 2.9 | 24.5 ± 4.8 | 0.102 | 0.726 |
| Height (cm) | 159.4 ± 11.6 | 156.8 ± 8.8 | 156.4 ± 6.8 | 152.6 ± 7.8 | 0.007 | 0.059 |
| Weight (kg) | 63.1 ± 10.6 | 59.3 ± 11.5 | 60.9 ± 7.5 | 57.3 ± 13.3 | <0.001 | 0.263 |
| Hemoglobin | 13.3 ± 1.6 | 12.6 ± 1.8 | 12.9 ± 1.9 | 11.8 ± 1.8 | <0.001 | 0.042 |
| Platelet | 214.8 ± 63.5 | 221.7 ± 70.9 | 210.0 ± 54.6 | 190.0 ± 73.2 | 0.282 | 0.245 |
| BUN | 20.1 ± 32.2 | 18.6 ± 7.4 | 17.6 ± 5.7 | 29.0 ± 35.2 | 0.515 | 0.158 |
| Creatinine | 0.96 ± 0.5 | 0.94 ± 0.6 | 1.0 ± 0.7 | 1.5 ± 1.7 | 0.593 | 0.185 |
| AST | 29.3 ± 23.1 | 26.3 ± 14.5 | 23.2 ± 8.9 | 30.4 ± 26.2 | 0.101 | 0.148 |
| ALT | 22.9 ± 13.9 | 21 ± 16.9 | 19.8 ± 9.6 | 20.9 ± 18.4 | 0.212 | 0.771 |
| eGFR (CKD-EPI) | 71.7 ± 17.6 | 67.9 ± 17.5 | 67.3 ± 22.1 | 53.2 ± 21.2 | 0.024 | 0.020 |
| Alcohol | 19 (7.9) | 13 (6.4) | 1 (2.9) | 2 (9.1) | 0.556 | 0.553 |
| Smoking | 27 (11.2) | 9 (4.4) | 1 (2.9) | 1 (4.5) | 0.010 | 1.000 |
| Hypertension | 157 (64.9) | 149 (73.4) | 22 (62.9) | 11 (50.0) | 0.053 | 0.339 |
| DM | 62 (25.6) | 53 (25.1) | 15 (42.9) | 7 (31.8) | 0.907 | 0.405 |
| PTE/DVT | 1 (0.4) | 3 (1.5) | 4 (11.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0.335 | 0.151 |
| CVA | 30 (12.4) | 25 (12.3) | 3 (8.6) | 5 (22.7) | 0.979 | 0.239 |
| CHF | 17 (7.0) | 17 (8.4) | 3 (8.6) | 4 (18.2) | 0.593 | 0.411 |
| CKD | 4 (1.7) | 8 (3.9) | 1 (2.9) | 2 (9.1) | 0.154 | 0.553 |
| COPD | 8 (3.3) | 11 (5.4) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (13.6) | 0.272 | 0.053 |
| CAD | 39 (16.1) | 22 (10.8) | 5 (14.3) | 8 (36.4) | 0.107 | 0.053 |
| CHA2DS2-VA score | 3.1 ± 1.3 | 3.5 ± 1.1 | 3.2 ± 1.4 | 3.8 ± 1.6 | 0.003 | 0.157 |
| Use of antiplatelet drugs | 15 (6.2) | 4 (2.0) | 1 (2.9) | 2 (9) | 0.033 | 0.553 |
| OAC | Age 70–79 | Age ≥ 80 | p-Value (Event Rate) | Univariate HR (95% CI) | p-Value | Multivariate HR ** (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All-cause death | DOAC | 25 (10.3) | 13 (6.4) | 0.173 | 1.021 (0.519–2.009) | 0.953 | 0.545 (0.265–1.121) | 0.099 |
| Ischemic stroke/ systemic thromboembolism | 23 (9.5) | 13 (6.4) | 0.295 | 1.204 (0.595–2.436) | 0.605 | 0.611 (0.296–1.259) | 0.182 | |
| Major bleeding | 27 (11.2) | 21 (10.3) | 0.878 | 1.885 (1.058–3.360) | 0.031 | 0.832 (0.456–1.518) | 0.549 | |
| ICH | 4 (1.7) | 5 (2.5) | 0.738 | 2.816 (0.749–10.590) | 0.126 | 1.815 (0.446–7.390) | 0.406 | |
| All-cause death | Warfarin | 6 (17.1) | 2 (9.1) | 0.466 | 0.810 (0.161–4.075) | 0.798 | 0.437 (0.071–2.699) | 0.373 |
| Ischemic stroke/ systemic thromboembolism | 5 (14.3) | 4 (18.2) | 0.722 | 2.695 (0.694–10.458) | 0.152 | 0.747 (0.099–5.626) | 0.777 | |
| Major bleeding | 2 (5.7) | 5 (22.7) | 0.095 | 6.929 (1.328–36.159) | 0.022 | 3.617 (0.600–21.804) | 0.161 | |
| ICH | 2 (5.7) | 0 (0.0) | 0.518 | 0.026 (0.000–59766.431) | 0.625 | 0.964 (0.500–1.858) | 0.912 |
| OAC | Male (Event Rate) | Female (Event Rate) | Adjusted HR ** (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All-cause death | DOAC | 19 (9.7) | 19 (7.6) | 1.071 (0.527–2.176) | 0.849 |
| Ischemic stroke/ systemic thromboembolism | 13 (6.6) | 23 (9.2) | 0.647 (0.301–1.389) | 0.264 | |
| Major bleeding | 20 (10.2) | 28 (11.2) | 0.944 (0.859–1.038) | 0.573 | |
| ICH | 5 (2.6) | 4 (1.6) | 1.212 (0.263–5.582) | 0.805 | |
| All-cause death | Warfarin | 1 (6.3) | 7 (17.1) | 0.815 (0.418–1.588) | 0.548 |
| Ischemic stroke/ systemic thromboembolism | 3 (18.7) | 6 (14.6) | 0.191 (0.018–1.991) | 0.166 | |
| Major bleeding | 1 (6.3) | 6 (14.6) | 0.328 (0.034–3.176) | 0.336 | |
| ICH | 0 (0.0) | 2 (4.9) | 0.824 (0.423–1.605) | 0.570 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.; Hwang, Y.; Choi, S.-S.; Lee, H.; Son, Y.-J.; Yoo, M. Clinical Outcomes of Oral Anticoagulation in Elderly East Asian Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Life 2025, 15, 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081298
Kim K, Hwang Y, Choi S-S, Lee H, Son Y-J, Yoo M. Clinical Outcomes of Oral Anticoagulation in Elderly East Asian Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Life. 2025; 15(8):1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081298
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kyunyeon, YouMi Hwang, Sang-Suk Choi, Hunjoo Lee, Young-Jun Son, and Myungjae Yoo. 2025. "Clinical Outcomes of Oral Anticoagulation in Elderly East Asian Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Single-Center Study" Life 15, no. 8: 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081298
APA StyleKim, K., Hwang, Y., Choi, S.-S., Lee, H., Son, Y.-J., & Yoo, M. (2025). Clinical Outcomes of Oral Anticoagulation in Elderly East Asian Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Retrospective Single-Center Study. Life, 15(8), 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15081298






