Acute Rheumatic Fever in Caucasians: A Case Report and Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
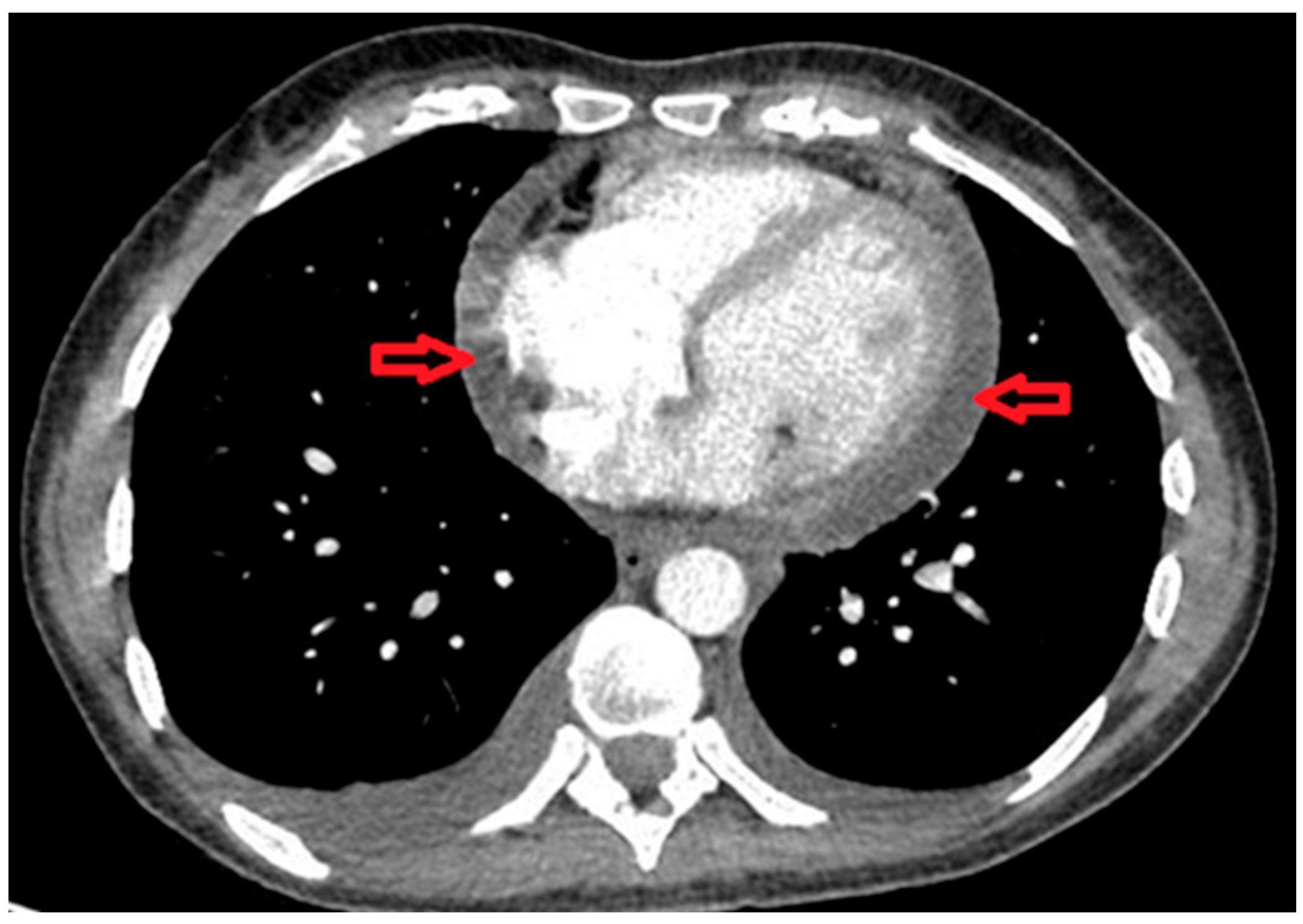
2. Case Presentation
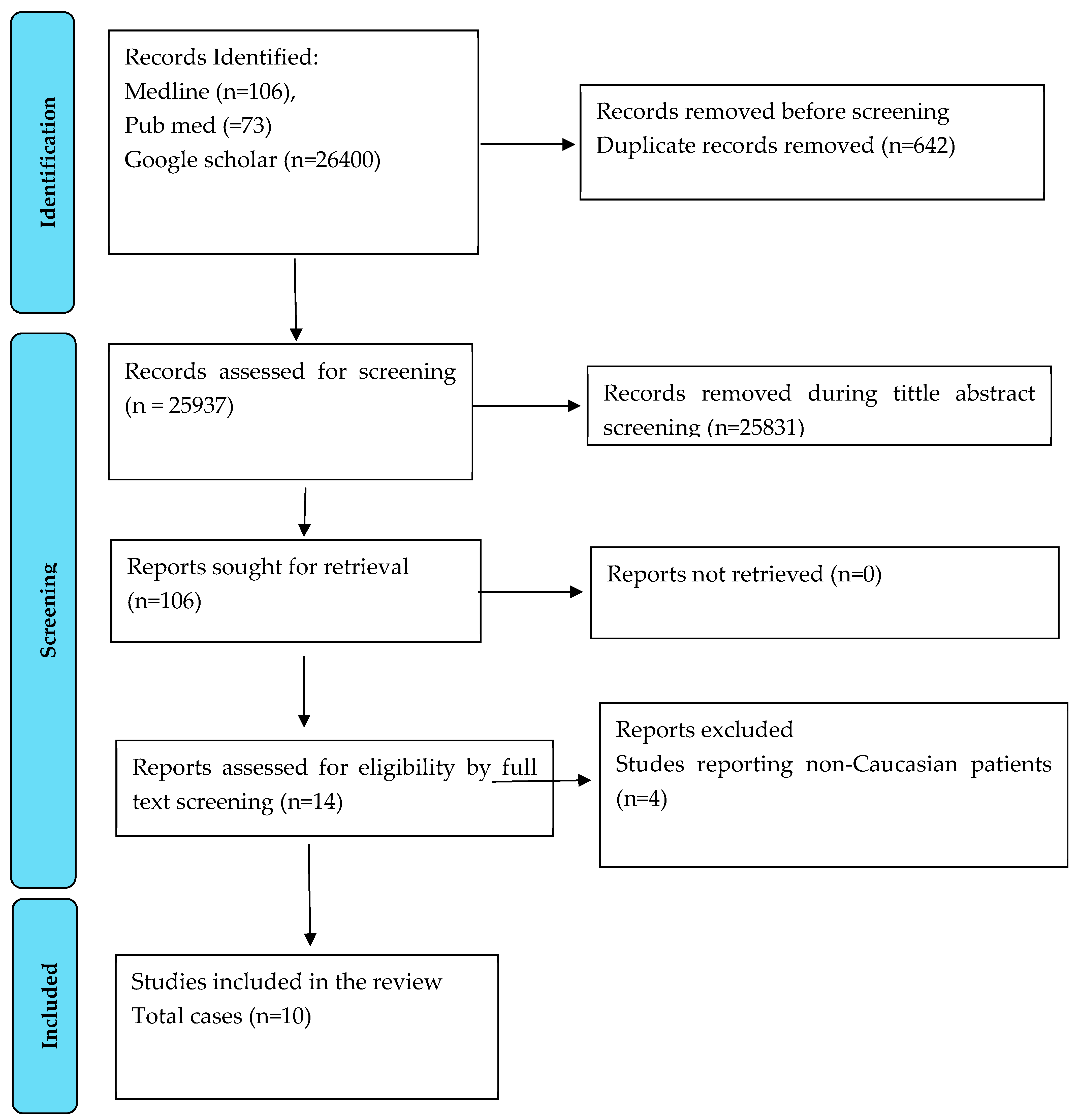
3. Methods
4. Results
| SN | Article | Age | Sex | Country | Presenting Complains | Met modified Jones Criteria | Evidence of Rheumatic Heart Disease | CRP (mg/L) | ESR (mm/h) | Raised ASOT | Treatment Received | ITU Admission | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Farrell 1990 [9] | 40 | F | UK | Rash, fever, arthralgia | Yes | None | 92 | 70 | Yes | Penicillin, Aspirin | No | Survived |
| 2 | Sahi 1993 [12] | 38 | F | Cyprus | Malaise, flu-like symptoms | Yes | None | N/A | 100 | Yes | Penicillin | No | Survived |
| 3 | Barold 1996 [7] | 39 | M | USA | Sore throat, fever, myalgia | Yes | Yes | 41 | 111 | Yes | Penicillin, Aspirin | No | Survived |
| 4 | Grover 2009 [11] | 25 | M | USA | Polyarthritis, fever | Yes | None | N/A | 115 | Yes | Penicillin, Prednisolone | No | Survived |
| 5 | Ilgenfritz 2013 [10] | 27 | M | USA | Knee pain and swelling, fever | Yes | None | N/A | 58 | Yes | Penicillin, Aspirin | No | Survived |
| 6 | Khan 2018 [13] | 41 | F | Australia | Fever, polyarthritis | Yes | None | 116 | 103 | Yes | Cephalexin | No | Survived |
| 7 | Wilson 2021 [14] | 24 | M | UK | Shoulder pain, shortness of breath | Yes | None | 200 | N/A | Yes | Penicillin | No | Survived |
| 8 | Batta 2022 [15] | 41 | F | USA | Erythematous papules, Fever | Yes | None | 37 | N/A | Yes | Ceftriaxone | No | Survived |
| 9 | Our case 2022 | 39 | F | UK | Fever, sore, throat, myalgia | Yes | None | 171 | 108 | Yes | Penicillin | No | Survived |
| 10 | Coyle 2025 [8] | 18 | F | Ireland | Malaise, fever, diarrhea and vomiting. | Yes | Yes | 503 | 115 | Yes | Ceftriaxone | Yes (inotrope support) | Survived |
| 11 | Reel 2025 [16] | 39 | F | Cuban | Fever, sore throat, wrist and chest pain | Yes | None | 180 | 61 | Yes | Azithormycin | No | Survived |
5. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stollerman, G.H. Rheumatic Fever in the 21st Century. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, G.; Guilherme, L. Acute rheumatic fever. Lancet 2018, 392, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilliers, A.M. Rheumatic fever and its management. BMJ 2006, 333, 1153–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.R.; Garst, P.D.; Papadimos, T.J.; Oldfield, E.C., 3rd. The return of acute rheumatic fever in young adults. JAMA 1989, 262, 2557–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasitanon, N.; Sukitawut, W.; Louthrenoo, W. Acute rheumatic fever in adults: Case report together with an analysis of 25 patients with acute rheumatic fever. Rheumatol. Int. 2009, 29, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Larissa, S.; Jennifer, M.T.; Elie, A.A.; Sue, E.B.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barold, S.S.; Sischy, D.; Punzi, J.; Kaplan, E.L.; Chessin, L. Advanced atrioventricular block in a 39-year-old man with acute rheumatic fever. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1998, 21 Pt 1, 2025–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyle, M.; McGreal, A.; McCormick, J.; Galvin, O.; McInerney, A.; Holmes, A.; Smyth, Y. Acute Rheumatic Fever in a Low Prevalence Setting. JACC Case Rep. 2025, 30, 103178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, A.J.; Zaphiropoulos, G.C. First attack of rheumatic fever in an adult: The case for greater awareness. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1990, 49, 1008–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilgenfritz, S.; Dowlatshahi, C.; Salkind, A. Acute rheumatic fever: Case report and review for emergency physicians. J. Emerg. Med. 2013, 45, e103–e106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, V.; Dibner, R. Polyarthritis following a streptococcal infection, a doctor’s dilemma in treatment: A case report. Cases J. 2009, 2, 9140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahi, S.P. Rheumatic Fever: Atypical Presentation in an Adult. J. R. Army Med. Corps 1993, 139, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Sutcliffe, N.; Jawad, A.S. An old disease re-emerging: Acute rheumatic fever. Clin. Med. 2018, 18, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, Z.M.; Craster, K. Suspected acute rheumatic fever in a young man in England. BMJ Case Rep. 2021, 14, e244469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batta, S.; Pederson, H.; Brust, K.B.; Fiala, K.H. Acute rheumatic fever and erythema marginatum in an adult patient. In Baylor University Medical Center Proceedings; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2022; Volume 35, pp. 550–551. [Google Scholar]
- Reel, M.; Haidar, J.; Blanco, A.; Boccio, E. Acute Rheumatic Fever in an Adult Female Patient Presenting with Chest Pain: A Case Report. Cureus 2025, 17, e80133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Carapetis, J.R.; Currie, B.J. Rheumatic fever in a high incidence population: The importance of monoarthritis and low grade fever. Arch. Dis. Child. 2001, 85, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewitz, M.H.; Baltimore, R.S.; Tani, L.Y.; Sable, C.A.; Shulman, S.T.; Carapetis, J.; Remenyi, B.; Taubert, K.; Bolger, A.; Beerman, L.; et al. Revision of the Jones Criteria for the Diagnosis of Acute Rheumatic Fever in the Era of Doppler Echocardiography: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 131, 1806–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dajani, A.S.; Ayoub, E.; Bierman, F.Z.; Bisno, A.L.; Denny, F.W.; Durack, D.T.; Ferrieri, P.; Freed, M.; Gerber, M.; Kaplan, E.L.; et al. Guidelines for the Diagnosis of Rheumatic Fever: Jones Criteria, 1992 Update. JAMA 1992, 268, 2069–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, R.D. Anti-Streptolysin Titres of Human Sera in Health and in Various Streptococcal Infections. Epidemiol. Infect. 1936, 36, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.R.; Lee, N.Y.; Tsai, H.W.; Yang, C.C.; Lee, C.H. Acute rheumatic fever in adult patients. Medicine 2022, 101, e29833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, C.B. Review of the literature on acute rheumatism during the years 1939–1945. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1947, 6, 162–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLiee, E.M.; Dodge, K.G.; McEwen, C. The prognostic significance of age at onset in initial attacks of rheumatic fever. Am. Heart J. 1943, 26, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojha, U.; Marshall, D.; Salciccioli, J.; Al-Khayatt, B.; Goodall, R.; Borsky, K.; Crowley, C.; Shalhoub, J.; Hartley, A. An observational analysis of trends in rheumatic heart disease incidence and mortality in EU15+ countries over 29 years. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43 (Suppl. S2), ehac544.2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Loizaga, S.R.; Arthur, L.; Arya, B.; Beckman, B.; Belay, W.; Brokamp, C.; Hyun Choi, N.; Connolly, S.; Dasgupta, S.; Dibert, T.; et al. Rheumatic Heart Disease in the United States: Forgotten But Not Gone: Results of a 10 Year Multicenter Review. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e020992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nune, A.; Ling, S.; Gorodkin, R.; Hoschtitzky, A.; Jenkins, P. 014. Rheumatologists Beware, Rheumatic Fever Remains Prevalent: A Case of Acute Rheumatic Fever. Rheumatology 2015, 54 (Suppl. S1), i54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Okello, E.; Ndagire, E.; Muhamed, B.; Sarnacki, R.; Murali, M.; Pulle, J.; Atala, J.; Bowen, A.C.; DiFazio, M.P.; Nakitto, M.G.; et al. Incidence of acute rheumatic fever in northern and western Uganda: A prospective, population-based study. Lancet Glob. Heal. 2021, 9, e1423–e1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitik, B.; Kucuksahin, O.; Yesil, N.K.; Yesil, H.; Erten, S. SAT0570 An ignored disease in adults: Acute rheumatic fever. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasekara, H.; Wickramarathne, J.S.; Jayasinghe, P.A. Adult-onset acute rheumatic fever with chorea and carditis. BMJ Case Rep. 2024, 17, e258920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, A.; Pham, V.; Fong, M. Recurrent acute rheumatic fever in adulthood, a case of failed secondary prevention. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, C.Y.; Gauvreau, K.; Tani, L.Y.; Sundel, R.P.; Newburger, J.W. Characteristics of Children Discharged from Hospitals in the United States in 2000 with the Diagnosis of Acute Rheumatic Fever. Pediatrics 2007, 120, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, J.; Fualautoalasi-Lam, L.; Ferdinand, A.; Tiatia, R.; Jones, B.; Engelman, D.; Gibney, K.B.; Steer, A.C.; Poonawala, H. Living with rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease in Victoria, Australia: A qualitative study. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurahara, D.K.; Grandinetti, A.; Galario, J.; Reddy, D.V.; Tokuda, A.; Langan, S.; Tanabe, B.; Yamamoto, K.S.; Yamaga, K.M. Ethnic differences for developing rheumatic fever in a low-income group living in Hawaii. Ethn. Dis. 2006, 16, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ayoub, E.M.; Barrett, D.J.; Maclaren, N.K.; Krischer, J.P. Association of class II human histocompatibility leukocyte antigens with rheumatic fever. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 77, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Kumar, D.; Grover, A.; Khanduja, K.; Kaplan, E.; Gray, E.; Ganguly, N. Ethnic differences in expression of susceptibility marker(s) in rheumatic fever/rheumatic heart disease patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 1998, 64, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhamed, B.; Shaboodien, G.; Engel, M.E. Genetic variants in rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease. Am. J. Med Genet. Part C Semin. Med Genet. 2020, 184, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, L.-A.; D’Antoine, A.H.; Tong, S.Y.C.; McKinnon, M.; Bessarab, D.; Brown, N.; Reményi, B.; Steer, A.; Syn, G.; Blackwell, J.M.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of Genetic Risk Factors for Rheumatic Heart Disease in Aboriginal Australians Provides Support for Pathogenic Molecular Mimicry. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 1460–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khriesat, I.; Najada, A.H. Acute rheumatic fever without early carditis: An atypical clinical presentation. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2003, 162, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sika-Paotonu, D.; Beaton, A.; Raghu, A.; Steer, A.; Carapetis, J. Acute Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease. In Streptococcus Pyogenes: Basic Biology to Clinical Mani-Festations; Ferretti, J.J., Stevens, D.L., Fischetti, V.A., Eds.; 10 March 2017 [updated 3 April 2017]; University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center: Oklahoma City, OK, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Tsang, L.S.-L.; Zhao, M.; Shi, W.; Lu, Q. Adult-onset Still’s disease: A disease at the crossroad of innate immunity and autoimmunity. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 881431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Efthimiou, P.; Kadavath, S.; Mehta, B. Life-threatening complications of adult-onset Still’s disease. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 33, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bawazir, Y.; Towheed, T.; Anastassiades, T. Post-Streptococcal Reactive Arthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2020, 16, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, A.-F.; Bungau, S.G. Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Overview. Cells 2021, 10, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
| Bloods on each Hospital Admission | CRP NORMAL (<4) mg/L | Hb Normal (115–165) g/L | WCC Normal (4–11) 10*9/L | Neutrophils Normal (1.8–7.5) 10 × 9/L | Lymphocytes Normal (1–4) 10 × 9/L | Alkaline Phosphatase Norm (30–130) u/L | GGT Normal (0–39) u/L | Blood Cultures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st visit (week 0) | 171 | 120 | 6.0 | 4.9 | 0.6 | 142 | 66 | Not taken |
| 2nd visit (week 1) | 191 | 97 | 4.5 | 3.5 | 0.6 | 210 | 115 | Negative |
| 3rd visit (week 2) | 106 | 109 | 5.6 | 4.8 | 0.6 | 214 | 181 | Negative |
| 4th visit (week 4) | 74 | 113 | 5.9 | 4.7 | 0.8 | 170 | 159 | Not taken |
| At discharge | <4 | 123 | 3.6 | 2.1 | 1.1 | 78 | Not taken | Not taken |
| Major Criteria | |
| Low-risk Population | High-risk Population |
| Carditis (clinical or subclinical) Arthritis—only polyarthritis Chorea Erythema marginatum Subcutaneous nodules | Carditis (clinical or subclinical) Arthritis—monoarthritis or polyarthritis Polyarthralgia Chorea Erythema marginatum Subcutaneous nodules |
| Minor Criteria | |
| Low-risk population | High-risk population |
| Polyarthralgia Hyperpyrexia (≥38.5 °C) ESR ≥ 60 mm/h and/or CRP ≥ 3.0 mg/dL Prolonged PR interval (after considering the differences related to age, if there is no carditis as a major criterion) | Monoarthralgia Hyperpyrexia (≥8.0 °C) ESR ≥ 30 mm/h and/or CRP ≥ 3.0 mg/dL Prolonged PR interval (after considering the differences related to age, if there is no carditis as a major criterion) |
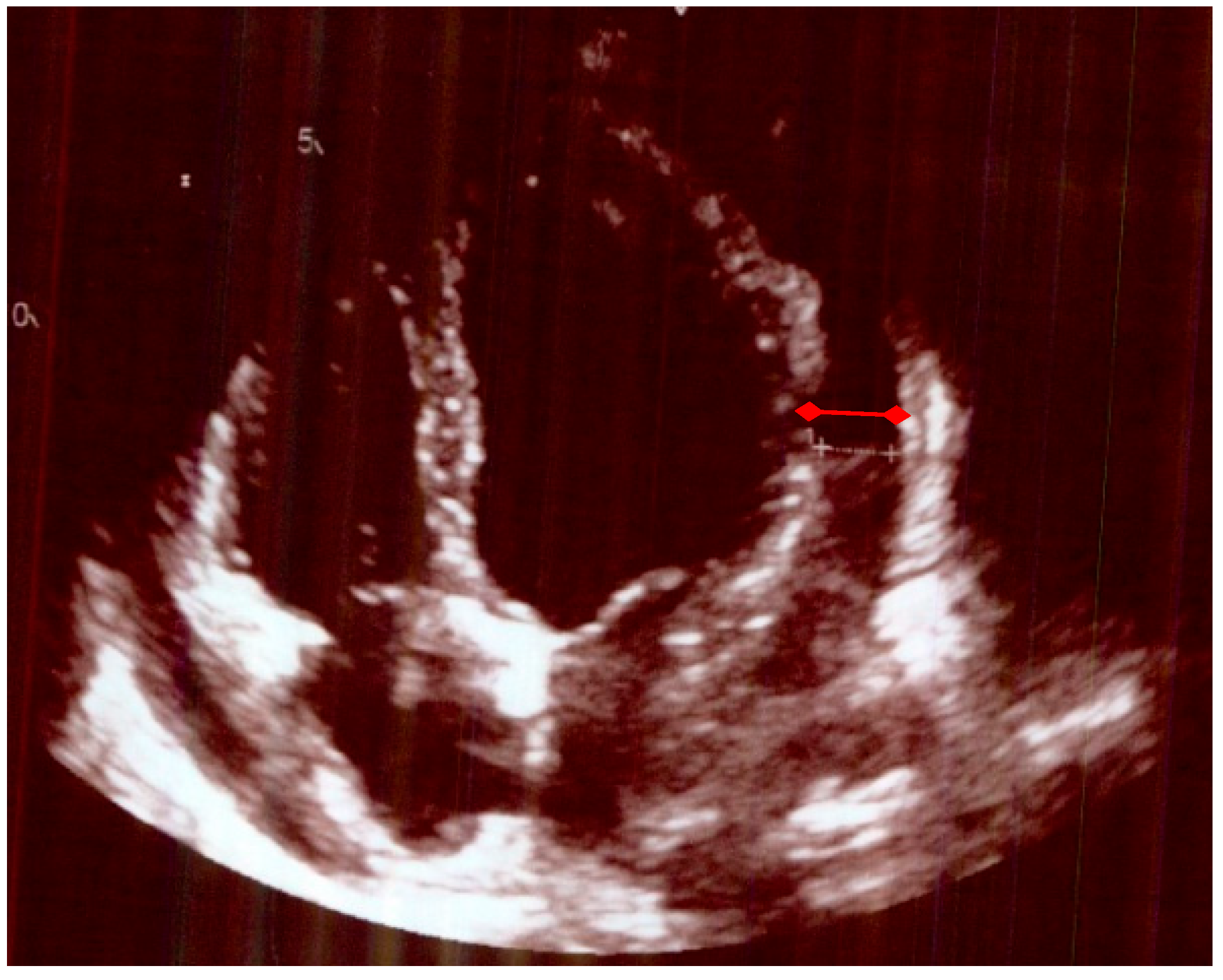
| Echocardiogram Pre-Treatment | Echocardiogram Post-Treatment after 4 Months. |
|---|---|
| A small/moderate global pericardial effusion Normal LV structure and function. Valves appeared structurally and functionally normal Mobile atrial septum, no shunt seen. No evidence of subacute bacterial endocarditis | No obvious residual pericardial effusion Normal LV structure and function No evidence of valve thickening but mild dilation of the non-coronary sinus of Valsalva and trivial AR and MR Normal RV structure and function |
| Acute Rheumatic Fever in Children | Acute Rheumatic Fever in Adults | Adults’ Onset Still Disease | Post-Streptococcal Reactive Arthritis | Rheumatoid Arthritis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak age of onset (years) | 5–15 yrs (rare < 3 yrs) | Rare in adults | Two peaks: 15–25 and 36–46 | Bimodal peaks: 8–14 and 21–37 yrs | Typically, 40–60 |
| Genetics | HLA-DR7, DR2/DR4; D8/17 B-cells; twin heritability ~60% | (HLA-DR7, D8/17) | HLA-DRB1 | No strong HLA links; genetic link unclear | HLA-DRB1 shared epitope (DR4); twin concordance low (~12–15%) |
| Most common clinical features in descending order | Fever Migratory arthritis of large joints Carditis Subcutaneous nodules chorea, Erythema marginatum | Polyarthralgia (typically large joint) Fever Carditis | Quotidian fevers Salmon rash Arthritis Lymphadenopathy Hepatosplenomegaly | Non-migratory arthritis; small, axial, large joints Tenosynovitis Carditis (Rare) | Symmetric polyarthritis of small joints of hands and feet chronic erosive disease |
| Environmental triggers | Poor socioeconomic status. | Usually, recurrence form childhood | Triggered by viral infections, not GAS | GAS infection, but closer timing; less related to poverty | Smoking, silica, periodontal disease, obesity |
| Sex | Female preponderance | Female preponderance | Female predominance | Equal | Female preponderance |
| Most prevalent (region) | Asia, Aboriginals in Australia | N/A | Not restricted to any geographical location. | Not restricted to any geographical location. | Northern Europe and North America |
| Treatment | NSAIDs Penicillin Aspirin | NSAIDs Penicillin Aspirin | NSAIDs DMARDS Corticosteroids | NSAIDs Corticosteroids | NSAIDs DMARDS Corticosteroids |
| Complications | Rheumatic heart disease | Rheumatic heart disease | Macrophage activation syndrome | glomerulonephritis | Joint deformities Interstitial lung disease serositis |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasan, F.; Dey, M.; Nune, A. Acute Rheumatic Fever in Caucasians: A Case Report and Systematic Review. Life 2025, 15, 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071131
Hasan F, Dey M, Nune A. Acute Rheumatic Fever in Caucasians: A Case Report and Systematic Review. Life. 2025; 15(7):1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071131
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasan, Fuad, Mrinalini Dey, and Arvind Nune. 2025. "Acute Rheumatic Fever in Caucasians: A Case Report and Systematic Review" Life 15, no. 7: 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071131
APA StyleHasan, F., Dey, M., & Nune, A. (2025). Acute Rheumatic Fever in Caucasians: A Case Report and Systematic Review. Life, 15(7), 1131. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15071131







