The Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Levosimendan in Sepsis: An Experimental Study Using a LPS-Induced Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model
2.2. Sampling Method
2.3. Cytokine Assay
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Murine Sepsis Score (MSS)
3.2. Cytokine Levels
3.2.1. TNF-α
3.2.2. IL-1β
3.2.3. IL-6
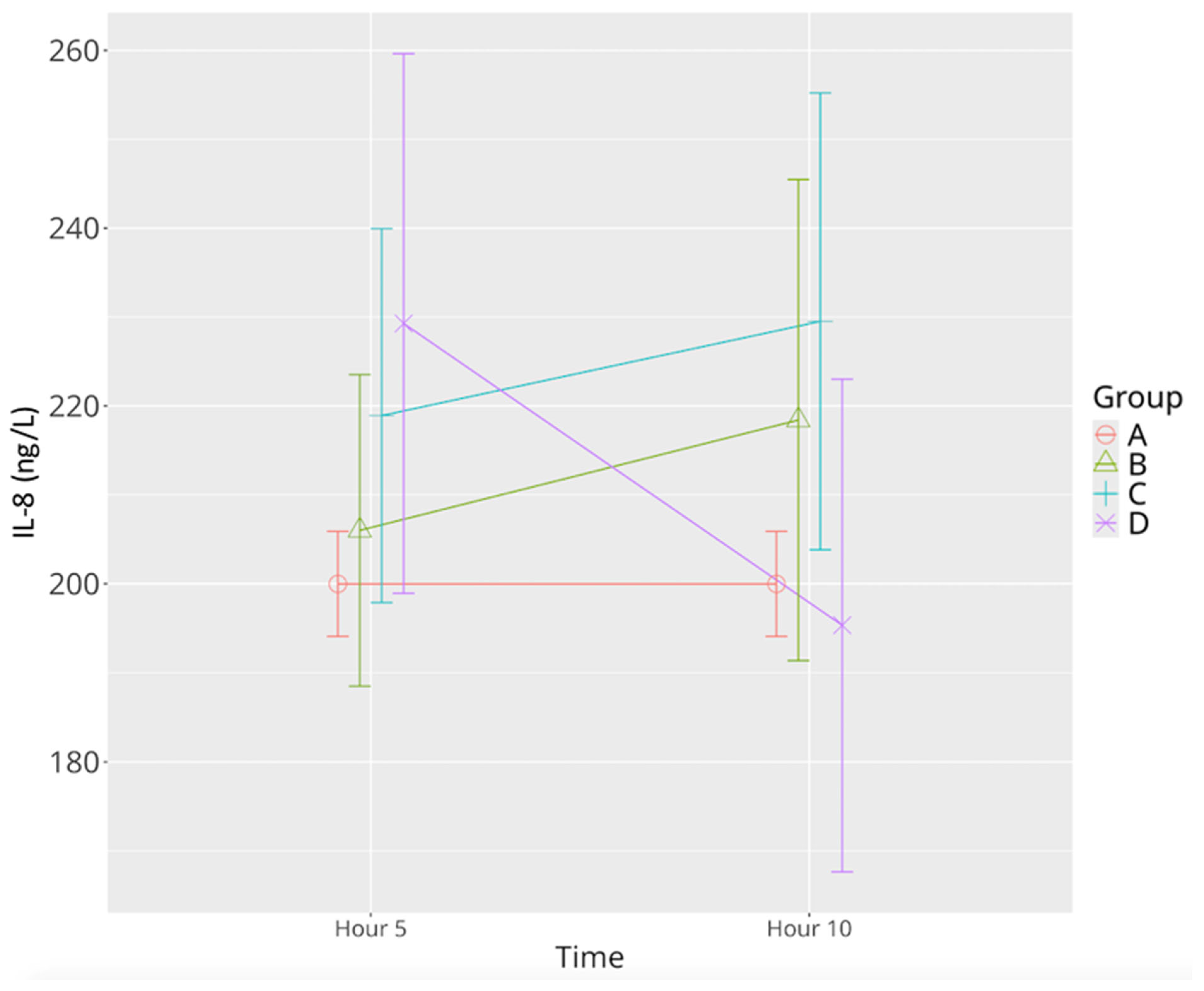
3.2.4. IL-8
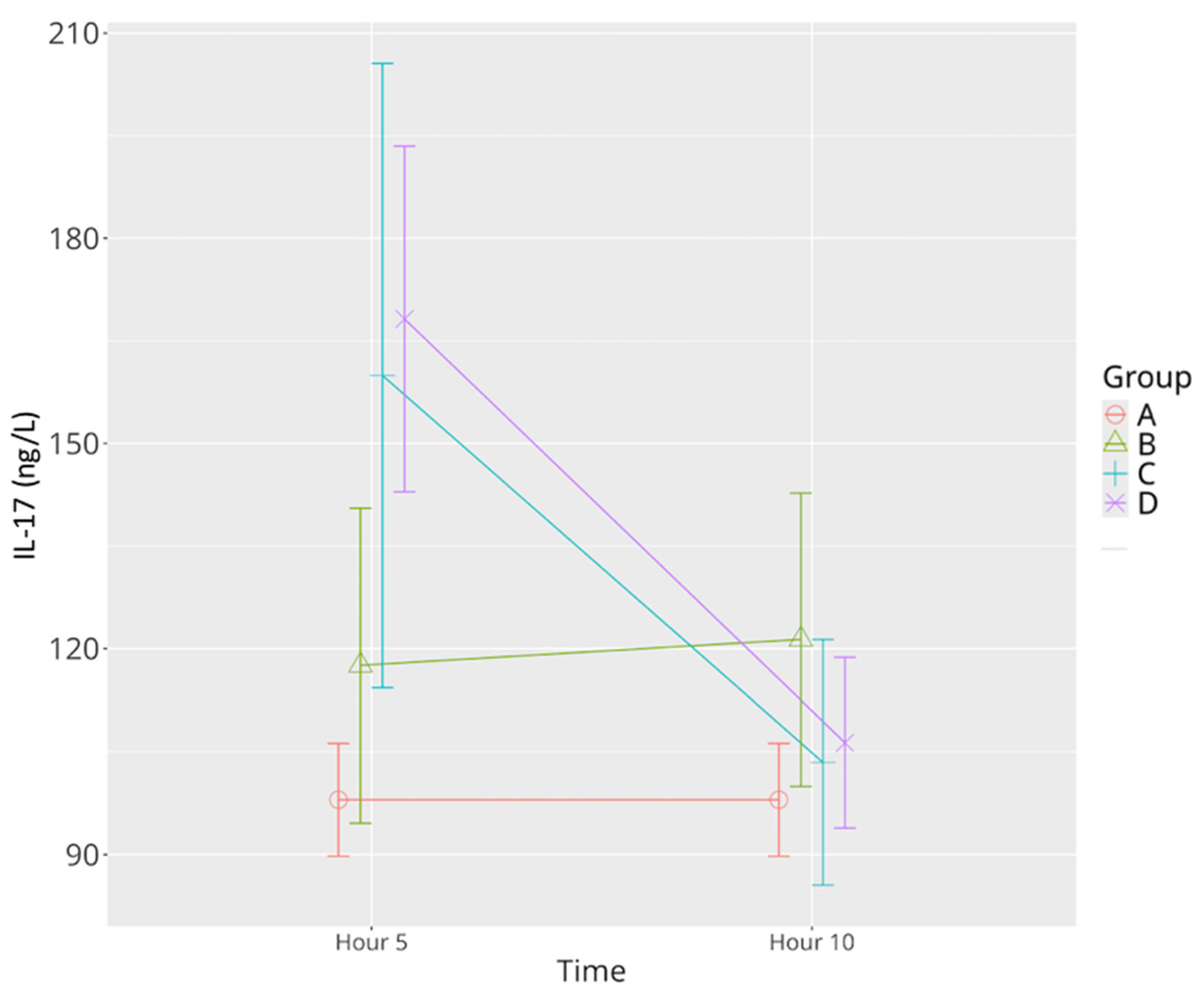
3.2.5. IL-17
3.2.6. MCP-1
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1-beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| L-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| IL-17 | Interleukin-17 |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 |
References
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.-L.; Marshall, J.C.; A Ñamendys-Silva, S.A.; François, B.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Lipman, J.; Reinhart, K.; Antonelli, M.; Pickkers, P.; Njimi, H.; et al. Assessment of the worldwide burden of critical illness: The Intensive Care Over Nations (ICON) audit. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, M.; Gerlach, H.; Vogelmann, T.; Preissing, F.; Stiefel, J.; Adam, D. Mortality in sepsis and septic shock in Europe, North America and Australia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugar, S.; Choudhary, C.; Duggal, A. Sepsis and septic shock: Guideline-based management. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2020, 87, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaillon, J.M.; Adib-Conquy, M.; Fitting, C.; Adrie, C.; Payen, D. Cytokine cascades in sepsis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 35, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-1 antagonism. Blood 1991, 77, 1627–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taenaka, H.; Evrard, B.; Maishan, M.; Calfee, C.S.; Matthay, M.A. Latent class analysis using plasma biomarkers identifies two inflammatory phenotypes with differential responses to therapy in a mouse model of bacterial pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2025, 211, A2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, K.; Yang, D.; Oppenheim, J.J. Interleukin-8: An evolving chemokine. Cytokine 2022, 153, 155828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, A.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; Chen, L.; Cui, J.; Fan, Z.; Li, Y. Comparative analysis of inflammatory biomarkers for the diagnosis of neonatal sepsis: IL-6, IL-8, SAA, CRP, and PCT. Open Life Sci. 2025, 20, 20221005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Abraham, D.; Ong, V. The yin and yang of il-17 in systemic sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 885609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cua, D.J.; Tato, C.M. Innate IL-17-producing cells: The sentinels of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barre, M.; Behnes, M.; Hamed, S.; Pauly, D.; Lepiorz, D.; Lang, S.; Akin, I.; Borggrefe, M.; Bertsch, T.; Hoffmann, U. Revisiting the prognostic value of monocyte chemotactic protein 1 and interleukin-6 in the sepsis-3 era. J. Crit. Care 2018, 43, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Anshita, D.; Ravichandiran, V. MCP-1: Function, regulation, and involvement in disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101 Pt B, 107598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.S.; Cheng, G. Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.J.; Seymour, C.W.; Rosengart, M.R. Current murine models of sepsis. Surg. Infect. 2016, 17, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Nicolás, M.Á.; Lázaro, A. Induction of sepsis in a rat model by the cecal ligation and puncture technique: Application for the study of experimental acute renal failure. Methods Cell Biol. 2025, 192, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawish, R.; Starkl, P.; Pimenov, L.; Hladik, A.; Lakovits, K.; Oberndorfer, F.; Cronin, S.J.; Ohradanova-Repic, A.; Wirnsberger, G.; Agerer, B.; et al. ACE2 is the critical in vivo receptor for SARS-CoV-2 in a novel COVID-19 mouse model with TNF- and IFNγ-driven immunopathology. eLife 2022, 11, e74623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freise, H.; Brückner, U.B.; Spiegel, H.U. Animal models of sepsis. J. Investig. Surg. 2001, 14, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, T.; Sumiyama, F.; Kotsuka, M.; Hatta, M.; Yoshida, T.; Hayashi, M.; Kaibori, M.; Sekimoto, M. Levosimendan increases survival in a D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide rat model. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogland, I.C.; Houbolt, C.; van Westerloo, D.J.; van Gool, W.A.; van de Beek, D. Systemic inflammation and microglial activation: Systematic review of animal experiments. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woehrle, T.; Mehringer, L.; Juchem, G.; Dashkevich, A.; Weis, M.; Schünemann, M.; Kilger, E. Individualisierter Einsatz von Levosimendan in der Herzchirurgie [Individualized use of levosimendan in cardiac surgery. Der Anaesthesist 2021, 70, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C.M.; Li, K.Y.; Chen, S.J.; Ka, S.M.; Liaw, W.J.; Huang, H.C.; Wu, C.C. Levosimendan attenuates multiple organ injury and improves survival in peritonitis-induced septic shock: Studies in a rat model. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union. Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, L276, 33–79. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2010/63/oj (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulzbacher, M.M.; Sulzbacher, L.M.; Passos, F.R.; Bilibio, B.L.E.; de Oliveira, K.; Althaus, W.F.; Frizzo, M.N.; Ludwig, M.S.; Da Cruz, I.B.M.; Heck, T.G. Adapted Murine Sepsis Score: Improving the research in experimental sepsis mouse model. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5700853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yokoo, H.; Takashina, M.; Sakata, K.; Ohashi, W.; Abedelzaher, L.A.; Imaizumi, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Hattori, K.; Matsuda, N.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory profile of levosimendan in cecal ligation-induced septic mice and in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 43, e508–e520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ateş, G.; Yaman, F.; Bakar, B.; Kısa, Ü.; Atasoy, P.; Büyükkoçak, Ü. Evaluation of the systemic antiinflammatory effects of levosimendan in an experimental blunt thoracic trauma model. Turk. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2017, 23, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsen, A.; Lehman, E.; Burrows, P.; Bonavia, A.S. Time-dependent variation in immunoparalysis biomarkers among patients with sepsis and critical illness. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1498974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krychtiuk, K.A.; Watzke, L.; Kaun, C.; Buchberger, E.; Hofer-Warbinek, R.; Demyanets, S.; Pisoni, J.; Kastl, S.P.; Rauscher, S.; Gröger, M.; et al. Levosimendan exerts anti-inflammatory effects on cardiac myocytes and endothelial cells in vitro. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 113, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhad, S.Z.; Rezazadeh, F.; Mohammadi, M. Interleukin—17 and Interleukin-10 as inflammatory and prevention biomarkers in periimplant diseases. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2019, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, M.S.; Hawthorne, W.J.; Bendall, J.; Whereat, S.; Huang, S.; Ting, I.; Simond, D.; McLean, A. No beneficial effects of levosimendan in acute porcine endotoxaemia. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2011, 55, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boost, K.A.; Hoegl, S.; Dolfen, A.; Czerwonka, H.; Scheiermann, P.; Zwissler, B.; Hofstetter, C. Inhaled levosimendan reduces mortality and release of proinflammatory mediators in a rat model of experimental ventilator-induced lung injury. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, 1873–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

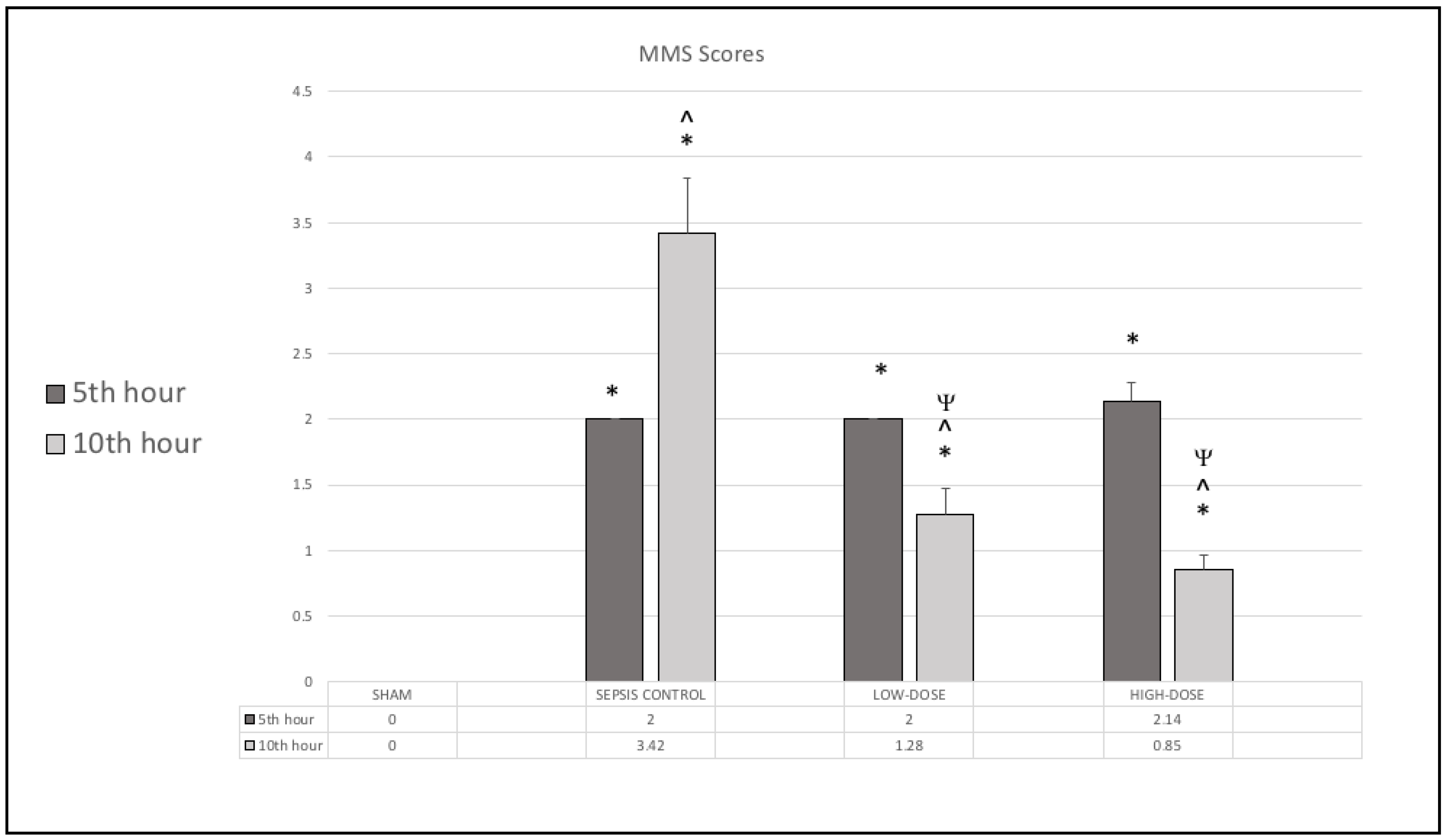
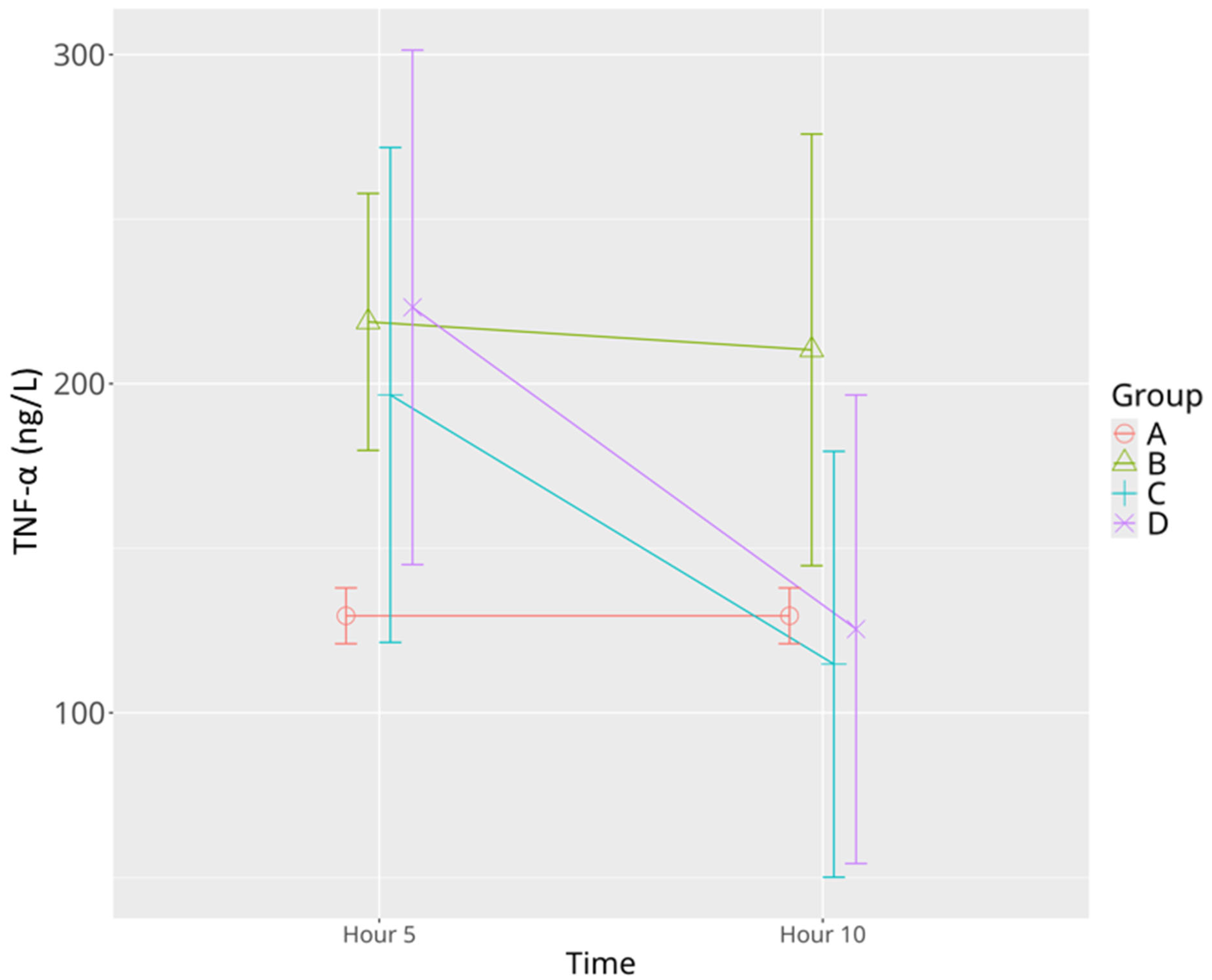
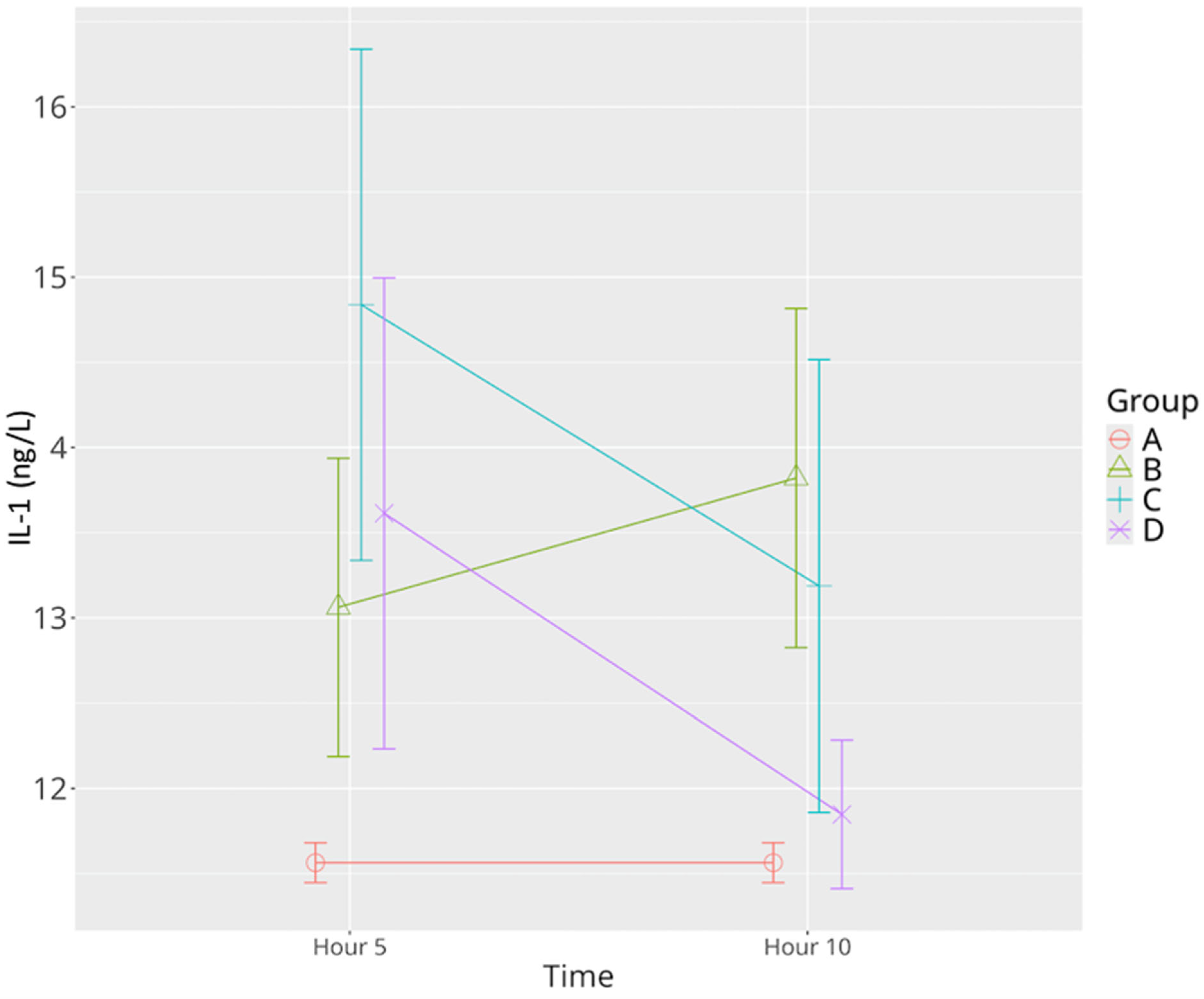
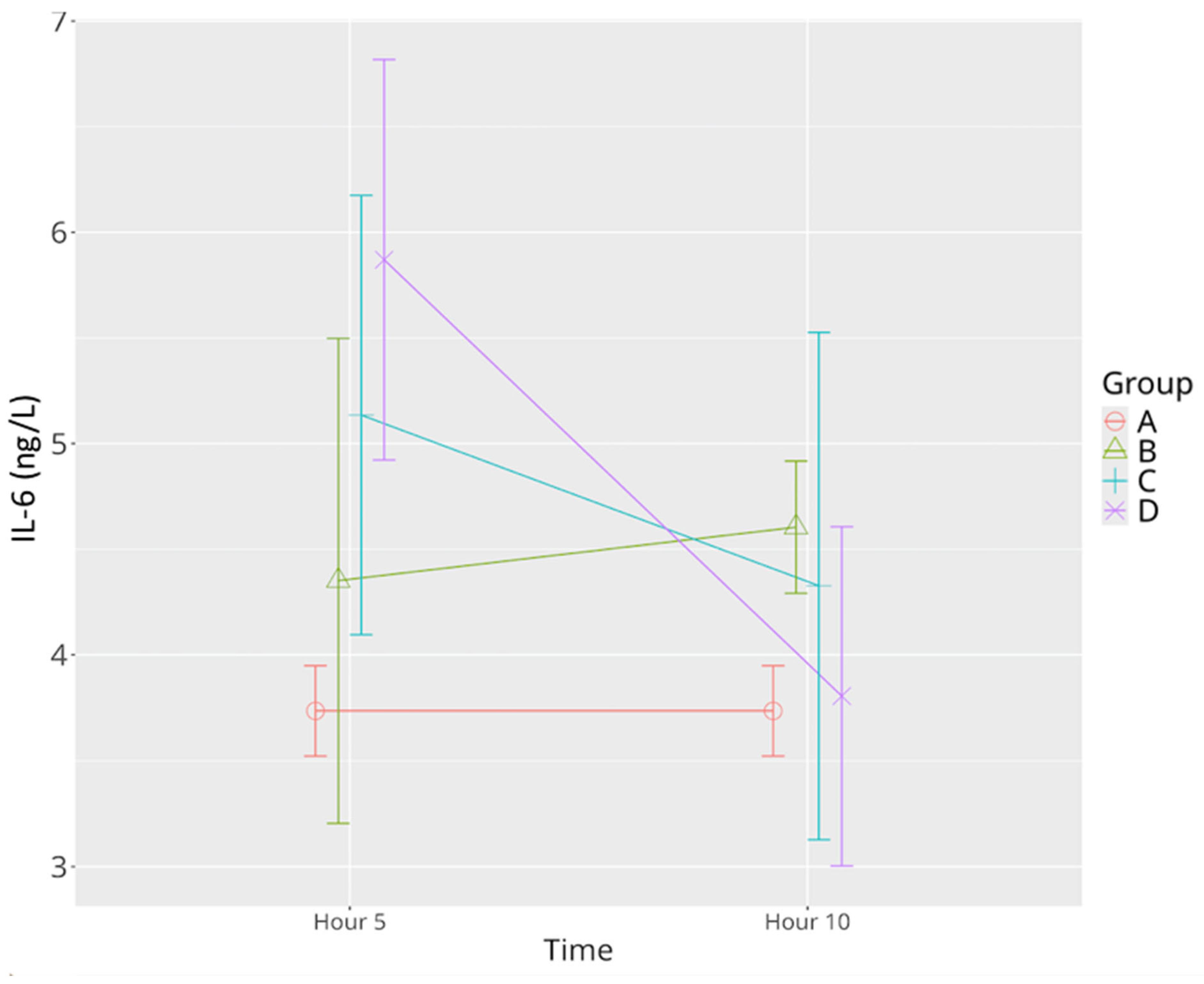

| [ng/L] | Group A | Group B 5th Hour | Group B 10th Hour | Group C 5th Hour | Group C 10th Hour | Group D 5th Hour | Group D 10th Hour |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | 129.46 ± 10.14 | 212.53 ± 54.28 * | 210.27 ± 78.44 * | 196.58 ± 19.0 | 114.78 ± 63.75 ^Ψ | 223.20 ± 43.28 * | 125.42 ± 20.98 Ψ |
| IL-1β | 11.56 ± 0.32 | 13.06 ± 0.97 | 13.82 ± 1.19 * | 14.83 ± 1.79 *^ | 13.18 ± 1.58 *Ψ | 13.61 ± 1.65 * | 11.84 ± 0.52 ^Ψ |
| IL-6 | 3.71 ± 0.21 | 4.29 ± 1.24 | 4.60 ±0.22 * | 5.13± 1.11 * | 4.32 ±1.21 | 5.87 ± 1.13 ^* | 3.78 ± 0.81 Ψ |
| IL-8 | 200.37 ± 7.22 | 205.99 ± 20.95 | 218.40 ± 32.37 | 218.90 ± 25.15 | 229.50 ± 24.34 | 229.27 ± 36.31 | 195.32 ± 33.10 Ψ |
| IL-17 | 97.99 ± 9.83 | 117.55 ± 27.47 | 121.33 ± 25.59 | 159.93 ± 28.64 *^ | 103.43 ± 21.39 Ψ | 168.19 ± 30.22 *^ | 106.30 ± 14.86 Ψ |
| MCP-1 | 116.34 ± 6.17 | 186.26 ± 45.25 * | 143.79 ± 14.21 Ψ | 154.63 ± 37.8 * | 171.82 ± 20.51 * | 198.77 ± 72.66 * | 107.16 ± 18.57 Ψ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dedeler Ertanıdır, E.; Duman, I.; Eryavuz, D.O.; Ünlü, A.; Ertanıdır, M.; Duman, A. The Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Levosimendan in Sepsis: An Experimental Study Using a LPS-Induced Rat Model. Life 2025, 15, 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060928
Dedeler Ertanıdır E, Duman I, Eryavuz DO, Ünlü A, Ertanıdır M, Duman A. The Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Levosimendan in Sepsis: An Experimental Study Using a LPS-Induced Rat Model. Life. 2025; 15(6):928. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060928
Chicago/Turabian StyleDedeler Ertanıdır, Elif, Ipek Duman, Duygu Onmaz Eryavuz, Ali Ünlü, Mehmet Ertanıdır, and Ateş Duman. 2025. "The Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Levosimendan in Sepsis: An Experimental Study Using a LPS-Induced Rat Model" Life 15, no. 6: 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060928
APA StyleDedeler Ertanıdır, E., Duman, I., Eryavuz, D. O., Ünlü, A., Ertanıdır, M., & Duman, A. (2025). The Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Levosimendan in Sepsis: An Experimental Study Using a LPS-Induced Rat Model. Life, 15(6), 928. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060928





