Veno-Arterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Cardiotoxic Drug-Induced Cardiogenic Shock: A Systematic Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
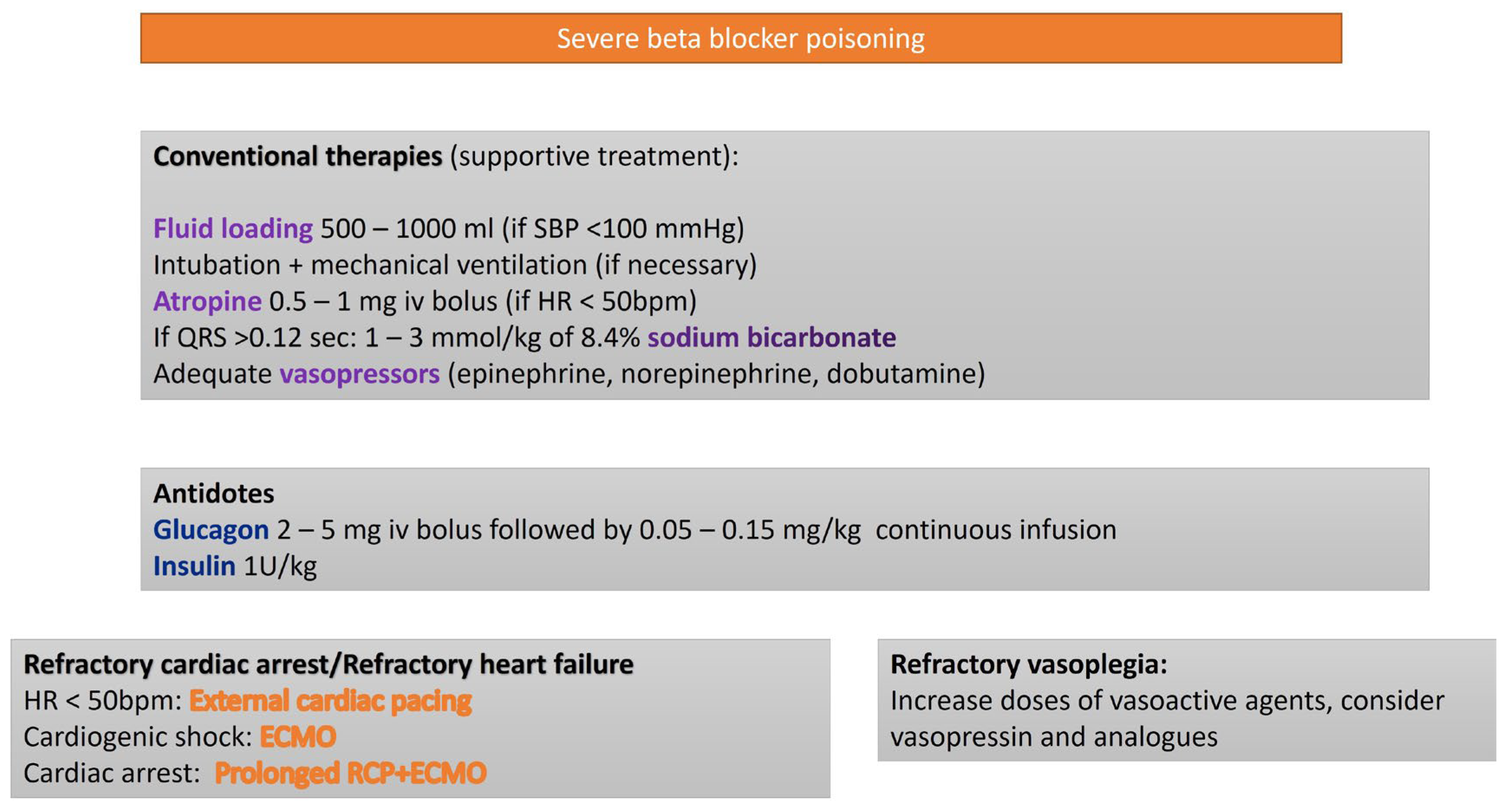
3.1. Beta Blockers (BBs)
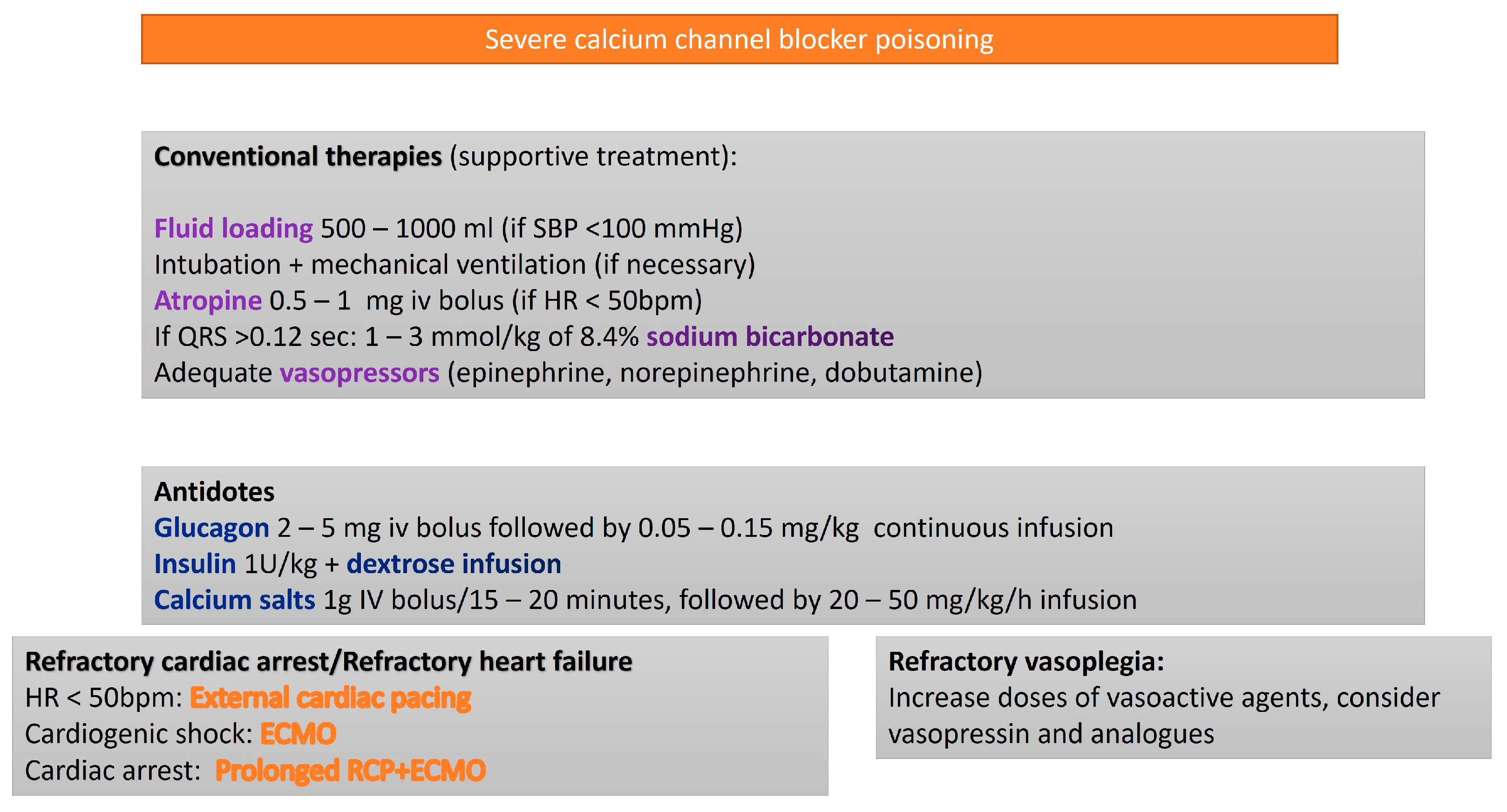
3.2. Calcium Channel Blockers
- Dihydropyridines (e.g., nifedipine, amlodipine, lercanidipine), which primarily induce peripheral vasodilation with minimal negative inotropic effect.
- Non-dihydropyridines (e.g., diltiazem, verapamil), which exert greater cardiac effects, particularly on the sinoatrial and atrioventricular nodes, leading to heart rate reduction (negative chronotropy).
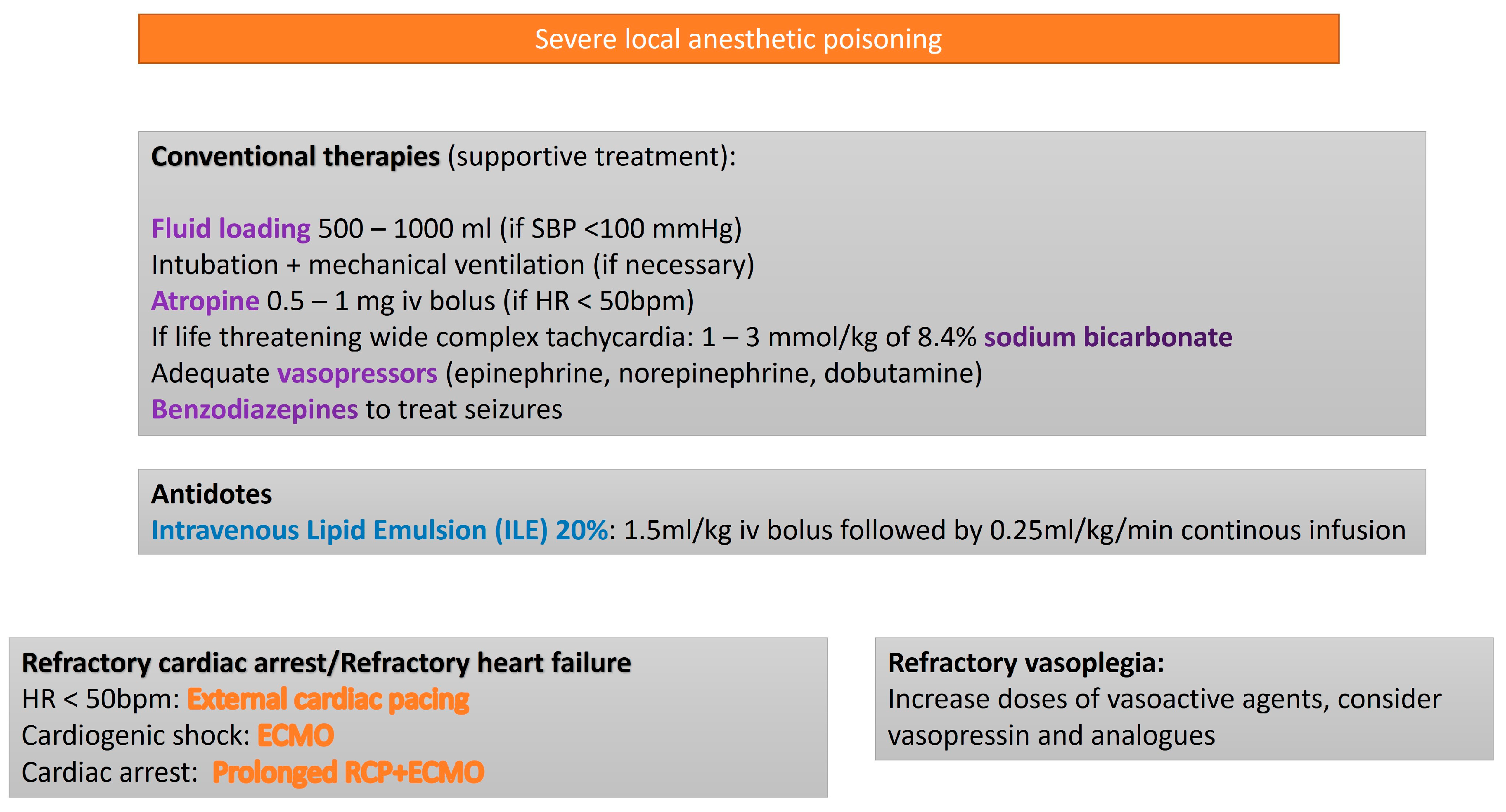
3.3. Local Anesthetics
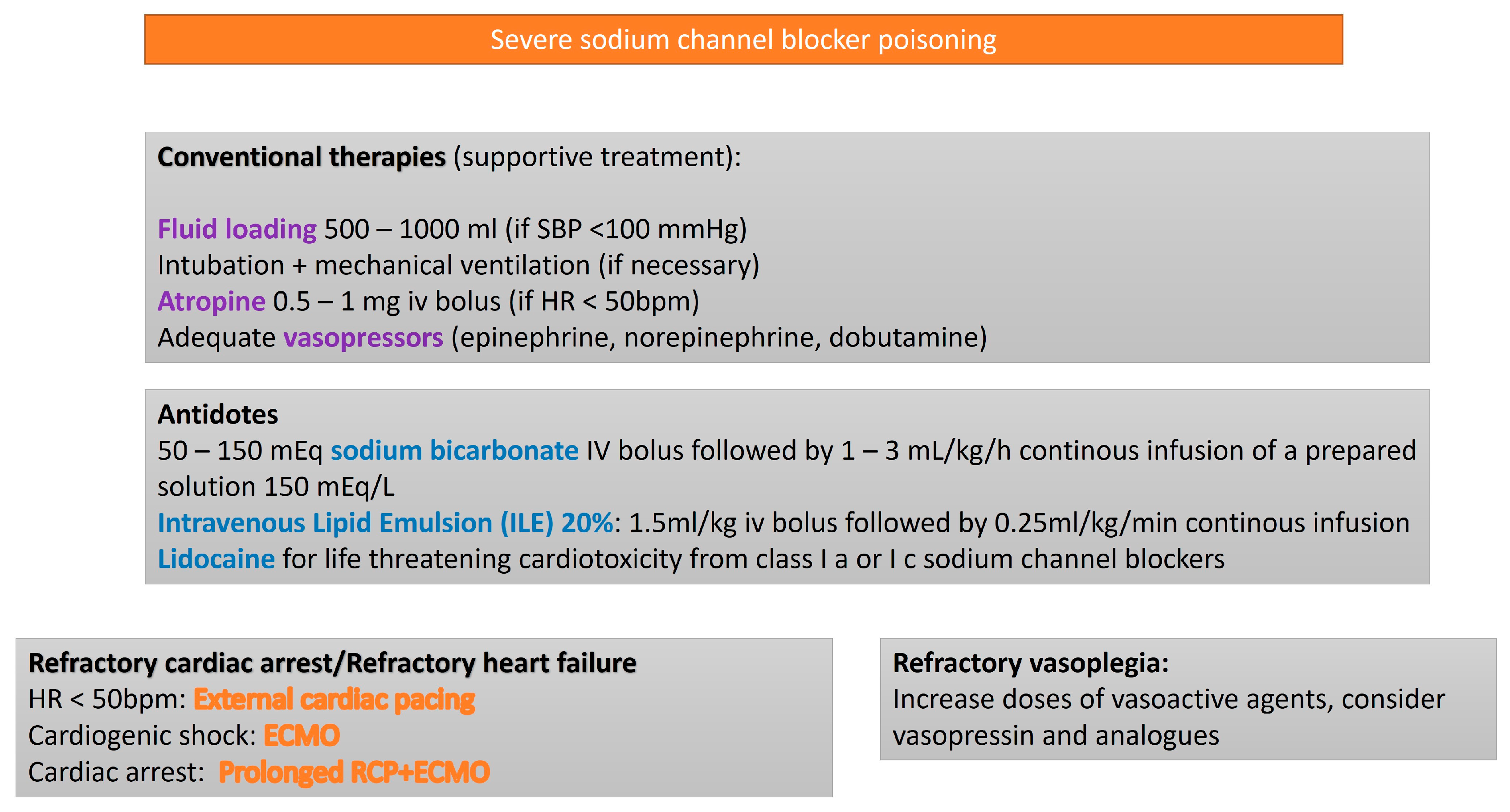
3.4. Sodium Channel Blockers (SCBs)
3.5. Sympathomimetics
3.6. Intoxication from Other Cardiotoxic Drugs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECLS | Extracorporeal life support |
| V-A ECMO | Veno-arterial Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| BBs | Beta blockers |
| CCBs | Calcium Channel blockers |
| SCBs | Sodium Channel blockers |
| LAs | Local Anesthetics |
| ILE | Intravenous Lipid Emulsion |
| RCP | Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation |
| LVEF | Left ventricular ejection fraction |
References
- Gummin, D.D.; Mowry, J.B.; Beuhler, M.C.; Spyker, D.A.; Bronstein, A.C.; Rivers, L.J.; Pham, N.P.T.; Weber, J. 2020 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers’ National Poison Data System (NPDS): 38th Annual Report. Clin. Toxical. 2021, 59, 1282–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, M.; Wu, L.; Terrar, D.A.; Huang, C.L. Modernized Classification of Cardiac Antiarrhythmic Drugs. Circulation 2018, 138, 1879–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mégarbane, B.; Leprince, P.; Deye, N.; Résière, D.; Guerrier, G.; Rettab, S.; Théodore, J.; Karyo, S.; Gandjbakhch, I.; Baud, F.J. Emergency feasibility in medical intensive care unit of extracorporeal life support for refractory cardiac arrest. Intensive Care Med. 2007, 33, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lange, D.W.; Sikma, M.A.; Meulenbelt, J. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in the treatment of poisoned patients. Clin. Toxical. 2013, 51, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, N.J.; Gaieski, D.F.; Allen, S.R.; Perrone, J.; DeRoos, F. A review of emergency cardiopulmonary bypass for severe poisoning by cardiotoxic drugs. J. Med. Toxicol. 2013, 9, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Voicu, S.; M’Rad, A.; Malissin, I.; Deye, N.; Mégarbane, B. Extracorporeal life support in cardiotoxicant poisoning-A narrative review. Basic. Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 132, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedrichson, B.; Jasny, T.; Old, O.; Piekarski, F.; Ippolito, A.; Raimann, F.J.; Zacharowski, K.; Kloka, J.A. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in cardiovascular medication poisoning. A German-wide retrospective study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Finn, D.; Stevens, J.; Tolkacz, M.; Robinson, J.; Mangla, J.; Iacco, A. Calcium Channel Blocker Overdose: What Role Does Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Have in Support? A Systematic Review of the Literature. ASAIO J. 2024, 70, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeWitt, C.R.; Waksman, J.C. Pharmacology, pathophysiology and management of calcium channel blocker and beta-blocker toxicity. Toxicol. Rev. 2004, 23, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murad, M.H.; Coto-Yglesias, F.; Wang, A.T.; Sheidaee, N.; Mullan, R.J.; Elamin, M.B.; Erwin, P.J.; Montori, V.M. Clinical review: Drug-induced hypoglycemia: A systematic review. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, C.B.; Ryan, N.M.; Isbister, G.K. The safety of high-dose insulin euglycaemia therapy in toxin-induced cardiac toxicity. Clin. Toxical. 2018, 56, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotella, J.A.; Greene, S.L.; Koutsogiannis, Z.; Graudins, A.; Hung Leang, Y.; Kuan, K.; Baxter, H.; Bourke, E.; Wong, A. Treatment for beta-blocker poisoning: A systematic review. Clin. Toxical. 2020, 58, 943–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, R.; Ghosh, A. Glucagon for the treatment of symptomatic beta blocker overdose. Emerg. Med. J. 2003, 20, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sebe, A.; Dişel, N.R.; Açıkalın Akpınar, A.; Karakoç, E. Role of intravenous lipid emulsions in the management of calcium channel blocker and β-blocker overdose: 3 years experience of a university hospital. Postgrad. Med. 2015, 127, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, R.; Colas, V.; Parienti, J.J.; Lehoux, P.; Massetti, M.; Charbonneau, P.; Saulnier, F.; Daubin, C. A comparison of survival with and without extracorporeal life support treatment for severe poisoning due to drug intoxication. Resuscitation 2012, 83, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horward, P.; Lambermont, B.; Defraigne, J.O.; Gurdebeke, C.; Morimont, P. Comment je traite…l’intoxication massive aux bêta-bloquants: Approches pharmacologiques et place de l’ECMO [How I treat…severe beta-blocker poisoning: Pharmacological approaches and ECMO]. Rev. Med. Liege 2017, 72, 115–120. (In French) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vandroux, D.; Aujoulat, T.; Gaüzère, B.A.; Puech, B.; Guihard, B.; Martinet, O. Predicting factors for the need of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for suicide attempts by cardiac medication: A single-center cohort study. World J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 13, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mégarbane, B.; Deye, N.; Malissin, I.; Baud, F.J. Usefulness of the serum lactate concentration for predicting mortality in acute beta-blocker poisoning. Clin. Toxical. 2010, 48, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramoska, E.A.; Spiller, H.A.; Myers, A. Calcium channel blocker toxicity. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1990, 19, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howarth, D.M.; Dawson, A.H.; Smith, A.J.; Buckley, N.; Whyte, I.M. Calcium channel blocking drug overdose: An Australian series. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 1994, 13, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schult, R.F.; Nacca, N.; Grannell, T.L.; Jorgensen, R.M.; Acquisto, N.M. Evaluation of high-dose insulin/euglycemia therapy for suspected β-blocker or calcium channel blocker overdose following guideline implementation. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2022, 79, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warrick, B.J.; Tataru, A.P.; Smolinske, S. A systematic analysis of methylene blue for drug-induced shock. Clin. Toxical. 2016, 54, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosselin, S.; Hoegberg, L.C.; Hoffman, R.S.; Graudins, A.; Stork, C.M.; Thomas, S.H.; Stellpflug, S.J.; Hayes, B.D.; Levine, M.; Morris, M.; et al. Evidence-based recommendations on the use of intravenous lipid emulsion therapy in poisoning. Clin. Toxical. 2016, 54, 899–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duburcq, T.; Goutay, J.; Preau, S.; Mugnier, A.; Rousse, N.; Moussa, M.D.; Vincentelli, A.; Cuny, J.; Parmentier-Decrucq, E.; Poissy, J. Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Severe Drug Intoxication: A Retrospective Comparison of Survivors and Nonsurvivors. ASAIO J. 2022, 68, 907–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.B.; Olives, T.D.; Ulici, A.; Litell, J.M.; Bangh, S.A.; Arens, A.M.; Puskarich, M.A.; Prekker, M.E. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Poisonings Reported to U.S. Poison Centers from 2000 to 2018: An Analysis of the National Poison Data System. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldfine, C.E.; Troger, A.; Erickson, T.B.; Chai, P.R. Beta-blocker and calcium-channel blocker toxicity: Current evidence on evaluation and management. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2024, 13, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, M.; Sterz, F.; Schoerkhuber, W.; Behringer, W.; Domanovits, H.; Weinmar, D.; Weinstabl, C.; Stimpfl, T. Successful resuscitation of a verapamil-intoxicated patient with percutaneous cardiopulmonary bypass. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 27, 2818–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, K.; Mohanty, B.; Tang, S.; MacLaren, G. Extracorporeal therapy for amlodipine poisoning. J. Artif. Organs 2020, 23, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, I.Z.; Ng, M.; Sewa, D.W.; Yao, Y.J.; Jose, M.C.; Tan, K.B.K.; Ponampalam, R. Use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in massive amlodipine overdose. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 3403–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusuke, M.; Hidetoshi, Y.; Yusuke, T.; Koji, I.; Masahito, T.; Susumu, Y.; Takayuki, O. Intoxication with massive doses of amlodipine and candesartan requiring venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Acute Med. Surg. 2023, 10, e878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Groot, M.W.; Grewal, S.; Meeder, H.J.; van Thiel, R.J.; den Uil, C.A. Extracorporele life support bij calciumblokkerintoxicatie [Extracorporeal life support in calcium antagonist intoxication]. Ned. Tijdschr. Geneeskd. 2017, 161, D1960. (In Dutch) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sorabella, R.A.; Gray, W.H.; Dabal, R.J.; Padilla, L.A.; Hock, K.; Clark, M.G.; O’Meara, C.; Hawkins, J.; Richter, R.P.; Borasino, S.; et al. Central Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Support Following Calcium Channel Blocker Overdose in Children. ASAIO J. 2024, 70, e92–e96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Chavez, S.; Gottlieb, M.; Montrief, T.; Brady, W.J. Local anesthetic systemic toxicity: A narrative review for emergency clinicians. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 59, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiz, S.; Nath, S. Cardiotoxicity of local anaesthetic agents. Br. J. Anaesth. 1986, 58, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magid, D.J.; Aziz, K.; Cheng, A.; Hazinski, M.F.; Hoover, A.V.; Mahgoub, M.; Panchal, A.R.; Sasson, C.; Topjian, A.A.; Rodriguez, A.J.; et al. Part 2: Evidence Evaluation and Guidelines Development: 2020 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation 2020, 142 (Suppl. S2), S358–S365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, G.L. Treatment of local anesthetic systemic toxicity (LAST). Reg. Anesth. Pain. Med. 2010, 35, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchal, A.R.; Bartos, J.A.; Cabañas, J.G.; Donnino, M.W.; Drennan, I.R.; Hirsch, K.G.; Kudenchuk, P.J.; Kurz, M.C.; Lavonas, E.J.; Morley, P.T.; et al. Adult Basic and Advanced Life Support Writing Group. Part 3: Adult Basic and Advanced Life Support: 2020 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation 2020, 142 (Suppl. S2), S366–S468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoegberg, L.C.; Bania, T.C.; Lavergne, V.; Bailey, B.; Turgeon, A.F.; Thomas, S.H.; Morris, M.; Miller-Nesbitt, A.; Mégarbane, B.; Magder, S.; et al. Lipid Emulsion Workgroup. Systematic review of the effect of intravenous lipid emulsion therapy for local anesthetic toxicity. Clin. Toxical. 2016, 54, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, W.B.; Rosenblum, S.; Grady, I.P. Successful resuscitation of bupivacaine-induced cardiac arrest using cardiopulmonary bypass. Anesth. Analg. 1989, 69, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltesz, E.G.; van Pelt, F.; Byrne, J.G. Emergent cardiopulmonary bypass for bupivacaine cardiotoxicity. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2003, 17, 357–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, K.S.; Høgberg, L.C.G.; Christensen, M.B.; Petersen, T.S.; Dalhoff, K.; Bøgevig, S. [Local anaesthetic systemic toxicity]. Ugeskr. Laeger 2020, 182, V11190656. (In Danish) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Neal, J.M.; Barrington, M.J.; Fettiplace, M.R.; Gitman, M.; Memtsoudis, S.G.; Mörwald, E.E.; Rubin, D.S.; Weinberg, G. The Third American Society of Regional Anesthesia and Pain Medicine Practice Advisory on Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity: Executive Summary 2017. Reg. Anesth. Pain Med. 2018, 43, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, B.; Silverton, N.; Katz, M.; Heath, E.; Bull, D.A.; Harig, J.; Tonna, J.E. Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity Induced Cardiac Arrest After Topicalization for Transesophageal Echocardiography and Subsequent Treatment With Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2019, 33, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, H.M.D.; Archer, J.R.H.; Dargan, P.I.; Wood, D.M. What are the adverse effects associated with the combined use of intravenous lipid emulsion and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in the poisoned patient? Clin. Toxicol. 2015, 53, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, D.E.; Stecco, C.; Porzionato, A.; Mangino, D.; Macchi, V.; De Caro, R.; Pirri, C. Ibrutinib-Induced Ventricular Electrical Storm Successfully Managed with Veno-Arterial ECMO and Intralipid Administration: A Rare Case Report. Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2024, 27, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Baud, F.J.; Megarbane, B.; Deye, N.; Leprince, P. Clinical review: Aggressive management and extracorporeal support for drug-induced cardiotoxicity. Crit. Care 2007, 11, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Conte, G.; Sieira, J.; Sarkozy, A.; de Asmundis, C.; Di Giovanni, G.; Chierchia, G.B.; Ciconte, G.; Levinstein, M.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Baltogiannis, G.; et al. Life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias during ajmaline challenge in patients with Brugada syndrome: Incidence, clinical features, and prognosis. Heart Rhythm. 2013, 10, 1869–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradberry, S.M.; Thanacoody, H.K.; Watt, B.E.; Thomas, S.H.; Vale, J.A. Management of the cardiovascular complications of tricyclic antidepressant poisoning: Role of sodium bicarbonate. Toxicol. Rev. 2005, 24, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foianini, A.; Joseph Wiegand, T.; Benowitz, N. What is the role of lidocaine or phenytoin in tricyclic antidepressant-induced cardiotoxicity? Clin. Toxical. 2010, 48, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagerman, G.A.; Hanashiro, P.K. Reversal of tricyclic-antidepressant-induced cardiac conduction abnormalities by phenytoin. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1981, 10, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angel-Isaza, A.M.; Bustamante-Cristancho, L.A.; Uribe-B, F.L. Successful Outcome Following Intravenous Lipid Emulsion Rescue Therapy in a Patient with Cardiac Arrest Due to Amitriptyline Overdose. Am. J. Case Rep. 2020, 21, e922206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Le Fevre, P.; Gosling, M.; Acharya, K.; Georgiou, A. Dramatic resuscitation with Intralipid in an epinephrine unresponsive cardiac arrest following overdose of amitriptyline and propranolol. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr2016218281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Williams, J.M.; Hollingshed, M.J.; Vasilakis, A.; Morales, M.; Prescott, J.E.; Graeber, G.M. Extracorporeal circulation in the management of severe tricyclic antidepressant overdose. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 1994, 12, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikejiri, K.; Akama, Y.; Ieki, Y.; Kawamoto, E.; Suzuki, K.; Yokoyama, K.; Ishikura, K.; Imai, H. Veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and targeted temperature management in tricyclic antidepressant-induced cardiac arrest: A case report and literature review. Medicine 2021, 100, e24980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hoffmann, M.; Akbas, S.; Kindler, R.; Bettex, D. Successful use of extracorporeal life support and hemadsorption in the context of venlafaxine intoxication requiring cardiopulmonary resuscitation: A case report. J. Artif. Organs 2024, 27, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Refstad, S. Paramethoxyamphetamine (PMA) poisoning; a ‘party drug’ with lethal effects. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 2003, 47, 1298–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potocka-Banaś, B.; Janus, T.; Majdanik, S.; Banaś, T.; Dembińska, T.; Borowiak, K. Fatal Intoxication with α-PVP, a Synthetic Cathinone Derivative. J. Forensic Sci. 2017, 62, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packe, G.E.; Garton, M.J.; Jennings, K. Acute myocardial infarction caused by intravenous amphetamine abuse. Br. Heart J. 1990, 64, 23–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hong, R.; Matsuyama, E.; Nur, K. Cardiomyopathy associated with the smoking of crystal methamphetamine. JAMA 1991, 265, 1152–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotinet, P.A.; Bizouarn, P.; Roux, F.; Rozec, B. Management of cardiogenic shock by circulatory support during reverse Tako-Tsubo following amphetamine exposure: A report of two cases. Heart Lung 2021, 50, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, C.Y.L.; Taylor, D.M.; Knott, J.C.; Taylor, S.E.; Phillips, G.A.; Karro, J.; Chan, E.W.; Kong, D.C.M.; Castle, D.J. Intravenous midazolam-droperidol combination, droperidol or olanzapine monotherapy for methamphetamine-related acute agitation: Subgroup analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Addiction 2017, 112, 1262–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derlet, R.W.; Albertson, T.E.; Rice, P. Antagonism of cocaine, amphetamine, and methamphetamine toxicity. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1990, 36, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, M.; Tang, H.; Feng, M.; Kou, B.; Zhu, N.; Liao, F.; Wu, L. Effects of endovascular and surface cooling on resuscitation in patients with cardiac arrest and a comparison of effectiveness, stability, and safety: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Richards, J.R.; Albertson, T.E.; Derlet, R.W.; Lange, R.A.; Olson, K.R.; Horowitz, B.Z. Treatment of toxicity from amphetamines, related derivatives, and analogues: A systematic clinical review. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015, 150, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, L.K.; Kromm, J.; Gaudet, J.; Zuege, D.; Button, B.; Warshawski, F.; Lucyk, S.N. Rescue extracorporeal membrane oxygenation therapy in methamphetamine toxicity. CJEM 2018, 20 (Suppl. S2), S14–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Abri, S.; Meier, K.H.; Colby, J.M.; Smollin, C.G.; Benowitz, N.L. Cardiogenic shock after use of fluoroamphetamine confirmed with serum and urine levels. Clin. Toxical. 2014, 52, 1292–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimm, J.C.; Balsara, K.R.; Kemp, C.D.; Miller, J.; Myers, M.; Schulman, S.P.; Sciortino, C.M. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for profound cardiogenic shock due to cocaine toxicity. J. Cardiol. Cases 2014, 11, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- De Vroey, F.; Plein, D.; Vercauteren, S.; Castadot, M.; Bettendorf, P. Rescue extracorporeal circulation as bridge to recovery in fulminant cocaine-induced heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2009, 133, e111–e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oredegbe, A.A.; Awad, M. Catecholamine Mega Storm Triggered by Cocaine Use and Thyrotoxicosis Crisis. Cureus 2023, 15, e38299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schreiber, N.; Manninger, M.; Pätzold, S.; Reisinger, A.C.; Hatzl, S.; Hackl, G.; Högenauer, C.; Eller, P. Cardiogenic shock due to yew poisoning rescued by VA-ECMO: Case report and literature review. Channels 2022, 16, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Daniels, Z.; Hays, H.; Carrillo, S.; Kamp, A.; Gauntt, J. Pediatric extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation for yew cardiotoxicity. Perfusion 2024, 39, 1743–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, G.; Rangasamy, A.; Kumar, D.; Varadharajan, R.; Ramalingam, G. Emergency Resuscitation Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ER ECMO) in 60 Saves Life. J. Emergencies Trauma. Shock. 2023, 16, 66–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, J.P.; Huang, D.C.; Jin, W.Y.; Xie, Q.H.; Zhu, W.L.; Tung, T.H.; Ying, A.F. Venous-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support for patients poisoned by Macleaya cordata. Perfusion 2023, 38, 1751–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, H.; Fukushima, H.; Nakatsukasa, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Kaizaki-Mitsumoto, A.; Numazawa, S.; Kamijo, Y. Fatal poisoning due to ingestion of boiled oleander leaf extract. J. Forensic Sci. 2024, 69, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundhawa, G.; Ali, M.; Jacob, R.; Obeng-Gyimah, E.; Vranian, M.N. Case report of entrectinib associated fulminant myocarditis. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2024, 9, ytae650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rateesh, S.; Shekar, K.; Naidoo, R.; Mittal, D.; Bhaskar, B. Use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for mechanical circulatory support in a patient with 5-fluorouracil induced acute heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2015, 8, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shah, S.; Haeger-Overstreet, K.; Flynn, B. Methotrexate-induced acute cardiotoxicity requiring veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2022, 16, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, Y.; Cao, C.; Luo, X.; Huang, L. Successful treatment of severe myocardial injury complicated with refractory cardiogenic shock caused by AOPP using extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A case report. Medicine 2021, 100, e26318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lorusso, R.; Shekar, K.; MacLaren, G.; Schmidt, M.; Pellegrino, V.; Meyns, B.; Haft, J.; Vercaemst, L.; Pappalardo, F.; Bermudez, C.; et al. ELSO Interim Guidelines for Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Adult Cardiac Patients. ASAIO J. 2021, 67, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorusso, R. Predictors of survival in VA-ECMO: Whom should we cannulate? Qatar Med. J. 2017, 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, B.J.; McKenna, W.J.; Danielson, G.K.; Kappenberger, L.J.; Kuhn, H.J.; Seidman, C.E.; Torbicki, A. American College of Cardiology/European Society of Cardiology clinical expert consensus document on hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: A report of the American College of Cardiology foundation task force on clinical expert consensus documents and the European Society of Cardiology committee for practice guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 1687–1713. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marasco, S.F.; Vale, M.; Pellegrino, V.; Preovolos, A.; Leet, A.; Kras, A.; Schulberg, E.; Bergin, P.; Esmore, D.S. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in primary graft failure after heart transplantation. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2010, 90, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napp, L.C.; Kühn, C.; Bauersachs, J. ECMO in cardiac arrest and cardiogenic shock. Herz 2017, 42, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schmidt, M.; Burrell, A.; Roberts, L.; Bailey, M.; Sheldrake, J.; Rycus, P.T.; Hodgson, C.; Scheinkestel, C.; Cooper, D.J.; Thiagarajan, R.R.; et al. Predicting survival after ECMO for refractory cardiogenic shock: The survival after veno-arterial-ECMO (SAVE)-score. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 2246–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzi, M.; Buzzi, R.; Hayek, A.; Portran, P.; Schweizer, R.; Fellahi, J.L.; Armoiry, X.; Flagiello, M.; Grinberg, D.; Obadia, J.F. Veno-arterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for drug intoxications: A single center, 14-year experience. J. Card. Surg. 2022, 37, 1512–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunet, J.; Valette, X.; Ivascau, C.; Lehoux, P.; Sauneuf, B.; Dalibert, Y.; Masson, R.; Sabatier, R.; Buklas, D.; Seguin, A.; et al. Extracorporeal Life Support for Refractory Cardiac Arrest or Shock: A 10-Year Study. ASAIO J. 2015, 61, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavonas, E.J.; Akpunonu, P.D.; Arens, A.M.; Babu, K.M.; Cao, D.; Hoffman, R.S.; Hoyte, C.O.; Mazer-Amirshahi, M.E.; Stolbach, A.; St-Onge, M.; et al. 2023 American Heart Association Focused Update on the Management of Patients With Cardiac Arrest or Life-Threatening Toxicity Due to Poisoning: An Update to the American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation 2023, 148, e149–e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.S.; Levitan, R.; Wiegand, T.J.; Lowry, J.; Schult, R.F.; Yin, S. Toxicology Investigators Consortium. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) for Severe Toxicological Exposures: Review of the Toxicology Investigators Consortium (ToxIC). J. Med. Toxicol. 2016, 12, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzi, M.; Koffel, C.; Djaref, C.; Grinberg, D.; Fellahi, J.L.; Hugon-Vallet, E.; Prieur, C.; Robin, J.; Obadia, J.F. High rate of arterial complications in patients supported with extracorporeal life support for drug intoxication-induced refractory cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kato, Y.; Kuriyama, A.; Hata, R.; Ikegami, T. Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for Hypokalemia and Refractory Ventricular Fibrillation Associated with Caffeine Intoxication. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 58, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labarinas, S.; Meulmester, K.; Greene, S.; Thomas, J.; Virk, M.; Erkonen, G. Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation After Diphenhydramine Ingestion. J. Med. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mehrpour, O.; Asadi, S.; Yaghoubi, M.A.; Azdaki, N.; Mahmoodabadi, N.; Javadmoosavi, S. Cardiogenic Shock Due to Aluminum Phosphide Poisoning Treated with Intra-aortic Balloon Pump: A Report of Two Cases. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2019, 19, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandran, K.; Quimby, D., Jr.; Bezerra, H.G.; Crousillat, D. Early use of intrapartum intra-aortic balloon pump support for haemodynamic stabilization of peripartum and anthracycline-induced cardiomyopathy: A case report. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2024, 8, ytae033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bagheri-Moghaddam, A.; Abbaspour, H.; Tajoddini, S.; Mohammadzadeh, V.; Moinipour, A.; Dadpour, B. Using Intra-Aortic Balloon Pump for Management of Cardiogenic Shock Following Aluminum Phosphide Poisoning; Report of 3 Cases. Emerg. 2018, 6, e3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sundaravel, S.; Alrifai, A.; Kabach, M.; Ghumman, W. FOLFOX Induced Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy Treated with Impella Assist Device. Case Rep. Cardiol. 2017, 2017, 8507096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Khaliel, F.; Moss, E.; Demers, P.; Bouchard, D. A bailout approach: Transaxillary Impella implantation in toxic cardiomyopathy. Asian Cardiovasc. Thorac. Ann. 2014, 22, 722–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanoverbeke, L.; Wouter, H.; François, D.; Ivan, E. Cardiogenic shock after 5-fluorouracil administration: A case report and literature review. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2023, 7, ytad596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cicci, J.D.; Jagielski, S.M.; Clarke, M.M.; Rayson, R.A.; Cavender, M.A. Loperamide overdose causing torsades de pointes and requiring Impella temporary mechanical support: A case report. Eur. Heart J. Case Rep. 2019, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| Toxic Agent | Indication Criteria for ECMO | Reported Survival Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Beta blockers | Persistent cardiogenic shock despite maximal inotropic and vasopressor support or evolution to cardiac arrest | 63.6% [7] |
| Calcium channel blockers | Persistent cardiogenic shock despite maximal inotropic and vasopressor support or evolution to cardiac arrest | 84.6% [8] |
| Local anesthetics | Persistent cardiogenic shock despite maximal inotropic and vasopressor support or evolution to cardiac arrest due to local anesthetic systemic toxicity (LAST) unresponsive to conventional resuscitation and lipid emulsion therapy | Survival reported in case series and isolated reports; exact rate not quantifiable due to rarity of cases |
| Sodium channel blockers | Persistent cardiogenic shock despite maximal inotropic and vasopressor support or evolution to cardiac arrest | Survival reported in case series and isolated reports; exact rate not quantifiable due to rarity of cases |
| Sympathomimetics | Cardiac arrest unresponsive to advanced resuscitation | Favorable outcomes in isolated cases; no consistent survival rate reported. |
| Other cardiotoxic drugs | Persistent cardiogenic shock despite maximal inotropic and vasopressor support or evolution to cardiac arrest | Favorable outcomes in isolated cases; no consistent survival rate reported. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torre, D.E.; Mangino, D.; Pirri, C. Veno-Arterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Cardiotoxic Drug-Induced Cardiogenic Shock: A Systematic Narrative Review. Life 2025, 15, 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060925
Torre DE, Mangino D, Pirri C. Veno-Arterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Cardiotoxic Drug-Induced Cardiogenic Shock: A Systematic Narrative Review. Life. 2025; 15(6):925. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060925
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorre, Debora Emanuela, Domenico Mangino, and Carmelo Pirri. 2025. "Veno-Arterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Cardiotoxic Drug-Induced Cardiogenic Shock: A Systematic Narrative Review" Life 15, no. 6: 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060925
APA StyleTorre, D. E., Mangino, D., & Pirri, C. (2025). Veno-Arterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Cardiotoxic Drug-Induced Cardiogenic Shock: A Systematic Narrative Review. Life, 15(6), 925. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15060925










