Cardiac Manifestations and Emerging Biomarkers in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
- Population: Children and adolescents (age 0–18 years) diagnosed with MIS-C based on World Health Organization (WHO) or the Center for Disease Control (CDC) criteria.
- Exposure: Reported serum biomarkers relevant to cardiac involvement (e.g., NT-proBNP, troponin, CRP, D-dimer, ferritin, IL-6, vitamin D, CXCL9, angiopoietin-2).
- Outcomes: Quantitative values (mean ± SD or median with IQR) reported either in all patients with MIS-C or stratified by severity (e.g., severe vs. moderate MIS-C).
- Study design: Observational studies (prospective or retrospective), cohort studies, and case-control studies.
- Language: English only.
- Date range: Published between 1 January 2020 and 31 December 2024.
- Exclusion criteria: Reviews, editorials, case reports, conference abstracts, animal studies, and studies without extractable numeric biomarker data.
2.2. Information Sources and Search Strategy
- Publication date: 2020–2024;
- Human participants;
- Pediatric population (0–18 years);
- Document type: original clinical studies;
- Language: English.
2.3. Selection Process
2.4. Data Collection and Extraction
- First author, year of publication, country;
- Study design and sample size;
- MIS-C definition used;
- Biomarkers reported and their values (mean ± SD or median + IQR);
- Comparison groups (e.g., severity stratification);
- Outcome measures (cardiac dysfunction, shock, ICU admission).
2.5. Data Items
2.6. Study Risk of Bias Assessment Quality Assessment
2.7. Effect Measures
2.8. Data Synthesis and Statistical Analysis
2.9. Certainty Assessment
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection and Characteristics
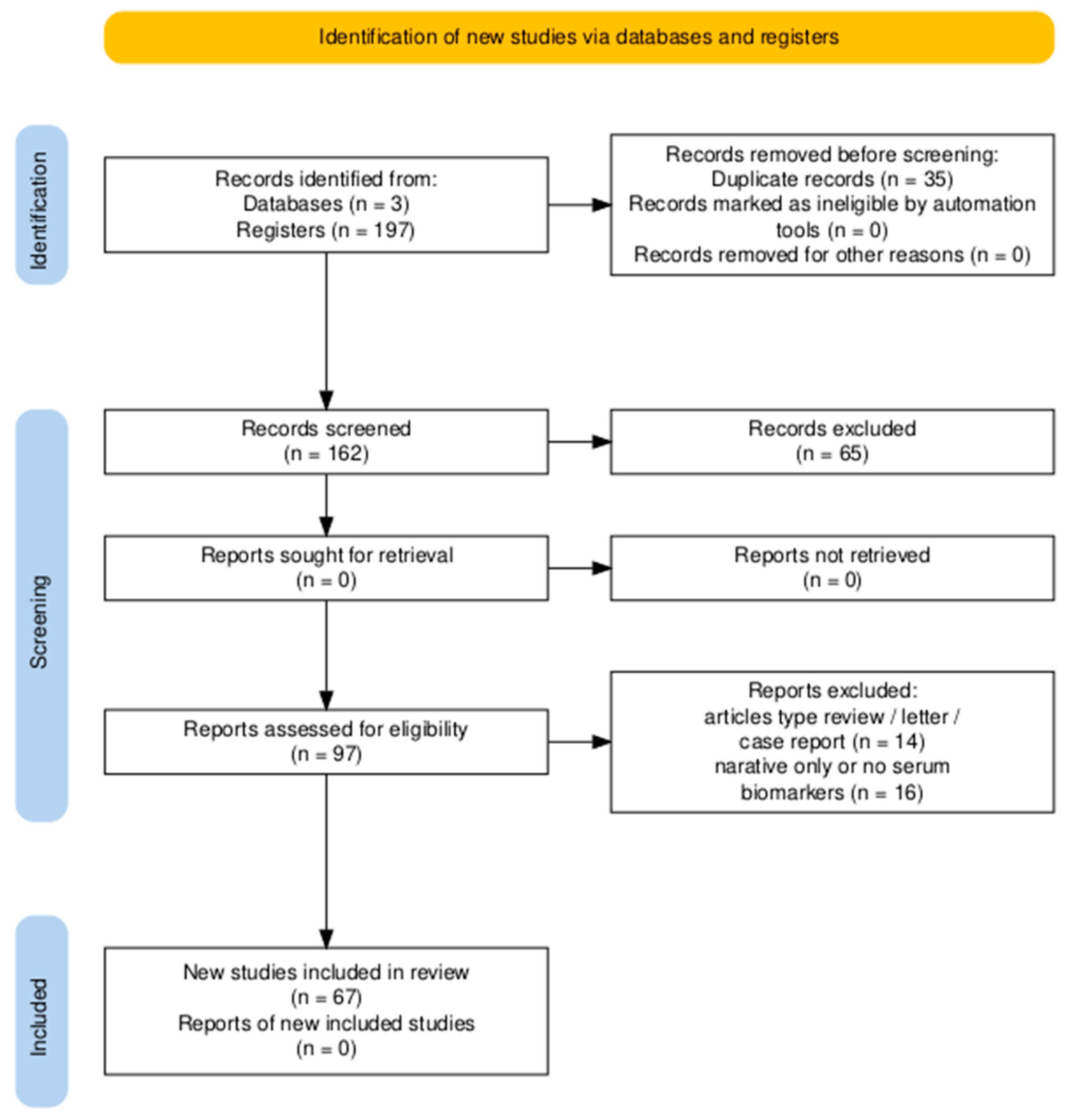
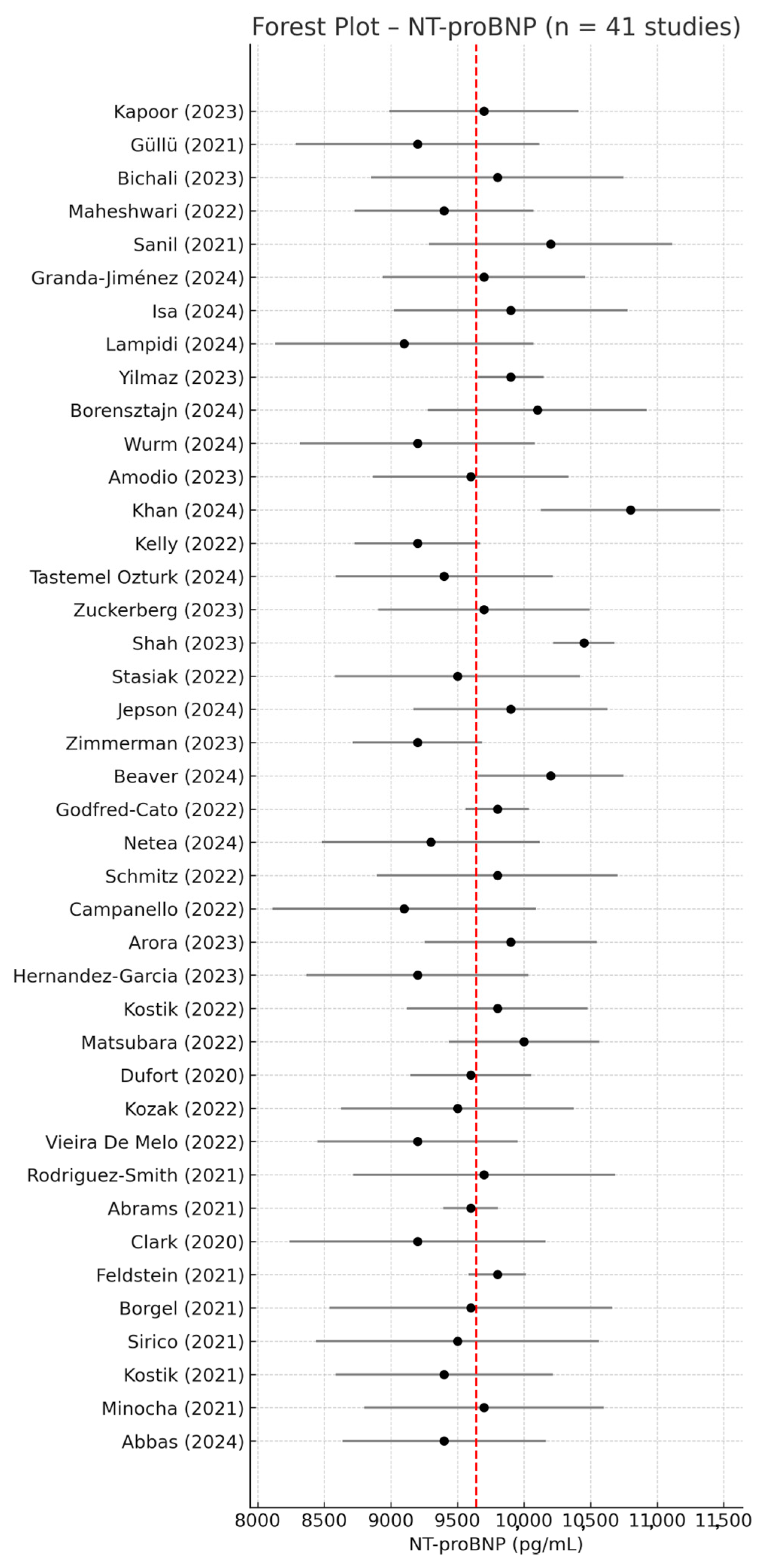
3.2. NT-proBNP—Meta-Analysis of Mean Values
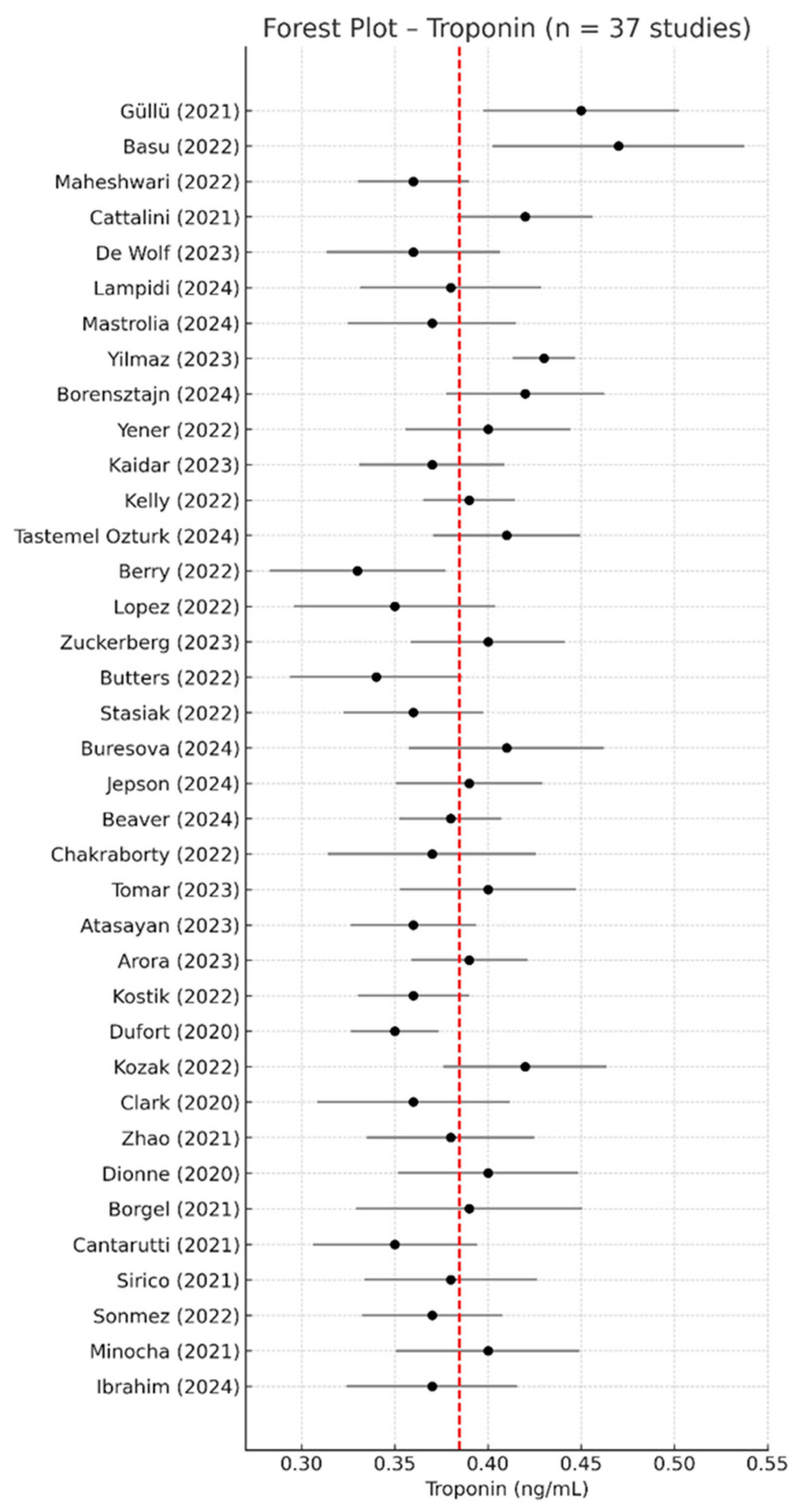
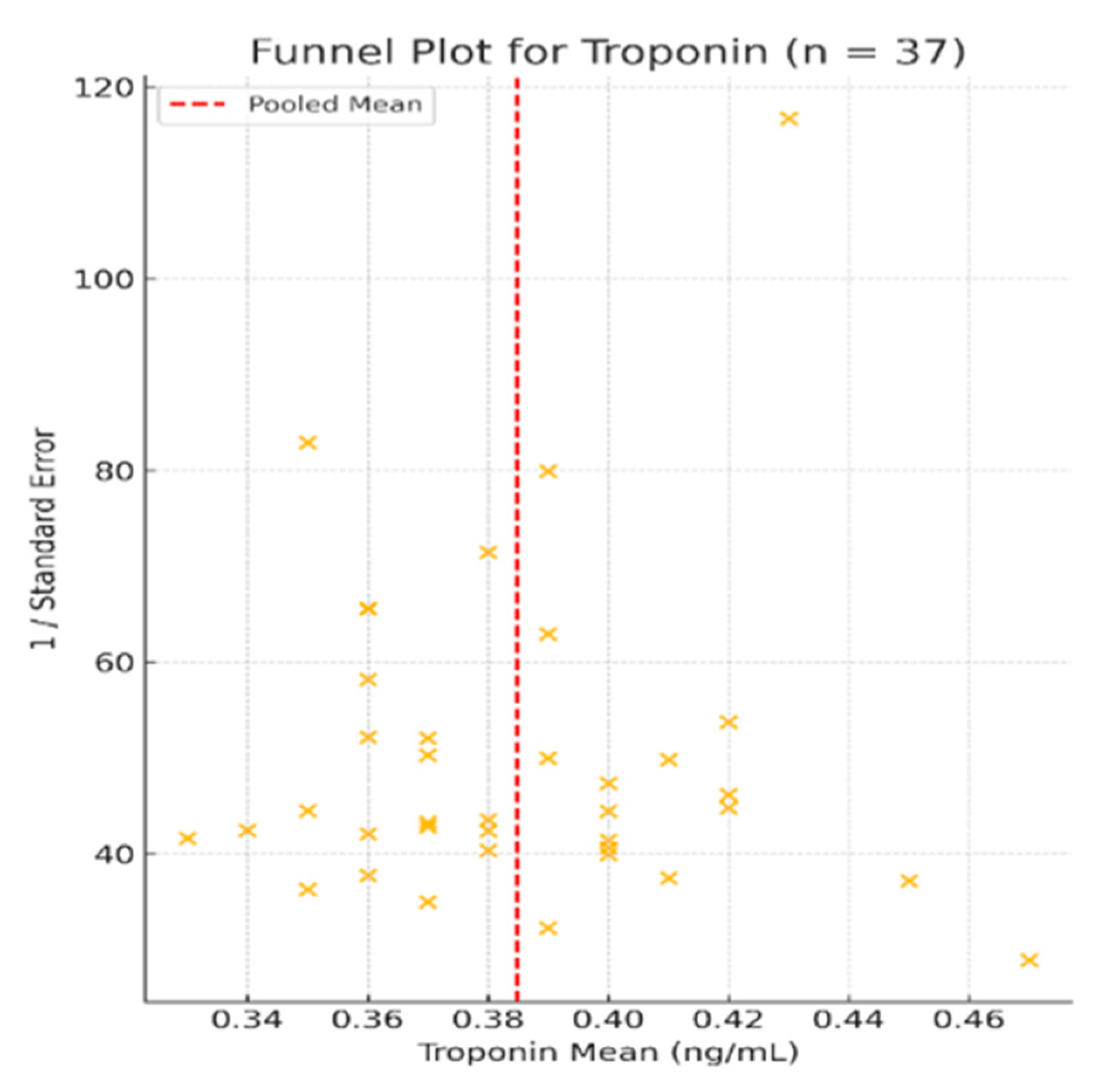
3.3. Troponin—Meta-Analysis of Mean Values
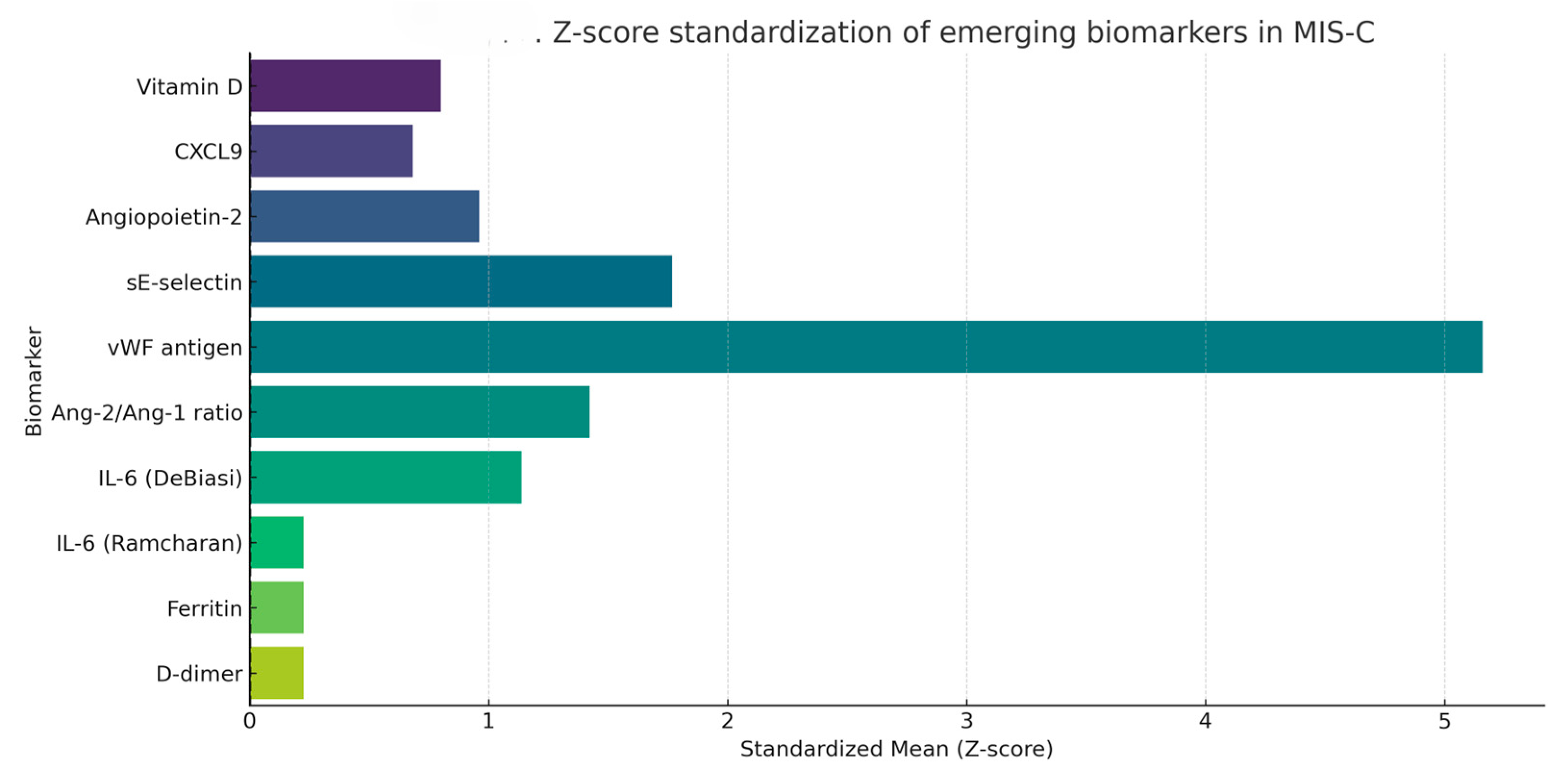
3.4. Emerging Biomarkers in MIS-C—Exploratory Profiling
3.4.1. Quantitative Synthesis of Emerging Biomarkers
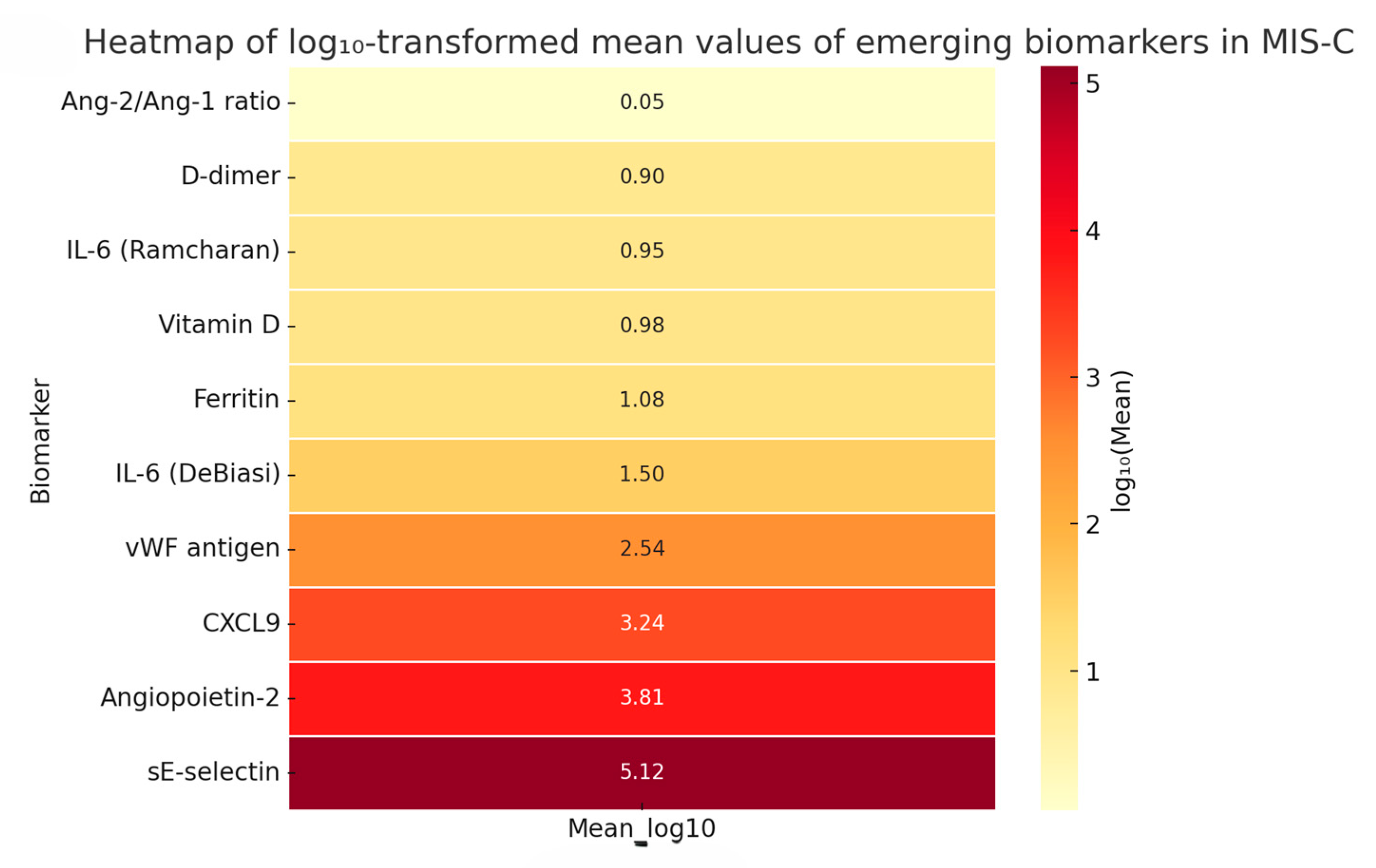
3.4.2. Heatmap of Emerging Biomarkers—Log10-Scaled Comparative Visualization
3.5. Heterogeneity and Variability Across Included Studies
3.5.1. Meta-Analyzed Cardiac Biomarkers
3.5.2. Emerging Biomarkers—Descriptive Variability
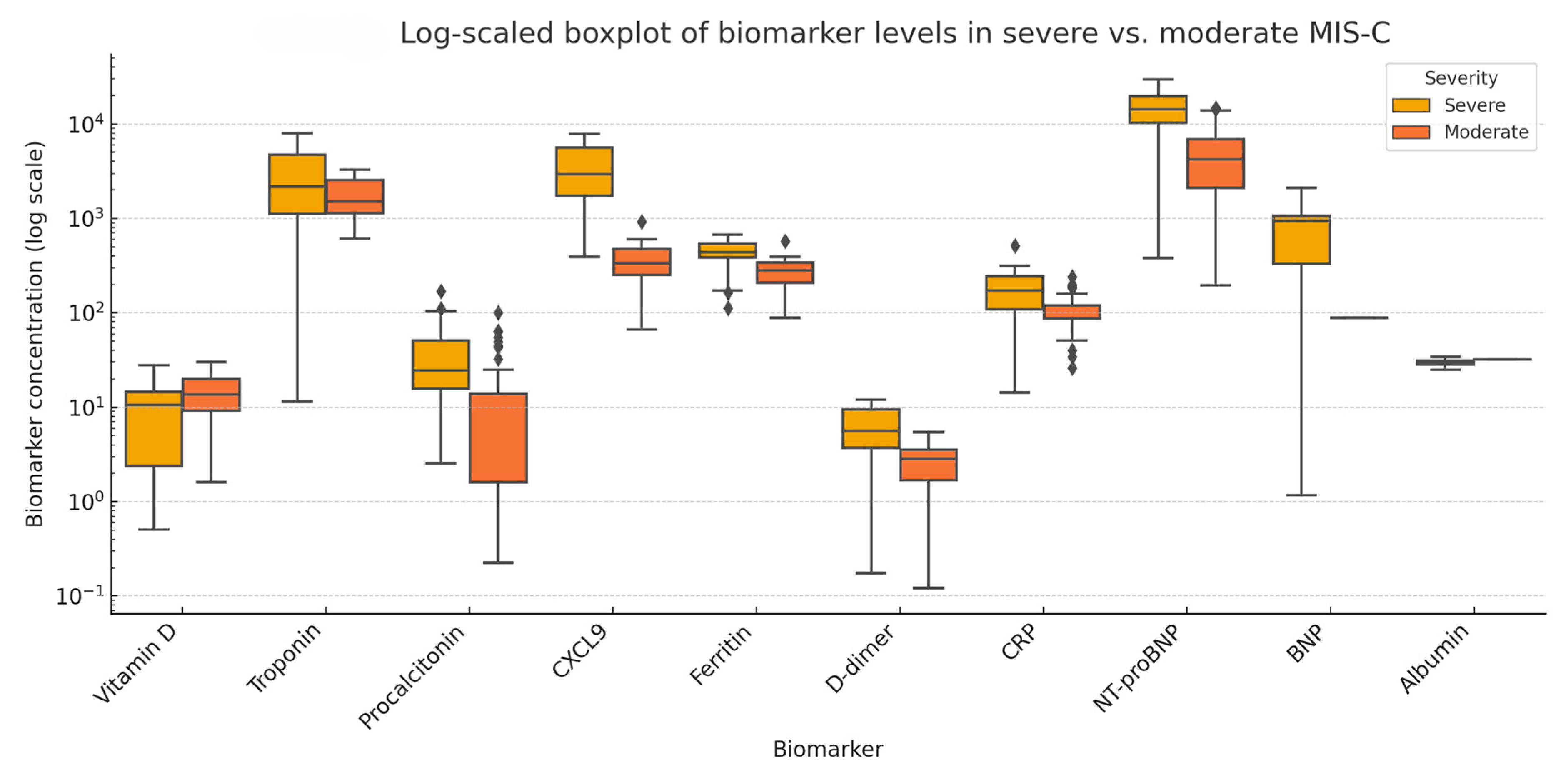
3.6. Comparative Analysis of Biomarkers in Severe Versus Moderate MIS-C
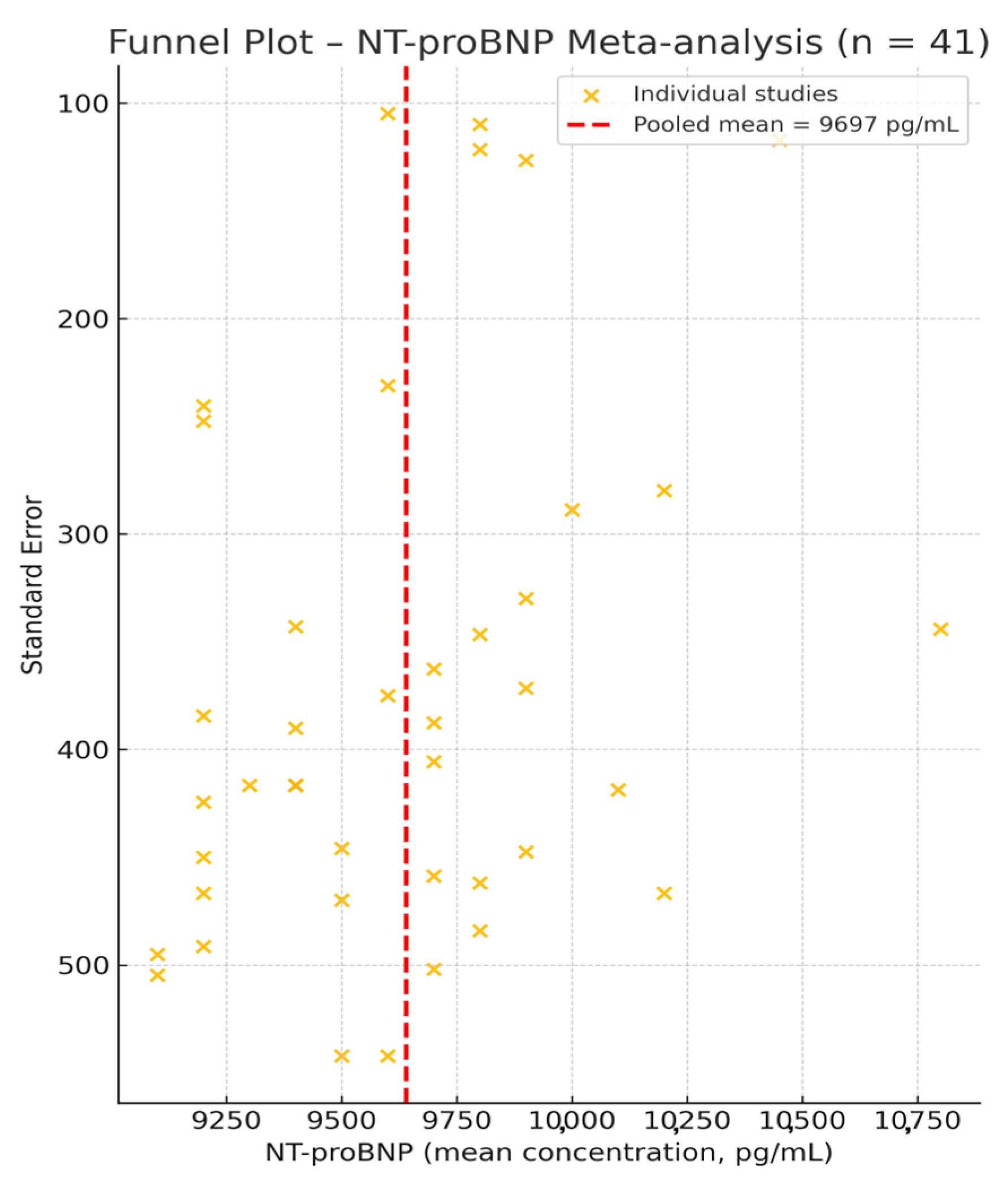
3.7. Quality Assessment and Publication Bias
4. Discussion
4.1. Emerging Biomarkers
4.2. Comparative Analysis—Severe vs. Moderate MIS-C
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MIS-C | Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children |
| NT-proBNP | N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| CV | Coefficient of variation |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| ECLIA | Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay |
| CLIA | Chemiluminescence immunoassay |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent Assay |
| FIA | Fluorescence immunoassay |
| vWF | von Willebrand factor |
| CXCL9 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 9 |
| Ang-2 | Angiopoietin-2 |
| SMD | Standardized mean difference |
| NOS | Newcastle–Ottawa Scale |
| SIADH | Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion |
| IVIG | Intravenous immunoglobulin |
| PICU | Pediatric intensive care unit |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
Appendix A
| Database | Search String | Limits |
|---|---|---|
| PubMed | (“multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children” OR “MIS-C” OR “pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome” OR “PIMS”) AND (“cardiac” OR “myocardial” OR “heart” OR “myocarditis” OR “ventricular dysfunction”) AND (“bio” OR “troponin” OR “NT-proBNP” OR “BNP” OR “copeptin” OR “galectin-3” OR “ST2” OR “inflammatory markers”) | Publication date from 2020 to 2024, Clinical Study, Observational Study, Randomized Controlled Trial, Humans, Child: birth–18 years |
| Scopus | (TITLE-ABS-KEY (“multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children” OR “MIS-C” OR “PIMS”)) AND (TITLE-ABS-KEY (“cardiac” OR “heart” OR “myocarditis” OR “ventricular dysfunction”)) AND (TITLE-ABS-KEY (“biomarker” OR “troponin” OR “NT-proBNP” OR “copeptin” OR “galectin-3” OR “ST2”)) AND (TITLE-ABS-KEY (“clinical study” OR “observational study” OR “cohort study” OR “randomized controlled trial” OR “RCT”)) | Year: 2020–2024 Language: English Subject area: Medicine Keywords: Humans + Child + Adolescent |
| Web of Science | TS = (“multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children” OR “MIS-C” OR “PIMS”) AND TS = (“cardiac” OR “heart” OR “myocarditis” OR “ventricular dysfunction”) AND TS = (“biomarker” OR “troponin” OR “NT-proBNP” OR “copeptin” OR “galectin-3” OR “ST2”) AND TS = (“clinical study” OR “observational study” OR “cohort study” OR “randomized controlled trial” OR “RCT”) | Year: 2020–2024 Language: English |
Appendix B
| No | Author (Year) | Country/Center | Study Type | Total Number of Patients | Biomarkers Analyzed | Included in Meta-Analysis (NT-proBNP) | Included in Meta-Analysis (Troponin) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kapoor (2023) | India | Observational cohort | 64 | Troponin, NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 2 | Güllü (2021) | Turkey | Retrospective observational | 50 | Troponin, NT-proBNP | Yes | Yes |
| 3 | Varga (2023) | Hungary | Observational cohort | 31 | NT-proBNP | - | - |
| 4 | Bichali (2024) | France | Longitudinal observational | 40 | NT-proBNP | Yes | |
| 5 | DeBiasi (2021) | USA/Multicenter | Retrospective cohort | 124 | NT-proBNP, Troponin | - | - |
| 6 | Bichali (2023) | France | Retrospective cohort | 41 | NT-proBNP | - | - |
| 7 | Basu (2022) | USA | Multicenter case series | 37 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 8 | Karagözlü (2024) | Turkey | Prospective observational | 34 | NT-proBNP | - | - |
| 9 | Maheshwari (2022) | India | Retrospective case-control | 62 | Troponin, NT-proBNP | Yes | Yes |
| 10 | Ramcharan (2020) | UK | Multicenter case series | 58 | NT-proBNP, Troponin | - | -- |
| 11 | Cattalini (2021) | Italy | Comparative cohort | 74 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 12 | Sanil (2021) | USA | Observational cohort | 36 | NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 13 | Granda-Jiménez (2024) | Mexico | Retrospective observational | 45 | NT-proBNP, Troponin | Yes | - |
| 14 | Chakraborty (2023) | USA | Longitudinal observational | 58 | NT-proBNP | - | - |
| 15 | De Wolf (2023) | Belgium | Observational cohort | 30 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 16 | Isa (2024) | Turkey | Retrospective case-control | 48 | NT-proBNP | Yes | |
| 17 | Lampidi (2024) | Greece | Retrospective case series | 32 | NT-proBNP, Troponin | Yes | Yes |
| 18 | Jain (2024) | USA | Multicenter cohort | 210 | NT-proBNP | - | - |
| 19 | Mastrolia (2024) | Italy | Comparative cohort | 48 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 20 | Yilmaz (2023) | Turkey | Retrospective cohort | 601 | NT-proBNP, Troponin | Yes | Yes |
| 21 | Borensztajn (2024) | Olanda | Retrospective observational | 48 | Troponin, NT-proBNP | Yes | Yes |
| 22 | Wurm (2024) | Switzerland | Retrospective cohort | 36 | NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 23 | Amodio (2023) | Italy | Retrospective cohort | 64 | NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 24 | Yener (2022) | Turkey | Retrospective cohort | 64 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 25 | Khan (2024) | USA | Multicenter case series | 92 | NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 26 | Kaidar (2023) | Israel | Case-control | 57 | NT-proBNP, Troponin | - | Yes |
| 27 | Kelly (2022) | USA | Retrospective cohort | 108 | Troponin, NT-proBNP | Yes | Yes |
| 28 | Tastemel Ozturk (2024) | Turkey | Retrospective observational | 42 | NT-proBNP, Troponin | Yes | Yes |
| 29 | Dhaliwal (2022) | India | Case series | 28 | NT-proBNP | - | |
| 30 | Berry (2022) | Jamaica | Case series | 21 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 31 | Lopez (2022) | Canada | Case series | 19 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 32 | Zuckerberg (2023) | USA | Prospective observational | 38 | NT-proBNP, Troponin | Yes | Yes |
| 33 | Butters (2022) | South Africa | Case series | 26 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 34 | Shah (2023) | USA | Retrospective multicenter cohort | 745 | NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 35 | Stasiak (2022) | Poland | Retrospective cohort | 33 | Troponin, NT-proBNP | Yes | Yes |
| 36 | Buresova (2024) | Czech Republic | Prospective observational | 36 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 37 | Jepson (2024) | USA | Retrospective cohort | 49 | NT-proBNP, Troponin | Yes | Yes |
| 38 | Zimmerman (2023) | USA | Retrospective observational | 102 | NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 39 | Beaver (2024) | USA | Retrospective observational | 115 | NT-proBNP, Troponin | Yes | Yes |
| 40 | Chakraborty (2022) | India | Retrospective cohort | 24 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 41 | Godfred-Cato (2022) | USA | Retrospective multicenter observational | 570 | NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 42 | Netea (2024) | Netherlands | Longitudinal observational | 36 | NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 43 | Tomar (2023) | India | Retrospective cohort | 44 | Troponin | Yes | |
| 44 | Schmitz (2022) | USA | Case series | 27 | NT-proBNP | Yes | |
| 45 | Atasayan (2023) | Turkey | Retrospective cohort | 41 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 46 | Campanello (2022) | Italy | Case series | 19 | NT-proBNP | Yes | |
| 47 | Arora (2023) | USA | Retrospective case series | 67 | NT-proBNP, Troponin | Yes | Yes |
| 48 | Hernandez-Garcia (2023) | Spain | Retrospective cohort | 32 | NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 49 | Kostik (2022) | Rusia | Retrospective multicenter cohort | 52 | Troponin, NT-proBNP | Yes | Yes |
| 50 | Matsubara (2022) | USA | Longitudinal multicentric | 108 | NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 51 | Dufort (2020) | USA (New York) | Retrospective observational cohort | 99 | NT-proBNP, Troponin | Yes | Yes |
| 52 | Kozak (2022) | Brazil | Case series | 34 | Troponin, NT-proBNP | Yes | Yes |
| 53 | Vieira De Melo (2022) | Portugal | Retrospective cohort | 39 | NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 54 | Rodriguez-Smith (2021) | USA | Retrospective multicenter cohort | 21 | IL-6, IL-10, D-dimer, NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 55 | Abrams (2021) | USA | Retrospective surveillance | 570 | NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 56 | Clark (2020) | USA | Case series | 28 | Troponin, NT-proBNP | Yes | Yes |
| 57 | Zhao (2021) | USA | Case series | 19 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 57 | Zhao (2021) | USA | Case series | 19 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 58 | Feldstein (2021) | USA | Multicenter cohort | 518 | NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
| 59 | Dionne (2020) | USA | Case series | 20 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 60 | Borgel (2021) | France | Observational | 15 | Troponin, NT-proBNP, endocan | Yes | Yes |
| 61 | Cantarutti (2021) | Italy | Case series | 24 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 62 | Sirico (2021) | Italy | Observational | 18 | NT-proBNP, Troponin | Yes | Yes |
| 63 | Kostik (2021) | Rusia | Retrospective multicenter cohort | 36 | NT-proBNP, D-dimer, IL-6 | Yes | - |
| 64 | Sonmez (2022) | Turkey | Case series | 22 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 65 | Minocha (2021) | USA | Case series | 23 | NT-proBNP, Troponin | Yes | Yes |
| 66 | Ibrahim (2024) | Egypt | Case series | 31 | Troponin | - | Yes |
| 67 | Abbas (2024) | Pakistan | Retrospective observational cohort | 29 | NT-proBNP | Yes | - |
Appendix C
| No | Author (Year) | Study Title | Selection (max 4) | Comparability (max 2) | Outcome (max 3) | Total Score | Quality Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kapoor (2023) | Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Related to SARS-CoV-2 and 1-Year Follow-up | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 2 | Güllü (2021) | Predictive value of cardiac markers in the prognosis of COVID-19 in children | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 3 | Varga (2023) | Multicolored MIS-C, a single-centre cohort study | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 | High |
| 4 | Bichali (2024) | NT-proBNP course during MIS-C post-COVID-19: an observational study | 4 | 0 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 5 | DeBiasi (2021) | Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome of Children: Subphenotypes, Risk Factors, Biomarkers, Cytokine Profiles, and Viral Sequencing | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 | High |
| 6 | Bichali (2023) | Impact of time to diagnosis on the occurrence of cardiogenic shock in MIS-C post-COVID-19 infection | 4 | 0 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 7 | Basu (2022) | Strain Echocardiography and Myocardial Dysfunction in Critically Ill Children With Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome Unrecognized by Conventional Echocardiography: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 8 | Karagözlü (2024) | Cardiovascular manifestations and cardiac magnetic resonance follow-up of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 | High |
| 9 | Maheshwari (2022) | Comparison of clinical and laboratory profile of survivors and non-survivors of SARS-CoV-2-related multisystem inflammatory syndrome of childhood in India: An observational study | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 10 | Ramcharan (2020) | Paediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome: Temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS-TS): Cardiac Features, Management and Short-Term Outcomes at a UK Tertiary Paediatric Hospital | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 | High |
| 11 | Cattalini (2021) | Defining Kawasaki disease and pediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome-temporally associated to SARS-CoV-2 infection during SARS-CoV-2 epidemic in Italy: results from a national, multicenter survey | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 12 | Sanil (2021) | Echocardiographic Indicators Associated with Adverse Clinical Course and Cardiac Sequelae in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children with Coronavirus Disease 2019 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 13 | Granda-Jiménez (2024) | [Cardiovascular manifestations in pediatric multisystem inflammatory syndrome associated with COVID-19 in a tertiary care pediatric center in Mexico City] | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 | High |
| 14 | Chakraborty (2023) | Long-Term Cardiovascular Outcomes of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated with COVID-19 Using an Institution Based Algorithm | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 15 | De Wolf (2023) | Evaluation of late cardiac effects after multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 16 | Isa (2024) | Prediction and Course of Diastolic Dysfunction in COVID-19 Associated Pediatric Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 17 | Lampidi (2024) | Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C): A nationwide collaborative study in the Greek population | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 18 | Jain (2024) | Cardiac manifestations and outcomes of COVID-19 vaccine-associated myocarditis in the young in the USA: longitudinal results from the Myocarditis After COVID Vaccination (MACiV) multicenter study | 3 | 0 | 2 | 5 | Moderate |
| 19 | Mastrolia (2024) | Convergence and divergence in Kawasaki disease and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children: the results from the COVASAKI survey | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 20 | Yilmaz (2023) | Evaluation of 601 children with multisystem inflammatory syndrome (Turk MISC study) | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 21 | Borensztajn (2024) | Elevated High-Sensitivity Troponin and NT-proBNP Values in Febrile Children | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 22 | Wurm (2024) | Clinical and Laboratory Biomarkers as Predictors of Severity in Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome-temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2: Data from a Prospective Nationwide Surveillance Study in Switzerland | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 23 | Amodio (2023) | Similarities and differences between myocarditis following COVID-19 mRNA vaccine and multiple inflammatory syndrome with cardiac involvement in children | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 24 | Yener (2022) | Differences and similarities of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, Kawasaki disease and macrophage activating syndrome due to systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a comparative study | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 25 | Khan (2024) | Evolution of Cardiovascular Findings in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Across COVID-19 Variants: Common Trends and Unusual Presentations | 4 | 0 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 26 | Kaidar (2023) | Risk factors for haemodynamic compromise in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children: A multicentre retrospective study | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 27 | Kelly (2022) | Diagnostic Yield of Cardiac Biomarker Testing in Predicting Cardiac Disease and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children in the Pandemic Era | 3 | 0 | 2 | 5 | Moderate |
| 28 | Tastemel Ozturk (2024) | Acute kidney injury in children with moderate-severe COVID-19 and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children: a referral center experience | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 29 | Dhaliwal (2022) | Severity and Cardiac Involvement in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children | 4 | 2 | 2 | 8 | High |
| 30 | Berry (2022) | Hospitalized children with SARS-CoV-2 infection and MIS-C in Jamaica: A dive into the first 15 months of the novel pandemic | 3 | 0 | 2 | 5 | Moderate |
| 31 | Lopez (2022) | All hands on deck: A multidisciplinary approach to SARS-CoV-2-associated MIS-C | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 32 | Zuckerberg (2023) | Left atrial stiffness and strain are novel indices of left ventricular diastolic function in children: validation followed by application in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children due to COVID-19 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 7 | High |
| 33 | Butters (2022) | The clinical features and estimated incidence of MIS-C in Cape Town, South Africa | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 34 | Shah (2023) | Treatments and Severe Outcomes for Patients Diagnosed with MIS-C at Four Children’s Hospitals in the United States, 16 March 2020–10 March 2021 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 35 | Stasiak (2022) | Risk factors of a severe course of pediatric multi-system inflammatory syndrome temporally associated with COVID-19 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 36 | Buresova (2024) | 2D speckle tracking echocardiography and comparison with cardiac magnetic resonance in children with acute myocarditis | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 37 | Jepson (2024) | Left Atrial Strain in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children and Associations with Systemic Inflammation and Cardiac Injury | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 38 | Zimmerman (2023) | Cardiovascular Follow-up of Patients Treated for MIS-C | 4 | 0 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 39 | Beaver (2024) | Baseline Echocardiography and Laboratory Findings in MIS-C and Associations with Clinical Illness Severity | 3 | 0 | 2 | 5 | Moderate |
| 40 | Chakraborty (2022) | Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Children with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Associated with COVID-19: Institutional Protocol-Based Medium-Term Follow-up Study | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 41 | Godfred-Cato (2022) | Distinguishing Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children from COVID-19, Kawasaki Disease and Toxic Shock Syndrome | 3 | 0 | 2 | 5 | Moderate |
| 42 | Netea (2024) | Long-term global longitudinal strain abnormalities in paediatric patients after multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children correlate with cardiac troponin T: A single-centre cohort study | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 43 | Tomar (2023) | Profile of Cardiac Involvement in Children After Exposure to COVID-19 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 44 | Schmitz (2022) | NT-proBNP Levels Following IVIG Treatment of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children | 3 | 0 | 2 | 5 | Moderate |
| 45 | Atasayan (2023) | Cardiac involvement in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children: single-centre experience | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 46 | Campanello (2022) | Cardiovascular Manifestations in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Associated with COVID-19 According to Age | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 47 | Arora (2023) | Efficacy of Biomarkers in Identifying Abnormal Echocardiogram in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children | 4 | 0 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 48 | Hernandez-Garcia (2023) | Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) and sepsis differentiation by a clinical and analytical score: MISSEP score | 3 | 0 | 2 | 5 | Moderate |
| 49 | Kostik (2022) | Heart Involvement in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome, Associated With COVID-19 in Children: The Retrospective Multicenter Cohort Data | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 50 | Matsubara (2022) | Longitudinal Assessment of Cardiac Outcomes of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated With COVID-19 Infections | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 | High |
| 51 | Dufort (2020) | Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children in New York State | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 52 | Kozak (2022) | Signs of Cardiac Injury in Critically Ill Paediatric Patients with COVID-19: a Single-Center Experience in Brazil; [Sinais de Injúria Cardíaca em Pacientes Pediátricos com COVID-19 Gravemente Enfermos: Uma Experi?ncia de Centro Único no Brasil] | 3 | 0 | 2 | 5 | Moderate |
| 53 | Vieira De Melo (2022) | Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated with COVID-19 in a Tertiary Level Hospital in Portugal; [Síndrome Inflamatória Multissistémica em Crianças Associada a COVID-19 num Hospital de Nível III em Portugal] | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 54 | Rodriguez-Smith (2021) | Inflammatory biomarkers in COVID-19-associated multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children, Kawasaki disease, and macrophage activation syndrome: a cohort study | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 55 | Abrams (2021) | Factors linked to severe outcomes in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) in the USA: a retrospective surveillance study | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 56 | Clark (2020) | Cardiac abnormalities seen in pediatric patients during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: An international experience | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 57 | Zhao (2021) | Cardiac markers of multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) in COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis | 3 | 0 | 2 | 5 | Moderate |
| 57 | Zhao (2021) | Characteristics and Outcomes of US Children and Adolescents with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Compared with Severe Acute COVID-19 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 58 | Feldstein (2021) | Atrioventricular Block in Children with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 59 | Dionne (2020) | Endothelial Dysfunction as a Component of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2–Related Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children with Shock | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 | High |
| 60 | Borgel (2021) | Cardiac manifestations in children with SARS-CoV-2 infection: 1-year pediatric multicenter experience | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 61 | Cantarutti (2021) | Early echocardiographic and cardiac MRI findings in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 62 | Sirico (2021) | Distinguishing Between Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome, Associated With COVID-19 in Children and the Kawasaki Disease: Development of Preliminary Criteria Based on the Data of the Retrospective Multicenter Cohort Study | 4 | 0 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 63 | Kostik (2021) | The Multifaceted Presentation of the Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: Data from a Cluster Analysis | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
| 64 | Sonmez (2022) | Cardiac Findings in Pediatric Patients With Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated With COVID-19 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 | High |
| 65 | Minocha (2021) | Clinical, laboratory, and echocardiographic characteristics of critical multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children: a retrospective, observational study | 3 | 0 | 2 | 5 | Moderate |
| 66 | Ibrahim (2024) | Short- and medium-term longitudinal outcomes of children diagnosed with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children—report from a single centre in Pakistan | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 | High |
| 67 | Abbas (2024) | Treatments and Severe Outcomes for Patients Diagnosed with MIS-C at Four Children’s Hospitals in the United States, 16 March 2020–10 March 2021 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 6 | Moderate |
References
- Feldstein, L.R.; Tenforde, M.W.; Friedman, K.G.; Newhams, M.; Rose, E.B.; Dapul, H.; Soma, V.L.; Maddux, A.B.; Mourani, P.M.; Bowens, C.; et al. Characteristics and Outcomes of US Children and Adolescents With Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Compared With Severe Acute COVID-19. JAMA 2021, 325, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufort, E.M.; Koumans, E.H.; Chow, E.J.; Rosenthal, E.M.; Muse, A.; Rowlands, J.; Barranco, M.A.; Maxted, A.M.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Easton, D.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children in New York State. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, E.; Bamford, A.; Kenny, J.; Kaforou, M.; Jones, C.E.; Shah, P.; Ramnarayan, P.; Fraisse, A.; Miller, O.; Davies, P.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 58 Children with a Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2. JAMA 2020, 324, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhadjer, Z.; Méot, M.; Bajolle, F.; Khraiche, D.; Legendre, A.; Abakka, S.; Auriau, J.; Grimaud, M.; Oualha, M.; Beghetti, M.; et al. Acute Heart Failure in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children in the Context of Global SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic. Circulation 2020, 142, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolhnikoff, M.; Ferreira Ferranti, J.; de Almeida Monteiro, R.A.; Duarte-Neto, A.N.; Soares Gomes-Gouvêa, M.; Viu Degaspare, N.; Figueiredo Delgado, A.; Montanari Fiorita, C.; Nunes Leal, G.; Rodrigues, R.M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 in Cardiac Tissue of a Child with COVID-19-Related Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 790–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diorio, C.; McNerney, K.O.; Lambert, M.; Paessler, M.; Anderson, E.M.; Henrickson, S.E.; Chase, J.; Liebling, E.J.; Burudpakdee, C.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Evidence of Thrombotic Microangiopathy in Children with SARS-CoV-2 across the Spectrum of Clinical Presentations. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 6051–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, L.A.; Canna, S.W.; Friedman, K.G.; Gorelik, M.; Lapidus, S.K.; Bassiri, H.; Behrens, E.M.; Kernan, K.F.; Schulert, G.S.; Seo, P.; et al. American College of Rheumatology Clinical Guidance for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated With SARS–CoV-2 and Hyperinflammation in Pediatric COVID-19: Version 3. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, E1–E20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Smith, J.J.; Verweyen, E.L.; Clay, G.M.; Esteban, Y.M.; de Loizaga, S.R.; Baker, E.J.; Do, T.; Dhakal, S.; Lang, S.M.; Grom, A.A.; et al. Inflammatory Biomarkers in COVID-19-Associated Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children, Kawasaki Disease, and Macrophage Activation Syndrome: A Cohort Study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2021, 3, e574–e584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgel, D.; Chocron, R.; Grimaud, M.; Philippe, A.; Chareyre, J.; Brakta, C.; Lasne, D.; Bonnet, D.; Toubiana, J.; Angoulvant, F.; et al. Endothelial Dysfunction as a Component of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2–Related Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children With Shock. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e1151–e1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darren, A.; Osman, M.; Masilamani, K.; Habib Ali, S.; Kanthimathinathan, H.K.; Chikermane, A.; Al-Abadi, E.; Welch, S.B.; Hackett, S.; Scholefield, B.R.; et al. Vitamin D Status of Children with Paediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (PIMS-TS). Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, P.; Balajthy, A.; Biró, E.; Bíró, B.; Reiger, Z.; Szikszay, E.; Mogyorósy, G.; Káposzta, R.; Szabó, T. Multicolored MIS-C, a Single-Centre Cohort Study. BMC Pediatr. 2023, 23, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Amrousy, D.; Abdelhai, D.; Nassar, M. Predictive Value of Plasma Copeptin Level in Children with Acute Heart Failure. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2022, 43, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciortea, D.-A.; Petrea (Cliveți), C.L.; Berbece, S.I.; Fotea, S.; Vivisenco, I.C.; Gurău, G.; Matei, M.N.; Nechita, A. Impact of Hyponatremia and ADH Secretion in MIS-C and COVID-19: An Integrative Approach of Prognostic and Diagnostic Markers. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 11749–11771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the Sample Mean and Standard Deviation from the Sample Size, Median, Range and/or Interquartile Range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Chandra, T.; Singh, C.P.; Singh, R.; Pandey, I. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Related to SARS-CoV-2 and 1-Year Follow-Up. Indian. J. Pediatr. 2023, 90, 1008–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güllü, U.U.; Güngör, Ş.; İpek, S.; Yurttutan, S.; Dilber, C. Predictive Value of Cardiac Markers in the Prognosis of COVID-19 in Children. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 48, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bichali, S.; Ouldali, N.; Godart, F.; Maboudou, P.; Houeijeh, A.; Leteurtre, S. NT-ProBNP Course during MIS-C Post-COVID-19: An Observational Study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2024, 183, 1667–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, A.; Mahto, D.; Kumar, V.; Gulati, S.; Pemde, H.; Saha, A.; Mukherjee, S.B.; Pandit, K.; Paharia, K.; Basu, S. Comparison of Clinical and Laboratory Profile of Survivors and Non-survivors of SARS-CoV-2-related Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome of Childhood in India: An Observational Study. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2022, 58, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanil, Y.; Misra, A.; Safa, R.; Blake, J.M.; Eddine, A.C.; Balakrishnan, P.; Garcia, R.U.; Taylor, R.; Dentel, J.N.; Ang, J.; et al. Echocardiographic Indicators Associated with Adverse Clinical Course and Cardiac Sequelae in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children with Coronavirus Disease 2019. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2021, 34, 862–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granda-Jiménez, M.J.; Rios-Olivares, I.E.; González-Rebeles-Guerrero, C.; Marquez-Aguirre, M.P.; Gutiérrez-Hernández, J.A.; Camacho-Reyes, L.; De Rubens-Figueroa, J.; Corona-Villalobos, C.A. Alteraciones Cardiovasculares En El Síndrome Inflamatorio Multisistémico Pediátrico Asociado a COVID-19 En Un Hospital Pediátrico de Tercer Nivel de La Ciudad de México. Arch. Cardiol. Mex. 2024, 94, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozyilmaz, I.; Yakut, K.; Yakut, N.; Bekece, E.; Cansaran Tanıdır, I.; Öztürk, E. Prediction and Course of Diastolic Dysfunction in COVID-19 Associated Pediatric Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome. Iran. J. Pediatr. 2024, 34, e143648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampidi, S.; Maritsi, D.; Charakida, M.; Eleftheriou, I.; Farmaki, E.; Spyridis, N.; Charisi, K.; Vantsi, P.; Filippatos, F.; Skourti, K.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C): A Nationwide Collaborative Study in the Greek Population. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2024, 183, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, D.; Ekemen Keles, Y.; Emiroglu, M.; Duramaz, B.B.; Ugur, C.; Aldemir Kocabas, B.; Celik, T.; Ozdemir, H.; Bayturan, S.; Turel, O.; et al. Evaluation of 601 Children with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome (Turk MISC Study). Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 5531–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borensztajn, D.M.; Tan, C.D.; de Rijke, Y.; Hagedoorn, N.N.; Verbruggen, S.C.; Moll, H.A.; Vermont, C.L. Elevated High-Sensitivity Troponin and NT-ProBNP Values in Febrile Children. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2023, 40, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurm, J.; Uka, A.; Buettcher, M.; Kottanattu, L.; Schöbi, N.; Trück, J.; Villiger, R.; Ritz, N.; Zimmermann, P. Clinical and Laboratory Biomarkers as Predictors of Severity in Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome-Temporally Associated With SARS-CoV-2: Data From a Prospective Nationwide Surveillance Study in Switzerland. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2024, 43, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodio, D.; Pascucci, G.R.; Cotugno, N.; Rossetti, C.; Manno, E.C.; Pighi, C.; Morrocchi, E.; D’Alessandro, A.; Perrone, M.A.; Valentini, A.; et al. Similarities and Differences between Myocarditis Following COVID-19 MRNA Vaccine and Multiple Inflammatory Syndrome with Cardiac Involvement in Children. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 255, 109751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.S.; Ordog, T.; Hong, S.D.; Schmitz, A.H.; Thattaliyath, B.; Sharathkumar, A.A. Evolution of Cardiovascular Findings in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Across COVID-19 Variants: Common Trends and Unusual Presentations. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2024, 45, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, M.S.; Fernandes, N.D.; Carr, A.V.; Beaute, J.I.; Lahoud-Rahme, M.; Cummings, B.M.; Chiu, J.S. Diagnostic Yield of Cardiac Biomarker Testing in Predicting Cardiac Disease and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children in the Pandemic Era. Pediatr. Emerg. Care 2022, 38, e1584–e1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tastemel Ozturk, T.; Düzova, A.; Oygar, P.D.; Baltu, D.; Ozcilingir Hakverdi, P.; Lacinel Gurlevik, S.; Kurt-Sukur, E.D.; Aykan, H.H.; Ozen, S.; Ertugrul, I.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury in Children with Moderate-Severe COVID-19 and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Referral Center Experience. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2024, 39, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerberg, J.C.; Matsubara, D.; Kauffman, H.L.; Chang, J.C.; Calderon-Anyosa, R.; Patel, C.; Hogarty, A.N.; Falkensammer, C.B.; Mercer-Rosa, L.M.; Quartermain, M.D.; et al. Left Atrial Stiffness and Strain Are Novel Indices of Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in Children: Validation Followed by Application in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Due to COVID-19. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2023, 24, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.B.; Abrams, J.Y.; Godfred-Cato, S.; Kunkel, A.; Hammett, T.A.; Perez, M.A.; Hsiao, H.-M.; Baida, N.; Rostad, C.A.; Ballan, W.; et al. and Severe Outcomes for Patients Diagnosed With MIS-C at Four Children’s Hospitals in the United States, March 16, 2020–March 10, 2021. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2023, 42, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiak, A.; Perdas, E.; Smolewska, E. Risk Factors of a Severe Course of Pediatric Multi-System Inflammatory Syndrome Temporally Associated with COVID-19. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 3733–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jepson, B.M.; Beaver, M.; Colquitt, J.L.; Truong, D.T.; Crandall, H.; McFarland, C.; Williams, R.; Ou, Z.; Jensen, D.; Minich, L.L.; et al. Left Atrial Strain in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children and Associations with Systemic Inflammation and Cardiac Injury. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2024, 45, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, D.; Shwayder, M.; Souza, A.; Su, J.A.; Votava-Smith, J.; Wagner-Lees, S.; Kaneta, K.; Cheng, A.; Szmuszkovicz, J. Cardiovascular Follow-up of Patients Treated for MIS-C. Pediatrics 2023, 152, e2023063002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaver, M.; Jepson, B.; Binka, E.; Truong, D.; Crandall, H.; McFarland, C.; Williams, R.; Ou, Z.; Treemarcki, E.; Jensen, D.; et al. Baseline Echocardiography and Laboratory Findings in MIS-C and Associations with Clinical Illness Severity. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2024, 45, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfred-Cato, S.; Abrams, J.Y.; Balachandran, N.; Jaggi, P.; Jones, K.; Rostad, C.A.; Lu, A.T.; Fan, L.; Jabbar, A.; Anderson, E.J.; et al. Distinguishing Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children From COVID-19, Kawasaki Disease and Toxic Shock Syndrome. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2022, 41, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netea, S.A.; Biesbroek, G.; Groenink, M.; Planken, R.N.; de Winter, R.J.; Blom, N.A.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Kuipers, I.M. Long-Term Global Longitudinal Strain Abnormalities in Paediatric Patients after Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Correlate with Cardiac Troponin T: A Single-Centre Cohort Study. Cardiol. Young 2024, 34, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, A.; Wood, K.E.; Badheka, A.; Burghardt, E.; Wendt, L.; Sharathkumar, A.; Koestner, B. NT-ProBNP Levels Following IVIG Treatment of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. Hosp. Pediatr. 2022, 12, e261–e265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanello, C.; Mercuri, C.; Derchi, M.; Trocchio, G.; Consolaro, A.; Caorsi, R.; Ravelli, A.; Rimini, A.; Marasini, M.; Gattorno, M. Cardiovascular Manifestations in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Associated with COVID-19 According to Age. Children 2022, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.; Sethuraman, U.; Merolla, D.M.; Sanil, Y.; Bharadwaj, M.; Kannikeswaran, N. Efficacy of Biomarkers in Identifying Abnormal Echocardiogram in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. Clin. Pediatr. 2023, 62, 908–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-García, M.; Roldan-Berengue, E.; Guitart, C.; Girona-Alarcón, M.; Argüello, G.; Pino, R.; de Sevilla, M.F.; García-García, J.J.; Jordan, I. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) and Sepsis Differentiation by a Clinical and Analytical Score: MISSEP Score. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 5109–5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostik, M.M.; Bregel, L.V.; Avrusin, I.S.; Efremova, O.S.; Belozerov, K.E.; Dondurei, E.A.; Kornishina, T.L.; Isupova, E.A.; Abramova, N.N.; Felker, E.Y.; et al. Heart Involvement in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome, Associated With COVID-19 in Children: The Retrospective Multicenter Cohort Data. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 829420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, D.; Chang, J.; Kauffman, H.L.; Wang, Y.; Nadaraj, S.; Patel, C.; Paridon, S.M.; Fogel, M.A.; Quartermain, M.D.; Banerjee, A. Longitudinal Assessment of Cardiac Outcomes of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated With COVID-19 Infections. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e023251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozak, M.F.; Pessoa, Y.C.; Silva, L.O.C.e; Cabral, M.B.; Leite, B.C.P.; Diniz, J.D.; Saliba, A.; Kawahara, S.H. Sinais de Injúria Cardíaca Em Pacientes Pediátricos Com COVID-19 Gravemente Enfermos: Uma Experiência de Centro Único No Brasil. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2022, 118, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira de Melo, J.; Valsassina, R.; Garcia, A.M.; Silva, T.; Gouveia, C.; Brito, M.J. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated with COVID-19 in a Tertiary Level Hospital in Portugal. Acta Med. Port. 2022, 35, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, J.Y.; Oster, M.E.; Godfred-Cato, S.E.; Bryant, B.; Datta, S.D.; Campbell, A.P.; Leung, J.W.; Tsang, C.A.; Pierce, T.J.; Kennedy, J.L.; et al. Factors Linked to Severe Outcomes in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) in the USA: A Retrospective Surveillance Study. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2021, 5, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, B.C.; Sanchez-de-Toledo, J.; Bautista-Rodriguez, C.; Choueiter, N.; Lara, D.; Kang, H.; Mohsin, S.; Fraisse, A.; Cesar, S.; Shaikh, A.S.; et al. Cardiac Abnormalities Seen in Pediatric Patients During the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Pandemic: An International Experience. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e018007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirico, D.; Basso, A.; Reffo, E.; Cavaliere, A.; Castaldi, B.; Sabatino, J.; Meneghel, A.; Martini, G.; Da Dalt, L.; Zulian, F.; et al. Early Echocardiographic and Cardiac MRI Findings in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostik, M.M.; Bregel, L.V.; Avrusin, I.S.; Dondurei, E.A.; Matyunova, A.E.; Efremova, O.S.; Isupova, E.A.; Kornishina, T.L.; Masalova, V.V.; Snegireva, L.S.; et al. Distinguishing Between Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome, Associated With COVID-19 in Children and the Kawasaki Disease: Development of Preliminary Criteria Based on the Data of the Retrospective Multicenter Cohort Study. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 787353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minocha, P.K.; Phoon, C.K.L.; Verma, S.; Singh, R.K. Cardiac Findings in Pediatric Patients With Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated With COVID-19. Clin. Pediatr. 2021, 60, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, Q.; Shahbaz, F.; Amjad, F.; Khalid, F.; Aslam, N.; Mohsin, S. Short- and Medium-Term Longitudinal Outcomes of Children Diagnosed with Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children—Report from a Single Centre in Pakistan. Cardiol. Young 2024, 34, 2670–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Ray, K.; Ghosh, A. Biomarker Profile in Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporarily Associated with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS-TS)/Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C). Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 57, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattalini, M.; Della Paolera, S.; Zunica, F.; Bracaglia, C.; Giangreco, M.; Verdoni, L.; Meini, A.; Sottile, R.; Caorsi, R.; Zuccotti, G.; et al. Defining Kawasaki Disease and Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome-Temporally Associated to SARS-CoV-2 Infection during SARS-CoV-2 Epidemic in Italy: Results from a National, Multicenter Survey. Pediatr. Rheumatol. 2021, 19, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wolf, R.; Zaqout, M.; Tanaka, K.; Muiño-Mosquera, L.; van Berlaer, G.; Vandekerckhove, K.; Dewals, W.; De Wolf, D. Evaluation of Late Cardiac Effects after Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1253608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrolia, M.V.; Martini, M.; Memmini, G.; Ferrara, G.; Bernardini, R.; Peroni, D.; Consolini, R.; Marrani, E.; Agostiniani, R.; Maccora, I.; et al. Convergence and Divergence in Kawasaki Disease and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: Results from the COVASAKI Survey. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2024, 42, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otar Yener, G.; Paç Kısaarslan, A.; Ulu, K.; Atalay, E.; Haşlak, F.; Özdel, S.; Bozkaya Yücel, B.; Gezgin Yıldırım, D.; Çakmak, F.; Öztürk, K.; et al. Differences and Similarities of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children, Kawasaki Disease and Macrophage Activating Syndrome Due to Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: A Comparative Study. Rheumatol. Int. 2021, 42, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaidar, K.; Dizitzer, Y.; Hashkes, P.J.; Wagner-Weiner, L.; Tesher, M.; Butbul Aviel, Y.; Inbar, K.; Berkun, Y.; Eisenstein, E.M.; Saied, M.H.; et al. Risk Factors for Haemodynamic Compromise in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Multicentre Retrospective Study. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 2829–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, C.-L.S.; Melbourne-Chambers, R.H.; Harrison, A.N.; Anzinger, J.J.; Gordon-Johnson, K.-A.M.; Deyde, V.M.; Christie, C.D.C. Hospitalized Children with SARS-CoV-2 Infection and MIS-C in Jamaica: A Dive into the First 15 Months of the Novel Pandemic. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 904788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Johnson, J.N.; Spagnoli, J.; Amin, N.; Mccoy, M.; Swaminathan, N.; Yohannan, T.; Philip, R. Long-Term Cardiovascular Outcomes of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Associated with COVID-19 Using an Institution Based Algorithm. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2023, 44, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomar, M.; Chaudhuri, M.; Goel, T.; Agarwal, V.; Bidhan, S.; Jain, A.; Rastogi, A.; Saxena, V.; Tomar, H.S. Profile of Cardiac Involvement in Children After Exposure to COVID-19. Indian. Pediatr. 2023, 60, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atasayan, V.; Akbay, Ö.P.; Çağlayan, Ş.; Sözeri, B.; Hasbal Akkuş, C.; Vuran, A.; Öner, T.; Karacan, M. Cardiac Involvement in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: Single-Centre Experience. Cardiol. Young 2023, 33, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.; Houlden, R.L. Oxytocin Deficiency and Spontaneous Onset of Labor and Lactation in Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis. AACE Clin. Case Rep. 2018, 4, e394–e397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Patel, J.; Huang, Y.; Yin, L.; Tang, L. Cardiac Markers of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) in COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 49, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionne, A.; Mah, D.Y.; Son, M.B.F.; Lee, P.Y.; Henderson, L.; Baker, A.L.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Fulton, D.R.; Newburger, J.W.; Friedman, K.G. Atrioventricular Block in Children With Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome. Pediatrics 2020, 146, e2020009704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarutti, N.; Battista, V.; Adorisio, R.; Cicenia, M.; Campanello, C.; Listo, E.; Campana, A.; Trocchio, G.; Drago, F. Cardiac Manifestations in Children with SARS-COV-2 Infection: 1-Year Pediatric Multicenter Experience. Children 2021, 8, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönmez, H.E.; Çağlayan, Ş.; Otar Yener, G.; Başar, E.Z.; Ulu, K.; Çakan, M.; Guliyeva, V.; Bağlan, E.; Öztürk, K.; Demirkol, D.; et al. The Multifaceted Presentation of the Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: Data from a Cluster Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Habeeb, N.; Elhakeem, I.; Abo-Bakr, A.; Magdy, S. Clinical, Laboratory, and Echocardiographic Characteristics of Critical Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Retrospective, Observational Study. Egypt. Pediatr. Assoc. Gaz. 2024, 72, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.A.; Patel, M.; Rayment, J.H.; Tam, H.; Roberts, A.; Laskin, S.; Tucker, L.; Biggs, C.M.; Ahmed, M.A.; Barakauskas, V.; et al. All Hands on Deck: A Multidisciplinary Approach to SARS-CoV-2-Associated MIS-C. Paediatr. Child. Health 2022, 27 (Suppl. S1), S53–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butters, C.; Abraham, D.R.; Stander, R.; Facey-Thomas, H.; Abrahams, D.; Faleye, A.; Allie, N.; Soni, K.; Rabie, H.; Scott, C.; et al. The Clinical Features and Estimated Incidence of MIS-C in Cape Town, South Africa. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burešová, M.; Pavlíček, J.; Hanzlíková, P.; Tomášková, H.; Rybníček, O. 2D Speckle Tracking Echocardiography and Comparison with Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in Children with Acute Myocarditis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1446602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zengin, N.; Bal, A.; Goren, T.A.; Bayturan, S.S.; Alkan, F.; Akcali, S. Serum Vitamin D Levels in Relation to Development of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Pediatric COVID-19. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. 2022, 17, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBiasi, R.L.; Harahsheh, A.S.; Srinivasalu, H.; Krishnan, A.; Sharron, M.P.; Parikh, K.; Smith, K.; Bell, M.; Michael, D.; Delaney, M.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome of Children: Subphenotypes, Risk Factors, Biomarkers, Cytokine Profiles, and Viral Sequencing. J. Pediatr. 2021, 237, 125–135.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramcharan, T.; Nolan, O.; Lai, C.Y.; Prabhu, N.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Richter, A.G.; Jyothish, D.; Kanthimathinathan, H.K.; Welch, S.B.; Hackett, S.; et al. Paediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome: Temporally Associated with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS-TS): Cardiac Features, Management and Short-Term Outcomes at a UK Tertiary Paediatric Hospital. Pediatr. Cardiol. 2020, 41, 1391–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consiglio, C.R.; Cotugno, N.; Sardh, F.; Pou, C.; Amodio, D.; Rodriguez, L.; Tan, Z.; Zicari, S.; Ruggiero, A.; Pascucci, G.R.; et al. The Immunology of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children with COVID-19. Cell 2020, 183, 968–981.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacevičienė, I.; Ivaškevičienė, I.; Kinčinienė, O.; Kilaitė, L.; Jankauskienė, A. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) in a Lithuanian Paediatric Tertiary Care Center. Medicina 2024, 60, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, L.A.; Giles, J.R.; Baxter, A.E.; Oldridge, D.A.; Diorio, C.; Kuri-Cervantes, L.; Alanio, C.; Pampena, M.B.; Wu, J.E.; Chen, Z.; et al. Deep Immune Profiling of MIS-C Demonstrates Marked but Transient Immune Activation Compared with Adult and Pediatric COVID-19. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabf7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diorio, C.; Henrickson, S.E.; Vella, L.A.; McNerney, K.O.; Chase, J.; Burudpakdee, C.; Lee, J.H.; Jasen, C.; Balamuth, F.; Barrett, D.M.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children and COVID-19 Are Distinct Presentations of SARS–CoV-2. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 5967–5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodero, G.; Gentili, C.; Mariani, F.; Pulcinelli, V.; Valentini, P.; Buonsenso, D. Procalcitonin and Presepsin as Markers of Infectious Respiratory Diseases in Children: A Scoping Review of the Literature. Children 2024, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciortea, D.-A.; Petrea (Cliveți), C.L.; Bujoreanu Bezman, L.; Vivisenco, I.C.; Berbece, S.I.; Gurău, G.; Matei, M.N.; Nechita, A. Diagnostic Utility of Copeptin in Pediatric Patients with Polyuria-Polydipsia Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrea (Cliveți), C.L.; Ciortea, D.-A.; Candussi, I.-L.; Gurău, G.; Matei, N.M.; Bergheș, S.-E.; Chirila, S.I.; Berbece, S.I. A Study of Hydroelectrolytic and Acid–Base Disturbances in MIS-C Patients: A Perspective on Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 40, 11438–11459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Biomarker | Mean | Standard Deviation | N | Coefficient of Variation (%) | Estimated Minimum (Mean − SD) | Estimated Maximum (Mean + SD) | Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D | 9.5 | 11.85 | 34 | 124.7 | −14.2 | 33.2 | Zengin (2022) [72] |
| CXCL9 | 2861 | 4193.33 | 19 | 146.6 | –1332.00 | 7054.66 | Rodriguez-Smith (2021) [8] |
| Angiopoietin-2 | 6426 | 6682.96 | 28 | 104 | −6939.92 | 19,791.92 | Borgel (2021) [9] |
| sE-Selectin | 130,405 | 73,712.59 | 28 | 56.5 | −17,020.2 | 277,830.2 | Borgel (2021) [9] |
| vWF antigen | 344 | 66.67 | 28 | 19.4 | 210.66 | 477.34 | Borgel (2021) [9] |
| Ang-2/Ang-1 ratio | 1.11 | 0.78 | 28 | 70.3 | −0.45 | 2.67 | Borgel (2021) [9] |
| IL-6 | 31.8 | 27.95 | 24 | 87.9 | −24.1 | 87.7 | DeBiasi (2021) [73] |
| Ferritin | 12 | 53.33 | 36 | 444.4 | −94.66 | 118.66 | Ramcharan (2020) [74] |
| D-dimer | 8 | 35.56 | 36 | 444.5 | −63.12 | 79.12 | Ramcharan (2020) [74] |
| IL-6 | 9 | 40 | 36 | 444.4 | −71 | 89 | Ramcharan (2020) [74] |
| Study | Biomarker | Severe MIS-C (Mean or Median) | Moderate or Other MIS-C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zengin (2022) [72] | Vitamin D | 7.5 ± 11.11 | 9.0 ± 9.63 |
| Zengin (2022) [72] | Troponin | 211.0 ± 3363.11 | 14.2 ± 2268.59 |
| Zengin (2022) [72] | Procalcitonin | 7.6 ± 60.07 | 1.7 ± 30.96 |
| Rodriguez-Smith (2021) [8] | CXCL9 | 1730.0 ± 4219.26 | 278.0 ± 313.33 |
| Stacevičienė (2024) [76] | BNP | 611.4 ± 649.63 | 88.5 ± 0.0 |
| Stacevičienė (2024) [76] | CRP | 165.5 ± 125.11 | 87.5 ± 0.0 |
| Stacevičienė (2024) [76] | Procalcitonin | 12.0 ± 21.78 | 1.6 ± 0.0 |
| Stacevičienė (2024) [76] | Albumin | 30.0 ± 2.96 | 32.0 ± 0.0 |
| Bichali (2023) [18] | NT-proBNP | 12,543 ± 9800 | 3896 ± 3120 |
| Varga (2023) [11] | Ferritin | 420.5 ± 150.3 | 236.4 ± 112.1 |
| Varga (2023) [11] | D-dimer | 6.2 ± 3.1 | 2.7 ± 1.6 |
| Varga (2023) [11] | CRP | 175.6 ± 80.7 | 116.8 ± 49.3 |
| Varga (2023) [11] | NT-proBNP | 15,727 ± 10,020 | 5334 ± 4908 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciortea, D.-A.; Matei, M.N.; Debita, M.; Lupu, A.; Mătăsaru, M.; Verga, G.I.; Fotea, S. Cardiac Manifestations and Emerging Biomarkers in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life 2025, 15, 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050805
Ciortea D-A, Matei MN, Debita M, Lupu A, Mătăsaru M, Verga GI, Fotea S. Cardiac Manifestations and Emerging Biomarkers in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life. 2025; 15(5):805. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050805
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiortea, Diana-Andreea, Mădălina Nicoleta Matei, Mihaela Debita, Ancuța Lupu, Mirela Mătăsaru, Gabriela Isabela Verga (Răuță), and Silvia Fotea. 2025. "Cardiac Manifestations and Emerging Biomarkers in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Life 15, no. 5: 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050805
APA StyleCiortea, D.-A., Matei, M. N., Debita, M., Lupu, A., Mătăsaru, M., Verga, G. I., & Fotea, S. (2025). Cardiac Manifestations and Emerging Biomarkers in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Life, 15(5), 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050805







