Current Understanding of the Pathogenesis of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis and Novel Treatment Options Targeting Complement Activation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. ANCA-Vasculitis Pathogenesis
3. Risk Factors and Potential Initiating Events
4. Investigating the Role of Complement System in ANCA-Vasculitis
5. Histopathological Evidence for the Role of Alternative Complement Pathway in Pathogenesis of ANCA-Vasculitis
6. Current Therapeutic Targets for ANCA-Vasculitis and Glomerulonephritis
7. Targets: B-Cells, T Lymphocytes, Inflammatory Agents
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Bacon, P.A.; Basu, N.; Cid, M.C.; Ferrario, F.; Flores-Suarez, L.F.; Gross, W.L.; Guillevin, L.; Hagen, E.C.; et al. 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Andrassy, K.; Bacon, P.A.; Churg, J.; Gross, W.L.; Hagen, E.C.; Hoffman, G.S.; Hunder, G.G.; Kallenberg, C.G.; et al. Nomenclature of systemic vasculitidies. Proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum. 1994, 37, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitching, A.R.; Anders, H.J.; Basu, N.; Brouwer, E.; Gordon, J.; Jayne, D.R.; Kullman, J.; Lyons, P.A.; Merkel, P.A.; Savage, C.O.S.; et al. ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahr, A.; Guillevin, L.; Poissonnet, M.; Aymé, S. Prevalences of polyarteritis nodosa, microscopic polyangiitis, Wegener’s granulomatosis, and Churg-Strauss syndrome in a French urban multiethnic population in 2000: A capture-recapture estimate. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 51, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Schmitz, J.L.; Yang, J.; Hogan, S.L.; Bunch, D.; Hu, Y.; Jennette, C.E.; Berg, E.A.; Arnett, F.C., Jr.; Jennette, J.C.; et al. DRB1*15 allele is a risk factor for PR3-ANCA disease in African Americans. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1161–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J. Small-vessel vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1512–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, A.J.; Mortensen, K.H.; Babar, J.; Smith, R.; Jones, R.B.; Nakagomi, D.; Sivasothy, P.; Jayne, D.R.W. Pulmonary Involvement in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies (ANCA)-associated Vasculitis: The Influence of ANCA Subtype. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 44, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, G.S.; Kerr, G.S.; Leavitt, R.Y.; Hallahan, C.W.; Lebovics, R.S.; Travis, W.D.; Rottem, M.; Fauci, A.S. Wegener granulomatosis: An analysis of 158 patients. Ann. Intern. Med. 1992, 116, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noris, M.; Mescia, F.; Remuzzi, G. STEC-HUS, atypical HUS and TTP are all diseases of complement activation. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2012, 8, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nester, C.M.; Barbour, T.; de Cordoba, S.R.; Dragon-Durey, M.A.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Goodship, T.H.; Kavanagh, D.; Noris, M.; Pickering, M.; Sanchez-Corral, P.; et al. Atypical aHUS: State of the art. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 67, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Xing, G.Q.; Yu, F.; Liu, G.; Zhao, M.H. Complement deposition in renal histopathology of patients with ANCA-associated pauci-immune glomerulonephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, D.J.; Moran, J.E.; Niall, J.F.; Ryan, G.B. Segmental necrotising glomerulonephritis with antineutrophil antibody: Possible arbovirus aetiology? Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed). 1982, 285, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies with specificity for myeloperoxidase in patients with systemic vasculitis and idiopathic necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 318, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Woude, F.J.; Rasmussen, N.; Lobatto, S.; Wiik, A.; Permin, H.; van Es, L.A.; van der Giessen, M.; van der Hem, G.K.; The, T.H. Autoantibodies against neutrophils and monocytes: Tool for diagnosis and marker of disease activity in Wegener’s granulomatosis. Lancet 1985, 1, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tervaert, J.W.; Goldschmeding, R.; Elema, J.D.; van der Giessen, M.; Huitema, M.G.; van der Hem, G.K.; The, T.H.; von dem Borne, A.E.; Kallenberg, C.G. Autoantibodies against myeloid lysosomal enzymes in crescentic glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1990, 37, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, J.C.; Grayson, P.C.; Ponte, C.; Suppiah, R.; Craven, A.; Judge, A.; Khalid, S.; Hutchings, A.; Watts, R.A.; Merkel, P.A.; et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology Classification Criteria for Granulomatosis With Polyangiitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppiah, R.; Robson, J.C.; Grayson, P.C.; Ponte, C.; Craven, A.; Khalid, S.; Judge, A.; Hutchings, A.; Merkel, P.A.; Luqmani, R.A.; et al. 2022 American College of Rheumatology/European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology classification criteria for microscopic polyangiitis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Borstel, A.; Sanders, J.S.; Rutgers, A.; Stegeman, C.A.; Heeringa, P.; Abdulahad, W.H. Cellular immune regulation in the pathogenesis of ANCA-associated vasculitides. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018, 17, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, M.A.; Smyth, C.L.; Yadav, R.; Ambrose, L.; Cook, H.T.; Nourshargh, S.; Pusey, C.D. Antineutrophil cytoplasm antibodies directed against myeloperoxidase augment leukocyte-microvascular interactions in vivo. Blood 2005, 106, 2050–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, D.; Shida, H.; Tomaru, U.; Yoshida, M.; Nishio, S.; Atsumi, T.; Ishizu, A. Enhanced formation and disordered regulation of NETs in myeloperoxidase-ANCA-associated microscopic polyangiitis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayannopoulos, V.; Zychlinsky, A. NETs: A new strategy for using old weapons. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Krumbholz, M.; Schönermarck, U.; Back, W.; Gross, W.L.; Werb, Z.; Gröne, H.J.; Brinkmann, V.; Jenne, D.E. Netting neutrophils in autoimmune small-vessel vasculitis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, M.-H.; Chen, M. Neutrophil extracellular traps can activate alternative complement pathways. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 181, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffarzadeh, M.; Juenemann, C.; Queisser, M.A.; Lochnit, G.; Barreto, G.; Galuska, S.P.; Lohmeyer, J.; Preissner, K.T. Neutrophil extracellular traps directly induce epithelial and endothelial cell death: A predominant role of histones. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- McClure, M.; Gopaluni, S.; Jayne, D.; Jones, R. B cell therapy in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Current and emerging treatment options. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenert, P.; Lenert, A. Current and emerging treatment options for ANCA-associated vasculitis: Potential role of belimumab and other BAFF/APRIL targeting agents. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.H.; Merkel, P.A.; Spiera, R.; Seo, P.; Langford, C.A.; Hoffman, G.S.; Kallenberg, C.G.; St Clair, E.W.; Turkiewicz, A.; Tchao, N.K.; et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide for ANCA-associated vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.B.; Furuta, S.; Tervaert, J.W.; Hauser, T.; Luqmani, R.; Morgan, M.D.; Peh, C.A.; Savage, C.O.; Segelmark, M.; Tesar, V.; et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis: 2-year results of a randomised trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agosto-Burgos, C.; Wu, E.Y.; Iannone, M.A.; Hu, Y.; Hogan, S.L.; Henderson, C.D.; Kennedy, K.B.; Blazek, L.; Herrera, C.A.; Munson, D.; et al. The frequency of Treg subsets distinguishes disease activity in ANCA vasculitis. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2022, 11, e1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrot, P.A.; Kaplanski, G. Pathogenesis of ANCA-associated vasculitis: An update. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulahad, W.H.; Lamprecht, P.; Kallenberg, C.G. T-helper cells as new players in ANCA-associated vasculitides. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, C.A.; Jones, S.A. IL-6 as a keystone cytokine in health and disease. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 448–457, Erratum in Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 1271. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1117-1271b. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berti, A.; Dejaco, C. Update on the epidemiology, risk factors, and outcomes of systemic vasculitides. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 32, 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimojima, Y.; Kishida, D.; Nomura, S.; Sekijima, Y. Cerebrospinal fluid levels of BAFF and APRIL as direct indicators of disease activity in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-related hypertrophic pachymeningitis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 3145–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schönermarck, U.; Csernok, E.; Trabandt, A.; Hansen, H.; Gross, W.L. Circulating cytokines and soluble CD23, CD26 and CD30 in ANCA-associated vasculitides. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2000, 18, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimojima, Y.; Kishida, D.; Ichikawa, T.; Takamatsu, R.; Nomura, S.; Sekijima, Y. Features of BAFF and APRIL receptors on circulating B cells in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2023, 213, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bonasia, C.G.; Inrueangsri, N.; Bijma, T.; Borggrewe, M.; Post, A.I.; Mennega, K.P.; Abdulahad, W.H.; Rutgers, A.; Bos, N.A.; Heeringa, P. Circulating B cells display differential immune regulatory molecule expression in granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2025, 219, uxae096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xiao, H.; Heeringa, P.; Hu, P.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Aratani, Y.; Maeda, N.; Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies specific for myeloperoxidase cause glomerulonephritis and vasculitis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlieben, D.J.; Korbet, S.M.; Kimura, R.E.; Schwartz, M.M.; Lewis, E.J. Pulmonary-renal syndrome in a newborn with placental transmission of ANCAs. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 45, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falk, R.J.; Terrell, R.S.; Charles, L.A.; Jennette, J.C. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies induce neutrophils to degranulate and produce oxygen radicals in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 4115–4119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schreiber, A.; Luft, F.C.; Kettritz, R. Membrane proteinase 3 expression and ANCA-induced neutrophil activation. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 2172–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, L.A.; Caldas, M.L.; Falk, R.J.; Terrell, R.S.; Jennette, J.C. Antibodies against granule proteins activate neutrophils in vitro. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1991, 50, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, D.J.; Luu, N.T.; Hewins, P.; Nash, G.B.; Savage, C.O. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies stabilize adhesion and promote migration of flowing neutrophils on endothelial cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 2851–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, K.C.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, H.W.; Hong, H.K.; Lee, H.S. Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in human crescentic glomerulonephritis. Histopathology 2002, 41, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Heeringa, P.; Liu, Z.; Huugen, D.; Hu, P.; Maeda, N.; Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. The role of neutrophils in the induction of glomerulonephritis by anti-myeloperoxidase antibodies. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huugen, D.; Xiao, H.; van Esch, A.; Falk, R.J.; Peutz-Kootstra, C.J.; Buurman, W.A.; Tervaert, J.W.; Jennette, J.C.; Heeringa, P. Aggravation of anti-myeloperoxidase antibody-induced glomerulonephritis by bacterial lipopolysaccharide: Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jennette, J.C.; Xiao, H.; Falk, R.J. Pathogenesis of vascular inflammation by anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionaki, S.; Blyth, E.R.; Hogan, S.L.; Hu, Y.; Senior, B.A.; Jennette, C.E.; Nachman, P.H.; Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J. Classification of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody vasculitides: The role of antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody specificity for myeloperoxidase or proteinase 3 in disease recognition and prognosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3452–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lyons, P.A.; Rayner, T.F.; Trivedi, S.; Holle, J.U.; Watts, R.A.; Jayne, D.R.; Baslund, B.; Brenchley, P.; Bruchfeld, A.; Chaudhry, A.N.; et al. Genetically distinct subsets within ANCA-associated vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Roth, A.J.; Ooi, J.D.; Hess, J.J.; van Timmeren, M.M.; Berg, E.A.; Poulton, C.E.; McGregor, J.; Burkart, M.; Hogan, S.L.; Hu, Y.; et al. Epitope specificity determines pathogenicity and detectability in ANCA-associated vasculitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1773–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xiao, H.; Hu, P.; Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. Overview of the Pathogenesis of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. Kidney Dis. 2016, 1, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alberici, F.; Martorana, D.; Vaglio, A. Genetic aspects of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30 (Suppl. S1), i37–i45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, K.M.; Drögemöller, B.I.; Foell, D.; Benseler, S.M.; Graham, J.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Luqmani, R.A.; Cabral, D.A.; Brown, K.L.; Ross, C.J.; et al. Association Between HLA-DPB1 and Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis in Children. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmattulla, C.; Mooyaart, A.L.; van Hooven, D.; Schoones, J.W.; Bruijn, J.A.; Dekkers, O.M.; European Vasculitis Genetics Consortium; Bajema, I.M. Genetic variants in ANCA-associated vasculitis: A meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlqvist, J.; Ekman, D.; Sennblad, B.; Kozyrev, S.V.; Nordin, J.; Karlsson, Å.; Meadows, J.R.S.; Hellbacher, E.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Berglin, E.; et al. Identification and functional characterization of a novel susceptibility locus for small vessel vasculitis with MPO-ANCA. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 3461–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, L.; Zhong, H.; Zhu, Y.; Li, L.; Wei, J.; Huang, L.; Xue, C. Association of ATG7 gene polymorphisms with microscopic polyangiitis in Chinese individuals. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 7239–7251. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.P.; McInnis, E.A.; Wu, E.Y.; Stember, K.G.; Hogan, S.L.; Hu, Y.; Henderson, C.D.; Blazek, L.N.; Mallal, S.; Karosiene, E.; et al. Immunological Interaction of HLA-DPB1 and Proteinase 3 in ANCA Vasculitis is Associated with Clinical Disease Activity. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.P.; Aiello, C.P.; McCoy, D.; Stamey, T.; Yang, J.; Hogan, S.L.; Hu, Y.; Derebail, V.K.; Wu, E.Y.; Jennette, J.C.; et al. PRTN3 variant correlates with increased autoantigen levels and relapse risk in PR3-ANCA versus MPO-ANCA disease. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e166107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavatta, D.J.; Yang, J.; Preston, G.A.; Badhwar, A.K.; Xiao, H.; Hewins, P.; Nester, C.M.; Pendergraft, W.F., 3rd; Magnuson, T.R.; Jennette, J.C.; et al. Epigenetic basis for aberrant upregulation of autoantigen genes in humans with ANCA vasculitis. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3209–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jones, B.E.; Yang, J.; Muthigi, A.; Hogan, S.L.; Hu, Y.; Starmer, J.; Henderson, C.D.; Poulton, C.J.; Brant, E.J.; Pendergraft, W.F., 3rd. Gene-Specific DNA Methylation Changes Predict Remission in Patients with ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnis, E.A.; Badhwar, A.K.; Muthigi, A.; Lardinois, O.M.; Allred, S.C.; Yang, J.; Free, M.E.; Jennette, J.C.; Preston, G.A.; Falk, R.J.; et al. Dysregulation of autoantigen genes in ANCA-associated vasculitis involves alternative transcripts and new protein synthesis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yang, J.; Ge, H.; Poulton, C.J.; Hogan, S.L.; Hu, Y.; Jones, B.E.; Henderson, C.D.; McInnis, E.A.; Pendergraft, W.F., 3rd; Jennette, J.C.; et al. Histone modification signature at myeloperoxidase and proteinase 3 in patients with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated vasculitis. Clin. Epigenetics 2016, 8, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.E.; Herrera, C.A.; Agosto-Burgos, C.; Starmer, J.; Bass, W.A.; Poulton, C.J.; Blazek, L.; Henderson, C.D.; Hu, Y.; Hogan, S.L.; et al. ANCA autoantigen gene expression highlights neutrophil heterogeneity where expression in normal-density neutrophils correlates with ANCA-induced activation. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 744–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegeman, C.A.; Tervaert, J.W.; Sluiter, W.J.; Manson, W.L.; de Jong, P.E.; Kallenberg, C.G. Association of chronic nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus and higher relapse rates in Wegener granulomatosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1994, 120, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, E.R.; Stegeman, C.A.; Abdulahad, W.H.; van der Meer, B.; Arends, J.; Manson, W.M.; Bos, N.A.; Kallenberg, C.G.; Tervaert, J.W. Staphylococcal toxic-shock-syndrome-toxin-1 as a risk factor for disease relapse in Wegener’s granulomatosis. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.K.; Merkel, P.A.; Walker, A.M.; Niles, J.L. Drug-associated antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-positive vasculitis: Prevalence among patients with high titers of antimyeloperoxidase antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendergraft, W.F.; Niles, J.L. Trojan horses: Drug culprits associated with antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA) vasculitis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2014, 26, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoriello, D.; Bomback, A.S.; Kudose, S.; Batal, I.; Stokes, M.B.; Canetta, P.A.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Appel, G.B.; D’Agati, V.D.; Markowitz, G.S. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody associated glomerulonephritis complicating treatment with hydralazine. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunton, J.E.; Stiel, J.; Clifton-Bligh, P.; Wilmshurst, E.; McElduff, A. Prevalence of positive anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) in patients receiving anti-thyroid medication. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2000, 142, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slot, M.C.; Links, T.P.; Stegeman, C.A.; Tervaert, J.W.C. Occurrence of antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies and associated vasculitis in patients with hyperthyroidism treated with antithyroid drugs: A long-term followup study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 53, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, D.C.; Lindsay, R.H. Accumulation of 2-[14C]propylthiouracil in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1979, 28, 2289–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Hirouchi, M.; Hosokawa, M.; Sayo, H.; Kohno, M.; Kariya, K. Inactivation of peroxidases of rat bone marrow by repeated administration of propylthiouracil is accompanied by a change in the heme structure. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1988, 37, 2151–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Puerta, J.A.; Gedmintas, L.; Costenbader, K.H. The association between silica exposure and development of ANCA-associated vasculitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudreuil, S.; Lasfargues, G.; Lauériere, L.; El Ghoul, Z.; Fourquet, F.; Longuet, C.; Halimi, J.M.; Nivet, H.; Büchler, M. Occupational exposure in ANCA-positive patients: A case-control study. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 1961–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, S.L.; Satterly, K.K.; Dooley, M.A.; Nachman, P.H.; Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J. Silica exposure in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated glomerulonephritis and lupus nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2001, 12, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, G.; Fu, X.; Stone, J.H.; Wallwork, R.; Zhang, Y.; Choi, H.K.; Wallace, Z.S. Association of Cigarette Smoking With Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merle, N.S.; Church, S.E.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Roumenina, L.T. Complement System Part I—Molecular Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathern, D.R.; Heeger, P.S. Molecules Great and Small: The Complement System. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1636–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennette, J.C.; Wilkman, A.S.; Falk, R.J. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated glomerulonephritis and vasculitis. Am. J. Pathol. 1989, 135, 921–930. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, G.Q.; Chen, M.; Liu, G.; Heeringa, P.; Zhang, J.J.; Zheng, X.; Jie, E.; Kallenberg, C.G.; Zhao, M.H. Complement activation is involved in renal damage in human antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody associated pauci-immune vasculitis. J. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 29, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villacorta, J.; Diaz-Crespo, F.; Acevedo, M.; Guerrero, C.; Campos-Martin, Y.; García-Díaz, E.; Mollejo, M.; Fernandez-Juarez, G. Glomerular C3d as a novel prognostic marker for renal vasculitis. Hum. Pathol. 2016, 56, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, E.Y.; McInnis, E.A.; Boyer-Suavet, S.; Mendoza, C.E.; Aybar, L.T.; Kennedy, K.B.; Poulton, C.J.; Henderson, C.D.; Hu, Y.; Hogan, S.L.; et al. Measuring Circulating Complement Activation Products in Myeloperoxidase- and Proteinase 3-Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionaki, S.; Marinaki, S.; Liapis, G.; Kalaitzakis, E.; Fragkioudaki, S.; Kalogeropoulos, P.; Michelakis, I.; Goules, A.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Boletis, J.N. Hypocomplementemia at Diagnosis of Pauci-immune Glomerulonephritis Is Associated With Advanced Histopathological Activity Index and High Probability of Treatment Resistance. Kidney Int. Rep. 2021, 6, 2425–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Augusto, J.F.; Langs, V.; Demiselle, J.; Lavigne, C.; Brilland, B.; Duveau, A.; Poli, C.; Chevailler, A.; Croue, A.; Tollis, F.; et al. Low Serum Complement C3 Levels at Diagnosis of Renal ANCA-Associated Vasculitis Is Associated with Poor Prognosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Villacorta, J.; Diaz-Crespo, F.; Acevedo, M.; Cavero, T.; Guerrero, C.; Praga, M.; Fernandez-Juarez, G. Circulating C3 levels predict renal and global outcome in patients with renal vasculitis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 2733–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshayes, S.; Aouba, A.; Khoy, K.; Mariotte, D.; Lobbedez, T.; Silva, N.M. Hypocomplementemia is associated with worse renal survival in ANCA-positive granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manenti, L.; Vaglio, A.; Gnappi, E.; Maggiore, U.; Allegri, L.; Allinovi, M.; Urban, M.L.; Delsante, M.; Galetti, M.; Nicastro, M.; et al. Association of Serum C3 Concentration and Histologic Signs of Thrombotic Microangiopathy with Outcomes among Patients with ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 2143–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Schreiber, A.; Heeringa, P.; Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. Alternative Complement Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Disease Mediated by Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibodies. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Wang, F.M.; Li, Z.Y.; Yu, F.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.H. Myeloperoxidase influences the complement regulatory activity of complement factor H. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 2213–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, H.; Richards, A. Complement-mediated injury and protection of endothelium: Lessons from atypical haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Wang, F.M.; Li, Z.Y.; Yu, F.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.H. Complement Factor H Inhibits Anti-Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody-Induced Neutrophil Activation by Interacting With Neutrophils. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lucientes-Continente, L.; Fernández-Juárez, G.; Márquez-Tirado, B.; Jiménez-Villegas, L.; Acevedo, M.; Cavero, T.; Cámara, L.S.; Draibe, J.; Anton-Pampols, P.; Caravaca-Fontán, F.; et al. Complement alternative pathway determines disease susceptibility and severity in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charles Jennette, J.; Xiao, H.; Hu, P. Complement in ANCA-associated vasculitis. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Daha, M.R.; Kallenberg, C.G.M. The complement system in systemic autoimmune disease. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 34, J276–J286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Dairaghi, D.J.; Powers, J.P.; Ertl, L.S.; Baumgart, T.; Wang, Y.; Seitz, L.C.; Penfold, M.E.; Gan, L.; Hu, P.; et al. C5a receptor (CD88) blockade protects against MPO-ANCA GN. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayne, D.R.W.; Bruchfeld, A.N.; Harper, L.; Schaier, M.; Venning, M.C.; Hamilton, P.; Burst, V.; Grundmann, F.; Jadoul, M.; Szombati, I.; et al. Randomized Trial of C5a Receptor Inhibitor Avacopan in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2756–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennette, J.C.; Falk, R.J.; Hu, P.; Xiao, H. Pathogenesis of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Autoantibody–Associated Small-Vessel Vasculitis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2013, 8, 139–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilhorst, M.; van Paassen, P.; van Rie, H.; Bijnens, N.; Heerings-Rewinkel, P.; van Breda Vriesman, P.; Cohen Tervaert, J.W. Limburg Renal Registry Complement in ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, A.; Salviani, C.; Giannakakis, K.; Rosato, E.; Barbano, B.; Moroso, A.; Gasperini, M.L.; Nofroni, I.; Salsano, F.; Cianci, R.; et al. Clinical and histological outcome predictors in renal limited pauci-immune crescentic glomerulonephritis: A single centre experience. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2012, 25, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Shen, C.; Zhong, Y.; Ooi, J.D.; Eggenhuizen, P.; Zhou, Y.O.; Luo, H.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.B.; Wu, T.; et al. Glomerular immune deposition in MPO-ANCA associated glomerulonephritis is associated with poor renal survival. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 625672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, E.; Kluge, I.A.; Hakroush, S.; Korsten, P.; Tampe, B. Serum Uric Acid Associates with Systemic Complement C3 Activation in Severe ANCA-Associated Renal Vasculitides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakroush, S.; Tampe, D.; Baier, E.; Kluge, I.A.; Ströbel, P.; Tampe, B. Intrarenal synthesis of complement C3 localized to distinct vascular compartments in ANCA- associated renal vasculitis. J. Autoimmun. 2022, 133, 102924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huugen, D.; van Esch, A.; Xiao, H.; Peutz-Kootstra, C.J.; Buurman, W.A.; Tervaert, J.W.; Jennette, J.C.; Heeringa, P. Inhibition of complement factor C5 protects against anti-myeloperoxidase antibody-mediated glomerulonephritis in mice. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geetha, D.; Jefferson, J.A. ANCA-Associated Vasculitis: Core Curriculum 2020. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Timmeren, M.M.; van der Veen, B.S.; Stegeman, C.A.; Petersen, A.H.; Hellmark, T.; Collin, M.; Heeringa, P. IgG glycan hydrolysis attenuates ANCA-mediated glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Miao, D.; Li, D.Y.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.H. Platelets are activated in ANCA-associated vasculitis via thrombin-PARs pathway and can activate the alternative complement pathway. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassard, A.; Kounde, C.; Bouillet, L.; Goulenok, T.; Ribes, D.; Mesbah, R.; Langlois, V.; Delas, A.; Fortenfant, F.; Humbert, S.; et al. Are serum C3 levels or kidney C3 deposits useful markers for predicting outcomes in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis? J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2023, 7, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floege, J.; Jayne, D.R.W.; Sanders, J.-S.F.; Tesar, V.; Rovin, B.H. KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)–Associated Vasculitis. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S71–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalkia, A.; Jayne, D. ANCA-associated vasculitis-treatment standard. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2024, 39, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Walsh, M.; Merkel, P.A.; Peh, C.A.; Szpirt, W.M.; Puéchal, X.; Fujimoto, S.; Hawley, C.M.; Khalidi, N.; Floßmann, O.; Wald, R.; et al. PEXIVAS Investigators. Plasma Exchange and Glucocorticoids in Severe ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nezam, D.; Porcher, R.; Grolleau, F.; Morel, P.; Titeca-Beauport, D.; Faguer, S.; Karras, A.; Solignac, J.; Jourde-Chiche, N.; Maurier, F.; et al. Kidney Histopathology Can Predict Kidney Function in ANCA-Associated Vasculitides with Acute Kidney Injury Treated with Plasma Exchanges. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 33, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Walsh, M.; Collister, D.; Zeng, L.; Merkel, P.A.; Pusey, C.D.; Guyatt, G.; Au Peh, C.; Szpirt, W.; Ito-Hara, T.; Jayne, D.R.W. Plasma exchange and glucocorticoid dosing for patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis BMJ Rapid Recommendations Group. The effects of plasma exchange in patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2022, 376, e064604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmich, B.; Sanchez-Alamo, B.; Schirmer, J.H.; Berti, A.; Blockmans, D.; Cid, M.C.; Holle, J.U.; Hollinger, N.; Karadag, O.; Kronbichler, A.; et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis: 2022 update. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Heeringa, P.; Liu, Z.; Hu, P.; Zhao, M.; Aratani, Y.; Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. Induction of necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis (NCGN) and small-vessel vasculitis (SVV) by adoptive transfer of anti-myeloperoxidase (anti-MPO) lymphocytes into recombinase activating gene-2 deficient (RAG-2 −/−) mice. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2002, 69 (Suppl. S2), SII-13. [Google Scholar]
- Falk, R.J.; Jennette, J.C. Rituximab in ANCA-associated disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 285–286, Erratum in N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.B.; Tervaert, J.W.; Hauser, T.; Luqmani, R.; Morgan, M.D.; Peh, C.A.; Savage, C.O.; Segelmark, M.; Tesar, V.; van Paassen, P.; et al. Rituximab versus cyclophosphamide in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, D.R.; Gaskin, G.; Rasmussen, N.; Abramowicz, D.; Ferrario, F.; Guillevin, L.; Mirapeix, E.; Savage, C.O.; Sinico, R.A.; Stegeman, C.A.; et al. Randomized trial of plasmaexchange or high-dosage methylprednisolone as adjunctive therapy for severe renalvasculitis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2180–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, R.; Hashimoto, M. Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis: Latest Findings and Updated Treatment Recommendations. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wechsler, M.E.; Akuthota, P.; Jayne, D.; Khoury, P.; Klion, A.; Langford, C.A.; Merkel, P.A.; Moosig, F.; Specks, U.; Cid, M.C.; et al. Mepolizumab or Placebo for Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1921–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wechsler, M.E.; Nair, P.; Terrier, B.; Walz, B.; Bourdin, A.; Jayne, D.R.W.; Jackson, D.J.; Roufosse, F.; Börjesson Sjö, L.; Fan, Y.; et al. Benralizumab versus Mepolizumab for Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayne, D. Complement inhibition in ANCA vasculitis. Nephrol. Ther. 2019, 15, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanberg, J.S.; Miloslavsky, E.M. Steroid sparing in vasculitis: Myth or reality? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 37, 101843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, S.; Jayne, D.R. Antineutrophil cytoplasm antibody-associated vasculitis: Recent developments. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Jayne, D.; Zhao, M.H. Complement in ANCA-associated vasculitis: Mechanisms and implications for management. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkel, P.A.; Niles, J.; Jimenez, R.; Spiera, R.F.; Rovin, B.H.; Bomback, A.; Pagnoux, C.; Potarca, A.; Schall, T.J.; Bekker, P.; et al. Adjunctive Treatment With Avacopan, an Oral C5a Receptor Inhibitor, in Patients With Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2020, 2, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Jayne, D.R.W.; Merkel, P.A.; Schall, T.J.; Bekker, P. ADVOCATE Study Group: Avacopan for the Treatment of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manenti, L.; Urban, M.L.; Maritati, F.; Galetti, M.; Vaglio, A. Complement blockade in ANCA-associated vasculitis: An index case, current concepts and future perspectives. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2017, 12, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribes, D.; Belliere, J.; Piedrafita, A.; Faguer, S. Glucocorticoid-free induction regimen in severe ANCA-associated vasculitis using a combination of rituximab and eculizumab. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 2335–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, C.G.; Jackson, R.L. Successful use of eculizumab in immediate ANCA vasculitis recurrence in a pediatric kidney transplant. Pediatr. Transplant. 2024, 28, e14760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.W. Optimizing the use of vilobelimab for the treatment of COVID-19. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2023, 23, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, P.; Hellmich, B.; Pfaff, A.; Müller, C.; Startseva, E.; Jayne, D. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase II Study of Glucocorticoid Replacement by Vilobelimab, an Anti-C5a Monoclonal Antibody, in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74 (Suppl. S9), S1054–S1055. [Google Scholar]
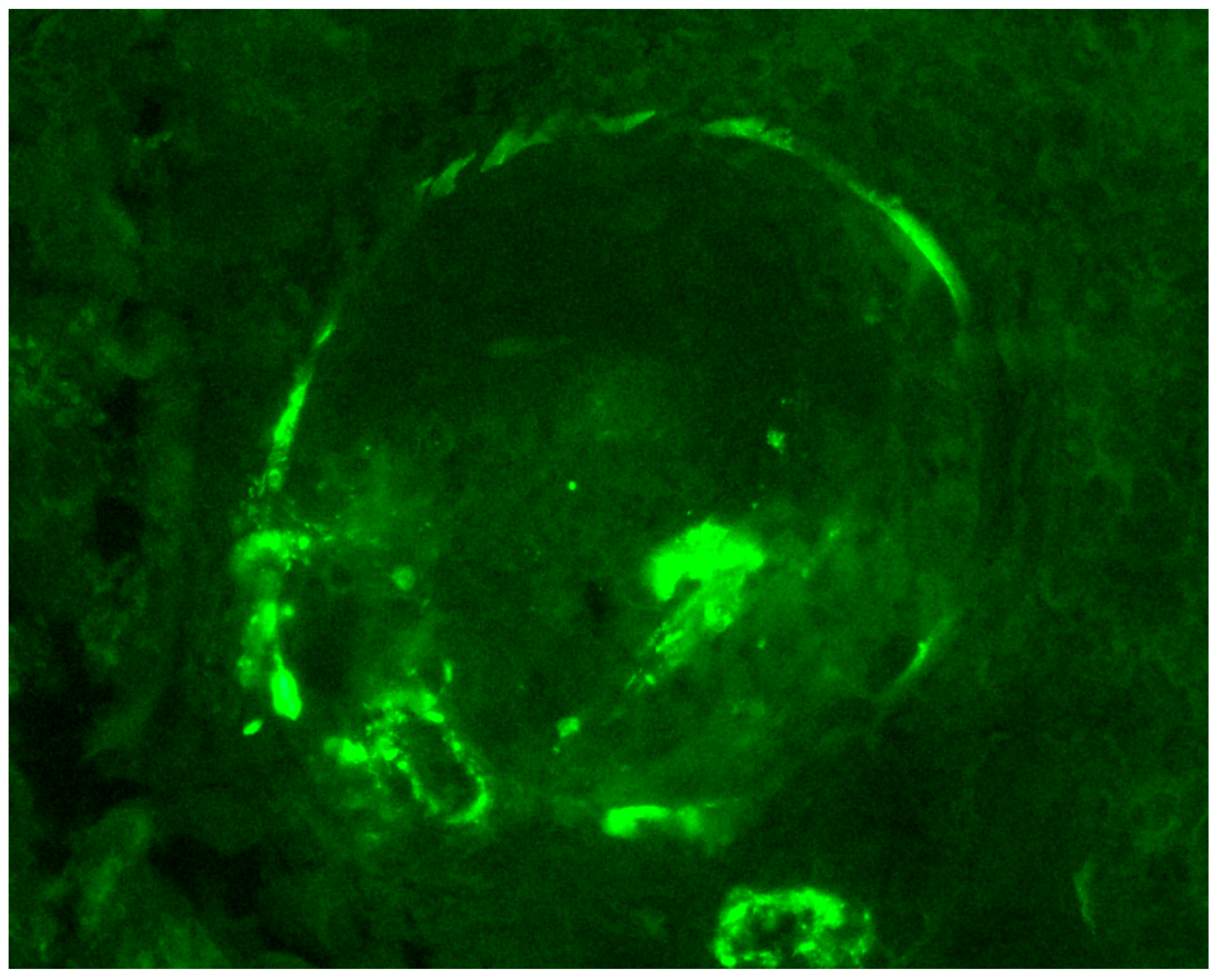
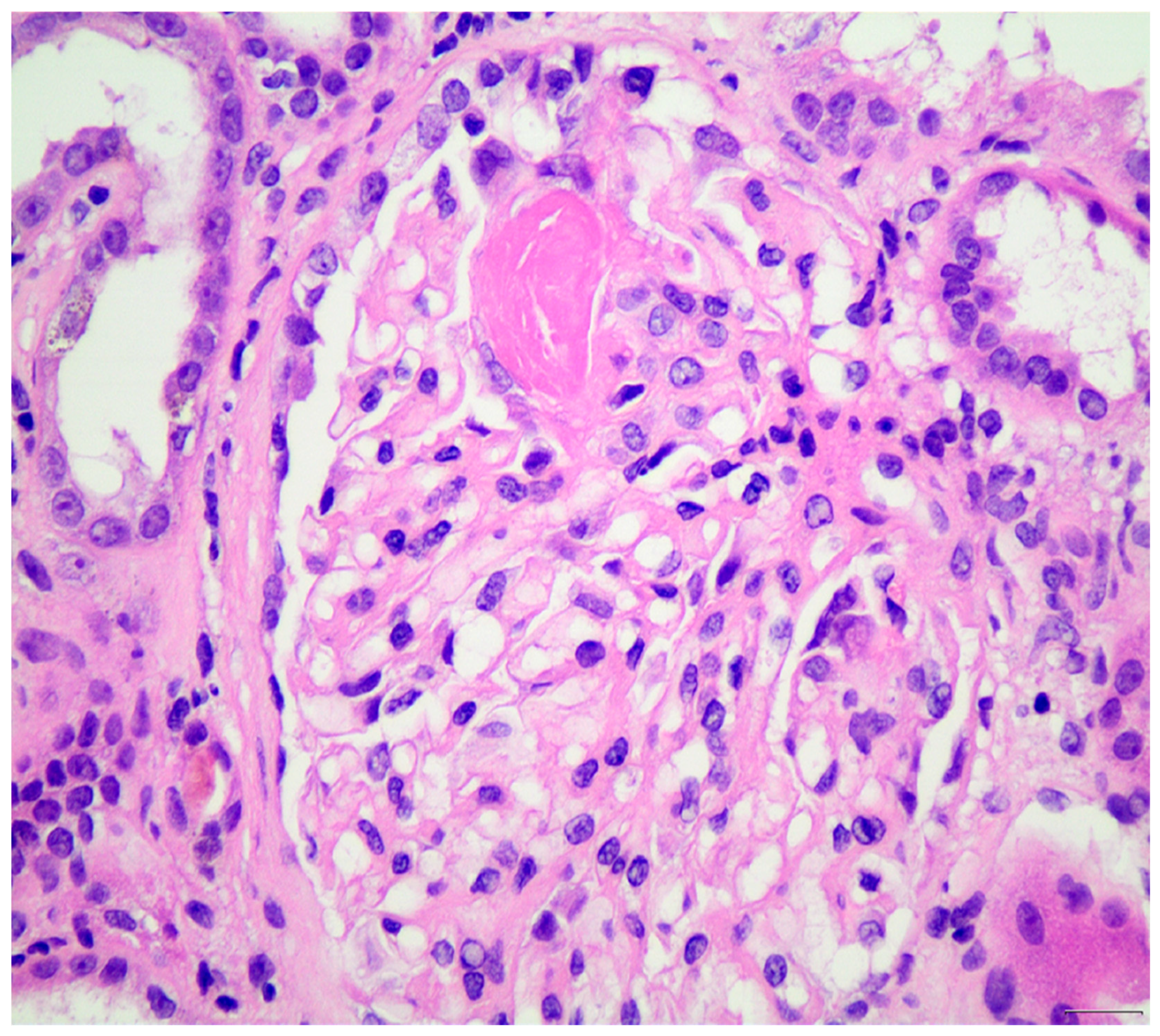
| Study/Author | Design | Number of Participants | Clinical Phenotype/Organ Involvement | Complement Inhibitor/Comparator | Predefined Trial Endpoints | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLEAR [96] | Phase 2, Placebo-controlled three-arm RCT | N = 67 | GPA 49% MPA 49% Renal involvement 95% | Avacopan without GC Avacopan + low-dose GC Placebo + high-dose GC | Primary: Response at 12 weeks Secondary: Renal response at 12 weeks | 81%/86%/70% Effectiveness in replacing high-dose GC |
| CLASSIC [125] | Phase 3, double-blind, placebo-controlled three-arm RCT | N = 42 | GPA 69% MPA 26% Renal involvement 64% | Avacopan 10 mg + SOC Avacopan 30 mg + SOC SOC only | Primary: Incidence of AEs Response to treatment at day 85 Secondary: Infections, renal response, QoL | 85%/90%/100% * Similar efficacy * AEs statistically n.s. Better renal response with 30 mg avacopan |
| ADVOCATE [126] | Phase 3, RCT | N = 331 | GPA or MPA under CYC or Rituximab | Avacopan Oral GC | Primary Clinical remission at week 26 Sustained remission at week 52 Secondary GC toxicity, renal response, QoL | 72.3% vs. 70.1% 65.7% vs. 54.9% Superiority for sustained remission |
| Author | Type of Publication | Clinical Phenotype | Complement Inhibitor/Comparator | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [127] | Case report | MPA, RPGN, AKI stage 3 | Eculizumab 900 mg weekly for 1 month, 1200 mg every other week thereafter plus SOC | Almost complete renal function recovery |
| [128] | Case report | MPA, pulmonary–renal syndrome; RPGN, AKI stage 3 | Eculizumab 900 mg weekly for 1 month, 1200 mg every other week thereafter plus RTx | Partial renal response, remission of symptoms |
| [129] | Case report | MPA, recurrence after pediatric kidney transplantation, AKI stage 2 | Eculizumab 600 mg every week for 15 days, then every 2 weeks followed by Ravulizumab 2100 mg every 2 months | Complete renal recovery after 5 months |
| IXCHANGE [131] | Phase 2, double-blind 2 stages RCT, N = 57 patients involved | MPA or GPA | Vilobelimab + reduced GC dose vs. standard-dose GC plus RTx or CYC Vilobelimab alone vs. standard-dose plus RTx or CYC | Vilobelimab alone 89% remission rate Vilobelimab + red. GC 77% remission rate Standard-dose GC 96% remission rate No inferiority, lesser AEs with Vilobelimab |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drouzas, K.; Kalogeropoulos, P.; Liapis, G.; Lionaki, S. Current Understanding of the Pathogenesis of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis and Novel Treatment Options Targeting Complement Activation. Life 2025, 15, 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050756
Drouzas K, Kalogeropoulos P, Liapis G, Lionaki S. Current Understanding of the Pathogenesis of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis and Novel Treatment Options Targeting Complement Activation. Life. 2025; 15(5):756. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050756
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrouzas, Konstantinos, Petros Kalogeropoulos, George Liapis, and Sophia Lionaki. 2025. "Current Understanding of the Pathogenesis of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis and Novel Treatment Options Targeting Complement Activation" Life 15, no. 5: 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050756
APA StyleDrouzas, K., Kalogeropoulos, P., Liapis, G., & Lionaki, S. (2025). Current Understanding of the Pathogenesis of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis and Novel Treatment Options Targeting Complement Activation. Life, 15(5), 756. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15050756







