A Review of Artificial Intelligence-Based Systems for Non-Invasive Glioblastoma Diagnosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
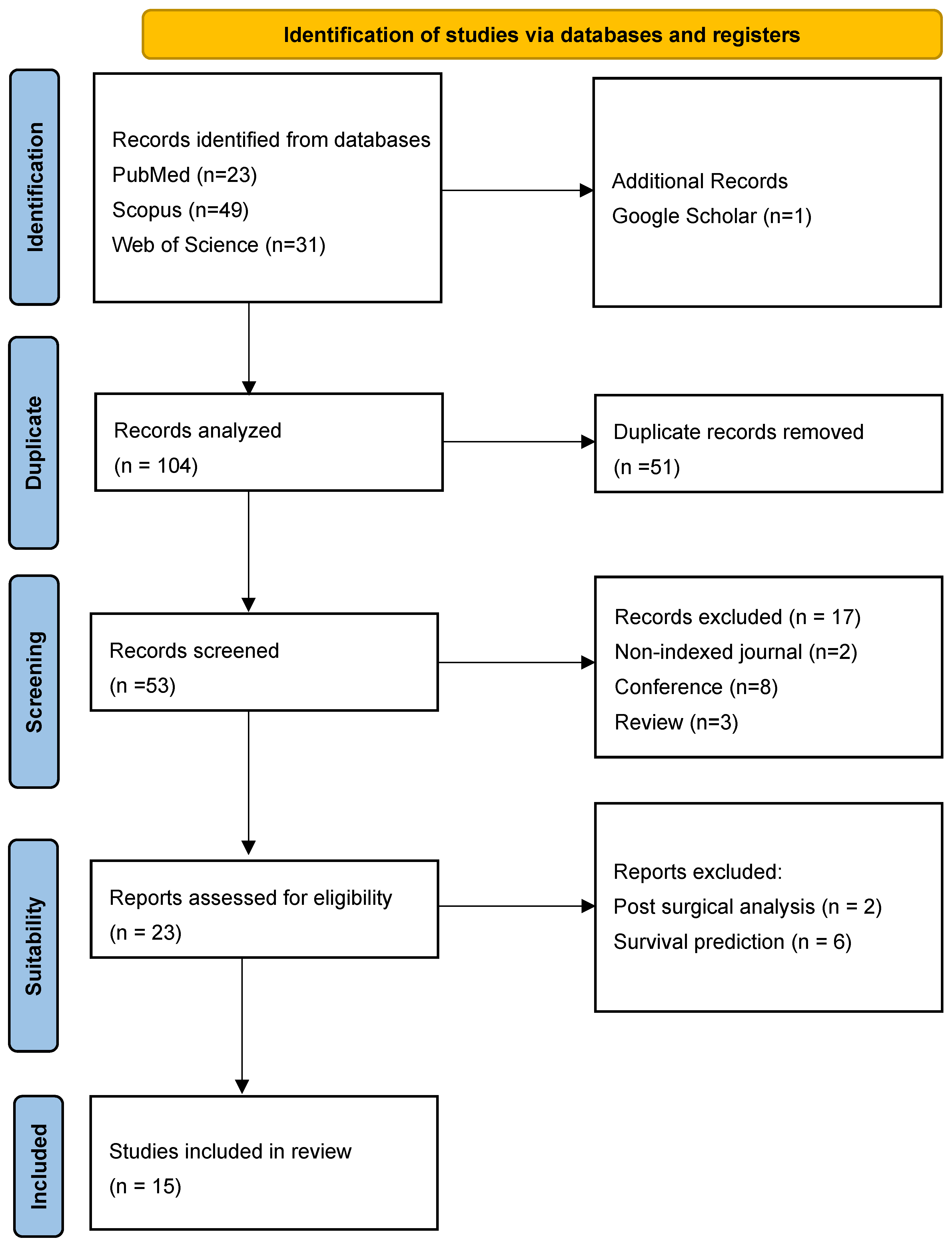
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Systematic Search
- Scopus: 49 articles
- Web of Science: 31 articles
- PubMed: 23 articles
- Google Scholar: 1 article
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
- Scientific literature focused on artificial intelligence techniques.
- Scientific literature employed magnetic resonance imaging.
- Studies to address the diagnosis of GBM.
- Scientific literature exclusively of Quartils Q1 to Q2 from journals indexed in the Journal Citation Report (JCR).
2.4. Exclusion Criteria
- Studies related to imaging techniques other than MRI.
- Evidence lacking sufficient methodological rigor or clinical relevance.
- Scientific literature in languages other than English.
- Editorials and other non-peer reviewed articles.
- Full-text not available.
- Studies conducted in animals.
2.5. Study Selection
2.6. Data Extraction
3. Results
3.1. Tumor Type and Grade Classification
3.2. Molecular Biomarker Prediction
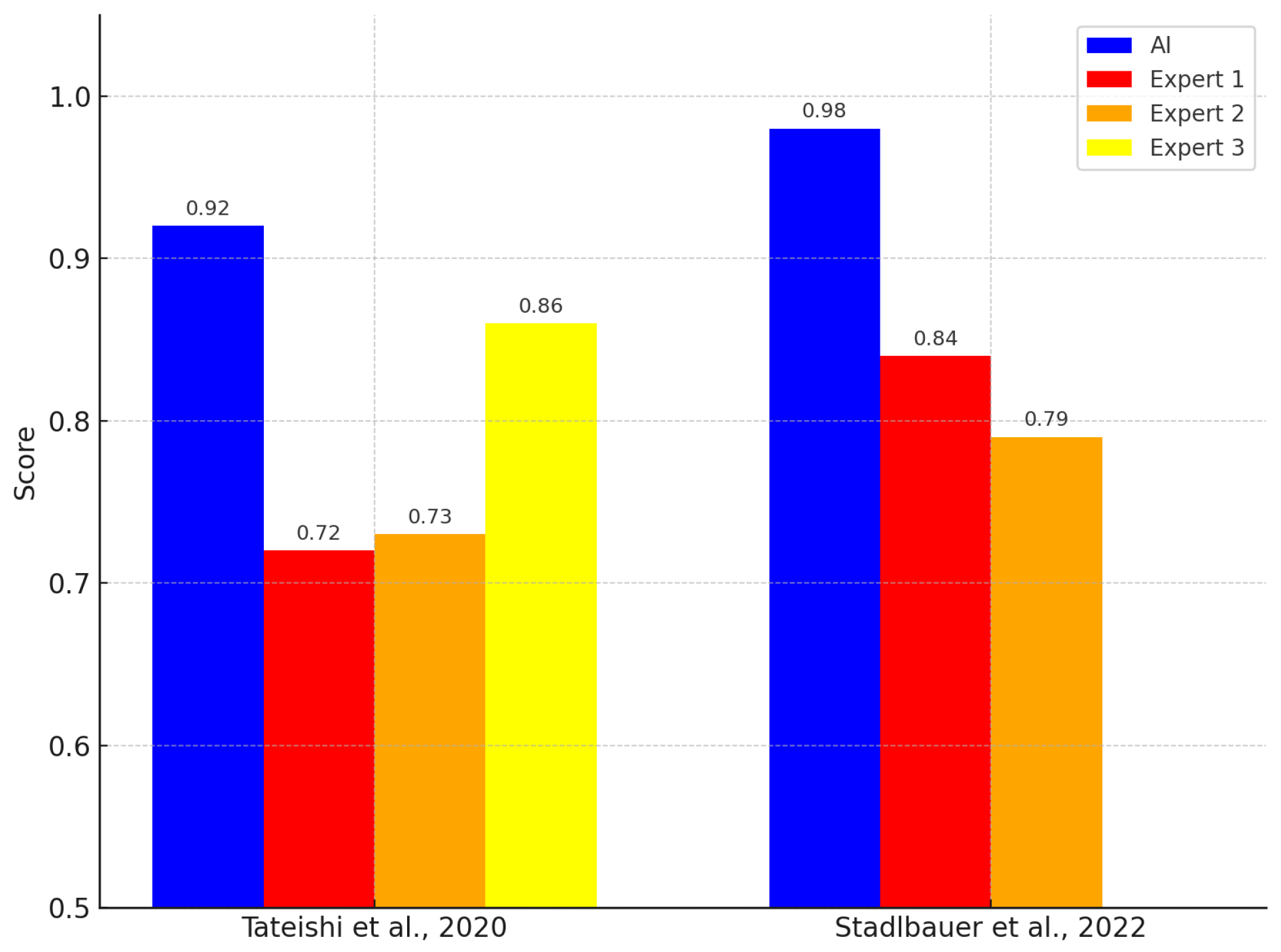
3.3. Comparison with Clinical Experts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GBM | Glioblastoma multiforme |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| ML | Machine learning |
| DL | Deep learning |
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| FLAIR | Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery |
| ADC | Apparent diffusion coefficient |
| T1WI | T1-weighted imaging |
| T2WI | T2-weighted imaging |
| T1C | T1-weighted contrast-enhanced imaging |
| DWI | Diffusion-weighted imaging |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| SVM | Support vector machine |
| RF | Random forest |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
| LR | Logistic regression |
| LASSO | Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator |
| GBDT | Gradient boosting decision tree |
| TPOT | Tree-based pipeline optimization tool |
| RSF | Random survival forest |
| PCNSL | Primary central nervous system lymphoma |
| BM | Brain metastases |
| MP | MaxPooling |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| CE-T1WI | Contrast-enhanced T1-weighted imaging |
References
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.E.; Kahng, J.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.S.; Yoon, S.J.; Um, J.-Y.; Kim, W.K.; Lee, J.-K.; Park, J.; et al. Human glioblastoma arises from subventricular zone cells with low-level driver mutations. Nature 2018, 560, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneswaran, K.; Neill, S.; Hadjipanayis, C.G. Beyond the World Health Organization grading of infiltrating gliomas: Advances in the molecular genetics of glioma classification. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.; Wang, L.; Ji, B.; Lei, Y.; Ali, A.; Liu, T.; Curran, W.J.; Mao, H.; Yang, X. Machine-learning based classification of glioblastoma using delta-radiomic features derived from dynamic susceptibility contrast enhanced magnetic resonance images: Introduction. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2019, 9, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinburne, N.C.; Schefflein, J.; Sakai, Y.; Oermann, E.K.; Titano, J.J.; Chen, I.; Tadayon, S.; Aggarwal, A.; Doshi, A.; Nael, K. Machine learning for semiautomated classification of glioblastoma, brain metastasis and central nervous system lymphoma using magnetic resonance advanced imaging. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, S.K.; Brothers, S.P.; Wahlestedt, C. Emerging treatment strategies for glioblastoma multiforme. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampie, L.; Woolf, E.C.; Dardis, C. Immunotherapeutic advancements for glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichardo-Rojas, P.S.; Pichardo-Rojas, D.; Marín-Castañeda, L.A.; Palacios-Cruz, M.; Rivas-Torres, Y.I.; Calderón-Magdaleno, L.F.; Sánchez-Serrano, C.D.; Chandra, A.; Dono, A.; Karschnia, P.; et al. Prognostic value of surgical resection over biopsy in elderly patients with glioblastoma: A meta-analysis. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2024, 169, 469–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerritsen, J.K.W.; Broekman, M.L.D.; De Vleeschouwer, S.; Schucht, P.; Nahed, B.V.; Berger, M.S.; Vincent, A.J.P.E. Safe surgery for glioblastoma: Recent advances and modern challenges. Neuro-Oncol. Pract. 2022, 9, 364–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrabalek, L.; Kalita, O.; Vaverka, M.; Zlevorova, M.; Ehrmann, J.; Cechakova, E.; Adamus, M.; Novak, V.; Langova, K. Resection versus biopsy of glioblastomas in eloquent brain areas. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2015, 159, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.S.; Ning, S.; Eschbacher, J.M.; Baxter, L.C.; Gaw, N.; Ranjbar, S.; Plasencia, J.; Dueck, A.C.; Peng, S.; Smith, K.A.; et al. Radiogenomics to characterize regional genetic heterogeneity in glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2017, 19, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.S.; Ning, S.; Eschbacher, J.M.; Gaw, N.; Dueck, A.C.; Smith, K.A.; Nakaji, P.; Plasencia, J.; Ranjbar, S.; Price, S.J.; et al. Multi-parametric MRI and texture analysis to visualize spatial histologic heterogeneity and tumor extent in glioblastoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; Van Den Bent, M.; Tonn, J.C.; Stupp, R.; Preusser, M.; Cohen-Jonathan-Moyal, E.; Henriksson, R.; Le Rhun, E.; Balana, C.; Chinot, O.; et al. European Association for Neuro-Oncology (EANO) guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of adult astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e315–e329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ahn, S.S.; Chang, J.H.; Suh, C.-O. Hypofractionated re-irradiation after maximal surgical resection for recurrent glioblastoma: Therapeutic adequacy and its prognosticators of survival. Yonsei Med. J. 2018, 59, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.; Vattoth, S.; Jacob, R.; Manzil, F.F.P.; O’Malley, J.P.; Borghei, P.; Patel, B.N.; Curé, J.K. Radiation necrosis in the brain: Imaging features and differentiation from tumor recurrence. Radiographics 2012, 32, 1343–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Luo, Z.-W.; Ovcjak, A.; Alanazi, R.; Bao, M.-H.; Feng, Z.-P.; Sun, H.-S. Role of TRPM2 in brain tumours and potential as a drug target. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.-W.; Yang, L.-T.; Liu, J.; Dai, Z.-Y.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Liang, X.-S.; Luo, P.; Zhang, J.; et al. A TGF-β signaling-related lncRNA signature for prediction of glioma prognosis, immune microenvironment, and immunotherapy response. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suter, Y.; Knecht, U.; Alão, M.; Valenzuela, W.; Hewer, E.; Schucht, P.; Wiest, R.; Reyes, M. Radiomics for glioblastoma survival analysis in pre-operative MRI: Exploring feature robustness, class boundaries, and machine learning techniques. Cancer Imaging 2020, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, J.N.; Dorr, F.; Goicochea, M.T.; Slezak, D.F.; Farez, M. Acute Headache Diagnosis in the Emergency Department: Accuracy and Safety of an Artificial Intelligence System (P5. 10-002); AAN Enterprises: Bengaluru, India, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Raab, S.S.; Grzybicki, D.M.; Janosky, J.E.; Zarbo, R.J.; Meier, F.A.; Jensen, C.; Geyer, S.J. Clinical impact and frequency of anatomic pathology errors in cancer diagnoses. Cancer Interdiscip. Int. J. Am. Cancer Soc. 2005, 104, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, M.; Nakaura, T.; Kitajima, M.; Uetani, H.; Nakagawa, M.; Inoue, T.; Kuroda, J.-I.; Mukasa, A.; Yamashita, Y. An initial experience of machine learning based on multi-sequence texture parameters in magnetic resonance imaging to differentiate glioblastoma from brain metastases. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 410, 116514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Yin, X.-C.; Jiao, B.-Y.; Li, J.; Jia, P.; Zhang, X.-W.; Cheng, X.-H.; Ren, J.-X.; Lan, H.-D.; Hou, W.-B.; et al. Evaluation of adverse effects/events of genetically modified food consumption: A systematic review of animal and human studies. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2022, 34, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Singhrao, K.; Zhong, X.; Gao, Y.; Qi, S.X.; Yang, Y.; Ruan, D.; Lewis, J.H. An automatic deep learning–based workflow for glioblastoma survival prediction using preoperative multimodal MR images: A feasibility study. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 6, 100746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, B.-S.; Jeon, S.H.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, I.A. Prediction of pseudoprogression versus progression using machine learning algorithm in glioblastoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhao, F.; Tian, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, X.; Xu, J. Radiomics-based machine learning technology enables better differentiation between glioblastoma and anaplastic oligodendroglioma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, F.-Y.; Le, N.Q.K.; Chen, C.-Y. A multiparametric MRI-based radiomics analysis to efficiently classify tumor subregions of glioblastoma: A pilot study in machine learning. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zheng, A.; Ou, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, X. Comparison of radiomics-based machine-learning classifiers in diagnosis of glioblastoma from primary central nervous system lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, M.; Radakovich, N.; Nazha, A. Machine learning in oncology: What should clinicians know? JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2020, 4, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; Prisma-P Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathla, G.; Priya, S.; Liu, Y.; Ward, C.; Le, N.H.; Soni, N.; Maheshwarappa, R.P.; Monga, V.; Zhang, H.; Sonka, M. Radiomics-based differentiation between glioblastoma and primary central nervous system lymphoma: A comparison of diagnostic performance across different MRI sequences and machine learning techniques. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 8703–8713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Fan, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, S.; Liang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, H.; et al. Image-based differentiation of intracranial metastasis from glioblastoma using automated machine learning. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 855990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hu, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Shen, H.; Zheng, F.; Zang, Y.; Chen, X. Machine learning-based analysis of magnetic resonance radiomics for the classification of gliosarcoma and glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 699789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquini, L.; Napolitano, A.; Tagliente, E.; Dellepiane, F.; Lucignani, M.; Vidiri, A.; Ranazzi, G.; Stoppacciaro, A.; Moltoni, G.; Nicolai, M.; et al. Deep learning can differentiate IDH-mutant from IDH-wild GBM. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadlbauer, A.; Heinz, G.; Marhold, F.; Meyer-Bäse, A.; Ganslandt, O.; Buchfelder, M.; Oberndorfer, S. Differentiation of glioblastoma and brain metastases by MRI-based oxygen metabolomic radiomics and deep learning. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Meng, L.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, H.; Li, J.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Handcrafted and deep learning-based radiomic models can distinguish GBM from brain metastasis. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 5518717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, M.; Nakaura, T.; Namimoto, T.; Kitajima, M.; Uetani, H.; Tateishi, M.; Oda, S.; Utsunomiya, D.; Makino, K.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Machine learning based on multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging to differentiate glioblastoma multiforme from primary cerebral nervous system lymphoma. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018, 108, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.; Agarwal, A.; Ward, C.; Locke, T.; Monga, V.; Bathla, G. Survival prediction in glioblastoma on post-contrast magnetic resonance imaging using filtration based first-order texture analysis: Comparison of multiple machine learning models. Neuroradiol. J. 2021, 34, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cepeda, S.; Pérez-Nuñez, A.; García-García, S.; García-Pérez, D.; Arrese, I.; Jiménez-Roldán, L.; García-Galindo, M.; González, P.; Velasco-Casares, M.; Zamora, T.; et al. Predicting short-term survival after gross total or near total resection in glioblastomas by machine learning-based radiomic analysis of preoperative MRI. Cancers 2021, 13, 5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
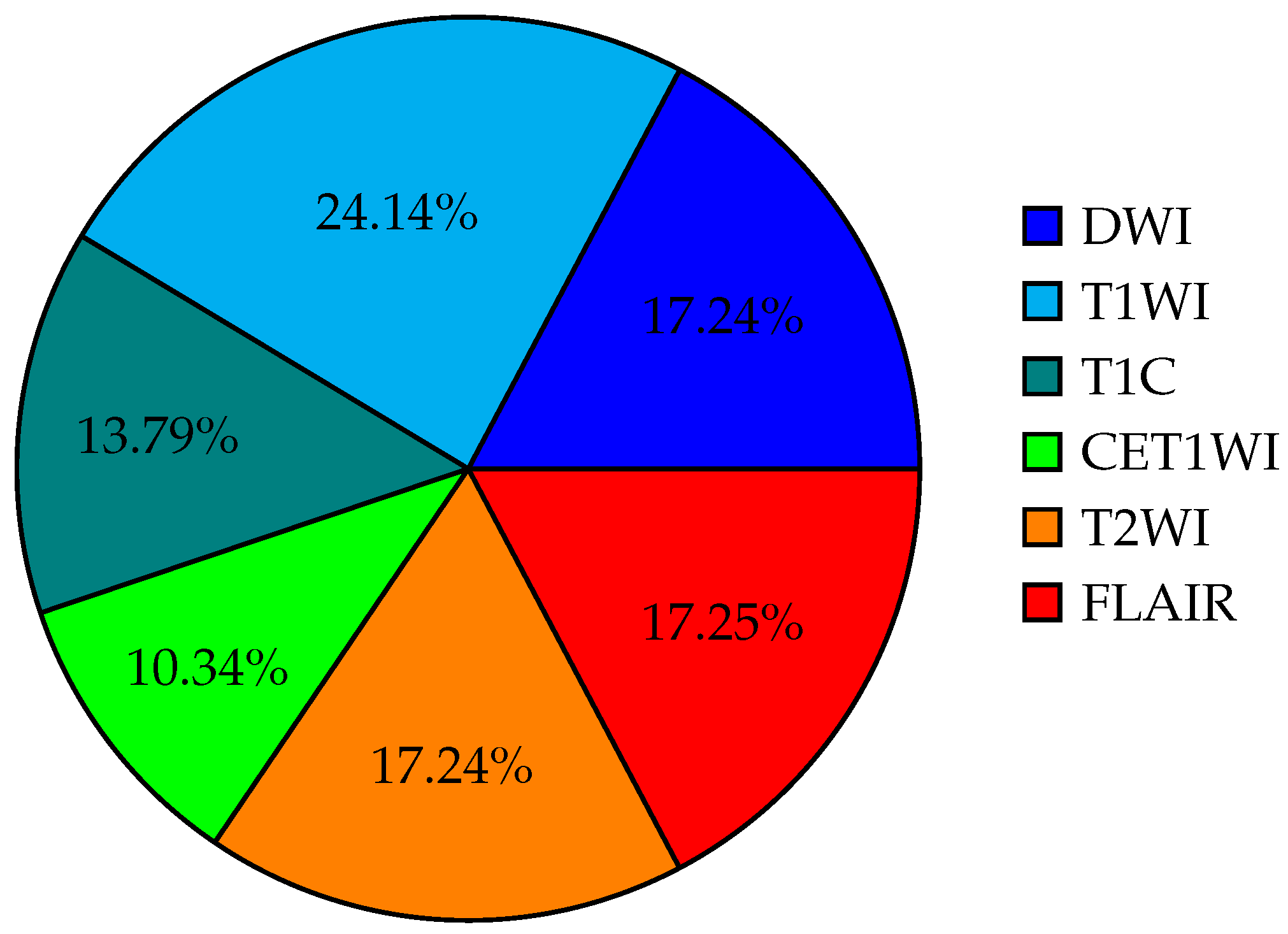
| Reference Country Year | Description | Sample | Images | Model | Metric AUC | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient | DWI | T1WI | T1C | ADS | CET1WI | T2WI | FLAIR | AI | Exp. 1 Exp. 2 Exp. 3 | |||
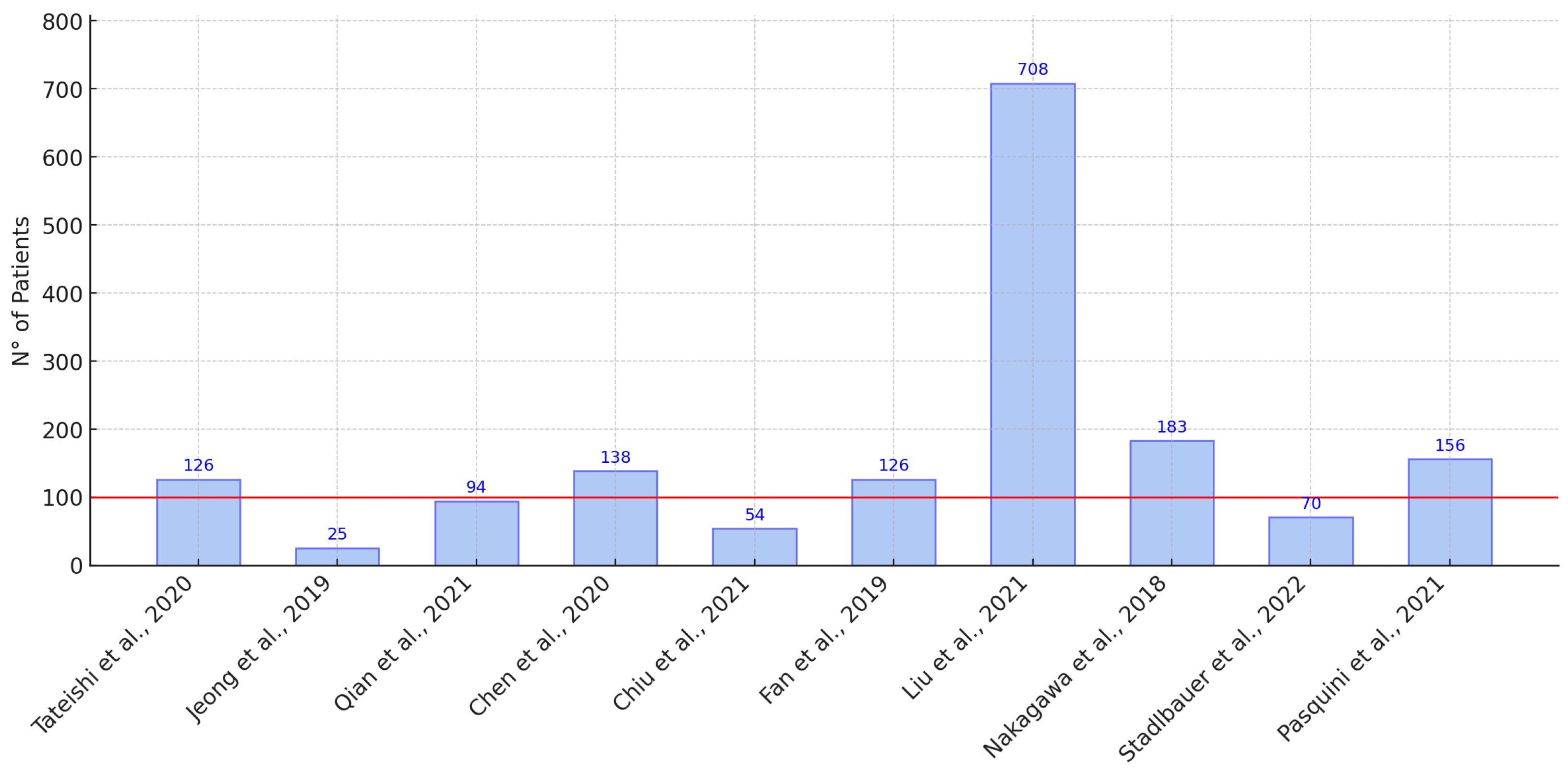
| [20] JAPAN 2020 | Initial machine-learning approach using multi-sequence MRI textures to differentiate glioblastoma from metastases. | 126 | X | X | X | X | X | SVM | 0.92 | 0.72 0.73 0.86 | ||
| [3] CHINA 2019 | Classification of glioma using machine learning and delta-radiomic features from dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced MRI. | 25 | X | X | X | X | RF | 0.94 | — — — | |||
| [30] USA 2021 | Radiomics-based differentiation between GBM and primary CNS lymphoma using multiple MRI sequences and machine-learning models. | 94 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ML RF, SVM, | 0.97 | — — — | |
| [26] CHINA 2020 | Comparative radiomics study for GBM and primary CNS lymphoma diagnosis using machine-learning classifiers. | 138 | X | X | X | LDA SVM LR | LDA: 0.978 SVM: 0.959 LR: 0.933 | — — — | ||||
| [25] TAIWAN 2021 | Multiparametric MRI-based radiomics analysis for efficient tumor subregion classification of glioblastoma. | 54 | X | X | X | X | RF | Necrosis: 93.6 Solid part: 90.4 Peritumoral tissue: 95.8 Edema: 0.904 | — — — | |||
| [24] CHINA 2019 | Radiomics-based differentiation of GBM from anaplastic oligodendroglioma using advanced machine-learning techniques. | 126 | X | LDA, SVM | LDA + Dist. corr: 0.986 LDA + LASSO: 0.994 LDA + GBDT: 0.970 SVM + Dist. corr: 0.923 SVM + LASSO: 0.817 | — — — | ||||||
| [31] CHINA 2022 | Automated machine learning for image-based differentiation between GBM and metastasis. | 708 | X | X | TPOT | 0.867 | — — — | |||||
| [32] CHINA 2021 | Machine-learning analysis of MRI radiomics for gliosarcoma vs. glioblastoma classification. | 183 | X | X | X | SVM, AdaBoost, RF | 0.85 | — — — | ||||
| [33] ITALY 2021 | Deep-learning differentiation of IDH status in glioblastoma using multi-parametric MRI. | 156 | X | X | X | X | X | X | CNN | T1: 0.71 T2: 0.63 FLAIR: 0.74 MPRAGE: 0.62 ADC: 0.45 | — — — | |
| [4] USA 2019 | Machine-learning semi-automation for classifying GBM, metastasis, and CNS lymphoma. | 26 | X | X | X | X | MLP, SVM | 0.692 | — — — | |||
| [34] AUSTRIA 2022 | Differentiation of glioblastoma and brain metastases using oxygen metabolomic radiomics and deep learning. | 133 | X | X | X | X | X | 1D-CNN | 0.91 | — — — | ||
| [35] CHINA 2021 | Radiomic models for distinguishing GBM from brain metastasis using handcrafted and deep-learning features. | 268 | X | X | X | X | X | X | ML | 0.97 | — — — | |
| [36] JAPAN 2018 | Machine learning based on multi-parametric MRI to differentiate GBM from primary CNS lymphoma. | 70 | X | X | X | X | XGBoost | 0.98 | 0.84 0.79 — | |||
| [37] USA 2021 | Survival analysis in GBM using post-contrast MRI and multiple machine-learning models. | 85 | X | X | X | X | SVM XGBoost | 0.811 | — — — | |||
| [38] SPAIN 2021 | Machine-learning analysis for predicting short-term survival after surgery in GBM cases. | 203 | X | X | X | X | RSF | 0.769 | — — — | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Contreras, K.; Velez-Varela, P.E.; Casanova-Carvajal, O.; Alvarez, A.L.; Urbano-Bojorge, A.L. A Review of Artificial Intelligence-Based Systems for Non-Invasive Glioblastoma Diagnosis. Life 2025, 15, 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040643
Contreras K, Velez-Varela PE, Casanova-Carvajal O, Alvarez AL, Urbano-Bojorge AL. A Review of Artificial Intelligence-Based Systems for Non-Invasive Glioblastoma Diagnosis. Life. 2025; 15(4):643. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040643
Chicago/Turabian StyleContreras, Kebin, Patricia E. Velez-Varela, Oscar Casanova-Carvajal, Angel Luis Alvarez, and Ana Lorena Urbano-Bojorge. 2025. "A Review of Artificial Intelligence-Based Systems for Non-Invasive Glioblastoma Diagnosis" Life 15, no. 4: 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040643
APA StyleContreras, K., Velez-Varela, P. E., Casanova-Carvajal, O., Alvarez, A. L., & Urbano-Bojorge, A. L. (2025). A Review of Artificial Intelligence-Based Systems for Non-Invasive Glioblastoma Diagnosis. Life, 15(4), 643. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040643






