Dura Closure Tactics to Prevent CSF Leakage in Microvascular Decompression Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inoue, T.; Shitara, S.; Shima, A.; Goto, Y.; Fukushima, T. Double collagen matrix grafting for dural closure in microvascular decompression: An alternative use of autologous fascial grafting. Acta Neurochir. 2021, 163, 2395–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kshettry, V.R.; Lobo, B.; Lim, J.; Sade, B.; Oya, S.; Lee, J.H. Evaluation of Non-Watertight Dural Reconstruction with Collagen Matrix Onlay Graft in Posterior Fossa Surgery. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2016, 59, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhao, W.G.; Pu, C.H.; Shen, J.K. Clinical application of artificial dura mater to avoid cerebrospinal fluid leaks after microvascular decompression surgery. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 2005, 48, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narotam, P.K.; Qiao, F.; Nathoo, N. Collagen matrix duraplasty for posterior fossa surgery: Evaluation of surgical technique in 52 adult patients. Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narotam, P.K.; Reddy, K.; Fewer, D.; Qiao, F.; Nathoo, N. Collagen matrix duraplasty for cranial and spinal surgery: A clinical and imaging study. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 106, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Kong, D.S.; Lee, J.A.; Park, K. Intraoperative management to prevent cerebrospinal fluid leakage after microvascular decompression: Dural closure with a ‘’plugging muscle’’ method. Neurosurg. Rev. 2007, 30, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samii, M.; Gunther, T.; Iaconetta, G.; Muehling, M.; Vorkapic, P.; Samii, A. Microvascular decompression to treat hemifacial spasm: Long-term results for a consecutive series of 143 patients. Neurosurgery 2002, 50, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoker, M.A.; Forbes, J.A.; Hanif, R.; Cooper, C.; Nian, H.; Konrad, P.E.; Neimat, J.S. Decreased Rate of CSF Leakage Associated with Complete Reconstruction of Suboccipital Cranial Defects. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2012, 73, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; You, N.; Liu, Y.; Yao, A.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, J.; Xu, B. Duraplasty with Cervical Fascia Autograft to Reduce Postoperative Complications of Posterior Fossa Tumor Surgery with Suboccipital Midline Approach. World Neurosurg. 2020, 134, e1115–e1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzayed, B.; Kafadar, A.M.; Oguzoglu, S.A.; Canbaz, B.; Kaynar, M.Y. Duraplasty using autologous fascia lata reenforced by on-site pedicled muscle flap: Technical note. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2009, 20, 435–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, I.; Vohra, A.H.; Shams, S. Management of Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak following Posterior Cranial Fossa Surgery. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 32, 1439–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinaci, A.; Algra, A.; Heuts, S.; O’Donnell, D.; van der Zwan, A.; van Doormaal, T. Effectiveness of Dural Sealants in Prevention of Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage After Craniotomy: A Systematic Review. World Neurosurg. 2018, 118, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sade, B.; Oya, S.; Lee, J.H. Non-watertight dural reconstruction in meningioma surgery: Results in 439 consecutive patients and a review of the literature. Clinical article. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litvack, Z.N.; West, G.A.; Delashaw, J.B.; Burchiel, K.J.; Anderson, V.C. Dural augmentation: Part I-evaluation of collagen matrix allografts for dural defect after craniotomy. Neurosurgery 2009, 65, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narotam, P.K.; van Dellen, J.R.; Bhoola, K.D. A clinicopathological study of collagen sponge as a dural graft in neurosurgery. J. Neurosurg. 1995, 82, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanrikulu, L.; Buchfelder, M.; Naraghi, R. Fleece-Bound Tissue Sealing in Microvascular Decompression. Turk. Neurosurg. 2017, 27, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Than, K.D.; Baird, C.J.; Olivi, A. Polyethylene glycol hydrogel dural sealant may reduce incisional cerebrospinal fluid leak after posterior fossa surgery. Neurosurgery 2008, 63, ONS182-186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickenbacher, A.; Breitenstein, S.; Lesurtel, M.; Frilling, A. Efficacy of TachoSil a fibrin-based haemostat in different fields of surgery—A systematic review. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2009, 9, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broggi, G.; Ferroli, P.; Franzini, A.; Servello, D.; Dones, I. Microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia: Comments on a series of 250 cases, including 10 patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2000, 68, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jodicke, A.; Winking, M.; Deinsberger, W.; Boker, D.K. Microvascular decompression as treatment of trigeminal neuralgia in the elderly patient. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 1999, 42, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkanis, S.N.; Eskandar, E.N.; Carter, B.S.; Barker, F.G., 2nd. Microvascular decompression surgery in the United States, 1996 to 2000: Mortality rates, morbidity rates, and the effects of hospital and surgeon volumes. Neurosurgery 2003, 52, 1251–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, M.R.; Jannetta, P.J.; Clyde, B.L.; Subach, B.R.; Comey, C.H.; Resnick, D.K. Microvascular decompression of cranial nerves: Lessons learned after 4400 operations. J. Neurosurg. 1999, 90, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Kassam, A.; Horowitz, M.; Chang, Y.F. Microvascular decompression in the management of glossopharyngeal neuralgia: Analysis of 217 cases. Neurosurgery 2002, 50, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aihara, N.; Yamada, H.; Takahashi, M.; Inagaki, A.; Murakami, S.; Mase, M. Postoperative Headache after Undergoing Acoustic Neuroma Surgery via the Retrosigmoid Approach. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2017, 57, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ducic, I.; Felder, J.M., 3rd; Endara, M. Postoperative headache following acoustic neuroma resection: Occipital nerve injuries are associated with a treatable occipital neuralgia. Headache 2012, 52, 1136–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Laulloo, A.; Vats, A.; Nath, F. Microvascular decompression: Incidence and prevention of postoperative CSF leakage in a consecutive series of 134 patients. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 34, 416–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretta, A.; Epskamp, M.; Ledermann, L.; Staartjes, V.E.; Neidert, M.C.; Regli, L.; Stienen, M.N. Collagen-bound fibrin sealant (TachoSil(R)) for dural closure in cranial surgery: Single-centre comparative cohort study and systematic review of the literature. Neurosurg. Rev. 2022, 45, 3779–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, J.C.; Spencer, R.F. The role of polymethylmethacrylate bone cement in modern orthopaedic surgery. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2007, 89, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, R.K.; Shafritz, A.B. Bone cement. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2011, 36, 1086–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibbaro, S.; Cebula, H.; Scibilia, A.; Spatola, G.; Todeschi, J.; Gubian, A.; Scheer, L.; Ligarotti, G.; Moghaddamjou, A.; Hajhouji, F.; et al. Retrosigmoid Approach: Investigating the Role of a C-Shaped Skin Incision and Muscle Flaps in Improving Functional Outcome and Reducing Postoperative Pain. World Neurosurg. 2018, 111, e340–e347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chibbaro, S.; Cebula, H.; Zaed, I.; Gubian, A.; Todeschi, J.; Scibilia, A.; Nannavecchia, B.; Scheer, L.; Bozzi, M.T.; Mahoudeau, P.; et al. A Laboratory Investigation on a Tailored Skin and Muscle Flap Variant for the Retrosigmoid Approach. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2022, 83, e438–e442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, F.G., 2nd; Jannetta, P.J.; Bissonette, D.J.; Larkins, M.V.; Jho, H.D. The long-term outcome of microvascular decompression for trigeminal neuralgia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.H.; Jee, T.K.; Lee, J.A.; Park, K. Postoperative complications of microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm: Lessons from experience of 2040 cases. Neurosurg. Rev. 2016, 39, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venable, G.T.; Roberts, M.L.; Lee, R.P.; Michael, L.M., 2nd. Primary Dural Closure for Retrosigmoid Approaches. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2018, 79, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, F.G., 2nd; Jannetta, P.J.; Bissonette, D.J.; Shields, P.T.; Larkins, M.V.; Jho, H.D. Microvascular decompression for hemifacial spasm. J. Neurosurg. 1995, 82, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbok, P.; Singhal, A.; Mills, J.; Cochrane, D.D.; Price, A.V. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak and pseudomeningocele formation after posterior fossa tumor resection in children: A retrospective analysis. Childs Nerv. Syst. 2007, 23, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linskey, M.E.; Ratanatharathorn, V.; Penagaricano, J. A prospective cohort study of microvascular decompression and Gamma Knife surgery in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 109, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazit, Y.A.; Celenk, F.; Duzlu, M.; Goksu, N. Management of cerebrospinal fluid leak following retrosigmoid posterior cranial fossa surgery. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2009, 71, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.; Sung, W.S.; Shaya, M.; Patwardhan, R.; Willis, B.; Smith, D.; Nanda, A. Complications of posterior cranial fossa surgery—An institutional experience of 500 patients. Surg. Neurol. 2009, 72, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.D.; Zhang, Y.; Ying, T.T.; Zhu, J.; Li, S.T. Operative Complications of Microvascular Decompression for Hemifacial Spasm: Experience of 1548 Cases. World Neurosurg. 2017, 107, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Ordaz, A.; Durcanova, B.; Viner, J.A.; Theodosopoulos, P.V.; Aghi, M.K.; McDermott, M.W. Cerebrospinal Fluid Leaks and Pseudomeningocele after Posterior Fossa Surgery: Effect of an Autospray Dural Sealant. Cureus 2020, 12, e8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, D.; Kobayashi, M.; Hirata, S.; Terano, N.; Wakiya, K.; Fujimaki, T. Natural Dural Defect of the Posterior Fossa Dura as a Risk Factor for Postoperative Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage. World Neurosurg. 2020, 142, e229–e232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
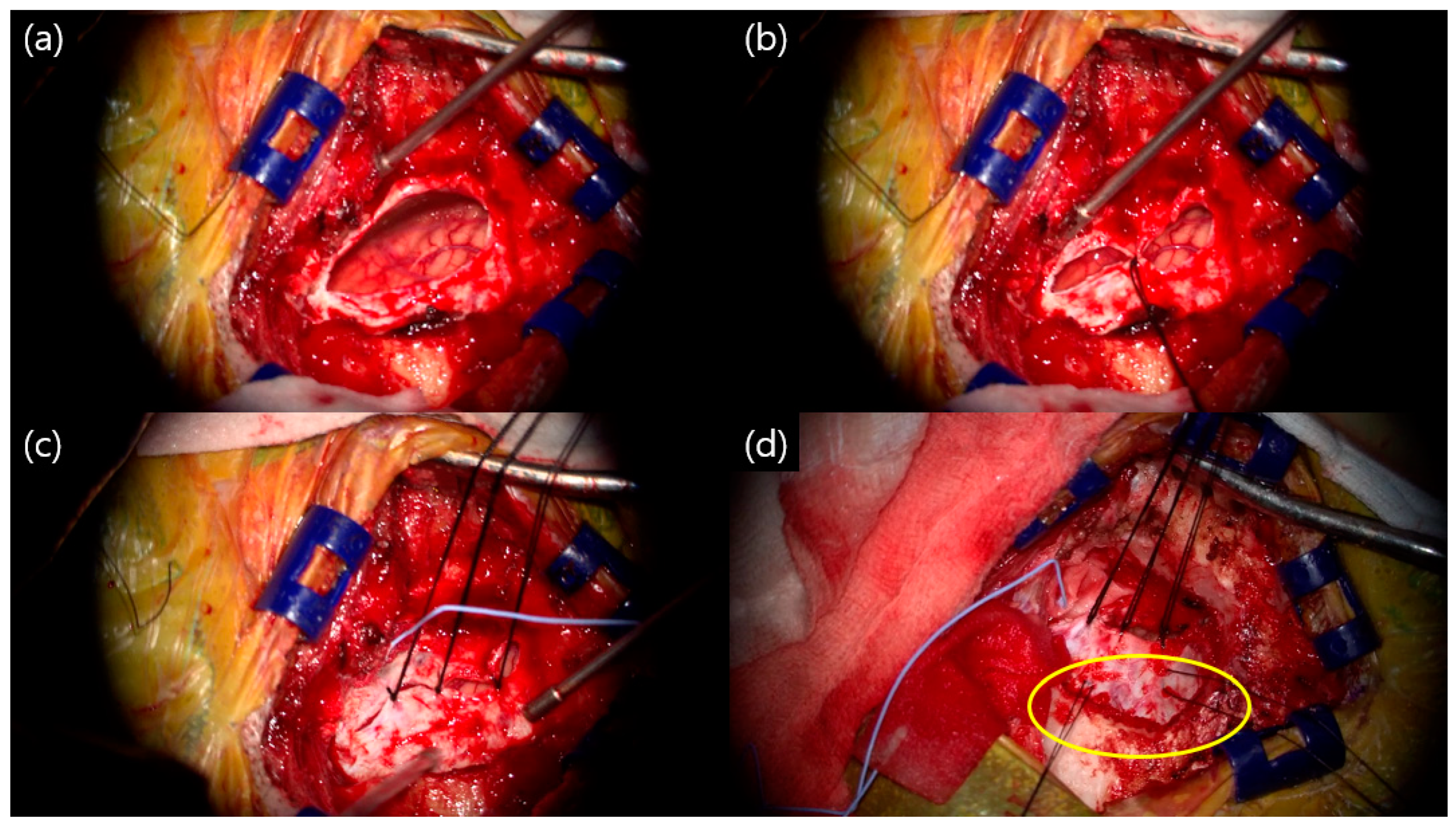
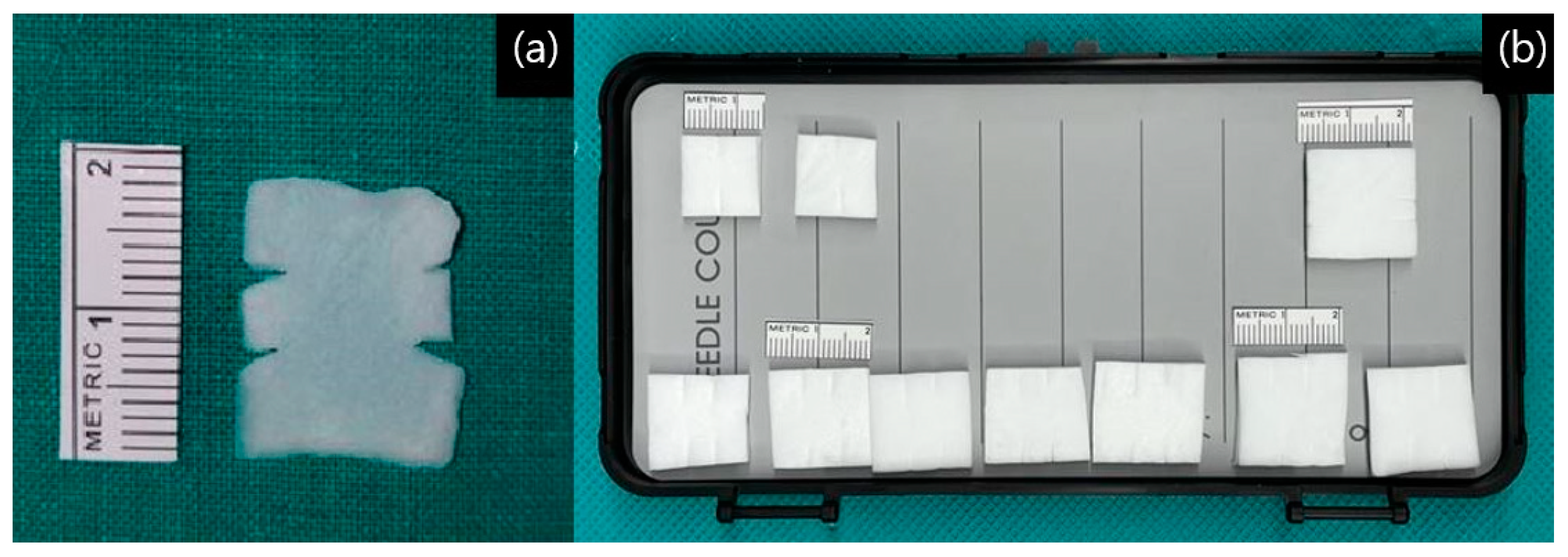
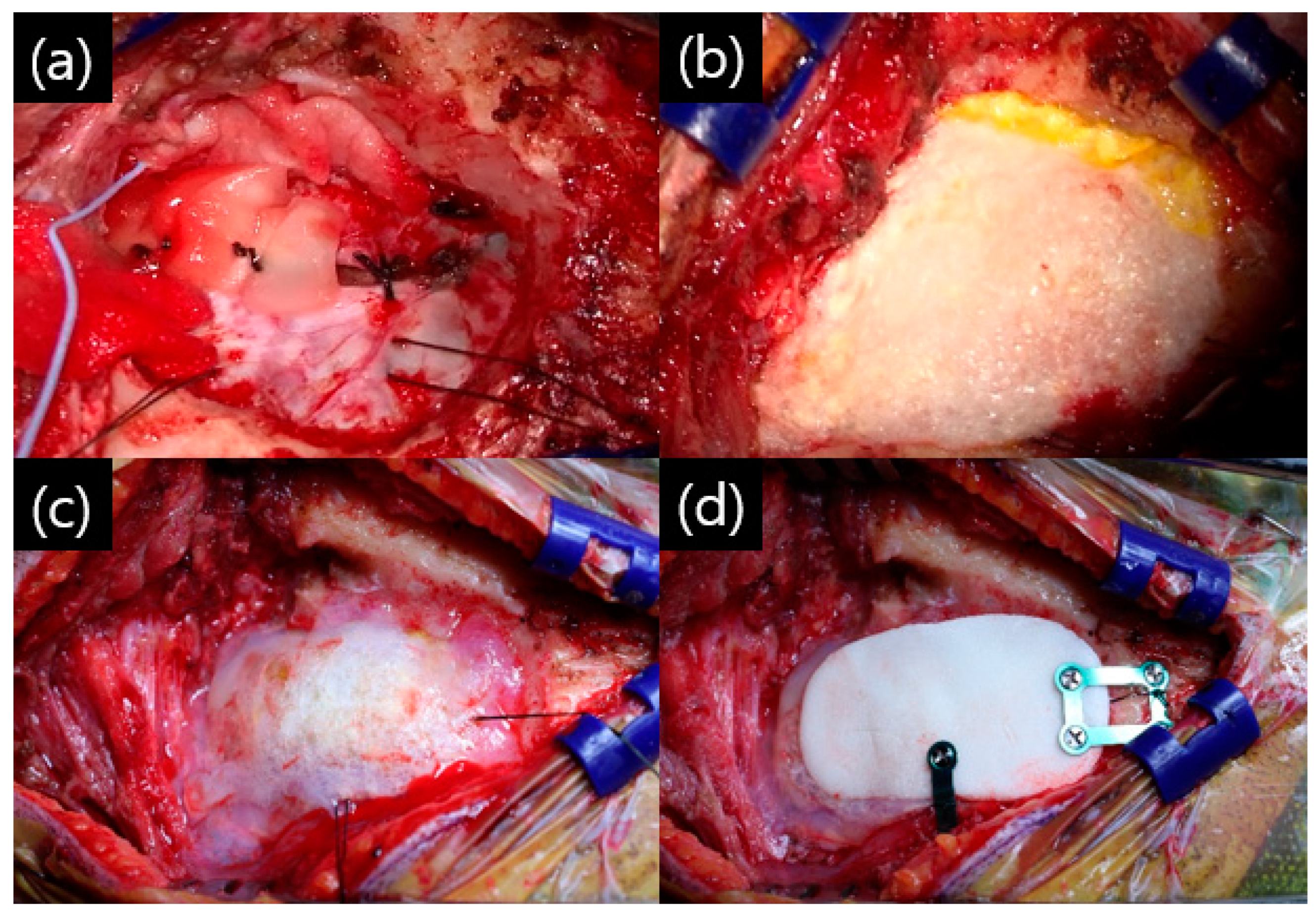
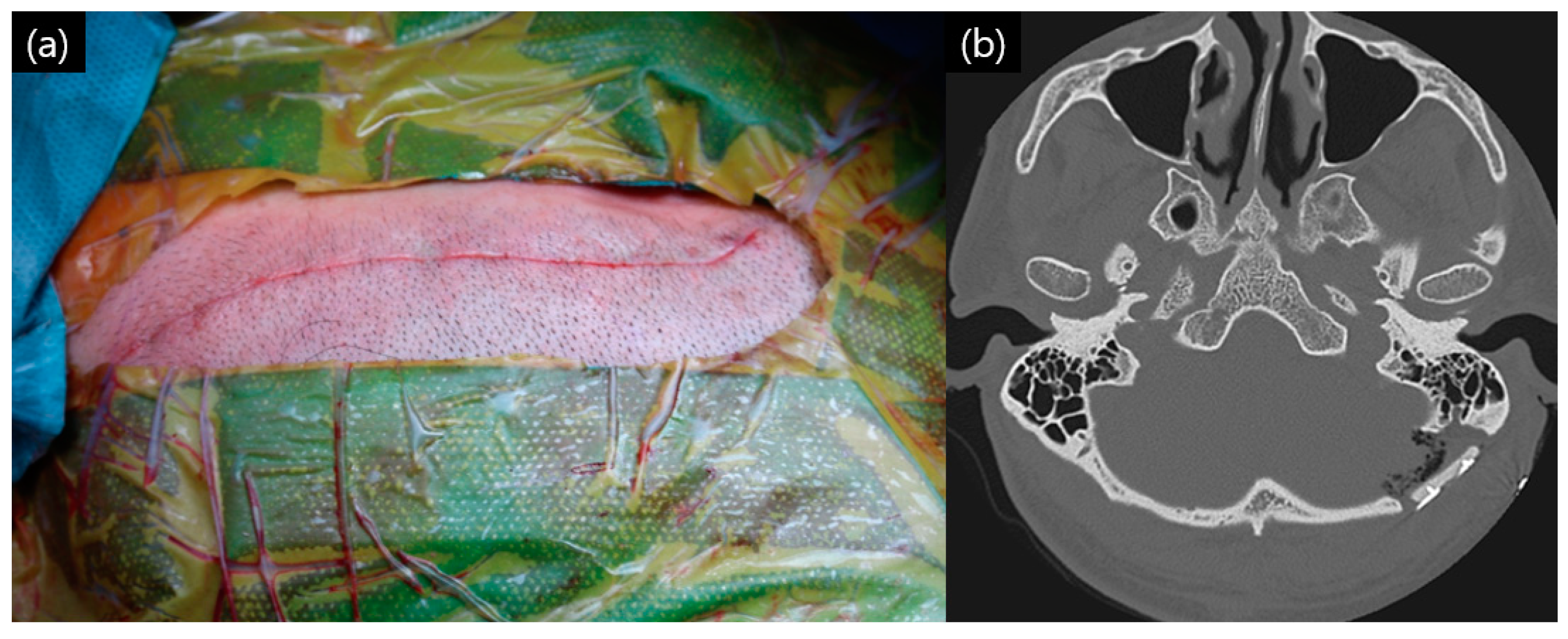
| Patients Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Median age at MVD (range) | 58 (19–82) |
| Sex (M:F) | 131:344 |
| Operation side (left:right) | 223:252 |
| Disease (TN/HFS/GPN) | 47/427/1 |
| Average hospital days (range) | 7.2 (4–18) |
| Re-do operation | 4 (0.8%) |
| Outcome associate with complication | |
| Suspected CSF leakage | 18 (3.8%) |
| CSF rhinorrhea | 5 (1.1%) |
| CSF diversion via LD catheter insertion | 5 (1.1%) |
| Revision operation | 0 (0.0%) |
| Infection associate with operation | 0 (0.0%) |
| Epidural hematoma | 0 (0.0%) |
| Sex/Age | Disease | Side | Symptom Duration (Months) | Offending Vessel | Past Medical History |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F/39 | HFS | Right | 18 | AICA | Prolactinoma |
| M/63 | HFS | Left | 36 | AICA-PICA-VA | HTN, dyslipidemia |
| F/30 | HFS | Left | 42 | AICA-PICA | - |
| M/38 | HFS | Right | 24 | AICA | Crohn’s disease |
| F/59 | HFS | Right | 26 | AICA-VA | Dyslipidemia, thyroid cancer |
| Trigeminal Neuralgia | |
|---|---|
| Total patients | 47 |
| Median age at MVD surgery (range) | 63.5 (28–80) |
| Operation side (left:right) | 17:30 |
| Sex (male:female) | 16:31 |
| Postoperative hearing difficulty | 1 (2.1%) |
| Suspected CSF leakage | 1 (2.1%) |
| Symptom free at 1 month after operation | 41 (87.2%) |
| Hemifacial spasm | |
| Total patients | 427 |
| Median age at MVD surgery (range) | 58 (19–82) |
| Operation side (left:right) | 227:200 |
| Sex (male:female) | 115:312 |
| Postoperative hearing difficulty | 32 (7.5%) |
| Suspected CSF leakage | 17 (4.0%) |
| Symptom free at 1 month after operation | 388 (90.9%) |
| Glossopharyngeal neuralgia | |
| Left side lesion, 65 years old female, with no complication, postoperative pain free | |
| Author | Year | N | Surgery | Dural Closing Method | Overall CSF Leakage Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Barker et al. [35] | 1995 | 782 | MVD surgery | Fascia, muscle | 2.4% |
| Barker et al. [32] | 1996 | 1336 | MVD surgery | Fascia, muscle | 1.5% |
| Samii et al. [7] | 2002 | 143 | MVD surgery | Muscle | 4.8% |
| Steinbok et al. [36] | 2007 | 174 | Posterior fossa surgery | Synthetic dura, mibrin glue | 33.3% |
| Park et al. * [6] | 2007 | 678 | MVD surgery | Muscle | 0.3% |
| Than et al. [17] | 2008 | 200 | Posterior fossa surgery | Various methods | 12.5% |
| Linskey et al. [37] | 2008 | 36 | MVD surgery | Fascia | 2.8% |
| Narotam et al. [4] | 2009 | 52 | Posterior fossa surgery | Collagen matrix | 3.8% |
| Bayazit et al. [38] | 2009 | 412 | Posterior fossa surgery | Primary closure | 7.7% |
| Litvack et al. [14] | 2009 | 150 | Posterior fossa surgery | Collagen matrix | 11.3% |
| Dubey et al. [39] | 2009 | 500 | Posterior fossa surgery | N/A | 13.0% |
| Stoker et al. [8] | 2012 | 100 | MVD surgery | Synthetic dura, pericranium | 17.0% |
| Tanrikulu et al. [16] | 2016 | 50 | MVD surgery | Collagen matrix | 2% |
| Atlaf et al. [11] | 2016 | 147 | Posterior fossa surgery | N/A | 17.0% |
| Kshettry et al. [2] | 2016 | 84 | Posterior fossa surgery | Collagen matrix | 11.9% |
| Park et al. * [33] | 2016 | 2040 | MVD surgery | N/A | 0.5% |
| Zhao et al. [40] | 2017 | 1548 | MVD surgery | N/A | 1.6% |
| Venable et al. [34] | 2018 | 86 | Posterior fossa surgery | Primary suture | 0% |
| Khan et al. [26] | 2020 | 134 | MVD surgery | Synthetic dura, histoacryl | 3.7% |
| Lee at al. [41] | 2020 | 122 | Posterior fossa surgery | Primary closure, fibrin glue | 27.0% |
| Inoue et al. [1] | 2021 | 120 | MVD surgery | Collagen matrix, fascia | 4.2% |
| Present study | 2023 | 475 | MVD surgery | Synthetic dura, collagen matrix, fibrin glue | 1.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.S.; Park, K. Dura Closure Tactics to Prevent CSF Leakage in Microvascular Decompression Surgery. Life 2025, 15, 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040574
Lee HS, Park K. Dura Closure Tactics to Prevent CSF Leakage in Microvascular Decompression Surgery. Life. 2025; 15(4):574. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040574
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyun Seok, and Kwan Park. 2025. "Dura Closure Tactics to Prevent CSF Leakage in Microvascular Decompression Surgery" Life 15, no. 4: 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040574
APA StyleLee, H. S., & Park, K. (2025). Dura Closure Tactics to Prevent CSF Leakage in Microvascular Decompression Surgery. Life, 15(4), 574. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040574






