Microbial Ecotoxicology—40 Years on
Abstract
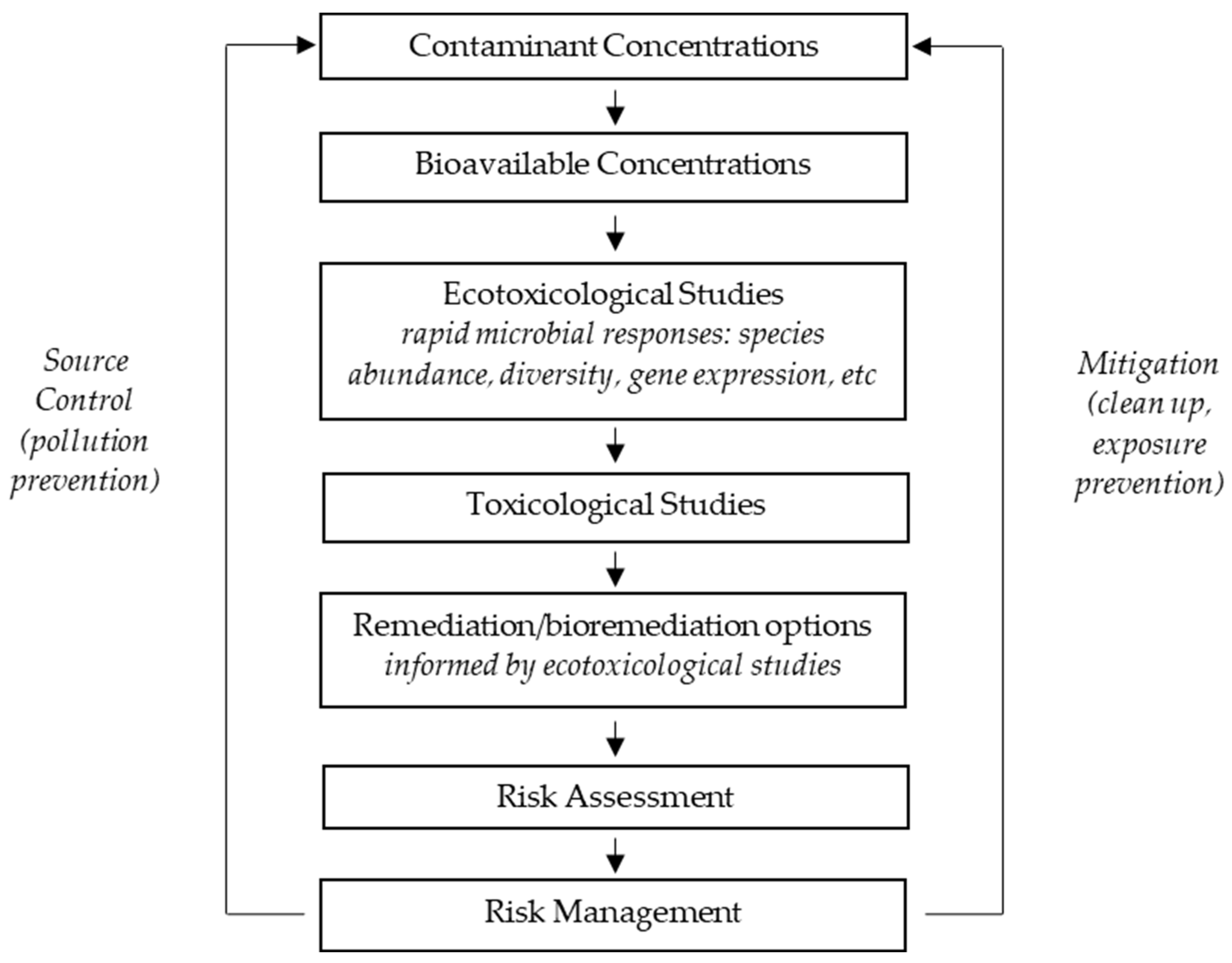
1. Introductory Thoughts
2. Some Conferences of Note
3. The Omics Age
| Omics * | Brief Description | Examples of High-Cost Instrumentation | Opportunities to Reduce Cost and Field Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genomics | Study of the gene: probably the first “omics” to emerge in microbial ecology, with the ability to examine presence of specific genes (i.e., metal resistance) to metagenomics (community DNA) [54]. | (HTS)/(NGS) | Nanopore sequencing [55]; Bento Lab portable PCR Station [56]; Microarrays ** |
| Transcript-omics | The study of all the RNA transcripts that are produced from the genome. Can reflect, for example, up- or down-regulation of transcription in relation to chemical exposures [57]. | RNA reverse-transcribed to cDNA followed by HTS/NGS | Nanopore sequencing; Bento Lab portable PCR Station |
| Proteomics | Study of protein expression: provides characterization of final gene products, including posttranslational modifications which could be used in ecotoxicology [58]. | Mass spectrometry; liquid chromatography | Sensor technologies, i.e., sensor-arrays [59] |
| Metabolomics | Study of metabolites—can be used to look at metabolic changes as a result of toxic chemical exposure or other stressors [60]. | Mass spectrometry; NMR | Sensor technologies—i.e., single cell metabolomics [61] |
| Volatilomics | The study of volatile metabolites ***. A largely untapped method for characterizing microbial communities [62,63]. | Mass spectrometry; NMR and others | Sensor technologies—as used in the food industry [64] |
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lomartire, S.; Marques, J.C.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Biomarkers Based Tools to Assess Environmental and Chemical Stressors in Aquatic Systems. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 122, 107207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connon, R.E.; Geist, J.; Werner, I. Effect-Based Tools for Monitoring and Predicting the Ecotoxicological Effects of Chemicals in the Aquatic Environment. Sensors 2012, 12, 12741–12771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, A.; Fan, F.; Broach, J.R. Microbial Adaptive Evolution. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 49, kuab076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.; Ho, K.T.; Burgess, R.M. Application of Biomarker Tools Using Bivalve Models Toward the Development of Adverse Outcome Pathways for Contaminants of Emerging Concern. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2020, 39, 1472–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norrgren, L. Fish Models for Ecotoxicology. Acta Vet. Scand. 2012, 54, S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, T.; Mitchell, R. The Ecology of Microbial Corrosion. Adv. Microb. Ecol. 1990, 11, 231–262. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, T.; Mitchell, R. Microbial Transport of Toxic Metals. In Environmental Microbiology; Wiley-Liss, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1992; pp. 83–101. [Google Scholar]
- Napa Conference on Genetic and Molecular Ecotoxicology. 12–15 October 1993, Yountville, California. Proceedings. Environ. Health Perspect. 1994, 102 (Suppl. S12), 1–108. [Google Scholar]
- Latimer, J.S.; Boothman, W.S.; Pesch, C.E.; Chmura, G.L.; Pospelova, V.; Jayaraman, S. Environmental Stress and Recovery: The Geochemical Record of Human Disturbance in New Bedford Harbor and Apponagansett Bay, Massachusetts (USA). Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 313, 153–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, T. Pollutant Effects on the Microbial Ecosystem. Environ. Health Perspect. 1994, 102 (Suppl. S12), 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, T.; Sorci, J.; Ika, R.; Shine, J. Interactions between Metals and Microbial Communities in New Bedford Harbor, Massachusetts. Environ. Health Perspect. 1998, 106 (Suppl. S4), 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joint, I.; Mühling, M.; Querellou, J. Culturing Marine Bacteria—An Essential Prerequisite for Biodiscovery. Microb. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorci, J.J.; Paulauskis, J.D.; Ford, T.E. 16S rRNA Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Analysis of Bacterial Diversity as a Biomarker of Ecological Health in Polluted Sediments from New Bedford Harbor, Massachusetts, USA. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1999, 38, 663–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP). Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/probe/docs/techrflp/ (accessed on 5 March 2025).
- Nguyen, J.; Lara-Gutiérrez, J.; Stocker, R. Environmental Fluctuations and Their Effects on Microbial Communities, Populations and Individuals. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2021, 45, fuaa068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, R.M.; Horowitz, A.; Krichevsky, M.; Asim, K. Bej Response of Microbial Populations to Environmental Disturbance. Microb. Ecol. 1991, 22, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkay, T. Adaptation of Aquatic Microbial Communities to Hg Stress. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1987, 53, 2725–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, A.; Atlas, R.M. Response of Microorganisms to an Accidental Gasoline Spillage in an Arctic Freshwater Ecosystem. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1977, 33, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, C.L.; Vestal, J.R. Effects of Environmental Toxicants on Metabolic Activity of Natural Microbial Communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, T. Response of Marine Microbial Communities to Anthropogenic Stress. J. Aquat. Ecosyst. Stress Recovery 2000, 7, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo de Almeida, E.; Tisserand, F.; Faria, M.; Chèvre, N. Efficiency of Several Cytochrome P450 Biomarkers in Highlighting the Exposure of Daphnia Magna to an Organophosphate Pesticide. Toxics 2022, 10, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, T.; Jay, J.; Patel, A.; Kile, M.; Prommasith, P.; Galloway, T.; Sanger, R.; Smith, K.; Depledge, M. Use of Ecotoxicological Tools to Evaluate the Health of New Bedford Harbor Sediments: A Microbial Biomarker Approach. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouskill, N.J.; Barnhart, E.P.; Galloway, T.S.; Handy, R.D.; Ford, T.E. Quantification of Changing Pseudomonas Aeruginosa sodA, htpX and Mt Gene Abundance In Response to Trace Metal Toxicity: A Potential in Situ Biomarker of Environmental Health. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 60, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouskill, N.J.; Barker-Finkel, J.; Galloway, T.S.; Handy, R.D.; Ford, T.E. Temporal Bacterial Diversity Associated with Metal-Contaminated River Sediments. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddamsetti, R.; Yao, Y.; Wang, T.; Gao, J.; Huang, V.T.; Hamrick, G.S.; Son, H.-I.; You, L. Duplicated Antibiotic Resistance Genes Reveal Ongoing Selection and Horizontal Gene Transfer in Bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Ford, T. Special Issue on Source Water Risk Control. Preface. Ecotoxicology 2009, 18, 643–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, T.E.; Bass, A.L.; Cheng, S.; Cherr, G.N.; Cole, B.; Fairbairn, E.; Gu, J.-D.; Halbrook, R.S.; Löffler, F.E.; Madsen, E.L.; et al. EHPC 2010: Sharing Knowledge on Environmental Health for Risk Mitigation. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 937–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Shi, X.; Wei, B.; Ye, L.; Zhang, S. PLFA Profiles of Drinking Water Biofilters with Different Acetate and Glucose Loadings. Ecotoxicology 2009, 18, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, X. Biofilms as Potential Indicators of Macrophyte-Dominated Lake Health. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiglione, J.-F.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Stachowski-Haberkorn, S.; Pesce, S.; Vuilleumier, S. The Coming of Age of Microbial Ecotoxicology: Report on the First Two Meetings in France. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2014, 21, 14241–14245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.-D.; Wang, Y. Geomicrobial Ecotoxicology as a New Subject in Environmental Sciences Is Proposed. Ecotoxicology 2014, 23, 1823–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiglione, J.-F.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Pesce, S. Microbial Ecotoxicology: An Emerging Discipline Facing Contemporary Environmental Threats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 3981–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larras, F.; Rimet, F.; Gregorio, V.; Bérard, A.; Leboulanger, C.; Montuelle, B.; Bouchez, A. Pollution-Induced Community Tolerance (PICT) as a Tool for Monitoring Lake Geneva Long-Term in Situ Ecotoxic Restoration from Herbicide Contamination. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 4301–4311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouanneau, S.; Durand-Thouand, M.-J.; Thouand, G. Design of a Toxicity Biosensor Based on Aliivibrio Fischeri Entrapped in a Disposable Card. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 4340–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.T. Bacteria in Ecotoxicology: Microtox Basic. In Encyclopedia of Aquatic Ecotoxicology; Férard, J.-F., Blaise, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 125–136. ISBN 978-94-007-5704-2. [Google Scholar]
- Modern Water. Available online: https://www.modernwater.com/ (accessed on 9 January 2025).
- Naresh, V.; Lee, N. A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halmi, M.I.E. Rapid Ecotoxicological Tests Using Bioassay Systems—A Review. J. Biochem. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 4, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergua, J.F.; Álvarez-Diduk, R.; Hu, L.; Hassan, A.H.A.; Merkoçi, A. Improved Aliivibrio Fischeri Based-Toxicity Assay: Graphene-Oxide as a Sensitivity Booster with a Mobile-Phone Application. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 406, 124434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.-K.; Hung, M.-C.; Hxu, C.-H.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-S. Pitfalls in Measuring Solution Toxicity Using the Level of Bioluminescence Inhibition in Aliivibrio Fischeri. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2025, 287, 110067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjani, M.; Soleimani, M.; Salari, V. Toxicity Assessment of Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons in Aquatic Environments Using the Bioluminescent Bacterium Aliivibrio Fischeri. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngoc, L.T.B.; Linh, D.N.; Van Minh, N.; Duy, N.P.H.; Phuong, P.T.T. A Novel Biosensing System for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Heavy Metal Toxicity in Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 126123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, P.G.; Depledge, M.H.; Butler, J.N.; Manock, J.J.; Knap, A.H. Rapid Toxicity Assessment and Biomonitoring of Marine Contaminants—Exploiting the Potential of Rapid Biomarker Assays and Microscale Toxicity Tests. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2001, 42, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, T.S.; Sanger, R.C.; Smith, K.L.; Fillmann, G.; Readman, J.W.; Ford, T.E.; Depledge, M.H. Rapid Assessment of Marine Pollution Using Multiple Biomarkers and Chemical Immunoassays. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2219–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, I.; Mujahid, A.; Palombo, E.A.; Müller, M. A Functional Gene-Array Analysis of Microbial Communities Settling on Microplastics in a Peat-Draining Environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 166, 112226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Yin, H.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Voordeckers, J.W.; Tu, Q.; Deng, Y.; Yuan, M.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, N.; et al. Functional Gene Array-Based Ultrasensitive and Quantitative Detection of Microbial Populations in Complex Communities. mSystems 2019, 4, e00296-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, P.; Padamsee, M.; Lee, K.; Lacap-Bugler, D.C. Soil Microbial Functional Gene Dataset Associated with Agathis Australis. Data Brief 2023, 51, 109791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Chaves, M.G.; Venturini, A.M.; Merloti, L.F.; Barros, D.J.; Rossetto, R.; Kuramae, E.E.; Tsai, S.M.; Navarrete, A.A. Combined Use of Vinasse and Nitrogen as Fertilizers Affects Nitrification, Ammonification, and Denitrification by Prokaryotes. Front. Soil Sci. 2021, 1, 746745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Liu, S.; Dong, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gao, Q. Tracking Virulence Genes and Their Interaction with Antibiotic Resistome during Manure Fertilization. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, W.; Qi, Q.; Dong, Q.; Lei, J.; et al. Uncovering the Virome and Its Interaction with Antibiotic Resistome during Compost Fertilization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 457, 131763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Lu, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.; Gu, C.; Jie, S.; Lei, P.; Gan, M.; Yin, H.; Zhu, J. Geochip 5.0 Insights into the Association between Bioleaching of Heavy Metals from Contaminated Sediment and Functional Genes Expressed in Consortiums. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2024, 31, 49575–49588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, D.; Patel, N.; Rawat, A.; Rosado, A.S. Cutting Edge Tools in the Field of Soil Microbiology. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2024, 6, 100226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, V.K.; Mohan, S.; Vijayan, J.; Abdulla, M.H.; Ammini, P. 16—An Overview of the Metagenomics-Based Assessment of Ecosystem Toxicology. In Metagenomics, 2nd ed.; Nagarajan, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 367–382. ISBN 978-0-323-91631-8. [Google Scholar]
- Oxford Nanopore Technologies. Available online: https://nanoporetech.com/ (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Bentolab: A Portble PCR Workstation. Available online: https://bento.bio/ (accessed on 19 December 2021).
- Mante, J.; Groover, K.E.; Pullen, R.M. Environmental Community Transcriptomics: Strategies and Struggles. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2025, 24, elae033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.; Hettich, R. Environmental Proteomics: A Paradigm Shift in Characterizing Microbial Activities at the Molecular Level. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2009, 73, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, C.V.; Cook, R.L.; Martelly, W.; Gushgari, L.R.; Mohan, M.; Takulapalli, B. Novel Sensor-Integrated Proteome on Chip (SPOC) Platform with Thousands of Folded Proteins on a 1.5 Sq-Cm Biosensor Chip to Enable High-Throughput Real-Time Label-Free Screening for Kinetic Analysis. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedia, C. Metabolomics in Environmental Toxicology: Applications and Challenges. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 34, e00161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yang, Z. Chapter 3—Biosensors for Single-Cell Metabolomic Characterization. In Biosensors for Single-Cell Analysis; Chen, J., Lu, Y., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 37–70. ISBN 978-0-323-89841-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo, K.; Ratel, J.; Mercier, F.; Gauriat, B.; Bouchard, P.; Engel, E. Volatolomics in Bacterial Ecotoxicology, A Novel Method for Detecting Signatures of Pesticide Exposure? Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meredith, L.K.; Tfaily, M.M. Capturing the Microbial Volatilome: An Oft Overlooked “Ome”. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt-Arango, J.; Villaroel-Solis, E.; Fiscal-Ladino, J.; Taborda-Ocampo, G. Volatilomics: An Emerging Discipline within Omics Sciences—A Systematic Review [Version 1; Peer Review: 1 Not Approved]. F1000Research 2024, 13, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santorsola, M.; Lescai, F. The Promise of Explainable Deep Learning for Omics Data Analysis: Adding New Discovery Tools to AI. New Biotechnol. 2023, 77, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-D.; Luo, K.; Chang, W.-H.; Lee, G.-B. A Microfluidic Chip Capable of Generating and Trapping Emulsion Droplets for Digital Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Analysis. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, D.J.; Cary, R.B. Lateral Flow Microarrays: A Novel Platform for Rapid Nucleic Acid Detection Based on Miniaturized Lateral Flow Chromatography. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revilla-Cuesta, A.; Abajo-Cuadrado, I.; Quadrini, L.; Failli, S.; Rodríguez-Rubio, A.; Cuevas, J.V.; Hernando-Muñoz, C.; García-Calvo, J.; Torroba, T. Chemical Speciation of Methylmercury and Mercury(II) Cations in Fish by New Fluorogenic Naphthalimide Alkynyl Gold Complexes: The Ultimate Test for Detecting Fish Contamination. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2024, 421, 136492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.A.; Arnaud, J.M.; Jasmin, P.M.; Hamner, S.; Hasan, N.A.; Colwell, R.R.; Ford, T.E. A Metagenomic Approach to Evaluating Surface Water Quality in Haiti. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamner, S.; Brown, B.L.; Hasan, N.A.; Franklin, M.J.; Doyle, J.; Eggers, M.J.; Colwell, R.R.; Ford, T.E. Metagenomic Profiling of Microbial Pathogens in the Little Bighorn River, Montana. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Stebbins, B.; Ajmani, A.; Comendul, A.; Hamner, S.; Hasan, N.A.; Colwell, R.; Ford, T. Nanopore-Based Metagenomics Analysis Reveals Prevalence of Mobile Antibiotic and Heavy Metal Resistome in Wastewater. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 1572–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echeverri-Jaramillo, G.; Jaramillo-Colorado, B.; Junca, H.; Consuegra-Mayor, C. Towards the Development of Microbial Ecotoxicology Testing Using Chlorpyrifos Contaminated Sediments and Marine Yeast Isolates as a Model. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascault, N.; Roux, S.; Artigas, J.; Pesce, S.; Leloup, J.; Tadonleke, R.D.; Debroas, D.; Bouchez, A.; Humbert, J.-F. A High-Throughput Sequencing Ecotoxicology Study of Freshwater Bacterial Communities and Their Responses to Tebuconazole. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 90, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beale, D.J.; Karpe, A.V.; Ahmed, W.; Cook, S.; Morrison, P.D.; Staley, C.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Palombo, E.A. A Community Multi-Omics Approach towards the Assessment of Surface Water Quality in an Urban River System. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2017, 14, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioti, A.; Theodosopoulou, D.; Bravakos, P.; Magoulas, A.; Kotoulas, G. The Bioinformatics Landscape in Environmental Omics: Lessons from a National ELIXIR Survey. iScience 2024, 27, 110062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, Z.; Peters, M.D.J.; Stern, C.; Tufanaru, C.; McArthur, A.; Aromataris, E. Systematic Review or Scoping Review? Guidance for Authors When Choosing between a Systematic or Scoping Review Approach. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellal, J.; Lise, B.; Annette, B.; Aurélie, C.; Giulia, C.; Simon, C.; Cristiana, C.-L.; Caroline, D.C.; Nicolas, G.; Marina, H.; et al. Unlocking Secrets of Microbial Ecotoxicology: Recent Achievements and Future Challenges. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2023, 99, fiad102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravo-Laureau, C.; Cagnon, C.; Lauga, B.; Duran, R. Microbial Ecotoxicology, 1st ed.; 2017 ed.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-61794-7. [Google Scholar]
- Machuca-Sepúlveda, J.; Miranda, J.; Lefin, N.; Pedroso, A.; Beltrán, J.F.; Farias, J.G. Current Status of Omics in Biological Quality Elements for Freshwater Biomonitoring. Biology 2023, 12, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagova-Mareckova, M.; Boenigk, J.; Bouchez, A.; Cermakova, K.; Chonova, T.; Cordier, T.; Eisendle, U.; Elersek, T.; Fazi, S.; Fleituch, T.; et al. Expanding Ecological Assessment by Integrating Microorganisms into Routine Freshwater Biomonitoring. Water Res. 2021, 191, 116767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, J.E.; Claborne, D.M.; Weller, Z.D.; Webb-Robertson, B.-J.M.; Waters, K.M.; Bramer, L.M. Missing Data in Multi-Omics Integration: Recent Advances through Artificial Intelligence. Front. Artif. Intell. 2023, 6, 1098308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxford Nanopore Technologies MinION. Available online: https://nanoporetech.com/products/minion (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Pomerantz, A.; Peñafiel, N.; Arteaga, A.; Bustamante, L.; Pichardo, F.; Coloma, L.A.; Barrio-Amorós, C.L.; Salazar-Valenzuela, D.; Prost, S. Real-Time DNA Barcoding in a Rainforest Using Nanopore Sequencing: Opportunities for Rapid Biodiversity Assessments and Local Capacity Building. Gigascience 2018, 7, giy033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.S.; Zaikova, E.; Goerlitz, D.S.; Bai, Y.; Tighe, S.W. Real-Time DNA Sequencing in the Antarctic Dry Valleys Using the Oxford Nanopore Sequencer. J. Biomol. Tech. 2017, 28, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Wallace, S.L.; Chiu, C.Y.; John, K.K.; Stahl, S.E.; Rubins, K.H.; McIntyre, A.B.R.; Dworkin, J.P.; Lupisella, M.L.; Smith, D.J.; Botkin, D.J.; et al. Nanopore DNA Sequencing and Genome Assembly on the International Space Station. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 18022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, L.; Holzer, A.; Baronas, J.J.; Hall, M.B.; Braeuninger-Weimer, P.; Scherm, M.J.; Kunz, D.J.; Perera, S.N.; Martin-Herranz, D.E.; Tipper, E.T.; et al. Freshwater Monitoring by Nanopore Sequencing. eLife 2021, 10, e61504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potvin, M.; Gauthier, J.; Langevin, C.; Mohit, V.; da Costa, N.B.; Deschênes, T.; Pomerleau, M.; Kukavica-Ibrulj, I.; Verreault, D.; Comte, J.; et al. Rapid On-Site Detection of Harmful Algal Blooms: Real-Time Cyanobacteria Identification Using Oxford Nanopore Sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1267652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curren, E.; Yoshida, T.; Kuwahara, V.S.; Leong, S.C.Y. Rapid Profiling of Tropical Marine Cyanobacterial Communities. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2019, 25, 100485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampe, F. The Use of Nanopore Sequencing in Ecotoxicology. Master’s Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Höner zu Siederdissen, C.; Spangenberg, J.; Bisdorf, K.; Krautwurst, S.; Srivastava, A.; Marz, M.; Taubert, M. Nanopore Sequencing Enables Novel Detection of Deuterium Incorporation in DNA. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2024, 23, 3584–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, S.; Ghiglione, J.-F.; Topp, E.; Martin-Laurent, F. Editorial: Microbial Ecotoxicology. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuilleumier, S.; Barthelmebs, L.; Corcoll, N.; Hery, M.; G Karpouzas, D.; Wick, L.Y. Editorial: Thematic Issue on Microbial Ecotoxicology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2024, 100, fiae097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cébron, A.; Karpouzas, D.G.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Morin, S.; Palacios, C.; Schmitt-Jansen, M. Editorial: Microbial Ecotoxicology Advances to Improve Environmental and Human Health Under Global Change. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 870404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In Proceedings of the EcotoxicoMic 2024: 4th International Conference in Microbial Ecotoxicology, Gothenburg, Sweden, 12–14 November 2024. Available online: https://ecotoxicomic24.sciencesconf.org/ (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Paul, J.; Scholin, C.; van den Engh, G.; Perry, M.J. In Situ Instrumentation. Oceanography 2007, 20, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-W.; Lin, C.; Nguyen, M.K.; Hussain, A.; Bui, X.-T.; Ngo, H.H. A Review of Biosensor for Environmental Monitoring: Principle, Application, and Corresponding Achievement of Sustainable Development Goals. Bioengineered 2023, 14, 58–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezeamii, G.C.; Idoko, F.A.; Ojochogwu, O.J. Biosensors and Technological Advances in Monitoring Marine Pollution in the USA. Glob. J. Eng. Technol. Adv. 2024, 20, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detecting Isoforms and RNA Modifications with PCR-Free, Direct RNA Nanopore Sequencing. Available online: https://nanoporetech.com/resource-centre/workflow-direct-rna-sequencing (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Dutka, B.J.; Nyholm, N.; Petersen, J. Comparison of Several Microbiological Toxicity Screening Tests. Water Res. 1983, 17, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ford, T. Microbial Ecotoxicology—40 Years on. Life 2025, 15, 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040514
Ford T. Microbial Ecotoxicology—40 Years on. Life. 2025; 15(4):514. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040514
Chicago/Turabian StyleFord, Tim. 2025. "Microbial Ecotoxicology—40 Years on" Life 15, no. 4: 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040514
APA StyleFord, T. (2025). Microbial Ecotoxicology—40 Years on. Life, 15(4), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15040514






