Sex-Dependent Changes in Risk-Taking Predisposition of Rats Following Space Radiation Exposure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Regulatory Compliance
2.2. Rat Demographics, Husbandry, Experimental Timeline, and Exercise Regimen
2.3. RTP Performance Screening
2.3.1. Stimulus Response Training (STR)
2.3.2. Risk-Taking Propensity (RTP) Task
2.4. Irradiation Procedure
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Pre-Exposure (Task Engagement and Learning Proficiency)
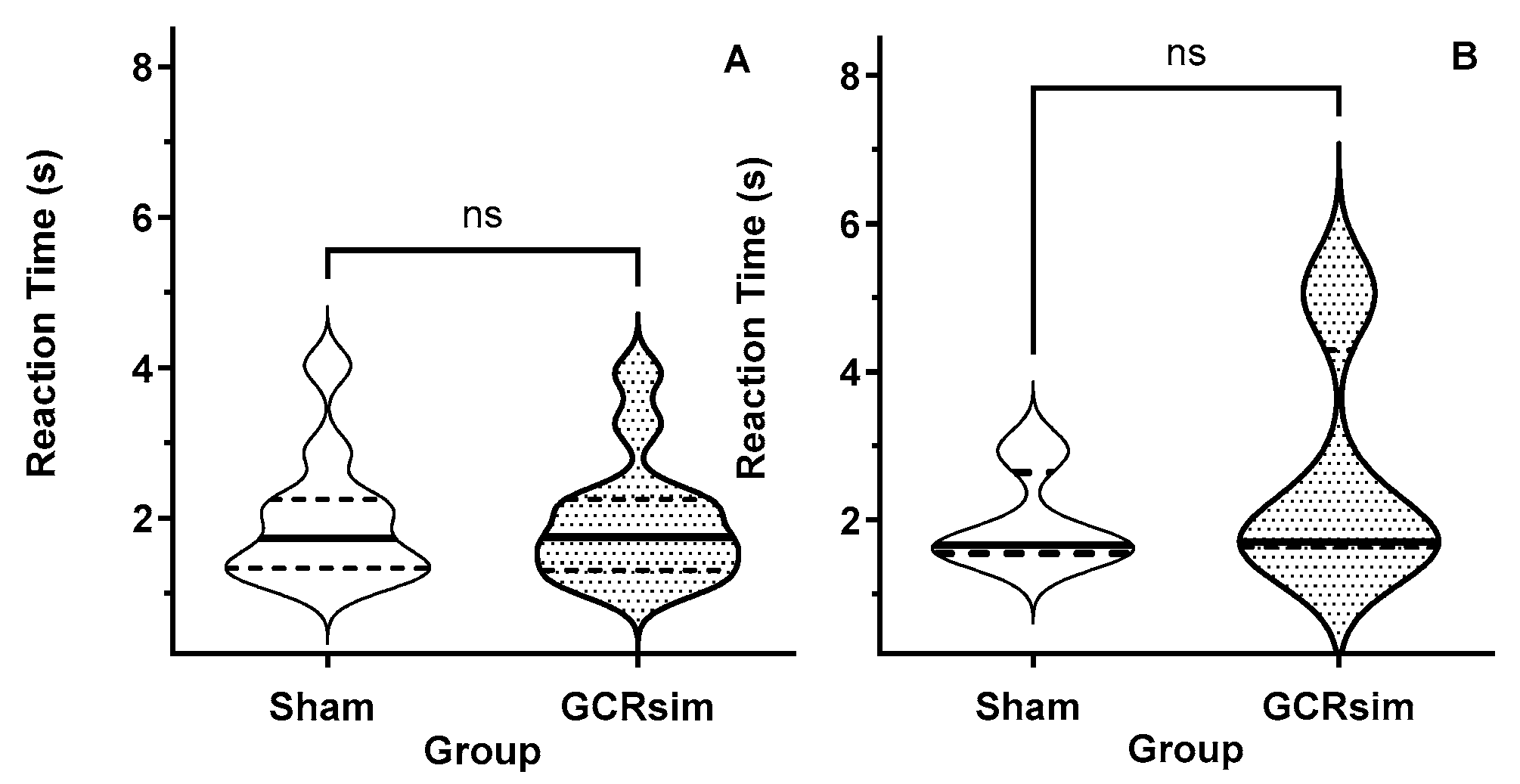
3.2. Pre-Exposure Processing Speed (Reaction Time)
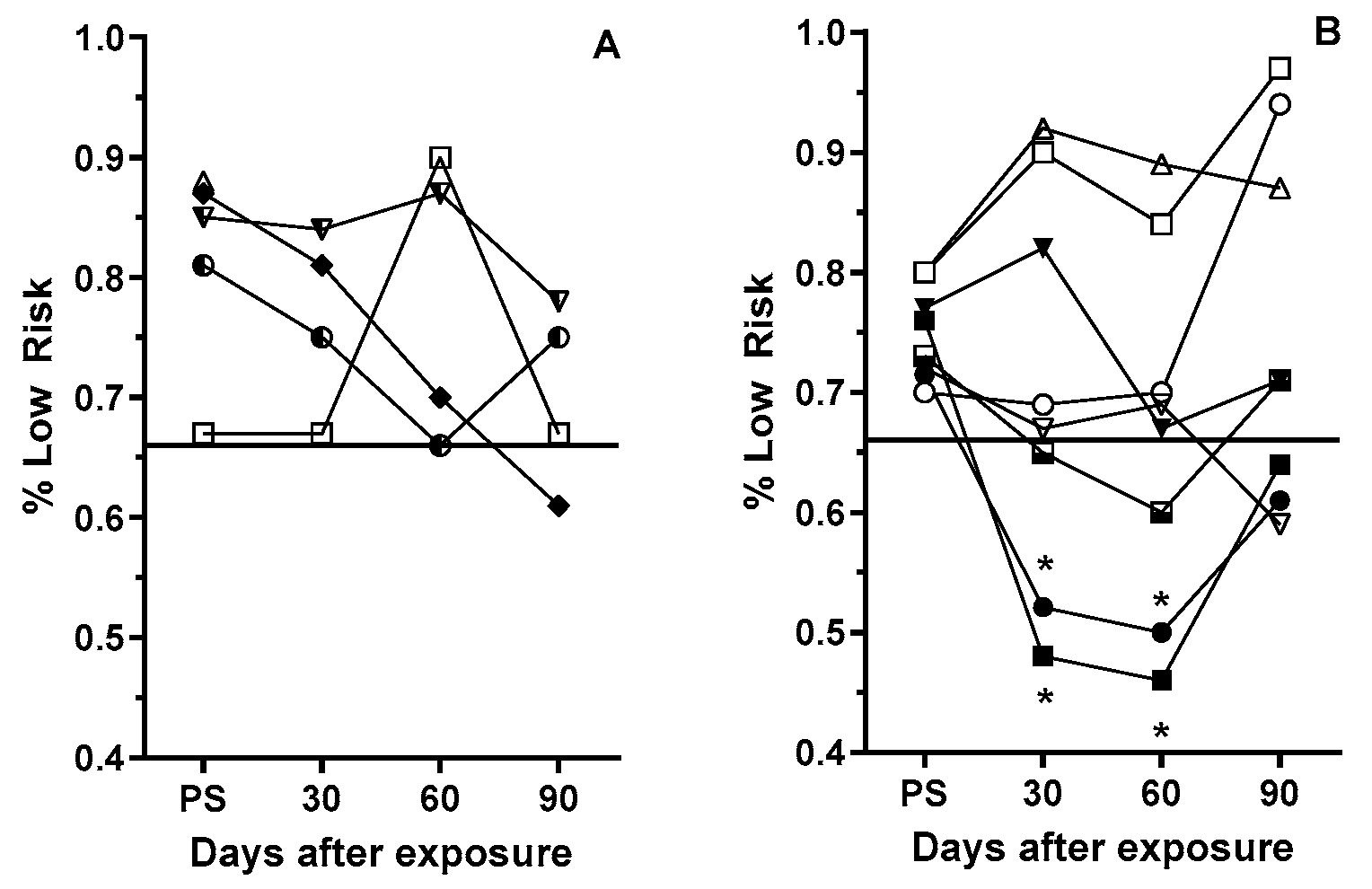
3.3. Post-Exposure Selection Choices
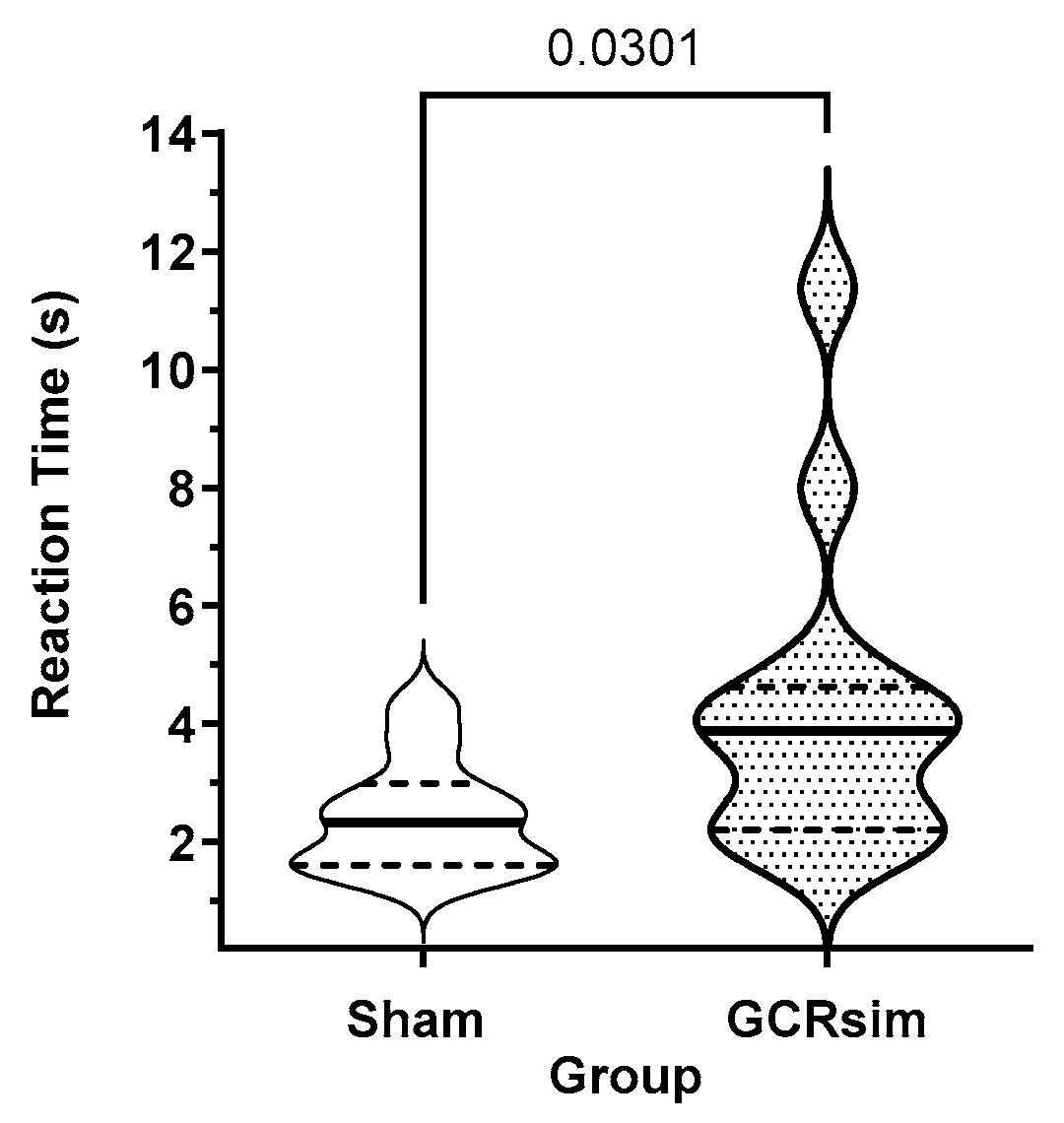
3.4. Post-Exposure Processing Speed
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nelson, G.A. Space Radiation and Human Exposures, A Primer. Radiat. Res. 2016, 185, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britten, R.A.; Wellman, L.L.; Sanford, L.D. Progressive increase in the complexity and translatability of rodent testing to assess space-radiation induced cognitive impairment. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 126, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cekanaviciute, E.; Rosi, S.; Costes, S.V. Central nervous system responses to simulated galactic cosmic rays. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucinotta, F.A.; Cacao, E. Risks of cognitive detriments after low dose heavy ion and proton exposures. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2019, 95, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiffer, F.; Boerma, M.; Allen, A. Behavioral effects of space radiation: A comprehensive review of animal studies. Life Sci. Space Res. 2019, 21, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whoolery, C.W.; Yun, S.; Reynolds, R.P.; Lucero, M.J.; Soler, I.; Tran, F.H.; Ito, N.; Redfield, R.L.; Richardson, D.R.; Shih, H.Y.; et al. Multi-domain cognitive assessment of male mice reveals whole body exposure to space radiation is not detrimental to high-level cognition and actually improves pattern separation. BioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britten, R.A.; Fesshaye, A.; Tidmore, A.; Blackwell, A.A. Similar Loss of Executive Function Performance after Exposure to Low (10 cGy) Doses of Single (4He) Ions and the Multi-Ion GCRSim Beam. Radiat. Res. 2022, 198, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britten, R.A.; Fesshaye, A.; Tidmore, A.; Liu, A.; Blackwell, A.A. Loss of Cognitive Flexibility Practice Effects in Female Rats Exposed to Simulated Space Radiation. Radiat. Res. 2023, 200, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, V.K.; Allen, B.D.; Caressi, C.; Kwok, S.; Chu, E.; Tran, K.K.; Chmielewski, N.N.; Giedzinski, E.; Acharya, M.M.; Britten, R.A.; et al. Cosmic radiation exposure and persistent cognitive dysfunction. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, J.S.; Duncan, V.D.; Fesshaye, A.; Tondin, A.; Macadat, E.; Britten, R.A. Exposure to ≤15 cgy of 600 mev/n 56 fe particles impairs rule acquisition but not long-term memory in the attentional set-shifting assay. Radiat. Res. 2018, 190, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britten, R.A.; Fesshaye, A.S.; Duncan, V.D.; Wellman, L.L.; Sanford, L.D. Sleep Fragmentation Exacerbates Executive Function Impairments Induced by Low Doses of Si Ions. Radiat. Res. 2020, 194, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burket, J.A.; Matar, M.; Fesshaye, A.; Pickle, J.C.; Britten, R.A. Exposure to Low (≤10 cGy) Doses of 4He Particles Leads to Increased Social Withdrawal and Loss of Executive Function Performance. Radiat. Res. 2021, 196, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, S.; Liu, A.; Blackwell, A.A.; Britten, R.A. Multiple decrements in switch task performance in female rats exposed to space radiation. Behav. Brain Res. 2023, 449, 114465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, S.; Britten, R. Simulated Space Radiation Exposure Effects on Switch Task Performance in Rats. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2022, 93, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bechara, A.; Martin, E.M. Impaired decision making related to working memory deficits in individuals with substance addictions. Neuropsychology 2004, 18, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, M.; Kalbe, E.; Labudda, K.; Fujiwara, E.; Kessler, J.; Markowitsch, H.J. Decision-making impairments in patients with pathological gambling. Psychiatry Res. 2005, 133, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romer, D.; Betancourt, L.; Giannetta, J.M.; Brodsky, N.L.; Farah, M.; Hurt, H. Executive cognitive functions and impulsivity as correlates of risk taking and problem behavior in preadolescents. Neuropsychologia 2009, 47, 2916–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.J.; Cobia, D.J.; Wang, L.; Alpert, K.I.; Cronenwett, W.J.; Goldman, M.B.; Mamah, D.; Barch, D.M.; Breiter, H.C.; Csernansky, J.G. Cannabis-related working memory deficits and associated subcortical morphological differences in healthy individuals and schizophrenia subjects. Schizophr. Bull. 2014, 40, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Phuyal, S.; Smits, E.; Reid, F.E.; Tamgue, E.N.; Arriaga, P.A.; Britten, R.A. Exposure to low (10 cGy) doses of (4)He ions leads to an apparent increase in risk taking propensity in female rats. Behav. Brain Res. 2024, 474, 115182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejuez, C.W.; Read, J.P.; Kahler, C.W.; Richards, J.B.; Ramsey, S.E.; Stuart, G.L.; Strong, D.R.; Brown, R.A. Evaluation of a behavioral measure of risk taking: The Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART). J. Exp. Psychol. Appl. 2002, 8, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, M.K.; Hopko, D.R.; Bare, R.; Lejuez, C.W.; Robinson, E.V. Construct validity of the Balloon Analog Risk Task (BART): Associations with psychopathy and impulsivity. Assessment 2005, 12, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejuez, C.W.; Aklin, W.M.; Jones, H.A.; Richards, J.B.; Strong, D.R.; Kahler, C.W.; Read, J.P. The Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART) differentiates smokers and nonsmokers. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2003, 11, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejuez, C.W.; Aklin, W.M.; Zvolensky, M.J.; Pedulla, C.M. Evaluation of the Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART) as a predictor of adolescent real-world risk-taking behaviours. J. Adolesc. 2003, 26, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickering, A.D.; Gray, J.A. Dopamine, appetitive reinforcement, and the neuropsychology of human learning: An individual differences approach. In Advances in Research on Temperament; Pabst Science Publishers: Lengerich, Germany, 2001; pp. 113–149. [Google Scholar]
- Slaba, T.C.; Blattnig, S.R.; Norbury, J.W.; Rusek, A.; La Tessa, C. Reference field specification and preliminary beam selection strategy for accelerator-based GCR simulation. Life Sci. Space Res. 2016, 8, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreollo, N.A.; Santos, E.F.D.; de Araujo, M.R.; Lopes, L.R. Rat’s age versus human’s age: What is the relationship? Arq. Bras. Cir. Dig. 2012, 25, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrus, M.M.; Winstanley, C.A. Dopamine D3 Receptors Modulate the Ability of Win-Paired Cues to Increase Risky Choice in a Rat Gambling Task. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaghband, Y.; Klein, P.M.; Kramár, E.A.; Cranston, M.N.; Perry, B.C.; Shelerud, L.M.; Kane, A.E.; Doan, N.-L.; Ru, N.; Acharya, M.M.; et al. Galactic cosmic radiation exposure causes multifaceted neurocognitive impairments. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2023, 80, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villasana, L.E.; Benice, T.S.; Raber, J. Long-term effects of 56Fe irradiation on spatial memory of mice: Role of sex and apolipoprotein E isoform. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villasana, L.; Rosenberg, J.; Raber, J. Sex-dependent effects of 56Fe irradiation on contextual fear conditioning in C57BL/6J mice. Hippocampus 2010, 20, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krukowski, K.; Grue, K.; Frias, E.S.; Pietrykowski, J.; Jones, T.; Nelson, G.; Rosi, S. Female mice are protected from space radiation-induced maladaptive responses. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 74, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiffer, F.; Alexander, T.; Anderson, J.E.; Groves, T.; Wang, J.; Sridharan, V.; Boerma, M.; Allen, A.R. Late effects of 16 O-particle radiation on female social and cognitive behavior and hippocampal physiology. Radiat. Res. 2019, 191, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, V.K.; Angulo, M.C.; Allen, B.D.; Syage, A.; Usmani, M.T.; de la Chapelle, E.P.; Amin, A.N.; Flores, L.; Lin, X.; Giedzinski, E.; et al. Sex-Specific Cognitive Deficits Following Space Radiation Exposure. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 535885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkle, J.J.; Olschowka, J.A.; Love, T.M.; Williams, J.P.; O’Banion, M.K. Cranial irradiation mediated spine loss is sex-specific and complement receptor-3 dependent in male mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Hinshaw, R.G.; Le, K.X.; Park, M.-A.; Wang, S.; Belanger, A.P.; Dubey, S.; Frost, J.L.; Shi, Q.; Holton, P.; et al. Space-like (56)Fe irradiation manifests mild, early sex-specific behavioral and neuropathological changes in wildtype and Alzheimer’s-like transgenic mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaillard, A.; Rossell, S.L.; Carruthers, S.P.; Sumner, P.J.; Michie, P.T.; Woods, W.; Neill, E.; Phillipou, A.; Toh, W.L.; Hughes, M.E. Greater activation of the response inhibition network in females compared to males during stop signal task performance. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 386, 112586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolla, K.I.; Eldreth, D.A.; Matochik, J.A.; Cadet, J.L. Sex-related Differences in a Gambling Task and Its Neurological Correlates. Cereb. Cortex 2004, 14, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grissom, N.M.; Reyes, T.M. Let’s call the whole thing off: Evaluating gender and sex differences in executive function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.K. Casualties as a Measure of the Loss of Combat Effectiveness of an Infantry Battalion; Operations Research Office, Johns Hopkins University: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Kepecs, A.; Uchida, N.; Zariwala, H.A.; Mainen, Z.F. Neural correlates, computation and behavioural impact of decision confidence. Nature 2008, 455, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, M.D.; Fountain, S.B. Concurrent cognitive processes in rat serial pattern learning: Item memory, serial position, and pattern structure. Learn. Motiv. 2010, 41, 252–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.H.V.; Fesshaye, A.S.; Tidmore, A.; Sanford, L.D.; Britten, R.A. Sleep Fragmentation Results in Novel Set-Shifting Decrements in GCR-Exposed Male and Female Rats. Radiat. Res. 2024, 203, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahalley, L.S.; Peterson, R.; Ris, M.D.; Janzen, L.; Okcu, M.F.; Grosshans, D.R.; Ramaswamy, V.; Paulino, A.C.; Hodgson, D.; Mahajan, A.; et al. Superior Intellectual Outcomes After Proton Radiotherapy Compared with Photon Radiotherapy for Pediatric Medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh-Le, M.-P.; Tibbs, M.D.; Karunamuni, R.; Salans, M.; Tringale, K.R.; Yip, A.; Connor, M.; Simon, A.B.; Vitzthum, L.K.; Reyes, A.; et al. Microstructural Injury to Corpus Callosum and Intrahemispheric White Matter Tracts Correlate with Attention and Processing Speed Decline After Brain Radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 110, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, L.; Semenza, C.; Vallesi, A. General Slowing and Education Mediate Task Switching Performance Across the Life-Span. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salthouse, T.A.; Fristoe, N.; McGuthry, K.E.; Hambrick, D.Z. Relation of task switching to speed, age, and fluid intelligence. Psychol. Aging 1998, 13, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, L.A.; Ryan, M.; Martin, R.B.; Ewen, J.; Mostofsky, S.H.; Denckla, M.B.; Mahone, E.M. Working memory influences processing speed and reading fluency in ADHD. Child Neuropsychol. 2011, 17, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.; Eckstrand, K.; Sharp, W.; Blumenthal, J.; Lerch, J.P.; Greenstein, D.; Clasen, L.; Evans, A.; Giedd, J.; Rapoport, J.L. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder is characterized by a delay in cortical maturation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19649–19654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.; Sharp, W.S.; Morrison, M.; Eckstrand, K.; Greenstein, D.K.; Clasen, L.S.; Evans, A.C.; Rapoport, J.L. Psychostimulant treatment and the developing cortex in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2009, 166, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.; Lalonde, F.; Lepage, C.; Rabin, C.; Eckstrand, K.; Sharp, W.; Greenstein, D.; Evans, A.; Giedd, J.N.; Rapoport, J. Development of cortical asymmetry in typically developing children and its disruption in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2009, 66, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, I.; Yun, S.; Reynolds, R.P.; Whoolery, C.W.; Tran, F.H.; Kumar, P.L.; Rong, Y.; DeSalle, M.J.; Gibson, A.D.; Stowe, A.M.; et al. Multi-Domain Touchscreen-Based Cognitive Assessment of C57BL/6J Female Mice Shows Whole-Body Exposure to (56)Fe Particle Space Radiation in Maturity Improves Discrimination Learning yet Impairs Stimulus-Response Rule-Based Habit Learning. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 722780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.H.; Lee, G.J.; Raven, E.P.; Tingus, K.; Khoo, T.; Thompson, P.M.; Bartzokis, G. Age-related slowing in cognitive processing speed is associated with myelin integrity in a very healthy elderly sample. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2011, 33, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.H.; Lee, G.J.; Tishler, T.A.; Meghpara, M.; Thompson, P.M.; Bartzokis, G. Myelin breakdown mediates age-related slowing in cognitive processing speed in healthy elderly men. Brain Cogn. 2013, 81, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickstein, D.L.; Talty, R.; Bresnahan, E.; Varghese, M.; Perry, B.; Janssen, W.G.M.; Sowa, A.; Giedzinski, E.; Apodaca, L.; Baulch, J.; et al. Alterations in synaptic density and myelination in response to exposure to high-energy charged particles. J. Comp. Neurol. 2018, 526, 2845–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Event | Time Relative to SR Exposure | Rat Age |
|---|---|---|
| Arrival at EVMS | ~12 weeks pre | ~3 months |
| Exercise | ~11–3 weeks pre | |
| Ship to BNL | 1 week pre | |
| SR exposure | - | ~6 months |
| Ship to EVMS | 1 week post | |
| Exercise | 1–14 weeks post | |
| RTP testing | 14–18 weeks post | ~10 months |
| Stage 1 | Response Window | # Correct Selections | Completion Rate | Permitted # Sessions | Days at Criterion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STR15 | N/A | ≥30 | ≥60% | 8 | 1 |
| STR4 | N/A | ≥30 | ≥60% | 8 | 1 |
| STR1-Timed | 30 s | ≥30 | ≥75% | 8 | 2 |
| STR1-Fast | 10 s | ≥30 | ≥75% | 10 | 2 |
| Hole | Reward Size 1 | Win Rate | Loss Time Penalty | Possible Reward 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 1 | 90% | 5 s | 216 |
| 7 | 4 | 40% | 35 s | 102 |
| 9 | 2 | 80% | 10 s | 320 |
| 10 | 3 | 50% | 20 s | 158 |
| Male | Female | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham | GCR | Sham | GCR | |||||
| TEST 1 | STRC 2 | Trials 3 | STRC | Trials | STRC | Trials | STRC | Trials |
| Pre | 3.09 ± 0.41 | 56.9 ± 2.9 | 2.69 ± 0.45 | 55.1 ± 4.4 | 2.2 ± 0.20 | 44.3 ± 2.43 | 3.12 ± 0.29 | 49.7 ± 1.51 |
| Post + 30 | 2.63 ± 0.31 | 55.6 ± 3.0 | 2.69 ± 0.33 | 51.7 ± 2.9 | 3.00 ± 0.31 | 31.2 ± 2.59 | 2.51 ± 0.19 | 35.2 ± 2.9 |
| Post + 60 | 2.45 ± 0.28 | 55.5 ± 2.5 | 2.38 ± 0.27 | 54.6 ± 2.6 | 3.1 ± 0.28 | 30.6 ± 2.5 | 2.75 ± 0.16 | 31.3 ± 2.25 |
| Post + 90 | 3.11 ± 0.48 | 48.9 ± 3.9 | 2.27 ± 0.27 | 53.2 ± 2.6 | 3.5 ± 0.50 | 30.7 ± 3.5 | 3.03 ± 0.23 | 35.8 ± 2.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smits, E.; Reid, F.E.; Tamgue, E.N.; Alvarado Arriaga, P.; Nguyen, C.; Britten, R.A. Sex-Dependent Changes in Risk-Taking Predisposition of Rats Following Space Radiation Exposure. Life 2025, 15, 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030449
Smits E, Reid FE, Tamgue EN, Alvarado Arriaga P, Nguyen C, Britten RA. Sex-Dependent Changes in Risk-Taking Predisposition of Rats Following Space Radiation Exposure. Life. 2025; 15(3):449. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030449
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmits, Elliot, Faith E. Reid, Ella N. Tamgue, Paola Alvarado Arriaga, Charles Nguyen, and Richard A. Britten. 2025. "Sex-Dependent Changes in Risk-Taking Predisposition of Rats Following Space Radiation Exposure" Life 15, no. 3: 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030449
APA StyleSmits, E., Reid, F. E., Tamgue, E. N., Alvarado Arriaga, P., Nguyen, C., & Britten, R. A. (2025). Sex-Dependent Changes in Risk-Taking Predisposition of Rats Following Space Radiation Exposure. Life, 15(3), 449. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030449







