Assessing Potential Reservoir of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in the Oral Microbiota of Captive Burmese and Royal Pythons †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Sample Processing and Isolation
2.3. Identification and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Bacterial Isolates
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Species Isolated
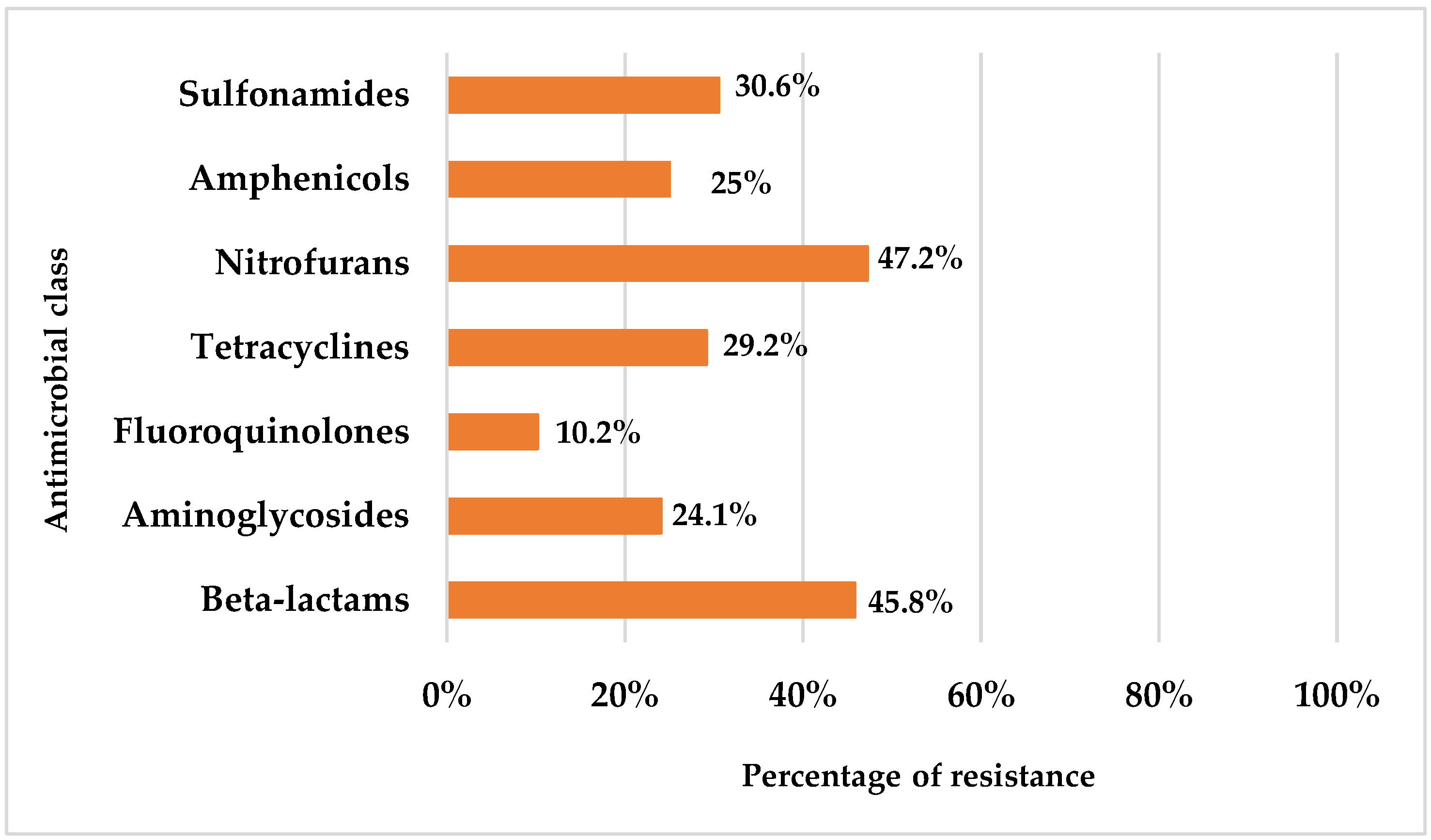
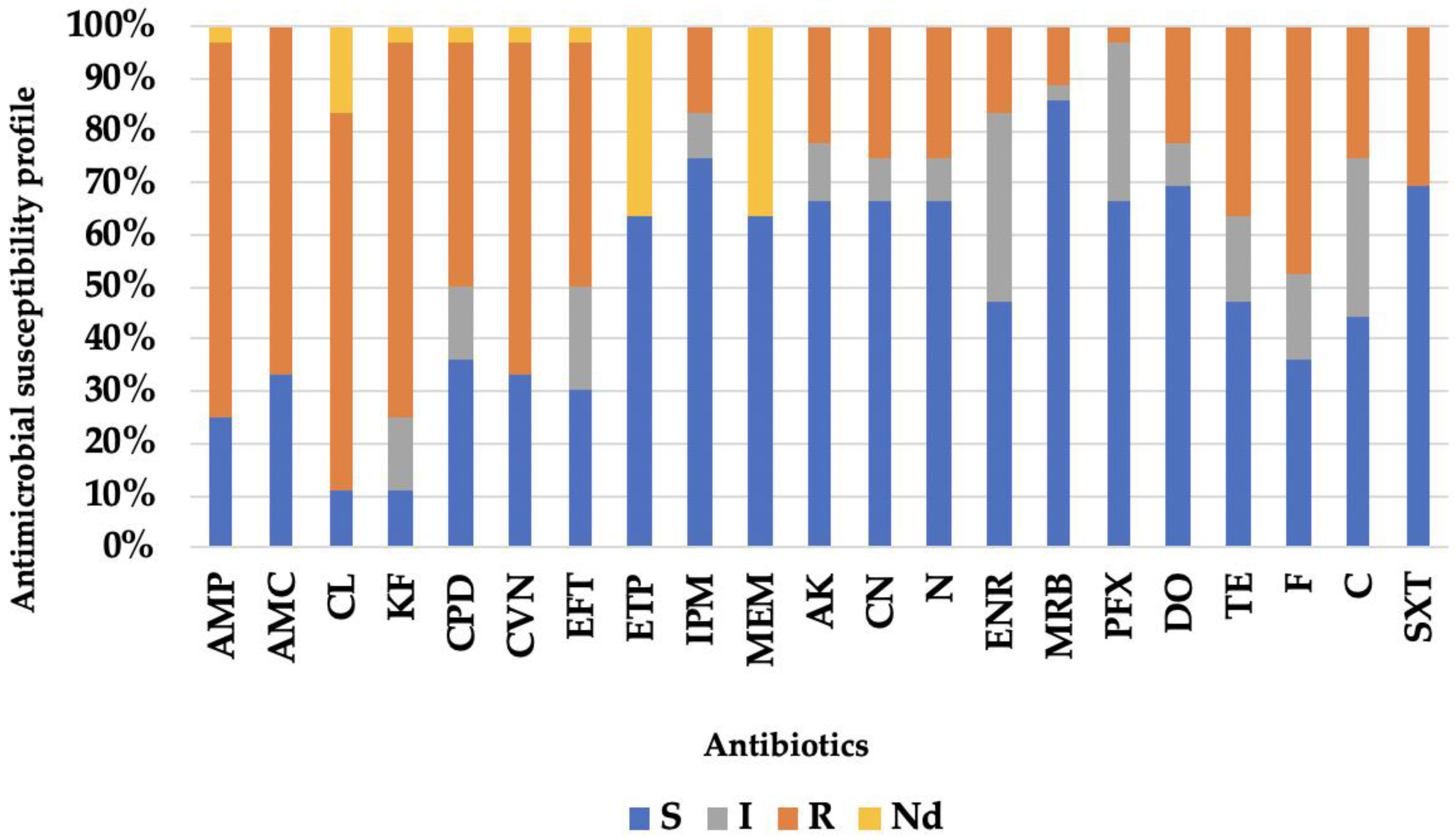
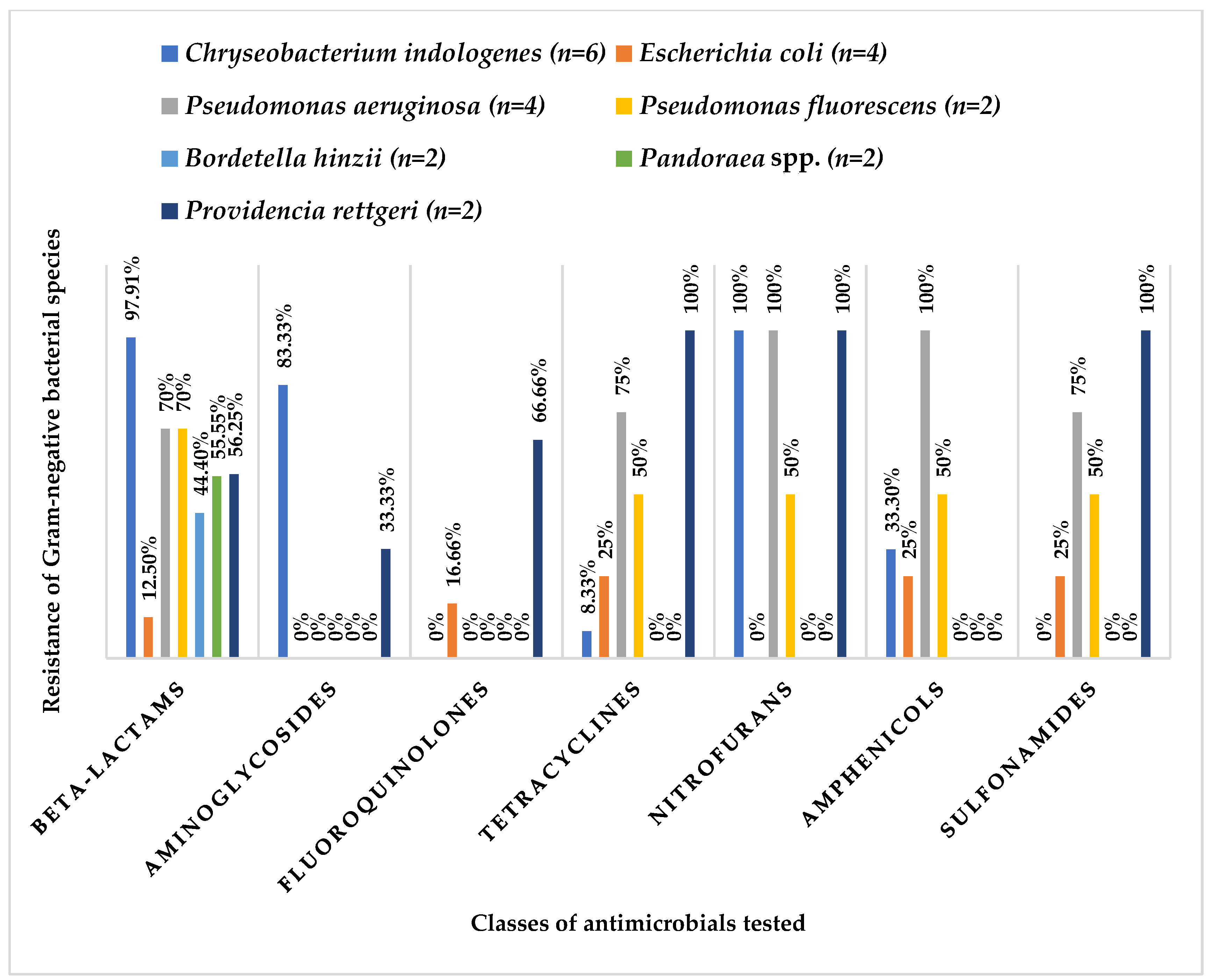
3.2. Antibiotic Resistance Profile
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Padhi, L.; Panda, S.K.; Mohapatra, P.P.; Sahoo, G. Antibiotic susceptibility of cultivable aerobic microbiota from the oral cavity of Echis carinatus from Odisha (India). Microb. Pathog. 2020, 143, 104121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehler, S.J.; Bennett, R.A. Oral, dental, and beak disorders of reptiles. Vet. Clin. North Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2003, 6, 477–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, J. Anatomy and disorders of the oral cavity of reptiles and amphibians. Vet. Clin. North Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2016, 19, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, S.; Popova, T. Enterobacter agglomerans—A cause of stomatitis in a snake. Tradit. Mod. Vet. Med. 2017, 1, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Grego, K.F.; Carvalho, M.P.N.; Cunha, M.P.V.; Knobl, T.; Pogliani, F.C.; Catão-Dias, J.L.; Sant´Anna, S.S.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Sellera, F.P. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy for infectious stomatitis in snakes: Clinical views and microbiological findings. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2017, 20, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shek, K.; Tsui, K.; Lam, K.; Crow, P.; Ng, K.; Ades, G.; Yip, K.; Grioni, A.; Tan, K.; Lung, D.; et al. Oral bacterial flora of the Chinese cobra (Naja atra) and bamboo pit viper (Trimeresurus albolabris) in Hong Kong SAR, China. Hong Kong Med. J. 2009, 15, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Artavia-León, A.; Romero-Guerrero, A.; Sancho-Blanco, C.; Rojas, N.; Umaña-Castro, R. Diversity of aerobic bacteria isolated from oral and cloacal cavities from free-living snakes species in Costa Rica rainforest. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2017, 2017, 8934285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babalola, M.O.; Balogun, J.A. The ecology and potential health risk of the oral microflora of Python regius and Clelia scyntalina. Int. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 5, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukač, M.; Horvatek Tomić, D.; Mandac, Z.; Mihoković, S.; Prukner-Radovčić, E.; Horvatek Tomić, D.; ManDac, Z.; Mihoković, S.; Prukner, E. Oral and cloacal aerobic bacterial and fungal flora of free-living four-lined snakes (Elaphe quatuorlineata) from Croatia. Veterinarski Arhiv 2017, 87, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, R.; Sharif, M.R.; Moniri, R.; Sharif, A.; Kashani, H.H. The identification of bacterial flora in oral cavity of snakes. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 25, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedley, J.; Whitehead, M.L.; Munns, C.; Pellett, S.; Abou-Zahr, T.; Calvo Carrasco, D.; Wissink-Argilaga, N. Antibiotic stewardship for reptiles. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 62, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jho, Y.-S.; Park, D.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Cha, S.-Y.; Han, J.S. Identification of bacteria from the oral cavity and cloaca of snakes imported from Vietnam. Lab. Anim. Res. 2011, 27, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zancolli, G.; Mahsberg, D.; Sickel, W.; Keller, A. Reptiles as reservoirs of bacterial infections: Real threat or methodological bias. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gospodinova, I.R.; Mustafa, S.; Popova, T.P. Microbiological analysis of laryngeal and oral swab samples from captive-bred snakes with respiratory tract infections in Bulgaria. Acta Microbiol. Bulg. 2024, 40, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Biswas, M.K.; Roy, P.; Guin, C. Short review of different microflora from the oral cavity of snakes. Uttar Pradesh J. Zool. 2017, 37, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Cheng, W. The mechanism of Bbcterial resistance and potential bacteriostatic strategies. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.A.; Diaz-Figueroa, O. Clinical reptile gastroenterology. Vet. Clin. North Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2005, 8, 277–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Requicha, J.F.; Martins, J.J.; Duarte, A.; Dias, I.R.; Viegas, C.A.; Saavedra, M.J. Black-and-white ruffed lemur (Varecia variegata) in captivity: Analysis of the oral microbiota in a one health perspective. Animals 2021, 11, 2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques, I.; Alvura, N.; Martins, J.J.; Requicha, J.F.; Saavedra, M.J. First report of Kocuria kristinae in the skin of a Cuban boa (Epicrates angulifer). Life 2023, 13, 2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, J.; Pinto, A.R.; Saavedra, M.J.; Cotovio, M. Equine Gram-negative oral microbiota: An antimicrobial aesistances watcher? Antibiotics 2023, 12, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Cheng, X.; Deng, M.; Deng, X.; Du, Q.; Ge, Y.; Guo, Q.; He, J.; Jia, W.; Kang, D.; et al. Oral mucosal microbes. In Atlas of Oral Microbiology: From Healthy Microflora to Disease; Zhou, X., Li, Y., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 95–107. [Google Scholar]
- D’Cruze, N.; Bates, J.; Assou, D.; Ronfot, D.; Coulthard, E.; Segniagbeto, G.H.; Auliya, M.; Megson, D.; Rowntree, J. A preliminary assessment of bacteria in “ranched” ball pythons (Python regius), Togo, West Africa. Nat. Conserv. 2020, 39, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Karade, S.; Kaur, K.; Ramamurthy, R.; Ranjan, P. Chryseobacterium indologenes pneumonitis in an infant: A case report. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamai, I.A.; Pakbin, B.; Kafi, Z.Z.; Brück, W.M. Oral abscess caused by Chryseobacterium indologenes in ball python (Python regius): A case report. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipineto, L.; Russo, T.P.; Calabria, M.; De Rosa, L.; Capasso, M.; Menna, L.F.; Borrelli, L.; Fioretti, A. Oral flora of Python regius kept as pets. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 58, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yak, R.; Lundin, A.-C.; Pin, P.Y.; Sebastin, S.J. Oral bacterial microflora of free-living reticulated pythons (Python reticulatus) in Singapore. J. Herpetol. Med. Surg. 2015, 25, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basatian-Tashkan, B.; Niakan, M.; Khaledi, M.; Afkhami, H.; Sameni, F.; Bakhti, S.; Mirnejad, R. Antibiotic resistance assessment of Acinetobacter baumannii isolates from Tehran hospitals due to the presence of efflux pumps encoding genes (adeA and adeS genes) by molecular method. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakidis, I.; Vasileiou, E.; Pana, Z.D.; Tragiannidis, A. Acinetobacter baumannii antibiotic resistance mechanisms. Pathogens 2021, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foti, M.; Giacopello, C.; Fisichella, V.; Latella, G. Multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from captive reptiles. J. Exot. Pet Med. 2013, 22, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Houdt, R.; Moons, P.; Jansen, A.; Vanoirbeek, K.; Michiels, C.W. Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of a biofilm-forming Serratia plymuthica isolate from a raw vegetable processing line. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 246, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaguirre-Anariba, D.E.; Sivapalan, V. Chryseobacterium indologenes, an emerging bacteria: A case report and review of literature. Cureus. 2020, 12, e6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachori, P.; Gothalwal, R.; Gandhi, P. Emergence of antibiotic resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa in intensive care unit; a critical review. Genes Dis. 2019, 6, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulová, N.; Mot’ková, P.; Brožková, I.; Pejchalová, M. Antibiotic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from hospital wastewater in the Czech Republic. J. Water Health 2022, 20, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, P.C.; Lin, W.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Chien, C.C.; Chiu IMTsai, T.S. Oral bacteria and their antibiotic susceptibilities in Taiwanese venomous snakes. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedict, S.; Shilton, C.M. Providencia rettgeri septicaemia in farmed crocodiles. Microbiol. Aust. 2016, 37, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, L.E.; Portela, R.W. Perfil de sensibilidade a antibióticos de um isolado de Providencia rettgeri proveniente de equino. Rev. Ciências Médicas Biológicas 2021, 20, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharina, O.; Jian, H.S.; Azlan, C. Bacterial stomatitis in wild reticulated pythons (Malayopython reticulatus) in Malaysia. World Vet. J. 2023, 13, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Mallik, S.; Nath, I.; Acharya, A.; Das, S.P.; Sethi, S.; Sahoo, M. Infectious stomatitis in an Indian rock python (Python molurus) and its therapeutic management. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6, 392–394. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency. Categorisation of Antibiotics Used in Animals Promotes Responsible Use to Protect Public and Animal Health. 2020. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/categorisation-antibiotics-european-union-answer-request-european-commission-updating-scientific-advice-impact-public-health-and-animal-health-use-antibiotics-animals_en.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Marques, I.; Pinto, A.R.; Alvura, N.; Telinhos, P.; Mendes, P.; Correia, M.; Martins, J.J.; Requicha, J.F.; Saavedra, M.J. Oral Microbiota in captive snakes: A study in Burmese and royal pythons. In Proceedings of the Book of the 31st European Veterinary Dental Forum, Nantes, France, 30 May–1 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
| Identification | No of Isolates (n = 36) |
|---|---|
| Chryseobacterium indologenes | 6 |
| Escherichia coli | 4 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 4 |
| Pseudomonas fluorescens | 2 |
| Pseudomonas putida | 1 |
| Bordetella hinzii | 2 |
| Pandoraea spp. | 2 |
| Providencia rettgeri | 2 |
| Acinetobacter baumannii | 1 |
| Achromobacter denitrificans | 1 |
| Achromobacter xylosoxidans | 1 |
| Delftia acidovorans | 1 |
| Enterobacter cloacae complex | 1 |
| Leclercia adecarboxylata | 1 |
| Pasteurella pneumotropica | 1 |
| Proteus mirabilis | 1 |
| Rahnella aquatilis | 1 |
| Salmonella group | 1 |
| Serratia plymuthica | 1 |
| Sphingobacterium thalpophilum | 1 |
| Sphingomonas paucimobilis | 1 |
| Animal | Sex | Age (Years) | No of Isolates | Species Identified |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB1 | M | 1 | 2 | Achromobacter xylosoxidans |
| Bordetella hinzii | ||||
| PB2 | F | 4 | 2 | Providencia rettgeri |
| Providencia rettgeri | ||||
| PB3 | M | 5 | 2 | Pasteurella pneumotropica |
| Achromobacter denitrificans | ||||
| PB4 | F | 5 | 2 | Escherichia coli |
| Escherichia coli | ||||
| PB5 | F | 5 | 3 | Escherichia coli |
| Delftia acidovorans | ||||
| Salmonella group | ||||
| PB6 | F | 4 | 2 | Proteus mirabilis |
| Escherichia coli | ||||
| PB7 | F | 4 | 1 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| PB8 | M | 4 | 2 | Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
| Animal | Sex | Age (Years) | No of Isolates | Species Identified |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR1 | F | 10 | 2 | Chryseobacterium indologenes |
| Chryseobacterium indologenes | ||||
| PR2 | M | 2 | 2 | Pseudomonas fluorescens |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | ||||
| PR3 | F | 2 | 1 | Pandoraea spp. |
| PR4 | F | 4 | 2 | Chryseobacterium indologenes |
| Chryseobacterium indologenes | ||||
| PR5 | F | 12 | 3 | Acinetobacter baumannii |
| Leclercia adecarboxylata | ||||
| Enterobacter cloacae complex | ||||
| PR6 | M | 2 | 1 | Sphingobacterium thalpophilum |
| PR7 | M | 10 | 1 | Pseudomonas putida |
| PR8 | F | 10 | 2 | Rahnella aquatilis |
| Serratia plymuthica | ||||
| PR9 | F | 2 | 2 | Pseudomonas fluorescens |
| Chryseobacterium indologenes | ||||
| PR10 | M | 12 | 2 | Pandoraea spp. |
| Sphingomonas paucimobilis | ||||
| PR11 | M | 4 | 2 | Bordetella hinzii |
| Chryseobacterium indologenes |
| Chryseobacterium indologenes | n | Escherichia coli | n | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | n | Pseudomonas putida | n |
| βLC-IMP-AMN-NIT | 4 | βLC-FL-TET-ANF-SUL | 1 | βLC-TET-NIT-ANF-SUL | 3 | βLC-NIT-SUL | 1 |
| βLC-AMN-TET-NIT-ANF | 1 | βLC-TET-NIT-ANF | 1 | ||||
| βLC-IMP-AMN-NIT-ANF | 1 | ||||||
| Pseudomonas fluorescens | n | Providencia rettgeri | n | Acinetobacter baumannii | n | Delftia acidovorans | n |
| βLC-TET-NIT-ANF-SUL | 1 | βLC-AMN-FL-TET-NIT-SUL | 2 | βLC-TET-SUL | 1 | βLC-AMN-FL | 1 |
| Lechercia adecarboxylata | n | Proteus mirabilis | n | Serratia plymuthica | n | Sphingomonas paucimobilis | n |
| AMN-FL-TET-SUL | 1 | βLC-TET-NIT | 1 | βLC- IMP-AMN-FL-TET-SUL | 1 | βLC-AMN-NIT | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marques, I.; Pinto, A.R.; Martins, J.J.; Alvura, N.; Telinhos, P.; Mendes, P.; Correia, M.; Requicha, J.F.; Saavedra, M.J. Assessing Potential Reservoir of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in the Oral Microbiota of Captive Burmese and Royal Pythons. Life 2025, 15, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030442
Marques I, Pinto AR, Martins JJ, Alvura N, Telinhos P, Mendes P, Correia M, Requicha JF, Saavedra MJ. Assessing Potential Reservoir of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in the Oral Microbiota of Captive Burmese and Royal Pythons. Life. 2025; 15(3):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030442
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarques, Inês, Ana R. Pinto, José J. Martins, Nuno Alvura, Paula Telinhos, Pedro Mendes, Mónica Correia, João F. Requicha, and Maria J. Saavedra. 2025. "Assessing Potential Reservoir of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in the Oral Microbiota of Captive Burmese and Royal Pythons" Life 15, no. 3: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030442
APA StyleMarques, I., Pinto, A. R., Martins, J. J., Alvura, N., Telinhos, P., Mendes, P., Correia, M., Requicha, J. F., & Saavedra, M. J. (2025). Assessing Potential Reservoir of Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in the Oral Microbiota of Captive Burmese and Royal Pythons. Life, 15(3), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15030442








