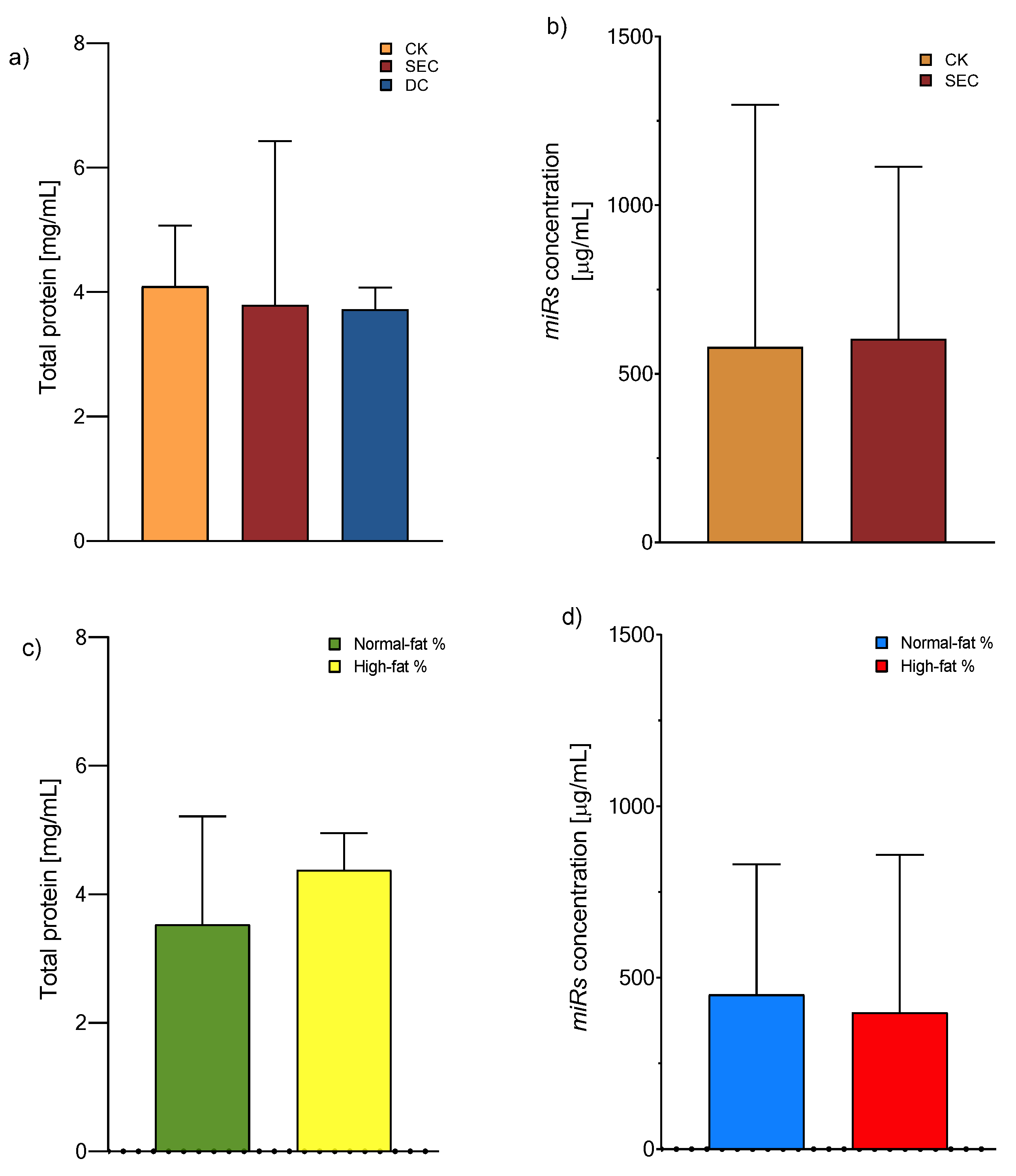Abstract
Adipose tissue is responsible for fat storage and is an important producer of extracellular vesicles (EVs). The biological content of exosomes, one kind of EV, provides information on aspects such as immunometabolic alterations. This study aimed to compare three plasma exosome isolation methods—using a commercial kit (CK), size exclusion chromatography (SEC), and differential centrifugation (DC)—and select the best one. Individuals categorized by normal and high body fat percentages were used. The DC and CK were proven to be the most advantageous out of the exosome isolation methods, so we suggest these methods for further protein and molecular analyses, respectively. Still, we emphasize the importance of selecting an appropriate methodology depending on the specific research objectives. At the same time, no statistical differences in exosome quality, morphology, total protein, or microRNA concentration were observed between individuals categorized by body fat percentage, so we suggest that the exosomal cargo varies in individuals with normal and high fat percentages.
1. Introduction
Exosomes, ranging in size from 50 to 150 nm, represent a subtype of extracellular vesicle (EV) due to their biogenesis and are found in several bodily fluids, including plasma, serum, urine, seminal fluid, tears, breast milk, the aqueous humor, and saliva, within diverse cell types, and in vitro cultures [1,2,3]. Exosomes work as carriers for biological material such as DNA, mRNA, microRNA, lipids, and proteins, thereby conveying information about the originating cells’ state and potentially influencing the function of recipient cells [4,5,6,7,8]. Adipose tissue (AT) is currently recognized as an essential source of circulating EVs, also known as adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicles (AdEVs), which function as a bridge between adipocytes and cells in the stromal fraction of AT, as well as cells from other systems [9,10]. AdEVs are filled with biological material that, in AT, plays a role in metabolic alterations, such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and related illnesses, and maintain the body’s homeostasis [9,11,12].
Even though it is unclear how, in fat depot accumulation, AdEV cargo is involved in obesity-related diseases and how these signaling molecules vary, exosomes are an alternative communication pathway that can influence cellular and tissue functions by exerting stimulatory or inhibitory effects, such as promoting cell proliferation, inducing apoptosis, modulating cytokine production, and regulating immune responses [13]. Consequently, the significance of exosome content in developing AT dysfunction lies in their role as carriers of proteins that recruit macrophages to the AT, mainly TNFα and IL-6, which contribute to the onset of insulin resistance (IR) [4], and an imbalance in lipid metabolism can occur as exosomes carry enzymes associated with lipogenesis. Consequently, these enzymes may influence lipogenic activity in recipient cells [10]. On the other hand, this scenario occurs within AT and distant organs, as exosomes can damage endothelial cells, compromise blood vessels, exacerbate liver fibrogenesis, and promote polarization to the M1 macrophage phenotype [9]. The increase in fat mass, which translates into the accumulation of triglycerides within adipocytes, triggers persistent cellular apoptosis. This process creates a hypoxic microenvironment characterized by chronic low-grade inflammation, leading to dysregulation in the secretion of cytokines, adipokines, and other factors essential for AT homeostasis [12,14].
To ensure precision and reproducibility, it is essential to compare other methods with the gold standard of exosome isolation, typically represented by differential centrifugation (DC) [15]. Traditionally, exosome isolation involves sequential centrifugation steps, including low-speed centrifugation to remove cells and debris, followed by higher-speed ultracentrifugation to pellet exosomes. Density gradient centrifugation and ultrafiltration have also been employed to enhance purity. Recently, alternative methods have been incorporated to reduce time-consuming procedures, the use of specialized equipment, the number of samples, and the supplies required. Depending on the source of exosomes and research objectives, these methods include polymer precipitation, immunoaffinity capture, chromatography [16], size exclusion [17], and commercial kits [18,19]. Alternatively, to characterize exosomes, both optical and non-optical techniques are available, each chosen based on the specific information required for research purposes. Optical methods include dynamic light scattering (DLS), multi-angle light scattering, nanoparticle tracking analysis, flow cytometry, and surface plasmon resonance [20,21]. Non-optical approaches encompass scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), cryogenic transmission electron microscopy (cryo-TEM), atomic force microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and the labeling of exosome membrane proteins such as CD9, CD63, CD81, and CD82 [20,22,23,24,25].
Based on the eight exosome isolation methods recently updated in the MISEV2023 guidelines, differential centrifugation (DC) in combination with other approaches demonstrates a higher level of specificity, whereas precipitation methods alone offer superior recovery [3,26,27]; therefore, this study aimed to compare three plasma exosome isolation techniques: precipitation using a commercial kit (CK, Invitrogen®), size exclusion chromatography (SEC), and differential centrifugation (DC). The isolated exosomes were characterized using dynamic light scattering (DLS), cryo-TEM, TEM, and Western blot analysis targeting the CD9 and CD81 markers to facilitate subsequent protein and molecular biology assays.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
Plasma Sample
Blood collection was approved by the Comisión de Investigación y Ética del Antiguo Hospital Civil de Guadalajara “Fray Antonio Alcalde” O.P.D Guadalajara, México. HCG/CEI-0835/22, N°. 130/22 after 118 participants aged 20 to 59 (71 women and 47 men) provided their written informed consent and were classified by fat percentage. A high fat percentage was considered to be more than 25% in men and 35% in women. We included 59 individuals with normal and 59 with high fat percentages. Ten milliliters of blood were obtained in EDTA-coated tubes and allowed to sit at room temperature for 30 min. The whole blood was centrifuged at 3000× g for 15 min at room temperature to separate plasma. The individual plasma samples were stored at 4 °C until the experiments. The clinical and anthropometric characteristics of the study subjects are described in Appendix A.
2.2. Exosome Isolation and Characterization
2.2.1. Isolation by Differential Centrifugation (DC)
Two mL of blood plasma was used, and all centrifugations were performed at 4 °C. We started with 300× g for 10 min (Heraeus Megafuge 2.0 R) and discarded the pellet; 2000× g for 20 min (Heraeus Megafuge 2.0 R) and discarded the pellet; 10,000× g for 20 min (Beckman Coulter JA-14 rotor, Brea, CA, USA; 250 mL NALGENE® bottles, Asheville, NC, USA) and discarded the pellet; 100,000 g for 70 min (Beckman Colter T70i rotor; 26.3 mL Beckman centrifuge tubes), discarding the supernatant and resuspending the pellet with 500 μL of 1X PBS; and 100,000 g for 70 min (150K rpm Thermo Sorvall Discovery M150 SE floor micro-ultracentrifuge; S150-AT rotor; 1 mL Eppendorf tubes PP) and resuspended the pellet in 200 μL of 1X PBS [28].
2.2.2. Isolation by Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
One mL of blood plasma at room temperature was used. Broadly speaking, we centrifugated it at 2000× g for 10 min and used the supernatant for a second centrifugation at 10,000× g for 30 min at 10 °C; the supernatant was filtrated through a 0.22 μm filter (CORNING; 45 mm diameter). Finally, we passed the sample through each column (Pkg of 50 #7321010 Econo-Pac® chromatography columns with Sepharose™ CL-2B (BioRad, Barcelona, Sapin)) with 1X PBS at room temperature filtrated through a 0.22 μm filter. Then, 200 μL of 15 fractions was collected [17,29].
2.2.3. Isolation by Precipitation with a Commercial Kit (CK)
A total exosome isolation (from plasma) kit (Invitrogen Cat. No. 4404450 (Vilnius, Lithuania)) was used according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. All centrifugations were performed at room temperature. Starting with 500 μL of blood plasma, followed by centrifugation at 10,000× g for 20 min, we added 0.5 volumes of PBS 1X to the supernatant, mixed it by vortexing, added 0.2 volumes of exosome precipitation reagent, and pipetted it up and down. This mix was incubated for 10 min at room temperature, then centrifugated at 10,000× g for 5 min, and the supernatant was discarded. Finally, the pellet was resuspended in 50 μL of PBS 1X.
2.2.4. Characterization by Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
The diameters of the EVs were analyzed by DLS using 500 μL of sample dissolved in 10 mM NaCl [30]. The equipment was set up at 25 °C for 60 min (Antor Paar. Litesizer DLS 700, Malverne Zetasizer Software v7.13 PSS0012-39. Gratz, Austria).
2.2.5. Characterization by Cryo-TEM and TEM
For TEM, negative staining was performed with a 1:1 proportion of isolated exosomes and glutaraldehyde; 6 μL of this mix was washed and collocated in the carbon mesh [31] for transmission electron microscopy (FEI Technology, Model Tecnai Spirit BioTwin, software FEI TIA v4.15), and 3 μL of isolated exosomes was used for cryo-TEM (Jeol JM-2011, Tokyo, Japan) [32].
2.2.6. Characterization by Western Blot
Starting with an exosome lysis buffer (25 mM Tris-HCl +120 mM NaCl + 1% Triton-X100 + complete Mini, EDTA-Free; Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), we added 20 μL of it to 150 μL of the sample in ice-cold conditions, then incubated it with rotational agitation at 4 °C for 1 h, and then centrifugated it at 15,000× g for 15 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was measured with a spectrophotometer (NanoDrop 1000 UV visible spectrophotometer, Thermo Scientific (San Diego, CA, USA)). We charged 5 μg of total protein on 14% acrylamide gel. Exosome markers were quantified using mouse monoclonal CD9 (1:1000; antibodies.com; Anti-CD9 (MEM-61) (A86089)), CD81 (1:1000; antibodies.com; Anti-CD81 (M38) (A86719)), and vinculin (1:500 Invitrogen Ref. MA5-11690 Barcelona, Spain). We used anti-mouse HRP (1:5000; Abcam; NA931V ECL Anti-mouse IgG) and ECL (BioRad Clarity Western ECL substrate 500 mL; #1705061. Barcelona, Spain) in a spectrophotometer (Li-cor, Odyssey XF, Lincoln, USA. LI-COR Acquisition Software v2.2).
2.3. MicroRNA Isolation
Trizol reagent was used to isolate microRNA—50 µL of isolated exosome was lysed in 200 µL Trizol + 1 µL (1 µg/µL glycogen, RNA grade; Thermo Scientific #R0551). Subsequently, 40 µL of chloroform was used for phase separation, and 100% isopropanol was used for microRNA precipitation. Finally, microRNA was eluted in 30 µL of RNase-free water after being washed twice in 75% ethanol. The microRNA concentration was assessed using Qubit® 4.0.
2.4. Statistical and Image Analyses
For each method, one-way ANOVA, post hoc Tukey tests, and the Mann–Whitney U test (mean ± SD) were used to compare the total protein and microRNA concentration differences between average and high fat percentages. p < 0.05 was considered significant. GraphPad Prism version 8.4.0 for macOS was used for data analysis and graphing. ImageJ2 version 2.1.4.0/1.54f was used for image analyses.
3. Results
3.1. The Exosome Isolation Methods Showed Equal Performances in Total Protein and microRNA Concentration, While an Inverse Pattern Was Observed Among Individuals with High Fat Mass Contents
The exosomes were isolated according to the manufacturer’s recommended instructions for the CK, whereas DC and SEC were utilized for classical ultracentrifugation and column fraction separation, respectively. The exosome yield was determined by the total protein concentration using a Qubit Protein Assay (Invitrogen™, Eugene, OR, USA). We observed that the precipitation-based total exosome isolation kit (Invitrogen) had the maximum yield, followed by SEC and DC (Figure 1a). After these results, we chose a CK and SEC for isolating the microRNA from the exosome with equal performances (Figure 1b). On the other hand, there is a tendency for the concentration of total proteins or miRNAs to increase, although the values did not reach statistical significance (Figure 1c,d).
Figure 1.
Exosome total protein and microRNA concentration. (a) Protein concentration means of 4.09, 3.97, and 3.97 mg/mL for the CK, SEC, and DC, respectively (one-way ANOVA and post hoc Tukey tests), and (b) microRNA concentration means of 579 and 603 mg/mL for the CK and SEC, respectively (Mann–Whitney U test). Both were measured from exosomes, n = 118, with no significance. (c) Total protein concentration and (d) total microRNA concentration (Qubit assay kits, Invitrogen™) from plasma exosomes isolated by a commercial kit (Mann–Whitney U test, no significance). Abbreviations: CK: commercial kit; SEC: size exclusion chromatography; and DC: differential centrifugation.
3.2. The Morphology and Quality of the Three Exosome Isolation Methods Were as Expected, with Inconsistencies in Purity
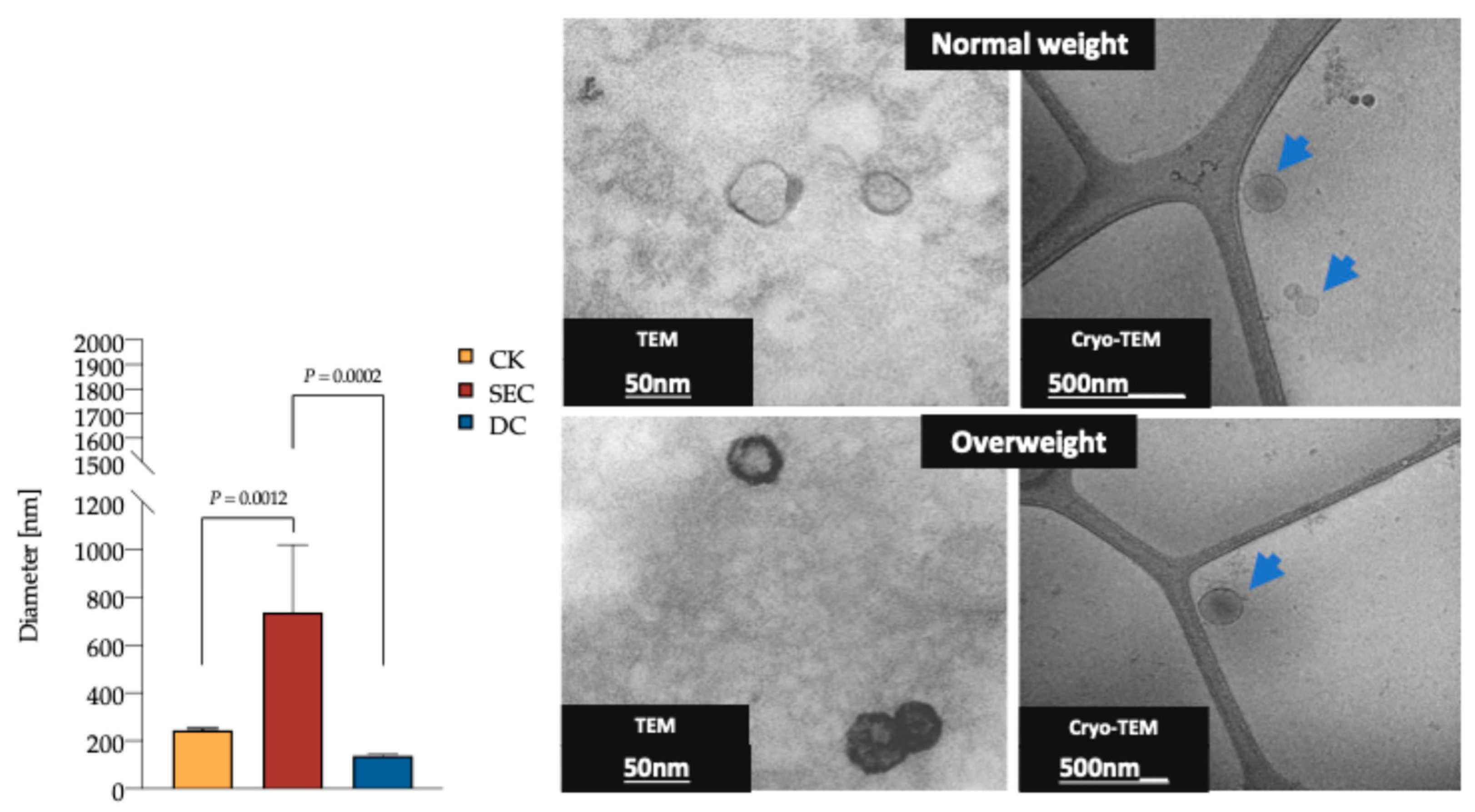
The DLS analysis revealed that the vesicle diameter measured in the CK and DC was consistent with the expected exosome size (Figure 2); however, the purity of the vesicle subpopulation varied between the CK and DC compared to SEC. The TEM and cryo-TEM analyses confirmed that the morphology and overall quality of exosomes were consistent across methods. Additionally, no morphological differences were observed between exosomes from individuals with normal and high fat percentages (Figure 2).
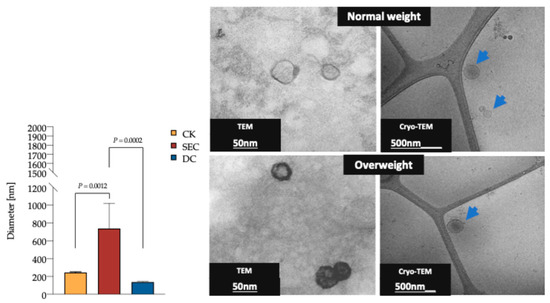
Figure 2.
DLS of plasma exosomes isolated by the CK, SEC, and DC, as well as TEM and cryo-TEM exosome photomicrography. The exosomes’ average diameter was 235.1 nm, 736.9 nm, and 138.2 nm for the CK, SEC, and DC, respectively (n = 15 for each method, one-way ANOVA, and post hoc Tukey tests; p < 0.05). TEM of exosomes isolated by the CK (Invitrogen Cat. No. 4404450). Diameter of 53.9 nm, scale of 50 nm. Cryo-TEM of exosomes isolated by SEC. Diameter of 191.7 (blue arrow) nm, scale of 500 nm. Exosomes from plasma samples of individuals were classified by fat percentage (59 for each group). Abbreviations: DLS: dynamic light scattering; CK: commercial kit; SEC: size exclusion chromatography; and TEM: transmission electron microscopy.
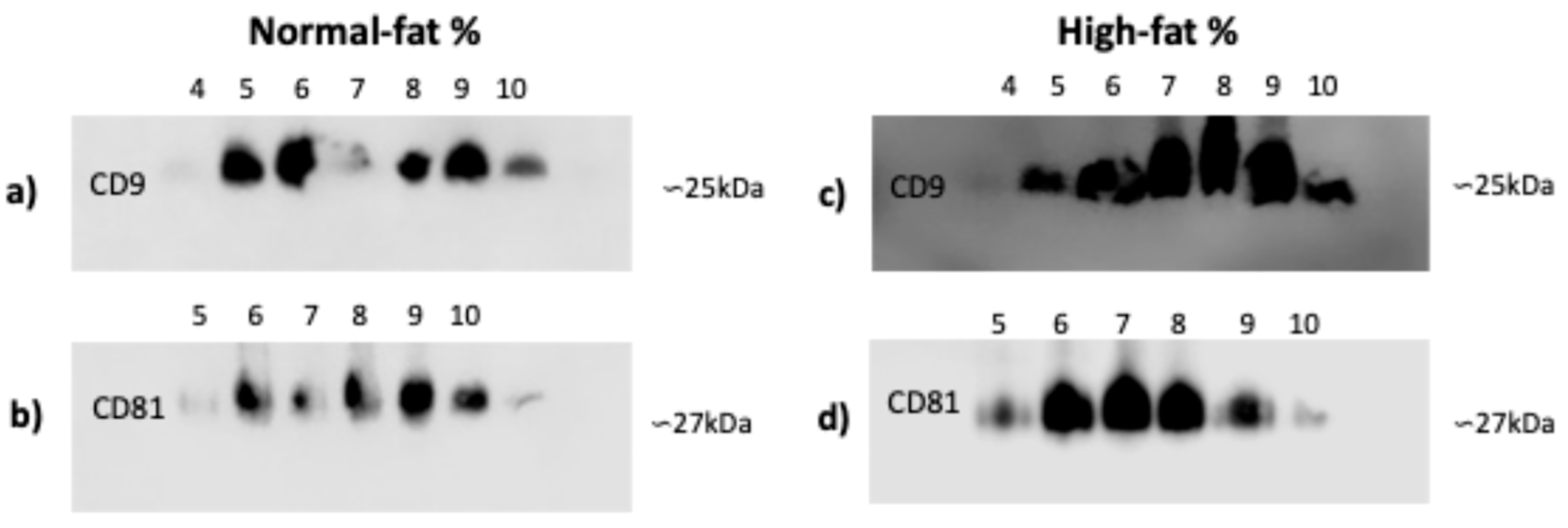
3.3. CD9 and CD81 Do Not Differ Between Normal- and High-Fat-Percentage Individuals in SEC Fractions
Since the integrity and quality of microscopy images and total protein did not differ, we chose an exosome isolation technique that was more cost-effective and equipment-efficient for identifying CD9 and CD81 in plasma exosomes from individuals with normal and high fat percentages. In individuals with normal and high fat percentages, there are no shifts in CD9 marker fractions from four to ten (Figure 3a,c) or in CD81 fractions from five to ten (Figure 3b,d).
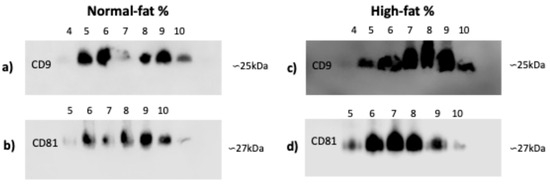
Figure 3.
CD9 and CD81 markers of exosomes isolated by SEC. (a,c) CD9 marker: the presence of exosomes of the exclusion fractions from 4 to 10. (b,d) CD81 marker: the presence of exosomes of the exclusion fractions from 5 to 10. Exosomes were isolated from plasma samples of individuals that were classified by fat percentage: (a–d) high (59 for each group). Abbreviation: SEC: size exclusion chromatography.
Based on our experience, we can establish some characteristics of these three exosome isolation methods, as shown in Table 1 below.

Table 1.
Comparison between three methods for exosome isolation.
4. Discussion
It is estimated that the prevalence of obesity and overweight will reach 1.7 billion people by 2030 [33], so understanding the mechanism by which AT acts under these conditions is critical to preventing, treating, and reversing the loss of homeostasis within this tissue. The adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicles play an essential role in developing obesity-associated diseases, like cancer [34], among others; as suggested by Delgadillo et al., AdEV size can be related to liver and systemic IR [35].
Currently, the choice of method with which to isolate exosomes is wide-ranging, depending on the application of these vesicles. Ultracentrifugation, preceded by low-speed centrifugation, is the gold-standard technique [36]. Still, the equipment and accessories for it are not available in all laboratories. In the present study, we gauged the material and equipment price, time consumption, vesicle yield, purity subpopulation, protein, and microRNA concentration of three isolation methods to define the one most suitable for further analyses. The results were as follows: (a) the CK presented the highest total protein concentration in contrast with the other two techniques; (b) there was a similarity in microRNA concentration between the exosomes isolated with the CK and SEC; and (c) there was a likeness in exosome total protein and microRNA concentration between normal- and high-fat-percentage individuals.
Even though total protein quantification is a suitable method for estimating the concentration of exosomes, it cannot distinguish between contaminating proteins, like albumin, that are not associated with them [27]; therefore, between the three methods, the commercial kit is the most reproducible, as mentioned by Caradec et al. [37]. After comparing the concentrations of the total protein content of the exosomes by using the three methods, we decided to evaluate normal and high percentages of fat and the total microRNA by using the most straightforward method, which is less time-consuming and allows for the analysis of a more significant number of samples. Precipitation by a CK is an excellent alternative to a subsequent analysis of nucleic acid, even if we could not find a difference between the three methods, as Mohammad et al. also determined when comparing a commercial kit to ultracentrifugation [38]. In this context, without a difference between individuals with normal and high fat percentages, considering Wang et al.’s evaluation of the exosome proteome in obese and non-obese individuals with T2DM [39], we can propose that the exosomal cargo is linked to metabolic-associated disorders rather than fat content [40,41].
Many techniques have been used for exosome characterization [42], depending on the information that researchers require. In our case, we chose two that can be used for quality (protein marker, shape, and size) analyses: DLS, electron microscopy (TEM and cryo-TEM), and Western blot (CD9 and CD81 markers). DLS allowed for the characterization of plasma exosome subpopulations according to their diameters, as shown by the CK and DC methods. In contrast, SEC appears to yield a higher presence of aggregated exosomes and other plasma particles of similar sizes, probably due to the intrinsic nature of its isolation mechanism [43]. Electron microscopy enables the imaging of single exosomes, visualizing their size and morphology. Exosomes isolated by the CK and DC demonstrated the presence of fewer microvesicles, while SEC presented a considerable microvesicle population, as mentioned by Davidson et al. [44].
We chose two tetraspanins to verify that we isolated microvesicles compatible with the exosomes (CD9 and CD81). We analyzed normal- and high-fat-percentage individuals, in whom there was a difference in the delay of fractions between markers but not in fat condition. This pattern was shown in carcinoma exosomes [45] and circulating exosomes [46] isolated by SEC. Following our results, Sharif et al. mentioned that SEC is a suitable method for further nucleic acid analyses, by which they also found a distinct population of EVs [47]. Our decision to use the three exosome isolation methods and exosome characterization is supported by the latest update of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles (MISEV2023 [3]), as well as the advantages and disadvantages found according to our results (Table 1).
After evaluating the three exosome isolation techniques, we identified specific limitations linked with each method. In the case of differential centrifugation (DC), a major drawback is the requirement for access to ultracentrifugation or miniultracentrifugation equipment, which is not available in all laboratories. Similarly, for size exclusion chromatography (SEC), noteworthy challenges include the extended time required for sample processing and variability between protocols, particularly regarding the initial sample volume and the volume collected from each fraction.
Exosomes have garnered significant interest due to their potential as biomarkers, as they transport proteins and microRNAs capable of predicting the diseases associated with obesity. Furthermore, they enable the evaluation of the functional status of adipose tissue and are emerging as promising therapeutic vesicles for restoring homeostasis in this tissue. Notably, by conducting a comprehensive immunometabolic assessment of an individual, exosome-based therapies could be tailored, paving the way for personalized medical approaches.
5. Conclusions
We highlight the importance of selecting the most suitable exosome isolation method based on specific research objectives. For studies prioritizing exosome integrity, we recommend using SEC for plasma samples, as it yields a higher concentration of intact exosomes. However, if the focus is on achieving greater purity in EV subpopulations, DC or a commercial isolation kit are more appropriate methodologies. We suggest the DC and CK methods for further protein and molecular analyses, respectively.
Our results indicate that circulating exosomes do not differ in quantity and quality between individuals with normal and high body fat percentages; however, their compositions do vary. We recommend further investigations into the molecular cargo of circulating exosomes, as it may serve as an indicator of adipose tissue status and could help elucidate these differences.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.N.-V., I.Á. and R.N.; methodology, J.N.-V. and J.C.L.; formal analysis, J.N.-V., I.Á. and R.N.; investigation, J.N.-V., J.C.L., J.C., A.F., I.Á. and R.N.; resources, J.C., A.F., I.Á. and R.N.; data curation, J.N.-V., I.Á. and R.N.; writing—original draft preparation, J.N.-V., I.Á. and R.N.; writing—review and editing, J.N.-V., J.C.L., J.C., A.F., P.M., I.Á. and R.N.; visualization, J.N.-V., J.C.L., J.C., A.F., P.M., I.Á. and R.N.; supervision, I.Á. and R.N.; project administration, I.Á. and R.N.; funding acquisition, J.C., A.F., I.Á. and R.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Consejo Nacional de Humanidades, Ciencias y Tecnologías (CONAHCYT) SECIHTI-México for doctoral scholarship to Jacqueline Alejandra Noboa Velastegui (CVU number 1103690).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted by the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Comisión de Investigación y Ética del Antiguo Hospital Civil de Guadalajara “Fray Antonio Alcalde” O.P.D. HCG/CEI-0835/22, N°. 130/22 on 23 May 2022 for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Information is available upon reasonable request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This article is a revised and expanded version of a paper [48], which was presented at [European Congress of Immunology, Dublin, Ireland, 1–4 September 2024].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
Clinical and anthropometric characteristics of the study subjects.

| Groups | Normal Fat Percentage | High Fat Percentage | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 59 | 59 | |
| Sex (Men–Women) | 26:33 | 21:38 | |
| Age | 32 ± 9 | 38 ± 10 | |
| Lipid Profile | |||
| TC (mg/dL) | 173.4 ± 32.8 | 191.4 ± 44.5 | 0.01 * |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 95.6 ± 49.5 | 199.7 ± 202.3 | <0.0001 **** |
| Insulin Resistance Status | |||
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 75.6 ± 17.3 | 88.7 ± 42.7 | 0.01 * |
| Fasting insulin (uUI/mL) | 12.5 ± 9.8 | 21.9 ± 11.5 | <0.0001 **** |
| Evaluation of Body Adiposity Status | |||
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.5 ± 2.9 | 34.0 ± 5.4 | <0.0001 **** |
| Fat % | 24.5 ± 6.4 | 38.8 ± 7.7 | <0.0001 **** |
| AVI (cm2) | 14.2 ± 6.3 | 22.8 ± 7.7 | <0.0001 **** |
| VAI | 1.4 ± 3.3 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | <0.0001 **** |
| WC | 81.6 ± 14.1 | 103.2 ± 21.1 | <0.0001 **** |
Mann–Whitney U test (mean ± SD). Significance: * p < 0.05, **** p < 0.0001. Abbreviations: TC, total cholesterol; BMI, body mass index; BAI, body adiposity index; AVI, abdominal volume index; VAI, visceral adiposity index; and WC, waist circumference.
References
- Thery, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 3, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulmalek, O.; Husain, K.; AlKhalifa, H.; Alturani, M.; Butler, A.; Moin, A. Therapeutic Applications of Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrugger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.M.; Lin, X.; Xu, F.; Shan, S.K.; Guo, B.; Li, F.X.; Zheng, M.H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Q.S.; Yuan, L.Q. Exosomes and Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 651996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dance, A. The body’s tiny cargo carriers. Knowable Magazine, 8 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; You, L.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, X.; Zhong, H.; Sun, X.; Ji, C.; Chi, X. Biological Properties of Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles and Their Physiological Functions in Infant. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 693534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragusa, M.; Barbagallo, C.; Statello, L.; Caltabiano, R.; Russo, A.; Puzzo, L.; Avitabile, T.; Longo, A.; Toro, M.D.; Barbagallo, D.; et al. miRNA profiling in vitreous humor, vitreal exosomes and serum from uveal melanoma patients: Pathological and diagnostic implications. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, A.T.; Rahman, S.; Badierah, R.; Lee, E.J.; Mattar, E.H.; Redwan, E.M.; Choi, I. Expedition into Exosome Biology: A Perspective of Progress from Discovery to Therapeutic Development. Cancers 2021, 13, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, R.; Qin, W.; Zheng, Y.; Wan, Z.; Liu, L. Role of Adipose Tissue Derived Exosomes in Metabolic Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 873865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Wei, M.; Yang, G.; Yuan, L. Multifaceted Roles of Adipose Tissue-Derived Exosomes in Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 669429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Guo, X. The clinical potential of circulating microRNAs in obesity. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, S.T.; Calkin, A.C.; Drew, B.G. Adipose-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Systemic Messengers and Metabolic Regulators in Health and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 837001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camino, T.; Lago-Baameiro, N.; Pardo, M. Extracellular Vesicles as Carriers of Adipokines and Their Role in Obesity. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasshauer, M.; Bluher, M. Adipokines in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Zhao, T.; He, Z.; Cai, R.; Pang, W. Composition, isolation, identification and function of adipose tissue-derived exosomes. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.X.; Sun, C.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.L. New insight into isolation, identification techniques and medical applications of exosomes. J. Control. Release 2019, 308, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, L.; Hong, C.S.; Stolz, D.B.; Watkins, S.C.; Whiteside, T.L. Isolation of biologically-active exosomes from human plasma. J. Immunol. Methods 2014, 411, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Qu, X.; Dong, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Ma, X.; Jia, Y.; Li, R.; Jiang, X.; Williams, C.; Wang, T.; et al. Comparison of serum exosome isolation methods on co-precipitated free microRNAs. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, R.; Du, L. Review on Strategies and Technologies for Exosome Isolation and Purification. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 811971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rech, J.; Getinger-Panek, A.; Gałka, S.; Bednarek, I. Origin and Composition of Exosomes as Crucial Factors in Designing Drug Delivery Systems. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koritzinsky, E.H.; Street, J.M.; Star, R.A.; Yuen, P.S. Quantification of Exosomes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, C.; Luwor, R.; Morokoff, A.; Kaye, A.; Stylli, S. Cancer exosomes in cerebrospinal fluid. Transl. Cancer Res. 2017, 6 (Suppl. S8), S1352–S1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.Y.; Miller, J. A review on protein markers of exosome from different bio-resources and the antibodies used for characterization. J. Histotechnol. 2019, 42, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernyshev, V.S.; Rachamadugu, R.; Tseng, Y.H.; Belnap, D.M.; Jia, Y.; Branch, K.J.; Butterfield, A.E.; Pease, L.F., 3rd; Bernard, P.S.; Skliar, M. Size and shape characterization of hydrated and desiccated exosomes. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 3285–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Luo, H.; Ruan, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, B.; Xie, Y. Isolation and identification of exosomes from feline plasma, urine and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.L.; Khosroheidari, M.; Ravi, R.K.; DiStefano, J.K. Comparison of protein, microRNA, and mRNA yields using different methods of urinary exosome isolation for the discovery of kidney disease biomarkers. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.T.; Huang, Y.Y.; Zheng, L.; Qin, S.H.; Xu, X.P.; An, T.X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.S.; Hu, X.M.; Ping, B.H.; et al. Comparison of isolation methods of exosomes and exosomal RNA from cell culture medium and serum. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobb, R.J.; Becker, M.; Wen, S.W.; Wong, C.S.; Wiegmans, A.P.; Leimgruber, A.; Moller, A. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortina, P.; Londin, E.R.; Park, J.Y.; Kricka, L.J. Acute Myeloid Leukemia—Methods and Protocols; Methods in Molecular Biology Series; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 1633, pp. 258–266. [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri, V.; Lucchetti, D.; Gatto, I.; Maiorana, A.; Marcantoni, M.; Maulucci, G.; Papi, M.; Pola, R.; De Spirito, M.; Sgambato, A. Dynamic light scattering for the characterization and counting of extracellular vesicles: A powerful noninvasive tool. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikkert, L.G.; Nieuwland, R.; Terstappen, L.; Coumans, F.A.W. Quality of extracellular vesicle images by transmission electron microscopy is operator and protocol dependent. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1555419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernice, M.C.; Closa, D.; Garces, E. Cryo-electron microscopy of extracellular vesicles associated with the marine toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. Harmful Algae 2023, 123, 102389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Atlas. 2024. Available online: https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/WOF-Obesity-Atlas-v7.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Zhou, C.; Huang, Y.Q.; Da, M.X.; Jin, W.L.; Zhou, F.H. Adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicles: Bridging the communications between obesity and tumor microenvironment. Discov. Oncol. 2023, 14, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgadillo-Velázquez, J.; Alday, E.; Aguirre-García, M.M.; Canett-Romero, R.; Astiazaran-Garcia, H. The association between the size of adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicles and fasting serum triglyceride-glucose index as proxy measures of adipose tissue insulin resistance in a rat model of early-stage obesity. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1387521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coughlan, C.; Bruce, K.D.; Burgy, O.; Boyd, T.D.; Michel, C.R.; Garcia-Perez, J.E.; Adame, V.; Anton, P.; Bettcher, B.M.; Chial, H.J.; et al. Exosome Isolation by Ultracentrifugation and Precipitation and Techniques for Downstream Analyses. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2020, 88, e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caradec, J.; Kharmate, G.; Hosseini-Beheshti, E.; Adomat, H.; Gleave, M.; Guns, E. Reproducibility and efficiency of serum-derived exosome extraction methods. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 47, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.A.; Seo, B.; Hussaini, H.M.; Hibma, M.; Rich, A.M. Comparing Two Methods for the Isolation of Exosomes. J. Nucleic Acids 2022, 2022, 8648373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y. Comparison of Plasma Exosome Proteomes Between Obese and Non-Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2023, 16, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, H.Y.; Chen, M.; Xu, K.; Chen, B. The impact of obesity on adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicles. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 7275–7288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, T.; Jeong, I.; Park, J.; Jun, W.; Kim, A.; Kim, O.-K. Adipose tissue-derived exosomes contribute to obesity-associated liver diseases in long-term high-fat diet-fed mice, but not in short-term. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1162992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.J.; Chau, Z.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Hill, J.J.; Korpany, K.V.; Liang, N.W.; Lin, L.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Liu, J.K.; Liu, Y.C.; et al. Exosome Processing and Characterization Approaches for Research and Technology Development. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2103222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilsiz, N. A comprehensive review on recent advances in exosome isolation and characterization: Toward clinical applications. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 50, 102121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, S.M.; Boulanger, C.M.; Aikawa, E.; Badimon, L.; Barile, L.; Binder, C.J.; Brisson, A.; Buzas, E.; Emanueli, C.; Jansen, F.; et al. Methods for the identification and characterization of extracellular vesicles in cardiovascular studies: From exosomes to microvesicles. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 45–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakha, S.; Muramatsu, T.; Ueda, K.; Inazawa, J. Exosomal microRNA miR-1246 induces cell motility and invasion through the regulation of DENND2D in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, N.; Pinnick, K.E.; Paget, D.; Choudhury, R.P. Isolation and Characterization of Human Adipocyte-Derived Extracellular Vesicles using Filtration and Ultracentrifugation. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 170, e61979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, S.; Mozaffari-Jovin, S.; Alizadeh, F.; Mojarrad, M.; Baharvand, H.; Nouri, M.; Abbaszadegan, M.R. Isolation of plasma small extracellular vesicles by an optimized size-exclusion chromatography-based method for clinical applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 87, 104796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noboa, J.; León, J.; Castro, J.; Fletes, A.; Madrigal, P.; Álvarez, I.; Navarro, R. Comparing three methods for the isolation of exosomes from plasma in subjects with overweight and 3T3-L1 cell culture. In Proceedings of the European Congress of Immunology, Dublin, Ireland, 1–4 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).