Localization of Lesions in Autoimmune Blistering Diseases Is Independent of Site-Specific Target Antigen Expression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Material
2.2. Immunofluorescence Studies
2.3. Statistics
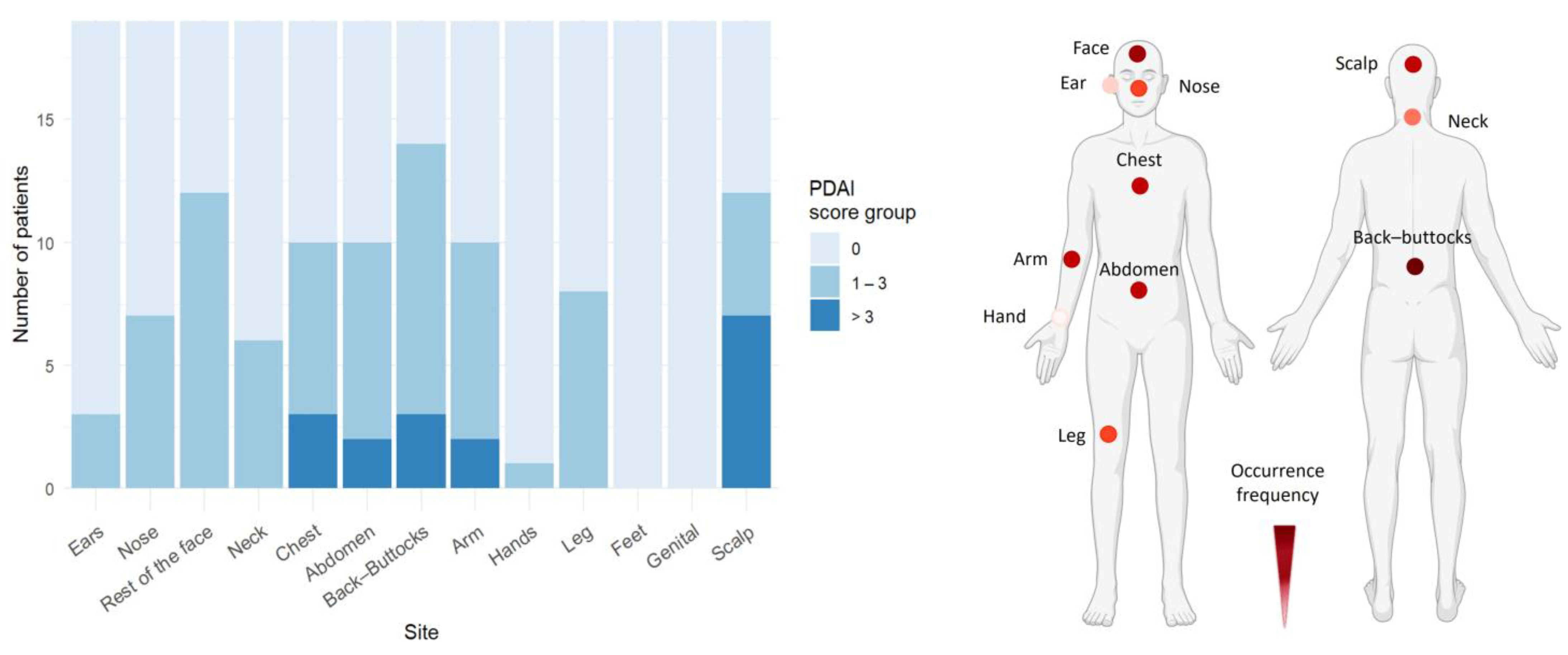
3. Results
3.1. Arms and Legs Are the Most Common Sites for Blisters/Erosions and Erythematous/Urticarial Lesions in BP
3.2. Trunk and Buccal Mucosa Are Predilection Sites in PV
3.3. Trunk and Face Are Predilection Sites for Skin Blistering in PF
3.4. AIBD Antigen Expression Shows Slight Variations in Different Skin and Mucosal Regions
3.5. Expression Levels of AIBD Antigens Do Not Correlate with Clinical Scores
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Zeng, F.A.P.; Murrell, D.F. State-of-the-art review of human autoimmune blistering diseases (AIBD). Vet. Dermatol. 2021, 32, 524-e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emtenani, S.; Hertl, M.; Schmidt, E.; Hudemann, C. Mouse models of pemphigus: Valuable tools to investigate pathomechanisms and novel therapeutic interventions. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1169947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, E.; Kasperkiewicz, M.; Joly, P. Pemphigus. Lancet 2019, 394, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, E.; Zillikens, D. Pemphigoid diseases. Lancet 2013, 381, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Beek, N.; Weidinger, A.; Schneider, S.W.; Kleinheinz, A.; Glaser, R.; Holtsche, M.M.; von Georg, A.; Hammers, C.M.; Hubner, F.; Lima, A.L.; et al. Incidence of pemphigoid diseases in Northern Germany in 2016—First data from the Schleswig-Holstein Registry of Autoimmune Bullous Diseases. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtsche, M.M.; Boch, K.; Schmidt, E. Autoimmune bullous dermatoses. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2023, 21, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Patzelt, S.; van Beek, N.; Schmidt, E. Mucous membrane pemphigoid. Autoimmun. Rev. 2022, 21, 103036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannides, D.; Hytiroglou, P.; Phelps, R.G.; Bystryn, J.C. Regional variation in the expression of pemphigus foliaceus, pemphigus erythematosus, and pemphigus vulgaris antigens in human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1991, 96, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borradori, L.; Van Beek, N.; Feliciani, C.; Tedbirt, B.; Antiga, E.; Bergman, R.; Bockle, B.C.; Caproni, M.; Caux, F.; Chandran, N.S.; et al. Updated S2 K guidelines for the management of bullous pemphigoid initiated by the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1689–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, E.; Goebeler, M.; Hertl, M.; Sardy, M.; Sitaru, C.; Eming, R.; Hofmann, S.C.; Hunzelmann, N.; Kern, J.S.; Kramer, H.; et al. S2k guideline for the diagnosis of pemphigus vulgaris/foliaceus and bullous pemphigoid. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2015, 13, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, D.F.; Daniel, B.S.; Joly, P.; Borradori, L.; Amagai, M.; Hashimoto, T.; Caux, F.; Marinovic, B.; Sinha, A.A.; Hertl, M.; et al. Definitions and outcome measures for bullous pemphigoid: Recommendations by an international panel of experts. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2012, 66, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, P.; Horvath, B.; Patsatsi, A.; Uzun, S.; Bech, R.; Beissert, S.; Bergman, R.; Bernard, P.; Borradori, L.; Caproni, M.; et al. Updated S2K guidelines on the management of pemphigus vulgaris and foliaceus initiated by the european academy of dermatology and venereology (EADV). J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 1900–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, D.F.; Dick, S.; Ahmed, A.R.; Amagai, M.; Barnadas, M.A.; Borradori, L.; Bystryn, J.C.; Cianchini, G.; Diaz, L.; Fivenson, D.; et al. Consensus statement on definitions of disease, end points, and therapeutic response for pemphigus. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 58, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, S. A Simple Sequentially Rejective Multiple Test Procedure. Scand. J. Stat. 1979, 6, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Cochran, W.G. The comparison of percentages in matched samples. Biometrika 1950, 37, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hothorn, T.; Bretz, F.; Westfall, P. Simultaneous inference in general parametric models. Biom. J. 2008, 50, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goletz, S.; Pigors, M.; Lari, T.R.; Hammers, C.M.; Wang, Y.; Emtenani, S.; Aumailley, M.; Holtsche, M.M.; Stang, F.H.; Weyers, I.; et al. Laminin beta4 is a constituent of the cutaneous basement membrane zone and additional autoantigen of anti-p200 pemphigoid. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2024, 90, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprenger, A.; Weber, S.; Zarai, M.; Engelke, R.; Nascimento, J.M.; Gretzmeier, C.; Hilpert, M.; Boerries, M.; Has, C.; Busch, H.; et al. Consistency of the proteome in primary human keratinocytes with respect to gender, age, and skin localization. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 2509–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lintzeri, D.A.; Karimian, N.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Kottner, J. Epidermal thickness in healthy humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Fonseca, M.; Wolner, Z.; Chung, E.; Wu, X.; Geller, S.; Dusza, S.W.; DeRosa, A.P.; Marghoob, A.A.; Busam, K.J.; et al. Reference values for skin microanatomy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of ex vivo studies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 1133–1144.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niebuhr, M.; Bieber, K.; Banczyk, D.; Maass, S.; Klein, S.; Becker, M.; Ludwig, R.; Zillikens, D.; Westermann, J.; Kalies, K. Epidermal Damage Induces Th1 Polarization and Defines the Site of Inflammation in Murine Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1713–1722.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinkus, H. Examination of the epidermis by the strip method of removing horny layers. I. Observations on thickness of the horny layer, and on mitotic activity after stripping. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1951, 16, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hundt, J.E.; Iwata, H.; Pieper, M.; Pfundl, R.; Bieber, K.; Zillikens, D.; Konig, P.; Ludwig, R.J. Visualization of autoantibodies and neutrophils in vivo identifies novel checkpoints in autoantibody-induced tissue injury. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Cruz, S.; Orozco-Covarrubias, L.; Saez-de-Ocariz, M. The Human Skin Microbiome in Selected Cutaneous Diseases. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 834135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belheouane, M.; Hermes, B.M.; Van Beek, N.; Benoit, S.; Bernard, P.; Drenovska, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glaser, R.; Goebeler, M.; Gunther, C.; et al. Characterization of the skin microbiota in bullous pemphigoid patients and controls reveals novel microbial indicators of disease. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 44, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufano, M.A.; Baroni, A.; Buommino, E.; Ruocco, E.; Lombardi, M.L.; Ruocco, V. Detection of herpesvirus DNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and skin lesions of patients with pemphigus by polymerase chain reaction. Br. J. Dermatol. 1999, 141, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, N.C.; Rampinelli, H.; Souza, L.M.; Guimaraes, M. Refractory pemphigus foliaceus associated with herpesvirus infection: Case report. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. 2017, 59, e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.; Jin, Y.J.; Yoon, C.H.; Kim, C.W.; Kim, L. Bullous pemphigoid associated with chronic hepatitis C virus infection in a hepatitis B virus endemic area: A case report. Medicine 2018, 97, e0377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Palacios, C.; Chan, L.S. Development of pemphigus herpetiformis in a patient with psoriasis receiving UV-light treatment. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2004, 31, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, Y.; Shimosegawa, M.; Mizukawa, Y.; Shiohara, T. Pemphigus foliaceus induced by exposure to sunlight. Report of a case and analysis of photochallenge-induced lesions. Dermatology 2000, 201, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safadi, M.G.; Turowski, M.; Murray, T.; Zahner, S.; Aronson, I. Pemphigus vulgaris and foliaceus localized to the nose: Report of 2 cases. JAAD Case Rep. 2021, 15, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, P.M. Bullous pemphigoid possibly induced by psoralen plus ultraviolet A therapy. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 1995, 11, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilczek, A.; Sticherling, M. Concomitant psoriasis and bullous pemphigoid: Coincidence or pathogenic relationship? Int. J. Dermatol. 2006, 45, 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massa, M.C.; Freeark, R.J.; Kang, J.S. Localized bullous pemphigoid occurring in a surgical wound. Dermatol. Nurs. 1996, 8, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Danescu, S.; Chiorean, R.; Macovei, V.; Sitaru, C.; Baican, A. Role of physical factors in the pathogenesis of bullous pemphigoid: Case report series and a comprehensive review of the published work. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Schiavo, A.; Caccavale, S.; Alfano, R.; Gambardella, A.; Cozzi, R. Bullous pemphigoid initially localized around the surgical wound of an arthroprothesis for coxarthrosis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2014, 53, e289–e290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, I.; Antonucci, V.A.; Balestri, R.; Tengattini, V.; Iozzo, I.; Bardazzi, F. Bullous pemphigoid appearing both on thermal burn scars and split-thickness skin graft donor sites. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2013, 11, 675–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghura, H.S.; Johnston, G.A.; Milligan, A. Development of a bullous pemphigoid after split-skin grafting. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 2001, 54, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro, F.; Fania, L.; Sinagra, J.L.M.; Salemme, A.; Di Zenzo, G. Bullous Pemphigoid: Trigger and Predisposing Factors. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, N.; Suzuki, K.; Tokura, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Takigawa, M. Bullous eruption associated with scabies: Evidence for scabetic induction of true bullous pemphigoid. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2000, 80, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroni, A.; Piccolo, V.; Russo, T.; Chessa, M.A. Localized bullous pemphigoid occurring on surgical scars: An instance of immunocompromised district. Indian. J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2014, 80, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.W.; Jones, S.A. Ectopic lymphoid follicles: Inducible centres for generating antigen-specific immune responses within tissues. Immunology 2016, 147, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, T.; Egawa, G.; Kabashima, K. Antigen presentation and adaptive immune responses in skin. Int. Immunol. 2019, 31, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashima, K.; Honda, T.; Ginhoux, F.; Egawa, G. The immunological anatomy of the skin. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Lee, A.Y.; Kim, T.; Choi, J.Y.; Cho, M.Y.; Song, A.; Kim, C.; Shim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.; et al. Microenvironmental network of clonal CXCL13+CD4+ T cells and Tregs in pemphigus chronic blisters. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e166357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L.; Ruan, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Huang, C.; Pan, M. Integrative single-cell analysis reveals distinct adaptive immune signatures in the cutaneous lesions of pemphigus. J. Autoimmun. 2023, 142, 103128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lu, M.; Zhao, Z.; Peng, X.; Li, L.; Cheng, C.; Fang, M.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y. Plasma levels of D-dimer and fibrin degradation products correlate with bullous pemphigoid severity: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbrich, M.; Kunstner, A.; Witte, M.; Busch, H.; Fahnrich, A. Genetics and Omics Analysis of Autoimmune Skin Blistering Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Li, Y.Y. Inflammatory bowel disease: Pathogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruano, J.; Suarez-Farinas, M.; Shemer, A.; Oliva, M.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Krueger, J.G. Molecular and Cellular Profiling of Scalp Psoriasis Reveals Differences and Similarities Compared to Skin Psoriasis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rastegar Lari, T.; Macias, L.; Robrahn, L.; Dikmen, H.O.; Prüßmann, J.; Kiehne, C.; Engster, S.; Weyers, I.; Szymczak, S.; van Beek, N.; et al. Localization of Lesions in Autoimmune Blistering Diseases Is Independent of Site-Specific Target Antigen Expression. Life 2025, 15, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020218
Rastegar Lari T, Macias L, Robrahn L, Dikmen HO, Prüßmann J, Kiehne C, Engster S, Weyers I, Szymczak S, van Beek N, et al. Localization of Lesions in Autoimmune Blistering Diseases Is Independent of Site-Specific Target Antigen Expression. Life. 2025; 15(2):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020218
Chicago/Turabian StyleRastegar Lari, Tina, Louis Macias, Lara Robrahn, Hasan Onur Dikmen, Jasper Prüßmann, Charlotte Kiehne, Simon Engster, Imke Weyers, Silke Szymczak, Nina van Beek, and et al. 2025. "Localization of Lesions in Autoimmune Blistering Diseases Is Independent of Site-Specific Target Antigen Expression" Life 15, no. 2: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020218
APA StyleRastegar Lari, T., Macias, L., Robrahn, L., Dikmen, H. O., Prüßmann, J., Kiehne, C., Engster, S., Weyers, I., Szymczak, S., van Beek, N., Hoffmann, M. H., Schmidt, E., & Emtenani, S. (2025). Localization of Lesions in Autoimmune Blistering Diseases Is Independent of Site-Specific Target Antigen Expression. Life, 15(2), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020218





