CT-Based Software-Generated Measurements Permit More Objective Assessments of Arithmetic Hip-Knee-Ankle Axis and Joint Line Obliquity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
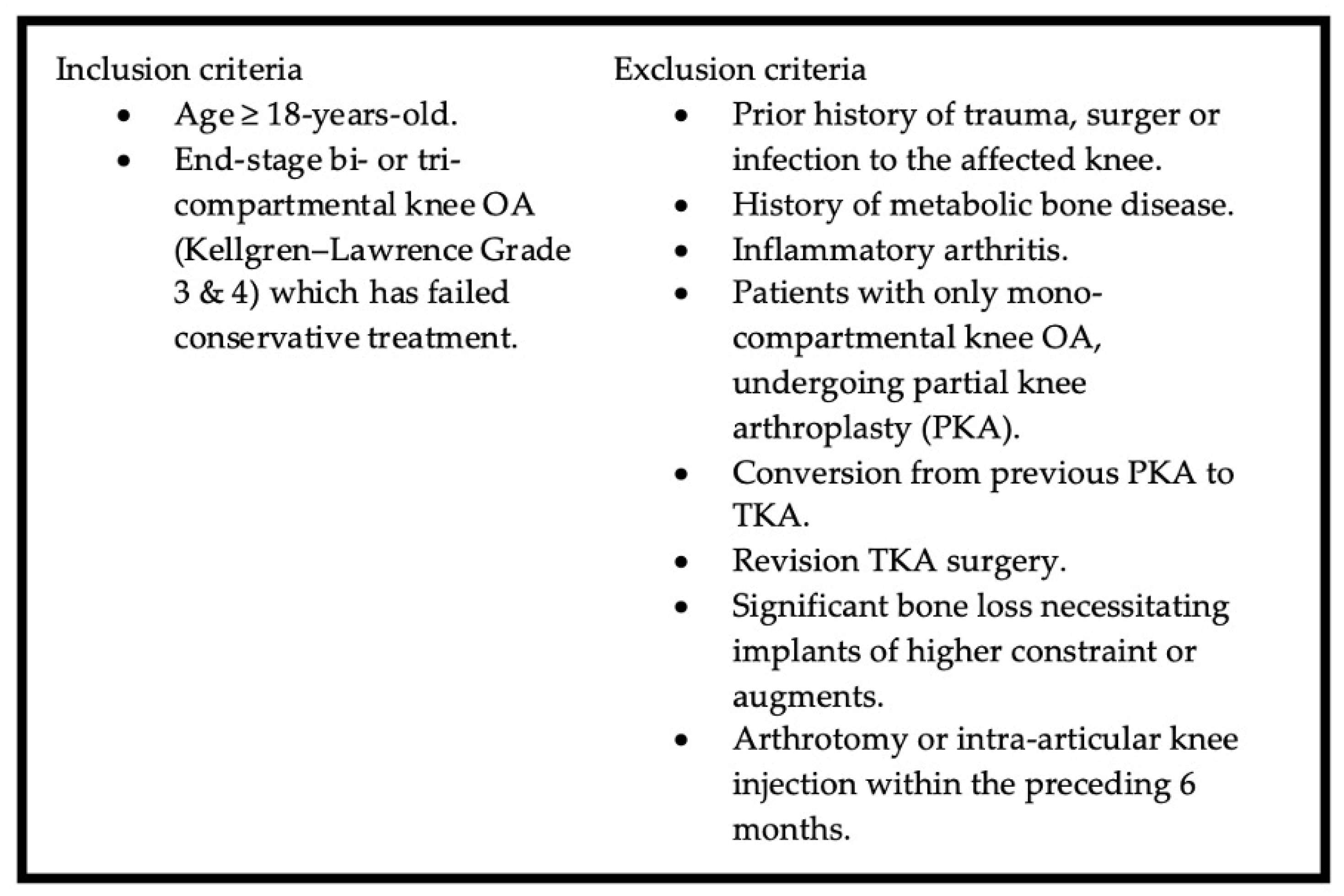
2.1. Patients
2.2. Radiological Assessment
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
3.2. Primary Outcome
3.3. Secondary Outcome
3.4. Intra- and Inter-Observer Reliability of Measurements
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CT | Computed tomography |
| RATKA | Robotic-assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty |
| aHKA | Arithmetic hip–knee–ankle axis |
| JLO | Joint line obliquity |
| CPAK | Coronal Plane Alignment of the Knee |
| LDFA | Lateral distal femoral angle |
| MPTA | Medial proximal tibial angle |
| TKA | Total Knee Arthroplasty |
| JLCA | Joint line convergence angle |
| LLR | Long limb radiographs |
| 3D | Three-dimensional |
References
- Huang, N.F.R.; Dowsey, M.M.; Ee, E.; Stoney, J.D.; Babazadeh, S.; Choong, P.F. Coronal alignment correlates with outcome after total knee arthroplasty: Five-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. J. Arthroplast. 2012, 27, 1737–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunaratne, R.; Pratt, D.; Banda, J.; Fick, D.; Khan, R.; Robertson, B. Patient Dissatisfaction Following Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 3854–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.F.; Eccles, C.J.; Bhimani, S.J.; Denehy, K.M.; Bhimani, R.B.; Smith, L.S.; Malkani, A.L. Improved Patient Satisfaction following Robotic- Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Knee Surg. 2021, 34, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellemans, J.; Colyn, W.; Vandenneucker, H.; Victor, J. The Chitranjan Ranawat Award: Is Neutral Mechanical Alignment Normal for All Patients?: The Concept of Constitutional Varus. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2012, 470, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDessi, S.J.; Griffiths-Jones, W.; Harris, I.A.; Bellemans, J.; Chen, D.B. Coronal Plane Alignment of the Knee (CPAK) classification. Bone Jt. J. 2021, 103, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths-Jones, W.; Chen, D.B.; Harris, I.A.; Bellemans, J.; MacDessi, S.J. Arithmetic hip-knee-ankle angle (aHKA): An algorithm for estimating constitutional lower limb alignment in the arthritic patient population. Bone Jt. Open 2021, 2, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDessi, S.J.; Griffiths-Jones, W.; Harris, I.A.; Bellemans, J.; Chen, D.B. The arithmetic HKA (aHKA) predicts the constitutional alignment of the arthritic knee compared to the normal contralateral knee: A matched-pairs radiographic study. Bone Jt. Open 2020, 1, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarassoli, P.; Corban, L.E.; Wood, J.A.; Sergis, A.; Chen, D.B.; MacDessi, S.J. Long leg radiographs underestimate the degree of constitutional varus limb alignment and joint line obliquity in comparison with computed tomography: A radiographic study. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2023, 31, 4755–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, D.; Vajapey, S.; Nunley, R.M.; Barrack, R.L. The Impact of Imaging Modality on the Measurement of Coronal Plane Alignment After Total Knee Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 2314–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solayar, G.N.; Chinappa, J.; Harris, I.A.; Chen, D.B.; Macdessi, S.J. A Comparison of Plain Radiography with Computer Tomography in Determining Coronal and Sagittal Alignments following Total Knee Arthroplasty. Malays. Orthop. J. 2017, 11, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- León-Muñoz, V.J.; López-López, M.; Martínez-Martínez, F.; Santonja-Medina, F. Comparison of weight-bearing full-length radiographs and computed-tomography-scan-based three-dimensional models in the assessment of knee joint coronal alignment. Knee 2020, 27, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paley, D. Principles of Deformity Correction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Mulpur, P.; Desai, K.; Mahajan, A.; Masilamani, A.; Hippalgaonkar, K.; Reddy, A. Radiological Evaluation of the Phenotype of Indian Osteoarthritic Knees based on the Coronal Plane Alignment of the Knee Classification (CPAK). Indian J. Orthop. 2022, 56, 2066–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şenel, A.; Eren, M.; Sert, S.; Gürpınar, T.; Çarkçı, E.; Polat, B. Phenotyping of the Turkish population according to Coronal Plane Alignment of the Knee classification: A retrospective cross-sectional study. Jt. Dis. Relat. Surg. 2024, 35, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coetzee, K.; Charilaou, J.; Burger, M.; Jordaan, J. Increased prevalence of valgus constitutional alignment subtypes in a South African arthritic population group using the coronal plane alignment of the knee (CPAK) classification. Knee 2024, 49, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Sengoku, M.; Shimokawa, T.; Sohmiya, K.; Ohnishi, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Akiyama, H. Medial proximal tibial angle at the posterior tibial plateau represents the pre-arthritic constitutional medial proximal tibial angle in anterior cruciate ligament-intact, advanced osteoarthritis of the knee. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2022, 30, 2941–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stryker-Corporation. Mako TKA 2.0 Surgical Guide; Stryker-Corporation: Kalamazoo, MI, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gieroba, T.J.; Marasco, S.; Babazadeh, S.; Bella, C.D.; Bavel, D. Arithmetic hip knee angle measurement on long leg radiograph versus computed tomography—Inter-observer and intra-observer reliability. Arthroplasty 2023, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbejuade, H.O.; White, P.; Hassaballa, M.; Porteous, A.J.; Robinson, J.R.; Murray, J.R. Do long leg supine CT scanograms correlate with weight-bearing full-length radiographs to measure lower limb coronal alignment? Knee 2014, 21, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holme, T.J.; Henckel, J.; Hartshorn, K.; Cobb, J.P.; Hart, A.J. Computed tomography scanogram compared to long leg radiograph for determining axial knee alignment. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 440–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paternostre, F.; Schwab, P.-E.; Thienpont, E. The difference between weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing alignment in patient-specific instrumentation planning. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2014, 22, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenmakers, D.A.L.; Feczko, P.Z.; Boonen, B.; Schotanus, M.G.M.; Kort, N.P.; Emans, P.J. Measurement of lower limb alignment: There are within-person differences between weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing measurement modalities. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2017, 25, 3569–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, A.; Ferguson, K.; Syme, B.; McMillan, J.; Holt, G. Pre-operative analysis of lower limb coronal alignment—A comparison of supine MRI versus standing full-length alignment radiographs. Knee 2014, 21, 1084–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry. Hip, Knee & Shoulder Arthroplasty Annual Report; Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Replacement Registry: Sydney, Australia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, G.; Khalil, L.S.; Wrubel, A.; Klochko, C.L.; Davis, J.J.; Soliman, S.B. Incidental findings detected on preoperative CT imaging obtained for robotic-assisted joint replacements: Clinical importance and the effect on the scheduled arthroplasty. Skelet. Radiol. 2021, 50, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, J.; Davis, E.T.; Parsons, H.; Mannion, E.G.; Khatri, C.; Ellard, D.R.; Blyth, M.J.; Clement, N.D.; Deehan, D.; Flynn, N.; et al. Robotic Arthroplasty Clinical and cost Effectiveness Randomised controlled trial (RACER-knee): A study protocol. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e068255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
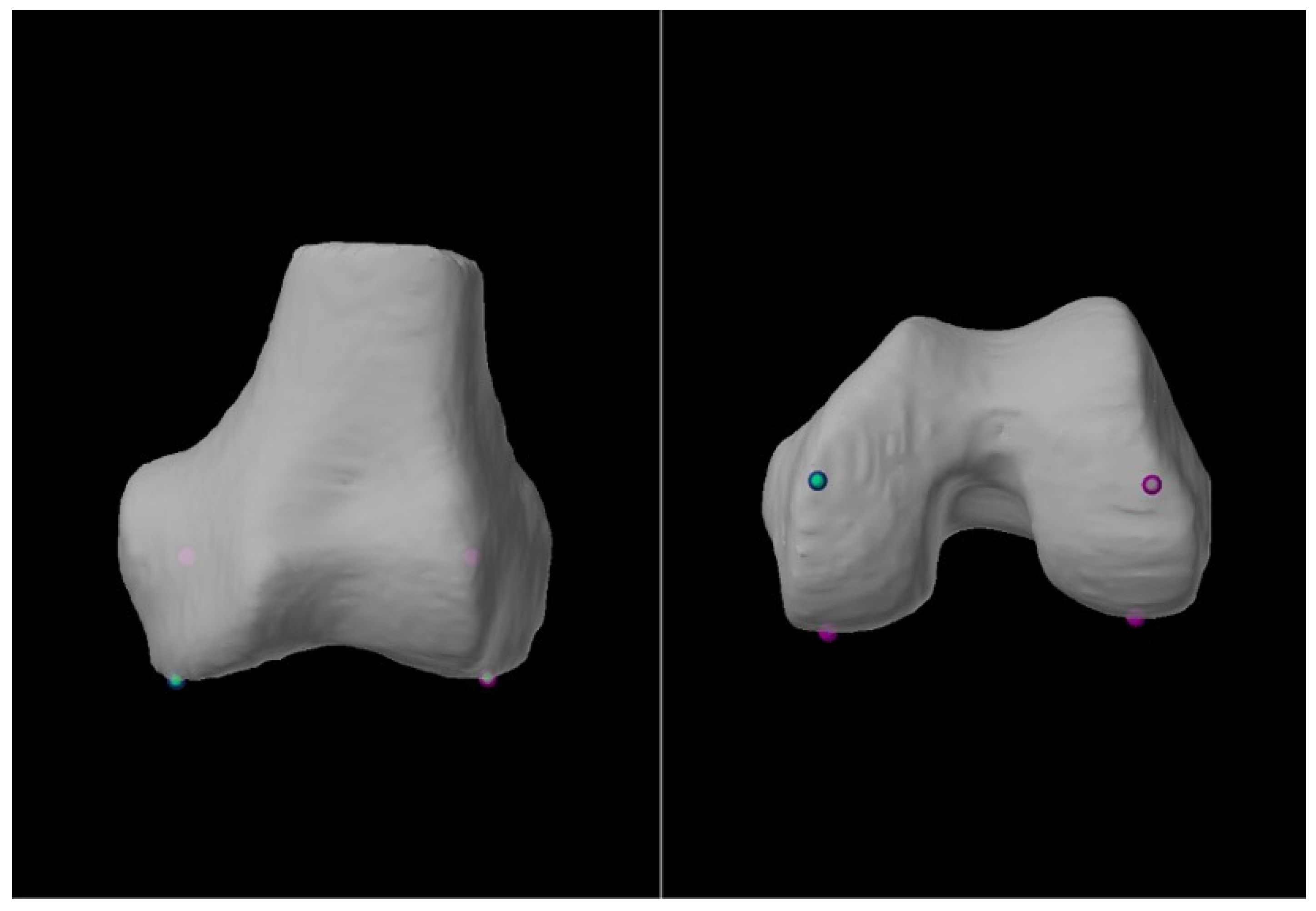
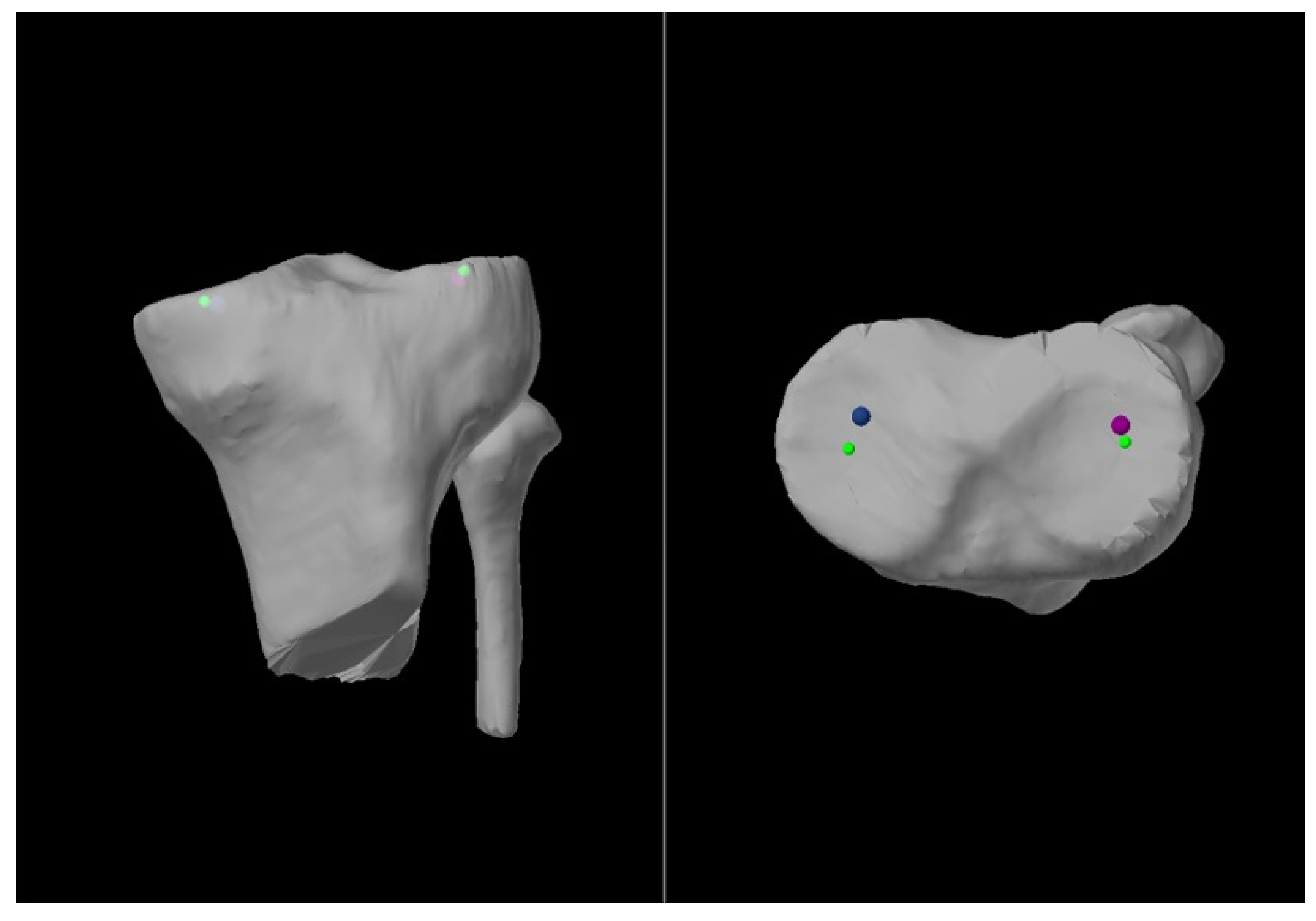
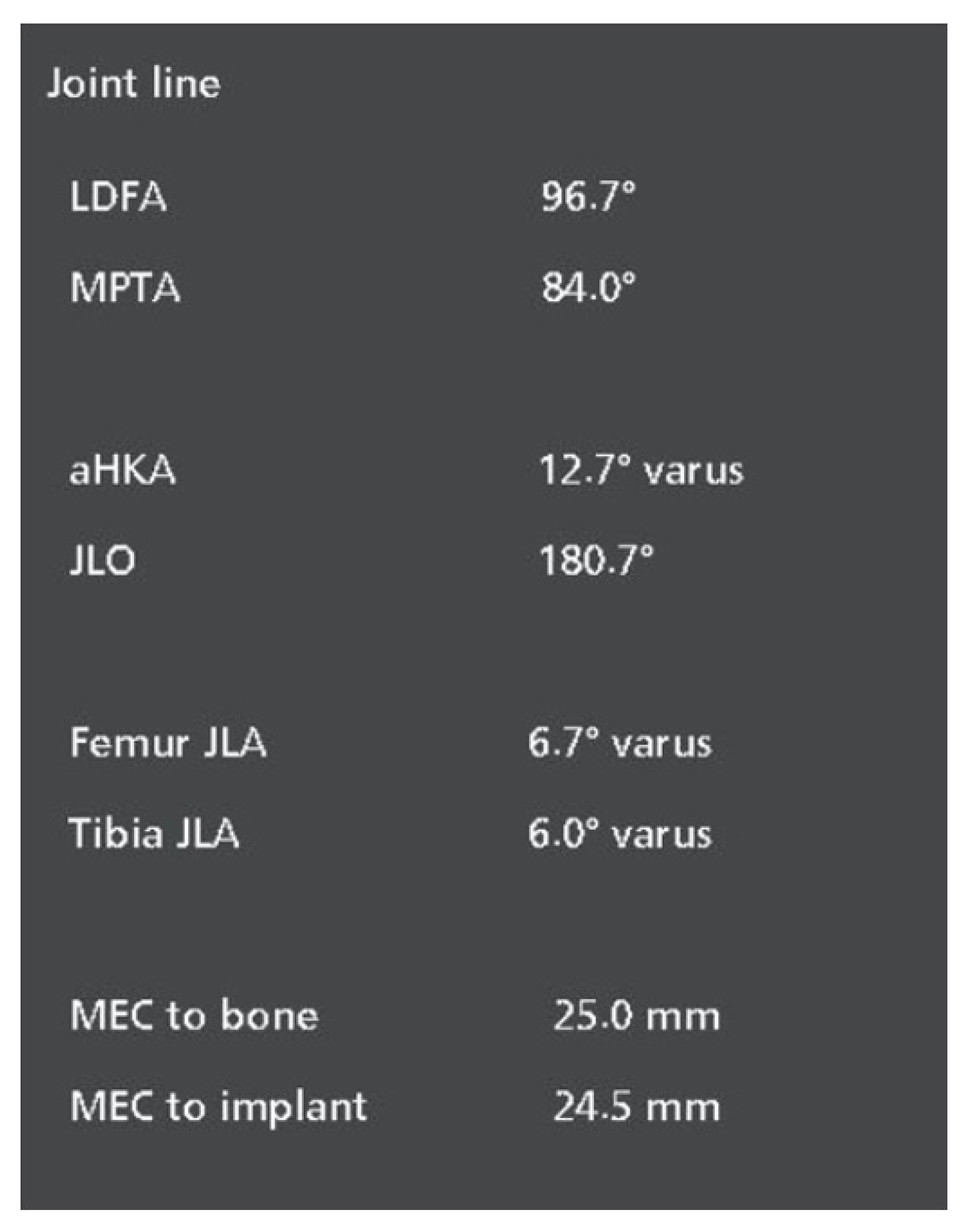
| Variable | LLR, ° (Mean ± SD) | CT, ° (Mean ± SD) | Difference, ° (Mean ± SD) | p Value α | Cohen’s d δ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDFA | 87.76 ± 2.53 | 88.02 ± 2.88 | 0.27 ± 2.95 | 0.045 | 0.09 |
| MPTA | 85.60 ± 2.93 | 84.45 ± 2.52 | 1.15 ± 2.20 | <0.001 | −0.52 |
| aHKA | −2.16 ± 4.26 | −3.57 ± 4.30 | 1.41 ± 3.85 | <0.001 | −0.37 |
| JLO | 173.36 ± 3.44 | 172.47 ± 3.27 | 0.89 ± 3.50 | <0.001 | −0.25 |
| Variable | Pearson’s r | Sample Size, N | p Value β |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDFA | 0.409 | 500 | <0.001 |
| MPTA | 0.683 | 500 | <0.001 |
| aHKA | 0.595 | 500 | <0.001 |
| JLO | 0.456 | 500 | <0.001 |
| CPAK Phenotype | LLR % (n) | CT % (n) | χ2 (df) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
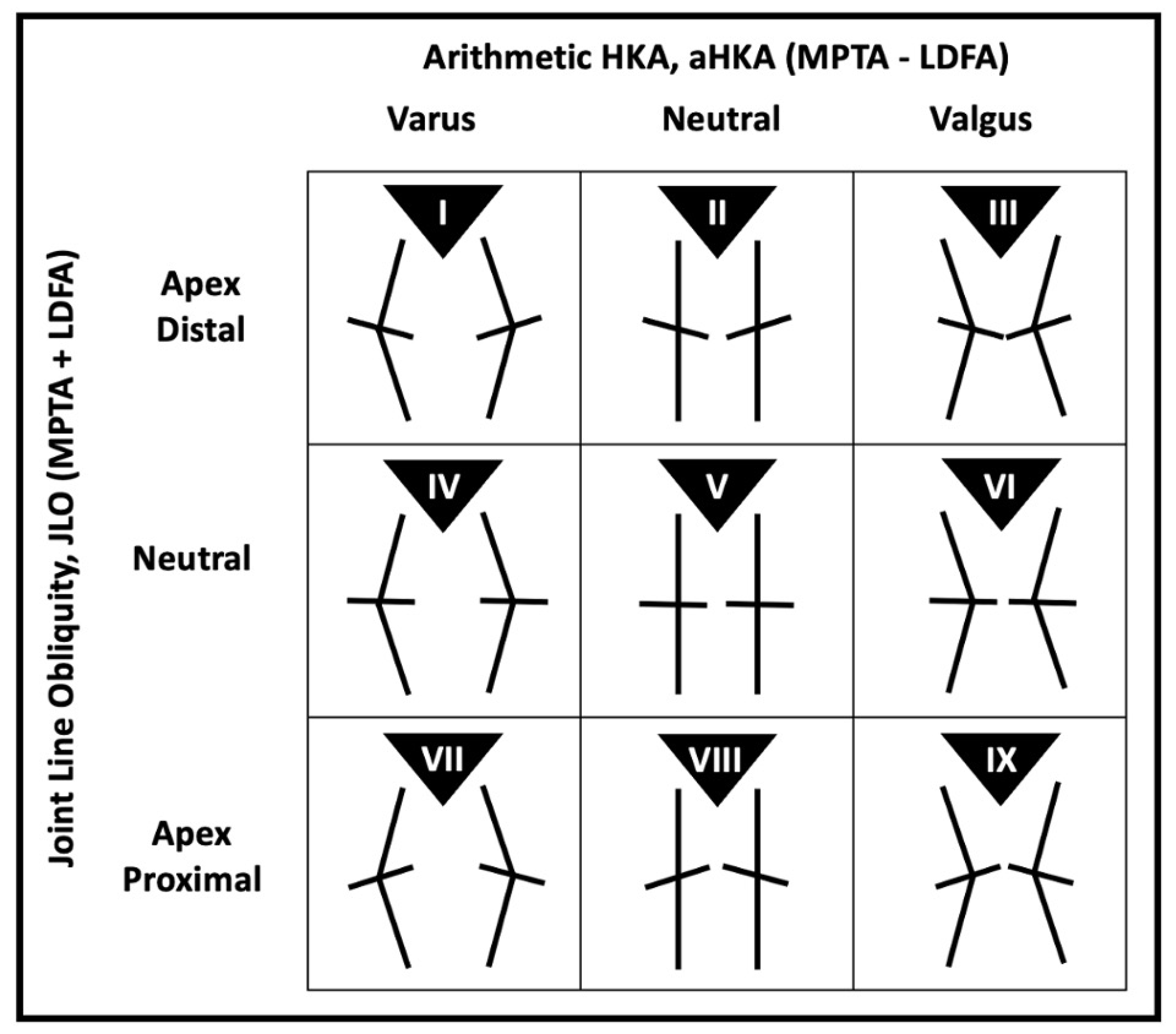
| Apex distal JLO | ||||
| Type I | 46.8 (234) | 59.8 (299) | 353.07 (4) | <0.001 |
| Type II | 25.2 (126) | 23.6 (118) | ||
| Type III | 13.8 (69) | 8.6 (43) | ||
| Proportion of total (n = 500) | 85.8 (429) | 92.0 (460) | ||
| Neutral JLO | ||||
| Type IV | 5.0 (25) | 6.6 (33) | 11.80 (2) | <0.001 |
| Type V | 7.2 (36) | 1.0 (5) | ||
| Type VI | 1.8 (9) | 0.2 (1) | ||
| Proportion of total (n = 500) | 14.0 (70) | 7.8 (39) | ||
| Apex proximal JLO | ||||
| Type VII | 0.2 (1) | 0.2 (1) | N/A | N/A |
| Type VIII | 0 | 0 | ||
| Type IX | 0 | 0 | ||
| Proportion of total (n = 500) | 0.2 (1) | 0.2 (1) | ||
| Parameter | Rater | Intraclass Correlation Coefficient | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-Observer | 95% Confidence Interval | Significance, p | Inter-Observer | 95% Confidence Interval | Significance, p | ||||
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||||
| LDFA | 1 | 0.984 | 0.972 | 0.992 | <0.001 | 0.991 | 0.982 | 0.995 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 0.993 | 0.986 | 0.996 | <0.001 | |||||
| 3 | 0.984 | 0.970 | 0.992 | <0.001 | |||||
| MPTA | 1 | 0.980 | 0.963 | 0.990 | <0.001 | 0.984 | 0.970 | 0.992 | <0.001 |
| 2 | 0.986 | 0.973 | 0.993 | <0.001 | |||||
| 3 | 0.978 | 0.959 | 0.989 | <0.001 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wong, W.K.; Zulkhairi, S.Z.; Chua, H.S. CT-Based Software-Generated Measurements Permit More Objective Assessments of Arithmetic Hip-Knee-Ankle Axis and Joint Line Obliquity. Life 2025, 15, 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020188
Wong WK, Zulkhairi SZ, Chua HS. CT-Based Software-Generated Measurements Permit More Objective Assessments of Arithmetic Hip-Knee-Ankle Axis and Joint Line Obliquity. Life. 2025; 15(2):188. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020188
Chicago/Turabian StyleWong, Wai Kit, Siti Zubaidah Zulkhairi, and Hwa Sen Chua. 2025. "CT-Based Software-Generated Measurements Permit More Objective Assessments of Arithmetic Hip-Knee-Ankle Axis and Joint Line Obliquity" Life 15, no. 2: 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020188
APA StyleWong, W. K., Zulkhairi, S. Z., & Chua, H. S. (2025). CT-Based Software-Generated Measurements Permit More Objective Assessments of Arithmetic Hip-Knee-Ankle Axis and Joint Line Obliquity. Life, 15(2), 188. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15020188






