In Vivo Micro-Computed Tomography for Evaluation of Osteogenic Capability of Dental Pulp Stem Cells Under the Influence of Extracellular Vesicles on Alloplastic and Xenogeneic Bone Scaffolds in Rodent Intrabony Defect Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Animals
2.2. DPSC Extraction
2.3. DPSC-Derived EV Isolation and Examination
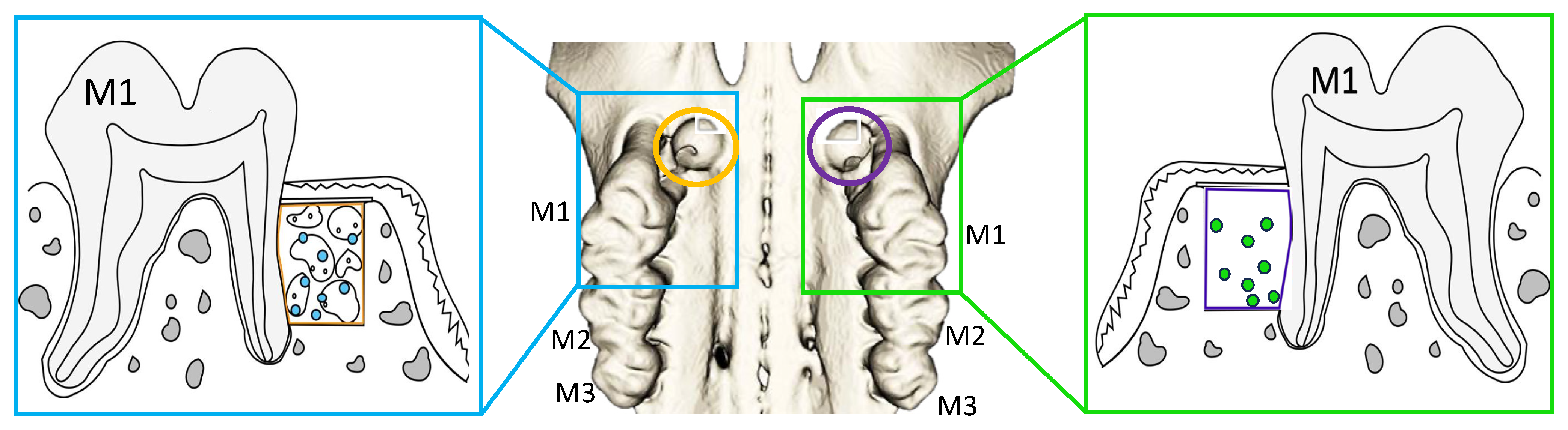
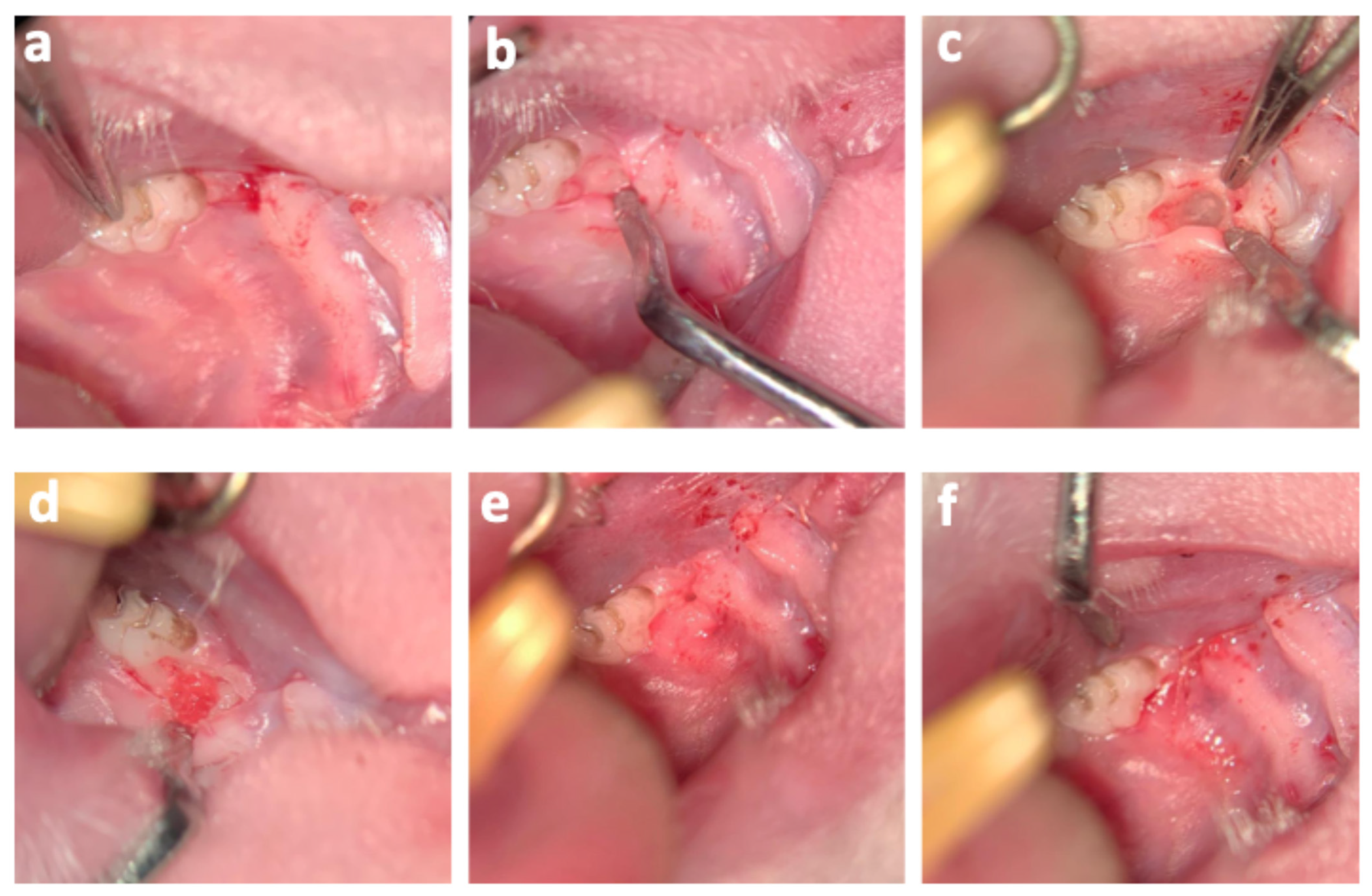
2.4. Reimplantation of DPSCs and EVs
2.5. Micro-Computed Tomography (µCT) Analysis
2.6. Power Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
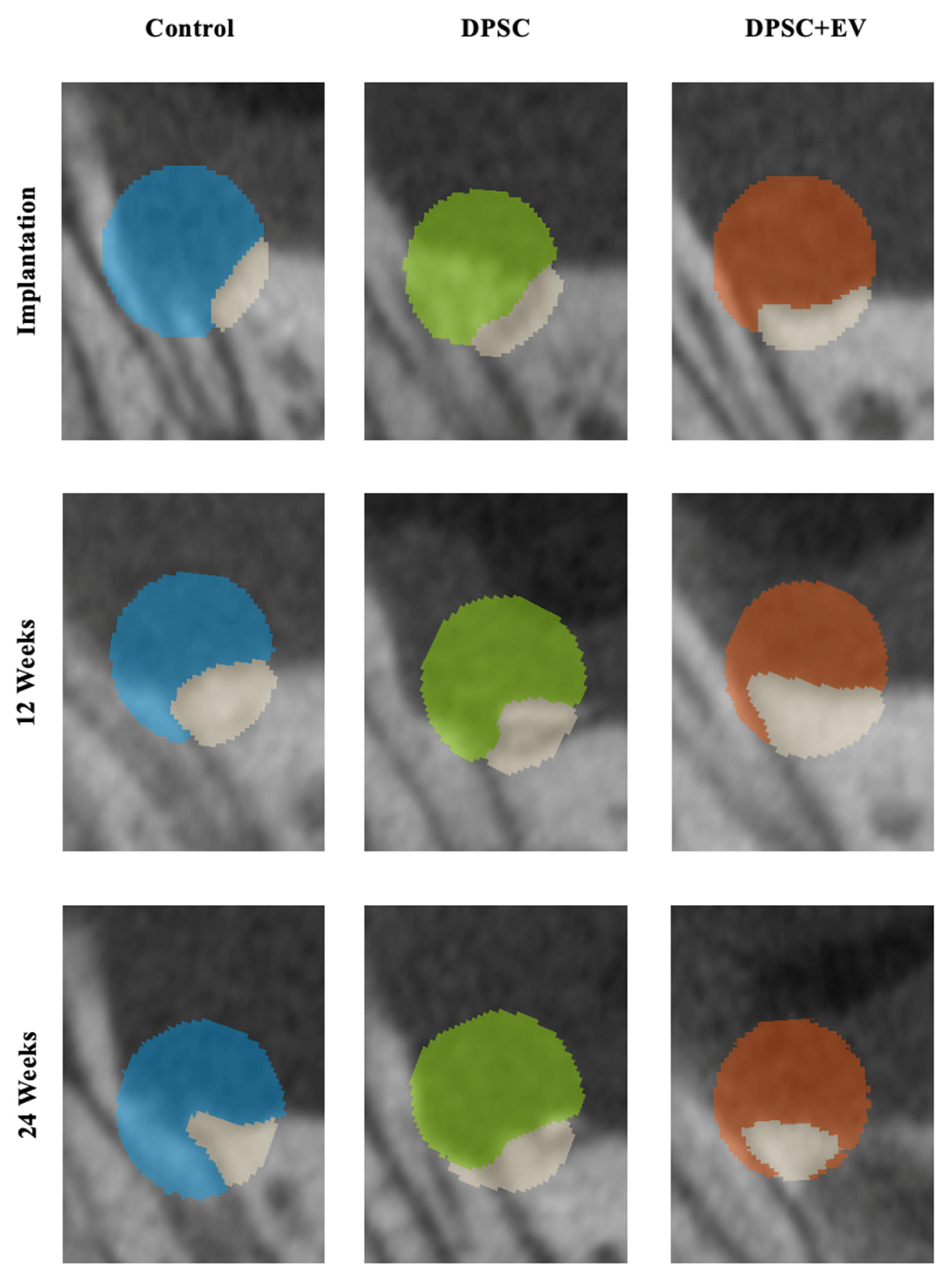
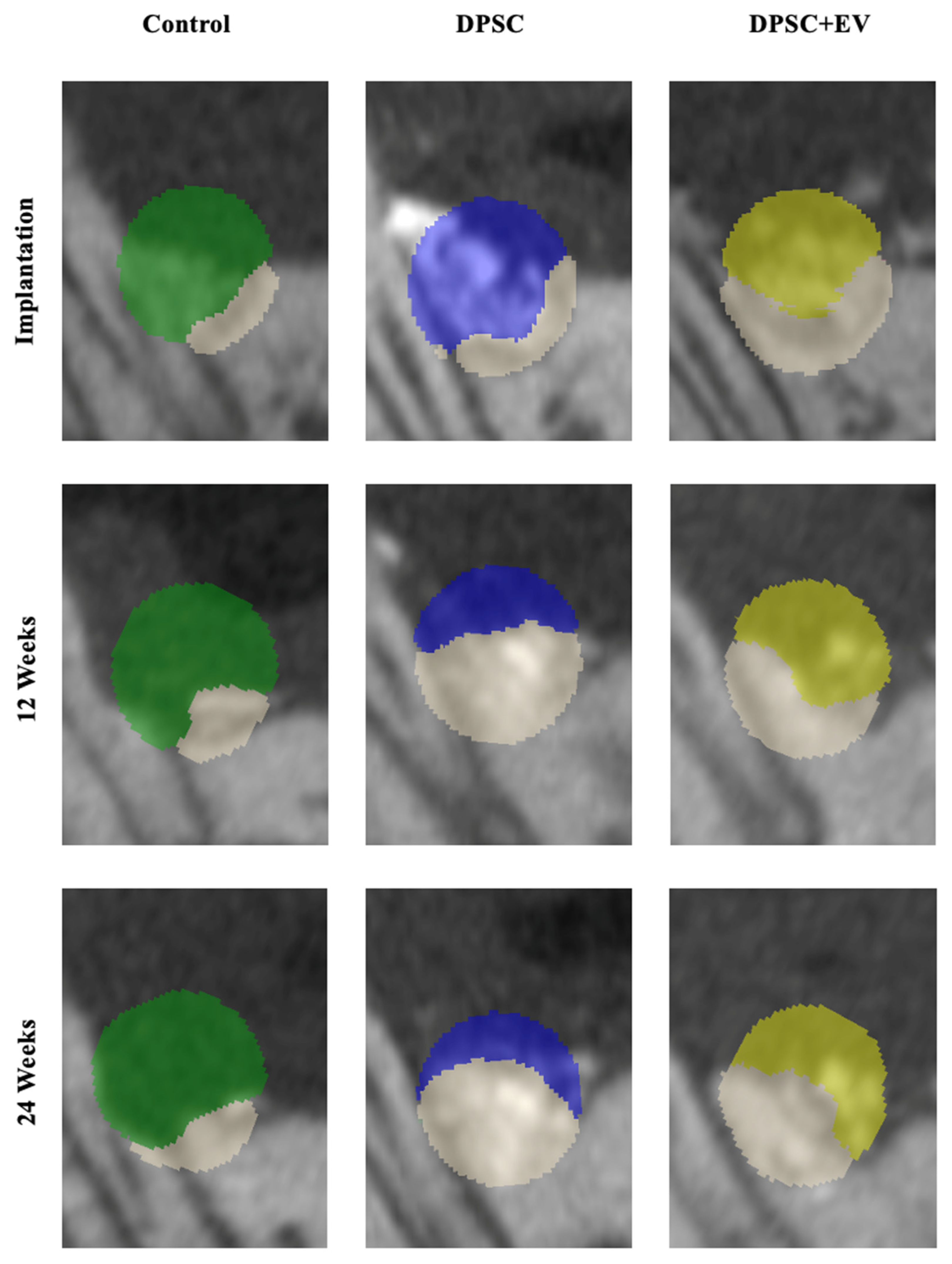
3.1. Bone Volume and Density
3.2. Radiological and Structural Observations
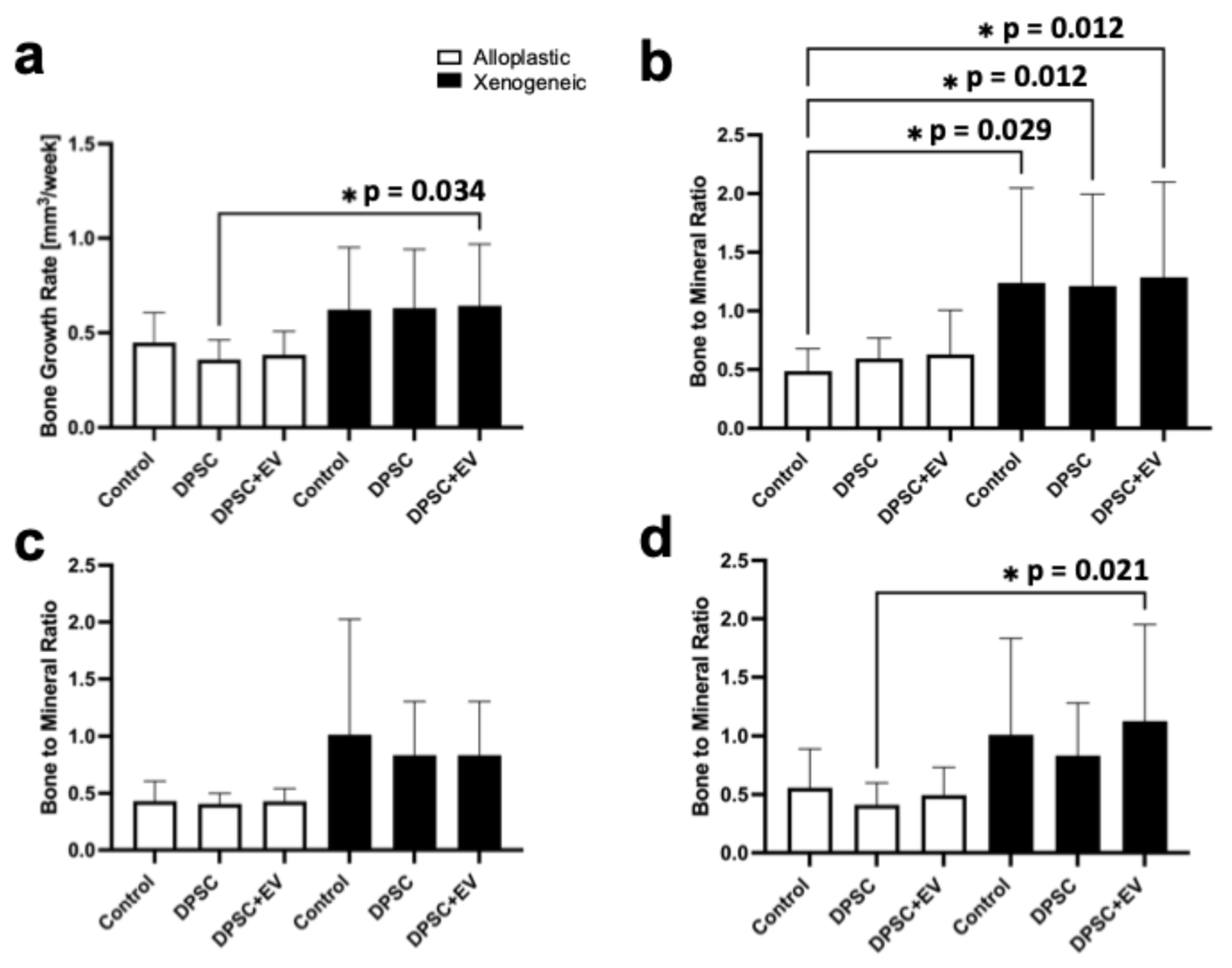
3.3. Bone Growth Rate and Bone-to-Mineral Ratio
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DPSC | Dental pulp stem cell |
| EVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| µCT | Microcomputed tomography |
| Tr.Th | Trabecular thickness |
| BV | Bone volume |
| BD | Bone density |
| BGR | Bone growth |
| BMR | Bone-to-mineral ratio |
References
- Shimizu, S.; Tsuchiya, S.; Hirakawa, A.; Kato, K.; Ando, M.; Mizuno, M.; Osugi, M.; Okabe, K.; Katagiri, W.; Hibi, H. Design of a Randomized Controlled Clinical Study of tissue-engineered osteogenic materials using bone marrow-derived mesenchymal cells for Maxillomandibular bone defects in Japan: The TEOM study protocol. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modabber, A.; Mohlhenrich, S.C.; Ayoub, N.; Hajji, M.; Raith, S.; Reich, S.; Steiner, T.; Ghassemi, A.; Hölzle, F. Computer-Aided Mandibular Reconstruction With Vascularized Iliac Crest Bone Flap and Simultaneous Implant Surgery. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 41, e189–e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitzer, M.; Zhao, Q.; Greven, J.; Winnand, P.; Zhang, X.; Blasius, F.M.; Buhl, E.M.; Wolf, M.; Neuss, S.; Hildebrand, F. Evaluation of in vitro biocompatibility of human pulp stem cells with allogeneic, alloplastic, and xenogeneic grafts under the influence of extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Cai, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, D.; Ou, M.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Z. The optimization of ligature/bone defect-induced periodontitis model in rats. Odontology 2022, 110, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Huang, P.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z. A standardized rat burr hole defect model to study maxillofacial bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019, 86, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Ortiz, G.; Elangovan, S.; Kramer, K.W.; Blanchette, D.; Dawson, D.V. Effect of alveolar ridge preservation after tooth extraction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Bone regeneration by stem cell and tissue engineering in oral and maxillofacial region. Front. Med. 2011, 5, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.J.; Zhang, Q.; Sculean, A.; Buser, D.; Pippenger, B.E.; Dard, M.; Shirakata, Y.; Chandad; Zhang, Y. Osteoinductive potential of 4 commonly employed bone grafts. Clin. Oral Investig. 2016, 20, 2259–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herford, A.S.; Dean, J.S. Complications in bone grafting. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2011, 23, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitzer, M.; Modabber, A.; Zhang, X.; Winnand, P.; Zhao, Q.; Blasius, F.M.; Buhl, E.M.; Wolf, M.; Neuss, S.; Hölzle, F. In vitro comparison of the osteogenic capability of human pulp stem cells on alloplastic, allogeneic, and xenogeneic bone scaffolds. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohlhenrich, S.C.; Heitzer, M.; Magnuska, Z.; Gremse, F.; Chhatwani, S.; Danesh, G.; Hölzle, F.; Modabber, A. Establishing a new alveolar cleft model in rats to investigate the influence of jaw reconstructions on orthodontic tooth movement. Ann. Anat. 2021, 236, 151713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Quintero, J.G.; Duran Riveros, J.Y.; Martinez Valbuena, C.A.; Pedraza Alonso, S.; Munevar, J.C.; Viafara-Garcia, S.M. Critical-sized mandibular defect reconstruction using human dental pulp stem cells in a xenograft model-clinical, radiological, and histological evaluation. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 24, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamedian, S.R.; Tabatabaei, F.S.; Akhlaghi, F.; Torshabi, M.; Gholamin, P.; Khojasteh, A. Response of Dental Pulp Stem Cells to Synthetic, Allograft, and Xenograft Bone Scaffolds. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2017, 37, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, F.; Gabusi, E.; Manferdini, C.; Russo, D.; Lisignoli, G. Bone Regeneration Improves with Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) Combined with Scaffolds: A Systematic Review. Biology 2021, 10, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.; Luo, L.; Gao, R.; Gong, L.; Du, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zhao, B.; Li, Q.; et al. Large extracellular vesicles secreted by human iPSC-derived MSCs ameliorate tendinopathy via regulating macrophage heterogeneity. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 21, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Ruan, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, W.; Chen, H.; Shen, H. Advances in extracellular vesicle functionalization strategies for tissue regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 25, 500–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Duan, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, G. Dental stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles as promising therapeutic agents in the treatment of diseases. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2022, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.; Choi, J.; Shi, S.; He, P.; Zhang, Q.; Le, A. DPSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Rat Jawbone Regeneration. J. Dent. Res. 2023, 102, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Zhao, S.; Yi, Z. Roles for miRNAs in osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q. Emerging Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Bone Remodeling. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Wang, L.; Gao, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C. Bone marrow stromal/stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles regulate osteoblast activity and differentiation in vitro and promote bone regeneration in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Contreras, M.; Shah, S.H.; Tamayo, A.; Robbins, P.D.; Golberg, R.B.; Mendez, A.J.; Ricordi, C. Plasma-derived exosome characterization reveals a distinct microRNA signature in long duration Type 1 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Jin, S.; Fu, C.; Cui, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Shen, S.G.F.; Jiang, N.; Liu, Y. Macrophage-derived small extracellular vesicles promote biomimetic mineralized collagen-mediated endogenous bone regeneration. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, X.; Wu, G.; Zhou, Y. Tissue-Engineered Bone Immobilized with Human Adipose Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes Promotes Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5240–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanishi, Y.; Hata, M.; Matsukawa, R.; Aoyagi, A.; Omi, M.; Mizutani, M.; Naruse, K.; Ozawa, S.; Honda, M.; Matsubara, T.; et al. Efficacy of extracellular vesicles from dental pulp stem cells for bone regeneration in rat calvarial bone defects. Inflamm. Regen. 2021, 41, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Wang, S.; Tang, H.; Li, D.; Zhou, F.; Xin, L.; He, Q.; Hu, S.; Zhang, T.; Chen, T.; et al. Dynamically Bioresponsive DNA Hydrogel Incorporated with Dual-Functional Stem Cells from Apical Papilla-Derived Exosomes Promotes Diabetic Bone Regeneration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 16082–16099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitzer, M.; Winnand, P.; Ooms, M.; Kniha, K.; Magnuska, Z.; Kiessling, F.; Hölzle, F.; Modabber, A. Establishing a new periodontitis-like intrabony maxillary defect in rats for investigation on bone regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 39358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gremse, F.; Stark, M.; Ehling, J.; Menzel, J.R.; Lammers, T.; Kiessling, F. Imalytics Preclinical: Interactive Analysis of Biomedical Volume Data. Theranostics 2016, 6, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Li, X.; Yin, Y.; He, X.T.; An, Y.; Tian, B.M.; Hong, Y.-L.; Wu, L.-A.; Chen, F.-M. The proangiogenic effects of extracellular vesicles secreted by dental pulp stem cells derived from periodontally compromised teeth. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Chen, C.; Hu, B.; Niu, X.; Li, Q.; Zhao, B.; Xie, Z.; Wang, Y. Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishavar, E.; Copus, J.S.; Atala, A.; Lee, S.J. Comparison Study of Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Enhanced Osteogenic Differentiation. Tissue Eng. Part A 2021, 27, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoda, S.; Murata, S.; Nishida, K.; Kato, H.; Uehara, N.; Kyumoto, Y.N.; Yamaza, H.; Takahashi, I.; Kukita, T.; Yamaza, T. Extracellular vesicles from deciduous pulp stem cells recover bone loss by regulating telomerase activity in an osteoporosis mouse model. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, F.; Inchingolo, F.; Dipalma, G.; Postiglione, F.; Fulle, S.; Scarano, A. Synthetic Scaffold/Dental Pulp Stem Cell (DPSC) Tissue Engineering Constructs for Bone Defect Treatment: An Animal Studies Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bud, E.; Pop, S.I.; Bud, A.; Steele, B.R.; Vlasa, A. Bony Defect Regeneration in Periodontitis: A Systematic Review of the Literature Regarding the Use of Enamel Matrix Derivative Proteins. Dent. J. 2025, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ruangsawasdi, N.; Pumpaluk, P.; Yuan, Q.; Peng, Y.; Seriwatanachai, D. Bone regeneration property of tooth-derived bone substitute prepared chairside for periodontal bone defects: An experimental study. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lei, Q.; Zhao, A.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Chen, Z. Extracellular Vesicle-functionalized Decalcified Bone Matrix Scaffolds with Enhanced Pro-angiogenic and Pro-bone Regeneration Activities. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Kishida, R.; Tsuchiya, A.; Ishikawa, K. Granular Honeycombs Composed of Carbonate Apatite, Hydroxyapatite, and beta-Tricalcium Phosphate as Bone Graft Substitutes: Effects of Composition on Bone Formation and Maturation. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 1787–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rh Owen, G.; Dard, M.; Larjava, H. Hydoxyapatite/beta-tricalcium phosphate biphasic ceramics as regenerative material for the repair of complex bone defects. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 2493–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, M.; Deng, Y.; Chen, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X. Fabrication and Properties of Ca-P Bioceramic Spherical Granules with Interconnected Porous Structure. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 1557–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogose, A.; Hotta, T.; Kawashima, H.; Kondo, N.; Gu, W.; Kamura, T.; Endo, N. Comparison of hydroxyapatite and beta tricalcium phosphate as bone substitutes after excision of bone tumors. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2005, 72, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Alloplastic (AP) | Xenogeneic (XG) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left Jaw | Right Jaw | Left Jaw | Right Jaw | |
| Control | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| DPSC | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
| DPSC + EV | 7 | 7 | 7 | 8 |
| Alloplastic (AP) | Xenogeneic (XG) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | DPSC | DPSC + EV | Control | DPSC | DPSC + EV | |||||||||||||
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | |
| BV (mm3) | 0.42 (0.20) | 0.40 (0.31) | 0.45 (0.25) | 0.54 (0.12) | 0.39 (0.18) | 0.37 (0.17) | 0.53 (0.06) | 0.41 (0.15) | 0.41 (0.21) | 0.92 (0.18) | 0.43 (0.33) | 0.56 (0.65) | 0.46 (0.32) | 0.54 (0.34) | 0.61 (0.50) | 0.89 (0.32) | 0.48 (0.26) | 0.60 (0.64) |
| BD (HU) | 2588 (648) | 3400 (853) | 3570 (752) | 2905 (280) | 3402 (441) | 3549 (379) | 2773 (336) | 3321 (365) | 3467 (265) | 2738 (147) | 2838 (864) | 2836 (844) | 2706 (440) | 2601 (734) | 2660 (850) | 2699 (237) | 2864 (834) | 3216 (945) |
| Tr.Th (cm) | 0.06 (0.01) | 0.07 (0.02) | 0.06 (0.02) | 0.06 (0.01) | 0.05 (0.01) | 0.07 (0.02) | 0.06 (0.01) | 0.05 (0.01) | 0.06 (0.01) | 0.06 (0.02) | 0.05 (0.03) | 0.06 (0.03) | 0.06 (0.02) | 0.08 (0.02) | 0.06 (0.04) | 0.05 (0.01) | 0.06 (0.03) | 0.06 (0.03) |
| BMR (AU) | 0.49 (0.22) | 0.40 (0.31) | 0.54 (0.43) | 0.60 (0.30) | 0.40 (0.14) | 0.38 (0.20) | 0.46 (0.47) | 0.41 (0.15) | 0.48 (0.32) | 0.93 (1.27) | 0.46 (1.67) | 0.65 (1.22) | 1.03 (0.79) | 0.66 (0.88) | 0.62 (0.69) | 0.82 (1.47) | 0.56 (1.68) | 0.88 (1.31) |
| Alloplastic | Xenogeneic | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | DPSC | DPSC + EV | Control | DPSC | DPSC + EV | |||||||
| T2/T1 | T3/T1 | T2/T1 | T3/T1 | T2/T1 | T3/T1 | T2/T1 | T3/T1 | T2/T1 | T3/T1 | T2/T1 | T3/T1 | |
| BV | 0.79 (0.85) | 0.95 (0.55) | 0.72 (0.31) | 0.68 (0.36) | 0.89 (0.36) | 0.87 (0.51) | 0.46 (0.67) | 0.62 (0.54) | 0.58 (0.37) | 0.63 (0.28) | 0.61 (0.31) | 0.66 (0.55) |
| BD | 0.97 (0.05) | 0.99 (0.05) | 0.98 (0.04) | 0.99 (0.04) | 0.97 (0.02) | 0.98 (0.02) | 1.01 (0.34) | 1.05 (0.126) | 1.02 (0.28) | 1.04 (0.17) | 1.02 (0.17) | 1.12 (0.18) |
| Tr.Th | 1.33 (0.67) | 1.12 (0.55) | 0.89 (0.26) | 1.17 (0.38) | 0.89 (0.38) | 0.99 (0.23) | 1.02 (0.64) | 1.09 (0.45) | 1.43 (0.62) | 1.01 (0.52) | 1.14 (0.68) | 1.03 (0.50) |
| BMR | 0.97 (0.49) | 1.14 (0.59) | 0.68 (0.36) | 0.59 (0.62) | 0.86 (0.56) | 0.73 (0.42) | 0.64 (1.09) | 0.67 (0.54) | 0.69 (0.43) | 0.70 (0.31) | 0.89 (0.57) | 0.92 (0.53) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heitzer, M.; Winnand, P.; Ooms, M.; Balmayor, E.R.; Hildebrand, F.; Apel, C.; Magnuska, Z.; Kiessling, F.; Hölzle, F.; Modabber, A. In Vivo Micro-Computed Tomography for Evaluation of Osteogenic Capability of Dental Pulp Stem Cells Under the Influence of Extracellular Vesicles on Alloplastic and Xenogeneic Bone Scaffolds in Rodent Intrabony Defect Model. Life 2025, 15, 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15121797
Heitzer M, Winnand P, Ooms M, Balmayor ER, Hildebrand F, Apel C, Magnuska Z, Kiessling F, Hölzle F, Modabber A. In Vivo Micro-Computed Tomography for Evaluation of Osteogenic Capability of Dental Pulp Stem Cells Under the Influence of Extracellular Vesicles on Alloplastic and Xenogeneic Bone Scaffolds in Rodent Intrabony Defect Model. Life. 2025; 15(12):1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15121797
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeitzer, Marius, Philipp Winnand, Mark Ooms, Elizabeth R. Balmayor, Frank Hildebrand, Christian Apel, Zuzanna Magnuska, Fabian Kiessling, Frank Hölzle, and Ali Modabber. 2025. "In Vivo Micro-Computed Tomography for Evaluation of Osteogenic Capability of Dental Pulp Stem Cells Under the Influence of Extracellular Vesicles on Alloplastic and Xenogeneic Bone Scaffolds in Rodent Intrabony Defect Model" Life 15, no. 12: 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15121797
APA StyleHeitzer, M., Winnand, P., Ooms, M., Balmayor, E. R., Hildebrand, F., Apel, C., Magnuska, Z., Kiessling, F., Hölzle, F., & Modabber, A. (2025). In Vivo Micro-Computed Tomography for Evaluation of Osteogenic Capability of Dental Pulp Stem Cells Under the Influence of Extracellular Vesicles on Alloplastic and Xenogeneic Bone Scaffolds in Rodent Intrabony Defect Model. Life, 15(12), 1797. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15121797








