Improvement of Cystic Fibrosis-Associated Liver Disease in Adults on Long-Term Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Modulators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design of the Study
2.2. CFLD Patients
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Total Patients
3.2. CFLD Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALP | Alkaline Phosphatase |
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| APRI | AST to Platelet Ratio Index |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CF | Cystic Fibrosis |
| CFLD | Cystic Fibrosis-associated Liver Disease |
| CFTR | Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator modulators |
| ETI | Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor |
| FIB-4 | Fibrosis-4 Index |
| gammaGT | Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase |
| GI | Gastrointestinal |
| Hb | Hemoglobin |
| INR | International Normalized Ratio |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| LI | Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor |
| LS | Liver Stiffness |
| LSM | Liver Stiffness Measurement |
| NITs | Non-Invasive Liver Fibrosis Tests |
| SWE | ShearWave Elastography |
| TE | Transient Elastography |
References
- Elborn, J.S. Cystic fibrosis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2519–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, C.; Cuppens, H.; Macek, M., Jr.; Cassiman, J.J.; Kerem, E.; Durie, P.; Tullis, E.; Assael, B.M.; Bombieri, C.; Brown, A.; et al. Consensus on the use and interpretation of cystic fibrosis mutation analysis in clinical practice. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2008, 7, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnay, P.R.; Siklosi, K.R.; Van Goor, F.; Kaniecki, K.; Yu, H.; Sharma, N.; Ramalho, A.S.; Amaral, M.D.; Dorfman, R.; Zielenski, J.; et al. Defining the disease liability of variants in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator gene. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boëlle, P.Y.; Debray, D.; Guillot, L.; Clement, A.; Corvol, H.; on behalf of the French CF Modifier Gene Study Investigators. Cystic Fibrosis Liver Disease: Outcomes and Risk Factors in a Large Cohort of French Patients. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1648–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamireau, T.; Monnereau, S.; Martin, S.; Marcotte, J.E.; Winnock, M.; Alvarez, F. Epidemiology of liver disease in cystic fibrosis: A longitudinal study. J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldredge, J.A.; Oliver, M.R.; Ooi, C.Y. Cystic fibrosis liver disease in the new era of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) modulators. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2024, 50, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, J.; Debray, D.; Beaufrère, A.; Hillaire, S.; Fabre, M.; Reinhold, C.; Baumert, T.F.; Berteloot, L.; Vilgrain, V. Cystic fibrosis-related liver disease: Clinical presentations, diagnostic and monitoring approaches in the era of CFTR modulator therapies. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, C. Liver disease in cystic fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2007, 13, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblad, A.; Glaumann, H.; Strandvik, B. Natural history of liver disease in cystic fibrosis. Hepatology 1999, 30, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debray, D.; Kelly, D.; Houwen, R.; Strandvik, B.; Colombo, C. Best practice guidance for the diagnosis and management of cystic fibrosis-associated liver disease. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2011, 10, S29–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, E.K.; Loomba, R. Recommendations for Diagnosis, Referral for Liver Biopsy, and Treatment of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewindon, P.J.; Shepherd, R.W.; Walsh, M.J.; Greer, R.M.; Williamson, R.; Pereira, T.N.; Frawley, K.; Bell, S.C.; Smith, J.L.; Ramm, G.A. Importance of hepatic fibrosis in cystic fibrosis and the predictive value of liver biopsy. Hepatology 2011, 53, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, C.; Sakiani, S.; Surana, P.; Zhao, X.; Eccleston, J.; Kleiner, D.E.; Herion, D.; Liang, T.J.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; Chernick, M.; et al. Adult-onset cystic fibrosis liver disease: Diagnosis and characterization of an underappreciated entity. Hepatology 2017, 66, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulou, A.; Pouriki, S.; Vasilieva, L.; Alexopoulos, T.; Filaditaki, V.; Gioka, M.; Diamantea, F.; Dourakis, S.P. Evaluation of noninvasive markers for the diagnosis of cystic fibrosis liver disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, C.E.; Elborn, J.S.; Ramsey, B.W.; Marigowda, G.; Huang, X.; Cipolli, M.; Colombo, C.; Davies, J.C.; De Boeck, K.; Flume, P.A.; et al. Lumacaftor-Ivacaftor in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Homozygous for Phe508del CFTR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1783–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, S.M.; Daines, C.; Ringshausen, F.C.; Kerem, E.; Wilson, J.; Tullis, E.; Nair, N.; Simard, C.; Han, L.; Ingenito, E.P.; et al. Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor in Residual-Function Heterozygotes with Cystic Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2024–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijerman, H.G.M.; McKone, E.F.; Downey, D.G.; Van Braeckel, E.; Rowe, S.M.; Tullis, E.; Mall, M.A.; Welter, J.J.; Ramsey, B.W.; McKee, C.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of the elexacaftor plus tezacaftor plus ivacaftor combination regimen in people with cystic fibrosis homozygous for the F508del mutation: A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1940–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, P.G.; Mall, M.A.; Dřevínek, P.; Lands, L.C.; McKone, E.F.; Polineni, D.; Ramsey, B.W.; Taylor-Cousar, J.L.; Tullis, E.; Vermeulen, F.; et al. Elexacaftor-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor for Cystic Fibrosis with a Single Phe508del Allele. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgel, P.R.; Paillasseur, J.L.; Durieu, I.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Hamidfar, R.; Murris-Espin, M.; Danner-Boucher, I.; Chiron, R.; Leroy, S.; Douvry, B.; et al. Multisystemic Effects of Elexacaftor-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor in Adults with Cystic Fibrosis and Advanced Lung Disease. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2024, 21, 1053–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewindon, P.J.; Ramm, G.A. Cystic fibrosis-cirrhosis, portal hypertension, and liver biopsy: Reply. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1065–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, S.C.; Ye, W.; Leung, D.H.; Navarro, O.M.; Weymann, A.; Karnsakul, W.; Freeman, A.J.; Magee, J.C.; Narkewicz, M.R. Liver Ultrasound Patterns in Children with Cystic Fibrosis Correlate with Noninvasive Tests of Liver Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 69, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, J.; Girard, M.; Franchi-Abella, S.; Berteloot, L.; Benoit-Cherifi, M.; Imbert-Bismut, F.; Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Debray, D. Comparison of Transient Elastography, ShearWave Elastography, Magnetic Resonance Elastography and FibroTest as routine diagnostic markers for assessing liver fibrosis in children with Cystic Fibrosis. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2022, 46, 101855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, K.J.; Marchetti, P.; Sawicki, G.S.; Uluer, A.; Cernadas, M.; Cagnina, R.E.; Kennedy, J.C.; Putman, M.S. The effect of elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor (ETI) on glycemia in adults with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenberg, S.J.; Vu, P.T.; Skalland, M.; Hoffman, L.R.; Pope, C.; Gelfond, D.; Narkewicz, M.R.; Nichols, D.P.; Heltshe, S.L.; Donaldson, S.H.; et al. Elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor and gastrointestinal outcomes in cystic fibrosis: Report of promise-GI. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2023, 22, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Muallem, D.; Kiselyov, K.; Lee, M.G.; Thomas, P.J.; Muallem, S. Aberrant CFTR-dependent HCO3− transport in mutations associated with cystic fibrosis. Nature 2001, 410, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, J.K.; Volkova, N.; Ahluwalia, N.; Sahota, G.; Xuan, F.; Chin, A.; Weinstock, T.G.; Ostrenga, J.; Elber, A. Real-world safety and effectiveness of elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor in people with cystic fibrosis: Interim results of a long-term registry-based study. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2023, 22, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, A.; Jüngert, J.; Klett, D.; Hober, H.; Kaiser, N.; Ruppel, R.; Geppert, A.; Tremel, C.; Sobel, J.; Plattner, E.; et al. Increase of liver stiffness and altered bile acid metabolism after triple CFTR modulator initiation in children and young adults with cystic fibrosis. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, P.L.; Giugliano, L.; Evangelista, A.; Bignamini, E.; Pinon, M. Effects of CFTR modulator therapies on liver stiffness and bile flow: A single-centre experience. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, e76–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewkesbury, D.H.; Scott, J.; Barry, P.J.; Bright-Thomas, R.J.; Hanley, K.P.; Athwal, V.; Jones, A.M. Effects of elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor on liver fibrosis markers in adults with cystic fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2024, 23, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemanick, E.T.; Taylor-Cousar, J.L.; Davies, J.; Gibson, R.L.; Mall, M.A.; McKone, E.F.; McNally, P.; Ramsey, B.W.; Rayment, J.H.; Rowe, S.M.; et al. A Phase 3 Open-Label Study of Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor in Children 6 Through 11 Years of Age with Cystic Fibrosis and at Least One F508del Allele. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 1522–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | |
| Age at initiation of treatment (years) | 26 (23–35) |
| Gender (Male%) | 32 (56.1) |
| Median Age of CF diagnosis (months) | 6 (1.5–24) |
| Genotype (N%) | |
| DF508/DF508 | 19 (33.3) |
| DF508/0ther | 29 (50.9) |
| Other | 9 (15.8) |
| Chloride sweat test ≥60 mmol/L(N%) | 57 (100) |
| Type of treatment (N of patients) | Treatment duration in months [median (IQR) (range)] |
| LI+ETI (N = 19) * | 80 (IQR 63–102) (range 37–123) |
| LI only (N = 1) | 29 |
| ETI only (N = 37) | 39 (IQR 31–43.5) (range15–69) |
| Total duration of CFTR modulators treatment | 43 (IQR 35–67) (range 15–123) |
| Onset of CFT Modulators (T0) | Last Assessment (T2) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body mass index (BMI) (kg/m2) | 22.4 (19.6–24.1) | 23.3 (20.9–26.4) | <0.001 |
| Laboratory values | |||
| Hemoglobin (gr/dL) | 14.0 (12.8–15.1) | 14.4 (12.95–15.1) | 0.033 |
| White blood cell count(×109/L) | 8.12 (6.71–9.26) | 6.95 (5.88–8.51) | 0.065 |
| Platelet count (×109/L) | 292 (244–345) | 273 (223–311) | 0.002 |
| AST (IU/L) | 20 (17–26) | 21 (18–26.5) | 0.301 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 23 (16–35) | 23 (17–29) | 0.786 |
| ALP (Value/ULN) | 0.82 (0.64–1.02) | 0.82 (0.63–1.02) | 0.245 |
| gammaGT (IU/L) | 14 (10–24.5) | 14 (10–19.5) | 0.42 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.48 (0.31–0.67) | 0.63 (0.43–0.95) | <0.001 |
| Non-invasive Fibrosis markers | |||
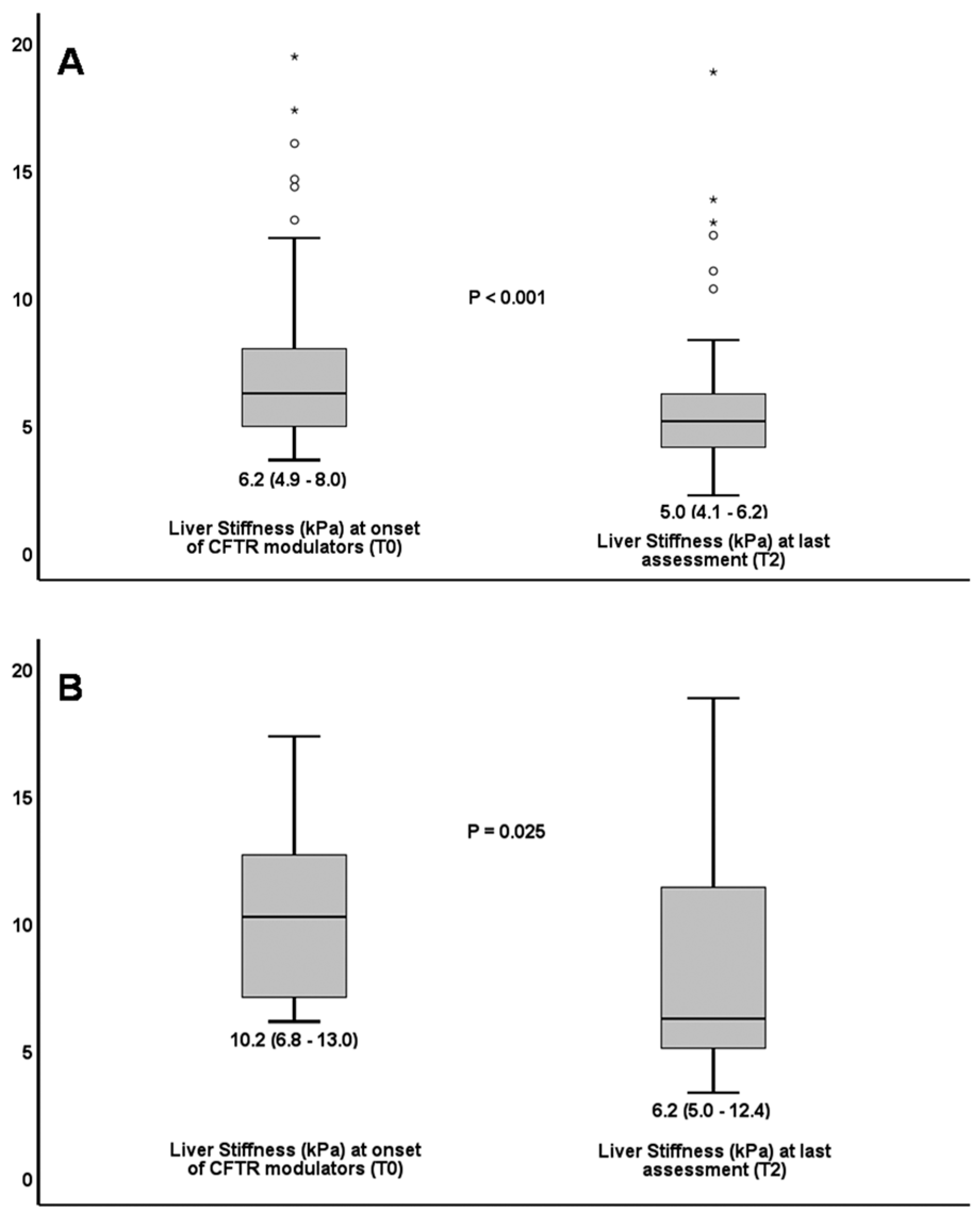
| Liver Stiffness (kPa) | 6.2 (4.9–8.0) | 5.0 (4.1–6.2) | <0.001 |
| APRI > 0.5 (N%) | 2 (3.5%) | 0 (0%) | NS |
| CFLD rate over time | |||
| CFLD (N%) | 15 (26.3%) | 8 (14.0%) | 0.016 |
| Pt # | Genotype | Age at Treatment Onset (years) | Gender | Total Treatment Duration (months) | ETI Duration (months) | LSM (kPa) at Treatment Onset (T0) | LSM (kPa) at Initiation of Prospective Period (T1) | LSM (kPa) at Last Assessment (T2) | CFLD at Treatment Onset | CFLD at Last Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DF508/DF508 | 14 | M | 116 | 40 | 10.4 | 19.7 | 18.8 | YES | YES |
| 2 | DF508/DF508 | 16 | M | 72 | 36 | 7.3 | 6.1 | 4.8 | YES | NO |
| 3 | DF508/G542X | 19 | F | 53 | 53 | 7.9 | 7.5 | 5.1 | YES | NO |
| 4 | DF508/DF508 | 23 | M | 93 | 40 | 9.0 | 7.6 | 6.1 | YES | NO |
| 5 | DF508/DF508 | 24 | M | 80 | 40 | 6.2 | 6.6 | 6.8 | YES | NO |
| 6 | DF508/621+1G>T | 25 | M | 39 | 39 | 6.8 | 5.0 | 5.2 | YES | NO |
| 7 | DF508/C524x | 26 | M | 39 | 39 | 6.1 | 6.1 | 4.9 | YES | NO |
| 8 | DF508/W496X | 26 | M | 61 | 61 | 6.8 | 6.8 | 3.3 | YES | NO |
| 9 | DF508/1677delTA | 27 | F | 34 | 34 | 10.2 | 5.4 | 5.0 | YES | YES |
| 10 | DF508/DF508 | 29 | M | 72 | 42 | 17.3 | 6.6 | 6.2 | YES | YES |
| 11 | DF508/DF508 | 30 | F | 101 | 44 | 11.4 | 10.5 | 10.3 | YES | YES |
| 12 | G542x/621+1G>T | 31 | M | 15 | 15 | 13.0 | 13.0 | 12.4 | YES | YES |
| 13 | DF508del/621+1G>T | 37 | M | 34 | 34 | 16.0 | 16.0 | 12.9 | YES | YES |
| 14 | DF508/G542X | 38 | M | 29 | 29 | 12.3 | 12.3 | 13.8 | YES | YES |
| 15 | DF508/N1303K | 33 | Μ | 41 | 41 | 14.6 | 7.9 | 7.9 | YES | ΥΕS |
| Patient # | (T0) Treatment Onset | (T2) Last Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Macronodular margin, coarse liver echotexture. Reduced size of right lobe. Enlargement of caudate lobe. Portal vein diameter 1 cm. Portosystemic collaterals: recanalization of umbilical vein, gastroesophageal varices, left gastric vein varices along lesser omentum, splenorenal shunts. Splenomegaly, spleen diameter 17.2 cm. | Liver enlarged, caudate lobe hypertrophy. Diffuse heterogeneous echotexture. Lobulated parenchymal margin. Splenomegaly, spleen diameter 17.4 cm. |
| 2 | Hepatomegaly, heterogeneous echotexture with features of fibrosis, increased echogenicity. Lobulated margin. Small collateral varices at splenic hilum. Splenomegaly, spleen size 15 cm. | Liver homogeneous. Increased echogenicity, consistent with mild fatty infiltration. Dimensions within normal limits. |
| 3 | Liver mildly enlarged. Diffuse increased parenchymal echogenicity with heterogeneous echotexture. Gallbladder with anechoic content. | Liver normal size. Mildly increased echogenicity. |
| 4 | Hepatic heterogeneous echotexture. Portal vein diameter 1.2–1.4 cm, flattened flow waveform. Gallbladder with cholelithiasis. Borderline splenomegaly, spleen 13 cm. Splenic vein diameter 1.2 cm with flattened flow waveform, consistent with portal hypertension. | Liver normal size, 14.2 cm. No focal lesions. Gallbladder with cholelithiasis. Spleen 12.4 cm. Splenic vein 0.8 cm, normal Doppler waveform. Portal vein diameter 1.1 cm, normal phasic Doppler waveform. |
| 5 | Diffuse increased liver echogenicity with heterogeneous echotexture. Mild splenomegaly, spleen 13.1 cm. Portal vein maximum diameter 1.0 cm, normal lumen and normal waveforms. Splenic vein diameter 0.7 cm with normal velocities. | Liver with mild heterogeneous echotexture. Spleen normal size, 11.7 cm. Splenoportal axis normal on triplex. |
| 6 | Hepatomegaly, liver size 17 cm. Diffuse increased parenchymal echogenicity with heterogeneous echotexture. Splenomegaly, spleen size 15.8 cm. | Liver normal size, no focal lesions. Spleen of normal size. |
| 7 | Liver enlarged, 16 cm. Heterogeneous echotexture due to multiple scattered nodular lesions, largest 2.2 cm. Findings may represent imaging features of focal biliary fibrosis. Multiple microlithiasis in gallbladder. | Liver normal size and echogenicity. Multiple microlithiasis and sludge in gallbladder. |
| 8 | Diffuse increased parenchymal echogenicity, fatty infiltration. No focal lesions. Borderline splenomegaly, spleen 13 cm. Splenic vein dilated, maximum lumen diameter 1.7 cm at splenic hilum, normal Doppler waveform. | Liver normal size (11 cm) and echogenicity, no focal lesion. |
| 9 | Normal findings | Normal findings |
| 10 | Liver enlarged, 15.7 cm. Significant heterogeneity and coarse liver echotexture, granular margin, no focal lesions. Borderline splenomegaly, 14.2 cm. | Liver enlarged, 17.1 cm, mild heterogeneous echotexture. Gallbladder sludge with wall aggregates. Focal anterior wall thickening, 1.32 cm, suggestive of chronic cholecystitis. Spleen enlarged, 15.4 cm. |
| 11 | Liver 15 cm, heterogeneous echotexture, mild fatty liver. Splenomegaly, spleen 14.8 cm. | Normal findings, spleen 11 cm. |
| 12 | Slightly increased liver echogenicity and coarse granular heterogeneous echotexture with mild focal lobulation of margin, findings suggestive of early cirrhotic changes. Contracted gallbladder. Splenomegaly, 15.6 cm. | Significant hepatic heterogeneous echotexture. Splenomegaly, 14.2 cm. Spectral Doppler: flattened waveform of portal vein, absence of respiratory alterations, findings consistent with portal hypertension. |
| 13 | Coarse hepatic echotexture, macrolobulated margin. Portal vein diameter 1.5 cm, periportal echogenic thickening. Gallbladder filled with echogenic material, Spleen 13.1 cm. | Cirrhotic liver with lobulated margin, mild hypertrophy of left and caudate lobes. Mild portal vein dilatation. Borderline splenomegaly, 13.5 cm. |
| 14 | Liver heterogeneous echotexture with few small hypoechoic elements in right lobe. Fatty liver infiltration. Hepatomegaly with inferior margin extended by 3 cm. Spleen, 13 cm. | Increased hepatic echogenicity consistent with fatty infiltration. Liver size within normal limits. Gallbladder with sludge. Mild splenomegaly, spleen 13.6 cm. |
| 15 | Focal increased liver echogenicity, consistent with fatty infiltration. Contracted gallbladder. | Heterogeneous hepatic echotexture. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manioudaki, S.; Vasilieva, L.; Geladari, E.; Mani, I.; Athanassa, Z.; Elefsiniotis, I.; Hadziyannis, E.; Sevastianos, V.; Oikonomou, A.; Theophilou, A.; et al. Improvement of Cystic Fibrosis-Associated Liver Disease in Adults on Long-Term Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Modulators. Life 2025, 15, 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15121794
Manioudaki S, Vasilieva L, Geladari E, Mani I, Athanassa Z, Elefsiniotis I, Hadziyannis E, Sevastianos V, Oikonomou A, Theophilou A, et al. Improvement of Cystic Fibrosis-Associated Liver Disease in Adults on Long-Term Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Modulators. Life. 2025; 15(12):1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15121794
Chicago/Turabian StyleManioudaki, Sofia, Larisa Vasilieva, Eleni Geladari, Iliana Mani, Zoe Athanassa, Ioannis Elefsiniotis, Emilia Hadziyannis, Vasilios Sevastianos, Aikaterini Oikonomou, Andreas Theophilou, and et al. 2025. "Improvement of Cystic Fibrosis-Associated Liver Disease in Adults on Long-Term Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Modulators" Life 15, no. 12: 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15121794
APA StyleManioudaki, S., Vasilieva, L., Geladari, E., Mani, I., Athanassa, Z., Elefsiniotis, I., Hadziyannis, E., Sevastianos, V., Oikonomou, A., Theophilou, A., Diamantea, F., & Alexopoulou, A. (2025). Improvement of Cystic Fibrosis-Associated Liver Disease in Adults on Long-Term Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Modulators. Life, 15(12), 1794. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15121794









