The Vicious Circle of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease When Micronutrient Deficiency Drives Microbial Imbalance and Liver Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Synergistic Mechanisms Between MASLD, Micronutrients, and Microbiota
4. Deficiency of Fat-Soluble Vitamins A, D, and E and Their Relationship with MASLD and Microbiota
4.1. Vitamin A
4.2. Vitamin D
Gut Microbiota in Vitamin D Interaction with MASLD
4.3. Vitamin E
5. Mineral Deficiency in MASLD and the Interrelationship with Microbiota
5.1. Copper
5.2. Iron
5.3. Selenium
5.4. Zinc
6. Clinical Implications and Future Perspectives
6.1. Micronutrient Supplementation: A Double-Edged Sword
6.2. Strength of Evidence for Probiotic/Prebiotic Therapies
6.3. Toward a Personalized Nutritional Medicine Approach
- Comprehensive Nutritional Assessment: Detailed dietary intake and micronutrient status profiling.
- Host Genetic Markers: Including polymorphisms in genes related to micronutrient metabolism (e.g., VDR) and MASLD risk (e.g., PNPLA3, HSD17B13).
7. Limitations
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carr, R.M.; Oranu, A.; Khungar, V. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Pathophysiology and Management. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 45, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abul-Husn, N.S.; Cheng, X.; Li, A.H.; Xin, Y.; Schurmann, C.; Stevis, P.; Liu, Y.; Kozlitina, J.; Stender, S.; Wood, G.C.; et al. A Protein-Truncating HSD17B13 Variant and Protection from Chronic Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speliotes, E.K.; Yerges-Armstrong, L.M.; Wu, J.; Hernaez, R.; Kim, L.J.; Palmer, C.D.; Gudnason, V.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Garcia, M.E.; Launer, L.J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analysis Identifies Variants Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease That Have Distinct Effects on Metabolic Traits. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hales, C.M.; Fryar, C.D.; Carroll, M.D.; Freedman, D.S.; Ogden, C.L. Trends in Obesity and Severe Obesity Prevalence in US Youth and Adults by Sex and Age, 2007–2008 to 2015–2016. JAMA 2018, 319, 1723–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.L.; Leung, J.C.-F.; Loong, T.C.-W.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Yeung, D.K.-W.; Chan, R.S.-M.; Chan, H.L.-Y.; Chim, A.M.-L.; Woo, J.; Chu, W.C.-W.; et al. Prevalence and Severity of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Non-Obese Patients: A Population Study Using Proton-Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 1306–1314, quiz 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bril, F.; Portillo-Sanchez, P.; Liu, I.-C.; Kalavalapalli, S.; Dayton, K.; Cusi, K. Clinical and Histologic Characterization of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in African American Patients. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Han, D.; Xu, R.; Li, S.; Wu, H.; Qu, C.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y. A Model of Metabolic Syndrome and Related Diseases with Intestinal Endotoxemia in Rats Fed a High Fat and High Sucrose Diet. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Jin, C.; Hao, L.; Mehal, W.Z.; Strowig, T.; Thaiss, C.A.; Kau, A.L.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Inflammasome-Mediated Dysbiosis Regulates Progression of NAFLD and Obesity. Nature 2012, 482, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifnia, T.; Antoun, J.; Verriere, T.G.C.; Suarez, G.; Wattacheril, J.; Wilson, K.T.; Peek, R.M.; Abumrad, N.N.; Flynn, C.R. Hepatic TLR4 Signaling in Obese NAFLD. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G270–G278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.-Z.; Wu, Q.-W.; Zhang, L. Association between Micronutrients Intake and Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. J. Nutr. Sci. 2023, 12, e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The Diagnosis and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Practice Guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blond, E.; Disse, E.; Cuerq, C.; Drai, J.; Valette, P.-J.; Laville, M.; Thivolet, C.; Simon, C.; Caussy, C. EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Severely Obese People: Do They Lead to over-Referral? Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1218–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, V.; Siotto, M.; Bedogni, G.; Ravà, L.; Pietrobattista, A.; Panera, N.; Alisi, A.; Squitti, R. Levels of Serum Ceruloplasmin Associate with Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowdley, K.V.; Belt, P.; Wilson, L.A.; Yeh, M.M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Chalasani, N.; Sanyal, A.J.; Nelson, J.E. Elevated Serum Ferritin Is an Independent Predictor of Histologic Severity and Advanced Fibrosis among Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2012, 55, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venu, M.; Martin, E.; Saeian, K.; Gawrieh, S. High Prevalence of Vitamin A Deficiency and Vitamin D Deficiency in Patients Evaluated for Liver Transplantation. Liver Transplant. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Study Liver Dis. Int. Liver Transplant. Soc. 2013, 19, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, S.; Mencarelli, A.; Palladino, G.; Fiorucci, S. FXR Activation Reverses Insulin Resistance and Lipid Abnormalities and Protects against Liver Steatosis in Zucker (Fa/Fa) Obese Rats. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Lavine, J.E.; Van Natta, M.L.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Chalasani, N.; Dasarathy, S.; Diehl, A.M.; Hameed, B.; et al. Farnesoid X Nuclear Receptor Ligand Obeticholic Acid for Non-Cirrhotic, Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (FLINT): A Multicentre, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Kallman, J.B.; Bai, C.; Pawloski, L.; Gewa, C.; Arsalla, A.; Sabatella, M.E.; Younossi, Z.M. Nutritional Assessments of Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Obes. Surg. 2010, 20, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas-Valdés, S.; Tostes, M.d.G.V.; Anunciação, P.C.; da Silva, B.P.; Sant’Ana, H.M.P. Association between Vitamin Deficiency and Metabolic Disorders Related to Obesity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3332–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, X.; Chen, T.; Chen, M.; Wu, L.; He, B. Exploring the Interactions between Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Micronutrients: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Applications. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1344924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, C.; Schwartz, B. The Effect of Bioactive Aliment Compounds and Micronutrients on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautiainen, S.; Manson, J.E.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Sesso, H.D. Dietary Supplements and Disease Prevention—A Global Overview. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Sun, R.; Xia, M. Association of Serum Retinoic Acid with Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Injury in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Jiang, Z.G. Low Vitamin A Levels Are Associated with Liver-Related Mortality: A Nationally Representative Cohort Study. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e0124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.-H.; Melis, M.; Lu, C.; Rappa, A.; Zhang, T.; Jessurun, J.; Gross, S.S.; Gudas, L.J. A Retinoic Acid Receptor Β2 Agonist Attenuates Transcriptome and Metabolome Changes Underlying Nonalcohol-Associated Fatty Liver Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.-J.; Yoon, Y.-S.; Hong, S.; Son, H.-Y.; Na, T.-Y.; Lee, M.-H.; Kang, H.-J.; Park, J.; Cho, W.-J.; Kim, S.-G.; et al. Retinoic Acid Receptor-Related Orphan Receptor α-Induced Activation of Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Results in Attenuation of Hepatic Steatosis. Hepatology 2012, 55, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, C.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, X.; Gao, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Fang, F.; et al. Retinoic Acid Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Liver Steatosis through Sirt1. Sci. China Life Sci. 2017, 60, 1234–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, L.; Farhad, N.; Abbasi, A. All-Trans Retinoic Acid (atRA) Effectively Improves Liver Steatosis in a Rabbit Model of High Fat Induced Liver Steatosis. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 128, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasino, S.E.; Tang, X.-H.; Jessurun, J.; Gudas, L.J. A Retinoic Acid Receptor Β2 Agonist Reduces Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Ebata, Y.; Kojima, C.; Katsuma, R.; Tsuruyama, T.; Sakabe, T.; Shomori, K.; Komeda, N.; Oshiro, S.; et al. Retinoids Ameliorate Insulin Resistance in a Leptin-Dependent Manner in Mice. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaner, W.S. Vitamin A Signaling and Homeostasis in Obesity, Diabetes, and Metabolic Disorders. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 197, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboul, E. Absorption of Vitamin A and Carotenoids by the Enterocyte: Focus on Transport Proteins. Nutrients 2013, 5, 3563–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Shaoyong, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Gan, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jin, M. The Functions of Gut Microbiota-Mediated Bile Acid Metabolism in Intestinal Immunity. J. Adv. Res. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghpour, A.; Rappolt, M.; Misra, S.; Kulkarni, C.V. Bile Salts Caught in the Act: From Emulsification to Nanostructural Reorganization of Lipid Self-Assemblies. Langmuir ACS J. Surf. Colloids 2018, 34, 13626–13637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnewski, P.; Das, S.; Parigi, S.M.; Villablanca, E.J. Retinoic Acid and Its Role in Modulating Intestinal Innate Immunity. Nutrients 2017, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.A.; Cannons, J.L.; Grainger, J.R.; Dos Santos, L.M.; Hand, T.W.; Naik, S.; Wohlfert, E.A.; Chou, D.B.; Oldenhove, G.; Robinson, M.; et al. Essential Role for Retinoic Acid in the Promotion of CD4(+) T Cell Effector Responses via Retinoic Acid Receptor Alpha. Immunity 2011, 34, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmytriv, T.R.; Storey, K.B.; Lushchak, V.I. Intestinal Barrier Permeability: The Influence of Gut Microbiota, Nutrition, and Exercise. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1380713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Tomita, M. Genetic Variations of Vitamin A-Absorption and Storage-Related Genes, and Their Potential Contribution to Vitamin A Deficiency Risks Among Different Ethnic Groups. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 861619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanza, C.; Romenskaya, T.; Longhitano, Y.; Piccolella, F.; Racca, F.; Tassi, M.F.; Rubulotta, F.; Abenavoli, L.; Shiffer, D.; Franceschi, F.; et al. Probiotic Bacterial Application in Pediatric Critical Illness as Coadjuvants of Therapy. Medicina 2021, 57, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassef, L.; Wirawan, R.; Chikindas, M.; Breslin, P.A.S.; Hoffman, D.J.; Quadro, L. β-Carotene–Producing Bacteria Residing in the Intestine Provide Vitamin A to Mouse Tissues In Vivo1, 2, 3. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Culligan, E.; Sleator, R.; Marchesi, J.; Hill, C. Metagenomic Identification of a Novel Salt Tolerance Gene from the Human Gut Microbiome Which Encodes a Membrane Protein with Homology to a Brp/Blh-Family Beta-Carotene 15,15’-Monooxygenase. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chewning, J.H.; Weaver, C.T. Development and Survival of Th17 Cells within the Intestines: The Influence of Microbiome- and Diet-Derived Signals. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 4769–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Xiong, X.-Q.; Yang, T.; Cui, T.; Hou, N.-L.; Lai, X.; Liu, S.; Guo, M.; Liang, X.-H.; et al. Effect of Vitamin A Supplementation on Gut Microbiota in Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders—A Pilot Study. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucurica, S.; Prodan, I.; Pavalean, M.; Taubner, C.; Bucurica, A.; Socol, C.; Calin, R.; Ionita-Radu, F.; Jinga, M. Association of Vitamin D Deficiency and Insufficiency with Pathology in Hospitalized Patients. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udomsinprasert, W.; Jittikoon, J. Vitamin D and Liver Fibrosis: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuluaga, P.; Casado-Carbajo, J.; Hernández-Rubio, A.; Bueno-Vélez, M.; García-Martin, C.; Muga, R.; Fuster, D. Vitamin D Deficiency Is Associated with Advanced Liver Fibrosis and Impaired Fasting Glucose in Alcohol Use Disorder. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlberg, C. Genome-Wide (over)View on the Actions of Vitamin D. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triantos, C.; Aggeletopoulou, I.; Thomopoulos, K.; Mouzaki, A. Vitamin D-Liver Disease Association: Biological Basis and Mechanisms of Action. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latic, N.; Erben, R.G. FGF23 and Vitamin D Metabolism. JBMR Plus 2021, 5, e10558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-J.; Yu, H.-C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Geng, T.-T.; Lu, Q.; Liao, Y.-F.; Guo, K.-Q.; Du, L.; Ruan, H.-L.; et al. Association between Serum 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D Concentrations and Mortality among Individuals with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Prospective Cohort Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 116, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hong, H. Vitamin D/Vitamin D Receptor Pathway in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2023, 27, 1145–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, B.A.; El-Khatib, A.S.; Attia, Y.M. Insights into the Role of Vitamin D in Targeting the Culprits of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Life Sci. 2023, 332, 122124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, X.; Ling, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Yuan, L.; Xiang, C. Association between Serum Vitamin D and Severity of Liver Fibrosis in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients: A Systematic Meta-Analysis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2014, 15, 900–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, C.S.; Krawczyk, M.; Reichel, C.; Lammert, F.; Grünhage, F. Vitamin D Deficiency Is Associated with Mortality in Patients with Advanced Liver Cirrhosis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 44, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardullo, S.; Muraca, E.; Cannistraci, R.; Perra, S.; Lattuada, G.; Perseghin, G. Low 25 (OH) Vitamin D Levels Are Associated with Increased Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Significant Liver Fibrosis. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2023, 39, e3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchetta, I.; Cimini, F.A.; Cavallo, M.G. Vitamin D and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): An Update. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Wei, C.-B.; Gu, W.; Hou, L.-L. Relevance of Vitamin D on NAFLD and Liver Fibrosis Detected by Vibration Controlled Transient Elastography in US Adults: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of NHANES 2017-2018. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 2209335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupprecht, M.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Schöpe, J.; Vieth, R.; Vogt, T.; Reichrath, J. Meta-Analysis of European Clinical Trials Characterizing the Healthy-Adult Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Response to Vitamin D Supplementation. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, O.; Juraschek, S.P.; Appel, L.J. Design Features of Randomized Clinical Trials of Vitamin D and Falls: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, A.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, X.; Giovannucci, E.L. Vitamin D and Human Health: Evidence from Mendelian Randomization Studies. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2024, 39, 467–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xu, L.; Chen, F.-H.; Zhou, Y.-B. Association of Serum Vitamin D Level and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 32, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, Y.; Luo, F.; Liu, J.; Xiu, L.; Qin, J.; Wang, T.; Yu, N.; Wu, H.; Zou, T. The Level of Vitamin D in Children and Adolescents with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 7643542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaruvongvanich, V.; Ahuja, W.; Sanguankeo, A.; Wijarnpreecha, K.; Upala, S. Vitamin D and Histologic Severity of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, N.; Amani, R. Vitamin D Supplementation and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Critical and Systematic Review of Clinical Trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelakovic, M.; Nikolova, D.; Bjelakovic, G.; Gluud, C. Vitamin D Supplementation for Chronic Liver Diseases in Adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2017, CD011564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, R.A.M.; Masroor, A.; Khorochkov, A.; Prieto, J.; Singh, K.B.; Nnadozie, M.C.; Abdal, M.; Shrestha, N.; Mohammed, L.; Abe, R.A.M.; et al. The Role of Vitamins in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2021, 13, e16855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Watanabe, K.; Kimura, I. Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis Drives and Implies Novel Therapeutic Strategies for Diabetes Mellitus and Related Metabolic Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunis, C.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Hanssen, N. Interactions between Tryptophan Metabolism, the Gut Microbiome and the Immune System as Potential Drivers of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Metabolic Diseases. Metabolites 2022, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szóstak, N.; Figlerowicz, M.; Philips, A. The Emerging Role of the Gut Mycobiome in Liver Diseases. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2211922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, R.; Luo, M.; Zhang, T.; Pan, L.; Xu, S.; Pan, L.; Ren, F.; Ji, C.; Hu, R.; et al. Liver Injury Impaired 25-Hydroxylation of Vitamin D Suppresses Intestinal Paneth Cell Defensins, Leading to Gut Dysbiosis and Liver Fibrogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 319, G685–G695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wan, B.; Zhang, H.; Wu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, N.; Lin, S.; et al. Association between Vitamin D Status and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Population-Based Study. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2019, 65, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Shang, X.; Jin, S.; Ma, Z.; Wang, H.; Ao, N.; Yang, J.; Du, J. Vitamin D Ameliorates High-Fat-Diet-Induced Hepatic Injury via Inhibiting Pyroptosis and Alters Gut Microbiota in Rats. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 705, 108894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-L.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Zhao, S.-S.; Jin, S.; Ao, N.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.-X.; Du, J. Vitamin D Alleviates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Restoring Gut Microbiota and Metabolism. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1117644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernia, F.; Valvano, M.; Longo, S.; Cesaro, N.; Viscido, A.; Latella, G. Vitamin D in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Implications. Nutrients 2022, 14, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, R.; Ma, Y. Combined Effect of Vitamin C and Vitamin D3 on Intestinal Epithelial Barrier by Regulating Notch Signaling Pathway. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akimbekov, N.S.; Digel, I.; Sherelkhan, D.K.; Lutfor, A.B.; Razzaque, M.S. Vitamin D and the Host-Gut Microbiome: A Brief Overview. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2020, 53, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.L.; Martoni, C.J.; Prakash, S. Oral Supplementation with Probiotic L. Reuteri NCIMB 30242 Increases Mean Circulating 25-Hydroxyvitamin D: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2944–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaebel, J.H.; Rakipovski, G.; Andersen, B.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. Dietary Intervention Accelerates NASH Resolution Depending on Inflammatory Status with Minor Additive Effects on Hepatic Injury by Vitamin E Supplementation. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusi, K.; Isaacs, S.; Barb, D.; Basu, R.; Caprio, S.; Garvey, W.T.; Kashyap, S.; Mechanick, J.I.; Mouzaki, M.; Nadolsky, K.; et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Primary Care and Endocrinology Clinical Settings: Co-Sponsored by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). Endocr. Pract. Off. J. Am. Coll. Endocrinol. Am. Assoc. Clin. Endocrinol. 2022, 28, 528–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallert, M.; Börmel, L.; Lorkowski, S. Inflammatory Diseases and Vitamin E-What Do We Know and Where Do We Go? Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, e2000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B.; Sahin, K.; Bilen, H.; Bahcecioglu, I.H.; Bilir, B.; Ashraf, S.; Halazun, K.J.; Kucuk, O. Carotenoids and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2015, 4, 16171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zhuge, F.; Nagashimada, M.; Ota, T. Novel Action of Carotenoids on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Macrophage Polarization and Liver Homeostasis. Nutrients 2016, 8, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bril, F.; Biernacki, D.M.; Kalavalapalli, S.; Lomonaco, R.; Subbarayan, S.K.; Lai, J.; Tio, F.; Suman, A.; Orsak, B.K.; Hecht, J.; et al. Role of Vitamin E for Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazhar, I.J.; Yasir, M.; Sarfraz, S.; Shlaghya, G.; Narayana, S.H.; Mushtaq, U.; Ameen, B.S.; Nie, C.; Nechi, D.; Penumetcha, S.S.; et al. Vitamin E and Pioglitazone: A Comprehensive Systematic Review of Their Efficacy in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Cureus 2023, 15, e43635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonyam, P.; Kritsanaviparkporn, C.; Chommaitree, P.; Soodcharoen, A. The Effects of Combined Vitamin E and C for Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2022, 23, 2891–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lema, I.; Araújo, J.R.; Rolhion, N.; Demignot, S. Jejunum: The Understudied Meeting Place of Dietary Lipids and the Microbiota. Biochimie 2020, 178, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, L.; Liu, A.B.; Lee, M.-J.; Xie, P.; Lin, Y.; Yang, C.S. Effects of Antibiotics on Degradation and Bioavailability of Different Vitamin E Forms in Mice. BioFactors Oxf. Engl. 2019, 45, 450–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Ha, J.; Oh, H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, Y. Vitamin E (α-Tocopherol) Consumption Influences Gut Microbiota Composition. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altarelli, M.; Ben-Hamouda, N.; Schneider, A.; Berger, M.M. Copper Deficiency: Causes, Manifestations, and Treatment. Nutr. Clin. Pract. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 34, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiela, P.R.; Ghishan, F.K. Physiology of Intestinal Absorption and Secretion. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 30, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Pei, P.; Yang, K.; Guo, L.; Li, Y. Copper in Colorectal Cancer: From Copper--related Mechanisms to Clinical Cancer Therapies. Clin. Transl. Med. 2024, 14, e1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallant, R.C.; Cameron, L.; Mithoowani, S. Copper Deficiency. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2025, 197, E456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonucci, L.; Porcu, C.; Iannucci, G.; Balsano, C.; Barbaro, B. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nutritional Implications: Special Focus on Copper. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marginean, C.M.; Pirscoveanu, D.; Cazacu, S.M.; Popescu, M.S.; Marginean, I.C.; Iacob, G.A.; Popescu, M. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Awareness of a Diagnostic Challenge—A Clinician’s Perspective. Gastroenterol. Insights 2024, 15, 1028–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, J.; Aizenman, E. The Physiological and Pathophysiological Roles of Copper in the Nervous System. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2024, 60, 3505–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Peng, G.; Lu, Y.; Wang, K.; Ju, Q.; Ju, Y.; Ouyang, M. Relationship between Copper and Immunity: The Potential Role of Copper in Tumor Immunity. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1019153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Kang, R.; Klionsky, D.J.; Tang, D.; Liu, J.; Chen, X. Copper Metabolism in Cell Death and Autophagy. Autophagy 2025, 19, 2175–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrell, A.; Tallino, S.; Yu, L.; Burkhead, J.L. The Role of Insufficient Copper in Lipid Synthesis and Fatty-Liver Disease. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Lee, G.; Heo, S.-Y.; Roh, Y.-S. Oxidative Stress Is a Key Modulator in the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Yuan, F.; Li, X.; Ma, X.; Yin, X.; Rouchka, E.C.; Zhang, X.; Deng, Z.; Prough, R.A.; McClain, C.J. Analysis of Sex Differences in Dietary Copper-Fructose Interaction-Induced Alterations of Gut Microbial Activity in Relation to Hepatic Steatosis. Biol. Sex Differ. 2021, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oates, J.R.; McKell, M.C.; Moreno-Fernandez, M.E.; Damen, M.S.M.A.; Deepe, G.S.; Qualls, J.E.; Divanovic, S. Macrophage Function in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Mac Attack. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aigner, E.; Weiss, G.; Datz, C. Dysregulation of Iron and Copper Homeostasis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaka, H.; Miida, T.; Inui, A.; Inoue, I.; Tsukahara, H.; Komatsu, H.; Hiejima, E.; Fujisawa, T.; Yorifuji, T.; Hiranao, K.; et al. Fatty Liver and Anti-Oxidant Enzyme Activities along with Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors γ and α Expressions in the Liver of Wilson’s Disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2012, 107, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stättermayer, A.F.; Traussnigg, S.; Dienes, H.-P.; Aigner, E.; Stauber, R.; Lackner, K.; Hofer, H.; Stift, J.; Wrba, F.; Stadlmayr, A.; et al. Hepatic Steatosis in Wilson Disease--Role of Copper and PNPLA3 Mutations. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Shi, H.; Vos, M.B.; Wei, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Rouchka, E.C.; Yin, X.; et al. Dietary Copper-Fructose Interactions Alter Gut Microbial Activity in Male Rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 314, G119–G130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jin, Y.; Wang, T.; Fu, D.; Ma, J.; Yu, X.; Lu, Y.; Song, J.; Chen, Y.; Yan, R.; et al. Gut Akkermansia Enhances Liver Protection and Facilitates Copper Removal during D-Penicillamine Treatment in a Wilson’s Disease Model. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e00573-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barra, N.G.; Anhê, F.F.; Cavallari, J.F.; Singh, A.M.; Chan, D.Y.; Schertzer, J.D. Micronutrients Impact the Gut Microbiota and Blood Glucose. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 250, R1–R21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Liao, S.; Zeng, Y.; Liang, L.; Chen, J.; Tao, C. Causal Relationships between Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Iron Status: Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2022, 42, 2759–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, S.; Izawa, T.; Mori, M.; Atarashi, M.; Yamate, J.; Kuwamura, M. Dietary Iron Overload Enhances Western Diet Induced Hepatic Inflammation and Alters Lipid Metabolism in Rats Sharing Similarity with Human DIOS. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Li, H.; Chen, P.; Wang, M.; Gu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L. Hyperferritinemia Correlates to Metabolic Dysregulation and Steatosis in Chinese Biopsy-Proven Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rametta, R.; Dongiovanni, P.; Baselli, G.A.; Pelusi, S.; Meroni, M.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Busti, F.; Castagna, A.; Scarlini, S.; Corradini, E.; et al. Impact of Natural Neuromedin-B Receptor Variants on Iron Metabolism. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Lanti, C.; Gatti, S.; Rametta, R.; Recalcati, S.; Maggioni, M.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Riso, P.; Cairo, G.; Fargion, S.; et al. High Fat Diet Subverts Hepatocellular Iron Uptake Determining Dysmetabolic Iron Overload. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrogiannaki, M.; Matak, P.; Peyssonnaux, C. The Gut in Iron Homeostasis: Role of HIF-2 under Normal and Pathological Conditions. Blood 2013, 122, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurusaki, S.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Koumura, T.; Nakasone, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Matsuoka, M.; Imai, H.; Yuet-Yin Kok, C.; Okochi, H.; Nakano, H.; et al. Hepatic Ferroptosis Plays an Important Role as the Trigger for Initiating Inflammation in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dai, X.; Wang, L.; Cai, J.; Shen, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y. Iron Overload Accelerated Lipid Metabolism Disorder and Liver Injury in Rats with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 961892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Jin, Z.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Wang, G.; Zhang, D.; Rocha, K.C.E.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D.A.; et al. Aberrant Iron Distribution via Hepatocyte-Stellate Cell Axis Drives Liver Lipogenesis and Fibrosis. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1201–1213.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyoum, Y.; Baye, K.; Humblot, C. Iron Homeostasis in Host and Gut Bacteria—A Complex Interrelationship. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1874855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Fernández-Real, J.M. The Role of Iron in Host-Microbiota Crosstalk and Its Effects on Systemic Glucose Metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2022, 18, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.-C.; Pantopoulos, K.; Chen, G.-H.; Zhong, C.-C.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, D.-G.; Luo, Z. Iron Increases Lipid Deposition via Oxidative Stress-Mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction and the HIF1α-PPARγ Pathway. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.L. Iron Deficiency Anemia: A Common and Curable Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a011866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Frazer, D.M.; Hu, M.; Song, R.; Liu, X.; Qin, X.; Ma, J.; Zhou, J.; Tan, Z.; Ren, F.; et al. Mechanism and Regulation of Iron Absorption throughout the Life Cycle. J. Adv. Res. 2025, 77, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Yung, K.K.L.; KongYeung, C. Effects of Common Prebiotics on Iron Status and Production of Colonic Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Anemic Rats. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2021, 10, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.M.R.; Ahmed, W.; Iqbal, S.; Javed, M.; Rashid, S.; Iahtisham-ul-Haq. Prebiotics and Iron Bioavailability? Unveiling the Hidden Association—A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, E.; Ganz, T. Hepcidin and Iron in Health and Disease. Annu. Rev. Med. 2023, 74, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, A.S.; Mauer, T.J.; Forest, K.T.; Goodrich-Blair, H. A Widespread Bacterial Secretion System with Diverse Substrates. mBio 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troxell, B.; Hassan, H.M. Transcriptional Regulation by Ferric Uptake Regulator (Fur) in Pathogenic Bacteria. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari, C.; Barbieri, F.; Magnani, M.; Grazia, L.; Gardini, F.; Tabanelli, G. Phenotypic Diversity of Lactobacillus sakei Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verplaetse, E.; André-Leroux, G.; Duhutrel, P.; Coeuret, G.; Chaillou, S.; Nielsen-Leroux, C.; Champomier-Vergès, M.-C. Heme Uptake in Lactobacillus sakei Evidenced by a New Energy Coupling Factor (ECF)-Like Transport System. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02847-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biesalski, H.K. Nutrition Meets the Microbiome: Micronutrients and the Microbiota. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1372, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iatsenko, I.; Marra, A.; Boquete, J.-P.; Peña, J.; Lemaitre, B. Iron Sequestration by Transferrin 1 Mediates Nutritional Immunity in Drosophila Melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 7317–7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, J.; Özkaya, Ö.; Kümmerli, R. Bacterial Siderophores in Community and Host Interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechardeur, D.; Cesselin, B.; Liebl, U.; Vos, M.H.; Fernandez, A.; Brun, C.; Gruss, A.; Gaudu, P. Discovery of Intracellular Heme-Binding Protein HrtR, Which Controls Heme Efflux by the Conserved HrtB-HrtA Transporter in Lactococcus Lactis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4752–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Weng, T.; Song, Y. Association of Serum Selenium with MASLD and Liver Fibrosis: A Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0314780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariharan, S.; Dharmaraj, S. Selenium and Selenoproteins: It’s Role in Regulation of Inflammation. Inflammopharmacology 2020, 28, 667–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Gupta, S. An Overview of Selenium Uptake, Metabolism, and Toxicity in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 7, 2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Seo, Y.A.; Park, S.K. Serum Selenium and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in U.S. Adults: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2011–2016. Environ. Res. 2021, 197, 111190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tan, L.; Liu, Z.; Shi, R. The Association between Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Advanced Fibrosis with Blood Selenium Level Based on the NHANES 2017–2018. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 2258–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zeng, C.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Lei, G.; Xie, D.; Wang, Y.; Wei, J.; Yang, T. Association Between Dietary Selenium Intake and the Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2020, 39, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, H.; Liu, B.; Lv, Z.; Guo, C.; Zhang, H. Effects of Selenium on Apoptosis and Abnormal Amino Acid Metabolism Induced by Excess Fatty Acid in Isolated Rat Hepatocytes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, M.; Matsushita, K.; Shindo, R.; Shimokawa, Y.; Sugiura, Y.; Yamashita, M. Selenoneine Ameliorates Hepatocellular Injury and Hepatic Steatosis in a Mouse Model of NAFLD. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinceti, M.; Filippini, T.; Giovane, C.D.; Dennert, G.; Zwahlen, M.; Brinkman, M.; Zeegers, M.P.; Horneber, M.; D’Amico, R.; Crespi, C.M. Selenium for Preventing Cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 1, CD005195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonska, E.; Gromadzinska, J.; Peplonska, B.; Fendler, W.; Reszka, E.; Krol, M.B.; Wieczorek, E.; Bukowska, A.; Gresner, P.; Galicki, M.; et al. Lipid Peroxidation and Glutathione Peroxidase Activity Relationship in Breast Cancer Depends on Functional Polymorphism of GPX1. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Chen, K.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, T.; Huang, J. Potential Applications and Risks of Supranutritional Selenium Supplementation in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Critical Review. Nutrients 2025, 17, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarczyk, J.; Koch, W. Dietary Zn—Recent Advances in Studies on Its Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability. Molecules 2025, 30, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Spiga, L.; Winter, S. Transition Metals and Host-Microbe Interactions in the Inflamed Intestine. BioMetals 2019, 32, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalsamy, G.L.; Alpers, D.H.; Binder, H.J.; Tran, C.D.; Ramakrishna, B.S.; Brown, I.; Manary, M.; Mortimer, E.; Young, G.P. The Relevance of the Colon to Zinc Nutrition. Nutrients 2015, 7, 572–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souffriau, J.; Libert, C. Mechanistic Insights into the Protective Impact of Zinc on Sepsis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018, 39, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieper, R.; Vahjen, W.; Neumann, K.; Van Kessel, A.G.; Zentek, J. Dose-Dependent Effects of Dietary Zinc Oxide on Bacterial Communities and Metabolic Profiles in the Ileum of Weaned Pigs. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 96, 825–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.; Knez, M.; Uzan, A.; Stangoulis, J.C.R.; Glahn, R.P.; Koren, O.; Tako, E. Alterations in the Gut (Gallus gallus) Microbiota Following the Consumption of Zinc Biofortified Wheat (Triticum aestivum)-Based Diet. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 6291–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, O.; Tako, E. Chronic Dietary Zinc Deficiency Alters Gut Microbiota Composition and Function. Proceedings 2020, 61, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zackular, J.P.; Moore, J.L.; Jordan, A.T.; Juttukonda, L.J.; Noto, M.J.; Nicholson, M.R.; Crews, J.D.; Semler, M.W.; Zhang, Y.; Ware, L.B.; et al. Dietary Zinc Alters the Microbiota and Decreases Resistance to Clostridium Difficile Infection. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Kolba, N.; Tako, E. The Effect of Dietary Zinc and Zinc Physiological Status on the Composition of the Gut Microbiome in Vivo. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 6432–6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaye, A.D.; Thomassen, A.S.; Mashaw, S.A.; MacDonald, E.M.; Waguespack, A.; Hickey, L.; Singh, A.; Gungor, D.; Kallurkar, A.; Kaye, A.M.; et al. Vitamin E (α-Tocopherol): Emerging Clinical Role and Adverse Risks of Supplementation in Adults. Cureus 2025, 17, e78679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpton, S.R.; Maraj, B.; Harding-Theobald, E.; Vittinghoff, E.; Terrault, N.A. Gut Microbiome–Targeted Therapies in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelhameed, F.; Mustafa, A.; Kite, C.; Lagojda, L.; Dallaway, A.; Than, N.N.; Kassi, E.; Kyrou, I.; Randeva, H.S. Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): Emerging Pathogenic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Livers 2025, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Dong, X.; Gao, Z.; Yan, H.; Shataer, D.; Wang, L.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Cui, J.; et al. Probiotics as a Therapeutic Strategy for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2025, 11, 101138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
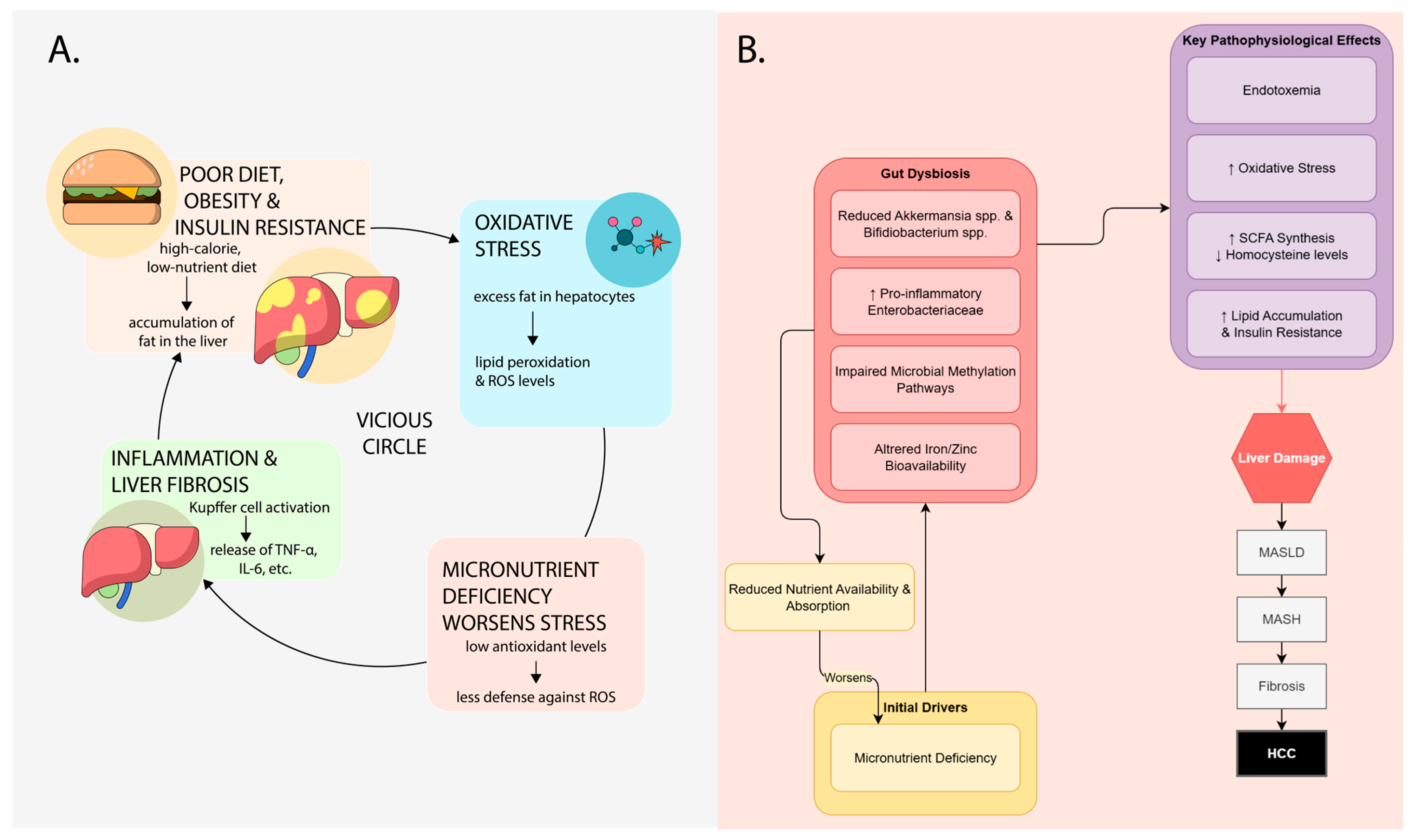
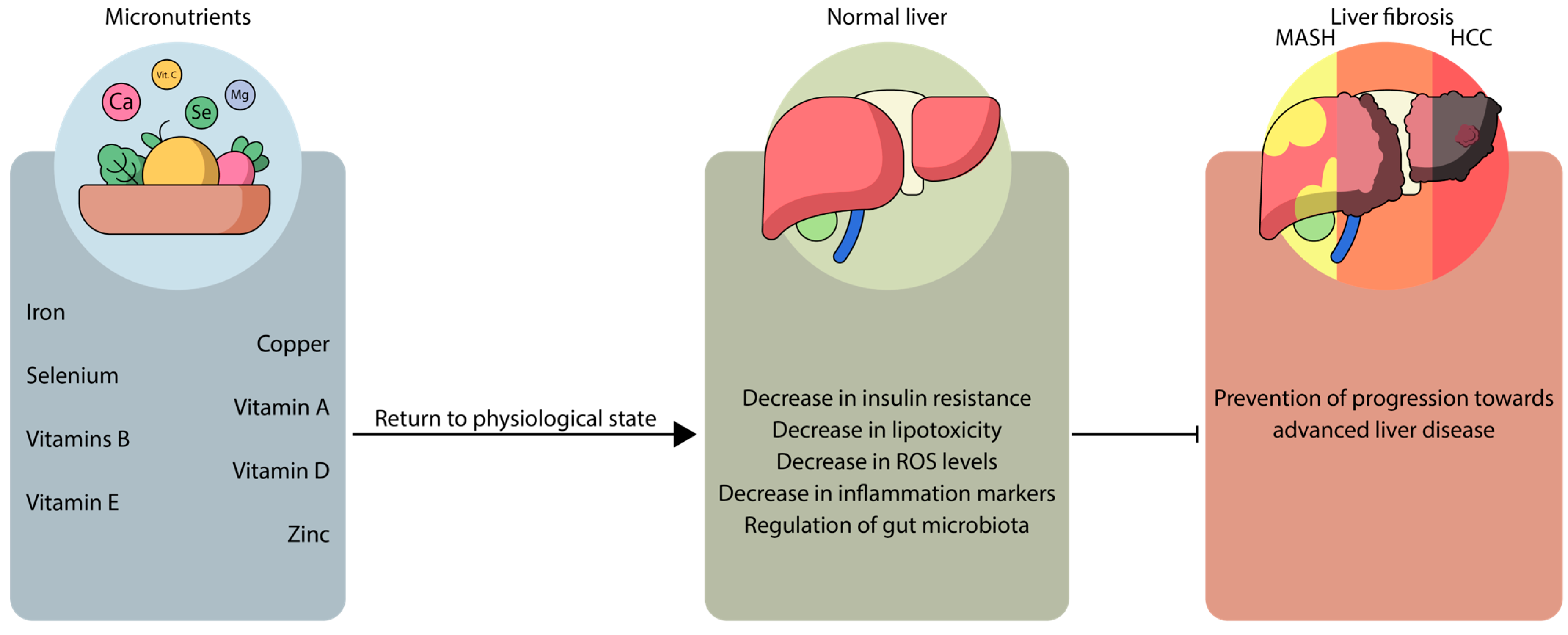
| Author(s) and Year | Type of Review | No. of Studies/Participants | Main Findings | Conclusion | Key Limitations/Context | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fang et al. (2024) | Mendelian Randomization | 133 MR Studies |
| Likely causal, protective effect of lifelong higher vitamin D status on MASLD risk. | MR assesses genetic predisposition, suggesting causality, but does not evaluate the effect of supplementation. | [60] |
| Liu et al. (2020) | Observational Meta-Analysis | 15 Studies/20,096 participants |
| Strong association between lower vitamin D levels and the presence of MASLD. | High heterogeneity (I2 = 99%); association stronger in Western populations. | [61] |
| Zhu et al. (2019) | Observational Meta-Analysis | 8 Studies (Pediatric) |
| Significant association between lower vitamin D and pediatric MASLD (medium effect size). | Focuses specifically on pediatric population. | [62] |
| Jaruvongvanich et al. (2017) | Observational Meta-Analysis | 6 Studies/974 participants (Biopsy-proven) |
| No association between vitamin D levels and histologic severity of MASLD. | Focuses on disease severity among those already diagnosed; biopsy-proven cohorts. | [63] |
| Sharifi & Amani (2019) | Systematic Review of Clinical Trials | 6 Trials/330 patients |
| Insufficient and inconsistent evidence for Vitamin D supplementation benefits on MASLD pathology. | Highlights the gap between raising serum levels and improving clinical outcomes. Small, short-term trials. | [64] |
| Bjelakovic et al. (2021) | Cochrane Review (RCTs) | 27 RCTs/1979 patients (Various CLD) |
| No reliable evidence for or against vitamin D supplementation in chronic liver diseases. | Includes various liver diseases (MASLD, HCV, cirrhosis); highlights very low quality of evidence for critical outcomes. | [65] |
| Abe et al. (2021) | Systematic Review (Narrative) | 17 Articles |
| Evidence is mixed. The role of Vitamin D is complex and not yet fully understood. | Provides a mechanistic hypothesis for inconsistencies (e.g., VDR in hepatocytes may promote lipid accumulation). | [66] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marginean, I.C.; Cazacu, S.M.; Popescu, M.; Iacob, G.A.; Sandulescu, L.D.; Iordache, S.; Marginean, C.M.; Vere, C.C. The Vicious Circle of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease When Micronutrient Deficiency Drives Microbial Imbalance and Liver Injury. Life 2025, 15, 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111764
Marginean IC, Cazacu SM, Popescu M, Iacob GA, Sandulescu LD, Iordache S, Marginean CM, Vere CC. The Vicious Circle of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease When Micronutrient Deficiency Drives Microbial Imbalance and Liver Injury. Life. 2025; 15(11):1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111764
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarginean, Iulia Cristina, Sergiu Marian Cazacu, Mihaela Popescu, George Alexandru Iacob, Larisa Daniela Sandulescu, Sevastita Iordache, Cristina Maria Marginean, and Cristin Constantin Vere. 2025. "The Vicious Circle of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease When Micronutrient Deficiency Drives Microbial Imbalance and Liver Injury" Life 15, no. 11: 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111764
APA StyleMarginean, I. C., Cazacu, S. M., Popescu, M., Iacob, G. A., Sandulescu, L. D., Iordache, S., Marginean, C. M., & Vere, C. C. (2025). The Vicious Circle of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease When Micronutrient Deficiency Drives Microbial Imbalance and Liver Injury. Life, 15(11), 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15111764





