A Study on the Performance Comparison of Brain MRI Image-Based Abnormality Classification Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Data Splitting
2.3. Data Preprocessing and Augmentation
2.4. Models and Training
2.5. Performance Evaluation

3. Results
3.1. Dataset
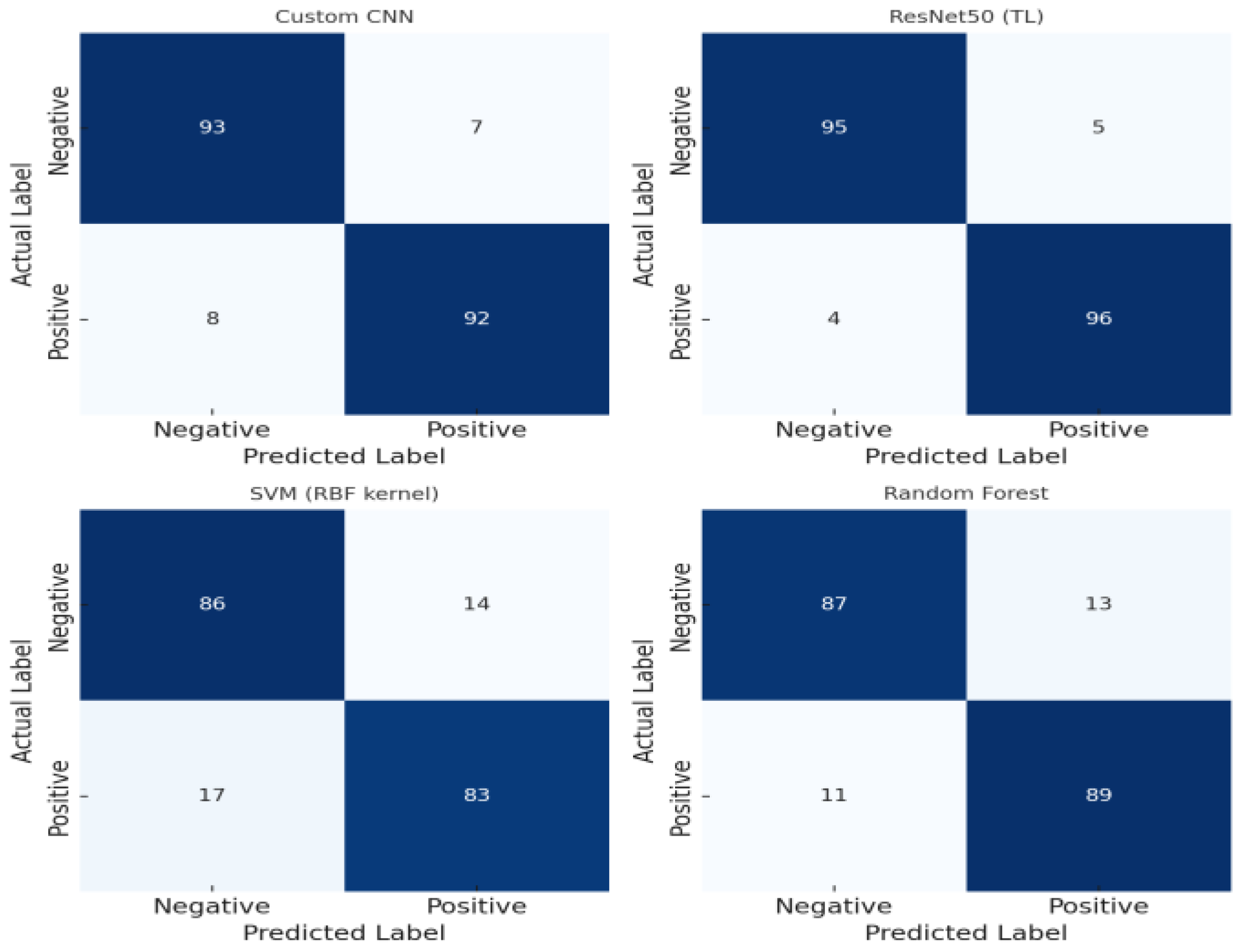
3.2. Confusion Matrix Analysis
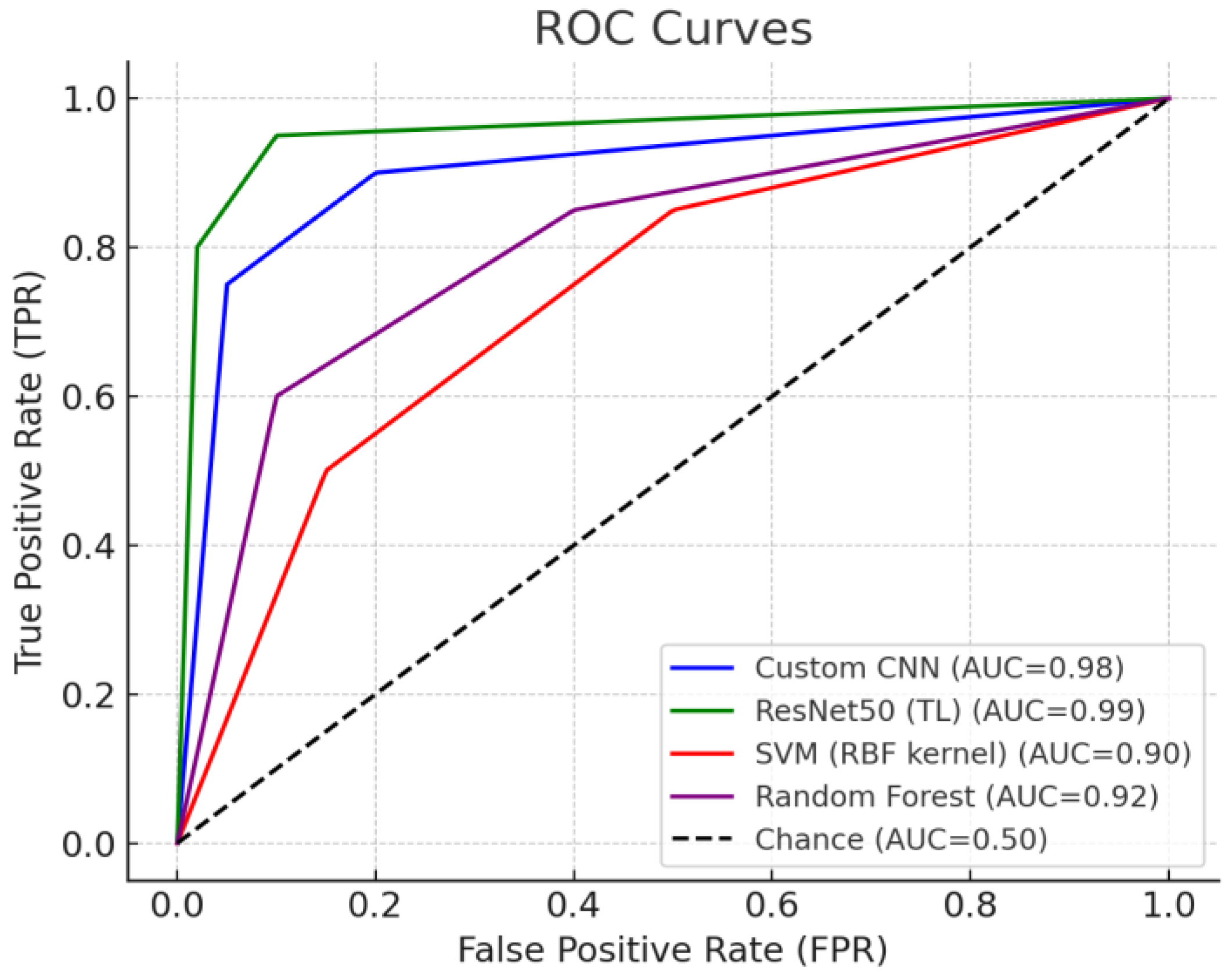
3.3. Comparison of ROC Curves and AUC
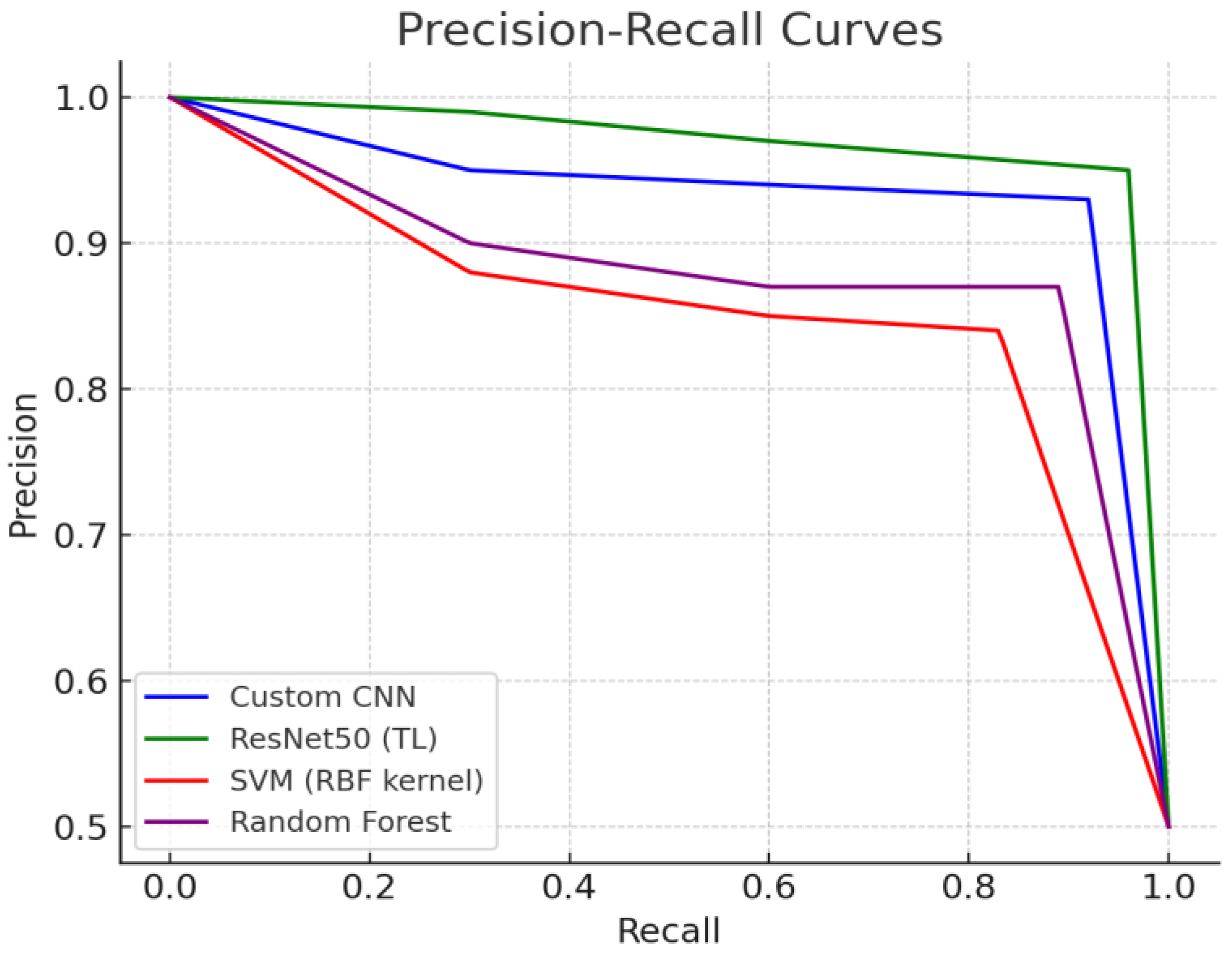
3.4. Comparison of Precision–Recall (PR) Curves
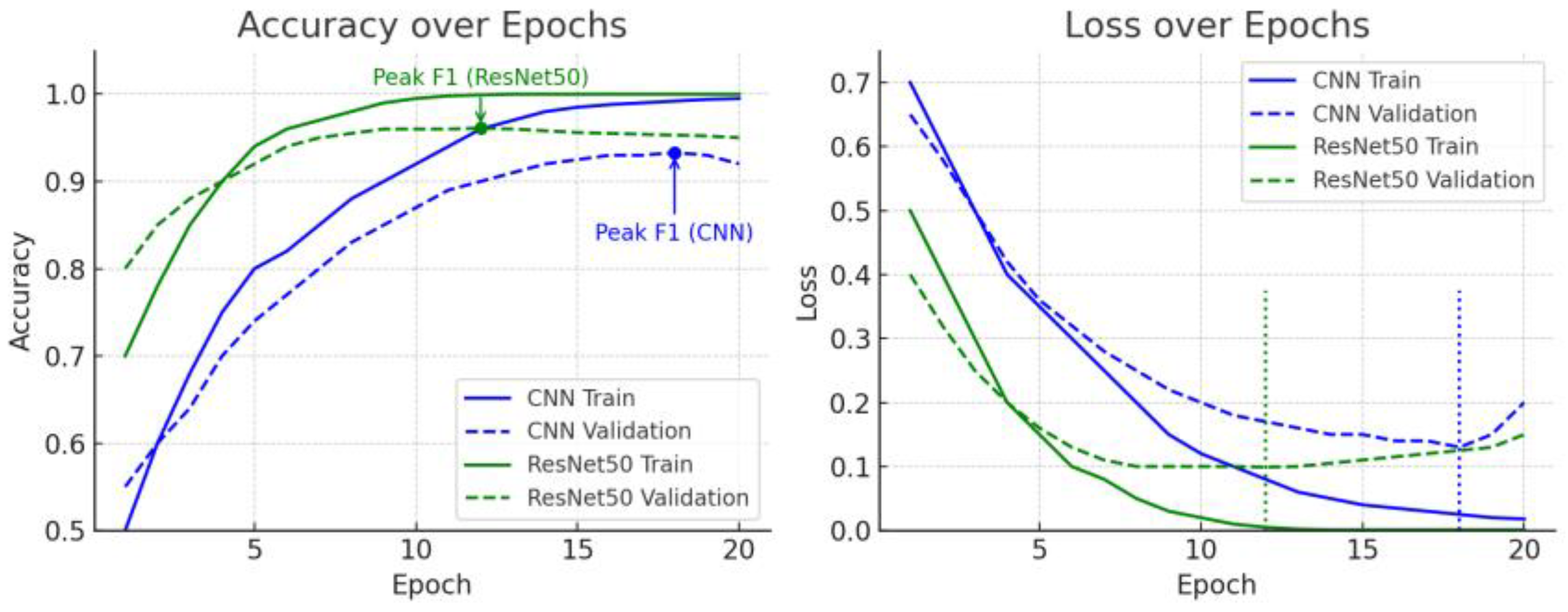
3.5. Training Accuracy and Loss Curve Analysis
3.6. F1 Score Trends and Early Stopping Discussion
4. Discussion
4.1. Model Performance Comparison
4.2. Performance Evaluation Metrics Analysis
4.3. The Effect of Transfer Learning
4.4. Comparison with Previous Studies
4.5. Limitations and Future Research
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasa, S.M.; Islam, M.M.; Talukder, M.A.; Uddin, M.A.; Khalid, M.; Kazi, M.; Kazi, M.Z. Brain tumor classification using fine-tuned transfer learning models on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images. Digit. Health 2024, 10, 20552076241286140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdan, S.A.; Ahmad, R.; Iqbal, N.; Rizwan, A.; Khan, A.N.; Kim, D.-H. An Efficient Multi-Scale Convolutional Neural Network Based Multi-Class Brain MRI Classification for SaMD. Tomography 2022, 8, 1905–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak, S.; Ameer, P.M. Brain tumor classification using deep CNN features via transfer learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 111, 103345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kufel, J.; Bargieł-Łączek, K.; Kocot, S.; Koźlik, M.; Bartnikowska, W.; Janik, M.; Czogalik, Ł.; Dudek, P.; Magiera, M.; Lis, A.; et al. What Is Machine Learning, Artificial Neural Networks and Deep Learning?—Examples of Practical Applications in Medicine. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, R.; Ansari, M.; Agrawal, R.; Anand, R. A Transfer Learning approach for AI-based classification of brain tumors. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2020, 2, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelghoum, R.; Ikhlef, A.; Hameurlaine, A.; Jacquir, S. Transfer learning using convolutional neural network architectures for brain tumor classification from MRI images. In Proceedings of the 16th IFIP International Conference Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations (AIAI), Neos Marmaras, Greece, 5–7 June 2020; pp. 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Huang, W.; Cao, S.; Yang, R.; Yang, W.; Yun, Z.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q. Enhanced Performance of Brain Tumor Classification via Tumor Region Augmentation and Partition. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Gwak, J. Deep Learning-Based Brain Tumor Classification in MRI Images using Ensemble of Deep Features. J. Korea Soc. Comput. Inf. 2021, 26, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, S.; Anjum, N.; Siddiqui, A.B.; Rehman, M.U.; Ramzan, N. Explainable CNN for brain tumor detection and classification through XAI-based key features identification. Brain Inform. 2025, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjoa, E.; Guan, C. A Survey on Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI): Toward Medical XAI. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 32, 4793–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, R.-K.; Pardeshi, M.S. A Survey on Medical Explainable AI (XAI): Recent Progress, Explainability Approach, Human Interaction and Scoring System. Sensors 2022, 22, 8068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, D.; Saha, P.; Kaplun, D.; Sinitca, A.; Sarkar, R. Brain tumor image generation using an aggregation of GAN models with style transfer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpakam, S.; Kumareshan, N. Enhanced brain tumor detection and classification using a deep image recognition generative adversarial network (DIR-GAN). Neural Comput. Appl. 2025, 37, 8731–8758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, S.M.; Sieniek, M.; Godbole, V.; Godwin, J.; Antropova, N.; Ashrafian, H.; Back, T.; Chesus, M.; Corrado, G.S.; Darzi, A.; et al. International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening. Nature 2020, 577, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdusalomov, A.B.; Mukhiddinov, M.; Whangbo, T.K. Brain tumor detection based on deep learning approaches and magnetic resonance imaging. Cancers 2023, 15, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

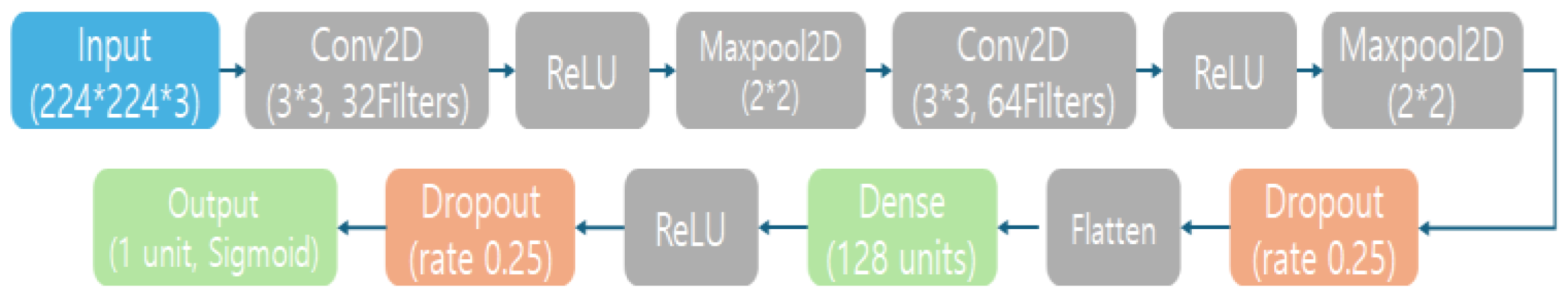

| Layer | Content |
|---|---|
| Input Layer | Accepts a 224 × 224 color MRI image with 3 channels (RGB). |
| Convolutional Layer 1 | 32 filters of size 3 × 3, with ReLU activation. Outputs feature maps of size 224 × 224 × 32 (using same padding to preserve spatial size). |
| Max Pooling Layer 1 | 2 × 2 pooling, which downsamples the feature maps to 112 × 112 × 32 (halving width and height). |
| Convolutional Layer 2 | 64 filters of size 3 × 3, ReLU activation. Outputs feature maps of size 112 × 112 × 64. |
| Max Pooling Layer 2 | 2 × 2 pooling, producing 56 × 56 × 64 output feature maps. |
| Dropout Layer 1 | 25% dropout rate (randomly zeroes 1/4 of the features) to reduce overfitting. Output shape remains 56 × 56 × 64. |
| Flatten Layer | Flattens the 2D feature maps into a 1D feature vector with a length of 200,704 (since 56 × 56 × 64 = 200,704). This prepares the data for the dense layers. |
| Dense (Fully Connected) Layer | 128 neurons with ReLU activation. Transforms the feature vector into a 128-dimensional output. |
| Dropout Layer 2 | 50% dropout rate applied to the 128-dimensional vector for regularization (commonly, 0.5 is used for fully connected layers medium.com). Output remains 128-dimensional. |
| Output Laye | Dense layer with 1 neuron and Sigmoid activation, producing a single probability between 0 and 1. |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | ROC AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Custom CNN | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.93 | 0.95 |
| ResNet50 transfer learning | 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.96 | 0.97 |
| SVM (RBF kernel) | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.88 |
| Random Forest | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, J.; Bang, S.; Jung, Y.; Jo, J. A Study on the Performance Comparison of Brain MRI Image-Based Abnormality Classification Models. Life 2025, 15, 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101614
Jeong J, Bang S, Jung Y, Jo J. A Study on the Performance Comparison of Brain MRI Image-Based Abnormality Classification Models. Life. 2025; 15(10):1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101614
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Jinhyoung, Sohyeon Bang, Yuyeon Jung, and Jaehyun Jo. 2025. "A Study on the Performance Comparison of Brain MRI Image-Based Abnormality Classification Models" Life 15, no. 10: 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101614
APA StyleJeong, J., Bang, S., Jung, Y., & Jo, J. (2025). A Study on the Performance Comparison of Brain MRI Image-Based Abnormality Classification Models. Life, 15(10), 1614. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101614





