Diffusion Basis Restricted Fraction as a Putative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Marker of Neuroinflammation: Histological Evidence, Diagnostic Accuracy, and Translational Potential
Abstract
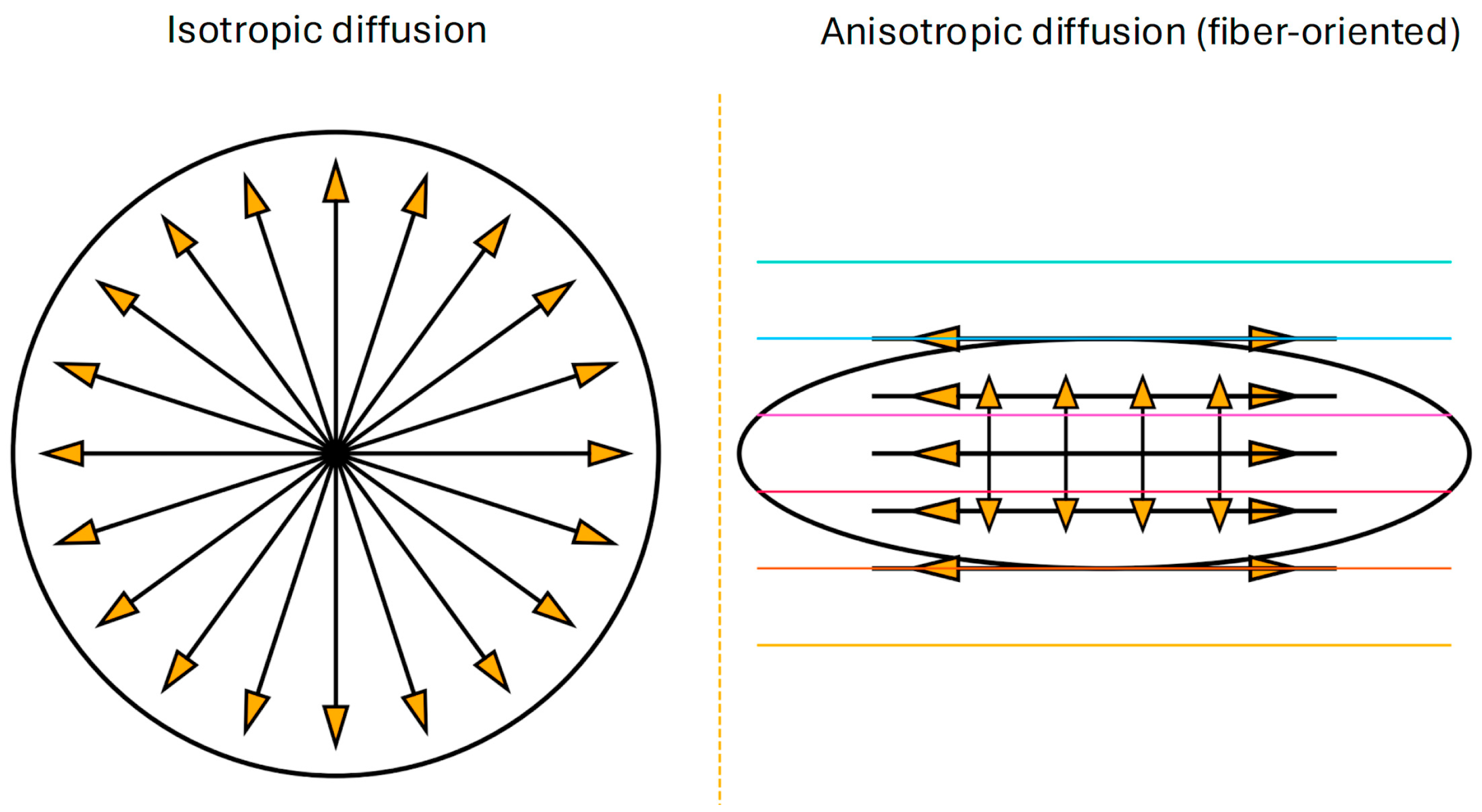
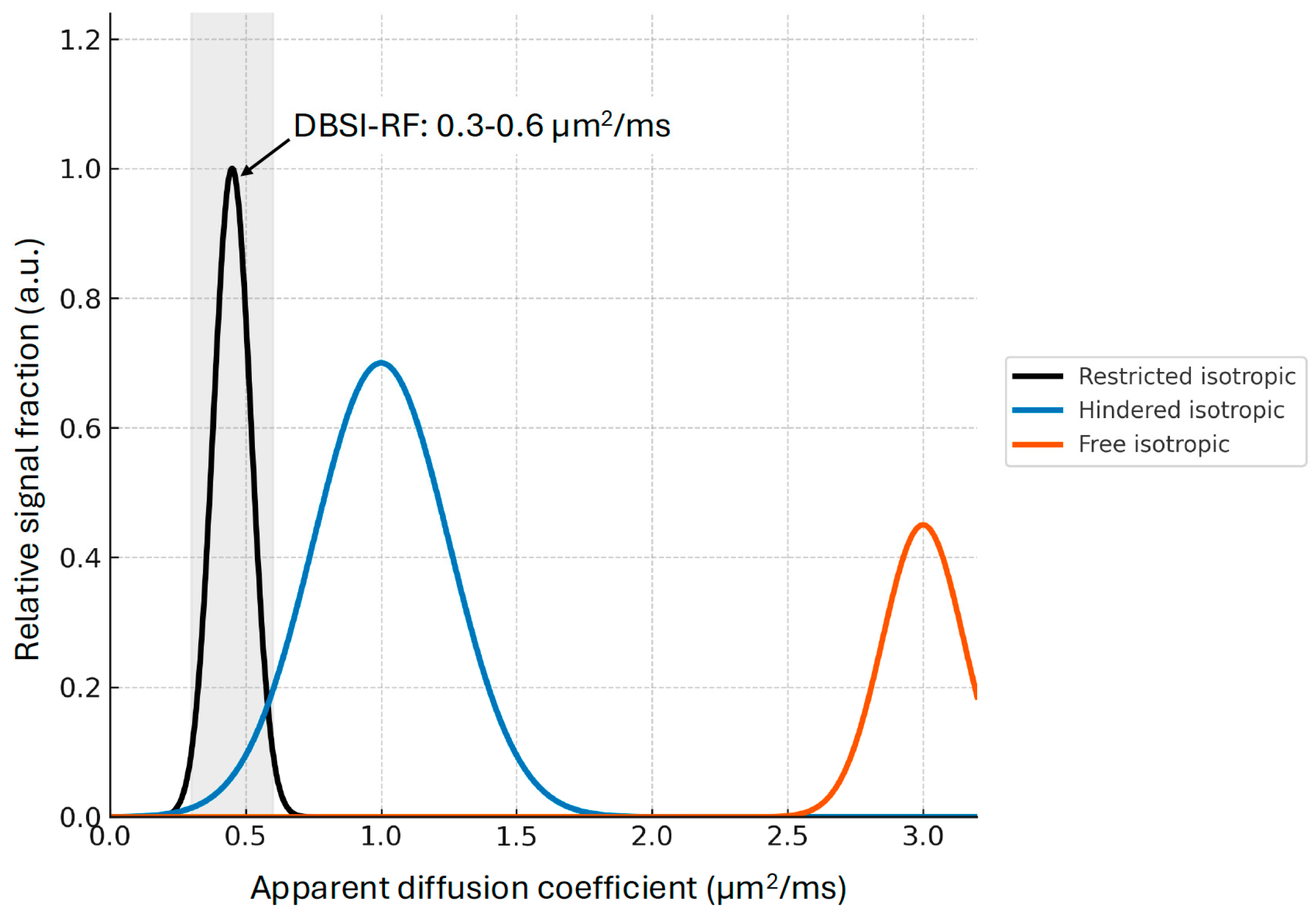
1. Introduction: Diffusion Imaging and Neuroinflammation
2. Methods
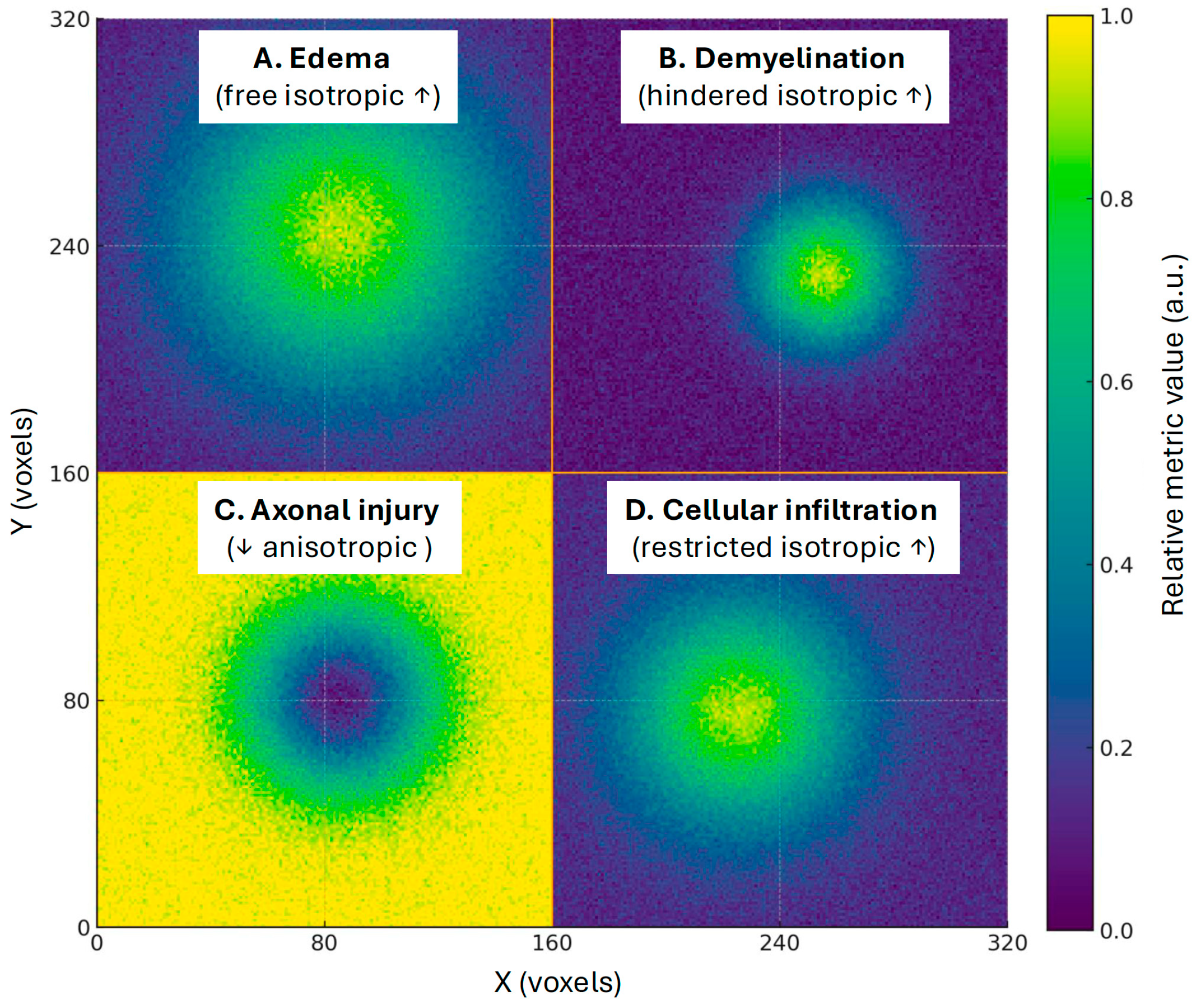
3. Correlation of DBSI-RF with Histopathological Markers
3.1. Animal Models of Inflammation and Demyelination
| Study | Target | Sample | Condition/MRI | Validation | Correlation with Histology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wang et al., 2015 [11] | Axonal loss, myelin loss, inflammation (restricted fraction, fiber fraction, radial diffusivity) | 3 autopsy, 5 controls, 6 multiple sclerosis patients | Multiple sclerosis 3T TIM Trio (Siemens, Munich, Germany ) voxel: 2 × 2 × 2 mm3 | Bielschowsk silver, H&E, Luxol fast blue-PAS; cervical spinal cord | Fiber fraction vs. silver: r = 0.70–0.83; radial diffusivity vs. Luxol fast blue: r = −0.84 to −0.42; restricted fraction vs. H&E: r = 0.84–0.39 |
| Wang et al., 2011 [10] | Cellularity (restricted fraction), axonal/ myelin injury | 5 mice/group | Cuprizone-induced demyelination 4.7T Varian DirectDrive (Palo Alto, California) 0.75 mm slice thickness, 128 × 128 data matrix (70 × 70 µm voxel dimension) | SMI-31, MBP, DAPI; corpus callosum | Cell ratio vs. DAPI: r = 0.76; axial diffusivity vs. SMI-31: r = 0.76; radial diffusivity vs. myelinated axon: r = −0.76 |
| Wang et al., 2014 [27] | Axonal injury, myelin integrity, inflammation (restricted fraction) | 5 mice/group | Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis 4.7T Agilent DirectDrive (Santa Clara, California) 1 mm slice thickness, 128 × 128 data matrix (70 × 70 µm voxel dimension) | DAPI, SMI31, myelin basic protein; spinal cord ventrolateral white matter | Restricted fraction vs. DAPI: r = 0.90; radial diffusivity vs. MBP: r = −0.78; parallel diffusivity vs. SMI31: r = 0.74 |
| Zhan et al., 2018 [30] | Dendritic injury, inflammation (restricted fraction, fiber fraction) | 5 mice/group | Theiler’s murine encephalomyelitis virus-induced hippocampal inflammation 11.74T Agilent DirectDrive (Santa Clara, California) 0.5 mm slice thickness, 192 × 192 data matrix | NeuN, MAP2, IBA1, DAPI; hippocampus | Restricted fraction vs. DAPI: r = 0.81; fiber fraction vs. MAP2: r = 0.79; FA vs. MAP2: r = 0.78; FA vs. DAPI: r = −0.82 |
| Lin et al., 2017 [17] | Axonal loss, demyelination, inflammation | 8 mice | Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis optic neuritis 4.7 T Agilent DirectDrive (Santa Clara, California) 1 mm slice thickness, in-plane resolution: 117 μm2 | SMI312, SMI31, MBP; optic nerve | Restricted fraction vs. DAPI: r = 0.99, fiber fraction vs. SMI312: r = 0.85 |
3.2. Animal Models of TBI
3.3. Autopsy from Human Spinal Cord in Inflammatory Demyelination
3.4. Neurodegenerative Diseases
3.5. Summary of Histopathological Evidence
4. Diagnostic Performance and Predictive Value
4.1. Lesion Identification, Classification, and Outcome in MS
4.2. Obesity and Neuroinflammation
4.3. Neuropsychiatric Disorders
4.4. Summary of Diagnostic Performance and Predictive Value
5. Strengths and Limitations of DBSI-RF Measurements
5.1. Strengths
5.2. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Aβ | Amyloid-beta |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DBSI-RF | Diffusion basis spectrum imaging–derived restricted fraction |
| DTI | Diffusion tensor imaging |
| FWI | Free-water imaging |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MS | Multiple sclerosis |
| NODDI | Neurite orientation dispersion and density |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| TBI | Traumatic brain injury |
| RF | Restricted fraction |
| SANDI | Soma and neurite density image |
| SANRA | Scale for the Assessment of Narrative Review Articles |
References
- Almulla, A.F.; Maes, M. Peripheral Immune-Inflammatory Pathways in Major Depressive Disorder, Bipolar Disorder, and Schizophrenia: Exploring Their Potential as Treatment Targets. CNS Drugs 2025, 39, 739–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmal, M.; Paul, J.K.; Prima, F.S.; Haque, A.; Meem, M.; Ghosh, A. Microglial dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: Mechanisms, emerging therapies, and future directions. Exp. Neurol. 2025, 392, 115374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Or, A.; Li, R. Cellular immunology of relapsing multiple sclerosis: Interactions, checks, and balances. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhurandhar, Y.; Tomar, S.; Das, A.; Prajapati, J.L.; Singh, A.P.; Bodake, S.H.; Namdeo, K.P. Chronic inflammation in obesity and neurodegenerative diseases: Exploring the link in disease onset and progression. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2025, 52, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obukohwo, O.M.; Oreoluwa, O.A.; Andrew, U.O.; Williams, U.E. Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in traumatic brain injury: A review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Liu, A.; Yan, J. Potential targets of microglia in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: Mechanism and therapeutic implications. Neural Regen. Res. 2026, 21, 1497–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caranova, M.; Soares, J.F.; Batista, S.; Castelo-Branco, M.; Duarte, J.V. A systematic review of microstructural abnormalities in multiple sclerosis detected with NODDI and DTI models of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 104, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, W. Editorial: Novel imaging technologies for neuroinflammation. Front. Neurol. 2023, 13, 1125045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Picker, L.J.; Morrens, M.; Branchi, I.; Haarman, B.C.M.; Terada, T.; Kang, M.S.; Boche, D.; Tremblay, M.E.; Leroy, C.; Bottlaender, M.; et al. TSPO PET brain inflammation imaging: A transdiagnostic systematic review and meta-analysis of 156 case-control studies. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 113, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Haldar, J.P.; Yeh, F.C.; Xie, M.; Sun, P.; Tu, T.W.; Trinkaus, K.; Klein, R.S.; Cross, A.H.; et al. Quantification of increased cellularity during inflammatory demyelination. Brain 2011, 134, 3590–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, P.; Wang, Q.; Trinkaus, K.; Schmidt, R.E.; Naismith, R.T.; Cross, A.H.; Song, S.K. Differentiation and quantification of inflammation, demyelination and axon injury or loss in multiple sclerosis. Brain 2015, 138, 1223–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooliscroft, L.; Salter, A.; Adusumilli, G.; Levasseur, V.A.; Sun, P.; Lancia, S.; Perantie, D.C.; Trinkaus, K.; Naismith, R.T.; Song, S.K.; et al. Diffusion basis spectrum imaging and diffusion tensor imaging predict persistent black hole formation in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2024, 84, 105494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Peterson, D.J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Grabowski, T.J.; Li, W.; Madhyastha, T.M. Empirical Comparison of Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging and Diffusion Basis Spectrum Imaging Using the Same Acquisition in Healthy Young Adults. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.H.; Johanns, T.M.; Roberts, K.F.; Tao, Y.; Luo, J.; Ye, Z.; Sun, P.; Blum, J.; Lin, T.-H.; Song, S.-K.; et al. Diffusion basis spectrum imaging as an adjunct to conventional MRI leads to earlier diagnosis of high-grade glioma tumor progression versus treatment effect. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2023, 5, vdad050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, R.G.; Martin, P.R.; Ali, F.; Clark, H.M.; Duffy, J.R.; Utianski, R.L.; Botha, H.; Machulda, M.M.; Dickson, D.W.; Josephs, K.A.; et al. Diffusion tractography of superior cerebellar peduncle and dentatorubrothalamic tracts in two autopsy confirmed progressive supranuclear palsy variants: Richardson syndrome and the speech-language variant. NeuroImage Clin. 2022, 35, 103030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, A.H.; Song, S.K. A new imaging modality to non-invasively assess multiple sclerosis pathology. J. Neuroimmunol. 2017, 304, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.H.; Chiang, C.W.; Perez-Torres, C.J.; Sun, P.; Wallendorf, M.; Schmidt, R.E.; Cross, A.H.; Song, S.K. Diffusion MRI quantifies early axonal loss in the presence of nerve swelling. J. Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, A.; Murphy, T.; Strain, J.; Rutlin, J.; Sun, P.; Neyman, O.; Sreevalsan, N.; Shimony, J.S.; Ances, B.M.; Song, S.-K.; et al. Neuroinflammation and White Matter Alterations in Obesity Assessed by Diffusion Basis Spectrum Imaging. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, A.; Sun, P.; Schmidt, R.E.; Trinkaus, K.; Naismith, R.T.; Song, S.K.; Cross, A.H. Histopathological correlation of diffusion basis spectrum imaging metrics of a biopsy-proven inflammatory demyelinating brain lesion: A brief report. Mult. Scler. 2019, 25, 1937–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-C.; Lavadi, R.S.; Sauerbeck, A.D.; Wallendorf, M.; Kummer, T.T.; Song, S.-K.; Lin, T.-H. Diffusion basis spectrum imaging detects subclinical traumatic optic neuropathy in a closed-head impact mouse model of traumatic brain injury. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1269817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strain, J.F.; Burdo, T.H.; Song, S.K.; Sun, P.; El-Ghazzawy, O.; Nelson, B.; Westerhaus, E.; Baker, L.; Vaida, F.; Ances, B.M. Diffusion Basis Spectral Imaging Detects Ongoing Brain Inflammation in Virologically Well-Controlled HIV+ Patients. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2017, 76, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, M.; Sato, N.; Matsuda, H.; Maikusa, N.; Shigemoto, Y.; Sone, D.; Yamao, T.; Ogawa, M.; Kimura, Y.; Chiba, E.; et al. Free water derived by multi-shell diffusion MRI reflects tau/neuroinflammatory pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 8, e12356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nir, T.M.; Villalón-Reina, J.E.; Salminen, L.E.; Haddad, E.; Zheng, H.; Thomopoulos, S.I.; Jack, C.R.; Weiner, M.W.; Thompson, P.M.; Jahanshad, N.; et al. Cortical microstructural associations with CSF amyloid and pTau. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavi, S.; Palombo, M.; Zacà, D.; Tazza, F.; Lapucci, C.; Castellan, L.; Costagli, M.; Inglese, M. Mapping tissue microstructure across the human brain on a clinical scanner with soma and neurite density image metrics. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2023, 44, 4792–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, J.R.; Morgan, C.A.; Dell’Acqua, F.; Sundram, F.; Hoeh, N.R.; Muthukumaraswamy, S.; Lin, J.C. Mapping Neuroinflammation With Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Randomized Crossover Study. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baethge, C.; Goldbeck-Wood, S.; Mertens, S. SANRA—A scale for the quality assessment of narrative review articles. Res. Integr. Peer Rev. 2019, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cusick, M.F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, P.; Libbey, J.E.; Trinkaus, K.; Fujinami, R.S.; Song, S.K. Diffusion basis spectrum imaging detects and distinguishes coexisting subclinical inflammation, demyelination and axonal injury in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis mice. NMR Biomed. 2014, 27, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Lin, T.-H.; Zhan, J.; Lai, S.; Song, C.; Sun, P.; Ye, Z.; Wallendorf, M.; George, A.; Cross, A.H.; et al. Diffusion basis spectrum imaging measures anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects of fingolimod on murine optic neuritis. NeuroImage Clin. 2021, 31, 102732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.H.; Zhan, J.; Song, C.; Wallendorf, M.; Sun, P.; Niu, X.; Yang, R.; Cross, A.H.; Song, S.K. Diffusion Basis Spectrum Imaging Detects Axonal Loss After Transient Dexamethasone Treatment in Optic Neuritis Mice. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 592063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Lin, T.H.; Libbey, J.E.; Sun, P.; Ye, Z.; Song, C.; Wallendorf, M.; Gong, H.; Fujinami, R.S.; Song, S.K. Diffusion Basis Spectrum and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Detect Hippocampal Inflammation and Dendritic Injury in a Virus-Induced Mouse Model of Epilepsy. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavadi, R.S.; Utt, K.L.; Housley, S.N.; Nouduri, S.; Lin, T.H.; Blum, J.; Pennicooke, B.H.; Song, S.K.; Agarwal, N. Diffusion basis spectrum imaging detects axonal injury in the optic nerve following traumatic brain injury. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2025, 122, 110451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taquet, M.; Jankovski, A.; Rensonnet, G.; Jacobs, D.; des Rieux, A.; Macq, B.; Warfield, S.K.; Scherrer, B. Extra-axonal restricted diffusion as an in-vivo marker of reactive microglia. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Sutphen, C.L.; Cruchaga, C.; Blazey, T.; Gordon, B.A.; Su, Y.; Chen, C.; Shimony, J.S.; et al. Quantification of white matter cellularity and damage in preclinical and early symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 22, 101767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wu, W.; Xu, H.; Flores, S.; Hobbs, D.A.; Perrin, R.J.; Franklin, E.E.; Schindler, S.E.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; Morris, J.C.; et al. Imaging and quantifying microglial activation in vivo and ex vivo using diffusion MRI—with validation by immunohistochemistry. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, e079302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criswell, S.R.; Nielsen, S.S.; Faust, I.M.; Shimony, J.S.; White, R.L.; Lenox-Krug, J.; Racette, B.A. Neuroinflammation and white matter alterations in occupational manganese exposure assessed by diffusion basis spectrum imaging. NeuroToxicology 2023, 97, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.C., Jr.; Gubert, P.; Villas Boas, G.R.; Meirelles Paes, M.; Santamaría, A.; Lee, E.; Tinkov, A.A.; Bowman, A.B.; Aschner, M. Manganese-induced neurodegenerative diseases and possible therapeutic approaches. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2020, 20, 1109–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Sun, P.; George, A.; Zeng, X.; Li, M.; Lin, T.-H.; Ye, Z.; Wei, X.; Jiang, X.; Song, S.-K.; et al. Diffusion basis spectrum imaging detects pathological alterations in substantia nigra and white matter tracts with early-stage Parkinson’s disease. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 9109–9119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; George, A.; Perantie, D.C.; Trinkaus, K.; Ye, Z.; Naismith, R.T.; Song, S.K.; Cross, A.H. Diffusion basis spectrum imaging provides insights into MS pathology. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2020, 7, e655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; George, A.; Wu, A.T.; Niu, X.; Lin, J.; Adusumilli, G.; Naismith, R.T.; Cross, A.H.; Sun, P.; Song, S.K. Deep learning with diffusion basis spectrum imaging for classification of multiple sclerosis lesions. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2020, 7, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavasour, I.M.; Sun, P.; Graf, C.; Yik, J.T.; Kolind, S.H.; Li, D.K.; Tam, R.; Sayao, A.L.; Schabas, A.; Devonshire, V.; et al. Characterization of multiple sclerosis neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration with relaxation and diffusion basis spectrum imaging. Mult. Scler. 2022, 28, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.A.; Samara, A.; Ray, M.K.; Rutlin, J.; Raji, C.A.; Shimony, J.S.; Sun, P.; Song, S.K.; Hershey, T.; Eisenstein, S.A. Childhood obesity is linked to putative neuroinflammation in brain white matter, hypothalamus, and striatum. Cereb. Cortex Commun. 2023, 4, tgad007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, M.; Malik, I.A.; Methi, A.; Cortés Silva, J.A.; Fey, D.; Wirths, O.; Fischer, A.; Wilting, J.; von Arnim, C.A.F. Cognitive decline and neuroinflammation in a mouse model of obesity: An accelerating role of ageing. Brain Behav. Immun. 2025, 125, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruppert, Z.; Neuperger, P.; Rákóczi, B.; Gémes, N.; Dukay, B.; Hajdu, P.; Péter, M.; Balogh, G.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Vígh, L.; et al. Characterization of obesity-related diseases and inflammation using single cell immunophenotyping in two different diet-induced obesity models. Int. J. Obes. 2024, 48, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Du, X.; Yan, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Prediction of cognitive conversion within the Alzheimer’s disease continuum using deep learning. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2025, 17, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samara, A.; Li, Z.; Rutlin, J.; Raji, C.A.; Sun, P.; Song, S.K.; Hershey, T.; Eisenstein, S.A. Nucleus accumbens microstructure mediates the relationship between obesity and eating behavior in adults. Obesity 2021, 29, 1328–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, M.; Yu, G.Z.; Mian, A.; Cramer, A.; Meysami, S.; Merrill, D.A.; Samara, A.; Eisenstein, S.A.; Hershey, T.; Babulal, G.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation: A Modifiable Pathway Linking Obesity, Alzheimer’s disease, and Depression. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2023, 31, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong-Guerra, M.; Calfio, C.; Maccioni, R.B.; Rojo, L.E. Revisiting the neuroinflammation hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease: A focus on the druggability of current targets. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1161850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.; Tripathi, A.; Pillai, A. Inflammatory Pathways in Psychiatric Disorders: The case of Schizophrenia and Depression. Curr. Behav. Neurosci. Rep. 2020, 7, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Ju, T.; Zeng, D.; Duan, F.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, W. “Inflamed” depression: A review of the interactions between depression and inflammation and current anti-inflammatory strategies for depression. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 207, 107322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Christensen, J.; Liu, J.; Fagan, A.M.; Cairns, N.J.; Ances, B.; Morris, J.C.; Benzinger, T.L.S. IC-P-169: Imaging Marker of Neuroinflammation Predicts Disease Progression in Alzheimer Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016, 12, P123–P124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, A.; Yang, Y.; Schilling, K.G.; Shashikumar, N.; Moore, E.; Dumitrescu, L.; Pechman, K.R.; Landman, B.A.; Gifford, K.A.; Hohman, T.J.; et al. Free-water: A promising structural biomarker for cognitive decline in aging and mild cognitive impairment. Imaging Neurosci. 2024, 2, imag–2–00293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Rutlin, J.; Eisenstein, S.A.; Wang, Y.; Barch, D.M.; Hershey, T.; Bogdan, R.; Bijsterbosch, J.D. Neuroinflammation in the Amygdala Is Associated With Recent Depressive Symptoms. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. 2023, 8, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamah, D.; Patel, A.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q. Diffusion basis spectrum imaging of white matter in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Brain Imaging Behav. 2025. Epub ahead of printing. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, T.; Ji, C.; Wei, W.; Wu, G.; Jin, K.; Jiang, G. Cortical-cerebellar circuits changes in preschool ASD children by multimodal MRI. Cereb. Cortex 2024, 34, bhae090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, T.; Li, W.; Wei, W.; Wu, G.; Jiang, G.; Gao, X.; Jin, K. Limbic/paralimbic connection weakening in preschool autism-spectrum disorder based on diffusion basis spectrum imaging. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2025, 61, e16615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaszás, A.; Kelemen, O.; Kéri, S. Magnetic resonance imaging signatures of neuroinflammation in major depressive disorder with religious and spiritual problems. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kéri, S.; Kelemen, O. Signatures of neuroinflammation in the hippocampus and amygdala in individuals with religious or spiritual problem. Relig. Brain Behav. 2025, 15, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kéri, S.; Kancsev, A.; Kelemen, O. Algorithm-Based Modular Psychotherapy Alleviates Brain Inflammation in Generalized Anxiety Disorder. Life 2024, 14, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Jing, H.; Utt, K.L.; Vetter, J.M.; Weimholt, R.C.; Bullock, A.D.; Klim, A.P.; Bergeron, K.A.; Frankel, J.K.; Smith, Z.L.; et al. An Artificial Intelligence Model Using Diffusion Basis Spectrum Imaging Metrics Accurately Predicts Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2025, 213, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Price, R.L.; Liu, X.; Lin, J.; Yang, Q.; Sun, P.; Wu, A.T.; Wang, L.; Han, R.H.; Song, C.; et al. Diffusion Histology Imaging Combining Diffusion Basis Spectrum Imaging (DBSI) and Machine Learning Improves Detection and Classification of Glioblastoma Pathology. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5388–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, D.S.; Veraart, J.; Jelescu, I.O.; Fieremans, E. Rotationally-invariant mapping of scalar and orientational metrics of neuronal microstructure with diffusion MRI. Neuroimage 2018, 174, 518–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelescu, I.O.; Veraart, J.; Fieremans, E.; Novikov, D.S. Degeneracy in model parameter estimation for multi-compartmental diffusion in neuronal tissue. NMR Biomed. 2016, 29, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, R.G.; Martin, P.R.; Utianski, R.L.; Duffy, J.R.; Clark, H.M.; Botha, H.; Machulda, M.M.; Josephs, K.A.; Whitwell, J.L. Diffusion tensor imaging-based multi-fiber tracking reconstructions can regionally differentiate phonetic versus prosodic subtypes of progressive apraxia of speech. Cortex 2024, 171, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, R.G.; Youssef, H.; Pham, N.T.T.; Ali, F.; Clark, H.M.; Stierwalt, J.; Stephens, Y.; Machulda, M.M.; Josephs, K.A.; Whitwell, J.L. Brain Microstructure Interrogation by Diffusion Tensor and Kurtosis Imaging in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Subtypes. J. Neuroimaging 2025, 35, e70062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Bossuyt, P.M. QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 3T MRI scanner MPRAGE (magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition gradient echo) 3D sagittal acquisition FOV (square field of view) = 5256 mm Voxel: 1 × 1 × 1 mm3 TI (inversion time) = 5900 ms TE (echo time, shortest) = 3.16 flip angle: 9 degrees no fat suppression full k space acquisition time: 6 min and 50 s acceleration factor: 2 multi-shell approach b1 = 1000 s/mm2 b2 = 2000 s/mm2 2 × 2 × 2 mm3 50 diffusion encoding directions for each shell corrections for head motion, outlier slices, and gradient distortion |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kéri, S. Diffusion Basis Restricted Fraction as a Putative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Marker of Neuroinflammation: Histological Evidence, Diagnostic Accuracy, and Translational Potential. Life 2025, 15, 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101599
Kéri S. Diffusion Basis Restricted Fraction as a Putative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Marker of Neuroinflammation: Histological Evidence, Diagnostic Accuracy, and Translational Potential. Life. 2025; 15(10):1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101599
Chicago/Turabian StyleKéri, Szabolcs. 2025. "Diffusion Basis Restricted Fraction as a Putative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Marker of Neuroinflammation: Histological Evidence, Diagnostic Accuracy, and Translational Potential" Life 15, no. 10: 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101599
APA StyleKéri, S. (2025). Diffusion Basis Restricted Fraction as a Putative Magnetic Resonance Imaging Marker of Neuroinflammation: Histological Evidence, Diagnostic Accuracy, and Translational Potential. Life, 15(10), 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101599






