The 15th Anniversary of Life—Sepsis Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Early Clinical Trials in Sepsis
3. Reasons for Failure: The Key Role of Heterogeneity
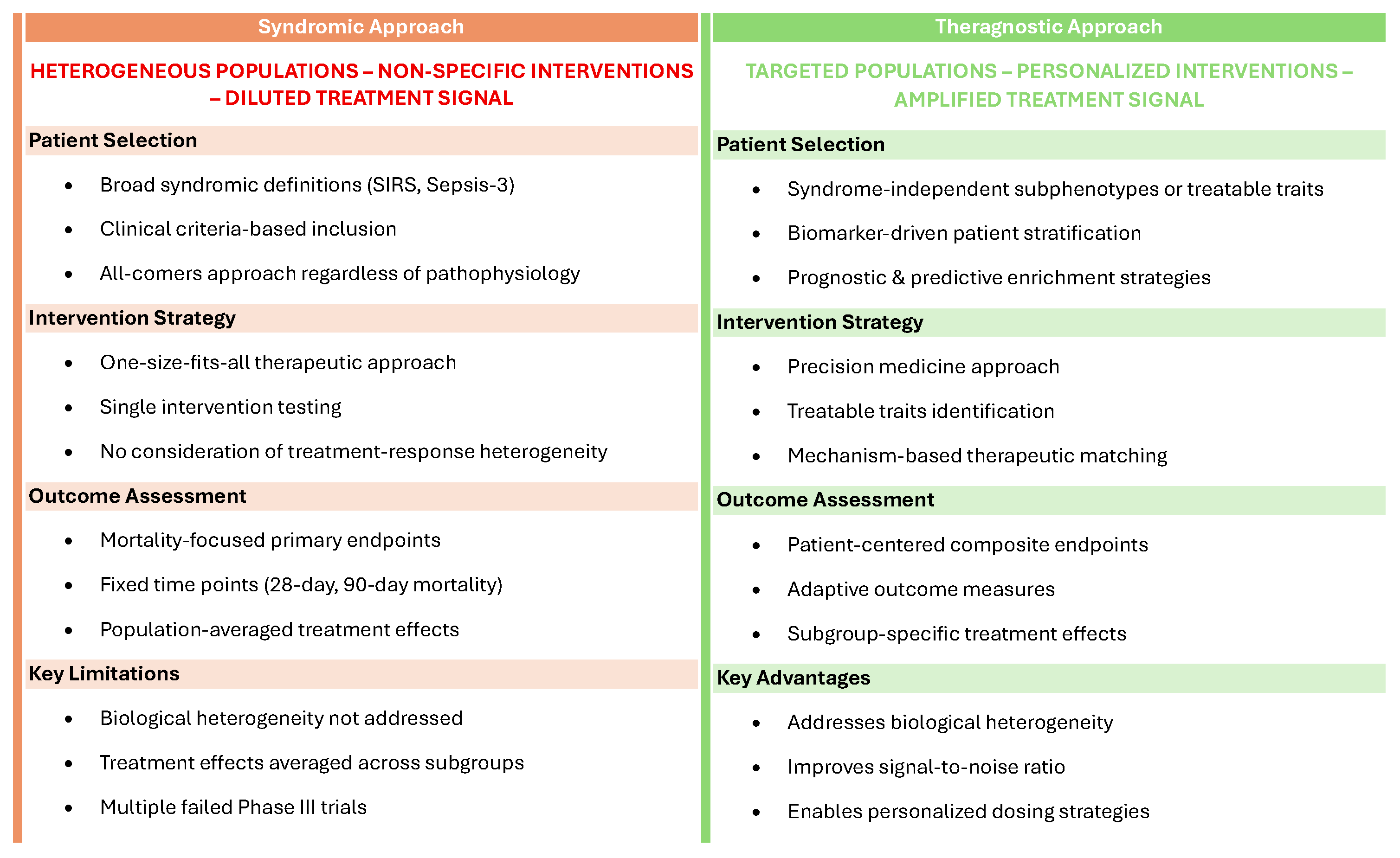
4. Subphenotyping in Sepsis
4.1. Clinical Approaches
4.2. Omics-Based Approaches
5. Using Subphenotyping for Trial Enrichment to Reduce Population Heterogeneity
5.1. Prognostic Enrichment
5.2. Predictive Enrichment
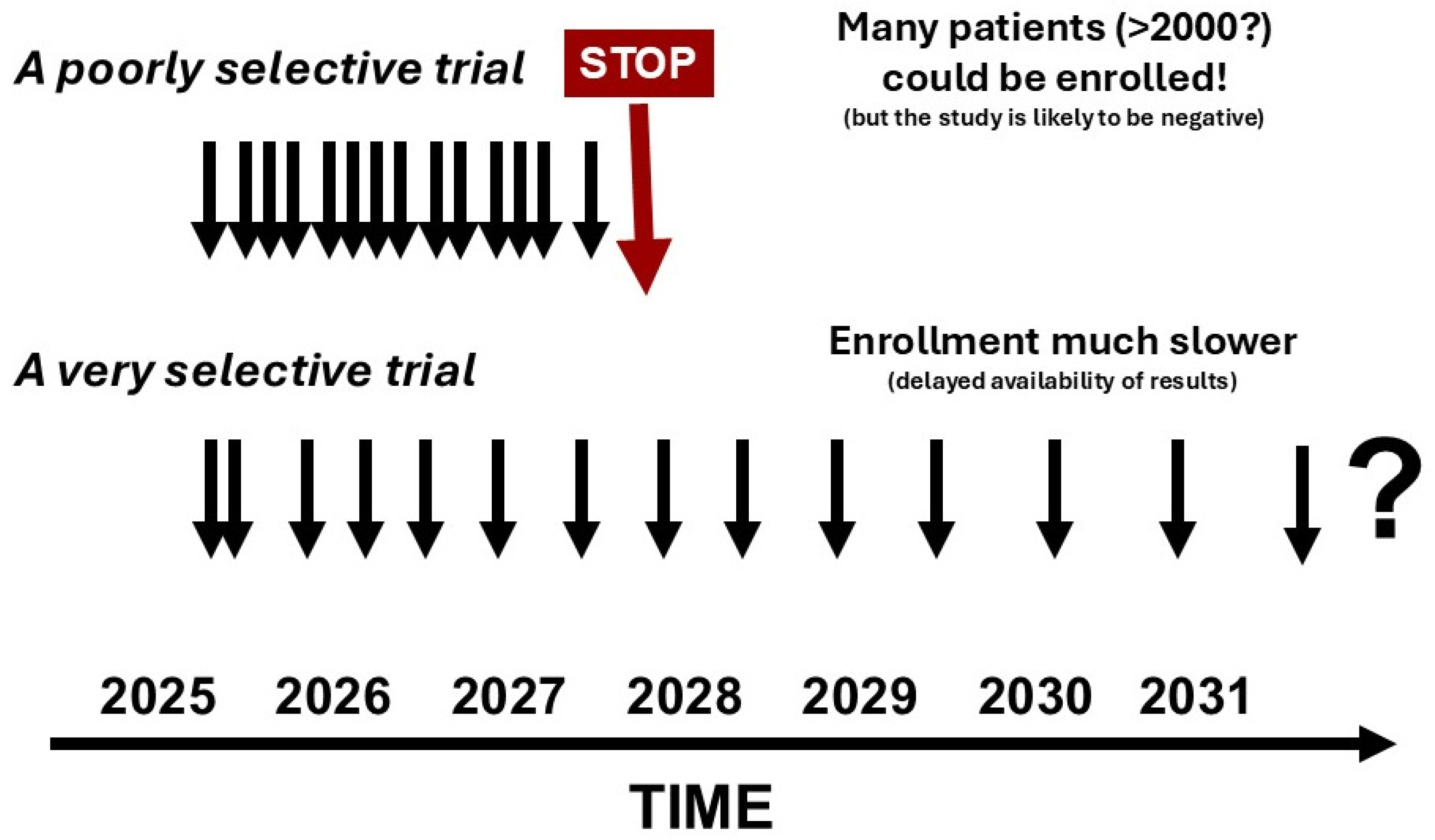
6. Challenges in Implementing Trial Enrichment
7. Changing Clinical Trial Design
8. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rudd, K.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Agesa, K.M.; Shackelford, K.A.; Tsoi, D.; Kievlan, D.R.; Colombara, D.V.; Ikuta, K.S.; Kissoon, N.; Finfer, S.; et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, E.J.; Fisher, C.J., Jr.; Sprung, C.L.; Straube, R.C.; Sadoff, J.C.; Foulke, G.E.; Wortel, C.H.; Fink, M.P.; Dellinger, R.P.; Teng, N.N.; et al. Treatment of gram-negative bacteremia and septic shock with HA-1A human monoclonal antibody against endotoxin. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The HA-1A Sepsis Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, E.; Anzueto, A.; Gutierrez, G.; Tessler, S.; San Pedro, G.; Wunderink, R.; Dal Nogare, A.; Nasraway, S.; Berman, S.; Cooney, R.; et al. Double-blind randomised controlled trial of monoclonal antibody to human tumor necrosis factor in treatment of septic shock. Lancet 1998, 351, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, C.J.; Dhainaut, J.F.; Opal, S.M.; Pribble, J.P.; Balk, R.A.; Slotman, G.J.; Iberti, T.J.; Rackow, E.C.; Shapiro, M.J.; Greenman, R.L.; et al. Recombinant human interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in the treatment of patients with sepsis syndrome. JAMA 1994, 271, 1836–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.; Lorente, J.A.; Steingrub, J.; Bakker, J.; McLuckie, A.; Willatts, S.; Brockway, M.; Anzueto, A.; Holzapfel, L.; Breen, D.; et al. Multiple-center, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor 546C88: Effect on survival in patients with septic shock. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, V.M.; Thompson, B.T.; Barie, P.S.; Dhainaut, J.F.; Douglas, I.S.; Finfer, S.; Gardlund, B.; Marshall, J.C.; Rhodes, A.; Artigas, A.; et al. Drotrecogin alfa (activated) in adults with septic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2055–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, R.C.; Balk, R.A.; Cerra, F.B.; Dellinger, R.P.; Fein, A.M.; Knaus, W.A.; Schein, R.M.; Sibbald, W.J. Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Chest 1992, 101, 1644–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.M.; Fink, M.P.; Marshall, J.C.; Abraham, E.; Angus, D.; Cook, D.; Cohen, J.; Opal, S.M.; Vincent, J.L.; Ramsay, G. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS International Sepsis Definitions Conference. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L.; van der Poll, T.; Marshall, J.C. The end of “one size fits all” sepsis therapies: Toward an individualized approach. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, A.C.; Alipanah-Lechner, N.; Bos, L.D.; Dianti, J.; Diaz, J.V.; Finfer, S.; Fujii, T.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Goligher, E.C.; Gong, M.N.; et al. From ICU syndromes to ICU subphenotypes: Consensus report and recommendations for developing precision medicine in the ICU. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 210, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, C.W.; Kennedy, J.N.; Wang, S.; Chang, C.H.; Elliott, C.F.; Xu, Z.; Berry, S.; Clermont, G.; Cooper, G.; Gomez, H.; et al. Derivation, validation, and potential treatment implications of novel clinical phenotypes for sepsis. JAMA 2019, 321, 2003–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soussi, S.; Sharma, D.; Juni, P.; Lebovic, G.; Brochard, L.; Marshall, J.C.; Lawler, P.R.; Herridge, M.; Ferguson, N.; Del Sorbo, L.; et al. Identifying clinical subtypes in sepsis-survivors with different one-year outcomes: A secondary latent class analysis of the FROG-ICU cohort. Crit. Care 2022, 26, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruse, N.; Motos, A.; van Amstel, R.; de Bie, E.; Kooistra, E.J.; Jansen, A.; van Lier, D.; Kennedy, J.; Schwarzkopf, D.; Thomas-Ruddel, D.; et al. Clinical phenotyping uncovers heterogeneous associations between corticosteroid treatment and survival in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Intensive Care Med. 2024, 50, 1884–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.P.; Bray, B.C.; Chou, S.H.; Burns, R.; Kowalkowski, M.A. Clinical subtypes of sepsis survivors predict readmission and mortality after hospital discharge. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2022, 19, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Goyal, H.; Mo, L.; Hong, Y. Identification of subclasses of sepsis that showed different clinical outcomes and responses to amount of fluid resuscitation: A latent profile analysis. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, F.; Peng, Z. Application of machine learning for clinical subphenotype identification in sepsis. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2022, 11, 1949–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, E.E.; Burnham, K.L.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Humburg, P.; Hutton, P.; Mills, T.C.; Rautanen, A.; Gordon, A.C.; Garrard, C.; Hill, A.V.S.; et al. Genomic landscape of the individual host response and outcomes in severe sepsis. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antcliffe, D.B.; Burnham, K.L.; Al-Beidh, F.; Santhakumaran, S.; Brett, S.J.; Hinds, C.J.; Ashby, D.; Knight, J.C.; Gordon, A.C. Transcriptomic signatures in sepsis and a differential response to steroids: From the VANISH randomized trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 199, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scicluna, B.P.; van Vught, L.A.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Wiewel, M.A.; Davenport, E.E.; Burnham, K.L.; Nurnberg, P.; Schultz, M.J.; Horn, J.; Cremer, O.L.; et al. Classification of patients with sepsis according to blood genomic endotype: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, T.E.; Azad, T.D.; Donato, M.; Haynes, W.A.; Perumal, T.M.; Henao, R.; Bermejo-Martin, J.F.; Almansa, R.; Tamayo, E.; Howrylak, J.A.; et al. Unsupervised analysis of transcriptomics in bacterial sepsis across multiple datasets reveals three robust clusters. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, A.J.; Leligdowicz, A.; Contrepois, K.; Jauregui, A.; Vessel, K.; Deiss, T.J.; Belzer, A.; Liu, T.; Lippi, M.; Ke, S.; et al. Plasma metabolites in early sepsis identify distinct clusters defined by plasma lipids. Crit. Care Explor. 2021, 3, e0478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antcliffe, D.B.; Harte, E.; Hussain, H.; Jimenez, B.; Browning, C.; Gordon, A.C. Metabolic septic shock sub-phenotypes, stability over time and association with clinical outcome. Intensive Care Med. 2025, 51, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. Enrichment Strategies for Clinical Trials to Support Determination of Effectiveness of Human Drugs and Biological Products—Guidance for Industry. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/enrichment-strategies-clinical-trials-support-approval-human-drugs-and-biological-products (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- Stanski, N.L.; Wong, H.R. Prognostic and predictive enrichment in sepsis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panacek, E.A.; Marshall, J.C.; Albertson, T.E.; Johnson, D.H.; Johnson, S.; MacArthur, R.D.; Miller, M.; Barchuk, W.T.; Fischkoff, S.; Kaul, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of the monoclonal anti-tumor necrosis factor antibody F(ab′)2 fragment afelimomab in patients with severe sepsis and elevated interleukin-6 levels. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, 2173–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, J.E.; Docherty, A.B. It ain’t what you do (it’s the way that you do it): Modulating the host response in sepsis. Anaesthesia 2024, 79, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslove, D.M.; Tang, B.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Lawler, P.R.; Angus, D.C.; Baillie, J.K.; Baron, R.M.; Bauer, M.; Buchman, T.G.; Calfee, C.S.; et al. Redefining critical illness. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venet, F.; Textoris, J.; Blein, S.; Rol, M.L.; Bodinier, M.; Canard, B.; Cortez, P.; Meunier, B.; Tan, L.K.; Tipple, C.; et al. Immune profiling demonstrates a common immune signature of delayed acquired immunodeficiency in patients with various etiologies of severe injury. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 50, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Mindrinos, M.N.; Seok, J.; Cuschieri, J.; Cuenca, A.G.; Gao, H.; Hayden, D.L.; Hennessy, L.; Moore, E.E.; Minei, J.P.; et al. A genomic storm in critically injured humans. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 2581–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neyton, L.P.A.; Zheng, X.; Skouras, C.; Doeschl-Wilson, A.; Gutmann, M.U.; Uings, I.; Rao, F.V.; Nicolas, A.; Marshall, C.; Wilson, L.M.; et al. Molecular patterns in acute pancreatitis reflect generalizable endotypes of the host response to systemic injury in humans. Ann. Surg. 2022, 275, e453–e462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rios-Toro, J.J.; Marquez-Coello, M.; Garcia-Alvarez, J.M.; Martin-Aspas, A.; Rivera-Fernandez, R.; Saez de Benito, A.; Giron-Gonzalez, J.A. Soluble membrane receptors, interleukin 6, procalcitonin and C reactive protein as prognostic markers in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, B.; Lambden, S.; Fivez, T.; Gibot, S.; Derive, M.; Grouin, J.M.; Salcedo-Magguilli, M.; Lemarie, J.; De Schryver, N.; Jalkanen, V.; et al. Prospective evaluation of the efficacy, safety, and optimal biomarker enrichment strategy for nangibotide, a TREM-1 inhibitor, in patients with septic shock (ASTONISH): A double-blind, randomised, controlled, phase 2b trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.L.; Francois, B.; Zabolotskikh, I.; Daga, M.K.; Lascarrou, J.B.; Kirov, M.Y.; Pettila, V.; Wittebole, X.; Meziani, F.; Mercier, E.; et al. Effect of a recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin on mortality in patients with sepsis-associated coagulopathy: The SCARLET randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2019, 321, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spectral Medical and Vantive Announce Topline Results from Spectral’s Tigris Trial Evaluating PMX Hemoadsorption Therapy for Endotoxic Septic Shock. Available online: https://www.vantive.com/news/press-releases/spectral-medical-tigris-trial (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Antcliffe, D.B.; Burrell, A.; Boyle, A.J.; Gordon, A.C.; McAuley, D.F.; Silversides, J. Sepsis subphenotypes, theragnostics and personalized sepsis care. Intensive Care Med. 2025, 51, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cajander, S.; Kox, M.; Scicluna, B.P.; Weigand, M.A.; Mora, R.A.; Flohe, S.B.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Lachmann, G.; Girardis, M.; Garcia-Salido, A.; et al. Profiling the dysregulated immune response in sepsis: Overcoming challenges to achieve the goal of precision medicine. Lancet Respir. Med. 2024, 12, 305–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antcliffe, D.B.; Peronnet, E.; Pene, F.; Stralin, K.; Brealey, D.; Blein, S.; Cleaver, R.; Cronhjort, M.; Diehl, J.L.; Voiriot, G.; et al. An international observational study validating gene-expression sepsis immune subgroups. Crit. Care 2025, 29, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Amstel, R.B.E.; Bartek, B.; Vlaar, A.P.J.; Gay, E.; van Vught, L.A.; Cremer, O.L.; Van der Poll, T.; Shapiro, N.I.; Matthay, M.A.; Calfee, C.S.; et al. Temporal transitions of the hyperinflammatory and hypoinflammatory phenotypes in critical illness. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2025, 211, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.; Sinha, P. Precision medicine in acute respiratory distress syndrome: Progress, challenges, and the road ahead. Clin. Chest Med. 2024, 45, 835–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanaway, I.B.; Morrell, E.D.; Mabrey, F.L.; Sathe, N.A.; Bailey, Z.; Speckmaier, S.; Lo, J.; Zelnick, L.R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Mikacenic, C.; et al. Urinary proteomics identifies distinct immunological profiles of sepsis associated AKI sub-phenotypes. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, L.D.J.; Calfee, C.; Castellvi-Font, A.; Cornelius, V.; Derde, L.P.G.; Docherty, A.; Fan, E.; Ferguson, N.; Goligher, E.C.; Gordon, A.C.; et al. The rise of adaptive platform trials in critical care. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2024, 209, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.L. Endpoints in sepsis trials: More than just 28-day mortality? Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, S209–S213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.L.; Sakr, Y. Clinical trial design for unmet clinical needs: A spotlight on sepsis. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slim, M.A.; van Mourik, N.; Bakkerus, L.; Fuller, K.; Acharya, L.; Giannidis, T.; Dionne, J.C.; Oczkowski, S.J.W.; Netea, M.G.; Pickkers, P.; et al. Towards personalized medicine: A scoping review of immunotherapy in sepsis. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vincent, J.-L. The 15th Anniversary of Life—Sepsis Trials. Life 2025, 15, 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101517
Vincent J-L. The 15th Anniversary of Life—Sepsis Trials. Life. 2025; 15(10):1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101517
Chicago/Turabian StyleVincent, Jean-Louis. 2025. "The 15th Anniversary of Life—Sepsis Trials" Life 15, no. 10: 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101517
APA StyleVincent, J.-L. (2025). The 15th Anniversary of Life—Sepsis Trials. Life, 15(10), 1517. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15101517





