Prediction of Seven Artificial Intelligence-Based Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulas in Medium-Long Caucasian Eyes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kane, J.X.; Melles, R.B. Intraocular lens formula comparison in axial hyperopia with a high-power intraocular lens of 30 or more diopters. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2020, 46, 1236–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, G.; Modis, L., Jr. Accuracy of the Hill-radial basis function method and the Barrett Universal II formula. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 31, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopyra, W. The exactness of intraocular lens power calculation formulas for short eyes and correlation between method accuracy and eyeball axial length. Czech Slovak Ophthalmol. 2022, 78, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Stein, J.; Nallasamy, N. AI-powered effective lens position prediction improves the accuracy of existing lens formulas. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 106, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopyra, W. Analysis of accuracy of twelve intraocular lens power calculation formulas for eyes with axial hyperopia. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 37, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Martinez, C.E.; Tsai, L.M. Update on Intraocular Lens Formulas and Calculations. Asia Pac. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 9, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xiong, R.; Liu, Z.; Young, C.A.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, X.; Jin, G. Network Meta-analysis of Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formula Accuracy in 1016 Eyes with Long Axial Length. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 257, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Ye, Z.; Luo, Y.; Li, Z. Comparing the accuracy of new-generation intraocular lens power calculation formulae in axial myopic eyes: A meta–analysis. Int. Ophthalmol. 2023, 43, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Li, H.; Gao, L.; Du, J.; Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Ye, Z.; Li, Z. Comparing the accuracy of new intraocular lens power calculation formulae in short eyes after cataract surgery: A systemic review and meta–analysis. Int. Ophthalmol. 2022, 42, 1939–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatinel, D.; Debellemaniére, G.; Saad, A.; Brenner, L.F.; Gauvin, M.; Wallerstein, A.; Malet, J. Impact of the Minimization of Standard Deviation Before Zeroization of the Mean Bias on the Performance of IOL Power Formulas. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2024, 13, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopyra, W. Effectiveness, Sensitivity, and Specificity of Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulas for Short Eyes. Turk. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 52, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voytsekhivskyy, O.; Tutchenko, L. Comparison of prediction accuracy of 13 formulas in long eyes. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2023, 261, 2575–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Liao, X. How to choose intraocular lens power calculation formulas in eyes with extremely long axial length? A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0296771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopyra, W. Analysis of accuracy of twelve intraocular lens power calculation formulas for eyes with axial myopia. Taiwan J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 13, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, G.P.; Burmeister, J. Comparison of intraocular lens computations using a neural network versus the Holladay formula. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 1997, 23, 1585–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, J.X.; Van Heerden, A.; Atik, A.; Petsoglou, C. Accuracy of 3 new methods for intraocular lens power selection. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2017, 43, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladas, J.G.; Siddiqui, A.A.; Devgan, U.; Jun, A.S. A 3-D “Super Surface” Combining Intraocular Lens Formulas to Generate a “Super Formula” and Maximize Accuracy. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2015, 133, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, B.J.; Kane, J.X. Comparison of the Kane formula with existing formulas for intraocular lens power selection. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2019, 4, e000251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debellemanière, G.; Dubois, M.; Gauvin, M.; Wallerstein, A.; Brenner, F.L.; Rampat, R.; Saad, A.; Gatinel, D. The PEARL-DGS Formula: The Development of an Open-source Machine Learning-based Thick IOL Calculation Formula. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 232, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Stein, J.; Nallasamy, N. Evaluation of the Nallasamy formula: A stacking ensemble machine learning method for refraction prediction in cataract surgery. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 107, 1066–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-González, D.; Palomino-Bautista, C. Accuracy of a new intraocular lens power calculation method based on artificial intelligence. Eye 2021, 35, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenny, P.I.; Kozhaya, K.; Truong, P.; Weikert, M.P.; Hill, W.E.; Koch, D.D. Efficacy of segmented axial length and artificial intelligence approaches to intraocular lens power calculation in short eyes. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2023, 49, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taroni, L.; Hoffer, K.J.; Pellegrini, M.; Lupardi, E.; Savini, G. Comparison of the New Hoffer QST with 4 Modern Accurate Formulas. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2023, 49, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; He, W.; Wei, L.; Song, Y.; Qi, J.; Yao, Y.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, X. The Zhu-Lu formula: A machine learning-based intraocular lens power calculation formula for highly myopic eyes. Eye Vis. 2023, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopyra, W.; Voytsekhivskyy, O.; Grzybowski, A. Accuracy of 20 Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulas in Medium-Long Eyes. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2024, 13, 1893–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitblat, O.; Heifetz, N.; Durnford, K.; Pattey, J.H.; Olson, R.J.; Livny, E.; Bernhisel, A.A.; Bahar, I.; Sella, R. Accuracy assessment of artificial intelligence IOL calculation formulae: Utilizing the heteroscedastic statistics and the Eyetemis Analysis Tool. Eye 2024, 38, 3578–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voytsekhivskyy, O.V.; Hoffer, K.J.; Tutchenko, L.; Cooke, D.L.; Savini, G. Accuracy of 24 IOL Power Calculation Methods. J. Refract. Surg. 2023, 39, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priji, P.; Jacob, S.C.; Kalikivayi, L.; Kalikivayi, V. Correlating Kane formula with existing intraocular lens formulae for corneal curvatures and axial lengths. Oman J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 14, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shammas, H.J.; Taroni, L.; Pellegrini, M.; Shammas, M.C.; Jivrajka, R.V. Accuracy of newer intraocular lens power formulas in short and long eyes using sum-of-segments biometry. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2022, 48, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona- González, D.; Castillo-Gόmez, A.; Palomino-Bautista, C.; Romero-Dominguez, M.; Gutiérez-Moreno, M.Á. Comparison of the accuracy of 11 intraocular lens power calculation formulas. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 31, 2370–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopyra, W. Comparison of the accuracy of six intraocular lens power calculation formulas for eyes of axial length exceeding 25.0 mm. J. Fr. Ophthalmol. 2021, 44, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melles, R.; Holladay, J.; Chang, W. The accuracy of intraocular lens calculation formulas. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, A.; Popovic, M.; Ahmed, Y.; Lloyd, J.C.; El-Defrawy, S.; Gorfinkel, J.; Schlenker, M.B. A comparative analysis of 12 intraocular lens power formulas. Int. Ophthalmol. 2021, 41, 4137–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darcy, K.; Gunn, D.; Tavassoli, S.; Sparrow, J.; Kane, J.X. Assesment of the accuracy of new and updated intraocular lens power calculation formulas in 10930 eyes from the UK National Health Service. J. Catarcact. Refract. Surg. 2020, 46, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, D.L.; Cooke, T.L. A comparison of two methods to calculate axial length. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2019, 45, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voytsekhivskyy, O.V. Development and Clinical Accuracy of a New Intraocular Lens Power Formula (VRF) Compared to Other Formulas. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 185, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savini, G.; Di Maita, M.; Hoffer, K.J.; Næser, K.; Schiano-Lomoriello, D.; Vagge, A.; Di Cello, L.; Traverso, C.E. Comparison of 13 formulas for IOL power calculation with measurements from partial coherence interferometry. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 105, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffer, K.J.; Savini, G. Update on Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Study Protocols: The Better Way to Design and Report Clinical Trials. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, e115–e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holladay, J.T.; Wilcox, R.R.; Koch, D.D.; Wang, L. Review and recommendations for univariate statistical analysis of spherical equivalent prediction error for IOL power calculations. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2021, 47, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holladay, J.T.; Wilcox, R.R.; Koch, D.D.; Wang, L. Statistics of prediction error for dependent and independent datasets. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2023, 49, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, M.J.; Charman, W.N. The effect of testing distance on intraocular lens power calculation. J. Refract. Surg. 2014, 30, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, G.; Kemeny-Beke, A.; Modis, L., Jr. Comparison of accuracy of different intraocular lens power calculation methods using artificial intelligence. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 32, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsessler, M.; Cohen, S.; Wang, L.; Koch, D.D.; Zadok, D.; Abulafia, A. Evaluating the prediction accuracy of the Hill-RBF 3.0 formula using heteroscedastic statistical method. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2022, 48, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stopyra, W.; Cooke, D.; Grzybowski, A. A Review of Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulas Based on Artificial Intelligence. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffer, K.J. Clinical results using the Holladay 2 intraocular lens power formula. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2000, 26, 1233–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narváez, J.; Zimmerman, G.; Stulting, R.D.; Chang, D.H. Accuracy of intraocular lens power prediction usng the Hoffer Q, Holladay 1, Holladay 2, and SRK/T formulas. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2006, 32, 2050–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landers, J.; Goggin, M. Comparison of refractive outcomes using immersion ultrasound biometry and IOLMaster biometry. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2009, 37, 566–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristodemou, P.; Knox Cartwright, N.E.; Sparrow, J.M.; Johnston, R.L. Formula choice: Hoffer Q, Holladay or SRK/T and refractive outcomes in 8108 eyes after cataract surgery with biometry by partial coherence interferometry. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2011, 37, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, J.X.; Van Heerden, A.; Atik, A.; Petsoglou, C. Intraocular lens power formula accuracy: Comparison of 7 formulas. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2016, 42, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopyra, W.; Voytsekhivskyy, O.; Grzybowski, A. Accuracy of 7 Artificial Intelligence Based Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulas in Extremely Long Caucasian Eyes. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, in press. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffer, K.J.; Aramberri, J.; Haigis, W.; Olsen, T.; Savini, G.; Shammas, H.J.; Bentow, S. Protocols for studies of intraocular lens formula accuracy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 160, 403–405.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sella, R.; Reitblat, O.; Durnford, K.M.; Pettey, J.H.; Olson, R.J.; Hahn, T.E.; Bernhisel, A.A.; Afshari, N.A. The effect of patient age on some new and older IOL power calculation formulas. Acta Ophthalmol. 2024, 102, e696–e704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teshigawara, T.; Meguro, A.; Mizuki, N. Influence of pupil dilation on the Barrett Universal II (new generation), Haigis (4th generation) and SRK/T (3rd generation) intraocular lens calculation formulas: A retrospective study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020, 20, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| AI Hybrid Formulas | Pure AI Formulas | Universal AI Algorithms |
|---|---|---|
| FullMonte Hoffer QST Kane LSF AI PEARL-DGS Zeiss AI Zhu-Lu | Hill-RBF 3.0 Karmona Nallasamy | PLUS method Sramka approach XGBoost Calculator |
| Demographics | Mean (±SD) | Range |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 71.88 ± 9.60 | 43–94 |
| Gender M/F, % | 90/124 | 42.05%/57.95% |
| Axial Length (mm) | 25.17 ± 0.42 | 24.50–25.97 |
| Corneal Power (D) | 42.89 ± 1.42 | 38.53–48.49 |
| Corneal Astigmatism Magnitude (D) | 0.69 ± 0.49 | 0.00–1.68 |
| Anterior Chamber Depth (mm) | 3.44 ± 0.40 | 2.38–4.48 |
| Lens Thickness (mm) | 4.23 ± 0.36 | 3.14–5.24 |
| Corneal Diameter (mm) | 12.26 ± 0.40 | 11.00–13.10 |
| Central Corneal Thickness (mm) | 0.557 ± 0.033 | 0.442–0.640 |
| IOL Power (D) | 17.42 ± 1.98 | 11.5–22.0 |
| Formulas p Value | Hill-RBF 3.0 | Hoffer QST | Kane | Karmona | LSF AI | Nallasamy | Pearl-DGS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bootstrap-t method | |||||||
| Hill-RBF 3.0 | ------ | ||||||
| Hoffer QST | 0.987 | ------ | |||||
| Kane | 0.948 | 0.987 | ------ | ||||
| Karmona | 0.021 * | 0.284 | 0.923 | ------ | |||
| LSF AI | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.686 | ------ | ||
| Nallasamy | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.336 | 0.987 | ------ | |
| Pearl-DGS | 0.987 | 0.987 | 0.826 | 0.140 | 0.987 | 0.987 | ------ |
| IOL | Alcon IQ SN60WF | |||||||||||
| Axial Length | 24.50–25.99 mm | |||||||||||
| n | 214 | |||||||||||
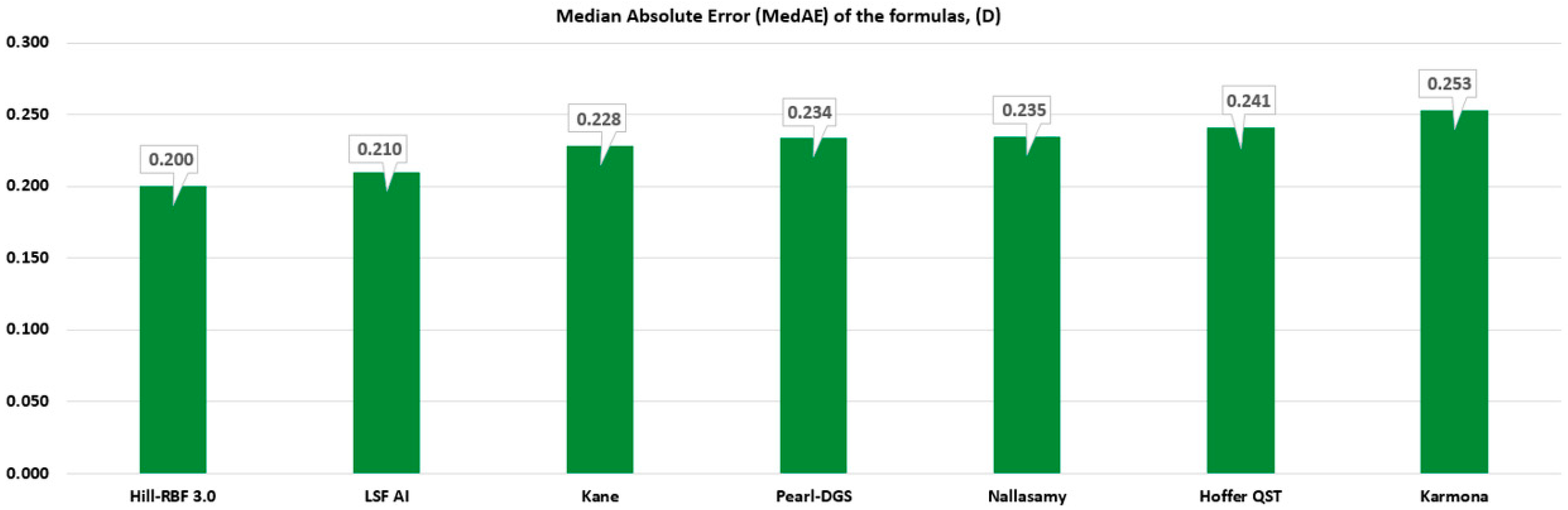
| Formula | Optimized Constants (ULIB) | PE | RMSAE | SD | MAD | MedAE | MAE | Eyes within PE (%) | ||||
| Alcon IQ SN60WF | PE ≤0.25 D | PE ≤0.50 D | PE ≤0.75 D | PE ≤1.00 D | PE ≤2.00 D | |||||||
| Hill-RBF 3.0 | 119.00 | 0.008 | 0.368 | 0.367 | 0.271 | 0.200 | 0.271 | 61.21 | 86.45 | 94.86 | 98.13 | 100.00 |
| Hoffer QST | 119.00 | 0.014 | 0.378 | 0.378 | 0.287 | 0.241 | 0.288 | 54.67 | 85.05 | 95.79 | 98.60 | 100.00 |
| Kane | 119.00 | 0.029 | 0.387 | 0.385 | 0.287 | 0.228 | 0.289 | 55.14 | 83.64 | 94.39 | 98.60 | 100.00 |
| Karmona | 119.00 | 0.185 | 0.418 | 0.374 | 0.281 | 0.253 | 0.318 | 50.93 | 81.31 | 93.46 | 96.73 | 100.00 |
| LSF AI | 119.00 | 0.008 | 0.379 | 0.378 | 0.275 | 0.210 | 0.275 | 60.75 | 85.51 | 95.33 | 98.13 | 100.00 |
| Nallasamy | 119.00 | −0.021 | 0.381 | 0.380 | 0.286 | 0.235 | 0.288 | 57.01 | 84.58 | 93.93 | 98.13 | 100.00 |
| Pearl-DGS | 119.00 | 0.038 | 0.374 | 0.372 | 0.280 | 0.234 | 0.283 | 54.21 | 85.05 | 95.79 | 98.13 | 100.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stopyra, W.; Voytsekhivskyy, O.; Grzybowski, A. Prediction of Seven Artificial Intelligence-Based Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulas in Medium-Long Caucasian Eyes. Life 2025, 15, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010045
Stopyra W, Voytsekhivskyy O, Grzybowski A. Prediction of Seven Artificial Intelligence-Based Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulas in Medium-Long Caucasian Eyes. Life. 2025; 15(1):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010045
Chicago/Turabian StyleStopyra, Wiktor, Oleksiy Voytsekhivskyy, and Andrzej Grzybowski. 2025. "Prediction of Seven Artificial Intelligence-Based Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulas in Medium-Long Caucasian Eyes" Life 15, no. 1: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010045
APA StyleStopyra, W., Voytsekhivskyy, O., & Grzybowski, A. (2025). Prediction of Seven Artificial Intelligence-Based Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulas in Medium-Long Caucasian Eyes. Life, 15(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/life15010045







