Confronting a New Challenge in Plastic Surgery: MDR Infections in Patients with Chronic Wounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
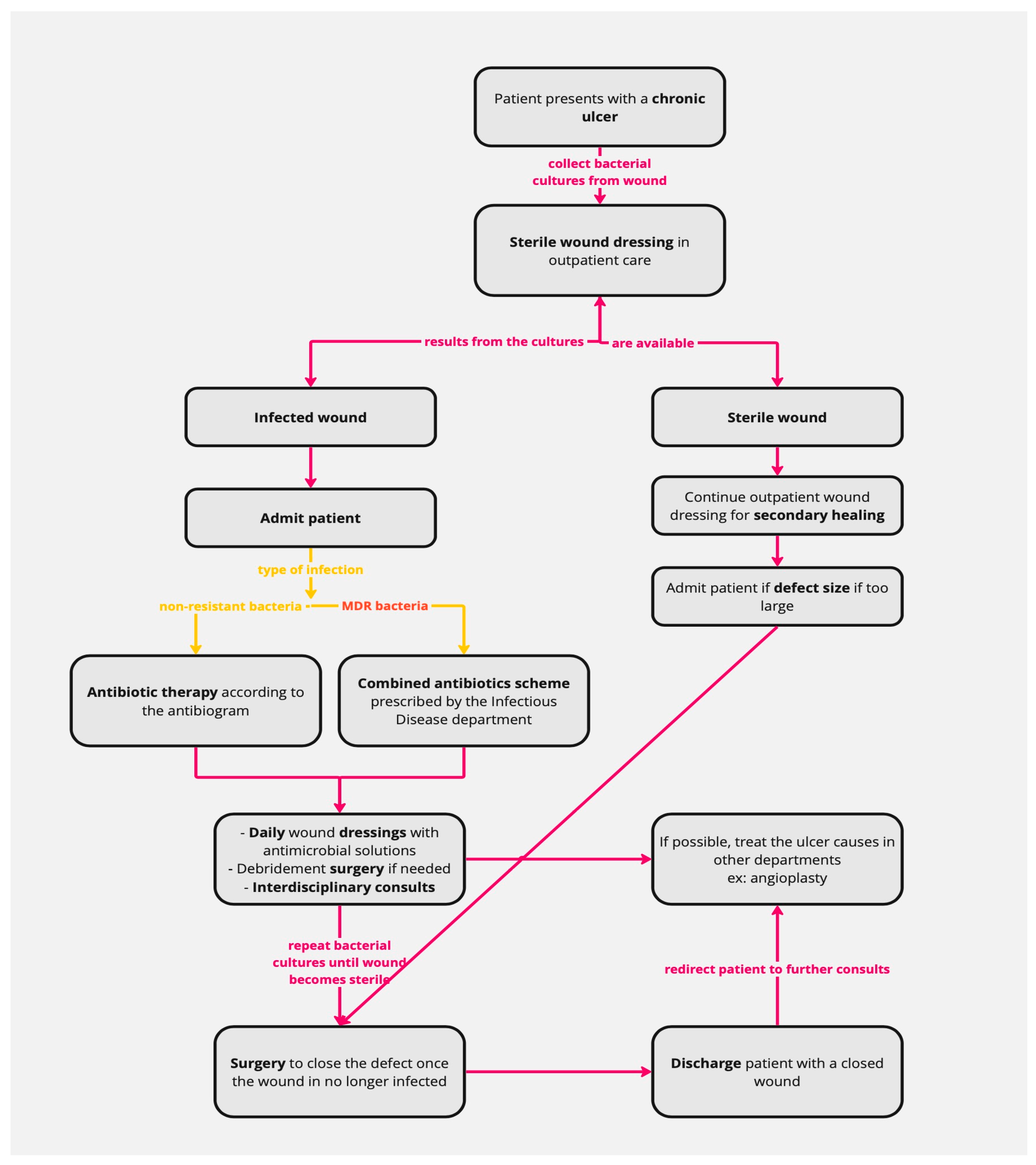
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ho, J.; Walsh, C.; Yue, D.; Dardik, A.; Cheema, U. Current Advancements and Strategies in Tissue Engineering for Wound Healing: A Comprehensive Review. Adv. Wound Care 2017, 6, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, P.; Nunan, R. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of repair in acute and chronic wound healing. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastar, I.; Stojadinovic, O.; Krzyzanowska, A.; Barrientos, S.; Stuelten, C.; Zimmerman, K.; Blumenberg, M.; Brem, H.; Tomic-Canic, M. Attenuation of the transforming growth factor β-signaling pathway in chronic venous ulcers. Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brem, H.; Stojadinovic, O.; Diegelmann, R.F.; Entero, H.; Lee, B.; Pastar, I.; Golinko, M.; Rosenberg, H.; Tomic-Canic, M. Molecular markers in patients with chronic wounds to guide surgical debridement. Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Berendt, A.R.; Cornia, P.B.; Pile, J.C.; Peters, E.J.; Armstrong, D.G.; Deery, H.G.; Embil, J.M.; Joseph, W.S.; Karchmer, A.W.; et al. 2012 Infectious Diseases Society of America clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, e132–e173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Jiang, C.; Chen, H.; Chai, Y. Assessment of the Risk Factors of Multidrug-Resistant Organism Infection in Adults with Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Foot Ulcer. Can. J. Diabetes 2019, 44, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pendleton, J.N.; Gorman, S.P.; Gilmore, B.F. Clinical relevance of the ESKAPE pathogens. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2013, 11, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santajit, S.; Indrawattana, N. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2475067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troeman, D.P.R.; Hazard, D.; Timbermont, L.; Malhotra-Kumar, S.; van Werkhoven, C.H.; Wolkewitz, M.; Ruzin, A.; Goossens, H.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Harbarth, S.; et al. Postoperative Staphylococcus aureus Infections in Patients with and without Preoperative Colonization. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2339793, Erratum in: JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e244564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Uckay, I.; Lipsky, B.A. In diabetic foot infections antibiotics are to treat infection, not to heal wounds. Expert Opin. Parmacother. 2015, 16, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prompers, L.; Huijberts, M.; Apelqvist, J.; Jude, E.; Piaggesi, A.; Bakker, K.; Edmonds, M.; Holstein, P.; Jirkovska, A.; Mauricio, D. High prevalence of ischaemia, infection and serious comorbidity in patients with diabetic foot disease in Europe: Baseline results from the Eurodiale study. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrepnek, G.H.; Mills, J.L.; Laverly, L.A.; Armstrong, D.G. Health Care Service and Outcomes Among an Estimated 6.7 Million Ambulatory Care Diabetic Foot Cases in the U.S. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Ying, G.; Jing, O.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Deng, M.; Long, S. Influencing factors for the recurrence of diabetic foot ulcers: A meta-analysis. Int. Wound J. 2023, 20, 1762–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Jin, P.; Chu, Y.; Feng, S.; Wang, P. Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors of Diabetic Foot Ulcer with Multidrug-Resistant Organism Infection. Int. J. Low Extrem. Wounds 2014, 13, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodea, F.-V.; Lazarescu, A.-L.; Grosu-Bularda, A.; Cretu, A.; Teodoreanu, R.N.; Lascar, I.; Hariga, C.S. Antimicrobial Resistance of Eskape Pathogens in Major Burns Patients—One-Year Retrospective Study. Farmacia 2023, 71, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, H.H. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacaroiu, I.A.; Cuiban, E.; Geavlete, B.F.; Gheorghita, V.; David, C.; Ene, C.V.; Bulai, C.; Lupusoru, G.E.; Lupusoru, M.; Balcangiu-Stroescu, A.E.; et al. Chronic Kidney Disease—An Underestimated Risk Factor for Antimicrobial Resistance in Patients with Urinary Tract Infections. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouget, C.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Pantel, A.; Boutet-Dubois, A.; Schuldiner, S.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.P.; Loubet, P. Alternative Approaches for the Management of Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 747618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uckay, I.; Gariani, K.; Pataky, Z.; Lipsky, B.A. Diabetic foot infections: State-of-the-art. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, L.; Bowling, F.L.; Armstrong, D.G.; Boulton, A.J.M. Saving the Diabetic Foot during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Tale of Two Cities. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1704–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guest, J.F.; Fuller, G.W. Cohort study assessing the impact of COVID-19 on venous leg ulcer management and associated clinical outcomes in clinical practice in the UK. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e068845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, J.A. Controlling multiple-drug-resistant organisms at the hospital level. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2006, 7, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founou, R.C.; Founou, L.L.; Essack, S.Y. Clinical and economic impact of antibiotic resistance in developing countries: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad Bugs, No Drugs: No ESKAPE! An Update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulani, M.S.; Kamble, E.E.; Kumkar, S.N.; Tawre, M.S.; Pardesi, K.R. Emerging Strategies to Combat ESKAPE Pathogens in the Era of Antimicrobial Resistance: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, A.; Kwiatkowska, A.; Potocki, L. Antibiotics and Bacterial Resistance—A Short Story of an Endless Arms Race. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C.; Schultsz, C. Surveillance in infection control: Are we making progress? Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2002, 15, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-H.; Tsai, J.-S.; Huang, C.-H.; Lin, C.-H.; Yang, H.-M.; Chan, Y.-S.; Hsieh, S.-H.; Hsu, B.R.-S.; Huang, Y.-Y. Risk factors for lower extremity amputation in diabetic foot disease categorized by Wagner classification. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 95, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa ECosta, T.; Duarte, B.; João, A.L.; Coelho, M.; Formiga, A.; Pinto, M.; Neves, J. Multidrug-resistant bacteria in diabetic foot infections: Experience from a portuguese tertiary centre. Int. Wound J. 2020, 17, 1835–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, P.; Yang, X. Influencing factors of recurrences of the healed diabetic foot ulcers. Chin. J. Mult. Organ Dis. Elder. 2018, 17, 501–504. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaoling, X. Analysis of factors affecting the recurrence of diabetic foot ulcers wounds after wound healing. Nurs. Pract. Res. 2020, 17, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yihua, W.; Ruiliang, W.; Ye, G.; Xiaoxin, S. Clinical efficacy of Ozagrel in the treatment of elderly patients with diabetic foot and analysis of related factors affecting recurrence. J. Navy Med. 2021, 42, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Baker, A.; Țigăran, A.E.; Peligrad, T.; Ion, D.E.; Gheoca-Mutu, D.E.; Avino, A.; Hariga, C.S.; Moraru, O.E.; Răducu, L.; Jecan, R.C. Exploring an Innovative Approach: Integrating Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy with Silver Nanoparticle Dressings in Skin Graft Procedures. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Francesco, F.; De Francesco, M.; Riccio, M. Hyaluronic Acid/Collagenase Ointment in the Treatment of Chronic Hard-to-Heal Wounds: An Observational and Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Francesco, F.; Riccio, M.; Jimi, S. Contribution of Topical Agents such as Hyaluronic Acid and Silver Sulfadiazine to Wound Healing and Management of Bacterial Biofilm. Medicina 2022, 58, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sganga, G.; Tascini, C.; Sozio, E.; Colizza, S. Early recognition of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus surgical site infections using risk and protective factors identified by a group of Italian surgeons through Delphi method. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2017, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morbach, S.; Icks, A.; Rumenapf, G.; Armstrong, D. Comment on: Bernstein. Reducing foot wounds in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, e48. [Google Scholar]
- Bus, S.A.; van Natten, J.J.; Lavery, L.A. IWGDF guidance on the prevention of foot ulcers in at-risk patients with diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2016, 32, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bus, S.A. Priorities in offloading the diabetic foot. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2012, 28, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.G.; Boulton, A.J.; Bus, A.A. Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Their Recurrence. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2367–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Song, J.F.; Zhang, L.; Li, X. Analysis of risk factors for multidrug-resistant organisms in diabetic foot infection. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simms, K.W.; Ennen, K. Lower extremity ulcer management: Best practice algorithm. J. Clin. Nurs. 2010, 20, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, C.; Zanette, G.; Da Ros, R. Diabetic foot disease during the COVID-19 pandemic: Lessons learned for our future. Arch. Med. Sci. Atheroscler. Dis. 2022, 7, e94–e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, L.A. Evaluating Diabetes Mellitus as a Risk Factor for Community-Acquired Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banu, A.; Noorul Hassan, M.M.; Rajkumar, J.; Srinivasa, S. Spectrum of bacteria associated with diabetic foot ulcer and biofilm formation: A prospective study. Australas. Med. J. 2015, 8, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepäntalo, M.; Apelqvist, J.; Setacci, C.; Ricco, J.B.; de Donato, G.; Becker, F.; Robert-Ebadi, H.; Cao, P.; Eckstein, H.H.; De Rango, P.; et al. Chapter V: Diabetic foot. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2011, 42, S60–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iversen, M.M.; Tell, G.S.; Riise, T.; Hanestad, B.R.; Østbye, T.; Graue, M.; Midthjell, K. History of foot ulcer increases mortality among individuals with diabetes: Ten-year follow-up of the Nord-Trøndelag Health Study, Norway. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 2193–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Enterococcus faecium | Staphylococcus aureus | Klebsiella pneumoniae | Acinetobacter baumanii | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Enterobacter spp. | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| nr (7) | % | nr (135) | % | nr (33) | % | nr (8) | % | nr (51) | % | nr (21) | % | |
| Amoxicillin/ clavulanic acid | 3 | 42.86 | 27 | 20.00 | 1 | 3.03 | 4 | 50.00 | 16 | 31.37 | 11 | 52.38 |
| Oxacillin | 1 | 14.29 | 27 | 20.00 | 1 | 3.03 | 3 | 37.50 | 6 | 11.76 | 3 | 14.29 |
| Benzylpenicillin | 2 | 28.57 | 64 | 47.41 | 4 | 12.12 | 3 | 37.50 | 7 | 13.73 | 4 | 19.05 |
| Ticarcillin/ clavulanic acid | 2 | 28.57 | 23 | 17.04 | 16 | 48.48 | 2 | 25.00 | 11 | 21.57 | 4 | 19.05 |
| Piperacillin/ tazobactam | 2 | 28.57 | 27 | 20.00 | 17 | 51.52 | 2 | 25.00 | 11 | 21.57 | 4 | 19.05 |
| Cefuroxime | 5 | 71.43 | 41 | 30.37 | 4 | 12.12 | 3 | 37.50 | 19 | 37.25 | 2 | 9.52 |
| Ceftriaxone | 4 | 57.14 | 29 | 21.48 | 3 | 9.09 | 2 | 25.00 | 16 | 31.37 | 2 | 9.52 |
| Ceftazidime | 1 | 14.29 | 14 | 10.37 | 4 | 12.12 | 2 | 25.00 | 7 | 13.73 | 3 | 14.29 |
| Cefepime | 1 | 14.29 | 12 | 8.89 | 3 | 9.09 | 2 | 25.00 | 5 | 9.80 | 4 | 19.05 |
| Imipenem | 0 | 0.00 | 9 | 6.67 | 2 | 6.06 | 2 | 25.00 | 10 | 19.61 | 0 | 0.00 |
| Meropenem | 0 | 0.00 | 4 | 2.96 | 1 | 3.03 | 2 | 25.00 | 6 | 11.76 | 0 | 0.00 |
| Ciprofloxacin | 4 | 57.14 | 31 | 22.96 | 7 | 21.21 | 3 | 37.50 | 13 | 25.49 | 7 | 33.33 |
| Amikacin | 0 | 0.00 | 4 | 2.96 | 1 | 3.03 | 1 | 12.50 | 1 | 1.96 | 0 | 0.00 |
| Gentamicin | 2 | 28.57 | 21 | 15.56 | 6 | 18.18 | 3 | 37.50 | 10 | 19.61 | 5 | 23.81 |
| Tobramycin | 0 | 0.00 | 15 | 11.11 | 5 | 15.15 | 2 | 25.00 | 6 | 11.76 | 1 | 4.76 |
| Aztreonam | 1 | 14.29 | 15 | 11.11 | 4 | 12.12 | 1 | 12.50 | 6 | 11.76 | 4 | 19.05 |
| Streptomycin | 2 | 28.57 | 5 | 3.70 | 2 | 6.06 | 1 | 12.50 | 3 | 5.88 | 1 | 4.76 |
| Colistin | 0 | 0.00 | 7 | 5.19 | 1 | 3.03 | 1 | 12.50 | 5 | 9.80 | 1 | 4.76 |
| Trimethoprim/ sulfamethoxazole | 1 | 14.29 | 14 | 10.37 | 5 | 15.15 | 2 | 25.00 | 7 | 13.73 | 6 | 28.57 |
| Teicoplanin | 1 | 14.29 | 3 | 2.22 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 2 | 3.92 | 1 | 4.76 |
| Minocycline | 0 | 0.00 | 7 | 5.19 | 3 | 9.09 | 1 | 12.50 | 1 | 1.96 | 1 | 4.76 |
| Fosfomycin | 0 | 0.00 | 3 | 2.22 | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 12.50 | 3 | 5.88 | 0 | 0.00 |
| Tetracycline | 2 | 28.57 | 38 | 28.15 | 5 | 15.15 | 2 | 25.00 | 12 | 23.53 | 5 | 23.81 |
| Vancomycin | 1 | 14.29 | 2 | 1.48 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 1 | 1.96 | 0 | 0.00 |
| Erythromycin | 3 | 42.86 | 40 | 29.63 | 4 | 12.12 | 2 | 25.00 | 11 | 21.57 | 7 | 33.33 |
| Clindamycin | 1 | 14.29 | 36 | 26.67 | 2 | 6.06 | 1 | 12.50 | 4 | 7.84 | 3 | 14.29 |
| Fusidic acid | 0 | 0.00 | 8 | 5.93 | 0 | 0.00 | 0 | 0.00 | 3 | 5.88 | 1 | 4.76 |
| MDR Bacteria | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absent | Present | ||||
| Antibiotic | Did not receive antibiotic | Count | 51 | 71 | 122 |
| Expected count | 43.7 | 78.3 | 122.0 | ||
| Did receive antibiotic | Count | 25 | 65 | 90 | |
| Expected count | 32.3 | 57.7 | 90.0 | ||
| Total | Count | 76 | 136 | 212 | |
| Expected count | 76.0 | 136.0 | 212.0 | ||
| No. MDR Bacteria | Hospitalization (Days) | Surgery Number | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of MDR bacteria | Pearson correlation | 1 | 0.464 ** | 0.347 ** |
| Significant (2-tailed) | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| N | 212 | 212 | 211 | |
| Hospitalization (days) | Pearson correlation | 0.464 ** | 1 | 0.745 ** |
| Significant (2-tailed) | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| N | 212 | 212 | 211 | |
| Surgery number | Pearson correlation | 0.347 ** | 0.745 ** | 1 |
| Significant (2-tailed) | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| N | 211 | 211 | 211 | |
| Site | Total | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digits | Foot | Calf | Other | |||
| Diabetes | Non-diabetic | 14 | 21 | 39 | 56 | 130 |
| Diabetic | 28 | 25 | 13 | 16 | 82 | |
| Total | 42 | 46 | 52 | 72 | 212 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Răducu, L.; Moraru, O.E.; Gheoca-Mutu, D.-E.; Peligrad, T.; Țigăran, A.-E.; Abu-Baker, A.; Ion, D.-E.; Ursuț, B.M.; Jecan, C.-R.; Avino, A. Confronting a New Challenge in Plastic Surgery: MDR Infections in Patients with Chronic Wounds. Life 2024, 14, 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14040444
Răducu L, Moraru OE, Gheoca-Mutu D-E, Peligrad T, Țigăran A-E, Abu-Baker A, Ion D-E, Ursuț BM, Jecan C-R, Avino A. Confronting a New Challenge in Plastic Surgery: MDR Infections in Patients with Chronic Wounds. Life. 2024; 14(4):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14040444
Chicago/Turabian StyleRăducu, Laura, Oriana Elena Moraru, Daniela-Elena Gheoca-Mutu, Teodora Peligrad, Andrada-Elena Țigăran, Abdalah Abu-Baker, Daniela-Elena Ion, Bogdan Mihai Ursuț, Cristian-Radu Jecan, and Adelaida Avino. 2024. "Confronting a New Challenge in Plastic Surgery: MDR Infections in Patients with Chronic Wounds" Life 14, no. 4: 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14040444
APA StyleRăducu, L., Moraru, O. E., Gheoca-Mutu, D.-E., Peligrad, T., Țigăran, A.-E., Abu-Baker, A., Ion, D.-E., Ursuț, B. M., Jecan, C.-R., & Avino, A. (2024). Confronting a New Challenge in Plastic Surgery: MDR Infections in Patients with Chronic Wounds. Life, 14(4), 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14040444







