Exosome-Derived miRNAs in Liquid Biopsy for Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
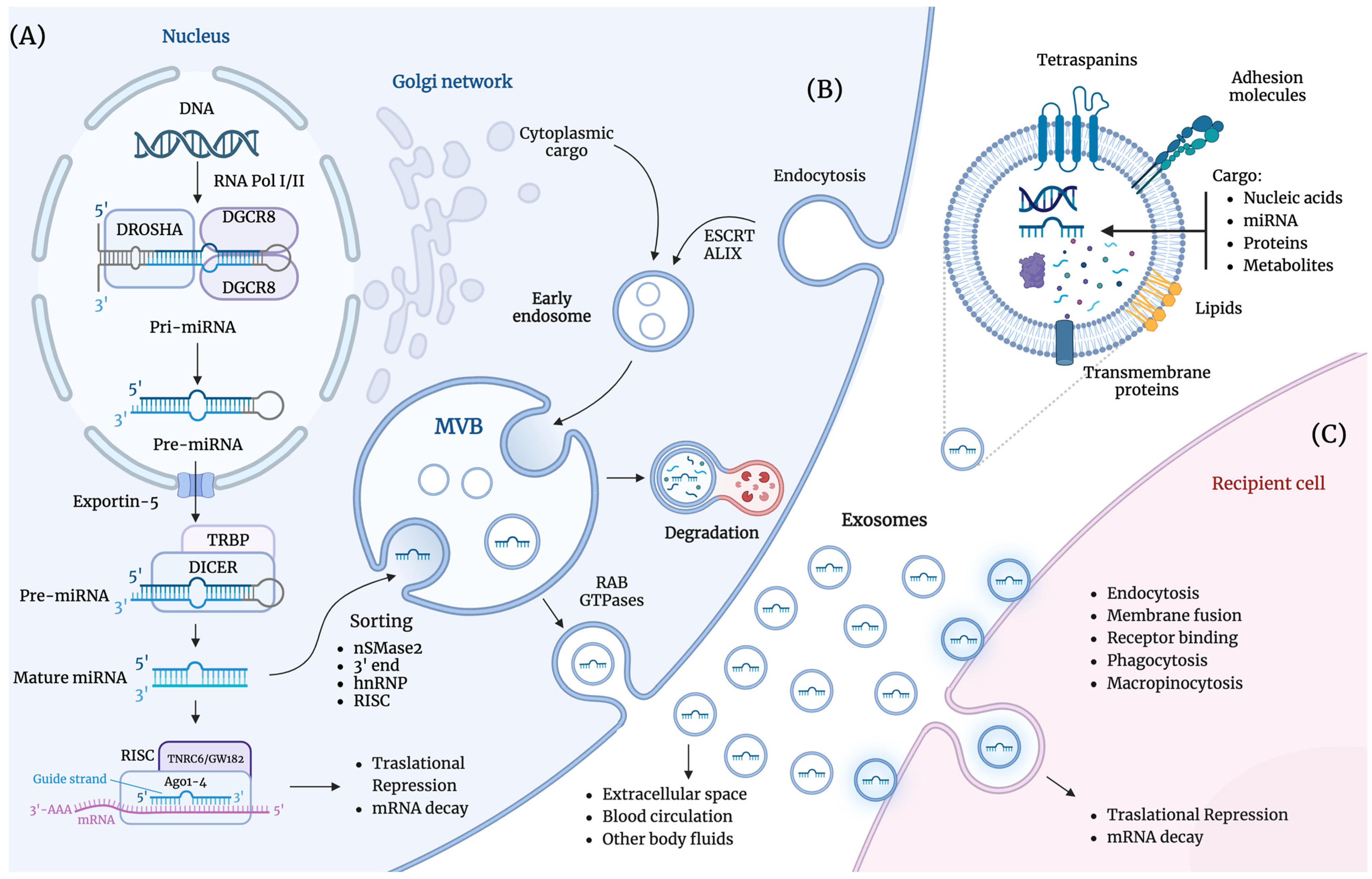
2. Exosome-Derived miRNAs
2.1. Exosomes
2.2. miRNAs
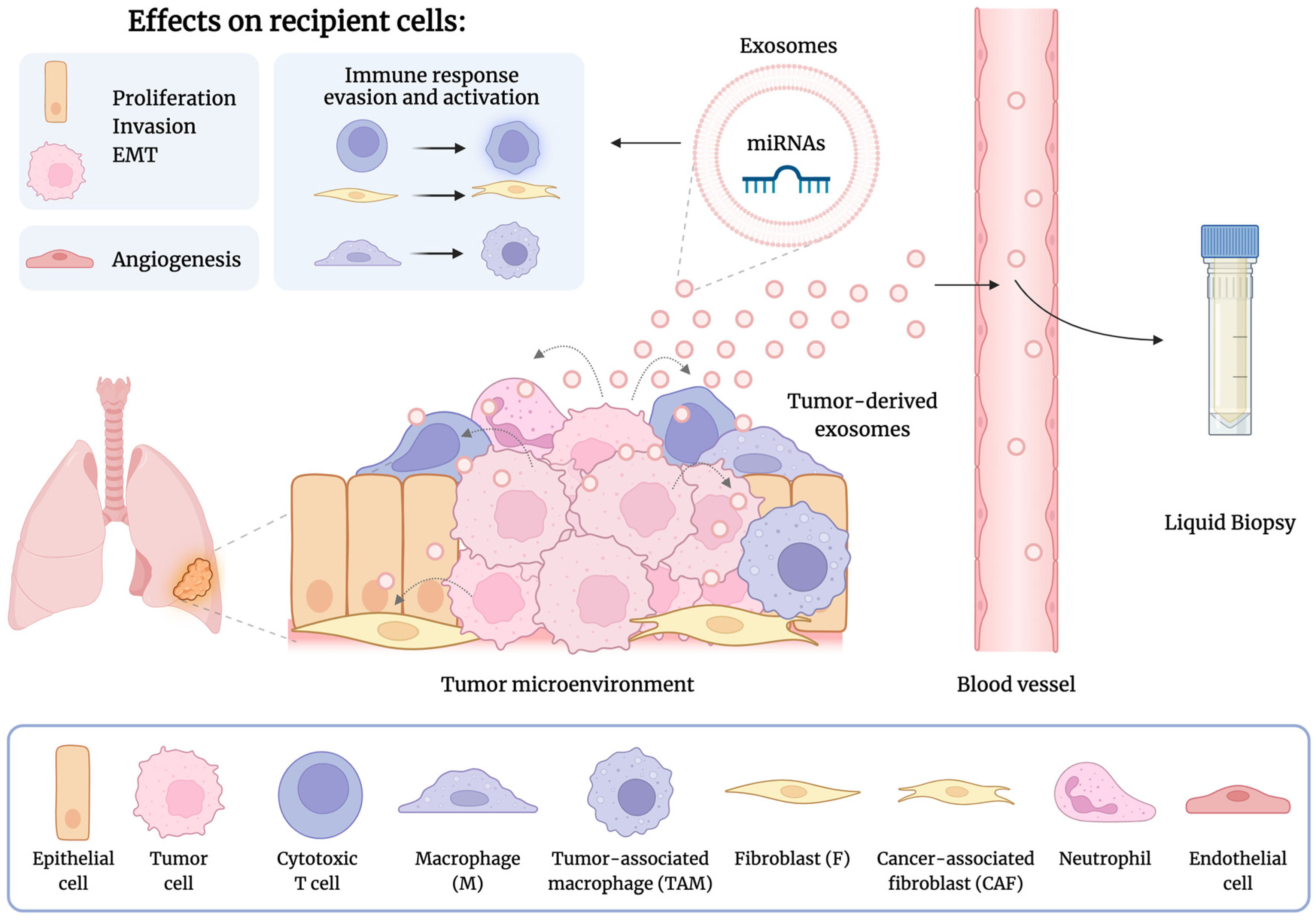
2.3. Role of Exosome-Derived miRNAs in Lung Cancer
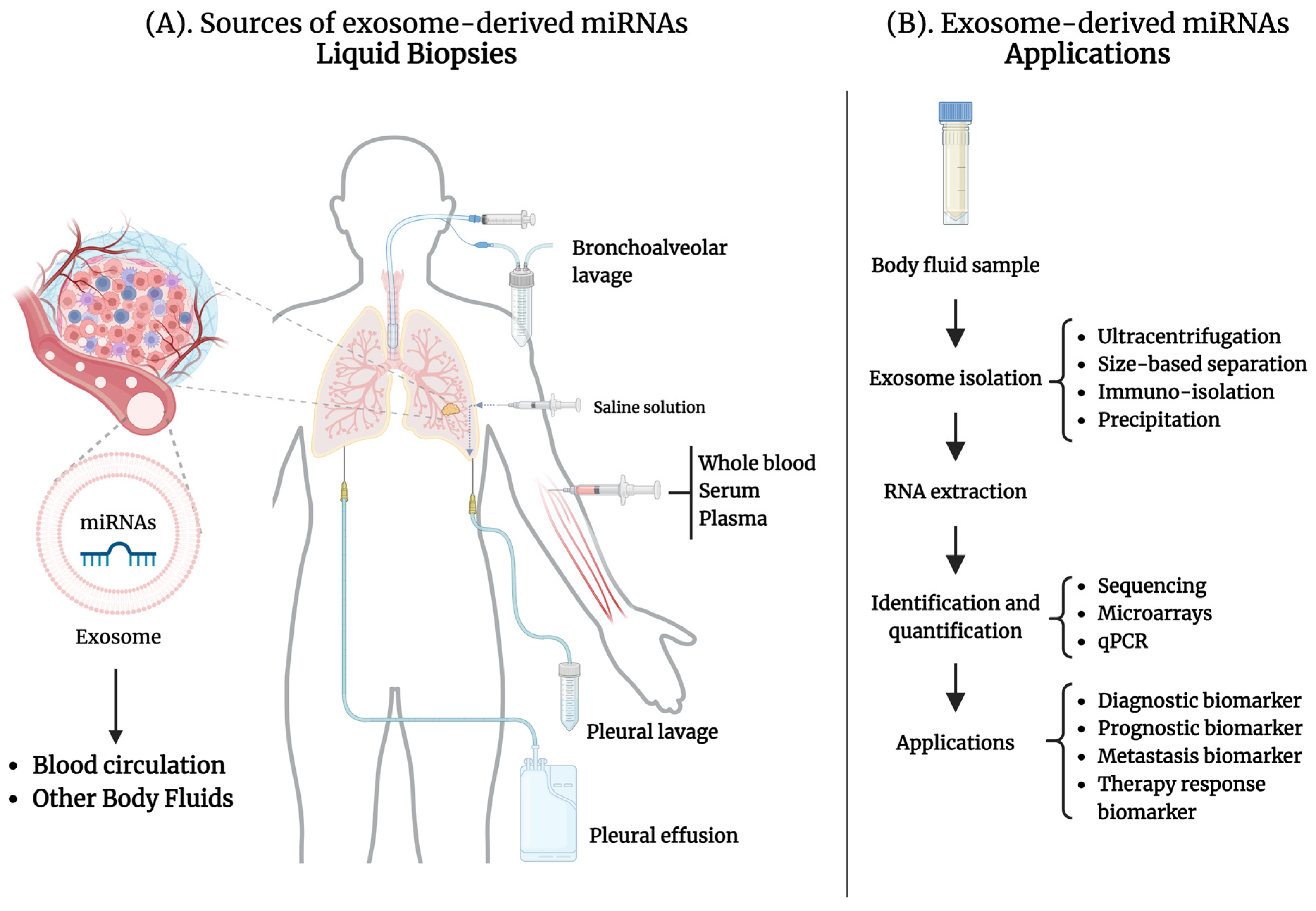
2.4. Exosome-Derived miRNAs in Liquid Biopsies for Lung Cancer
3. Exosome-Derived miRNAs from Peripheral Blood in Lung Cancer
3.1. Exosome-Derived miRNAs as Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers
3.2. Exosome-Derived miRNAs as Metastasis Biomarkers
3.3. Exosome-Derived miRNAs as Therapeutic Response Biomarkers
4. Exosome-Derived miRNAs from Other Body Fluids as Biomarkers
5. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO); International Agency for Research of Cancer (IARC). GLOBOCAN 2020, Section of Cancer Surveillance. Available online: http://globocan.iarc.fr (accessed on 6 September 2024).
- American Cancer Society. Lung Cancer Survival Rates. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/lung-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival-rates.html (accessed on 6 September 2024).
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (iarc) WHO. Cancer Today. Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr/today/home (accessed on 26 August 2024).
- Araghi, M.; Mannani, R.; Heidarnejad Maleki, A.; Hamidi, A.; Rostami, S.; Safa, S.H.; Faramarzi, F.; Khorasani, S.; Alimohammadi, M.; Tahmasebi, S.; et al. Recent advances in non-small cell lung cancer targeted therapy; an update review. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, D.; Zhao, J.; Han, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Li, W.; Xia, Y. Management of locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: State of the art and future directions. Cancer Commun. 2024, 44, 23–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, M.; Yan, Y.; Yu, J.; Xu, Y. Radiation combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors for unresectable locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Synergistic mechanisms, current state, challenges, and orientations. Cell Commun. Signal 2023, 21, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, J.B.; Hou, L.K.; Yu, F.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Tang, X.M.; Sun, F.; Lu, H.M.; Deng, J.; et al. Liquid biopsy in lung cancer: Significance in diagnostics, prediction, and treatment monitoring. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Fei, Q.; Qiu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L. Liquid biopsy techniques and lung cancer: Diagnosis, monitoring and evaluation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siravegna, G.; Mussolin, B.; Venesio, T.; Marsoni, S.; Seoane, J.; Dive, C.; Papadopoulos, N.; Kopetz, S.; Corcoran, R.B.; Siu, L.L.; et al. How liquid biopsies can change clinical practice in oncology. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiadis, M.; Sledge, G.W.; Jeffrey, S.S. Liquid biopsy enters the clinic-implementation issues and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connal, S.; Cameron, J.M.; Sala, A.; Brennan, P.M.; Palmer, D.S.; Palmer, J.D.; Perlow, H.; Baker, M.J. Liquid biopsies: The future of cancer early detection. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rubis, G.; Rajeev Krishnan, S.; Bebawy, M. Liquid Biopsies in Cancer Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Prognosis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Hurley, J.; Roberts, D.; Chakrabortty, S.K.; Enderle, D.; Noerholm, M.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J.K. Exosome-based liquid biopsies in cancer: Opportunities and challenges. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, T.; Chen, J.; Li, R.; Chen, H.; Luo, S.; Chen, D.; Cai, C.; Li, W. The role of Exosomal miRNAs in cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Quintero, B. Extracellular MicroRNAs as Intercellular Mediators and Noninvasive Biomarkers of Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Di, K.; Fan, B.; Wu, J.; Gu, X.; Sun, Y.; Khan, A.; Li, P.; Li, Z. MicroRNAs in extracellular vesicles: Sorting mechanisms, diagnostic value, isolation, and detection technology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 948959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Fei, S.; Chen, D.; Cai, X.; Liu, L.; Lin, B.; Su, H.; Zhao, L.; et al. Evaluation of Tumor-Derived Exosomal miRNA as Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Early-Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using Next-Generation Sequencing. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5311–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.X.; Yu, R.; Wu, X.; Wu, S.Y.; Pi, C.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, X.C.; Gao, C.Y.; Shao, Y.W.; Liu, L.; et al. Correlation of plasma exosomal microRNAs with the efficacy of immunotherapy in EGFR/ALK wild-type advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, H.; Choi, Y.J.; Im, K.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, D.S.; Pack, C.G.; Kim, H.Y.; Choi, C.M.; Lee, J.C.; et al. Identification of exosomal microRNA panel as diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for small cell lung cancer. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, V.V.; Svistunov, A.A.; Chubarev, V.N.; Dostdar, S.A.; Sokolov, A.V.; Brzecka, A.; Sukocheva, O.; Neganova, M.E.; Klochkov, S.G.; Somasundaram, S.G.; et al. Extracellular vesicles in cancer nanomedicine. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 69, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, M.; Fonseka, P.; Chitti, S.V.; Kang, T.; Sanwlani, R.; Van Deun, J.; Hendrix, A.; Mathivanan, S. Vesiclepedia 2019: A compendium of RNA, proteins, lipids and metabolites in extracellular vesicles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D516–D519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juan, T.; Furthauer, M. Biogenesis and function of ESCRT-dependent extracellular vesicles. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 74, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Thery, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, R.; Lee, S.; Senavirathne, G.; Lai, E.C. microRNAs in action: Biogenesis, function and regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 816–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bofill-De Ros, X.; Vang Orom, U.A. Recent progress in miRNA biogenesis and decay. RNA Biol. 2024, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.C.; Tambe, A.; Kidwell, M.A.; Noland, C.L.; Schneider, C.P.; Doudna, J.A. Dicer-TRBP complex formation ensures accurate mammalian microRNA biogenesis. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; He, J.; Pu, W.; Peng, Y. The Role of Exportin-5 in MicroRNA Biogenesis and Cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirle, N.T.; Sheu-Gruttadauria, J.; MacRae, I.J. Structural basis for microRNA targeting. Science 2014, 346, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Hagiwara, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. Neutral sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2)-dependent exosomal transfer of angiogenic microRNAs regulate cancer cell metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 10849–10859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppers-Lalic, D.; Hackenberg, M.; Bijnsdorp, I.V.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.J.; Sadek, P.; Sie, D.; Zini, N.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Ylstra, B.; de Menezes, R.X.; et al. Nontemplated nucleotide additions distinguish the small RNA composition in cells from exosomes. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gutierrez-Vazquez, C.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Perez-Hernandez, D.; Vazquez, J.; Martin-Cofreces, N.; Martinez-Herrera, D.J.; Pascual-Montano, A.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Espinosa, I.; Serrato, J.A.; Ortiz-Quintero, B. The Role of Exosome-Derived microRNA on Lung Cancer Metastasis Progression. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Espinosa, I.; Serrato, J.A.; Ortiz-Quintero, B. MicroRNAs in Lung Cancer Brain Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Park, H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kang, M.H.; Kim, T.K.; Pack, C.G.; Choi, C.M.; Lee, J.C.; Rho, J.K. Exosomal miR-1260b derived from non-small cell lung cancer promotes tumor metastasis through the inhibition of HIPK2. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wang, G.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, C.; Li, Q. MicroRNA-550a-3-5p controls the brain metastasis of lung cancer by directly targeting YAP1. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cao, L.; Li, Y.; Deng, P.; Pan, P.; Hu, C.; Yang, H. Pirfenidone promotes the levels of exosomal miR-200 to down-regulate ZEB1 and represses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of non-small cell lung cancer cells. Hum. Cell 2022, 35, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, S.M.; Zhang, F.; Ding, C.; Montoya-Durango, D.E.; Hu, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, F.; Fox, M.; Zhang, H.G.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomes drive immunosuppressive macrophages in a pre-metastatic niche through glycolytic dominant metabolic reprogramming. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 2040–2058.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Liang, M.; Huang, Y.; Wu, W.; Zheng, B.; Chen, C. Hypoxic tumor-derived exosomal miR-31-5p promotes lung adenocarcinoma metastasis by negatively regulating SATB2-reversed EMT and activating MEK/ERK signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zeng, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Ji, W.; Xia, W.; Lu, S. Exosomal miR-499a-5p promotes cell proliferation, migration and EMT via mTOR signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 379, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, C.Y.; Yan, Y.Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J.J.; Fu, J.J.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.Y. Exosomes of A549 Cells Induced Migration, Invasion, and EMT of BEAS-2B Cells Related to let-7c-5p and miR-181b-5p. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 926769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siravegna, G.; Marsoni, S.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, A. Integrating liquid biopsies into the management of cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, F.; Chen, L.; Ma, L.; Larcher, L.M.; Chen, S.; Liu, N.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Progress, opportunity, and perspective on exosome isolation-efforts for efficient exosome-based theranostics. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3684–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, R.; Du, L. Review on Strategies and Technologies for Exosome Isolation and Purification. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 811971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanin, A.A.I.; Ramos, K.S. Circulating Exosomal miRNA Profiles in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers. Cells 2024, 13, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genova, C.; Marconi, S.; Chiorino, G.; Guana, F.; Ostano, P.; Santamaria, S.; Rossi, G.; Vanni, I.; Longo, L.; Tagliamento, M.; et al. Extracellular vesicles miR-574-5p and miR-181a-5p as prognostic markers in NSCLC patients treated with nivolumab. Clin. Exp. Med. 2024, 24, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, K.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W.; Nan, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Plasma exosomal miR-1290 and miR-29c-3p as diagnostic biomarkers for lung cancer. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, C.; Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Lan, Y.; Gu, W.; Xing, Z.; Liang, L.; et al. Tumor-derived circulating exosomal miR-342-5p and miR-574-5p as promising diagnostic biomarkers for early-stage Lung Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 1428–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, B.; Peng, M.; Gong, J.; Li, C.; Cheng, H.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y. Circulating exosomal microRNA-4497 as a potential biomarker for metastasis and prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 248, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Song, X.; Xie, L.; Zhao, S.; Song, X. Tumor-Derived Exosomal miRNAs as Diagnostic Biomarkers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 560025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cao, P.; Huang, C.; Wu, Q.; Chen, S.; Chen, F. Serum exosomal miR-7977 as a novel biomarker for lung adenocarcinoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 3382–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, H. Serum exosomal miR-378 upregulation is associated with poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Guo, W.; Song, X.; Liu, L.; Niu, L.; Song, X.; Xie, L. Tumor-associated exosomal miRNA biomarkers to differentiate metastatic vs. nonmetastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, W.; Shen, K.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhan, P.; Lv, T.; et al. Elevated exosome-derived miRNAs predict osimertinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukuya, T.; Ghai, V.; Amann, J.M.; Okimoto, T.; Shilo, K.; Kim, T.K.; Wang, K.; Carbone, D.P. Circulating MicroRNAs and Extracellular Vesicle-Containing MicroRNAs as Response Biomarkers of Anti-programmed Cell Death Protein 1 or Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Therapy in NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janpipatkul, K.; Trachu, N.; Watcharenwong, P.; Panvongsa, W.; Worakitchanon, W.; Metheetrairut, C.; Oranratnachai, S.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chairoungdua, A. Exosomal microRNAs as potential biomarkers for osimertinib resistance of non-small cell lung cancer patients. Cancer Biomark. 2021, 31, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Eom, J.S.; Kim, W.Y.; Jo, E.J.; Mok, J.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.U.; Park, H.K.; Lee, M.K.; Kim, M.H. Diagnostic value of microRNAs derived from exosomes in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of early-stage lung adenocarcinoma: A pilot study. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehbein, G.; Schmidt, B.; Fleischhacker, M. Extracellular microRNAs in bronchoalveolar lavage samples from patients with lung diseases as predictors for lung cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 450, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bao, L.; Yu, G.; Wang, H. Exosomal miRNA-profiling of pleural effusion in lung adenocarcinoma and tuberculosis. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 1050242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watabe, S.; Kikuchi, Y.; Morita, S.; Komura, D.; Numakura, S.; Kumagai-Togashi, A.; Watanabe, M.; Matsutani, N.; Kawamura, M.; Yasuda, M.; et al. Clinicopathological significance of microRNA-21 in extracellular vesicles of pleural lavage fluid of lung adenocarcinoma and its functions inducing the mesothelial to mesenchymal transition. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 2879–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman-Canal, B.; Moiola, C.P.; Gatius, S.; Bonnin, S.; Ruiz-Miro, M.; Gonzalez, E.; Ojanguren, A.; Recuero, J.L.; Gil-Moreno, A.; Falcon-Perez, J.M.; et al. EV-associated miRNAs from pleural lavage as potential diagnostic biomarkers in lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrugger, U.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| miRNAs | Sample | Cohort Size (n) | Application | Biomarker Performance Value | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-126-3p, miR-221-5p, Let-7b-5p, and miR-222-3p | Plasma exosomes | AD (36), Ctr (36) | Diagnostic AD vs. Ctr | AUC = 0.764 | [47] |
| miR-21-5p, miR-221-5p, Let-7b-, and miR-9-5p | Plasma exosomes | SCC (36), Ctr (36) | Diagnostic SCC vs. Ctr | AUC = 0.842 | |
| miR-181a-5p and miR-574-5p | Plasma EVs | Advanced NSCLC (245) | Prognostic NSCLC with nivolumab therapeutic | OS = 9 months, AUC = 0.76 | [48] |
| miR-200b-3p, miR-3124-5p, and miR-92b-5p | Serum exosomes | SCLC (126), Ctr (50) | Diagnostic (SCLC vs. Ctr) | AUC = 0.93 | [19] |
| miR-1290 miR-29c-3p | Plasma exosomes | NSCLC (30), SCLC (8), BLD (19) | Diagnostic LC vs. BLD | AUC = 0.934 AUC = 0.868 | [49] |
| miR-1290 miR-29c-3p | Diagnostic early-stage LC vs. BLD | AUC = 0.947 AUC = 0.895 | |||
| miR-1290 and miR-29c-3p | Diagnostic NSCLC vs. SCLC | AUC = 0.860 | |||
| miR-4497 | Serum exosomes | NSCLC (84), BLL (30), Ctr (47) | Diagnostic NSCLC vs. Ctrl | AUC = 0.855, sensitivity 76.6%, and specificity 83.3% | [51] |
| Diagnostic NSCLC vs. BLL | AUC = 0.748, sensitivity 73.3%, and specificity 72.6% | ||||
| Prognostic Low levels = shorter OS | p < 0.05 | ||||
| miR-1260b | Plasma exosomes | NSCLC (48), Ctr (48) | Prognostic High levels = shorter OS | p = 0.029 | [37] |
| miR-342-5p and miR-574-5p | Plasma exosomes | AD (56), Ctr (40) | Diagnostic early-stage AD vs. Ctrl | AUC = 0.813, sensitivity 80.0%, and specificity 73.2% | [50] |
| miR-5684 and miR-125b-5p | Serum exosomes | NSCLC (330), Ctr (332) | Diagnostic NSCLC vs. Ctrl | AUC = 0.793, sensitivity 82.7%, and specificity 62.1% | [52] |
| Diagnostic early-stage NSCLC vs. Ctrl | AUC = 0.744, sensitivity 80.6%, and specificity 60.9% | ||||
| miR-7977 | Serum exosomes | AD (62), Ctr (62) | Diagnostic AD vs. Ctrl | AUC = 0.787 | [53] |
| miR-378 | Serum exosomes | NSCLC (103), Ctr (60) | Diagnostic NSCLC vs. Ctrl | AUC = 0.842 | [54] |
| High levels = shorter OS | p < 0.001 |
| miRNAs | Sample | Cohort Size (n) | Application | Biomarker Performance Value | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-184 and miR-3913-5p | Serum exosomes | NSCLC (67) | Biomarker for NSCLC patients resistant to osimertinib | AUC = 0.7059 | [56] |
| Biomarker for osimertinib resistance for patients with EGFR exon21 L858R mutation | AUC = 0.736 AUC = 0.759 | ||||
| miR-199a-3p, miR-21–5p, and miR-28–5p | Plasma EVs | NSCLC (50): 22 responders and 28 non-responders. | Predictive biomarkers for anti-PD-1/PD-L1 treatment response | AUC = 0.925 | [57] |
| miR-320d, miR-320c, miR-320b, and miR-125b-5p | Plasma exosomes | Advanced EGFR/ALK wild-type NSCLC (30) | Upregulated in non-responders after anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapeutic (p < 0.05) | Not determined | [18] |
| miR-323-3p, miR-1468-3p, miR-5189-5p, and miR-6513-5p | Plasma exosomes | NSCLC (27) | Upregulated in osimertinib-resistant NSCLC patients (p < 0.0001) | Not determined | [58] |
| miRNAs | Sample | Cohort Size (n) | Application | Biomarker Performance Value | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-150-5p, miR- 3614-5p, miR-200b-3p, miR-182-5p, and miR-629-5p | Pleural effusion exosomes | AD (6), TB (6) | Diagnostic AD vs. TB | Not determined | [61] |
| miR-21 | Pleural lavage EVs | AD (41) | Diagnostic High levels associated with positive cytology and pleural invasion | Not determined | [62] |
| miR-1-3p | Pleural lavage EVs | NSCLC (21), BPE patients (25) | Diagnostic NSCLC vs. BPE | AUC = 0.914 | [63] |
| miR-144-5p | AUC = 0.925 | ||||
| miR-150-5p | AUC = 0.939 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Espinosa, I.; Serrato, J.A.; Cabello-Gutiérrez, C.; Carlos-Reyes, Á.; Ortiz-Quintero, B. Exosome-Derived miRNAs in Liquid Biopsy for Lung Cancer. Life 2024, 14, 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14121608
Martínez-Espinosa I, Serrato JA, Cabello-Gutiérrez C, Carlos-Reyes Á, Ortiz-Quintero B. Exosome-Derived miRNAs in Liquid Biopsy for Lung Cancer. Life. 2024; 14(12):1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14121608
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Espinosa, Israel, José A. Serrato, Carlos Cabello-Gutiérrez, Ángeles Carlos-Reyes, and Blanca Ortiz-Quintero. 2024. "Exosome-Derived miRNAs in Liquid Biopsy for Lung Cancer" Life 14, no. 12: 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14121608
APA StyleMartínez-Espinosa, I., Serrato, J. A., Cabello-Gutiérrez, C., Carlos-Reyes, Á., & Ortiz-Quintero, B. (2024). Exosome-Derived miRNAs in Liquid Biopsy for Lung Cancer. Life, 14(12), 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14121608






