Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: A Case Report About a Patient with Cytology Negative for Malignancy
Abstract
1. Introduction
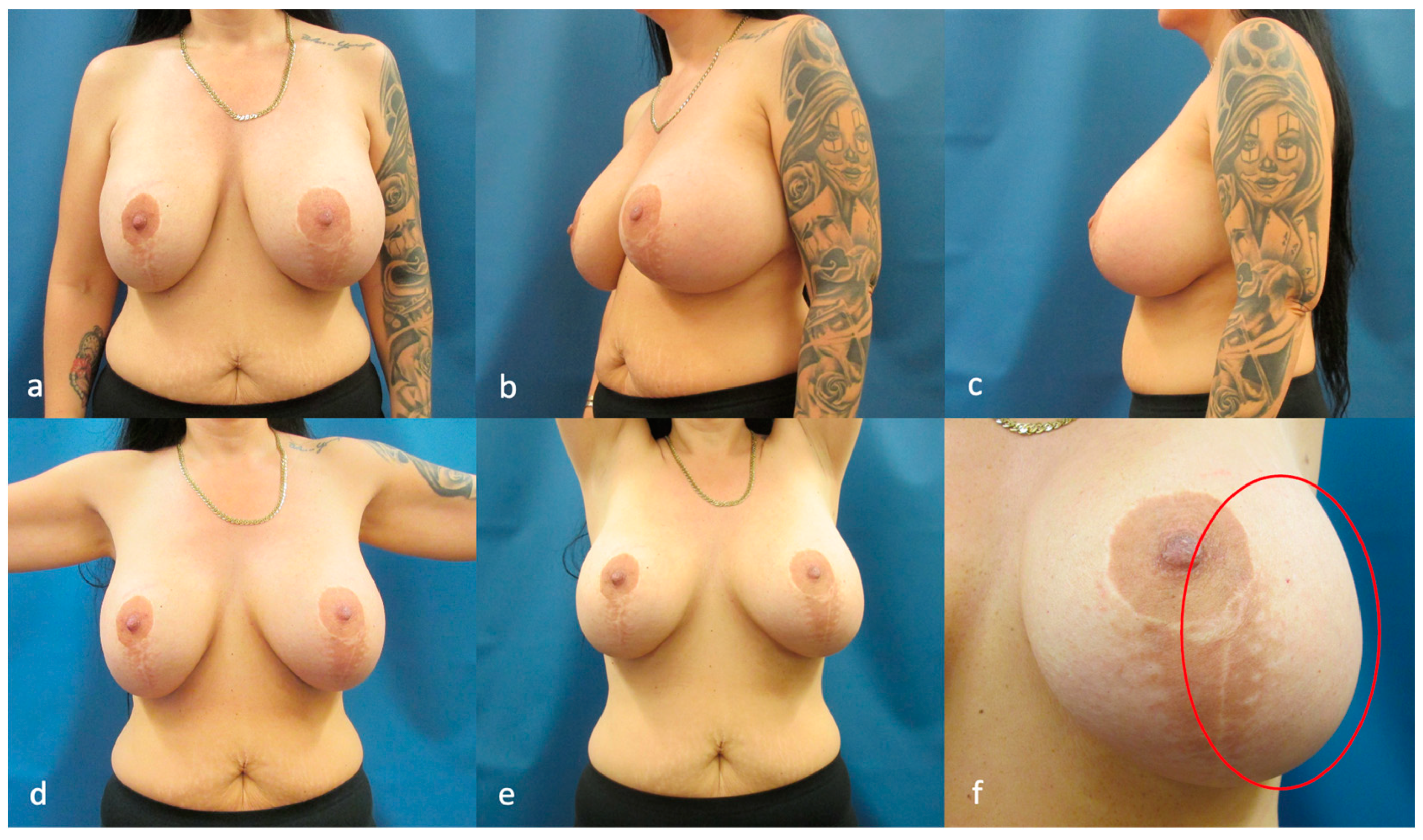
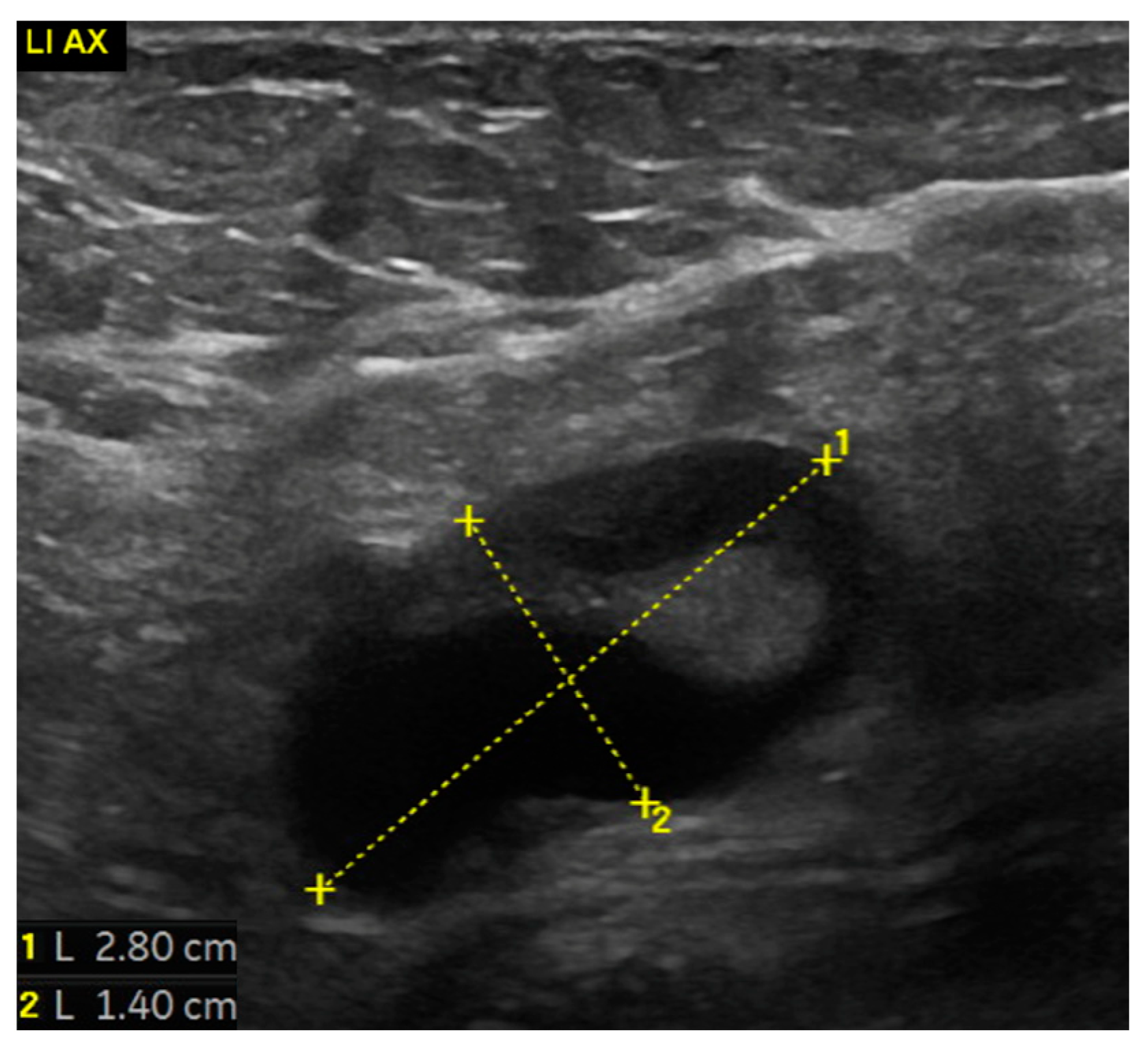
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keech, J.A.; Creech, B.J. Anaplastic T-cell lymphoma in proximity to a saline-filled breast implant. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1997, 100, 554–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). BIA-ALCL Physician Resources. 2024. Available online: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/for-medical-professionals/health-policy/bia-alcl-physician-resources (accessed on 28 July 2024).
- De Jong, W.H.; Panagiotakos, D.; Proykova, A.; Samaras, T.; Clemens, M.W.; De Jong, D.; Hopper, I.; Rakhorst, H.A.; di Pompeo, F.S.; Turner, S.D.; et al. Final opinion on the safety of breast implants in relation to anaplastic large cell lymphoma: Report of the scientific committee on health, emerging and environmental risks (SCHEER). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 125, 104982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, B.; Di Napoli, A.; Curigliano, G.; Veronesi, P.; Pileri, S.; Martelli, M.; De Vita, R.; Felici, N.; Cirillo, P.; Bernardi, C.; et al. Clinical recommendations for diagnosis and treatment according to current updated knowledge on BIA-ALCL. Breast 2022, 66, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, M.W.; Jacobsen, E.D.; Horwitz, S.M. 2019 NCCN Consensus Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL). Aesthet. Surg. J. 2019, 39 (Suppl. S1), 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Jurgensen-Rauch, A.; Pace, E.; Attygalle, A.D.; Sharma, R.; Bommier, C.; Wotherspoon, A.C.; Sharma, S.; Iyengar, S.; El-Sharkawi, D. Breast Implant-associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: Review and Multiparametric Imaging Paradigms. Radiographics 2020, 40, 609–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.L.; Hanby, A.M.; Wells, C.; Calaminici, M.; Johnson, L.; Turton, P.; Deb, R.; Provenzano, E.; Shaaban, A.; Ellis, I.O.; et al. Breast implant-associated anaplastic large cell lymphoma (BIA-ALCL): An overview of presentation and pathogenesis and guidelines for pathological diagnosis and management. Histopathology 2019, 75, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonaro, R.; Accardo, G.; Mazzocconi, L.; Pileri, S.; Derenzini, E.; Veronesi, P.; Caldarella, P.; De Lorenzi, F. BIA-ALCL in patients with genetic predisposition for breast cancer: Our experience and a review of the literature. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2023, 32, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elameen, A.M.; AlMarakby, M.A.; Atta, T.I.; Dahy, A.A. The Risk of Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma; A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, P.; Vibert, F.; Amé, S.; Mathelin, C. New Data on the Epidemiology of Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Eur. J. Breast Health 2021, 17, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, C.M.; Loyo-Berríos, N.; Qureshi, A.A.; Mullen, E.; Gordillo, G.; Pusic, A.L.; Ashar, B.S.; Sommers, K.; Clemens, M.W. Patient Registry and Outcomes for Breast Implants and Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Etiology and Epidemiology (PROFILE): Initial Report of Findings, 2012–2018. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 143, 65S–73S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, J.A.; Dabic, S.; Mehrara, B.J.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Disa, J.J.; Pusic, A.L.; Matros, E.; Dayan, J.H.; Allen, R.J.; Coriddi, M.; et al. Breast Implant-associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Incidence: Determining an Accurate Risk. Ann. Surg. 2020, 272, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, M.W.; Myckatyn, T.M.; Di Napoli, A.; Feldman, A.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Haymaker, C.L.; Horwitz, S.M.; Hunt, K.K.; Kadin, M.E.; McCarthy, C.M.; et al. Breast Implant Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: Evidence-Based Consensus Conference Statement From The American Association of Plastic Surgeons. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2024, 154, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Breast Implants—Certain Labeling Recommendations to Improve Patient Communication. 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/breast-implants-certain-labeling-recommendations-improve-patient-communication (accessed on 28 July 2024).
- Loch-Wilkinson, A.; Beath, K.J.; Knight, R.J.W.; Wessels, W.L.F.; Magnusson, M.; Papadopoulos, T.; Connell, T.; Lofts, J.; Locke, M.; Hopper, I.; et al. Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma in Australia and New Zealand: High-Surface-Area Textured Implants Are Associated with Increased Risk. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnusson, M.; Beath, K.; Cooter, R.; Locke, M.; Prince, H.M.; Elder, E.; Deva, A.K. The Epidemiology of Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma in Australia and New Zealand Confirms the Highest Risk for Grade 4 Surface Breast Implants. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 143, 1285–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boer, M.; van Leeuwen, F.E.; Hauptmann, M.; Overbeek, L.I.H.; de Boer, J.P.; Hijmering, N.J.; Sernee, A.; Klazen, C.A.H.; Lobbes, M.B.I.; van der Hulst, R.R.W.J.; et al. Breast Implants and the Risk of Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma in the Breast. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ün, D.; Rohrbeck, J.; Drach, M.; Ullrich, R.; Staber, P.B.; Helbich, T.H.; Freystätter, C.; Teufelsbauer, M.; Radtke, C. Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: A Case Report About a Patient with Cytology Negative for Malignancy. Life 2024, 14, 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14111494
Ün D, Rohrbeck J, Drach M, Ullrich R, Staber PB, Helbich TH, Freystätter C, Teufelsbauer M, Radtke C. Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: A Case Report About a Patient with Cytology Negative for Malignancy. Life. 2024; 14(11):1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14111494
Chicago/Turabian StyleÜn, Didem, Johannes Rohrbeck, Mathias Drach, Robert Ullrich, Philipp B. Staber, Thomas H. Helbich, Christian Freystätter, Maryana Teufelsbauer, and Christine Radtke. 2024. "Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: A Case Report About a Patient with Cytology Negative for Malignancy" Life 14, no. 11: 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14111494
APA StyleÜn, D., Rohrbeck, J., Drach, M., Ullrich, R., Staber, P. B., Helbich, T. H., Freystätter, C., Teufelsbauer, M., & Radtke, C. (2024). Breast Implant-Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma: A Case Report About a Patient with Cytology Negative for Malignancy. Life, 14(11), 1494. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14111494





