What We Know So Far About ECG for Pancreatic Pseudocysts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Cohort
Inclusion Criteria for ECG
2.2. Methods of Treatment
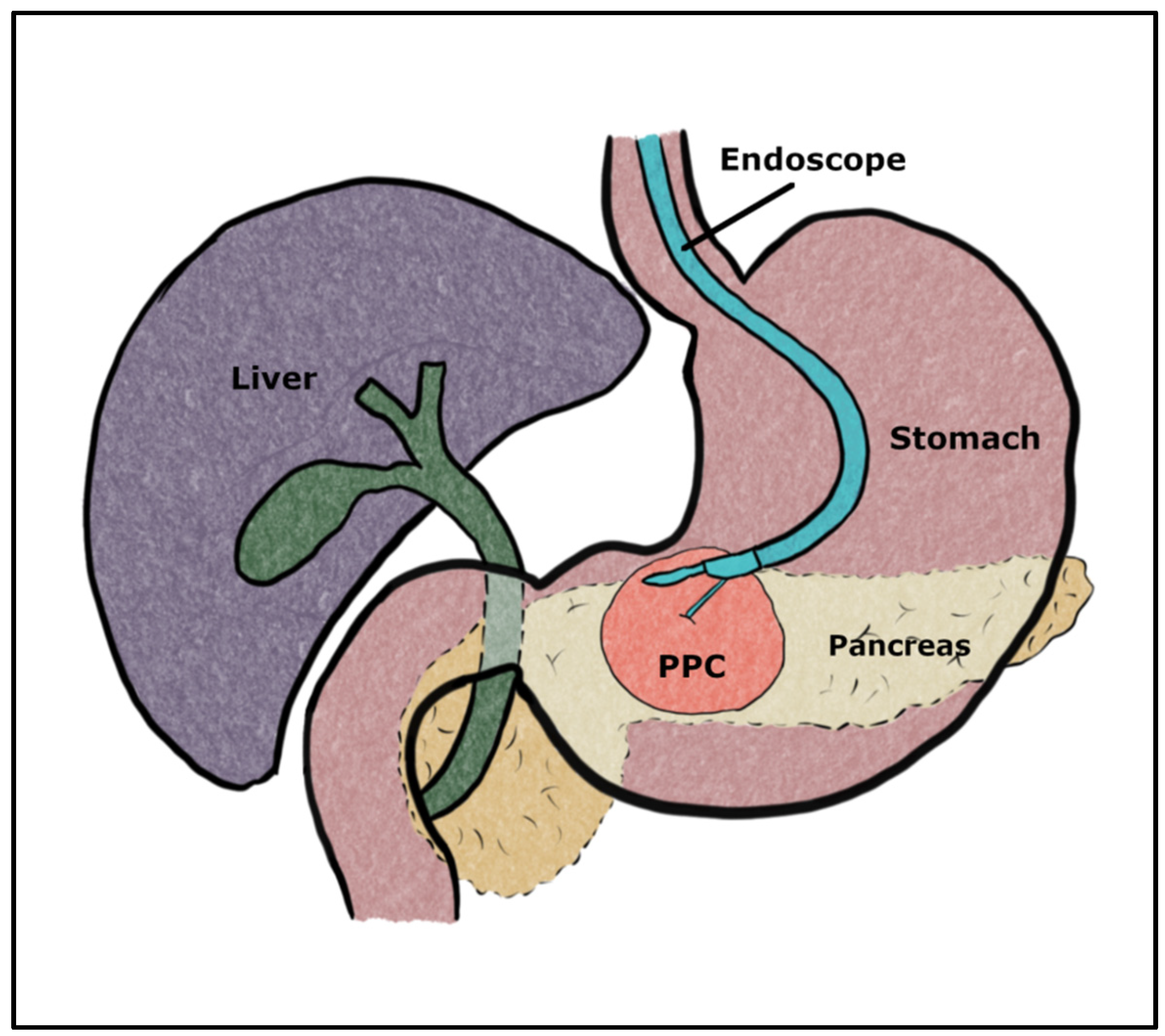
2.3. Endoscopic Cysto-Gastrostomy (ECG)
2.4. Analyzed Data
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Definitions
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
3.2. Cyst Characteristics
3.3. Short-Term Outcomes
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S.; Acute Pancreatitis Classification Working Group. Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habashi, S.; Draganov, P.V. Pancreatic pseudocyst. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabłońska, B. Pancreatic cysts: Etiology, diagnosis and management. Cent. Eur. J. Med. Open Med. 2014, 9, 92–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafin, M.; Kluszczyk, P.; Maślanka, S.; Kowalczyk, T.; Jabłońska, B.; Mrowiec, S. Hemorrhagic Cysts in the Pancreas: Risk Factors, Treatment, and Outcomes—Insights from a Single-Center Study. Med. Sci. Monit. 2024, 30, e941955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Radley, E.L. A Clinically Based Classification System for Acute Pancreatitis: Summary of the International Symposium on Acute Pancreatitis, Atlanta. Arch. Surg. 1993, 128, 586–590. [Google Scholar]
- Lerch, M.M.; Stier, A.; Wahnschaffe, U.; Mayerle, J. Pancreatic pseudocysts: Observation, endoscopic drainage, or resection? Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2009, 106, 614. [Google Scholar]
- Kudaravalli, P.; Garg, N.; Pendela, V.S.; Gambhir, H.S. Hemorrhagic pancreatic pseudocyst: A rare complication. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 43, 243–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, K.A.; Hendrick, L.E.; Behrman, S.W. Surgical management of complicated pancreatic pseudocysts after acute pancreatitis. Am. J. Surg. 2016, 211, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Wan, M.H.; Xie, K.L.; Li, W.; Hu, W.M.; Liu, X.B.; Tang, W.F.; Wu, H. Classification and Management of Pancreatic Pseudocysts. Medicine 2015, 94, e960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wang, L.; Lu, S.; Yang, D.; Hu, W.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Y. Clinical study on cystogastrostomy and Roux-en-Y-type cystojejunostomy in the treatment of pancreatic pseudocyst: A single-center experience. Medicine 2021, 100, e25029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakościelny, A.; Ćwik, G.; Wallner, G. Surgical treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts—Clinical experience. Pediatr. I Med. Rodz. 2014, 10, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, S.; Masica, D.L.; Dal Molin, M.; Douville, C.; Thoburn, C.J.; Afsari, B.; Li, L.; Cohen, J.D.; Thompson, E.; Allen, P.J.; et al. A multimodality test to guide the management of patients with a pancreatic cyst. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaav4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheruvu, C.; Clarke, M.; Prentice, M.; Eyre-Brook, I. Conservative treatment as an option in the management of pancreatic pseudocyst. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2003, 85, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, B.; Nilsson, E.; Willner, J.; Andersson, R. Treatment and outcome in pancreatic pseudocysts. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 41, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, B.; Dudzicz, B.; Burkacka, A.; Cywiński, T.; Stolorz, K.; Lekstan, A.; Lewiński, A.; Dranka-Bojarowska, D.; Olakowski, M.; Lampe, P. Surgical treatment of pancreatic cysts—Own experience. Postępy Nauk. Med. 2011, 24, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Knol, J.A.; Eckhauser, F.E.; Strodel, W.E. Surgical treatment of necrotizing pancreatitis by marsupialization. Am. Surg. 1984, 50, 324–328. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, E.G.; Scaife, C.L.; Mulvihill, S.J.; Glasgow, R.E. Roux-en-Y drainage of a pancreatic fistula for disconnected pancreatic duct syndrome after acute necrotizing pancreatitis. HPB 2012, 14, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiavillano, B.; Lakhtakia, S.; Samanta, J.; Auriemma, F.; Vargas-Madrigal, J.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Barbera, C.; Ashhab, H.; Song, T.J.; Pham, K.D.; et al. Lumen-apposing metal stents for the treatment of pancreatic and peripancreatic fluid collections and bleeding risk: A propensity matched study. Endoscopy 2024, 56, 249–257, Erratum in: Endoscopy 2024, 56, C2. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-2288-4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangiavillano, B.; Moon, J.H.; Crinò, S.F.; Larghi, A.; Pham, K.D.; Teoh, A.Y.B.; Paduano, D.; Lee, Y.N.; Yoo, H.W.; Shin, I.S.; et al. Safety and efficacy of a novel electrocautery-enhanced lumen-apposing metal stent in interventional EUS procedures (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Feng, T.; Ji, W. Endoscopic versus surgical treatment for pancreatic pseudocyst. Dig. Endosc. 2015, 28, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, D.E.; Draganov, P.V.; Wagh, M.S.; Forsmark, C.E.; Gupte, A.R.; Chauhan, S.S. Prospective evaluation of the use of fully covered self-expanding metal stents for EUS-guided transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2012, 76, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, J.Y.; Hasan, M.; Navaneethan, U.; Hawes, R.; Varadarajulu, S. Lumen-apposing metal stents (LAMS) for pancreatic fluid collection (PFC) drainage: May not be business as usual. Gut 2016, 66, 2054–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.B.; Lee, I.S.; Choi, M.G. Metal versus plastic stents for drainage of pancreatic fluid collection: A meta-analysis. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharaiha, R.Z.; DeFilippis, E.M.; Kedia, P.; Gaidhane, M.; Boumitri, C.; Lim, H.-W.; Han, E.; Singh, H.; Ghumman, S.S.; Kowalski, T.; et al. Metal versus plastic for pancreatic pseudocyst drainage: Clinical outcomes and success. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2015, 82, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bapaye, A.; Dubale, N.A.; Sheth, K.A.; Bapaye, J.; Ramesh, J.; Gadhikar, H.; Mahajani, S.; Date, S.; Pujari, R.; Gaadhe, R. Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided transmural drainage of walled-off pancreatic necrosis: Comparison between a specially designed fully covered bi-flanged metal stent and multiple plastic stents. Dig. Endosc. 2017, 29, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.A.; Kowalski, T.E.; Loren, D.E.; Khalid, A.; Soomro, A.; Mazhar, S.M.; Isby, L.; Kahaleh, M.; Karia, K.; Yoo, J.; et al. Fully covered self-expanding metal stents versus lumen-apposing fully covered self-expanding metal stent versus plastic stents for endoscopic drainage of pancreatic walled-off necrosis: Clinical outcomes and success. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2017, 85, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.U.; Song, T.J.; Lee, S.S.; Park, D.H.; Seo, D.-W.; Lee, S.-K.; Kim, M.-H. Newly designed, fully covered metal stents for endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided transmural drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections: A prospective randomized study. Endoscopy 2014, 46, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, S.; Itoi, T.; Baron, T.H.; Sofuni, A.; Itokawa, F.; Kurihara, T.; Tsuchiya, T.; Ishii, K.; Tsuji, S.; Ikeuchi, N.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided placement of plastic vs. biflanged metal stents for therapy of walled-off necrosis: A retrospective single-center series. Endoscopy 2015, 47, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, T.L.; Kongkam, P.; Kwek, A.; Orkoonsawat, P.; Rerknimitr, R.; Fock, K.M. A two-center comparative study of plastic and lumen-apposing large diameter self-expandable metallic stents in endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections. Endosc. Ultrasound 2016, 5, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitas, G.J.; Sarr, M.G. Selected management of pancreatic pseudocysts: Operative versus expectant management. Surgery 1992, 111, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee; Early, D.S.; Lightdale, J.R.; Vargo, J.J., 2nd; Acosta, R.D.; Chathadi, K.V.; Evans, J.A.; Fisher, D.A.; Fonkalsrud, L.; Hwang, J.H.; et al. Guidelines for sedation and anesthesia in GI endoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeo, C.J.; Bastidas, J.A.; Lynch-Nyhan, A.; Fishman, E.K.; Zinner, M.J.; Cameron, J.L. The natural history of pancreatic pseudocysts documented by computed tomography. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1990, 170, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lennon, A.M.; Vege, S.S. Pancreatic Cyst Surveillance. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1663–1667.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saluja, S.S.; Srivastava, S.; Govind, S.H.; Dahale, A.; Sharma, B.C.; Mishra, P.K. Endoscopic cystogastrostomy versus surgical cystogastrostomy in the management of acute pancreatic pseudocysts. J. Minimal Access Surg. 2020, 16, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miłek, T.; Ciostek, P.; Kielar, M.; Jarosz, M.; Słowik, K.; Petryka, R.; Błalejczyk, T. Multiple orifices are better than single in the endoscopic treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 25, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershfield, N.B. Drainage of a pancreatic pseudocyst at ERCP. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1984, 30, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozarek, R.; Brayko, C.; Harlan, J.; Sanowski, R.; Cintora, I.; Kovac, A. Endoscopic drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1985, 31, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, G.F.A.; Bernardo, W.M.; De Moura, D.T.H.; Guedes, H.G.; Brunaldi, V.O.; Visconti, T.A.d.C.; Gonçalves, C.V.T.; Sakai, C.M.; Matuguma, S.E.; Dos Santos, M.E.L.; et al. Endoscopic versus surgical treatment for pancreatic pseudocysts: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e14255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, M.E.; Rauws, E.A.; Tytgat, G.N.; Huibregtse, K. The efficacy of endoscopic treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1995, 42, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckman, L.; Kylanpaa, M.L.; Puolakkainen, P.; Halttunen, J. Endoscopic treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts. Surg Endosc. 2006, 20, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devière, J.; Bueso, H.; Baize, M.; Azar, C.; Love, J.; Moreno, E.; Cremer, M. Complete disruption of the main pancreatic duct: Endoscopic management. Gastrointest. Endosc. 1995, 42, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantino, I. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2012, 4, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, J.Y.; Hawes, R.; Bartolucci, A.; Varadarajulu, S. Efficacy of metal and plastic stents for transmural drainage of pancreatic fluid collections: A systematic review. Dig. Endosc. 2015, 27, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán-Calderón, E.; Chacaltana, A.; Díaz, R.; Li, B.; Martinez-Moreno, B.; Aparicio, J.R. Head-to-head comparison between endoscopic ultrasound guided lumen apposing metal stent and plastic stents for the treatment of pancreatic fluid collections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Sci. 2022, 29, 198–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, J.Y.; Wilcox, C.M.; Arnoletti, J.P.; Peter, S.; Christein, J.; Navaneethan, U.; Hawes, R.; Varadarajulu, S. Validation of the Orlando Protocol for endoscopic management of pancreatic fluid collections in the era of lumen-apposing metal stents. Dig. Endosc. 2022, 34, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Saul, A.; Luna, M.A.R.; Chan, C.; Uscanga, L.; Andraca, F.V.; Calleros, J.H.; Elizondo, J.; Avila, F.T. EUS-guided drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts offers similar success and complications compared to surgical treatment but with a lower cost. Surg Endosc. 2015, 30, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.G.; Sethi, A. Endoscopic Drainage of Pancreatic Fluid Collections. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 34, 553–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gornals, J.B.; De la Serna-Higuera, C.; Sánchez-Yague, A.; Loras, C.; Sánchez-Cantos, A.M.; Pérez-Miranda, M. Endosonography-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections with a novel lumen-apposing stent. Surg. Endosc. 2013, 27, 1428–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| DPPS (n = 21, 53.85%) | LAMS (n = 18, 46.15%) | Total | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 53.45 SD 13.55 (30–70) | 48.28 SD 12.49 (28–65) | 51.13 (28–77, SD 13.18 | 0.23 |
| Gender | 0.74 | |||
| Male | 12 (57.14%) | 12 (66.67%) | 24 (61.54%) | |
| Female | 9 (42.86%) | 6 (33.33%) | 15 (38.46%) | |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) | 24.29 SD 5.62 (14.90–34.93) | 24.51 SD 4.97 (15.42–36.41) | 24.40 SD 5.25 (14.90–36.41) | 0.90 |
| Symptoms | ||||
| Abdominal pain | 17 (80.95%) | 11 (61.11%) | 28 (71.79%) | 0.28 |
| Nausea and vomiting | 4 (19.05%) | 3 (16.67%) | 7 (17.95%) | 1 |
| Jaundice | 0 (0%) | 1 (5.56%) | 1 (2.56%) | 0.27 |
| Fever | 2 (9.52%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (5.13%) | 0.49 |
| Steatorrhea | 1 (4.76%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (2.56%) | 1 |
| Constipation | 1 (4.76%) | 3 (16.67%) | 4 (10.26%) | 0.22 |
| Diarrhea | 0 (0%) | 1 (5.56%) | 1 (2.56%) | 0.27 |
| Weight loss | 5 (23.81%) | 5 (27.78%) | 10 (25.64%) | 1 |
| None | 3 (14.29%) | 3 (16.67%) | 6 (15.38%) | 1 |
| American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score | ||||
| I | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 |
| II | 16 (76.19%) | 13 (72.22%) | 28 (71.79%) | 1 |
| III | 5 (23.81%) | 5 (27.78%) | 10 (25.64%) | 1 |
| IV | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 |
| DPPS (n = 21, 53.85%) | LAMS (n = 18, 46.15%) | Total | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Localization of the cyst | ||||
| Head of the pancreas | 4 (19.05%) | 4 (22.22%) | 8 (20.51%) | 0.81 |
| Body of the pancreas | 2 (9.52%) | 1 (5.56%) | 3 (7.69%) | 0.64 |
| Tail of the pancreas | 6 (28.57%) | 7 (38.89%) | 13 (33.33%) | 0.49 |
| Head and body of the pancreas | 3 (14.29%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (7.69%) | 0.09 |
| Body and tail of the pancreas | 6 (28.57%) | 6 (33.33%) | 12 (30.77%) | 0.75 |
| The greatest size of the cyst | 108 IQR 23 (65–216) | 140 IQR 30 (71–200) | 120 IQR 45 (65–216) | 0.04 |
| Cyst etiology | ||||
| Acute pancreatitis | 14 (66.67%) | 13 (72.22%) | 27 (69.23%) | 1 |
| Chronic pancreatitis | 6 (28.57%) | 2 (11.11%) | 8 (20.51%) | 0.18 |
| Both acute and chronic pancreatitis | 1 (4.76%) | 3 (16.67%) | 4 (10.26%) | 0.22 |
| DPPS (n = 21, 53.85%) | LAMS (n = 18, 46.15%) | Total | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
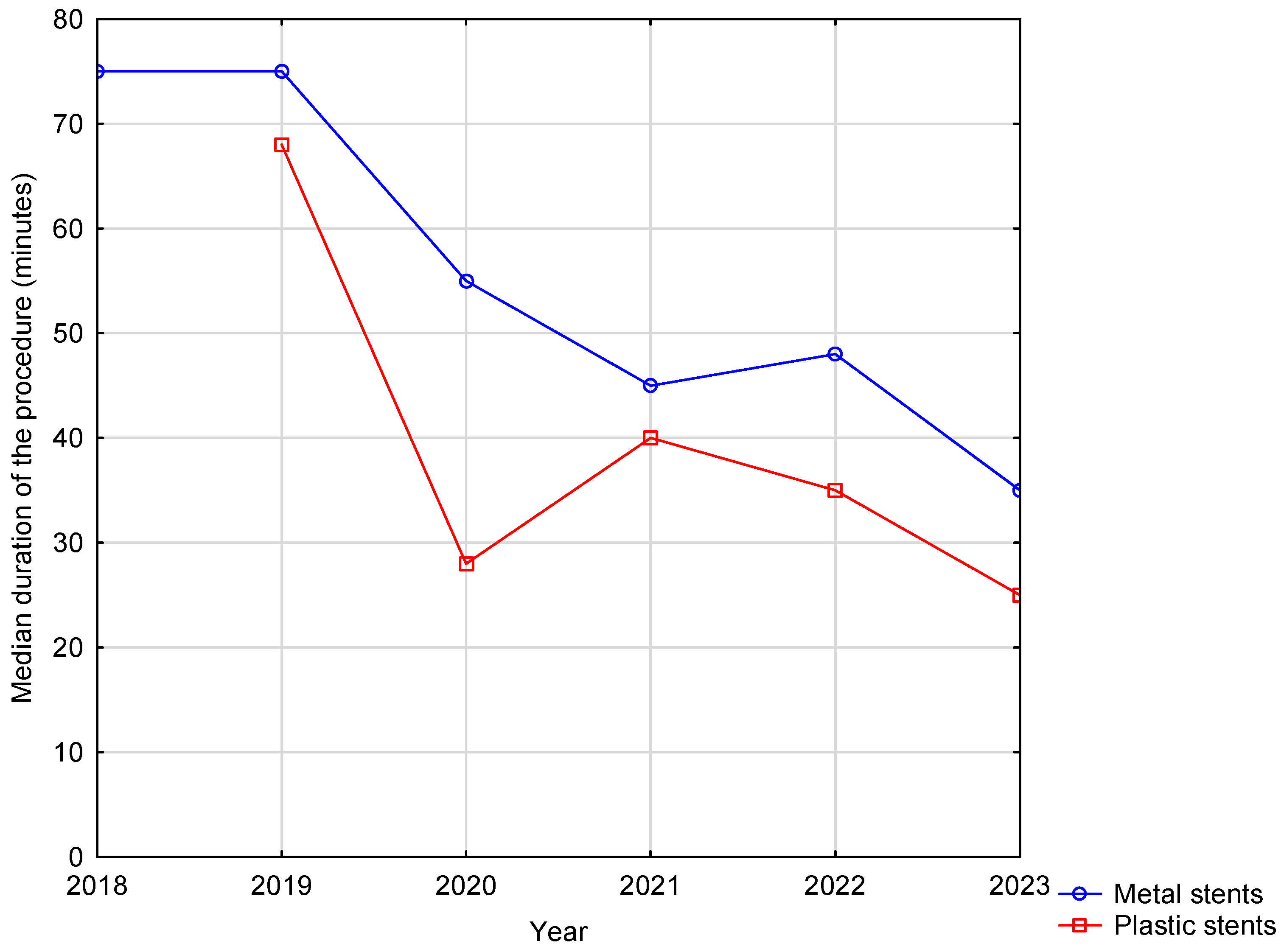
| Duration of procedure (minutes) | 35 IQR 15 (15–50) | 50 IQR 30 (30–75) | 40 IQR 30 (15–75) | <0.001 |
| Duration of hospitalization (days) | 5 IQR 8 (2–36) | 11 IQR 11(3–31) | 10 IQR 13 (2–31) | 0.07 |
| Duration of hospitalization after procedure (days) | 3 IQR 4 (1–25) | 8 IQR 8 (2–27) | 5 IQR 8 (1–27) | 0.002 |
| Complications | ||||
| Total | 3 (14.29%) | 2 (11.11%) | 5 (12.82%) | 0.77 |
| Bleeding into the cyst | 2 (9.52%) | 1 (5.56%) | 3 (5.13%) | 0.64 |
| Cyst infection | 1 (4.76%) | 1 (5.56%) | 2 (5.14%) | 0.91 |
| 30-day mortality | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 |
| Reintervention | 3 (14.29%) | 2 (11.11%) | 5 (12.89%) | 0.76 |
| Rehospitalization | 5 (23.81%) | 2 (11.11%) | 7 (17.96%) | 0.30 |
| Follow up | ||||
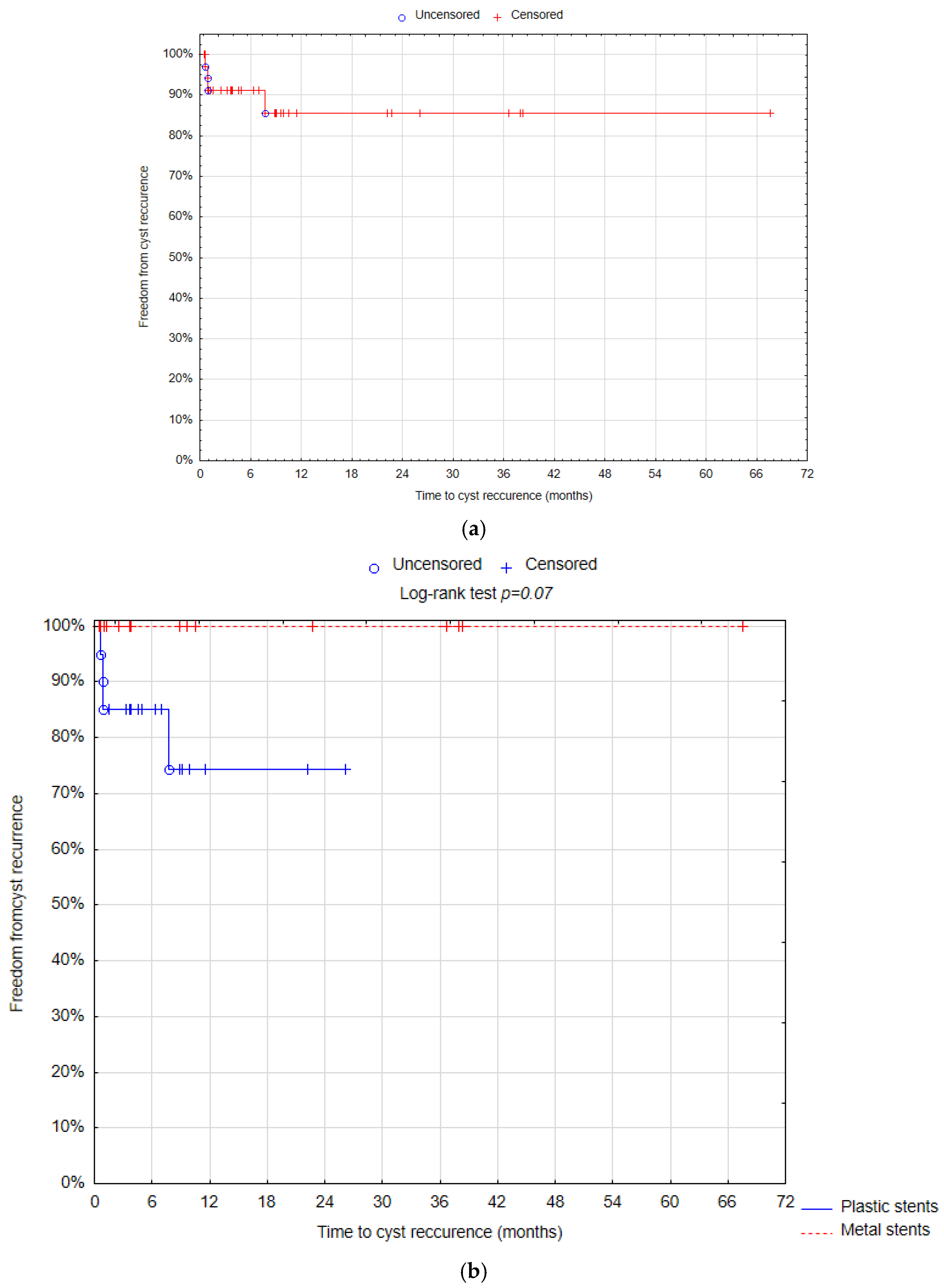
| Therapeutic success | 18 (85.71%) | 18 (100%) | 35 (89.74%) | 0.095 |
| Cyst recurrence | 4 (19.05%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (10.26%) | 0.05 |
| Median time of follow-up (days) | 268 IQR 430 (46–1108) | 317 IQR 984 (31–2027) | 280 IQR 551 (31–2027) | 0.34 |
| Time of the stent removal (days) | 106 IQR 89 (43–660) | 34 IQR 24.5 (15–355) | 45 IQR 68 (14–660) | 0.001 |
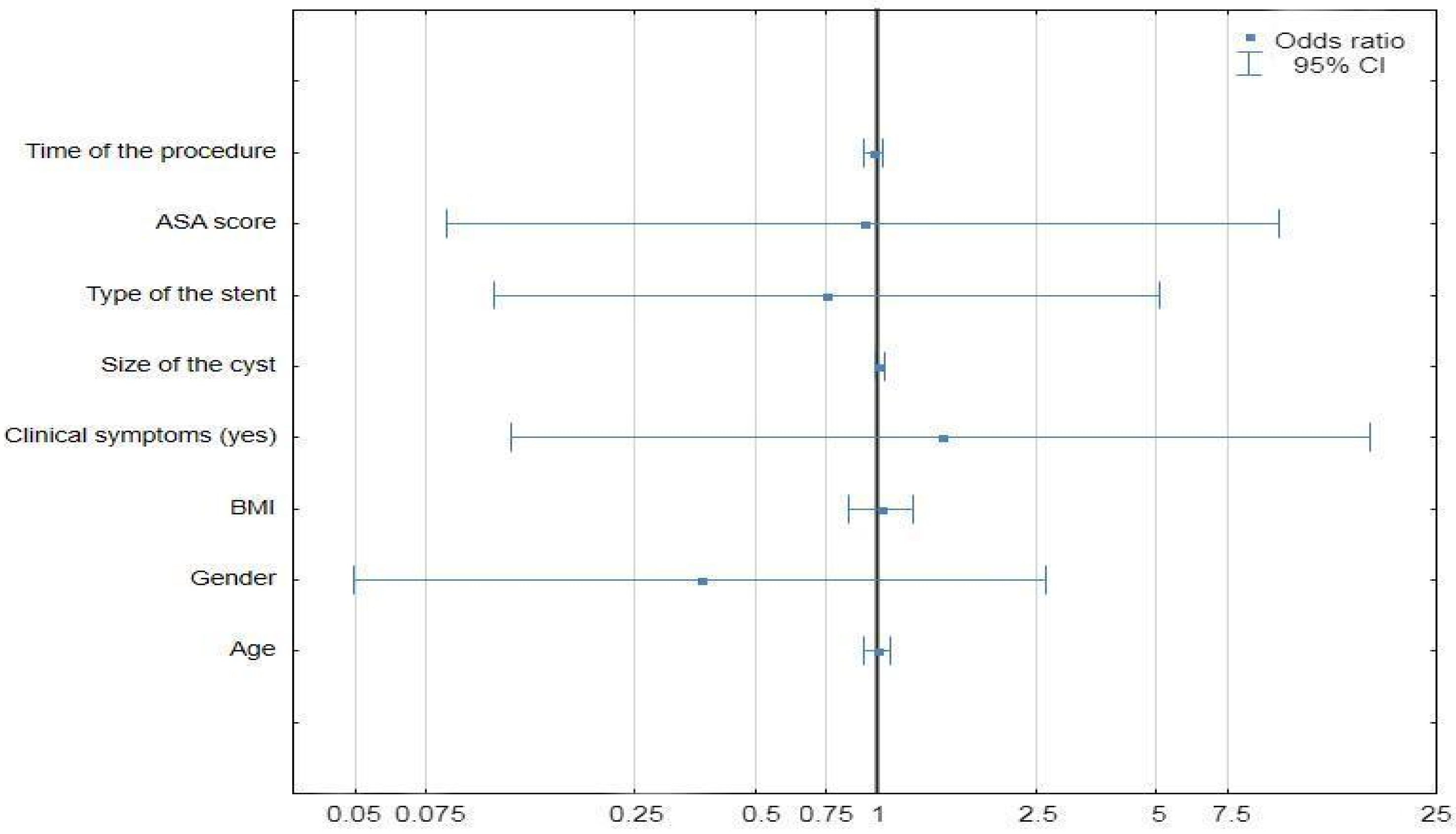
| Univariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | HR | 95% CI | p |
| Age | 1.08 | 0.98–1.19 | 0.09 |
| Gender | 0.53 | ||
| Male | 0.53 | 0.07–3.82 | |
| Female | 1 | ||
| BMI | 1.06 | 0.9–1.28 | 0.47 |
| Admission mode | 0.21 | ||
| Emergency | 3.55 | 0.49–25.39 | |
| Elective | 1 | ||
| Symptoms | 0.68 | ||
| No | 0.62 | 0.06–5.97 | |
| Yes | 1 | ||
| Alcohol usage | 0.69 | ||
| No | 0.66 | 0.09–4.76 | |
| Yes | 1 | ||
| Complications | 0.01 | ||
| Yes | 21.55 | 1.95–237.72 | |
| No | 1 | ||
| Cyst Size | 1.01 | 0.98–1.04 | 0.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kluszczyk, P.; Jabłońska, B.; Serafin, M.; Tobiasz, A.; Kowalczyk, T.; Maślanka, S.; Chapuła, M.; Wosiewicz, P.; Mrowiec, S. What We Know So Far About ECG for Pancreatic Pseudocysts. Life 2024, 14, 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14111419
Kluszczyk P, Jabłońska B, Serafin M, Tobiasz A, Kowalczyk T, Maślanka S, Chapuła M, Wosiewicz P, Mrowiec S. What We Know So Far About ECG for Pancreatic Pseudocysts. Life. 2024; 14(11):1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14111419
Chicago/Turabian StyleKluszczyk, Paulina, Beata Jabłońska, Michał Serafin, Aleksandra Tobiasz, Tomasz Kowalczyk, Sebastian Maślanka, Mateusz Chapuła, Piotr Wosiewicz, and Sławomir Mrowiec. 2024. "What We Know So Far About ECG for Pancreatic Pseudocysts" Life 14, no. 11: 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14111419
APA StyleKluszczyk, P., Jabłońska, B., Serafin, M., Tobiasz, A., Kowalczyk, T., Maślanka, S., Chapuła, M., Wosiewicz, P., & Mrowiec, S. (2024). What We Know So Far About ECG for Pancreatic Pseudocysts. Life, 14(11), 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14111419






