Hypoxia Modulates Sodium Chloride Co-transporter via CaMKII-β Pathway: An In Vitro Study with mDCT15 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Protocol
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Drug Treatments
2.4. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
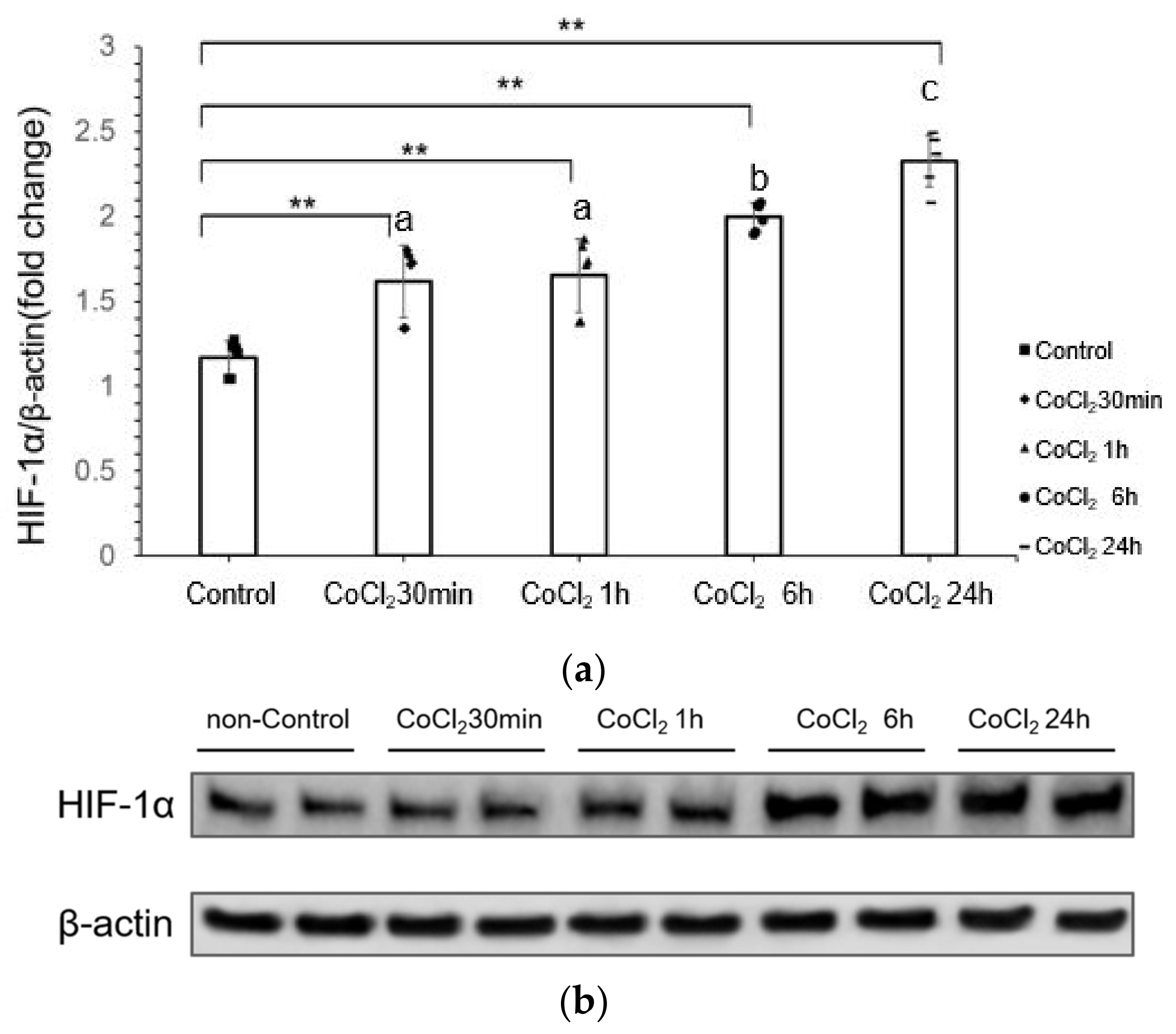
3.1. CoCl2 Incubation Induced Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α (HIF-1α) in mDCT15 Cells
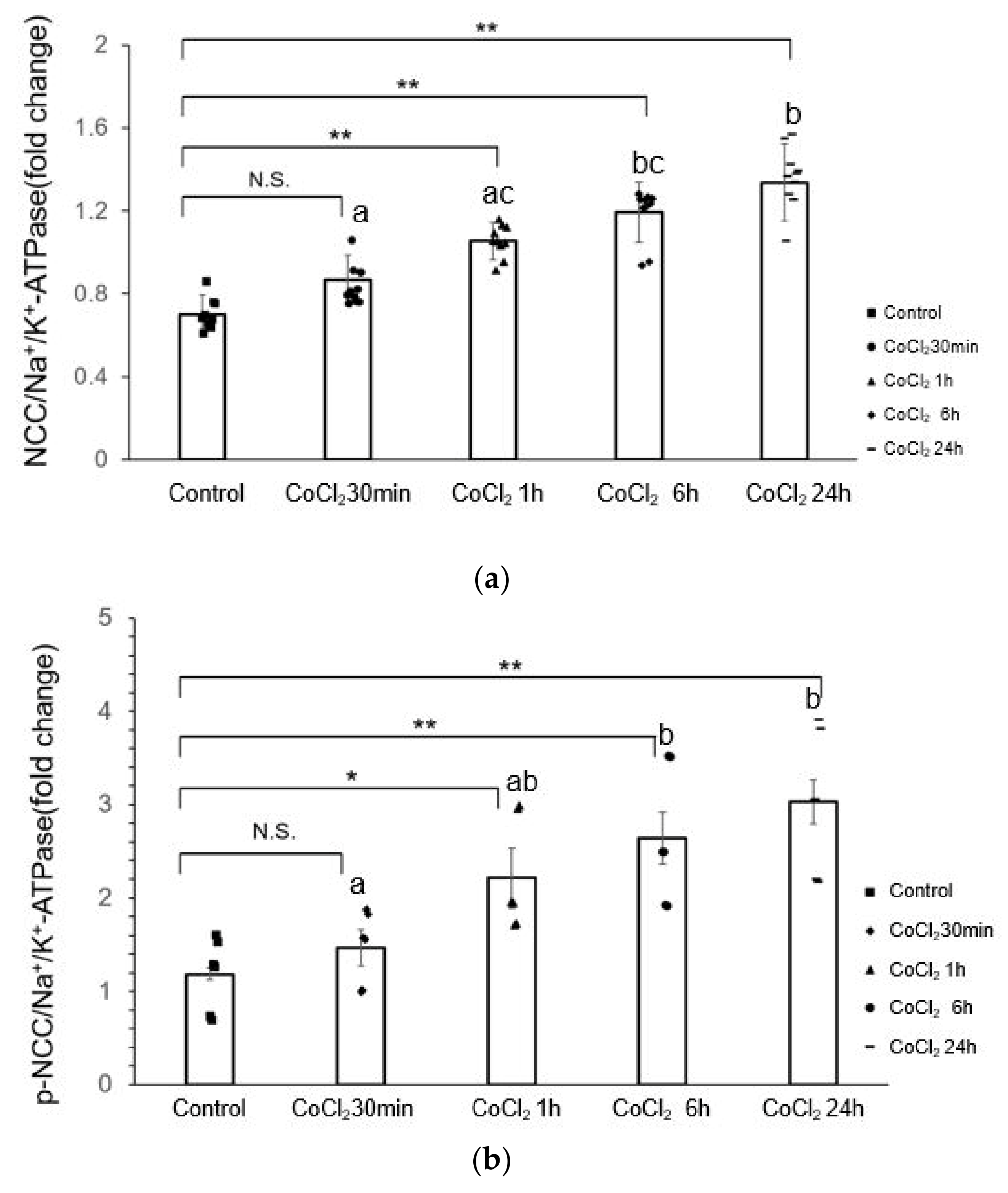
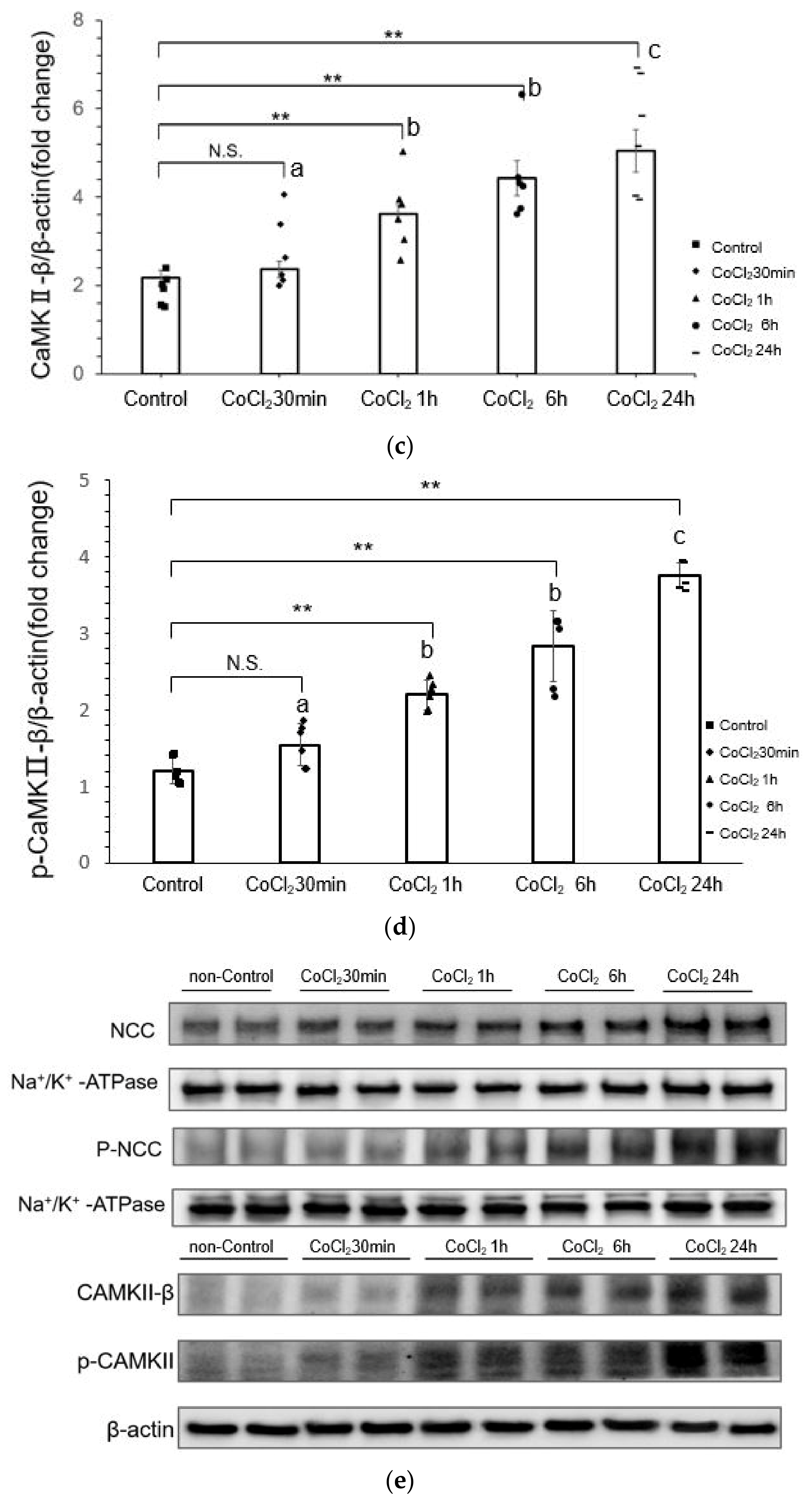
3.2. CoCl2 Incubation Induced NCC Activity and CAMKII-β Activity in mDCT15 Cells
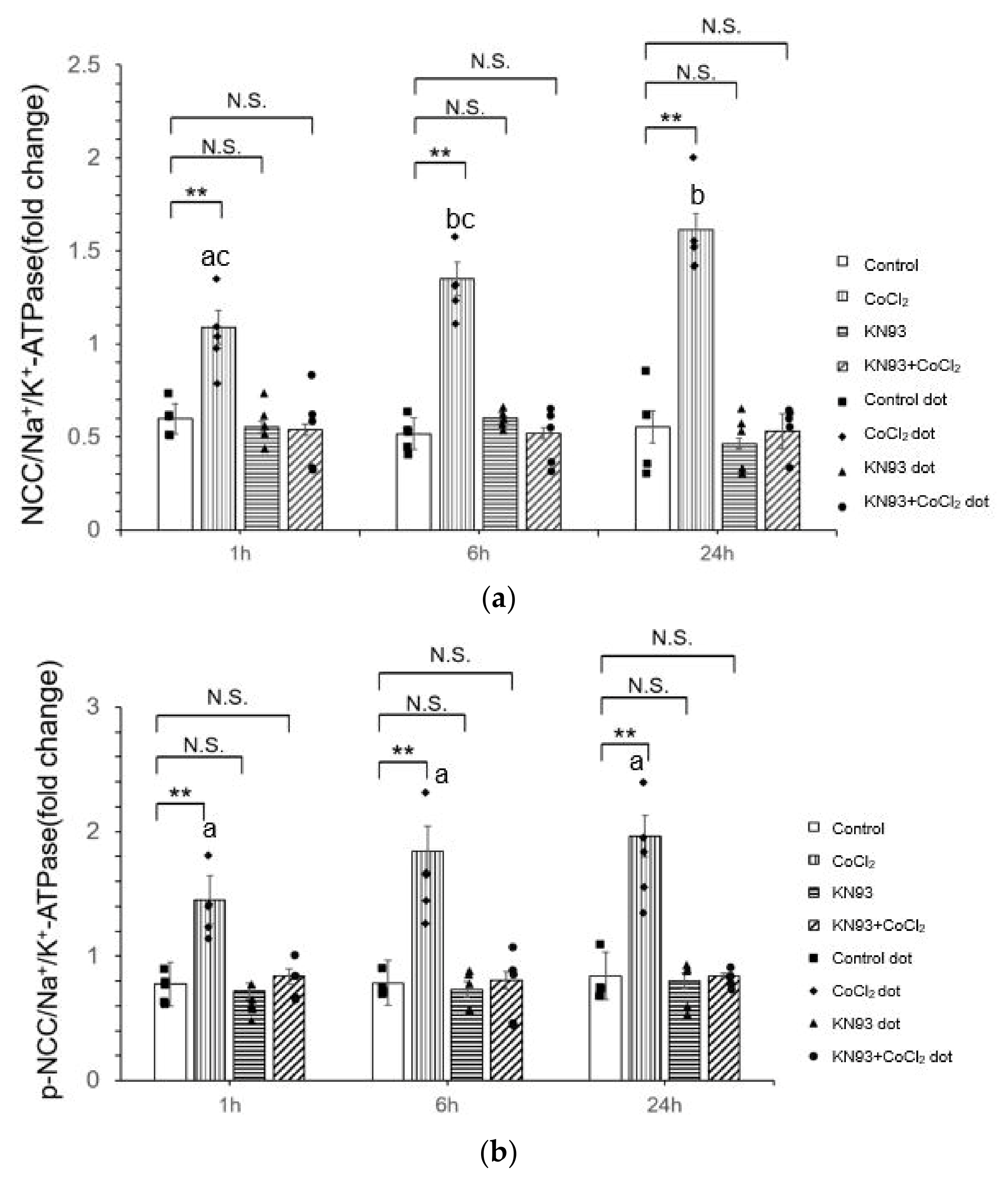
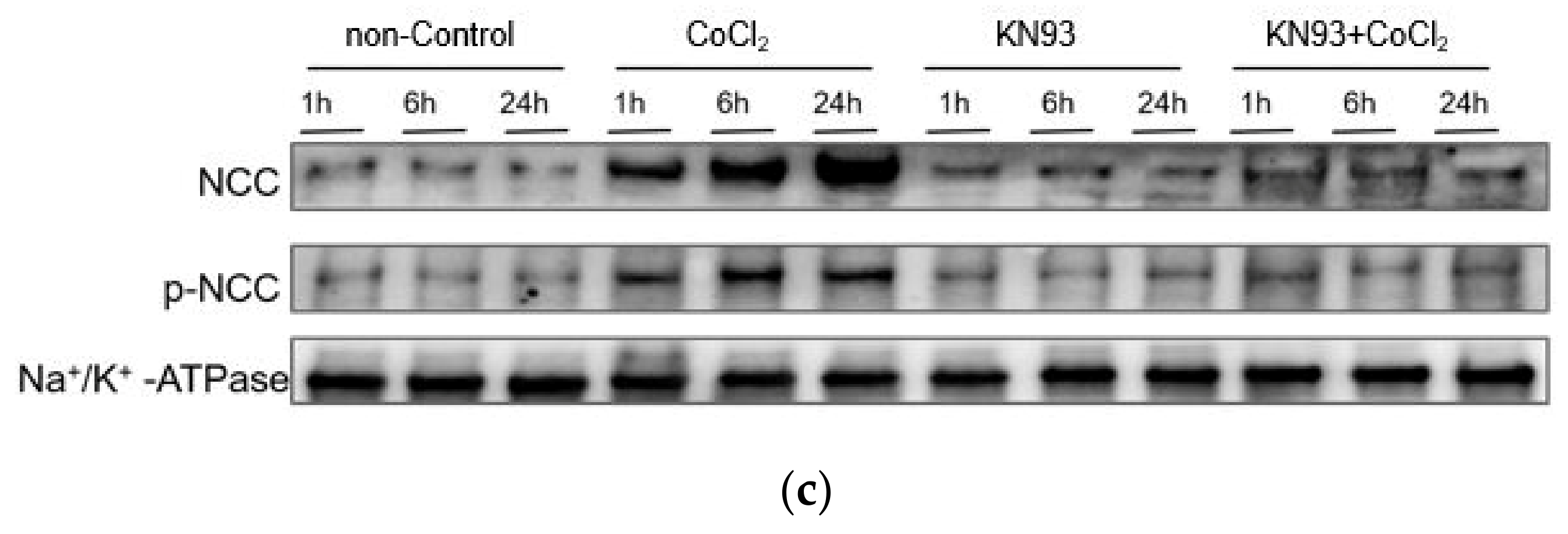
3.3. KN93 Inhibits the CoCl2-Induced Activity of NCC In Vitro via the CaMKII Pathway
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DCT | Distal convoluted tubule |
| NCC | Sodium-chloride co-transporter |
| CoCl2 | Cobalt chloride |
| CaMKII | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II |
| mDCT15 | mouse DCT15 |
| PHD | prolyl hydroxylases |
| pVHL | von Hippel-Lindau tumor-suppressor protein |
| KN93 | N-[2-[N-(4-chlorocinnamyl)-N-methylaminomethyl]phenyl]-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methoxybenzenesulfonamide |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α |
| p-NCC | phosphorylated NCC |
| lcn2 KO | lcn2 knockout |
| WT | Wild-type |
| CaM | Calmodulin |
| SAHA | Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid |
| I/R | Ischemia-reperfusion |
| NCX | Na⁺-Ca2⁺ exchanger |
| FDCA | Fasudil Dichloroacetate |
| PAH | Pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| SuH | SU5416 plus hypoxia |
| PASMC | Pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell |
References
- Subramanya, A.R.; Ellison, D.H. Distal convoluted tubule. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 2147–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamba, G. The thiazide-sensitive Na+-Cl− cotransporter: Molecular biology, functional properties, and regulation by WNKs. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 297, F838–F848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, K.; Shimosawa, T. Regulating distal tubule functions and salt sensitivity. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2024, 327, F566–F580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaysen, J.H.; Lassen, N.A.; Munck, O. Sodium transport and oxygen consumption in the mammalian kidney. Nature 1961, 190, 919–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Tanaka, T.; Nangaku, M. Hypoxia as a key player in the AKI-to-CKD transition. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2014, 307, F1187–F1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safran, M.; Kim, W.Y.; O’Connell, F.; Flippin, L.; Günzler, V.; Horner, J.W.; DePinho, R.A.; Kaelin, W.G., Jr. Mouse model for noninvasive imaging of HIF prolyl hydroxylase activity: Assessment of an oral agent that stimulates erythropoietin production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezis, M.; Rosen, S. Hypoxia of the renal medulla—Its implications for disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 332, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, S. Why is erythropoietin made in the kidney? The kidney functions as a critmeter. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 38, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnard, B.; El Moghrabi, S.; Ueda, K.; Lattenist, L.; Soulie, M.; López-Andrés, N.; Xhaard, C.; Shimosawa, T.; Rossignol, P.; Jaisser, F. NGAL is a novel target in hypertension by modulating the NCC-mediated renal NA balance. Hypertension 2023, 80, 1860–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubarack, M.; Muthalif, N.A. Functional Significance of Activation of Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II in Angiotensin II-Induced Vascular Hyperplasia and Hypertension. Hypertension 2002, 39, 704–709. [Google Scholar]
- Lisman, J.; Schulman, H.; Cline, H. The molecular basis of CaMKII function in synaptic and behavioural memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Brown, J.H. Role of Ca²⁺/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Cardiovasc. Res. 2004, 63, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Connelly, J.; Levitan, E.S.; Sun, D.; Wang, J.Q. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in cerebrovascular diseases. Transl. Stroke Res. 2021, 12, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, B.; Mistry, A.C.; Hanson, L.; Mallick, R.; Cooke, L.L.; Hack, B.K.; Cunningham, P.; Hoover, R.S. A new model of the distal convoluted tubule. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2012, 303, F700–F710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, V.K.; Subramaniyan, S.A.; Hwang, I. Molecular and cellular response of co-cultured cells toward cobalt chloride (CoCl₂)-induced hypoxia. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 20882–20893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fandrey, J.; Gorr, T.A.; Gassmann, M. Regulating cellular oxygen sensing by hydroxylation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 71, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, C.J.; Ratcliffe, P.J. Signalling hypoxia by HIF hydroxylases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 338, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengler, V.L.; Galbraith, M.D.; Espinosa, J.M. Transcriptional regulation by hypoxia inducible factors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foresto-Neto, O.; da Silva, A.R.P.A.; Cipelli, M.; Santana-Novelli, F.P.R.; Camara, N.O.S. The impact of hypoxia-inducible factors in the pathogenesis of kidney diseases: A link through cell metabolism. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2023, 42, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, A.V.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, H.J.; Lin, J.J.; Cheng, C.P. Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activation promotes kidney mesangial expansion in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Heliyon 2022, 8, e11653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.H.; Samal, A.B.; Lee, M.; Vlach, J.; Novikov, N.; Niedziela-Majka, A.; Feng, J.Y.; Koltun, D.O.; Brendza, K.M.; Kwon, H.J.; et al. The KN-93 molecule inhibits calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) activity by binding to Ca2+/CaM. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 1440–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Zhao, H.; Han, Y.; Li, L.; Xiong, S.; Zeng, L.; Xiao, Y.; Wei, L.; Xiong, X.; Gao, P.; et al. HIF-1α ameliorates tubular injury in diabetic nephropathy via HO-1-mediated control of mitochondrial dynamics. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumi, M.; Kiuchi, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Ishii, A.; Hagiwara, M.; Nagatsu, T.; Hidaka, H. The newly synthesized selective Ca2+ calmodulin dependent protein kinase II inhibitor KN-93 reduces dopamine contents in PC12h cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 181, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, L. Effects of CoCl2-simulated hypoxia on the expression levels of matrix metalloproteinases in renal adenocarcinoma cells and renal tubular epithelial cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizin, E.; Olivier, V.; Roth, I.; Sassi, A.; Arnoux, G.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Morel, S.; Kwak, B.R.; Loffing, J.; Hummler, E.; et al. Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor pathway inhibits epithelial sodium channel-mediated sodium transport in collecting duct principal cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 3130–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, C. Downregulation of Cullin 3 ligase signaling pathways contributes to hypertension in preeclampsia. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 654254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratimenos, P.; Vij, A.; Vidva, R.; Koutroulis, I.; Delivoria-Papadopoulos, M.; Gallo, V.; Sathyanesan, A. Computational analysis of cortical neuronal excitotoxicity in a large animal model of neonatal brain injury. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2022, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shioda, N.; Fukunaga, K. Physiological and pathological roles of CaMKII-PP1 signaling in the brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.E. Oxidant stress promotes disease by activating CaMKII. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2015, 89, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Nanduri, J.; Bhasker, C.R.; Semenza, G.L.; Prabhakar, N.R. Ca2+/calmodulin kinase-dependent activation of hypoxia inducible factor 1 transcriptional activity in cells subjected to intermittent hypoxia. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 4321–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yin, Y.; Guo, X.; Liu, M.; Ma, F.; Tian, L.; Zheng, M.; Liu, G. The histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA exerts a protective effect against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting sodium-calcium exchanger. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 671, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Huang, W.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Liang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Xie, W.; Kong, H. Fasudil dichloroacetate alleviates SU5416/hypoxia-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension by ameliorating dysfunction of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 1653–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholam, M.F.; Ko, B.; Ghazi, Z.M.; Hoover, R.S.; Alli, A.A. The pharmacological inhibition of CaMKII regulates sodium chloride cotransporter activity in mDCT15 cells. Biology 2021, 10, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, L.; Ueda, K.; Ogura, S.; Shimosawa, T. Hypoxia Modulates Sodium Chloride Co-transporter via CaMKII-β Pathway: An In Vitro Study with mDCT15 Cells. Life 2024, 14, 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14101229
Liang L, Ueda K, Ogura S, Shimosawa T. Hypoxia Modulates Sodium Chloride Co-transporter via CaMKII-β Pathway: An In Vitro Study with mDCT15 Cells. Life. 2024; 14(10):1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14101229
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Lijuan, Kohei Ueda, Sayoko Ogura, and Tatsuo Shimosawa. 2024. "Hypoxia Modulates Sodium Chloride Co-transporter via CaMKII-β Pathway: An In Vitro Study with mDCT15 Cells" Life 14, no. 10: 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14101229
APA StyleLiang, L., Ueda, K., Ogura, S., & Shimosawa, T. (2024). Hypoxia Modulates Sodium Chloride Co-transporter via CaMKII-β Pathway: An In Vitro Study with mDCT15 Cells. Life, 14(10), 1229. https://doi.org/10.3390/life14101229







