Gender-Related Differences in the Levels of Ambulatory BP and Intensity of Antihypertensive Treatment in Patients Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
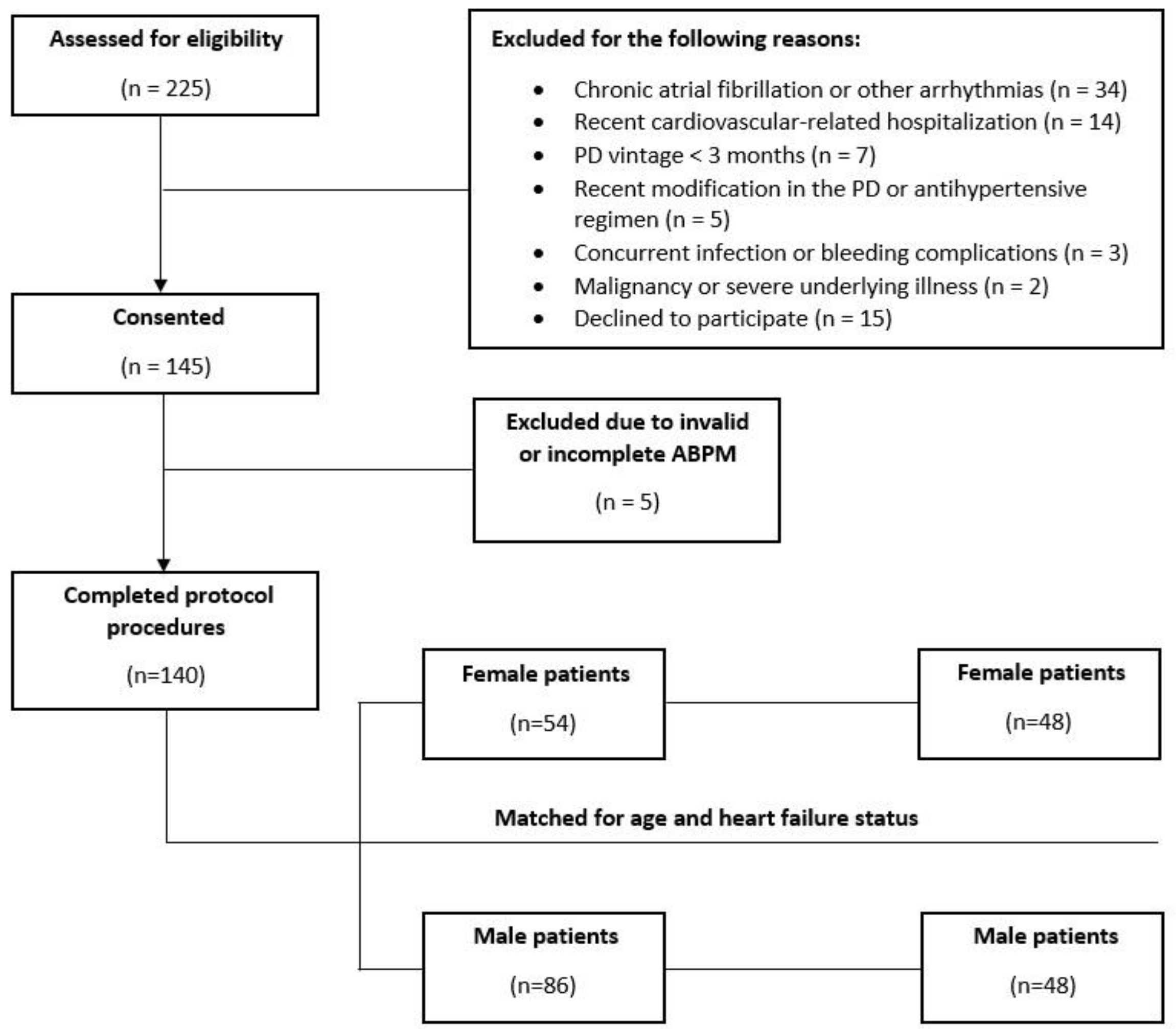
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Georgianos, P.I.; Vaios, V.; Sgouropoulou, V.; Eleftheriadis, T.; Tsalikakis, D.G.; Liakopoulos, V. Hypertension in Dialysis Patients: Diagnostic Approaches and Evaluation of Epidemiology. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vareta, G.; Georgianos, P.I.; Vaios, V.; Sgouropoulou, V.; Roumeliotis, S.; Georgoulidou, A.; Dounousi, E.; Eleftheriadis, T.; Papagianni, A.; Balaskas, E.V.; et al. Epidemiology of Hypertension among Patients on Peritoneal Dialysis Using Standardized Office and Ambulatory Blood Pressure Recordings. Am. J. Nephrol. 2022, 53, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Kim, A.; Ebinger, J.E.; Niiranen, T.J.; Claggett, B.L.; Bairey Merz, C.N.; Cheng, S. Sex Differences in Blood Pressure Trajectories Over the Life Course. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuspidi, C.; Gherbesi, E.; Sala, C.; Tadic, M. Sex, Gender, and Subclinical Hypertensiveorgan Damage—Heart. J. Hum. Hypertens 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuspidi, C.; Faggiano, A.; Tadic, M. Hypertensive Organ Damage: The Vulnerable Heart of Women. J. Hum. Hypertens 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrero, J.J.; Hecking, M.; Chesnaye, N.C.; Jager, K.J. Sex and Gender Disparities in the Epidemiology and Outcomes of Chronic Kidney Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricardo, A.C.; Yang, W.; Sha, D.; Appel, L.J.; Chen, J.; Krousel-Wood, M.; Manoharan, A.; Steigerwalt, S.; Wright, J.; Rahman, M.; et al. Sex-Related Disparities in CKD Progression. JASN 2019, 30, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minutolo, R.; Gabbai, F.B.; Agarwal, R.; Garofalo, C.; Borrelli, S.; Chiodini, P.; Signoriello, S.; Paoletti, E.; Ravera, M.; Bellizzi, V.; et al. Sex Difference in Ambulatory Blood Pressure Control Associates with Risk of ESKD and Death in CKD Patients Receiving Stable Nephrology Care. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 36, 2000–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 1953–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parati, G.; Stergiou, G.; O’Brien, E.; Asmar, R.; Beilin, L.; Bilo, G.; Clement, D.; de la Sierra, A.; de Leeuw, P.; Dolan, E.; et al. European Society of Hypertension Practice Guidelines for Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring. J. Hypertens. 2014, 32, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodorakopoulou, M.P.; Karagiannidis, A.G.; Alexandrou, M.-E.; Polychronidou, G.; Karpetas, A.; Giannakoulas, G.; Papagianni, A.; Sarafidis, P.A. Sex Differences in Ambulatory Blood Pressure Levels, Control and Phenotypes of Hypertension in Hemodialysis Patients. J. Hypertens. 2022, 40, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korogiannou, M.; Sarafidis, P.; Theodorakopoulou, M.P.; Alexandrou, M.E.; Xagas, E.; Argyris, A.; Protogerou, A.; Ferro, C.J.; Boletis, I.N.; Marinaki, S. Sex Differences in Ambulatory Blood Pressure Levels, Control, and Phenotypes of Hypertension in Kidney Transplant Recipients. J. Hypertens. 2022, 40, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.-J.; Ma, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.-X.; Zhong, J.-C. Gender Differences in Hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 2020, 13, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilliard, L.M.; Nematbakhsh, M.; Kett, M.M.; Teichman, E.; Sampson, A.K.; Widdop, R.E.; Evans, R.G.; Denton, K.M. Gender Differences in Pressure-Natriuresis and Renal Autoregulation: Role of the Angiotensin Type 2 Receptor. Hypertension 2011, 57, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.D.; Hilliard, L.M.; Head, G.A.; Jones, E.S.; Widdop, R.E.; Denton, K.M. Sex Differences in the Pressor and Tubuloglomerular Feedback Response to Angiotensin II. Hypertension 2012, 59, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fardoun, M.; Dehaini, H.; Shaito, A.; Mesmar, J.; El-Yazbi, A.; Badran, A.; Beydoun, E.; Eid, A.H. The Hypertensive Potential of Estrogen: An Untold Story. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 124, 106600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reckelhoff, J.F. Gender Differences in the Regulation of Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2001, 37, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, E.E.; Sullivan, J.C. Sex Differences in Hypertension: Recent Advances. Hypertension 2016, 68, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Men (n = 48) | Women (n = 48) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 62.5 (54.0–70.5) | 62 (53.3–70.8) | 0.956 |
| Weight (kg) | 77.9 ± 12.9 | 70.5 ± 15.2 | 0.012 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.6 ± 4.0 | 27.5 ± 5.9 | 0.356 |
| Time on PD (months) | 21.0 (6.0–39.0) | 21.5 (7.0–44.8) | 0.867 |
| Continuous ambulatory PD (n, %) | 14 (29.2%) | 26 (54.2%) | 0.013 |
| Peritoneal ultrafiltration (L) | 0.6 (0.4–1.0) | 0.8 (0.5–1.0) | 0.412 |
| Dialysate-to-plasma creatinine ratio | 0.69 ± 0.10 | 0.67 ± 0.11 | 0.232 |
| Peritoneal transport status (n, %) | |||
| Low | 3 (6.3%) | 6 (12.5%) | |
| Low-average | 13 (27.1%) | 13 (27.1%) | |
| High-average | 27 (56.3%) | 23 (47.9%) | |
| High | 5 (10.4%) | 6 (12.5%) | |
| Residual diuresis ≥ 0.5 L/day (n, %) | 35 (72.9%) | 33 (68.8%) | 0.653 |
| Comorbidities (n, %) | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 20 (41.7%) | 18 (37.5%) | 0.676 |
| Dyslipidemia | 33 (68.8%) | 33 (68.8%) | 1.000 |
| Coronary artery disease | 16 (33.3%) | 11 (22.9%) | 0.256 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 8 (16.7%) | 3 (6.3%) | 0.109 |
| Heart failure | 9 (18.8%) | 9 (18.8%) | 1.000 |
| Current smokers (n, %) | 11 (22.9%) | 7 (14.6%) | 0.296 |
| Laboratory parameters | |||
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.5 (10.9–12.6) | 11.2 (10.3–11.9) | 0.065 |
| Serum urea (mg/dL) | 123.9 ± 34.8 | 112.7 ± 32.4 | 0.106 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 8.0 (5.5–13.9) | 5.9 (4.8–7.6) | 0.008 |
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | 3.9 (3.5–4.0) | 3.7 (3.6–4.0) | 0.371 |
| Serum sodium (mEq/L) | 138 (137–140) | 138 (136–140) | 0.474 |
| Serum potassium (mEq/L) | 4.5 ± 0.6 | 4.4 ± 0.6 | 0.516 |
| Parameter | Men (n = 48) | Women (n = 48) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Office BP | |||
| Systolic (mmHg) | 135.5 ± 21.0 | 134.4 ± 18.2 | 0.768 |
| Diastolic (mmHg) | 79.6 ± 11.6 | 80.1 ± 14.1 | 0.856 |
| Ambulatory 24 h BP | |||
| Systolic (mmHg) | 129.0 ± 17.9 | 128.5 ± 17.6 | 0.890 |
| Diastolic (mmHg) | 81.5 ± 12.1 | 76.8 ± 10.3 | 0.042 |
| Ambulatory daytime BP | |||
| Systolic (mmHg) | 129.6 ± 17.6 | 129.7 ± 17.5 | 0.991 |
| Diastolic (mmHg) | 82.5 ± 11.8 | 78,1 ± 10.4 | 0.052 |
| Ambulatory nighttime BP | |||
| Systolic (mmHg) | 127.0 ± 19.8 | 125.9 ± 18.8 | 0.776 |
| Diastolic (mmHg) | 78.8 ± 14.0 | 73.8 ± 11.1 | 0.056 |
| HR (bpm) | |||
| Office HR | 73.7 ± 9.8 | 74.9 ± 11.7 | 0.573 |
| Ambulatory 24 h HR | 72.4 ± 8.1 | 72.3 ± 9.9 | 0.964 |
| Ambulatory daytime HR | 73.5 ± 0.3 | 73.6 ± 10.7 | 0.949 |
| Ambulatory nighttime HR | 69.6 ± 8.6 | 69.0 ± 9.1 | 0.730 |
| Prevalence of hypertension | |||
| Ambulatory BP ≥ 130/80 mmHg or antihypertensive drug use (n, %) | 45 (93.8%) | 44 (91.7%) | 0.695 |
| Office BP ≥ 140/90 mmHg or antihypertensive drug use (n, %) | 45 (93.8%) | 43 (89.6%) | 0.460 |
| Volume status | |||
| BIS-derived overhydration index (L) | 1.7 (0.1–3.3) | 0.8 (−0.3–1.9) | 0.071 |
| Overhydration index > 2.5 L (n, %) | 16 (33.3%) | 8 (16.7%) | 0.059 |
| Patients treated with antihypertensives (n, %) | 45 (93.8%) | 42 (87.5%) | 0.294 |
| Number of antihypertensive medications (n, %) | 2.4 ± 1.1 | 1.9 ± 1.1 | 0.019 |
| Antihypertensive agent classes | |||
| ACEIs/ARBs | 25 (52.1%) | 22 (45.8%) | 0.540 |
| CCBs | 34 (70.8%) | 21 (43.8%) | 0.007 |
| β-blockers | 41 (85.4%) | 32 (66.7%) | 0.031 |
| α-blockers | 6 (12.5%) | 1 (2.1%) | 0.111 |
| MRAs | 2 (4.2%) | 10 (20.8%) | 0.014 |
| Central acting agents | 7 (14.6%) | 3 (6.3%) | 0.181 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kontogiorgos, I.; Georgianos, P.I.; Vaios, V.; Vareta, G.; Georgianou, E.; Karligkiotis, A.; Sgouropoulou, V.; Kantartzi, K.; Zebekakis, P.E.; Liakopoulos, V. Gender-Related Differences in the Levels of Ambulatory BP and Intensity of Antihypertensive Treatment in Patients Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis. Life 2023, 13, 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051140
Kontogiorgos I, Georgianos PI, Vaios V, Vareta G, Georgianou E, Karligkiotis A, Sgouropoulou V, Kantartzi K, Zebekakis PE, Liakopoulos V. Gender-Related Differences in the Levels of Ambulatory BP and Intensity of Antihypertensive Treatment in Patients Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis. Life. 2023; 13(5):1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051140
Chicago/Turabian StyleKontogiorgos, Ioannis, Panagiotis I. Georgianos, Vasilios Vaios, Georgia Vareta, Eleni Georgianou, Apostolos Karligkiotis, Vasiliki Sgouropoulou, Konstantia Kantartzi, Pantelis E. Zebekakis, and Vassilios Liakopoulos. 2023. "Gender-Related Differences in the Levels of Ambulatory BP and Intensity of Antihypertensive Treatment in Patients Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis" Life 13, no. 5: 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051140
APA StyleKontogiorgos, I., Georgianos, P. I., Vaios, V., Vareta, G., Georgianou, E., Karligkiotis, A., Sgouropoulou, V., Kantartzi, K., Zebekakis, P. E., & Liakopoulos, V. (2023). Gender-Related Differences in the Levels of Ambulatory BP and Intensity of Antihypertensive Treatment in Patients Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis. Life, 13(5), 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13051140








