Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease-Associated Dermatitis with Pruritus: A Positive Response to Dupilumab
Abstract
1. Introduction
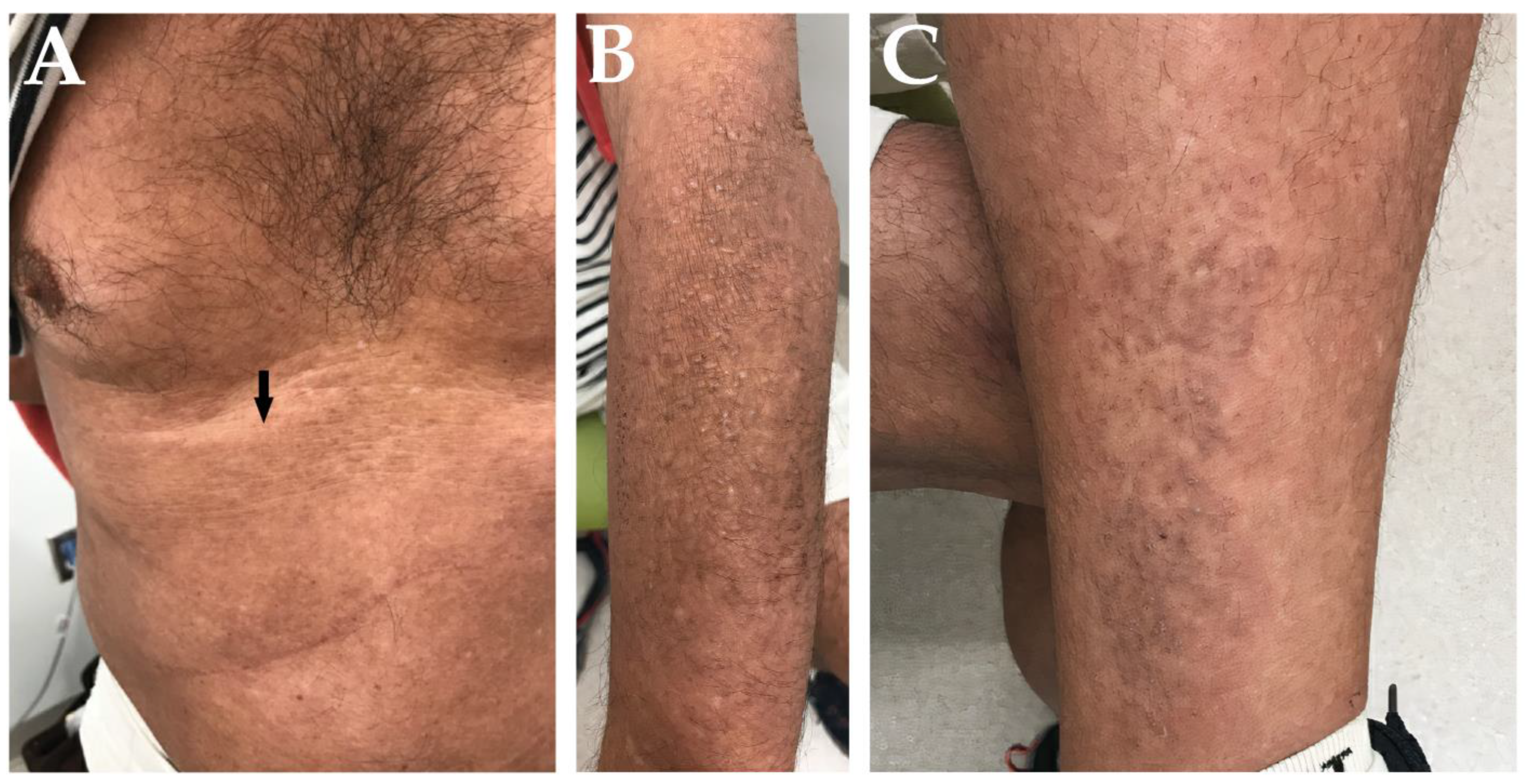
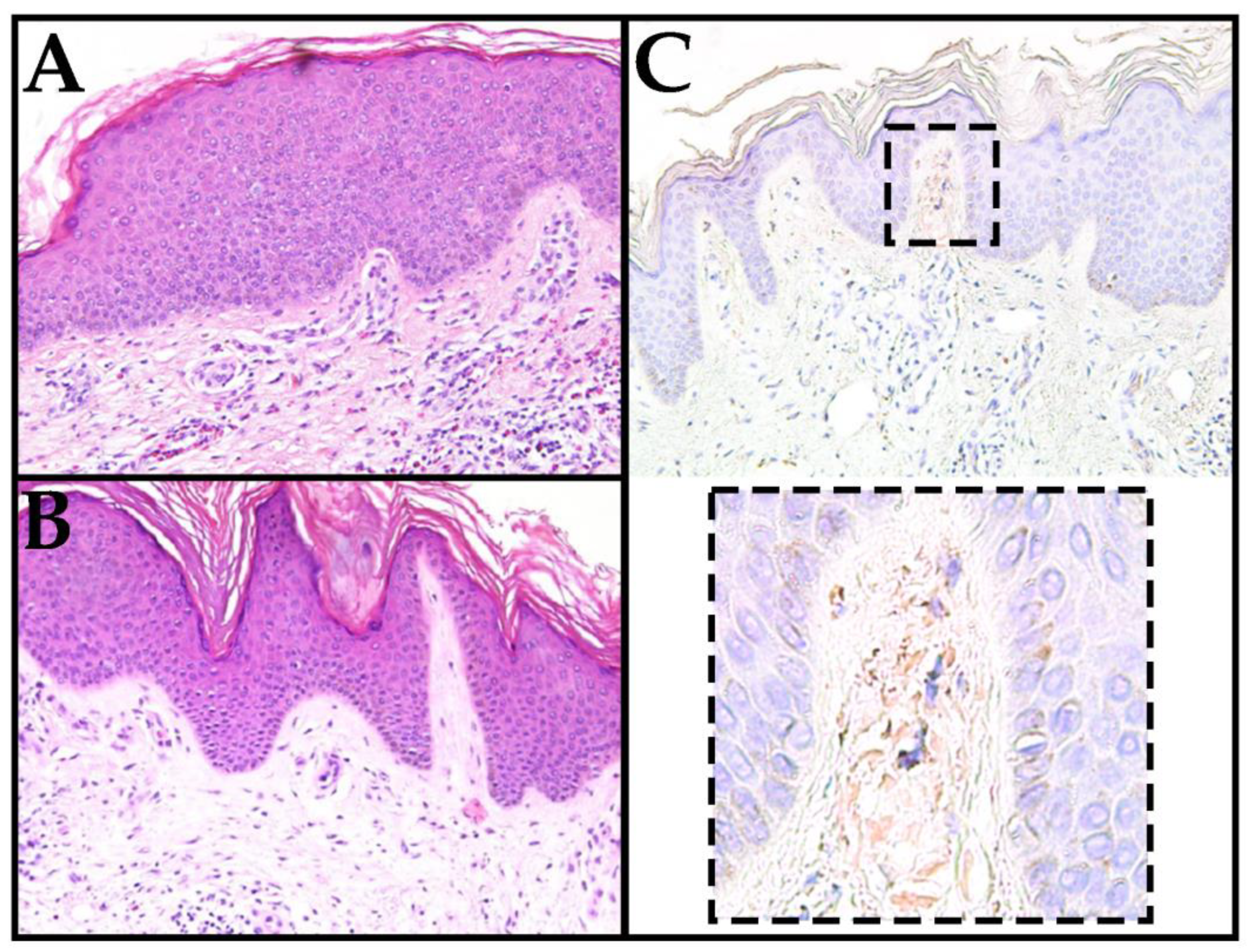
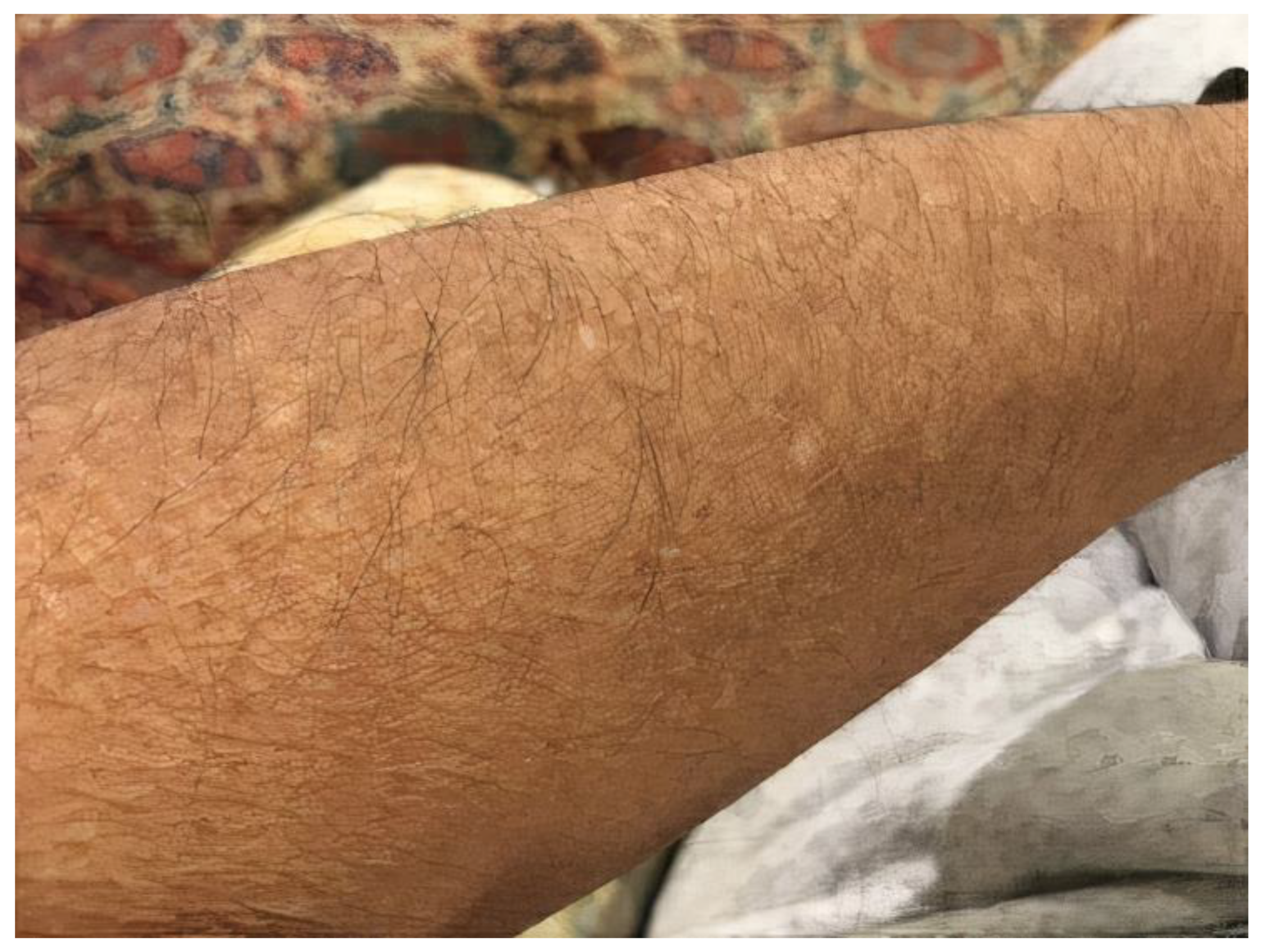
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| 4/16 | 1/17 | 11/19 | 6/20 | 8/20 | 11/20 | 1/21 | 3/21 | 9/21 | 2/22 | Units | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BUN | 68 | 61 | 51 | 45 | 79 | 45 | 48 | 41 | 43 | 47 | mg/dL |
| CR | 2.8 | 3.1 | 2.4 | 2.1 | 3.1 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 2.7 | mg/dL |
| eGFR | 23.0 | 20.0 | 27.0 | 32.0 | 20.0 | 23.5 | 24.6 | 23.5 | 22.3 | 23.3 | mL/min/1.73 sqm |
| Bili (Total) | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.1 | mg/dL |
| AST | 24 | 23 | 27 | 19 | 31 | 21 | 14 | 20 | 21 | 21 | U/L |
| ALT | 35 | 31 | 25 | 24 | 42 | 24 | 17 | 20 | 20 | 20 | U/L |
| ALP | 88 | 84 | 86 | 82 | 69 | 84 | 93 | 81 | 116 | 119 | U/L |
References
- Wisniowski-Yáñez, A.; Zavala-García, G.; Hernández-Molina, G.; González-Duarte, A.; la Mora, J.D.-D.; Ángeles-Ángeles, A.; Martín-Nares, E. Amyloid A amyloidosis secondary to immunoglobulin G4–related disease. Rheumatology 2020, 60, e97–e98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, R.; Ueno, T.; Saeki, H. Immunoglobulin G4-related disease and its skin manifestations. J. Dermatol. 2017, 44, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrow, A.; Imadojemu, S.; Stephen, S.; Ogunleye, T.; Takeshita, J.; Lipoff, J.B. Cutaneous manifestations of IgG4-related disease (RD): A systematic review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 75, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoy, A.; Mohandas, N.; Gottlieb, A. Cutaneous and systemic IgG4-related disease: A review for dermatologists. Dermatol. Online J. 2019, 25, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A.E.; Fenske, N.A.; Rodriguez-Waitkus, P.; Messina, J.L. IgG4-related skin disease may have distinct systemic manifestations: A systematic review. Int. J. Dermatol. 2016, 55, 1184–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirakashi, M.; Yoshifuji, H.; Kodama, Y.; Chiba, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Takahashi, H.; Uchida, K.; Okazaki, K.; Ito, T.; Kawa, S.; et al. Factors in glucocorticoid regimens associated with treatment response and relapses of IgG4-related disease: A multicentre study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidner, T.; Illing, T.; Elsner, P. Primary Localized Cutaneous Amyloidosis: A Systematic Treatment Review. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2017, 18, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltoft, B.; Schmidt, G.; Lauritzen, A.F.; Gimsing, P. Primary localised cutaneous amyloidosis--a systematic review. Dan. Med. J. 2013, 60, A4727. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mehrotra, K. Primary Cutaneous Amyloidosis: A Clinical, Histopathological and Immunofluorescence Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, WC01–WC05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humeda, Y.; Beasley, J.; Calder, K. Clinical resolution of generalized lichen amyloidosis with dupilumab: A new alternative therapy. Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 26, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladizinski, B.; Lee, K.C. Lichen amyloidosis. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2013, 186, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Torre, E.; Mattoo, H.; Mahajan, V.; Carruthers, M.; Pillai, S.; Stone, J.H. Prevalence of atopy, eosinophilia, and IgE elevation in IgG4-related disease. Allergy 2013, 69, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beck, T.C.; Plante, J.; Robinson, I.; Khatskevich, K.; Forcucci, J.A.; Valdebran, M. Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease-Associated Dermatitis with Pruritus: A Positive Response to Dupilumab. Life 2023, 13, 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030833
Beck TC, Plante J, Robinson I, Khatskevich K, Forcucci JA, Valdebran M. Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease-Associated Dermatitis with Pruritus: A Positive Response to Dupilumab. Life. 2023; 13(3):833. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030833
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeck, Tyler C., John Plante, India Robinson, Katsiaryna Khatskevich, Jessica A. Forcucci, and Manuel Valdebran. 2023. "Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease-Associated Dermatitis with Pruritus: A Positive Response to Dupilumab" Life 13, no. 3: 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030833
APA StyleBeck, T. C., Plante, J., Robinson, I., Khatskevich, K., Forcucci, J. A., & Valdebran, M. (2023). Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease-Associated Dermatitis with Pruritus: A Positive Response to Dupilumab. Life, 13(3), 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13030833







