DNA Damage Repair Defects and Targeted Radionuclide Therapies for Prostate Cancer: Does Mutation Really Matter? A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
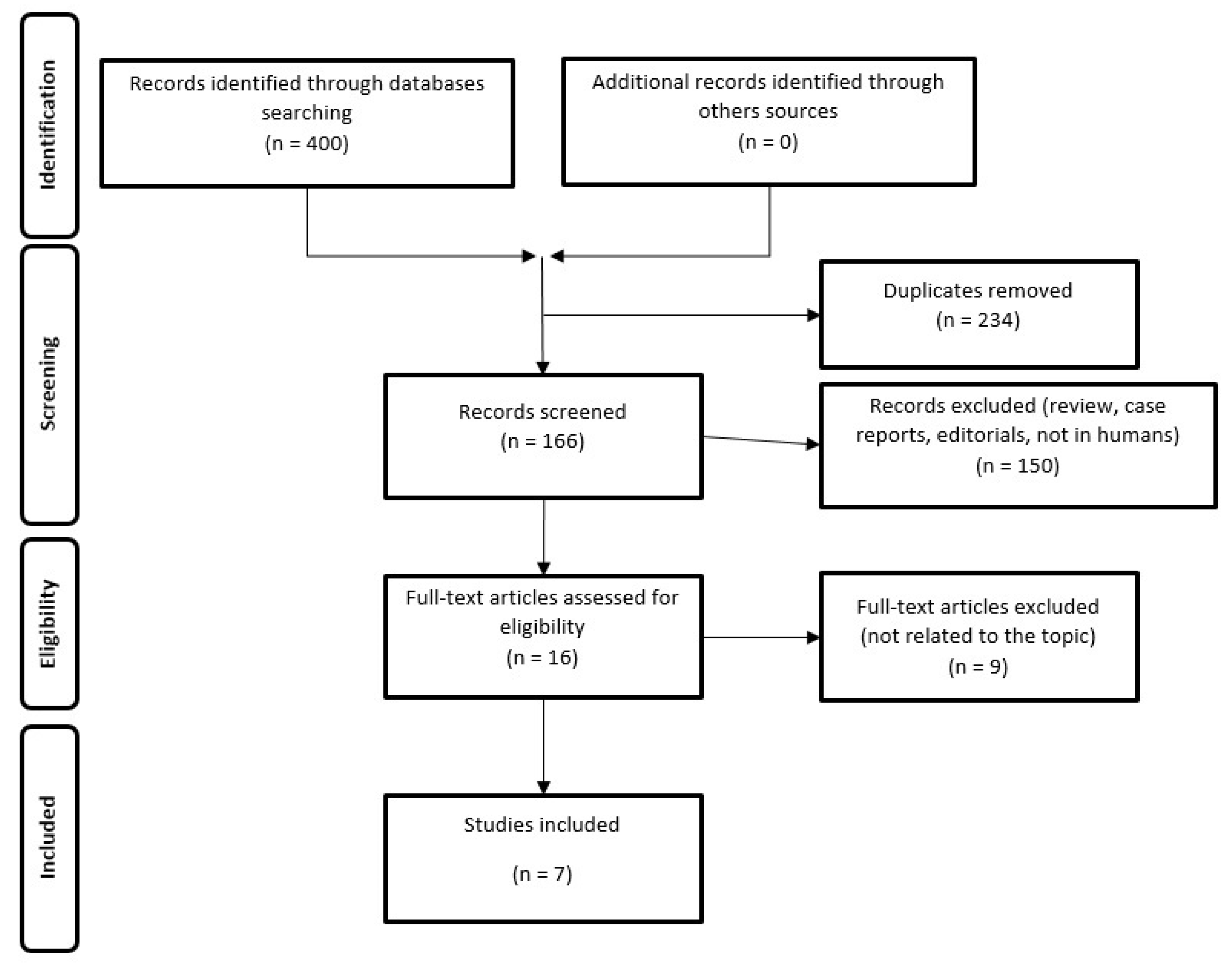
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
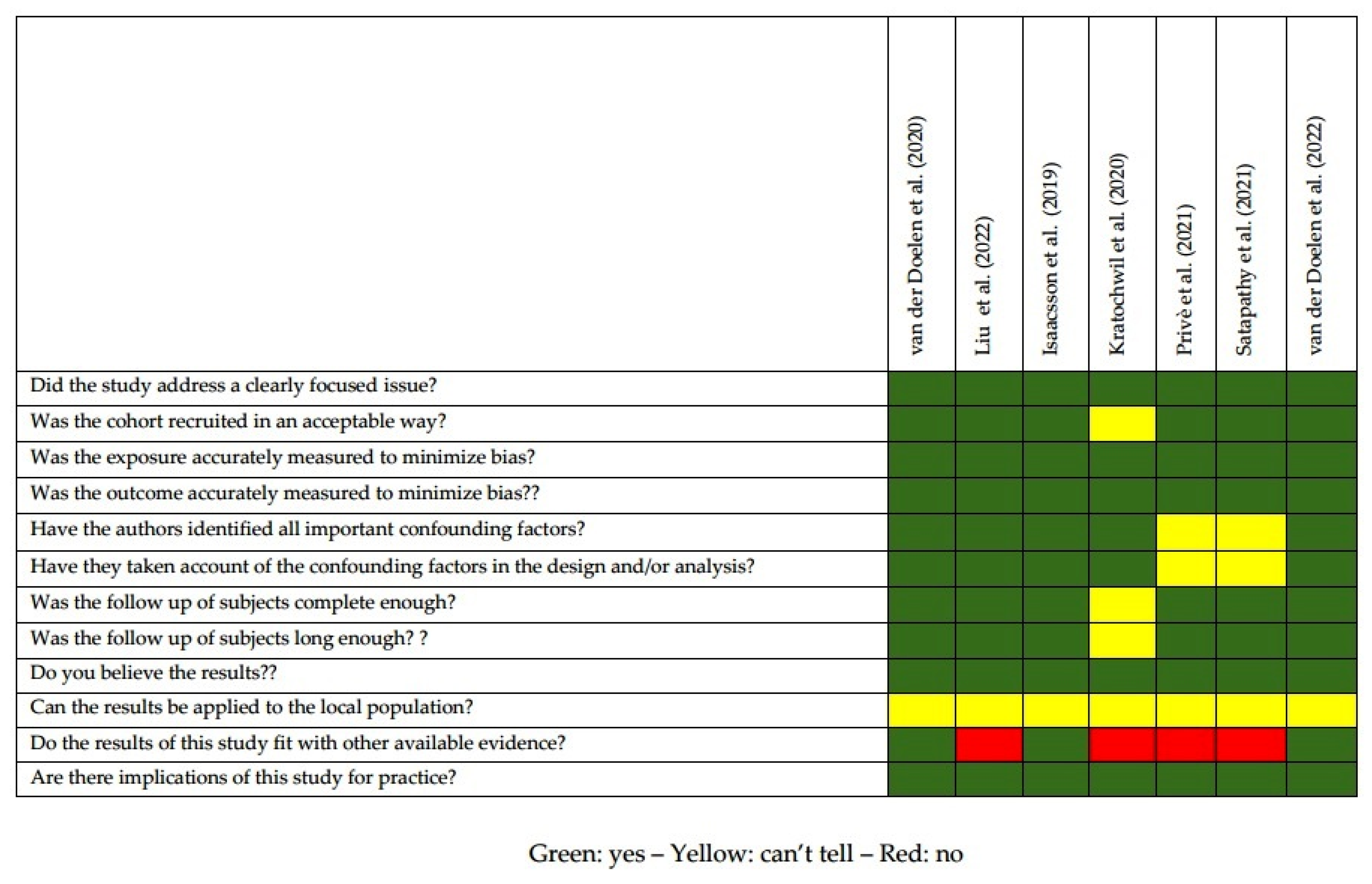
2.2. Quality of the Selected Studies
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Evidence
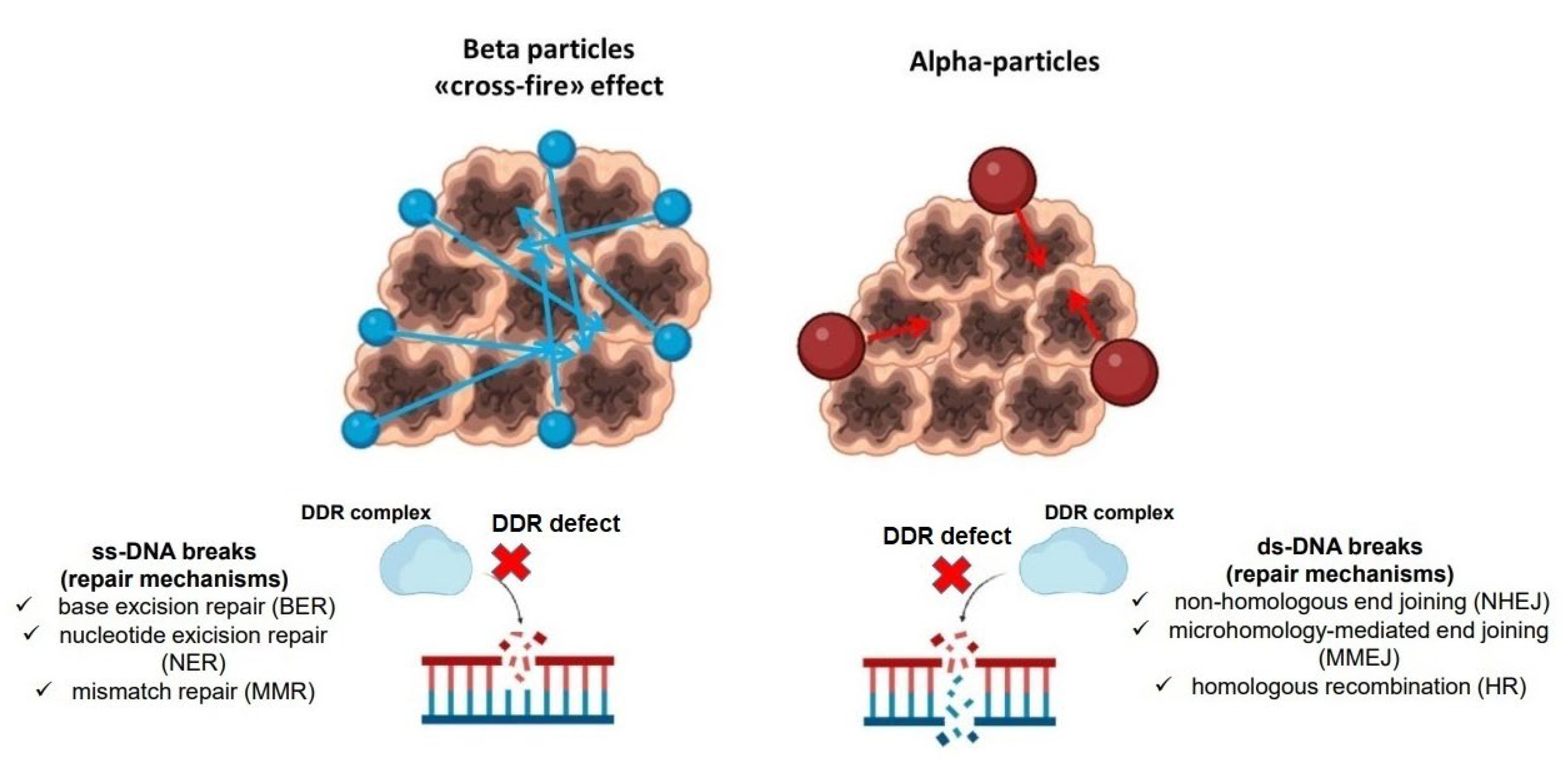
3.1.1. Targeted Alpha Therapy with 223Ra-Therapy
3.1.2. PSMA-Targeted Alpha and Beta Radioligand Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Lu, B.; He, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Du, L. Prostate Cancer Incidence and Mortality: Global Status and Temporal Trends in 89 Countries From 2000 to 2019. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 811044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desai, K.; McManus, J.M.; Sharifi, N. Hormonal Therapy for Prostate Cancer. Endocr. Rev. 2021, 42, 354–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liang, X.; Jiang, G. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of castration resistant prostate cancer (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 6063–6076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turco, F.; Gillessen, S.; Cathomas, R.; Buttigliero, C.; Vogl, U.M. Treatment Landscape for Patients with Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Patient Selection and Unmet Clinical Needs. Res. Rep. Urol. 2022, 14, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, C.; Nilsson, S.; Heinrich, D.; Helle, S.I.; O’Sullivan, J.M.; Fosså, S.D.; Chodacki, A.; Wiechno, P.; Logue, J.; Seke, M.; et al. Alpha Emitter Radium-223 and Survival in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kluetz, P.G.; Pierce, W.; Maher, V.E.; Zhang, H.; Tang, S.; Song, P.; Liu, Q.; Haber, M.T.; Leutzinger, E.E.; Al-Hakim, A.; et al. Radium Ra 223 Dichloride Injection: U.S. Food and Drug Administration Drug Approval Summary. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Hori, Y.; Shiota, M.; Blas, L.; Nakamura, M.; Seki, N.; Kuroiwa, K.; Yokomizo, A.; Morokuma, F.; Kiyoshima, K.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of radium-223 dichloride in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer and bone metastases in real-world practice: A multi-institutional study. Int. J. Urol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantellizzi, V.; Monari, F.; Mascia, M.; Costa, R.; Rubini, G.; Spanu, A.; di Rocco, A.; Lodi Rizzini, E.; Cindolo, L.; Licari, M.; et al. Validation of the 3-variable prognostic score (3-PS) in mCRPC patients treated with 223Radium-dichloride: A national multicenter study. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2020, 34, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, S.P.; Pomper, M.G. Molecular imaging in oncology: Current impact and future directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 333–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkowetz, A.; Linxweiler, J.; Fussek, S.; Wullich, B.; Saar, M.; on behalf of the German Prostate Cancer Consortium (DPKK). The Role of PSMA PET Imaging in Prostate Cancer Theranostics: A Nationwide Survey. Urol. Int. 2022, 106, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, L.; Chiaravalloti, A.; Schillaci, O.; Cianni, R.; Bagni, O. Theranostic approaches in nuclear medicine: Current status and future prospects. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2020, 17, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, L.; Bagni, O.; Nervi, C. Aptamer-based technology for radionuclide targeted imaging and therapy: A promising weapon against cancer. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2020, 17, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartor, O.; de Bono, J.; Chi, K.N.; Fizazi, K.; Herrmann, K.; Rahbar, K.; Tagawa, S.T.; Nordquist, L.T.; Vaishampayan, N.; El-Haddad, G.; et al. Lutetium-177–PSMA-617 for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennrich, U.; Eder, M. [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 (PluvictoTM): The First FDA-Approved Radiotherapeutical for Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, C.J.; Ashworth, A. The DNA damage response and cancer therapy. Nature 2012, 481, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nizialek, E.; Antonarakis, E.S. PARP Inhibitors in Metastatic Prostate Cancer: Evidence to Date. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 8105–8114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, L.; Chiaravalloti, A.; Basile, P.; Schillaci, O.; Bagni, O. Molecular and Metabolic Imaging of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: State of Art and Future Prospects. Curr. Mol. Med. 2022, 22, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velho, P.I.; Qazi, F.; Hassan, S.; Carducci, M.A.; Denmeade, S.R.; Markowski, M.C.; Thorek, D.L.; DeWeese, T.L.; Song, D.Y.; Tran, P.T.; et al. Efficacy of Radium-223 in Bone-metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer with and Without Homologous Repair Gene Defects. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Doelen, M.J.; Isaacsson Velho, P.; Slootbeek, P.H.J.; Pamidimarri Naga, S.; Bormann, M.; van Helvert, S.; Kroeze, L.I.; van Oort, I.M.; Gerritsen, W.R.; Antonarakis, E.S.; et al. Impact of DNA damage repair defects on response to radium-223 and overall survival in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 1990 2020, 136, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochwil, C.; Giesel, F.L.; Heussel, C.-P.; Kazdal, D.; Endris, V.; Nientiedt, C.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Kippenberger, M.; Rathke, H.; Leichsenring, J.; et al. Patients Resistant Against PSMA-Targeting α-Radiation Therapy Often Harbor Mutations in DNA Damage-Repair–Associated Genes. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Privé, B.M.; Slootbeek, P.H.J.; Laarhuis, B.I.; Naga, S.P.; van der Doelen, M.J.; van Kalmthout, L.W.M.; de Keizer, B.; Ezziddin, S.; Kratochwil, C.; Morgenstern, A.; et al. Impact of DNA damage repair defects on response to PSMA radioligand therapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.J.; Kosiorek, H.E.; Ueberroth, B.E.; Jaeger, E.; Ledet, E.; Kendi, A.T.; Tzou, K.; Quevedo, F.; Choo, R.; Moore, C.N.; et al. The impact of genetic aberrations on response to radium-223 treatment for castration-resistant prostate cancer with bone metastases. Prostate 2022, 82, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Doelen, M.J.; Mehra, N.; van Oort, I.M.; Looijen-Salamon, M.G.; Janssen, M.J.R.; Custers, J.A.E.; Slootbeek, P.H.J.; Kroeze, L.I.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Morgenstern, A.; et al. Clinical outcomes and molecular profiling of advanced metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients treated with 225Ac-PSMA-617 targeted alpha-radiation therapy. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2021, 39, 729.e7–729.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satapathy, S.; Das, C.K.; Aggarwal, P.; Sood, A.; Parihar, A.S.; Singh, S.K.; Mittal, B.R. Genomic characterization of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer patients undergoing PSMA radioligand therapy: A single-center experience. Prostate 2022, 83, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, H.I.; Morris, M.J.; Stadler, W.M.; Higano, C.; Basch, E.; Fizazi, K.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Beer, T.M.; Carducci, M.A.; Chi, K.N.; et al. Trial Design and Objectives for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: Updated Recommendations From the Prostate Cancer Clinical Trials Working Group 3. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 1402–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, L.H.; Litière, S.; de Vries, E.; Ford, R.; Gwyther, S.; Mandrekar, S.; Shankar, L.; Bogaerts, J.; Chen, A.; Dancey, J.; et al. RECIST 1.1—Update and clarification: From the RECIST committee. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 62, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O, J.H.; Wahl, R.L. PERCIST in Perspective. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2018, 52, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimini, A.; Ricci, M.; Chiaravalloti, A.; Filippi, L.; Schillaci, O. Theragnostic Aspects and Radioimmunotherapy in Pediatric Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodei, L.; Cremonesi, M.; Grana, C.M.; Chinol, M.; Baio, S.M.; Severi, S.; Paganelli, G. Yttrium-labelled peptides for therapy of NET. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2012, 39, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uccelli, L.; Boschi, A.; Cittanti, C.; Martini, P.; Panareo, S.; Tonini, E.; Nieri, A.; Urso, L.; Caracciolo, M.; Lodi, L.; et al. 90Y/177Lu-DOTATOC: From Preclinical Studies to Application in Humans. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschalis, A.; Sheehan, B.; Riisnaes, R.; Rodrigues, D.N.; Gurel, B.; Bertan, C.; Ferreira, A.; Lambros, M.B.K.; Seed, G.; Yuan, W.; et al. Prostate-specific Membrane Antigen Heterogeneity and DNA Repair Defects in Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, B.; Neeb, A.; Buroni, L.; Paschalis, A.; Riisnaes, R.; Gurel, B.; Gil, V.; Miranda, S.; Crespo, M.; Guo, C.; et al. Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Expression and Response to DNA Damaging Agents in Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 3104–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nombela, P.; Lozano, R.; Aytes, A.; Mateo, J.; Olmos, D.; Castro, E. BRCA2 and Other DDR Genes in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Terrin, N.; Schmid, C.H.; Olkin, I. The case of the misleading funnel plot. BMJ 2006, 333, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iizuka, J. Evaluating radium-223 response in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with imaging. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 14, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costelloe, C.M.; Chuang, H.H.; Madewell, J.E.; Ueno, N.T. Cancer Response Criteria and Bone Metastases: RECIST 1.1, MDA and PERCIST. J. Cancer 2010, 1, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopci, E.; Prasad, V. Editorial: Response assessment of radioligand therapies. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 904337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, V.; Huang, K.; Prasad, S.; Makowski, M.R.; Czech, N.; Brenner, W. In Comparison to PSA, Interim Ga-68-PSMA PET/CT Response Evaluation Based on Modified RECIST 1.1 after 2nd Cycle Is Better Predictor of Overall Survival of Prostate Cancer Patients Treated With 177Lu-PSMA. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 578093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delbart, W.; Karabet, J.; Marin, G.; Penninckx, S.; Derrien, J.; Ghanem, G.E.; Flamen, P.; Wimana, Z. Understanding the Radiobiological Mechanisms Induced by 177Lu-DOTATATE in Comparison to External Beam Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Arienzo, M.; Pimpinella, M.; Capogni, M.; de Coste, V.; Filippi, L.; Spezi, E.; Patterson, N.; Mariotti, F.; Ferrari, P.; Chiaramida, P.; et al. Phantom validation of quantitative Y-90 PET/CT-based dosimetry in liver radioembolization. EJNMMI Res. 2017, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippi, L.; Schillaci, O.; Cianni, R.; Bagni, O. Yttrium-90 resin microspheres and their use in the treatment of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Future Oncol. Lond. Engl. 2018, 14, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassis, A.I. Therapeutic Radionuclides: Biophysical and Radiobiologic Principles. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2008, 38, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frantellizzi, V.; Cosma, L.; Brunotti, G.; Pani, A.; Spanu, A.; Nuvoli, S.; de Cristofaro, F.; Civitelli, L.; de Vincentis, G. Targeted Alpha Therapy with Thorium-227. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2020, 35, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidoo, K.E.; Yong, K.; Brechbiel, M.W. Molecular Pathways: Targeted α-Particle Radiation Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.P.; Lin, F.I.; Escorcia, F.E. Why bother with alpha particles? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 49, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.; Tummala, H.; Zhelev, N. ATM in focus: A damage sensor and cancer target. BioDiscovery 2012, 5, e8936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattrini, C.; España, R.; Mennitto, A.; Bersanelli, M.; Castro, E.; Olmos, D.; Lorente, D.; Gennari, A. Optimal Sequencing and Predictive Biomarkers in Patients with Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Source | Year/Location | Study Design | Sample Size | Demographic Data (Median) | Radiopharmaceutical | Most Common Mutations | Response | Outcome | DDR Impact (Y/N) | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isaacsson et al. [19] | 2019/USA | Retrospective | 28 (10 HR+, 35.7%) | Age: 66 yr, Baseline PSA: 77.1 ng/mL, Baseline ALP: 130 U/L | 223Ra-therapy | Not specified | ALP response within 12 weeks: 64%, with a significantly higher response rate in HR+ patients | More favorable outcome was registered in HR+ than in HR- subjects (OS 36.9 vs. 19.0 mo) | Y | PCa patients harboring mutations in HR genes showed a higher response rate and more prolonged survival after 223Ra-therapy |
| van der Doelen et al. [20] | 2020/ The Netherlands + USA | 2-centre retrospective study | 93 (28 DDR+, 30.1%) | Age: 68 yr, Baseline PSA: 59.0 ng/mL, Baseline ALP: 124 U/L | 223Ra-therapy | ATM, BRCA2, CDK-12 | PSA response: 29.4% in DDR+ vs. 34.6% in DDR-ALP response: 33.0% in DDR+ versus −35.0% in DDR- | OS of the overall cohort: 21 mo DDR+ pts had longer OS than DDR- (median 36.3 vs. 17.0 mo) | Y | Patients harboring DDR alterations had a more favorable outcome after 223Ra-therapy. Time to ALP progression (TAP) and time to subsequent treatment (TST) resulted also longer in DDR+ patients than in DDR- ones |
| Kratochwil et al. [21] | 2020/ Germany | Retrospective | 10 (7 DDR+, 70%) | Age: not available, Baseline PSA: 481 ng/mL | [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-617 | TP53, CHEk2, ATM | The study was carried out in non-responders | Not specified | Not assessed | Patients resistant to radioligand therapy with [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-617 often harbor mutations in DDR genes |
| Privé et al. [22] | 2021/ The Netherlands | Observational cohort | 40 (17 DDR+, 42.5%) | Age: 61 yr, Baseline PSA: not available | [177Lu/225Ac]-PSMA-617 or PSMA-I&T | BRCA 1/2 | No significant differences in PSA response (59% in DDR+ vs. 65% in DDR-) | No OS difference among DDR + patients vs. DDR- patients (median OS 11.1 vs. 10.7 mo) | N | DDR defects did not show any significant impact on mCRPC patients’ response to PSMA-targeted therapy with beta or alpha emitters |
| Liu et al. [23] | 2022/ USA | Two-center retrospective study | 127 (127 DDR+) | Age: 61 yr, Baseline PSA: 21 ng/mL, Baseline ALP: 123 U/L | 223Ra-therapy | TP53, BRCA 1/2, PTEN | PSA response (entire cohort): 22.6%ALP response (entire cohort): 69.8% | TMPRSS2-ERG mutation was associated with a lower OS (15.4 mo), while RB deletion with a shorter PFS (6 mo). | N | DDR mutations did not represent a predictive factor on response to 223Ra-therapy, although certain mutations resulted associated with a trend towards a worse prognosis |
| van der Doelen et al. [24] | 2022/ The Netherlans + Germany | Observational cohort | 13 (2 DDR+, 15.3%) | Age: 71 yr, Baseline PSA: 878 ng/mL, Baseline ALP: 356 U/L | [225Ac]Ac-PSMA-617 | BRCA1 | PSA response (entire cohort): 69%, ALP response: 62%, RECIST response: 50%, PERCIST response: 86% | OS (entire cohort): 8.5 mo, | Y | Patients harboring DDR defects present a trend toward a longer OS after therapy than those without mutations |
| Satapathy et al. [25] | 2022/ india | Retrospective | 15 (10 DDR+, 66.6%) | Age: 66 yr, Baseline PSA: 87 ng/mL | [177Lu]Lu-PSMA-617 (n = 3) | ATM, BRCA2, TP53 | PSA response (entire cohort): 26.7% RECIST response: 12.5% | PFS (entire cohort): 3 mo, OS (entire cohort): 6 mo | N | DDR defects did not impact either on final outcome or theapy-response of mCRPC patients submitted to RLT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Filippi, L.; Palumbo, B.; Bagni, O.; Frantellizzi, V.; De Vincentis, G.; Schillaci, O. DNA Damage Repair Defects and Targeted Radionuclide Therapies for Prostate Cancer: Does Mutation Really Matter? A Systematic Review. Life 2023, 13, 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010055
Filippi L, Palumbo B, Bagni O, Frantellizzi V, De Vincentis G, Schillaci O. DNA Damage Repair Defects and Targeted Radionuclide Therapies for Prostate Cancer: Does Mutation Really Matter? A Systematic Review. Life. 2023; 13(1):55. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010055
Chicago/Turabian StyleFilippi, Luca, Barbara Palumbo, Oreste Bagni, Viviana Frantellizzi, Giuseppe De Vincentis, and Orazio Schillaci. 2023. "DNA Damage Repair Defects and Targeted Radionuclide Therapies for Prostate Cancer: Does Mutation Really Matter? A Systematic Review" Life 13, no. 1: 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010055
APA StyleFilippi, L., Palumbo, B., Bagni, O., Frantellizzi, V., De Vincentis, G., & Schillaci, O. (2023). DNA Damage Repair Defects and Targeted Radionuclide Therapies for Prostate Cancer: Does Mutation Really Matter? A Systematic Review. Life, 13(1), 55. https://doi.org/10.3390/life13010055








