Exploring the Role of Krebs von den Lungen-6 in Severe to Critical COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carfora, V.; Spiniello, G.; Ricciolino, R.; Di Mauro, M.; Migliaccio, M.G.; Mottola, F.F.; Verde, N.; Coppola, N.; Sagnelli, C.; De Pascalis, S.; et al. Anticoagulant treatment in COVID-19: A narrative review. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2021, 51, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigro, E.; Perrotta, F.; Polito, R.; D’Agnano, V.; Scialò, F.; Bianco, A.; Daniele, A. Metabolic Perturbations and Severe COVID-19 Disease: Implication of Molecular Pathways. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 2020, 8896536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Słomka, A.; Kowalewski, M.; Żekanowska, E. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID–19): A Short Review on Hematological Manifestations. Pathogens 2020, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, A.A.; Tamura, T.; Crowley, C.P.; DeGrado, J.R.; Haider, H.; Jezmir, J.L.; Keras, G.; Penn, E.H.; Massaro, A.F.; Kim, E.Y. Inflammatory Biomarker Trends Predict Respiratory Decline in COVID-19 Patients. Cell Rep. Med. 2020, 1, 100144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccia, M.; Aronne, L.; Celia, B.; Mazzeo, G.; Ceparano, M.; D’Agnano, V.; Parrella, R.; Valente, T.; Bianco, A.; Perrotta, F. COVID-19 and coagulative axis: Review of emerging aspects in a novel disease. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2020, 90, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, B.; Milara, J.; Cortijo, J. The role of mucin 1 in respiratory diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 200149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thathiah, A.; Blobel, C.P.; Carson, D.D. Tumor necrosis factor-α converting enzyme/ADAM 17 mediates MUC1 shedding. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 3386–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scialo, F.; Vitale, M.; Daniele, A.; Nigro, E.; Perrotta, F.; Gelzo, M.; Iadevaia, C.; Cerqua, F.S.; Costigliola, A.; Allocca, V.; et al. SARS-CoV-2: One year in the pandemic. What have we learned, the new vaccine era and the threat of SARS-CoV-2 variants. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, F.; Matera, M.G.; Cazzola, M.; Bianco, A. Severe respiratory SARS-CoV2 infection: Does ACE2 receptor matter? Respir. Med. 2020, 168, 105996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahel, R.A.; Gilks, W.R.; Lehmann, H.-P.; Schenker, T. Third international workshop on lung tumor and differentiation antigens: Overview of the results of the central data analysis. Int. J. Cancer 1994, 57 (Suppl. S8), 6–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligtenberg, M.J.L.; Buijs, F.; Vos, H.L.; Hilkens, J. Suppression of Cellular Aggregation by High Levels of Episialin. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 2318–2324. [Google Scholar]
- Hirasawa, Y.; Kohno, N.; Yokoyama, A.; Inoue, Y.; Abe, M.; Hiwada, K. KL-6, a Human MUC1 Mucin, Is Chemotactic for Human Fibroblasts. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1997, 17, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.S.; Lee, E.Y.; Ha, Y.J.; Kang, E.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Song, Y.W. Serum kl-6 levels reflect the severity of interstitial lung disease associated with connective tissue disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnold, D.T.; Donald, C.; Lyon, M.; Hamilton, F.W.; Morley, A.J.; Attwood, M.; Dipper, A.; Barratt, S.L. Krebs von den Lungen 6 (KL-6) as a marker for disease severity and persistent radiological abnormalities following COVID-19 infection at 12 weeks. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, N.; Rahimzadeh, M. Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6) as a clinical marker for severe COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Virology 2020, 566, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Fan, Q.; Yang, Y.; Deng, X.; He, R.; Tan, Y.; Lan, Y.; Deng, X.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Prognostic roles of KL-6 in disease severity and lung injury in COVID-19 patients: A longitudinal retrospective analysis. J. Med Virol. 2021, 93, 2505–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Alessandro, M.; Bergantini, L.; Cameli, P.; Curatola, G.; Remediani, L.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E.; Bennett, D.; Bianchi, F.; Perillo, F.; et al. Peripheral biomarkers’ panel for severe COVID-19 patients. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1230–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awano, N.; Inomata, M.; Kuse, N.; Tone, M.; Takada, K.; Muto, Y.; Fujimoto, K.; Akagi, Y.; Mawatari, M.; Ueda, A.; et al. Serum KL-6 level is a useful biomarker for evaluating the severity of coronavirus disease 2019. Respir. Investig. 2020, 58, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO COVID-19 Clinical Management. Living Guidance for Clinical Management of COVID-19; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, H.; Callister, M.; Mumby, S.; Quinlan, G.; Welsh, K.; Dubois, R.; Evans, T. KL-6 levels are elevated in plasma from patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 23, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhazzani, W.; Møller, M.H.; Arabi, Y.M.; Loeb, M.; Ng Gong, M.; Fan, E.; Oczkowski, S.; Levy, M.M.; Derde, L.; Dzierba, A.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: Guidelines on the management of critically ill adults with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 854–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oguz, E.O.; Kucuksahin, O.; Turgay, M.; Yildizgoren, M.T.; Ates, A.; Demir, N.; Kumbasar, O.O.; Kinikli, G.; Duzgun, N. Association of serum KL-6 levels with interstitial lung disease in patients with connective tissue disease: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2016, 35, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizaka, A.; Matsuda, T.; Albertine, K.H.; Koh, H.; Tasaka, S.; Hasegawa, N.; Kohno, N.; Kotani, T.; Morisaki, H.; Takeda, J.; et al. Elevation of KL-6, a lung epithelial cell marker, in plasma and epithelial lining fluid in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2004, 286, L1088–L1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotto, R.; Pinchera, B.; Perna, F.; Atripaldi, L.; Giaccone, A.; Sequino, D.; Zappulo, E.; Sardanelli, A.; Moriello, N.S.; Stanziola, A.; et al. Serum KL-6 Could Represent a Reliable Indicator of Unfavourable Outcome in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, D.-H.; Luo, Y.; Huang, L.-J.; Liao, F.-L.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Tang, P.; Hu, H.-N.; Chen, W. Correlation of Krebs von den Lungen-6 and fibronectin with pulmonary fibrosis in coronavirus disease 2019. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 517, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaya, T.; Hagiwara, E.; Baba, T.; Kitayama, T.; Murohashi, K.; Higa, K.; Sato, Y.; Otoshi, R.; Tabata, E.; Shintani, R.; et al. Serum Krebs von den Lungen-6 levels are associated with mortality and severity in patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Respir. Investig. 2021, 59, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpati, G.; Baldassarre, D.; Lacava, G.; Oliva, F.; Pascale, G.; Boffardi, M.; Pagliano, P.; Calabrese, V.; Tripepi, G.L.; Piazza, O. Krebs von den Lungen 6 levels in COVID-19 ICU Patients are Associated with Mortality. medRxiv 2021, 2021.11.17.21266464. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, M.; Zhang, T.; Chen, H.; Zeng, Y.; Lin, R.; Zhen, Y.; Li, N.; Huang, Z.; Hu, H.; Zhou, L.; et al. Krebs Von den Lungen-6 as a predictive indicator for the risk of secondary pulmonary fibrosis and its reversibility in COVID-19 patients. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Valente, T.; Perrotta, F.; Stellato, E.; Brunese, L.; Wood, B.J.; Carrafiello, G.; Parrella, R.; Aronne, L.; Boccia, M.; et al. Remarkable vessel enlargement within lung consolidation in COVID-19 compared to AH1N1 pneumonia: A retrospective study in Italy. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.; Bernheim, A.; Mei, X.; Zhang, N.; Huang, M.; Zeng, X.; Cui, J.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Fayad, Z.A.; et al. CT imaging features of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019–nCoV). Radiology 2020, 295, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dargent, A.; Chatelain, E.; Kreitmann, L.; Quenot, J.-P.; Cour, M.; Argaud, L.; The COVID-LUS Study Group. Lung ultrasound score to monitor COVID-19 pneumonia progression in patients with ARDS. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0236312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasi, E.; Manganaro, L.; Guiducci, E.; Ciaglia, S.; Dolciami, M. Association of serum Krebs von den Lungen-6 and chest CT as potential prognostic factors in severe acute respiratory syndrome SARS-CoV-2: A preliminary experience. Radiol. Med. 2022, 127, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjögren, L.; Stenberg, E.; Thuccani, M.; Martikainen, J.; Rylander, C.; Wallenius, V.; Olbers, T.; Kindblom, J.M. Impact of obesity on intensive care outcomes in patients with COVID-19 in Sweden—A cohort study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lewis, A.M.; Moley, J.R.; Brestoff, J.R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of obesity and COVID-19 outcomes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, E.J.; Longo, D.L.; Baden, L. R Interleukin-6 Receptor Inhibition in COVID-19—Cooling the Inflammatory Soup. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1564–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coomes, E.A.; Haghbayan, H. Interleukin-6 in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2020, 30, e2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
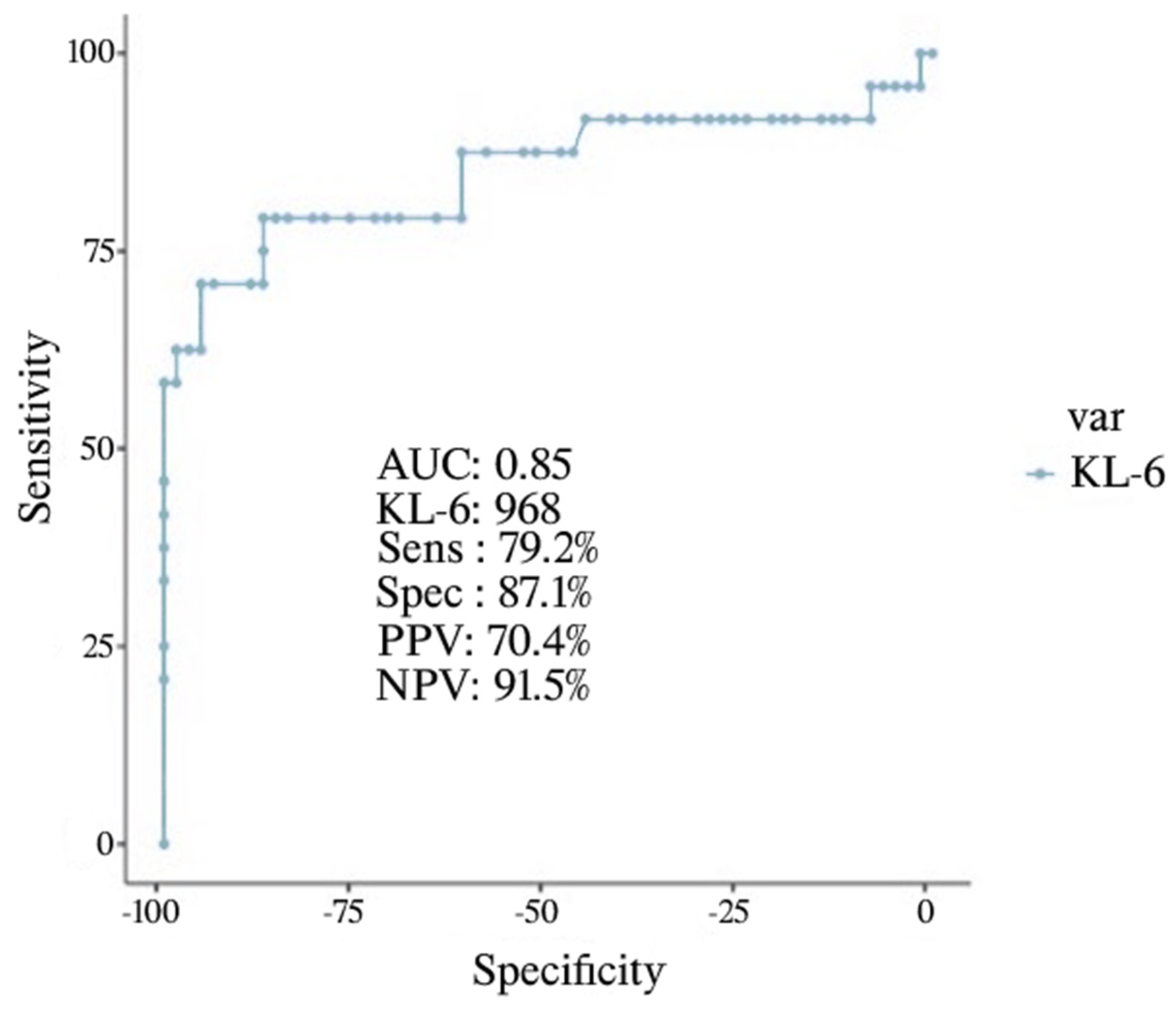
| Discharged (n = 63) | Death/IOT (n = 24) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 67 (60–73) | 75.5 (67–80.3) | 0.011 |
| Gender (Male) | 37 (58.7) | 8 (33.3) | |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 27.7 (25–31.5) | 31.2 (27.7–35.2) | 0.02 |
| Charlson Index | 3 (3–4) | 4 (3–4) | |
| LUS | 29 (23.8–32.3) | 36 (36–36) | <0.001 |
| Chung Score | 13 (12–15) | 15 (12–16) | 0.04 |
| WBC (103 cell/µL) | 8.65 (6.86–11.1) | 12.3 (9.5–12.9) | 0.008 |
| Neutrophils (103 cell/µL) | 7.46 (6.31–10.2) | 11 (7.66–11.5) | 0.014 |
| Lymphocytes (103 cell/µL) | 0.69 (0.497–1.02) | 0.685 (0.44–1.07) | 0.851 |
| Eosinophils (103 cell/µL) | 0 (0.00–0.01) | 0 (0.00–0.01) | 0.859 |
| NLR | 11.8 (6.51–16.3) | 13.1 (9.88–15.6) | 0.113 |
| RBC (106 cell/µL) | 4.72 (4.56–5.41) | 4.5 (3.89–4.92) | 0.003 |
| HGB (g/dL) | 13.7 (12.3–14.3) | 12.6 (9.6–14) | 0.058 |
| PLT (103 cell/µL) | 221 (183–272) | 203 (159–287) | 0.382 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 4.25 (2.27–9.4) | 6.5 (4–9.85) | 0.002 |
| D-Dimer (µg/L) | 281(162–519) | 499(435–903) | 0.307 |
| IL2R (U/mL) | 1121 (809–1507) | 973 (906–1737) | 0.987 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 25.3 (16.6–55.9) | 115 (42.2–160) | 0.003 |
| KL-6 (U/mL) | 530 (469–787) | 1969 (1036–3669) | <0.001 |
| PaO2/FiO2 | 119 (88–155) | 100 (91.3–110) | 0.211 |
| Respiratory Support | |||
| Nasal Cannula, face mask, or non-rebreathing mask | 4 (6.4) | 0 (0) | |
| HFNC | 20 (31.7) | 2 (8.3) | |
| CPAP | 33 (52.4) | 13 (54.2) | |
| NIV | 6 (9.5) | 9 (37.5) |
| KL6 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age | Pearson’s r | 0.174 |
| p-value | 0.110 | |
| BMI | Pearson’s r | 0.279 |
| p-value | 0.009 | |
| Charlson index | Pearson’s r | 0.194 |
| p-value | 0.073 | |
| LUS SCORE | Pearson’s r | 0.429 |
| p-value | < 0.001 | |
| CHUNG-SCORE | Pearson’s r | 0.390 |
| p-value | < 0.001 | |
| NLR | Pearson’s r | 0.236 |
| p-value | 0.030 | |
| D-DIMERO | Pearson’s r | 0.005 |
| p-value | 0.966 | |
| P/F | Pearson’s r | 0.180 |
| p-value | 0.101 |
| 95% Confidence Interval | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio | Lower | Upper | p | |
| Gender | 0.46967 | 0.101 | 2.18 | 0.334 |
| BMI | 1.09941 | 0.952 | 1.27 | 0.196 |
| Charlson index | 1.14269 | 0.631 | 2.07 | 0.66 |
| CHUNG-Score | 0.97959 | 0.712 | 1.35 | 0.899 |
| PaO2/FiO2 | 0.99005 | 0.97 | 1.01 | 0.328 |
| KL-6 | 1.00266 | 1.001 | 1.004 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Agnano, V.; Scialò, F.; Perna, F.; Atripaldi, L.; Sanduzzi, S.; Allocca, V.; Vitale, M.; Pastore, L.; Bianco, A.; Perrotta, F. Exploring the Role of Krebs von den Lungen-6 in Severe to Critical COVID-19 Patients. Life 2022, 12, 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081141
D’Agnano V, Scialò F, Perna F, Atripaldi L, Sanduzzi S, Allocca V, Vitale M, Pastore L, Bianco A, Perrotta F. Exploring the Role of Krebs von den Lungen-6 in Severe to Critical COVID-19 Patients. Life. 2022; 12(8):1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081141
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Agnano, Vito, Filippo Scialò, Francesco Perna, Lidia Atripaldi, Stefano Sanduzzi, Valentino Allocca, Maria Vitale, Lucio Pastore, Andrea Bianco, and Fabio Perrotta. 2022. "Exploring the Role of Krebs von den Lungen-6 in Severe to Critical COVID-19 Patients" Life 12, no. 8: 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081141
APA StyleD’Agnano, V., Scialò, F., Perna, F., Atripaldi, L., Sanduzzi, S., Allocca, V., Vitale, M., Pastore, L., Bianco, A., & Perrotta, F. (2022). Exploring the Role of Krebs von den Lungen-6 in Severe to Critical COVID-19 Patients. Life, 12(8), 1141. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12081141







