Understanding the Dynamics of the Structural States of Cannabinoid Receptors and the Role of Different Modulators
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protein Preparation
2.2. Ligand Preparation and Docking
2.3. System Setup
2.4. Vitamin E and THC System Setup
2.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.6. CB1R In Vitro Binding Assay
3. Results
3.1. Protein-Ligand Interaction Profile
3.1.1. CB1R Active and Inactive States
3.1.2. CB1R Intermediate States
3.1.3. CB2R Active and Inactive States
3.1.4. CB2R Intermediate States
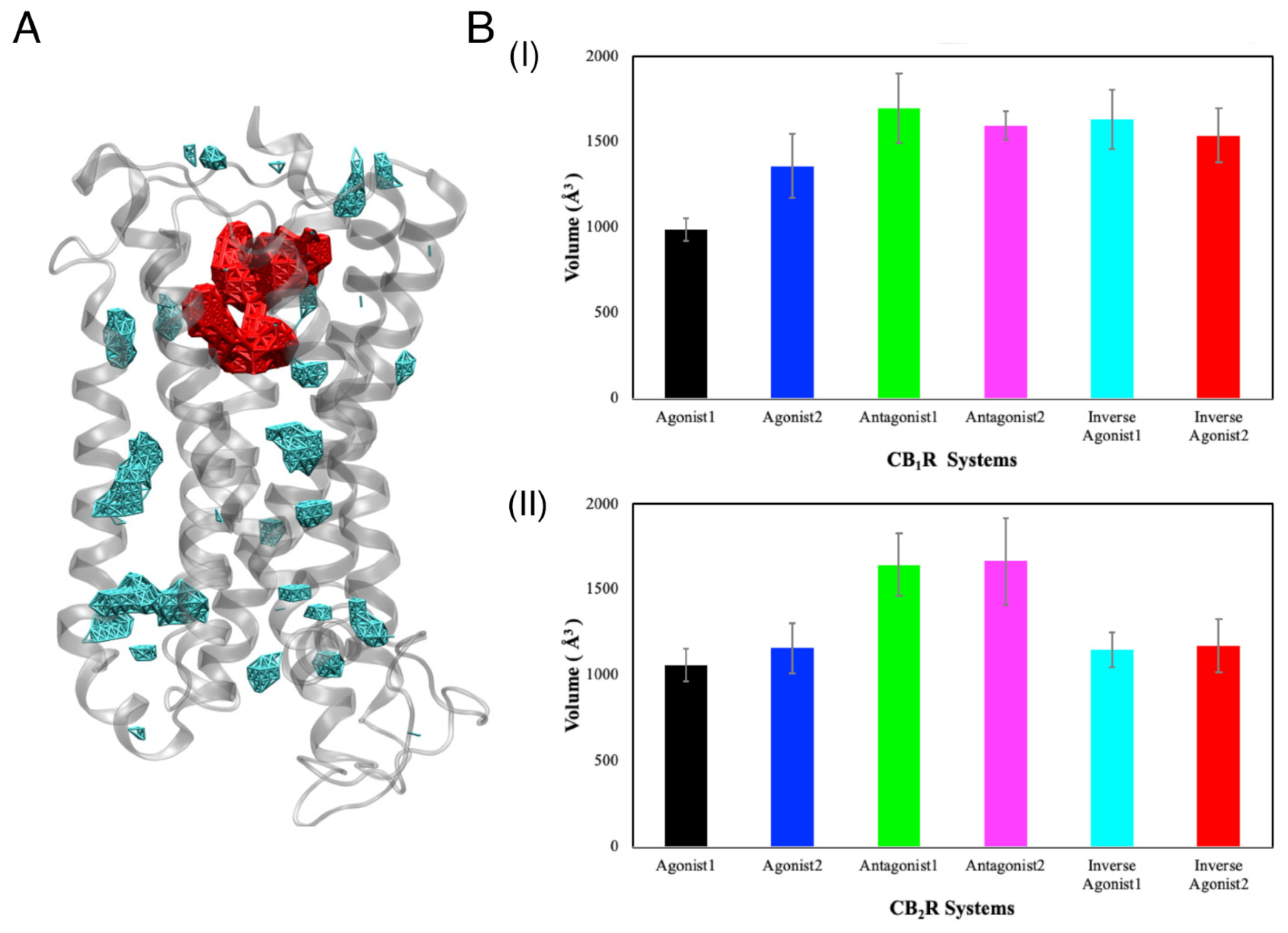
3.2. Binding Cavities
3.2.1. Position of the Binding Cavity
3.2.2. Volume of the Binding Cavity
3.2.3. Internal Waters
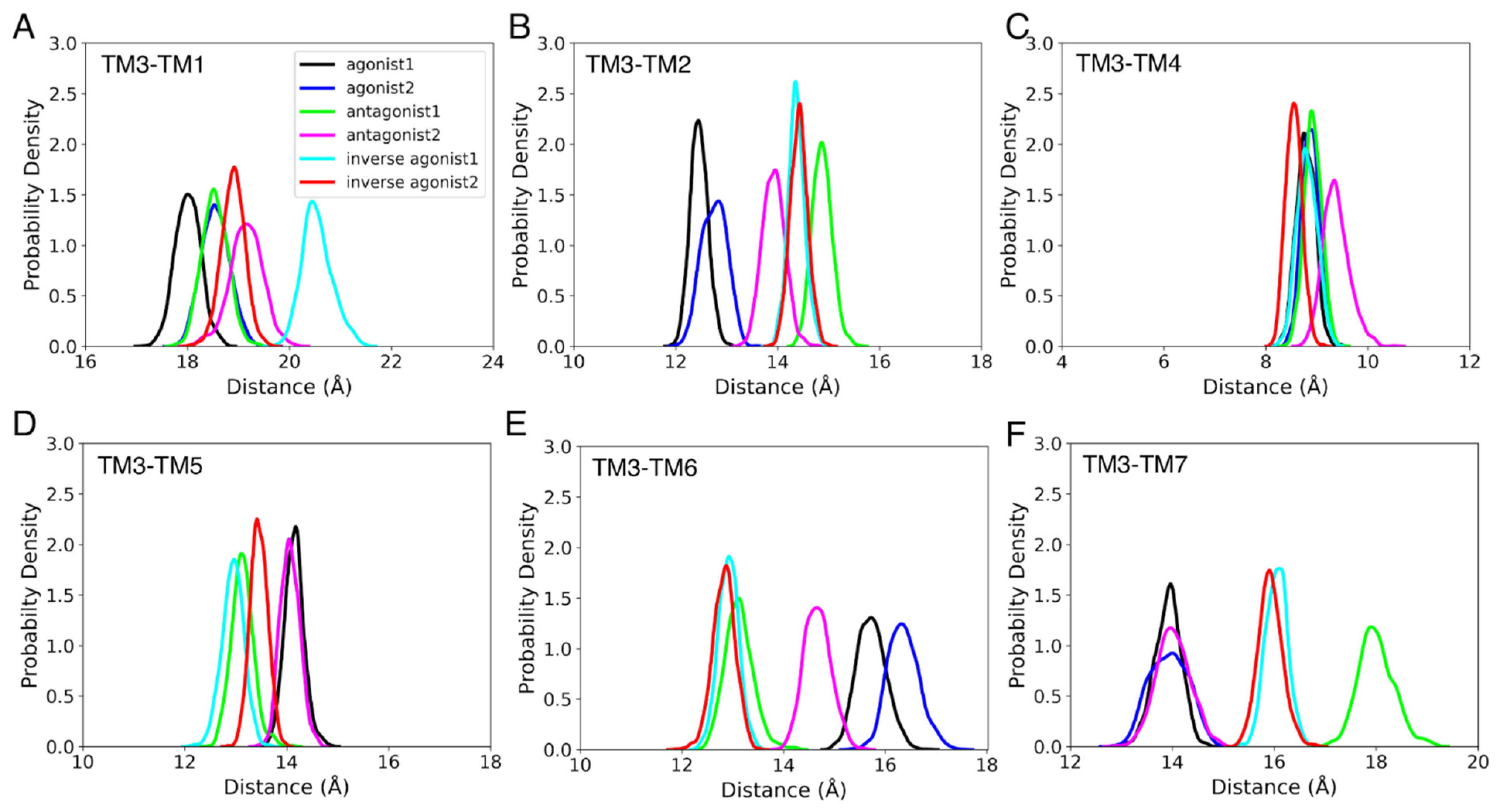
3.3. Structural Properties
3.3.1. Helix Conformational Analysis
3.3.2. Ionic Lock
3.3.3. Rotameric Toggle Switch
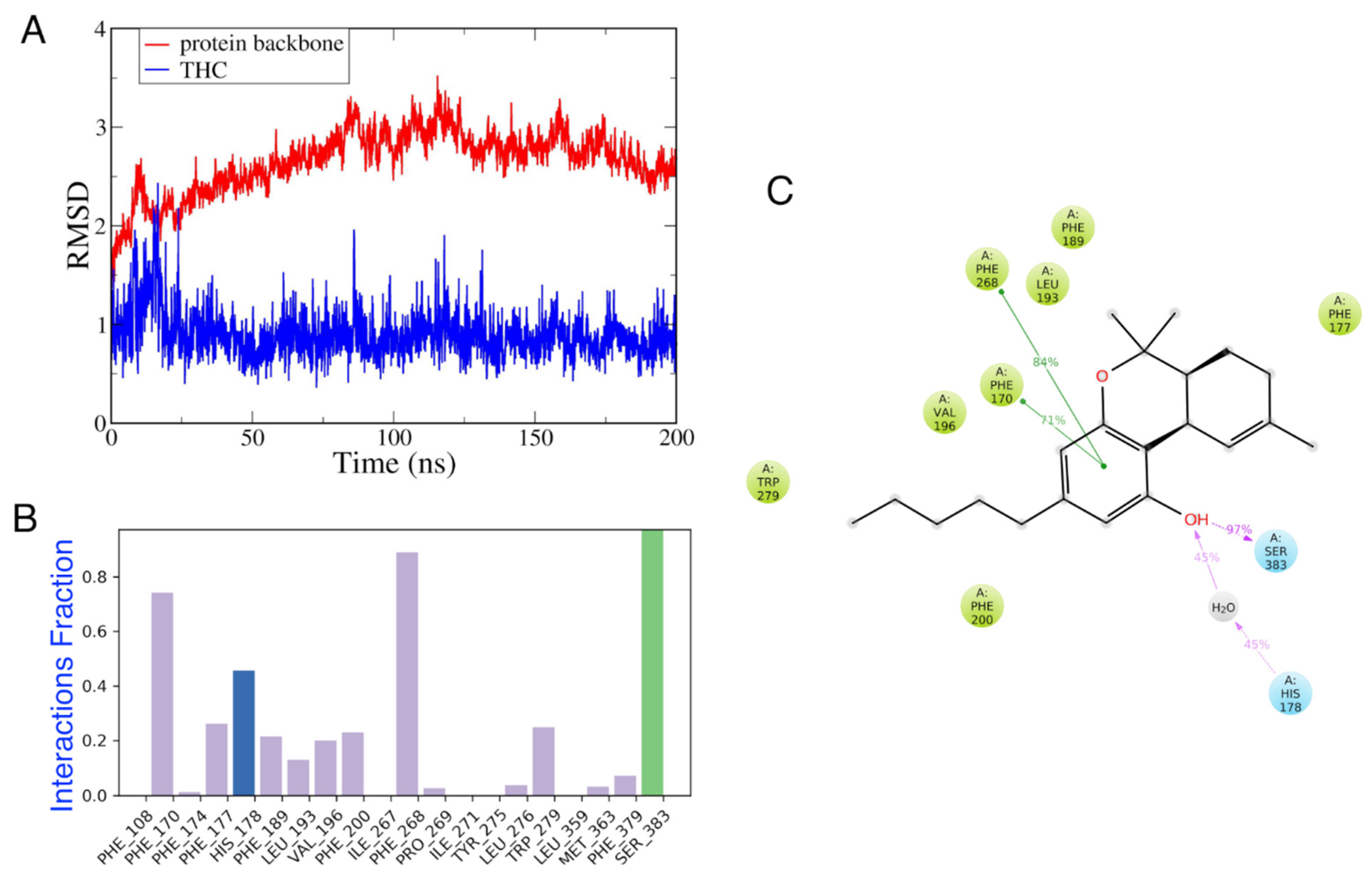
3.4. Effect of Vitamin E on THC Binding
3.4.1. Possible THC–CB1R Binding Modulation by Vitamin E Acetate In Vitro
3.4.2. MD Simulations of CB1 in the Presence and Absence of Vitamin E
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Latorraca, N.R.; Venkatakrishnan, A.J.; Dror, R.O. GPCR dynamics: Structures in motion. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Alqarni, M.H.; Yang, P.; Tong, Q.; Chowdhury, A.; Wang, L.; Xie, X.Q. Modeling, molecular dynamics simulation, and mutation validation for structure of cannabinoid receptor 2 based on known crystal structures of GPCRs. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 2483–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reggio, P. Endocannabinoid Binding to the Cannabinoid Receptors: What Is Known and What Remains Unknown. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 1468–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaoni, Y.; Mechoulam, R. Isolation, Structure, and Partial Synthesis of an Active Constituent of Hashish. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 1646–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devane, W.A.; Dysarz, F.A.; Johnson, M.R.; Melvin, L.S.; Howlett, A.C. Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 1988, 34, 605–613. [Google Scholar]
- Starowicz, K.; Malek, N.; Przewlocka, B. Cannabinoid receptors and pain. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Membr. Transp. Signal. 2013, 2, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G. Cannabinoid receptors and pain. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 63, 569–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, J.; Hohmann, A. The Endocannabinoid System and Pain. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets 2009, 8, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk-Slomka, M.; Dzik, A.; Budzynska, B.; Biala, G. Endocannabinoid System: The Direct and Indirect Involvement in the Memory and Learning Processes—A Short Review. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 8332–8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattes, R.D.; Engelman, K.; Shaw, L.M.; Elsohly, M.A. Cannabinoids and appetite stimulation. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1994, 49, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, S.; Thomas, K.L.; Abu-Shaar, M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature 1993, 365, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlett, A.C.; Barth, F.; Bonner, T.I.; Cabral, G.; Casellas, P.; Devane, W.A.; Felder, C.C.; Herkenham, M.; Mackie, K.; Martin, B.R.; et al. International Union of Pharmacology. XXVII. Classification of cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2002, 54, 161–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiègue, S.; Mary, S.; Marchand, J.; Dussossoy, D.; Carrière, D.; Carayon, P.; Bouaboula, M.; Shire, D.; LE Fur, G.; Casellas, P. Expression of Central and Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptors in Human Immune Tissues and Leukocyte Subpopulations. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 232, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rácz, I.; Nent, E.; Erxlebe, E.; Zimmer, A. CB1 receptors modulate affective behaviour induced by neuropathic pain. Brain Res. Bull. 2015, 114, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banister, S.D.; Krishna Kumar, K.; Kumar, V.; Kobilka, B.K.; Malhotra, S.V. Selective modulation of the cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptor as an emerging platform for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Medchemcomm 2019, 10, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkin, J.M.; Tzavara, E.T.; Nomikos, G.G. A role for cannabinoid CB1 receptors in mood and anxiety disorders. Behav. Pharmacol. 2005, 16, 315–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvin, Y.; Phan, A.; Hill, M.N.; Pfaff, D.W.; Mcewen, B.S. CB1 receptor signaling regulates social anxiety and memory. Genes Brain Behav. 2013, 12, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagotto, U.; Vicennati, V.; Pasquali, R. The endocannabinoid system and the treatment of obesity. Ann. Med. 2005, 37, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.R.; Murumkar, P.R. Advances in patented CB1 receptor antagonists for obesity. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 2018, 7, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.C.; Hammarsten, P.; Josefsson, A.; Stattin, P.; Granfors, T.; Egevad, L.; Mancini, G.; Lutz, B.; Bergh, A.; Fowler, C.J. A high cannabinoid CB1 receptor immunoreactivity is associated with disease severity and outcome in prostate cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, C.W.; Oti, F.E.; Erkan, M.; Sauliunaite, D.; Bergmann, F.; Pacher, P.; Batkai, S.; Müller, M.W.; Giese, N.A.; Friess, H.; et al. Cannabinoids in pancreatic cancer: Correlation with survival and pain. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermanson, D.J.; Marnett, L.J. Cannabinoids, endocannabinoids, and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011, 30, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aso, E.; Ferrer, I. Cannabinoids for treatment of alzheimer’s disease: Moving toward the clinic. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manuel, I.; De San Román, E.G.; Giralt, M.T.; Ferrer, I.; Rodríguez-Puertas, R. Type-1 cannabinoid receptor activity during Alzheimer’s disease progression. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2014, 42, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Romero, J.; Ramos, J.A. Endocannabinoids and neurodegenerative disorders: Parkinson’s disease, huntington’s chorea, alzheimer’s disease, and others. In Endocannabinoids; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2015; pp. 233–259. ISBN 9783319208251. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.L.; Carey, L.M.; Mackie, K.; Hohmann, A.G. Cannabinoid CB2 agonist GW405833 suppresses inflammatory and neuropathic pain through a CB1 mechanism that is independent of CB2 receptors in mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2017, 362, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whiteside, G.; Lee, G.; Valenzano, K. The Role of the Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor in Pain Transmission and Therapeutic Potential of Small Molecule CB2 Receptor Agonists. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 917–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusakabe, K.I.; Iso, Y.; Tada, Y.; Sakagami, M.; Morioka, Y.; Chomei, N.; Shinonome, S.; Kawamoto, K.; Takenaka, H.; Yasui, K.; et al. Selective CB2 agonists with anti-pruritic activity: Discovery of potent and orally available bicyclic 2-pyridones. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3154–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haruna, T.; Soga, M.; Morioka, Y.; Hikita, I.; Imura, K.; Furue, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Imura, C.; Ikeda, M.; Yamauchi, A.; et al. S-777469, a novel cannabinoid type 2 receptor agonist, suppresses itch-associated scratching behavior in rodents through inhibition of itch signal transmission. Pharmacology 2015, 95, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, J.; Hohmann, A.G. Cannabinoid CB 2 receptors: A therapeutic target for the treatment of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Deng, H.; Zvonok, A.; Cockayne, D.A.; Kwan, J.; Mata, H.P.; Vanderah, T.W.; Lai, J.; Porreca, F.; Makriyannis, A.; et al. Activation of CB2 cannabinoid receptors by AM1241 inhibits experimental neuropathic pain: Pain inhibition by receptors not present in the CNS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2003, 100, 10529–10533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lotersztajn, S.; Teixeira-Clerc, F.; Julien, B.; Deveaux, V.; Ichigotani, Y.; Manin, S.; Tran-Van-Nhieu, J.; Karsak, M.; Zimmer, A.; Mallat, A. CB2 receptors as new therapeutic targets for liver diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julien, B.; Grenard, P.; Teixeira-Clerc, F.; Van Nhieu, J.T.; Li, L.; Karsak, M.; Zimmer, A.; Mallat, A.; Lotersztajn, S. Antifibrogenic role of the cannabinoid receptor CB2 in the liver. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Kumar, U. Cannabinoid receptors and the endocannabinoid system: Signaling and function in the central nervous system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hua, T.; Vemuri, K.; Pu, M.; Qu, L.; Han, G.W.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Shui, W.; Li, S.; Korde, A.; et al. Crystal Structure of the Human Cannabinoid Receptor CB1. Cell 2016, 167, 750–762.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, Z.; Yin, J.; Chapman, K.; Grzemska, M.; Clark, L.; Wang, J.; Rosenbaum, D.M. High-resolution crystal structure of the human CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Nature 2016, 540, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hua, T.; Vemuri, K.; Nikas, S.P.; Laprairie, R.B.; Wu, Y.; Qu, L.; Pu, M.; Korde, A.; Jiang, S.; Ho, J.H.; et al. Crystal structures of agonist-bound human cannabinoid receptor CB 1. Nature 2017, 547, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Hua, T.; Vemuri, K.; Ho, J.H.; Wu, Y.; Wu, L.; Popov, P.; Benchama, O.; Zvonok, N.; Locke, K.; et al. Crystal Structure of the Human Cannabinoid Receptor CB2. Cell 2019, 176, 459–467.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manandhar, A.; Haron, M.H.; Ross, S.A.; Klein, M.L.; Elokely, K.M. Potential Pro-Inflammatory Effect of Vitamin E Analogs through Mitigation of Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) Binding to the Cannabinoid 2 Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blount, B.C.; Karwowski, M.P.; Shields, P.G.; Morel-Espinosa, M.; Valentin-Blasini, L.; Gardner, M.; Braselton, M.; Brosius, C.R.; Caron, K.T.; Chambers, D.; et al. Vitamin E Acetate in Bronchoalveolar-Lavage Fluid Associated with EVALI. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release 2020-2: BioLuminate; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2020.
- Zhu, K.; Day, T.; Warshaviak, D.; Murrett, C.; Friesner, R.; Pearlman, D. Antibody structure determination using a combination of homology modeling, energy-based refinement, and loop prediction. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinforma. 2014, 82, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salam, N.K.; Adzhigirey, M.; Sherman, W.; Pearlman, D.A. Structure-based Approach to the Prediction of Disulfide Bonds in Proteins. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2014, 27, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, H.; Cholleti, A.; Pearlman, D.; Sherman, W.; Loving, K.A. Applying Physics-Based Scoring to Calculate Free Energies of Binding for Single Amino Acid Mutations in Protein-Protein Complexes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schrödinger Release 2018-3: Protein Preparation Wizard; Epik, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA; Impact, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA; Prime, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 2020, pp. 2013–2014. [CrossRef]
- Harder, E.; Damm, W.; Maple, J.; Wu, C.; Reboul, M.; Xiang, J.Y.; Wang, L.; Lupyan, D.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Knight, J.L.; et al. OPLS3: A Force Field Providing Broad Coverage of Drug-like Small Molecules and Proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger Release 2020-4: Prime; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2020.
- Nikas, S.P.; Sharma, R.; Paronis, C.A.; Kulkarni, S.; Thakur, G.A.; Hurst, D.; Wood, J.T.; Gifford, R.S.; Rajarshi, G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Probing the carboxyester side chain in controlled deactivation (-)-δ8-tetrahydrocannabinols. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thakur, G.A.; Bajaj, S.; Paronis, C.; Peng, Y.; Bowman, A.L.; Barak, L.S.; Caron, M.G.; Parrish, D.; Deschamps, J.R.; Makriyannis, A. Novel adamantyl cannabinoids as CB1 receptor probes. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3904–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nanda, K.K.; Henze, D.A.; Della Penna, K.; Desai, R.; Leitl, M.; Lemaire, W.; White, R.B.; Yeh, S.; Brouillette, J.N.; Hartman, G.D.; et al. Benzimidazole CB2 agonists: Design, synthesis and SAR. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1218–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Thatte, J.; Buzard, D.J.; Jones, R.M. Therapeutic utility of cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2) selective agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8224–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, I.; Mastinu, A.; Olimpieri, F.; Falzoi, M.; Sani, M.; Ruiu, S.; Loriga, G.; Volonterio, A.; Tambaro, S.; Bottazzi, M.E.H.; et al. Novel pyrazole derivatives as neutral CB1 antagonists with significant activity towards food intake. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 62, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulp, A.; Bortoff, K.; Zhang, Y.; Seltzman, H.; Mathews, J.; Snyder, R.; Fennell, T.; Maitra, R. Diphenyl purine derivatives as peripherally selective cannabinoid receptor 1 antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 10022–10032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ragusa, G.; Gómez-Cañas, M.; Morales, P.; Hurst, D.P.; Deligia, F.; Pazos, R.; Pinna, G.A.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Goya, P.; Reggio, P.H.; et al. Synthesis, pharmacological evaluation and docking studies of pyrrole structure-based CB2 receptor antagonists. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 101, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiu, S.; Anzani, N.; Orrù, A.; Floris, C.; Caboni, P.; Maccioni, E.; Distinto, S.; Alcaro, S.; Cottiglia, F. N-Alkyl dien- and trienamides from the roots of Otanthus maritimus with binding affinity for opioid and cannabinoid receptors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 7074–7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Matthews, J.M.; Xia, M.; Black, S.; Chen, C.; Hou, C.; Liang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Macielag, M.J. Tetrahydropyrazolo [4,3-c]pyridine derivatives as potent and peripherally selective cannabinoid-1 (CB1) receptor inverse agonists. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5597–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.M.; McNally, J.J.; Connolly, P.J.; Xia, M.; Zhu, B.; Black, S.; Chen, C.; Hou, C.; Liang, Y.; Tang, Y.; et al. Tetrahydroindazole derivatives as potent and peripherally selective cannabinoid-1 (CB1) receptor inverse agonists. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 5346–5349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, S.; Mugnaini, C.; Ligresti, A.; Tafi, A.; Brogi, S.; Falciani, C.; Pedani, V.; Pesco, N.; Guida, F.; Luongo, L.; et al. Design, synthesis, and pharmacological characterization of indol-3-ylacetamides, indol-3-yloxoacetamides, and indol-3-ylcarboxamides: Potent and selective CB2 cannabinoid receptor inverse agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 5391–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghazadeh Tabrizi, M.; Baraldi, P.G.; Ruggiero, E.; Saponaro, G.; Baraldi, S.; Poli, G.; Tuccinardi, T.; Ravani, A.; Vincenzi, F.; Borea, P.A.; et al. Synthesis and structure activity relationship investigation of triazolo [1,5-a]pyrimidines as CB2 cannabinoid receptor inverse agonists. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 113, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LigPrep; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2020.
- Shelley, J.C.; Cholleti, A.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Timlin, M.R.; Uchimaya, M. Epik: A software program for pKa prediction and protonation state generation for drug-like molecules. J. Comput. Aided. Mol. Des. 2007, 21, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glide; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2020.
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 1. Method and Assessment of Docking Accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 2. Enrichment Factors in Database Screening. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra precision glide: Docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrödinger Release 2020-2: Desmond Molecular Dynamics System; D.E. Shaw Research: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Maestro-Desmond Interoperability Tools; Schrödinger: New York, NY, USA, 2020.
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomize, M.A.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Joo, H.; Mosberg, H.I.; Lomize, A.L. OPM database and PPM web server: Resources for positioning of proteins in membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D370–D376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martyna, G.J.; Tobias, D.J.; Klein, M.L. Constant pressure molecular dynamics algorithms. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 101, 4177–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyna, G.J.; Klein, M.L.; Tuckerman, M. Nosé-Hoover chains: The canonical ensemble via continuous dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuckerman, M.E.; Berne, B.J.; Rossi, A. Molecular dynamics algorithm for multiple time scales: Systems with disparate masses. J. Chem. Phys. 1991, 94, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toukmaji, A.Y.; Board, J.A. Ewald summation techniques in perspective: A survey. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1996, 95, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isberg, V.; De Graaf, C.; Bortolato, A.; Cherezov, V.; Katritch, V.; Marshall, F.H.; Mordalski, S.; Pin, J.P.; Stevens, R.C.; Vriend, G.; et al. Generic GPCR residue numbers—Aligning topology maps while minding the gaps. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ballesteros, J.A.; Weinstein, H. Integrated methods for the construction of three-dimensional models and computational probing of structure-function relations in G protein-coupled receptors. Methods Neurosci. 1995, 25, 366–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guilloux, V.; Schmidtke, P.; Tuffery, P. Fpocket: An open source platform for ligand pocket detection. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dror, R.O.; Arlow, D.H.; Maragakis, P.; Mildorf, T.J.; Pan, A.C.; Xu, H.; Borhani, D.W.; Shaw, D.E. Activation mechanism of the β 2-adrenergic receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011, 108, 18684–18689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hauser, A.S.; Kooistra, A.J.; Munk, C.; Heydenreich, F.M.; Veprintsev, D.B.; Bouvier, M.; Babu, M.M.; Gloriam, D.E. GPCR activation mechanisms across classes and macro/microscales. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2021, 28, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trzaskowski, B.; Latek, D.; Yuan, S.; Ghoshdastider, U.; Debinski, A.; Filipek, S. Action of Molecular Switches in GPCRs—Theoretical and Experimental Studies. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 1090–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Díaz, Ó.; Dalton, J.A.R.; Giraldo, J. Revealing the Mechanism of Agonist-Mediated Cannabinoid Receptor 1 (CB1) Activation and Phospholipid-Mediated Allosteric Modulation. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 5638–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAllister, S.D.; Hurst, D.P.; Barnett-Norris, J.; Lynch, D.; Reggio, P.H.; Abood, M.E. Structural mimicry in class A G protein-coupled receptor rotamer toggle switches: The importance of the F3.36(201)/W6.48(357) interaction in cannabinoid CB1 receptor activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48024–48037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dutta, S.; Selvam, B.; Das, A.; Shukla, D. Mechanistic origin of partial agonism of tetrahydrocannabinol for cannabinoid receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirin, S.; Kumar, R.; Martinez, C.; Karmilowicz, M.J.; Ghosh, P.; Abramov, Y.A.; Martin, V.; Sherman, W. A computational approach to enzyme design: Predicting W-Aminotransferase catalytic activity using docking and MM-GBSA scoring. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 2334–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zoubi, R.; Morales, P.; Reggio, P.H. Structural insights into cb1 receptor biased signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutta, S.; Shukla, D. Distinct Activation Mechanisms Regulate Subtype Selectivity of Cannabinoid Receptors. Biorxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| BDBM50233600 | BDBM50432728 |
 |  |
| Agonist 1 | Agonist 2 |
| BDBM50195530 | BDBM50399518 |
 |  |
| Antagonist 1 | Antagonist 2 |
| BDBM50198734 | BDBM50198718 |
 |  |
| Inverse Agonist 1 | Inverse Agonist 2 |
| BDBM50006259 | BDBM50005278 |
 |  |
| Agonist 1 | Agonist 2 |
| BDBM50116984 | BDBM50180022 |
 |  |
| Antagonist 1 | Antagonist 2 |
| BDBM50420884 | BDBM50154629 |
 |  |
| Inverse Agonist 1 | Inverse Agonist 2 |
| Systems | Docking Score | MM-GBSA ΔGBind (Kcal/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CB1 with vitamin E | Cluster 1 | −6.227 | −46.60 |
| Cluster 2 | −6.571 | −49.22 | |
| Cluster 3 | −6.913 | −10.72 | |
| Cluster 4 | −6.466 | −46.57 | |
| CB1–THC complex (last frame) | −11.404 | −86.45 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manandhar, A.; Haron, M.H.; Klein, M.L.; Elokely, K. Understanding the Dynamics of the Structural States of Cannabinoid Receptors and the Role of Different Modulators. Life 2022, 12, 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122137
Manandhar A, Haron MH, Klein ML, Elokely K. Understanding the Dynamics of the Structural States of Cannabinoid Receptors and the Role of Different Modulators. Life. 2022; 12(12):2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122137
Chicago/Turabian StyleManandhar, Anjela, Mona H. Haron, Michael L. Klein, and Khaled Elokely. 2022. "Understanding the Dynamics of the Structural States of Cannabinoid Receptors and the Role of Different Modulators" Life 12, no. 12: 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122137
APA StyleManandhar, A., Haron, M. H., Klein, M. L., & Elokely, K. (2022). Understanding the Dynamics of the Structural States of Cannabinoid Receptors and the Role of Different Modulators. Life, 12(12), 2137. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122137







