Sleep Endoscopy with Positive Airway Pressure: A Method for Better Compliance and Individualized Treatment of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Clinical Evaluation
2.3. Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy
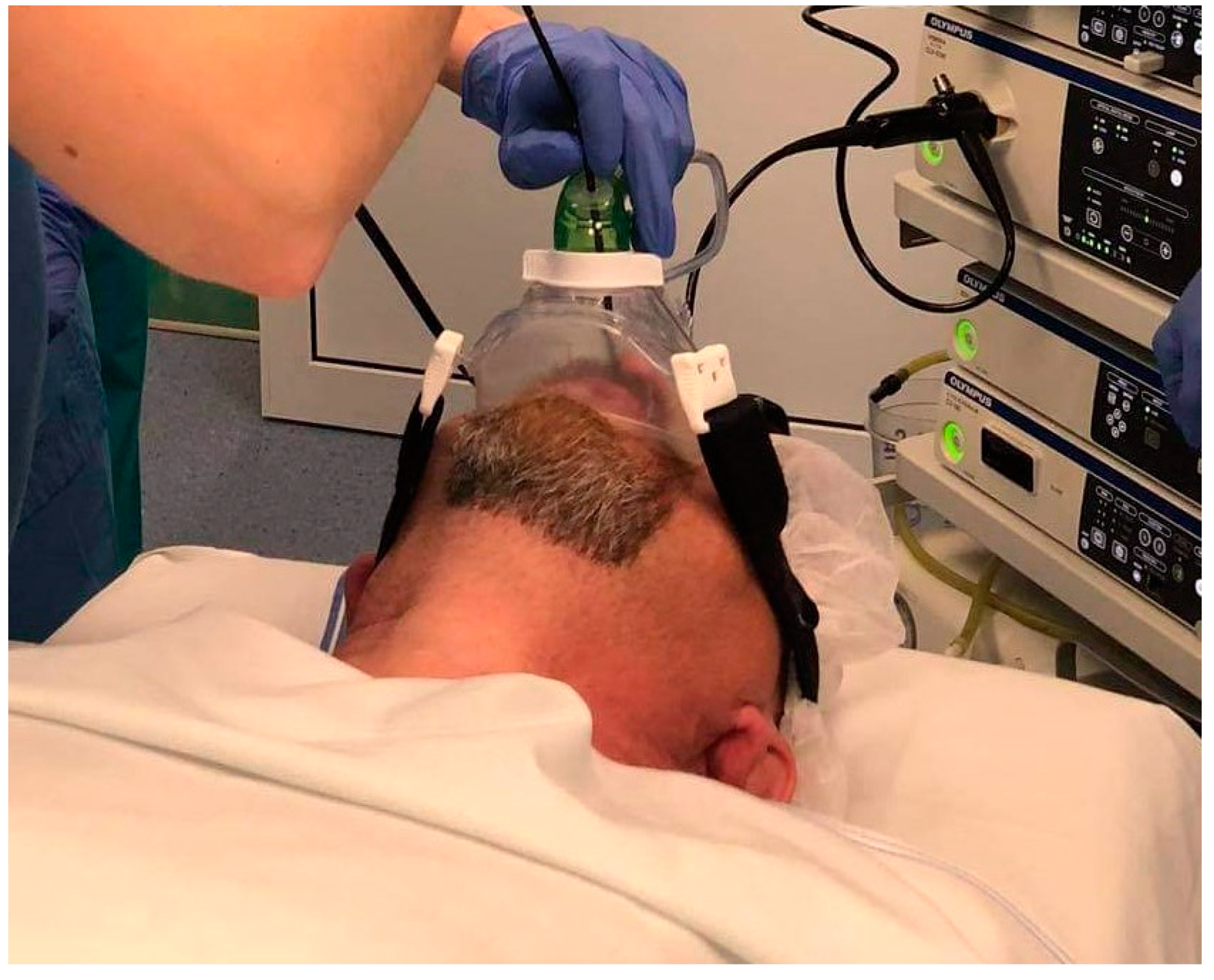
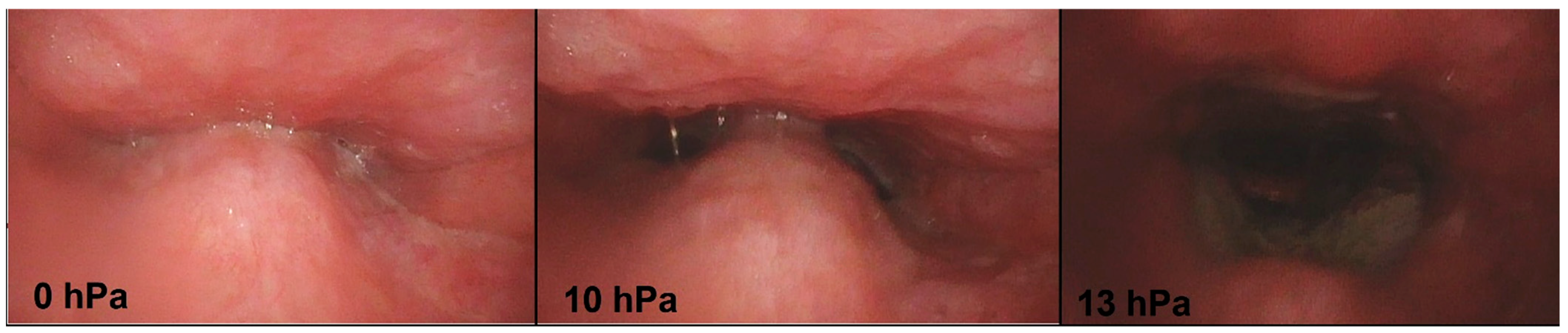
2.4. Positive Airway Pressure Titration during the Sleep Endoscopy
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients Characteristics
3.2. Effect of PAP
3.3. Ineffectiveness of PAP
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pavwoski, P.; Shelgikar, A.V. Treatment options for obstructive sleep apnea. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2016, 7, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, T. Alternative interventions for obstructive sleep apnea. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2019, 86, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, T.E.; Grunstein, R.R. Adherence to continuous positive airway pressure therapy: The challenge to effective treatment. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiser, M.E.; Schell, A.E.; Soose, R.J. DISE-PAP: A method for troubleshooting residual AHI elevation despite positive pressure therapy. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 631–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, C.; Liu, S.Y.; Kushida, C.A.; Nekhendzy, V.; Huon, L.K.; Capasso, R. Impact of continuous positive airway pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnea during drug-induced sleep endoscopy. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2017, 42, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaliere, M.; Russo, F.; Iemma, M. Awake versus druginduced sleep endoscopy: Evaluation of airway obstruction in obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnoea syndrome. Laryngoscope 2013, 123, 2315–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hybášková, J.; Jor, O.; Novák, V.; Matoušek, P.; Komínek, P. Možné využití spánkové endoskopie pro zvýšení efektivity léčby (operační i neoperační) u pacientů s obstrukční spánkovou apnoí. Cesk Slov Neurol N 2017, 80/113, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Certal, V.F.; Pratas, R.; Guimaraes, L.; Lugo, R.; Tsou, Y.; Camacho, M.; Capasso, R. Awake examination versus DISE for surgical decision making in patients with OSA: A systematic rewiew. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civelek, S.; Emre, I.E.; Dizdar, D.; Cuhadaroglu, C.; Eksioglu, B.K.; Eraslan, A.K.; Turgut, S. Comparison of conventional continuous positive airway pressure to continuous positive airway pressure titration performed with sleep endoscopy. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Koo, S.K.; Choi, J.W.; Moon, J.S.; Lee, S.H. Upper airway structural changes induced by CPAP in OSAS patients: A study using drug-induced sleep endoscopy. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.C.; Hsu, Y.B.; Lan, M.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Kao, M.C.; Huang, T.T.; Chiu, T.J.; Yang, M.C. The predictive value of drug-induced sleep endoscopy for CPAP titration in OSA patients. Sleep Breath. 2018, 22, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kezirian, E.J.; Hussey, H.M.; Brietzke, S.E.; Cohen, S.M.; Davis, G.E.; Shin, J.J.; Weinberger, D.G.; Cabana, M.D. Hypopharyngeal surgery in obstructive sleep apnea: Practice patterns, perceptions, and attitudes. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2012, 147, 964–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vito, A.; Carrasco, L.M.; Vanni, A.; Bosi, M.; Braghiroli, A.; Campanini, A.; De Vries, N.; Hamans, E.; Hohenhorst, W.; Kotecha, B.T.; et al. European position paper on drug-induced sedation endoscopy (DISE). Sleep Breath. 2014, 18, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, C.B.; Pringle, M. Sleep nasendoscopy: A technique of assessment in snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1991, 16, 504509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veer, V.; Zhang, H.; Mandavia, R.; Mehta, N. Introducing a new classification for drug-induced sleep endoscopy (DISE): The PTLTbE system. Sleep Breath. 2020, 24, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Corso, E.; Fiorita, A.; Rizzotto, G.; Mennuni, G.F.; Meucci, D.; Giuliani, M.; Marchese, M.R.; Levantesi, L.; Marca, G.D.; Paludetti, G.; et al. The role of drug-induced sleep endoscopy in the diagnosis and management of obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome: Our personal experience. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2013, 33, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachar, G.; Nageris, B.; Feinmesser, R.; Hadar, T.; Yaniv, E.; Shpitzer, T.; Eidelman, L. Novel grading system for quantifying upper-airway obstruction on sleep endoscopy. Lung 2012, 190, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.S.; Soh, S.; Kim, E.J.; Cho, H.J.; Shin, S.; Kim, H.J.; Koo, B.N. Comparison of three sedation regimens for drug-induced sleep endoscopy. Sleep Breath. 2015, 19, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hybášková, J.; Babiarová, V.; Jor, O.; Novák, V.; Matoušek, P.; Komínek, P. Flexibilní endoskopie horních dýchacích cest v léky navozeném spánku. Otorinolaryngol. Foniatr. 2016, 65, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, J.H.; Mandel, J.E. Drug-induced sleep endoscopy: From obscure technique to diagnostic tool for assessment of obstructive sleep apnea for surgical interventions. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2018, 31, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pépin, J.L.; Krieger, J.; Rodenstein, D.; Cornette, A.; Sforza, E.; Delguste, P.; Deschaux, C.; Grillier, V.; Lévy, P. Effective Compliance during the First 3 Months of Continuous Positive Airway Pressure A European Prospective Study of 121 Patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabil, A.; le Vaillant, M.; Stitt, C.; Goupil, F.; Pigeanne, T.; Leclair-Visonneau, L.; Masson, P.; Bizieux-Thaminy, A.; Humeau, M.-P.; Meslier, N.; et al. A CPAP Data–Based Algorithm for Automatic Early Prediction of Therapy Adherence. Sleep Breath. 2021, 25, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, R.J.; Pack, A.I.; Gupta, K.B.; Metzger, L.J.; Oh, E.; Getsy, J.E.; Hoffman, E.A.; Gefter, W.B. Upper airway and soft tissue structural changes incuded by CPAP in normal subjects. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1996, 154, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.C.; Friedman, M.; Lin, H.C.; Wang, P.C.; Hwang, M.S.; Hsu, C.M.; Lin, M.C.; Chin, C.H. Clinical predictors of effectivecontinuous positive airway pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnea/hypopnea syndrome. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 1983–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, C.; Camacho, M.; Liu, S.Y.; Huon, L.K.; Capasso, R. Epiglottis collapse in adult obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedhia, E.C.; Rosen, C.A.; Soose, R.J. What is the role of the larynx in adult obstructive sleep apnea? Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verse, T.; Pirsig, W. Age-related changes in the epiglottis causing failure of nasal continuous positive airway pressure therapy. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1999, 113, 1022–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, E.O.; Jung, S.Y.; Al-Dilaijan, K.; Min, J.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.W. Is Epiglottis Surgery Necessary for Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients With Epiglottis Obstruction? Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 2658–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roustan, V.; Barbieri, M.; Incandela, F.; Missale, F.; Camera, H.; Braido, F.; Mora, R.; Peretti, G. Transoral glossoepiglottopexy in the treatment of adult obstructive sleep apnoea: A surgical approach. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2018, 38, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betka, J.; Kubíčková, J.; Klozar, J.; Šonka, K. Poruchy Dýchání ve Spánku, 1st ed.; Tobiáš: Hradec Králové, Czech Republic, 2019; pp. 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Mickelson, S.A.; Rosenthal, L. Midline glossectomy and epiglottidectomy for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Laryngoscope 1997, 107, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, M. Endoscopic coblator-assisted epiglottoplasty in “obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome” patients. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2017, 42, 1112–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oluwasanmi, A.F.; Mal, R.K. Diathermy epiglottectomy: Endoscopic technique. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2001, 115, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalfumo, F.J.; Golz, A.; Westerman, S.T.; Gilbert, L.M.; Joachims, H.Z.; Goldenberg, D. The epiglottis and obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1998, 112, 940–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobbi, R.; Baiardi, S.; Mondini, S.; Cerritelli, L.; Piccin, O.; Scaramuzzino, G.; Milano, F.; Melotti, M.R.; Mordini, F.; Pirodda, A.; et al. Technique and Preliminary Analysis of Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy With Online Polygraphic Cardiorespiratory Monitoring in Patients With Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 143, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebben, M.R.; Narizhnaya, M.; Segal, A.Z.; Barone, D.; Krieger, A.C. A randomised controlled trial on the effect of mask choice on residual respiratory events with continuous positive airway pressure treatment. Sleep Med. 2014, 15, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Median (IQR) or n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Age, years | 46.0 (39; 55) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 29.2 (27.4; 31.3) |
| AHI | 26.4 (18.9; 31.8) |
| T90, % | 2.3 (0.6; 9.1) |
| Soft palate obstruction | 53 (94.6) |
| Oropharynx obstruction | 13 (23.2) |
| Tongue base obstruction | 39 (69.6) |
| Epiglottic pathology | --- |
| Mallampati | |
| I | 2 (3.6) |
| II | 10 (17.9) |
| III | 30 (53.6) |
| IV | 14 (25.0) |
| Friedman | |
| 0 | 4 (7.1) |
| 1 | 28 (50.0) |
| 2 | 22 (39.3) |
| 3 | 2 (3.6) |
| Soft Palate | Oropharynx | Tongue Base | Epiglottis | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obstruction—degree | |||||
| Complete | 51 (91.1) | 15 (26.8) | 23 (41.1) | 16 (28.6) | |
| Partial | 4 (7.1) | 27 (48.2) | 17 (30.4) | 5 (8.9) | |
| No | 1 (1.8) | 14 (25.0) | 16 (28.6) | 35 (62.5) | |
| Obstruction—type | |||||
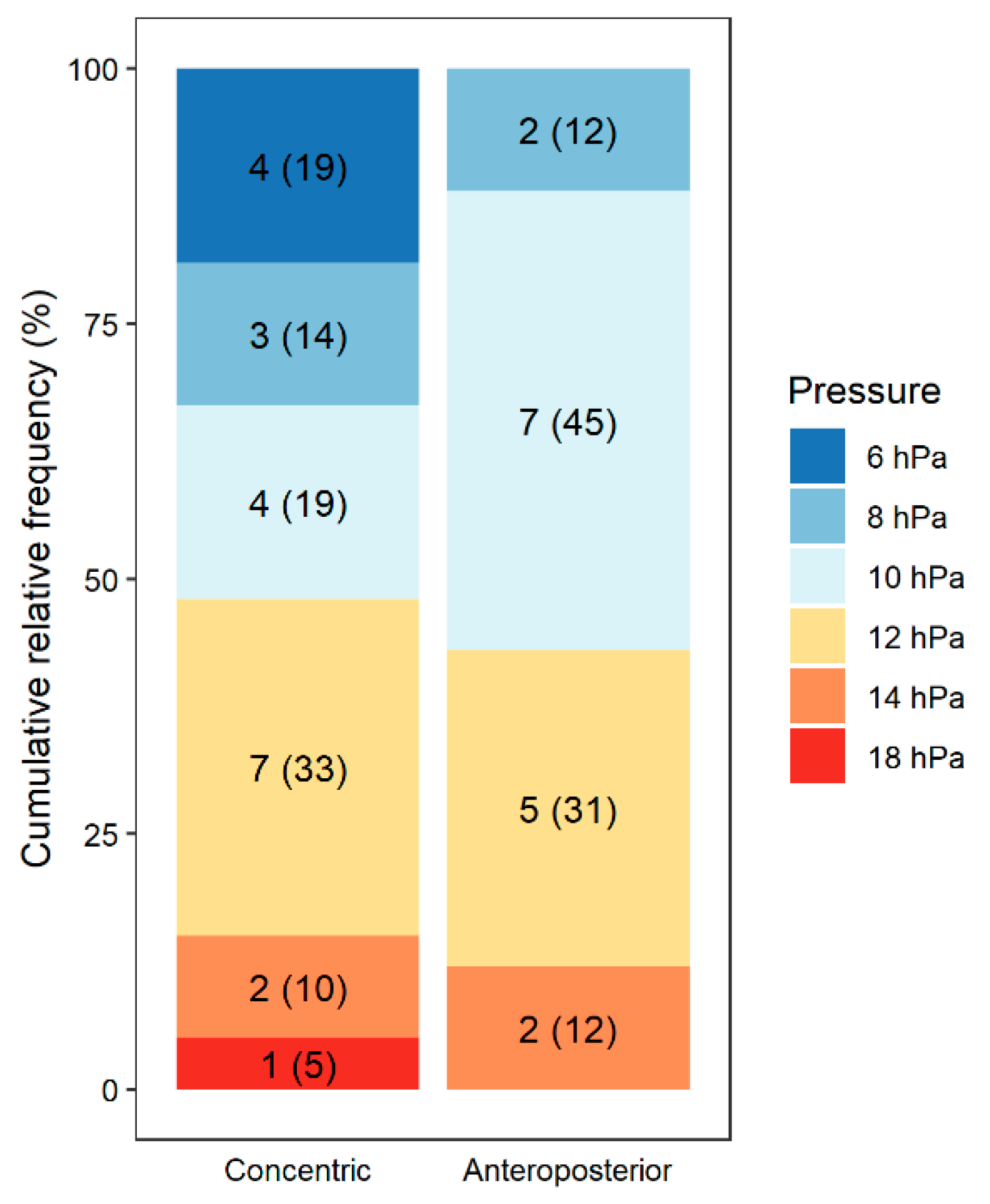
| Concentric | 33 (58.9) | --- | --- | --- | |
| Laterolateral | 2 (3.6) | 42 (75.0) | --- | 2 (3.6) | |
| Anteroposterior | 20 (35.7) | --- | 40 (71.4) | 19 (33.9) | |
| No | 1 (1.8) | 14 (25.0) | 16 (28.6) | 35 (62.5) | |
| Improvement | 38/51 (74.5) | 15/15 (100.0) | 20/23 (87.0) | 5/16 (31.3) | <0.001 |
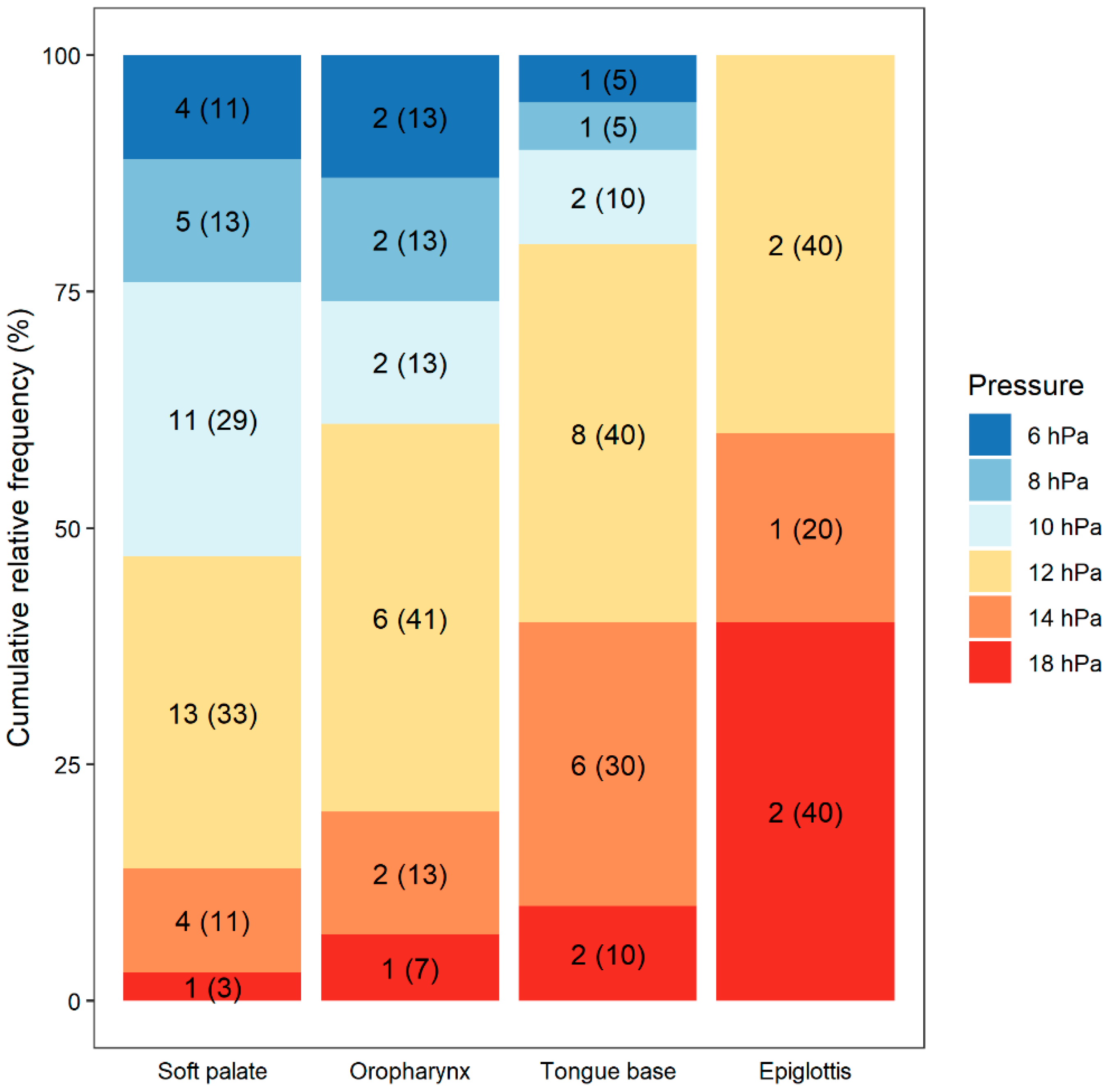
| Level of Obstruction | Type of Obstruction | Median Opening Pressure (hPa) | Ineffectiveness of PAP (% Patients) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soft palate | Anteroposterior | 10 | 20.0 |
| Concentric | 10 | 36.4 | |
| Oropharynx | Laterolateral | 12 | 0.0 |
| Tongue base | Anteroposterior | 12 | 13.0 |
| Epiglottis | Anteroposterior (collapse) | 14 | 68.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masárová, M.; Matoušek, P.; Jor, O.; Novák, V.; Vrtková, A.; Kubec, V.; Zeleník, K.; Komínek, P.; Formánek, M. Sleep Endoscopy with Positive Airway Pressure: A Method for Better Compliance and Individualized Treatment of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Life 2022, 12, 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122108
Masárová M, Matoušek P, Jor O, Novák V, Vrtková A, Kubec V, Zeleník K, Komínek P, Formánek M. Sleep Endoscopy with Positive Airway Pressure: A Method for Better Compliance and Individualized Treatment of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Life. 2022; 12(12):2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122108
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasárová, Michaela, Petr Matoušek, Ondřej Jor, Vilém Novák, Adéla Vrtková, Vojtěch Kubec, Karol Zeleník, Pavel Komínek, and Martin Formánek. 2022. "Sleep Endoscopy with Positive Airway Pressure: A Method for Better Compliance and Individualized Treatment of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea" Life 12, no. 12: 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122108
APA StyleMasárová, M., Matoušek, P., Jor, O., Novák, V., Vrtková, A., Kubec, V., Zeleník, K., Komínek, P., & Formánek, M. (2022). Sleep Endoscopy with Positive Airway Pressure: A Method for Better Compliance and Individualized Treatment of Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Life, 12(12), 2108. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122108






