The Bacterial Compositions of Nasal Septal Abscess in Patients with or without Diabetes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
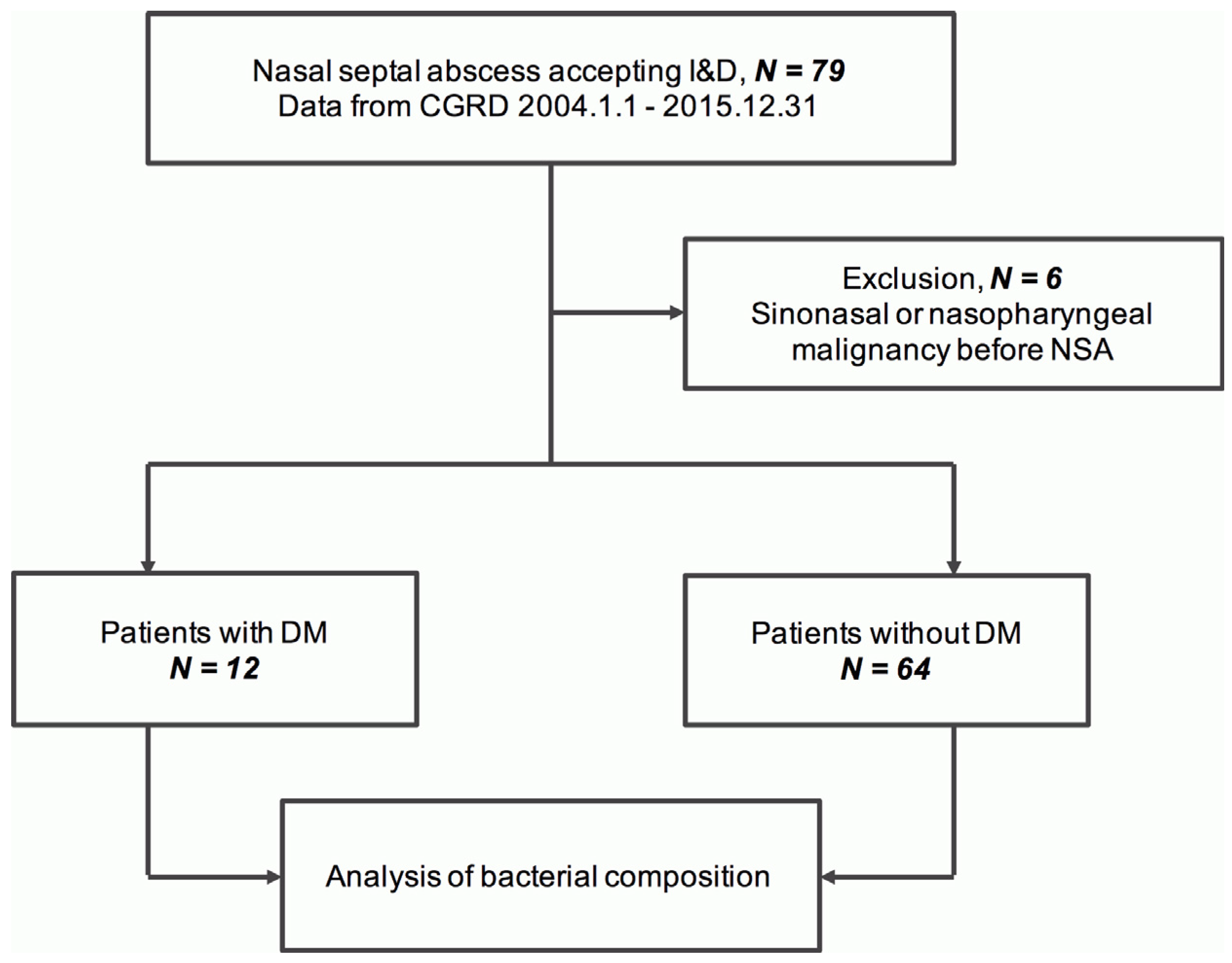
2.1. Study Population—NSA in Patients with or without DM
2.2. Medical Comorbidities
2.3. Classification and Analysis of Pathogenic Bacteria
2.4. Assessment of Prognosis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cases Included in the Analysis
3.2. Demographic Characteristics and Medical Comorbidities
3.3. Bacterial Cultures and Growths
3.4. Number of Bacteria Isolates in NSA
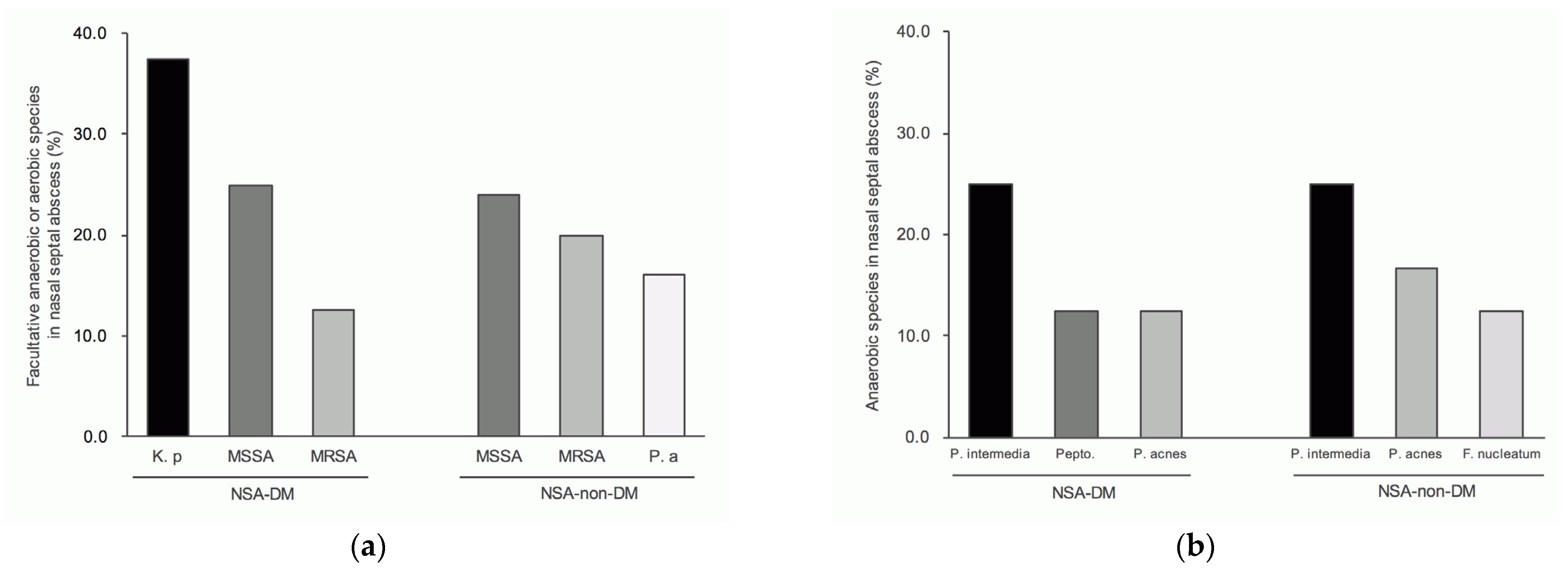
3.5. Top Three Genera for NSA
3.6. Top Three Species for NSA
3.7. Prognosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luan, C.W.; Tsai, M.S.; Liu, C.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Tsai, Y.T.; Hsu, C.M.; Wu, C.Y.; Chang, P.J.; Chang, G.H. Increased Risk of Nasal Septal Abscess after Septoplasty in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E2420–E2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalaludin, M. Nasal septal abscess-retrospective analysis of 14 cases from University Hospital, Kuala Lumpur. Singap. Med. J. 1993, 34, 435–437. [Google Scholar]
- Berlucchi, M.; Tomasoni, M.; Bosio, R.; Rampinelli, V. Spontaneous Abscess of the Posterior Nasal Septum: An Unusual Cause of Nasal Obstruction in Children. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2021, 130, 966–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowerby, L.J.; Wright, E.D. Intracranial abscess as a complication of nasal septal abscess. CMAJ 2013, 185, E270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, L.H.; Wu, P.C.; Shih, C.P.; Wang, H.W.; Chen, H.C.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chu, Y.H.; Lee, J.C. Nasal septal abscess: A 10-year retrospective study. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2019, 276, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinesh, R.; Avatar, S.; Haron, A. Nasal septal abscess with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. Med. J. Malays. 2011, 66, 253–254. [Google Scholar]
- Luan, C.W.; Liu, C.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Tsai, M.S.; Tsai, Y.T.; Hsu, C.M.; Wu, C.Y.; Chang, P.J.; Chang, G.H. The Pathogenic Bacteria of Deep Neck Infection in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes, and without Diabetes from Chang Gung Research Database. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.S.; Lin, M.H.; Lee, C.P.; Yang, Y.H.; Chen, W.C.; Chang, G.H.; Tsai, Y.T.; Chen, P.C.; Tsai, Y.H. Chang Gung Research Database: A multi-institutional database consisting of original medical records. Biomed. J. 2017, 40, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.S.; Yang, Y.H.; Huang, T.Y.; Tsai, Y.T.; Lu, A.; Wu, C.Y.; Hsu, C.Y.; Liu, C.P.; Lee, C.P.; Lin, M.H.; et al. Pathogens and Prognosis of Deep Neck Infection in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients. Laryngoscope 2022, 132, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.H.; Ding, M.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Chang, P.J.; Lee, C.P.; Lin, M.H.; Hsu, C.M.; Wu, C.Y.; et al. Real-world evidence for increased deep neck infection risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 1402–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.H.; Ding, M.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Lin, M.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Lin, M.H.; Tsai, M.S. High Risk of Deep Neck Infection in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsai, M.S.; Chang, G.H.; Chen, W.M.; Liu, C.Y.; Lin, M.H.; Chang, P.J.; Huang, T.Y.; Tsai, Y.T.; Wu, C.Y.; Hsu, C.M.; et al. The Association Between Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis and Deep Neck Infection: Real-World Evidence. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.R.; Shih, W.T.; Yang, Y.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Tsai, M.S.; Tsai, Y.T.; Hsu, C.M.; Wu, C.Y.; Chang, P.J.; Chang, G.H. The difference in pathogenic bacteria between chronic rhinosinusitis in patients with and without Sjogren’s syndrome: A retrospective case-control study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Araujo, E.; Palombini, B.C.; Cantarelli, V.; Pereira, A.; Mariante, A. Microbiology of middle meatus in chronic rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. 2003, 17, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Adappa, N.D.; Lautenbach, E.; Chiu, A.G.; Doghramji, L.J.; Cohen, N.A.; Palmer, J.N. Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus culture in chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015, 5, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menger, D.J.; Tabink, I.C.; Trenite, G.J. Nasal septal abscess in children: Reconstruction with autologous cartilage grafts on polydioxanone plate. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 134, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barros, M.M.; Cartagena, S.C.; Bavestrello, F.L. Prevention of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Rev. Chilena Infectol. 2005, 22, s67–s74. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, N.; Caputo, G.M.; Weitekamp, M.R.; Karchmer, A.W. Infections in patients with diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1906–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Adappa, N.D.; Lautenbach, E.; Chiu, A.G.; Doghramji, L.; Howland, T.J.; Cohen, N.A.; Palmer, J.N. The effect of diabetes mellitus on chronic rhinosinusitis and sinus surgery outcome. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014, 4, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hidaka, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hasegawa, J.; Yano, H.; Kakuta, R.; Ozawa, D.; Nomura, K.; Katori, Y. Clinical and bacteriological influence of diabetes mellitus on deep neck infection: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck. 2015, 37, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahly, H.; Podschun, R.; Ullmann, U. Klebsiella infections in the immunocompromised host. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2000, 479, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.R.; Sng, E.; Lee, K.O.; Molton, J.S.; Chan, M.; Kalimuddin, S.; Izharuddin, E.; Lye, D.C.; Archuleta, S.; Gan, Y.H. Comparison of Diabetic and Non-diabetic Human Leukocytic Responses to Different Capsule Types of Klebsiella pneumoniae Responsible for Causing Pyogenic Liver Abscess. Front. Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017, 7, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackowiak, P.A.; Martin, R.M.; Smith, J.W. The role of bacterial interference in the increased prevalence of oropharyngeal gram-negative bacilli among alcoholics and diabetics. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1979, 120, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.T.; Wang, F.D.; Wu, P.F.; Fung, C.P. Klebsiella pneumoniae liver abscess in diabetic patients: Association of glycemic control with the clinical characteristics. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shao, S.C.; Chan, Y.Y.; Kao Yang, Y.H.; Lin, S.J.; Hung, M.J.; Chien, R.N.; Lai, C.C.; Lai, E.C.C. The Chang Gung Research Database-A multi-institutional electronic medical records database for real-world epidemiological studies in Taiwan. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2019, 28, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, S.C.; Lai, E.C.; Huang, T.H.; Hung, M.J.; Tsai, M.S.; Yang, Y.H.; Chan, Y.Y. The Chang Gung Research Database: Multi-institutional real-world data source for traditional Chinese medicine in Taiwan. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2021, 30, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variables | NSA-DM | NSA-Non-DM | p-Value † | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 12 | N = 64 | ||||
| n | % | n | % | ||
| Gender | 0.110 | ||||
| Male | 10 | 83.3 | 36 | 56.3 | |
| Female | 2 | 16.7 | 28 | 43.8 | |
| Age (years) | 0.060 | ||||
| <50 | 4 | 33.3 | 41 | 64.1 | |
| ≥50 | 8 | 66.7 | 23 | 35.9 | |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| HTN | 6 | 50.0 | 4 | 6.3 | 0.001 |
| CVA | 4 | 33.3 | 1 | 1.6 | 0.002 |
| CAD | 1 | 8.3 | 3 | 4.7 | 0.505 |
| COPD | 1 | 8.3 | 2 | 3.1 | 0.407 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luan, C.-W.; Tsai, M.-S.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Hsu, C.-M.; Liu, C.-Y.; Yang, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chang, G.-H. The Bacterial Compositions of Nasal Septal Abscess in Patients with or without Diabetes. Life 2022, 12, 2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122093
Luan C-W, Tsai M-S, Tsai Y-T, Hsu C-M, Liu C-Y, Yang Y-H, Wu C-Y, Chang G-H. The Bacterial Compositions of Nasal Septal Abscess in Patients with or without Diabetes. Life. 2022; 12(12):2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122093
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuan, Chih-Wei, Ming-Shao Tsai, Yao-Te Tsai, Cheng-Ming Hsu, Chia-Yen Liu, Yao-Hsu Yang, Ching-Yuan Wu, and Geng-He Chang. 2022. "The Bacterial Compositions of Nasal Septal Abscess in Patients with or without Diabetes" Life 12, no. 12: 2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122093
APA StyleLuan, C.-W., Tsai, M.-S., Tsai, Y.-T., Hsu, C.-M., Liu, C.-Y., Yang, Y.-H., Wu, C.-Y., & Chang, G.-H. (2022). The Bacterial Compositions of Nasal Septal Abscess in Patients with or without Diabetes. Life, 12(12), 2093. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122093










