Effects of Different Types of Human Disturbance on Total and Nitrogen-Transforming Bacteria in Haihe River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Environmental Parameters Analysis
2.3. Extraction of Total Community DNA and Sequencing
2.4. Taxonomic and Functional Analysis of Metagenomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Data Deposition
3. Results
3.1. Subsection Physicochemical Characteristics of Haihe River
3.2. Microbial Community Structure of Sediment Samples
3.3. Correlations between Environmental Parameters and Bacterial Community
3.4. Function Potential of Total and Nitrogen-Transforming Bacteria
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, W.; Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.F.; Wang, L.F.; Niu, L.H.; Zhang, W.L. Vertical distribution and assemblages of microbial communities and their potential effects on sulfur metabolism in a black-odor urban river. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 235, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Huang, G.; Liu, L.; Zhai, M.; Gao, S. Multi-regional industrial wastewater metabolism analysis for the Yangtze River Economic Belt, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Z.K.; Wang, S.R. Economic development influences on sediment-bound nitrogen and phosphorus accumulation of lakes in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 18561–18573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, W.K. Eutrophication and trophic state in rivers and streams. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, Q.; Long, X.E.; Li, Z.L.; Liu, D.X.; Ye, D.H.; He, C.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Vaananen, K.; Chen, X.P. Anthropogenic activities drive the microbial community and its function in urban river sediment. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhouse, J.N.; Kinsela, A.S.; Collins, R.N.; Bowling, L.C.; Honeyman, G.L.; Holliday, J.K.; Neilan, B.A. Microbial communities reflect temporal changes in cyanobacterial composition in a shallow ephemeral freshwater lake. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1337–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, M.M.; Jarrell, W.M. Soil Phosphorus as a Potential Nonpoint Source for Elevated Stream Phosphorus Levels. J. Environ. Qual. 1995, 24, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, H.S.; Ohandja, D.G.; Voulvoulis, N. The role of sediments as a source of metals in river catchments. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1250–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, S.D.; Lee, J.; Melillo, J.M.; Six, J. The temperature response of soil microbial efficiency and its feedback to climate. Nat. Clim. Change 2013, 3, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiler, A.; Zaremba-Niedzwiedzka, K.; Martinez-Garcia, M.; McMahon, K.D.; Stepanauskas, R.; Andersson, S.G.E.; Bertilsson, S. Productivity and salinity structuring of the microplankton revealed by comparative freshwater metagenomics. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2682–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.G.; Tsui, M.M.P.; Lam, J.C.W.; Hu, C.Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, B.S.; Lam, P.K.S. Variation in microbial community structure in surface seawater from Pearl River Delta: Discerning the influencing factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotner, J.B.; Biddanda, B.A. Small players, large role: Microbial influence on biogeochemical processes in pelagic aquatic ecosystems. Ecosystems 2002, 5, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Liu, Y.X.; Ke, T.; Zhang, Y.R.; Xiao, L.; Li, S.X.; Wei, S.J.; Chen, L.Z.; Hu, T.S. Patterns of bacterial and archaeal communities in sediments in response to dam construction and sewage discharge in Lhasa River. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 178, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Z. The cycle of nitrogen in river systems: Sources, transformation, and flux. Environ. Sci.-Proc. Imp. 2018, 20, 863–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Miao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, L.; Peng, Y. Enhancing sewage nitrogen removal via anammox and endogenous denitrification: Significance of anaerobic/oxic/anoxic operation mode. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 289, 121665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.J.; Sun, J.L.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Gong, L.X.; Lu, J.A.; Feng, B.; Xu, R.C. Effects of different habitats on the bacterial community composition in the water and sediments of Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 44983–44994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Chen, N.W.; Yuan, X.; Tian, Q.; Hu, A.Y.; Zheng, Y. Impacts of human disturbance on the biogeochemical nitrogen cycle in a subtropical river system revealed by nitrifier and denitrifier genes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.L.; Huang, L.N.; Chen, L.X.; Hua, Z.S.; Li, S.J.; Hu, M.; Li, J.T.; Shu, W.S. Contemporary environmental variation determines microbial diversity patterns in acid mine drainage. ISME J. 2013, 7, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.C. Study on the Pollution Characteristics and Microbial Community Structure of the River Entering Baiyangdian Lake. Master’s Thesis, Hebei University, Baoding, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Li, Q.; Han, T.; Xie, J.P.; Hu, Y.H.; Chai, L.Y. Phylogenetic analysis of bacterial community composition in sediment contaminated with multiple heavy metals from the Xiangjiang River in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 70, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.P.; Song, Y.H.; Wei, J.; Hu, S.G.; Xu, Q.J. Combing and analysis of the 70-year governance course of Haihe River. Environmental Science Research. Environ. Sci. Res. 2021, 34, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, J.P.; Hoffmann, L.; Cabral, B.C.A.; Dias, V.H.G.; Miranda, M.R.; de Azevedo Martins, A.C.; Boschiero, C.; Bastos, W.R.; Silva, R. Contrasting the microbiomes from forest rhizosphere and deeper bulk soil from an Amazon rainforest reserve. Gene 2018, 642, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, A.; Modugno, R.L.; Cavarzeran, F.; Rosani, U. Metagenomic analysis of the conjunctival bacterial and fungal microbiome in vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Allergy 2021, 76, 3215–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohiuddin, M.M.; Salama, Y.; Schellhorn, H.E.; Golding, G.B. Shotgun metagenomic sequencing reveals freshwater beach sands as reservoir of bacterial pathogens. Water Res. 2017, 115, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathour, R.; Gupta, J.; Mishra, A.; Rajeev, A.C.; Dupont, C.L.; Thakur, I.S. A comparative metagenomic study reveals microbial diversity and their role in the biogeochemical cycling of Pangong lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjan, R.; Rani, A.; Metwally, A.; McGee, H.S.; Perkins, D.L. Analysis of the microbiome: Advantages of whole genome shotgun versus 16S amplicon sequencing. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poretsky, R.; Rodriguez, R.L.; Luo, C.; Tsementzi, D.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Strengths and limitations of 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing in revealing temporal microbial community dynamics. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.X.; Song, G.S.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, J. Switch of Bacteria Community Under Oxygen Depletion in Sediment of Bohai Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kan, J.J.; Qian, G.; Chen, J.F.; Xia, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.D.; Liu, H.J.; Sun, J. Denitrification and anammox: Understanding nitrogen loss from Yangtze Estuary to the east China sea (ECS). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 1659–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tringe, S.G.; Rubin, E.M. Metagenomics: DNA sequencing of environmental samples. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.; Pachter, L. Bioinformatics for whole-genome shotgun sequencing of microbial communities. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2005, 1, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, W.; He, M.C.; Yang, Z.F.; Lin, C.Y.; Quan, X.C. Aliphatic and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the Xihe River, an urban river in China's Shenyang City: Distribution and risk assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.A. Aggravating causes of water pollution in Haihe River Basin and its prevention and control measures. Haihe River Water Resour. 1998, 3, 8–9. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Zhang, K.; Li, Q. Study of health assessment system for main stream of Haihe River. Water Resour. Prot. 2016, 32, 142–146 + 153. [Google Scholar]
- Erisman, J.W.; Galloway, J.N.; Seitzinger, S.; Bleeker, A.; Dise, N.B.; Petrescu, A.M.R.; Leach, A.M.; de Vries, W. Consequences of human modification of the global nitrogen cycle. Philos. R. Soc. B. 2013, 368, 20130116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, L. Doing battle with the green monster of Taihu Lake. Science 2007, 317, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obhodas, J.; Romano, E.; Castellote, M.; Heise, S. Sediment as a dynamic natural resource—From catchment to open sea. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2541–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.L.; Yang, H.; Peng, C.; Peng, Z.S.; Lu, L. Shift in the microbial community composition of surface water and sediment along an urban river. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 627, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Gao, Y.C.; Huang, X.N.; Ni, P.; Wu, Y.N.; Deng, Y.; Zhan, A.B. Adaptive shifts of bacterioplankton communities in response to nitrogen enrichment in a highly polluted river. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, A.M.; Ma, J.C.; Murinda, S.E. Bacterial community composition and structure in an Urban River impacted by different pollutant sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.G.; Zhao, L.H.; Lu, W.H.; Jia, H.L.; Sun, Y.Q. Bacterial communities in water and sediment shaped by paper mill pollution and indicated bacterial taxa in sediment in Daling River. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Dai, X.; Chai, Y.; Jiang, J.J.A.S.C. Bacterial diversity study for the simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal system (MDAT-IAT) by 16S rDNA cloning method. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2006, 26, 903–911. [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin, D.Y.; Lücker, S.; Vejmelkova, D.; Kostrikina, N.A.; Kleerebezem, R.; Rijpstra, W.I.C.; Damsté, J.S.S.; Le Paslier, D.; Muyzer, G.; Wagner, M.; et al. Nitrification expanded: Discovery, physiology and genomics of a nitrite-oxidizing bacterium from the phylum Chloroflexi. ISME J. 2012, 6, 2245–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirchman, D.L.; Dittel, A.I.; Findlay, S.E.G.; Fischer, D. Changes in bacterial activity and community structure in response to dissolved organic matter in the Hudson River, New York. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2004, 35, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, J.C.; Giovannoni, S.J. Cultivation and growth characteristics of a diverse group of oligotrophic marine Gammaproteobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapovalova, A.A.; Khijniak, T.V.; Tourova, T.P.; Muyzer, G.; Sorokin, D.Y. Heterotrophic denitrification at extremely high salt and pH by haloalkaliphilic Gammaproteobacteria from hypersaline soda lakes. Extremophiles 2008, 12, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.; Lou, Y.; Xu, M.; Wu, C.; Meng, J.; Shi, L.; Xia, F.; Xu, Y. Spatial distribution and influencing factors on the variation of bacterial communities in an urban river sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Shu, H.Y.; Lin, X.R.; Zhou, Q.X.; Bramryd, T.; Shu, W.S.; Huang, L.N. Microbial community structure and function in sediments from e-waste contaminated rivers at Guiyu area of China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, S.L.; Newton, R.J.; Vandewalle, J.L.; Shanks, O.C.; Huse, S.M.; Eren, A.M.; Sogin, M.L. Sewage reflects the distribution of human faecal Lachnospiraceae. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 2213–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, R.T.; Robeson, M.S.; Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. A comprehensive survey of soil acidobacterial diversity using pyrosequencing and clone library analyses. ISME J. 2009, 3, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5111–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, X.; Wang, H.; Gong, L.; Liu, Q. Vertical variations and associated ecological function of bacterial communities from Sphagnum to underlying sediments in Dajiuhu Peatland. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orcutt, B.N.; Sylvan, J.B.; Knab, N.J.; Edwards, K.J. Microbial Ecology of the Dark Ocean above, at, and below the Seafloor. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 361–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mutlu, M.B.; Martiez-Garcia, M.; Santos, F.; Pena, A.; Guven, K.; Anton, J. Prokaryotic diversity in Tuz Lake, a hypersaline environment in Inland Turkey. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 65, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wery, N.; Lhoutellier, C.; Ducray, F.; Delgenes, J.P.; Godon, J.J. Behaviour of pathogenic and indicator bacteria during urban wastewater treatment and sludge composting, as revealed by quantitative PCR. Water Res. 2008, 42, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, M.; Consolandi, C.; Severgnini, M.; Biagi, E.; Castiglioni, B.; Vitali, B.; De Bellis, G.; Brigidi, P. High taxonomic level fingerprint of the human intestinal microbiota by Ligase Detection Reaction—Universal Array approach. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuypers, M.M.M.; Sliekers, A.O.; Lavik, G.; Schmid, M.; Jorgensen, B.B.; Kuenen, J.G.; Damste, J.S.S.; Strous, M.; Jetten, M.S.M. Anaerobic ammonium oxidation by anammox bacteria in the Black Sea. Nature 2003, 422, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsushima, I.; Ogasawara, Y.; Kindaichi, T.; Satoh, H.; Okabe, S. Development of high-rate anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (anammox) biofilm reactors. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1623–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spring, S.; Bunk, B.; Sproer, C.; Rohde, M.; Klenk, H.P. Genome biology of a novel lineage of planctomycetes widespread in anoxic aquatic environments. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2438–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenni, S.; Vlaeminck, S.E.; Morgenroth, E.; Udert, K.M. Successful application of nitritation/anammox to wastewater with elevated organic carbon to ammonia ratios. Water Res. 2014, 49, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strous, M.; Van Gerven, E.; Zheng, P.; Kuenen, J.G.; Jetten, M.S.M. Ammonium removal from concentrated waste streams with the anaerobic ammonium oxidation (Anammox) process in different reactor configurations. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Meng, H.; Huang, X.W.; Wang, Q.; Chen, W.H.; Gu, J.D.; Lee, P.H. Salinity-driven heterogeneity toward anammox distribution and growth kinetics. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1953–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasa, N.P.; Nnadozie, C.F.; Kosgey, K.; Bux, F.; Kumari, S. Effect of ammonium to nitrite ratio on reactor performance and microbial population structure in anammox reactors. Environ. Technol. 2020, 41, 3396–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.M.; Zhang, B.K.; Guo, W.; Ma, X.S. Analysis of Low C/N Wastewater Treatment and Structure by the CEM-UF Combined Membrane-Nitrification/Denitrification System. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2018, 39, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Bi, Y.; Deng, Y.; He, Z.L.; Wu, L.Y.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Shi, Z.; Li, J.J.; Wang, X.; Hu, Z.Y.; et al. Impacts of the Three Gorges Dam on microbial structure and potential function. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, G.; Radha, V.; Jagadeeshwari, U.; Sasikala, C.; Ramana, C.V. Bacterial communities of sponges from the wetland ecosystem of Little Rann of Kutch, India with particular reference to Planctomycetes. 3 Biotech 2020, 10, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, J.L.; Ward, B.B.; Morrison, H.G.; Hobbie, J.E.; Valiela, I.; Deegan, L.A.; Sogin, M.L. Microbial community composition in sediments resists perturbation by nutrient enrichment. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Wu, Y.Y.; Gu, B.J. Urban rivers as hotspots of regional nitrogen pollution. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 205, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, K.B.L.; Thoma, R.; Callbeck, C.M.; Niederdorfer, R.; Schubert, C.J.; Muller, B.; Lever, M.A.; Burgmann, H. Microbial Nitrogen Transformation Potential in Sediments of Two Contrasting Lakes Is Spatially Structured but Seasonally Stable. Msphere 2022, 7, e01013-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Chen, C.R.; Liu, G.H.; Liu, W.Z. Sediment nitrogen cycling rates and microbial abundance along a submerged vegetation gradient in a eutrophic lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Ishii, S.; Fujii, D.; Otsuka, S.; Senoo, K. Identification of Active Denitrifiers in Rice Paddy Soil by DNA- and RNA-Based Analyses. Microbes. Environ. 2012, 27, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Li, X.C.; Fang, W.K.; Cheng, Y.; Cai, H.; Zhang, S.Q. Impact of different types of anthropogenic pollution on bacterial community and metabolic genes in urban river sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.Y.; Li, B.B.; Yang, Z.C.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Liu, D.F.; Yu, H.Q. Mediation of functional gene and bacterial community profiles in the sediments of eutrophic Chaohu Lake by total nitrogen and season. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W.; Hecky, R.E.; Findlay, D.L.; Stainton, M.P.; Parker, B.R.; Paterson, M.J.; Beaty, K.G.; Lyng, M.; Kasian, S.E.M. Eutrophication of lakes cannot be controlled by reducing nitrogen input: Results of a 37-year whole-ecosystem experiment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11254–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.C.; Zhu, C.J.H.; He, Z.M.; Luan, T.G.; Xu, W.H.; Zhang, G. Preliminary studies on the pollution levels of antibiotic resistance genes in the water of Beijiang River, south China. Asia J. Ecotoxicol. 2009, 4, 655–660. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.M.; Guo, C.S.; Qiu, H.Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.C.; Meng, W. Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in a sewage treatment plant and its effluent-receiving river. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Zhang, T.; Fang, H.H.P. Antibiotic resistance genes in water environment. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 82, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Hu, X.L.; Xu, T.; Zhang, H.C.; Sheng, D.; Yin, D.Q. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes and their relationship with antibiotics in the Huangpu River and the drinking water sources, Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 458, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.P.; Li, J.; Yang, F.; Yang, J.; Yin, D.Q. Prevalence of sulfonamide and tetracycline resistance genes in drinking water treatment plants in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwanamoki, P.M.; Devarajan, N.; Thevenon, F.; Atibu, E.K.; Tshibanda, J.B.; Ngelinkoto, P.; Mpiana, P.T.; Prabakar, K.; Mubedi, J.I.; Kabele, C.G.; et al. Assessment of pathogenic bacteria in water and sediment from a water reservoir under tropical conditions (Lake Ma Vallee), Kinshasa Democratic Republic of Congo. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
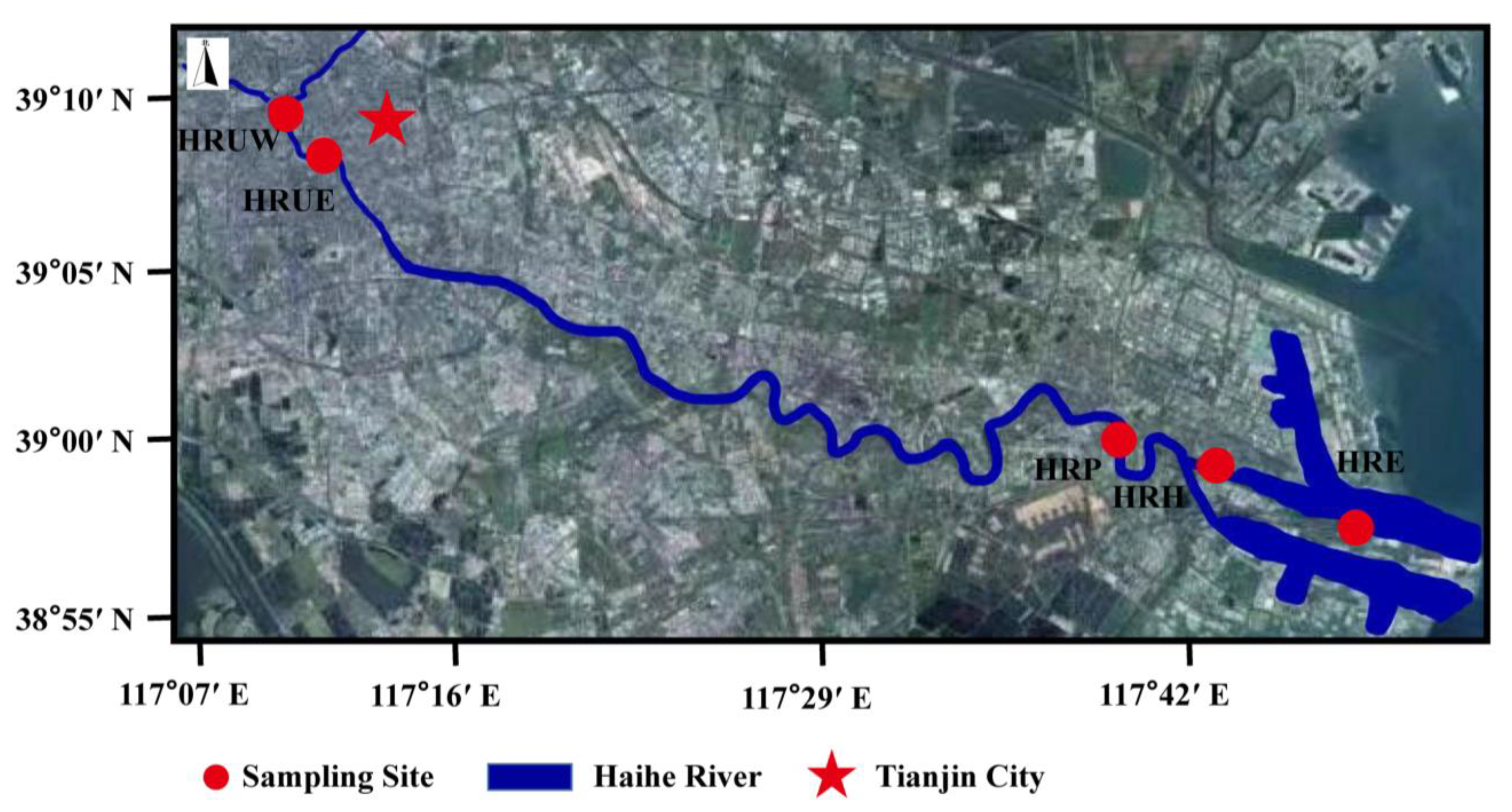
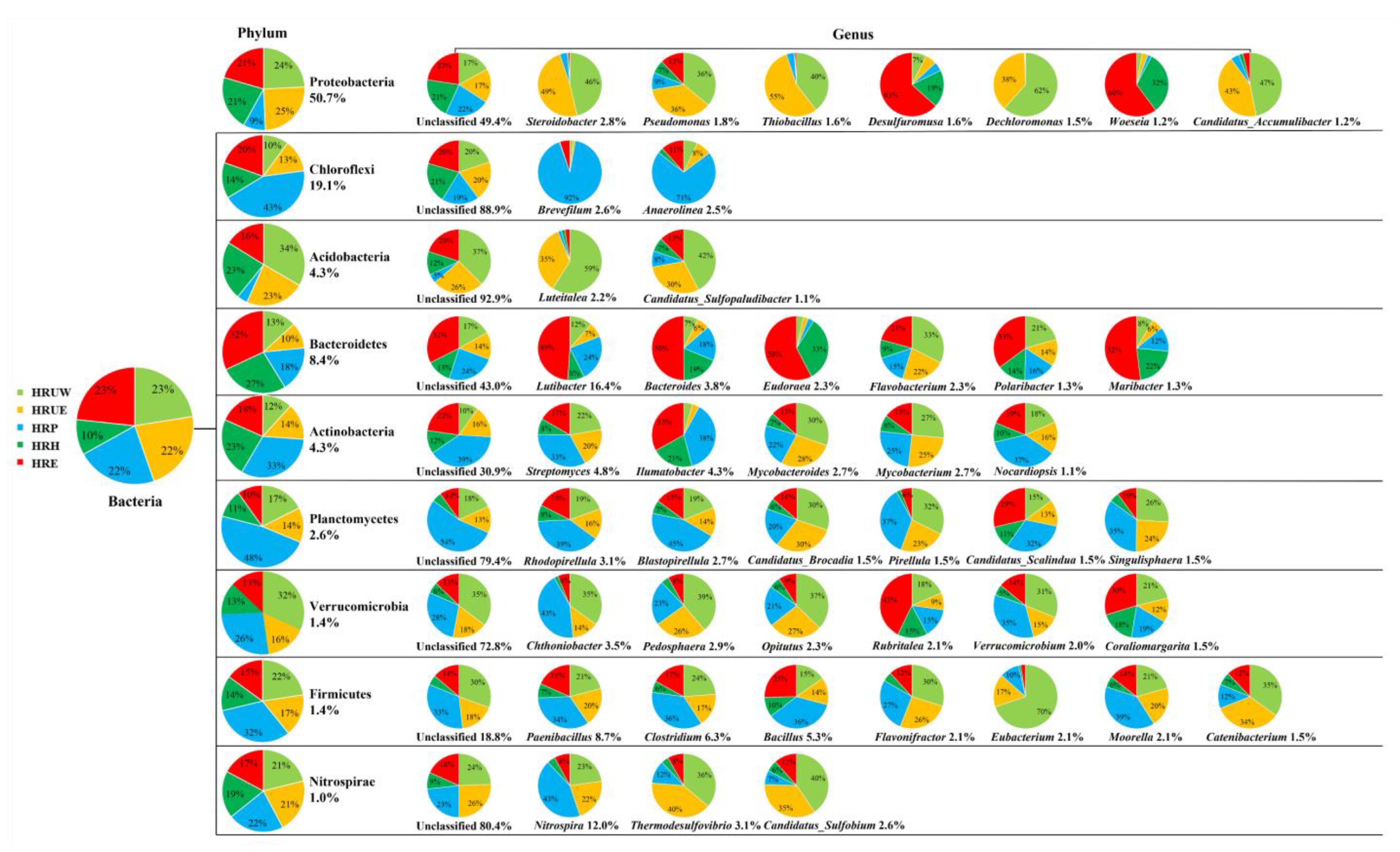
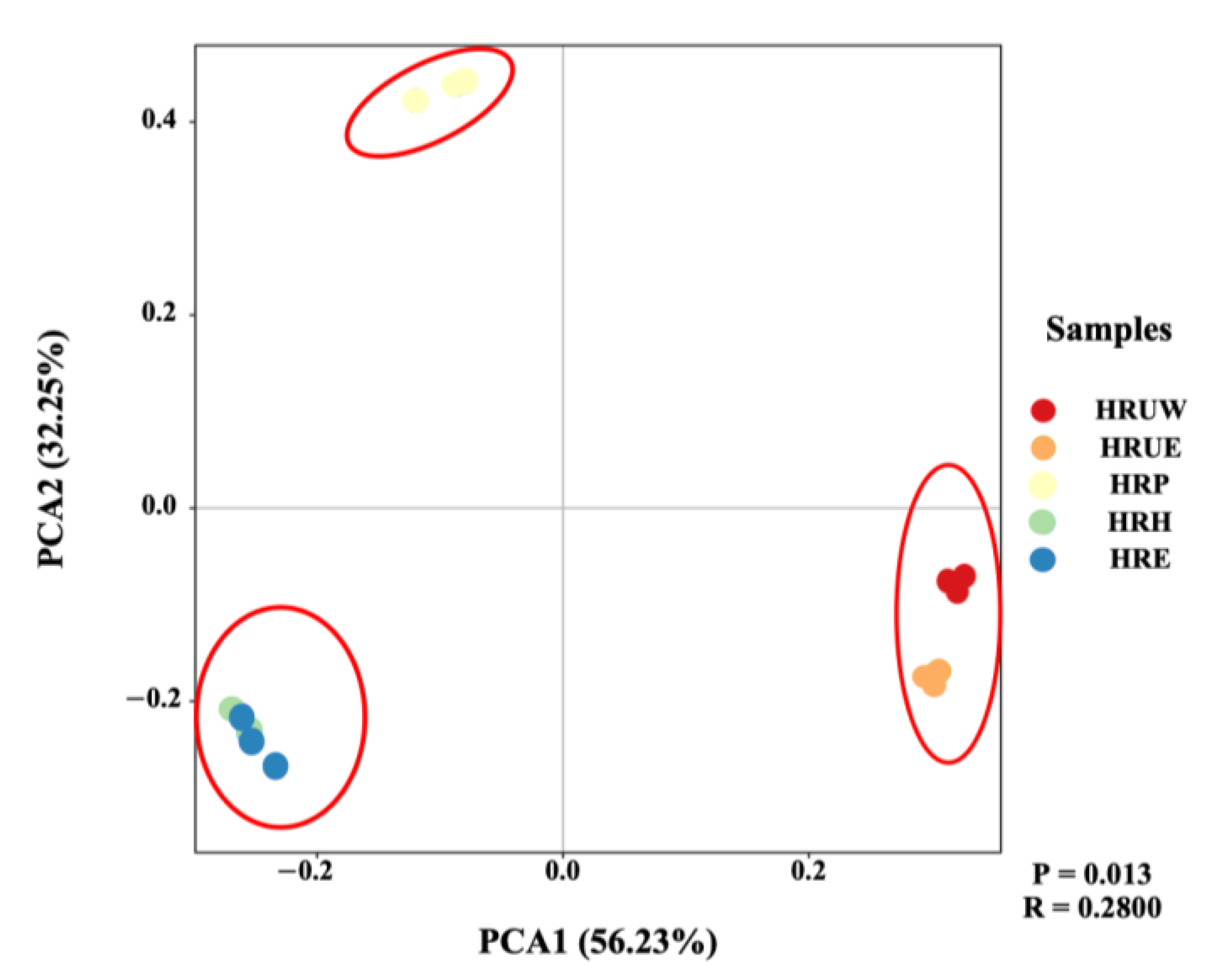
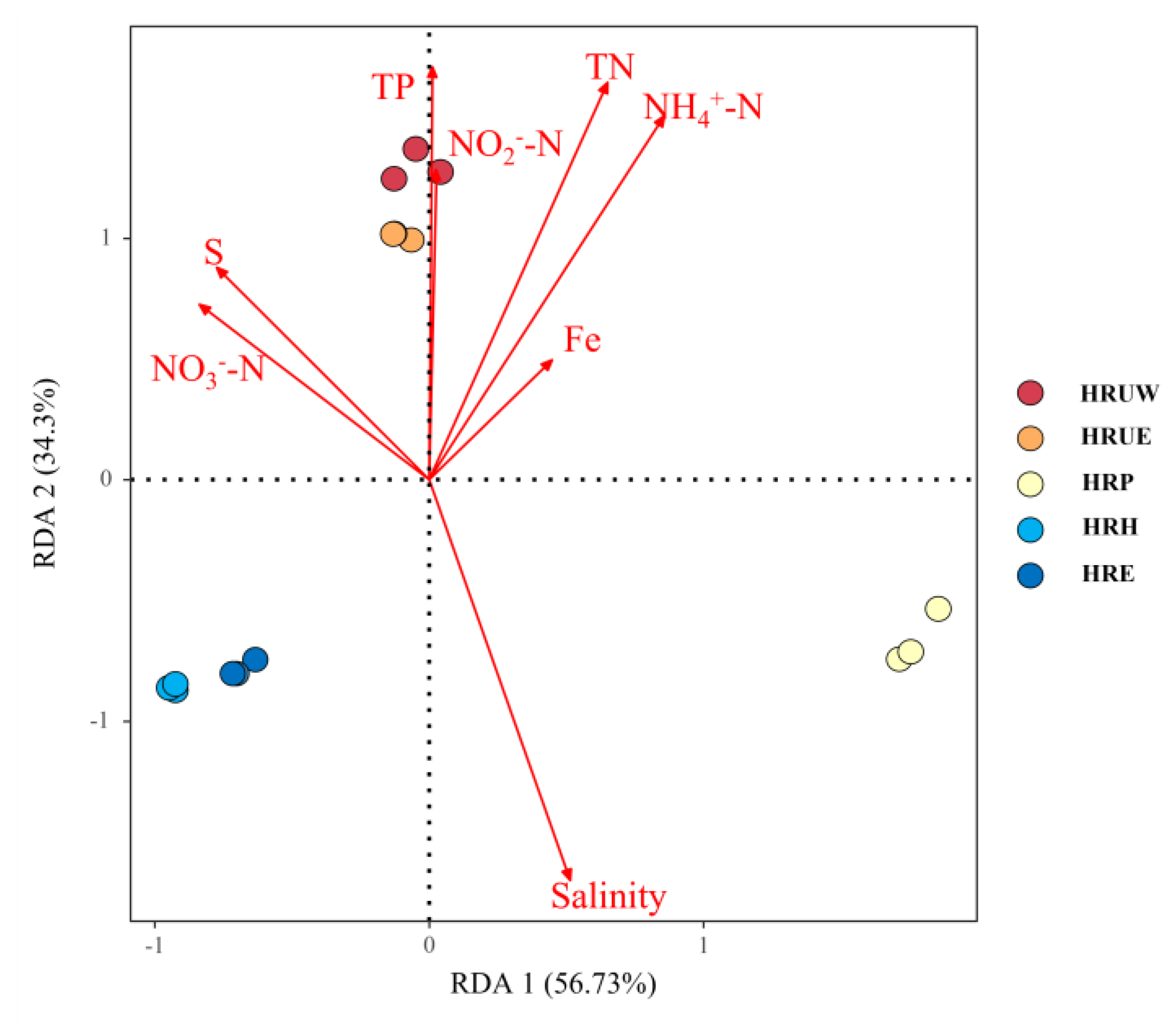
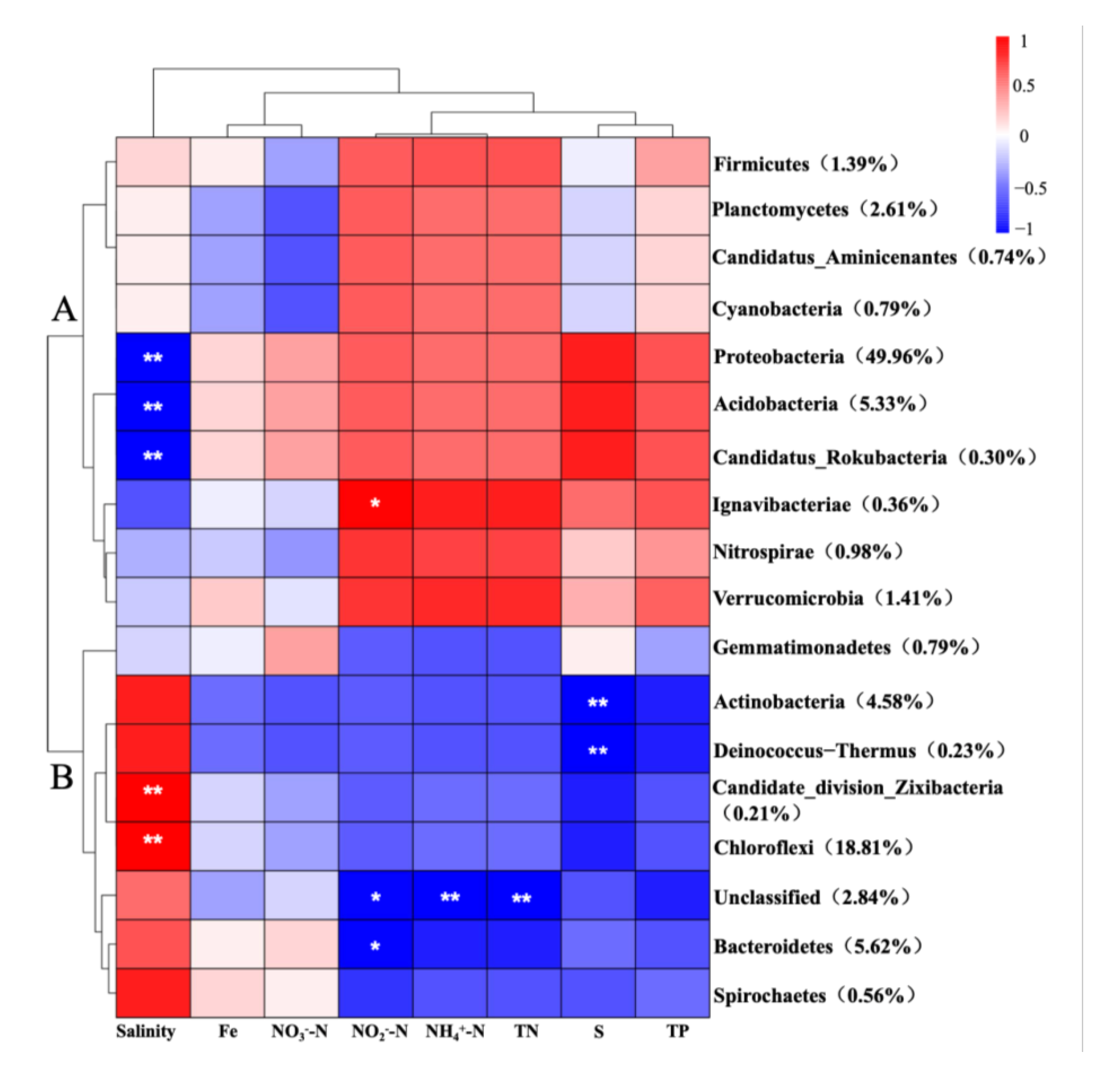
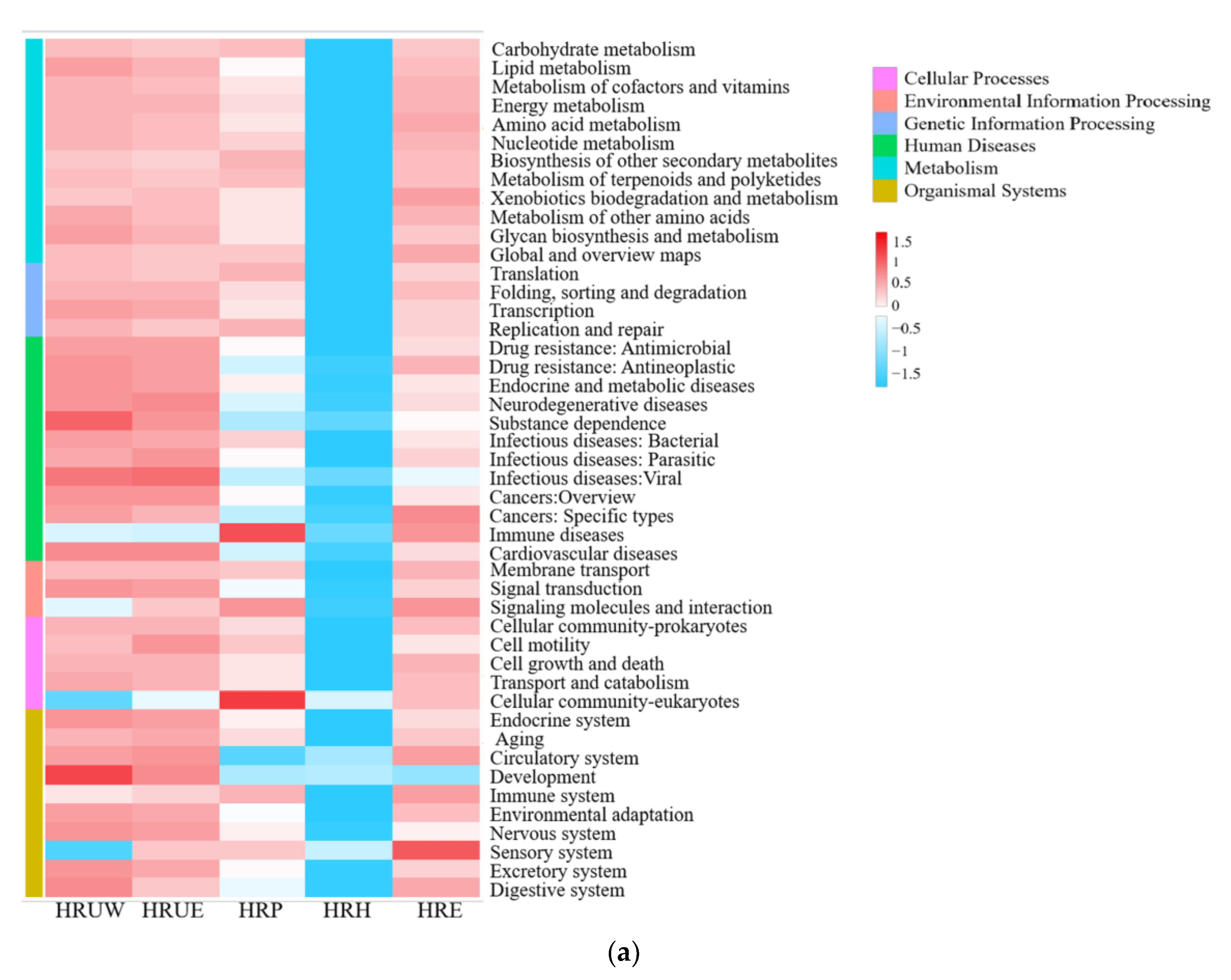
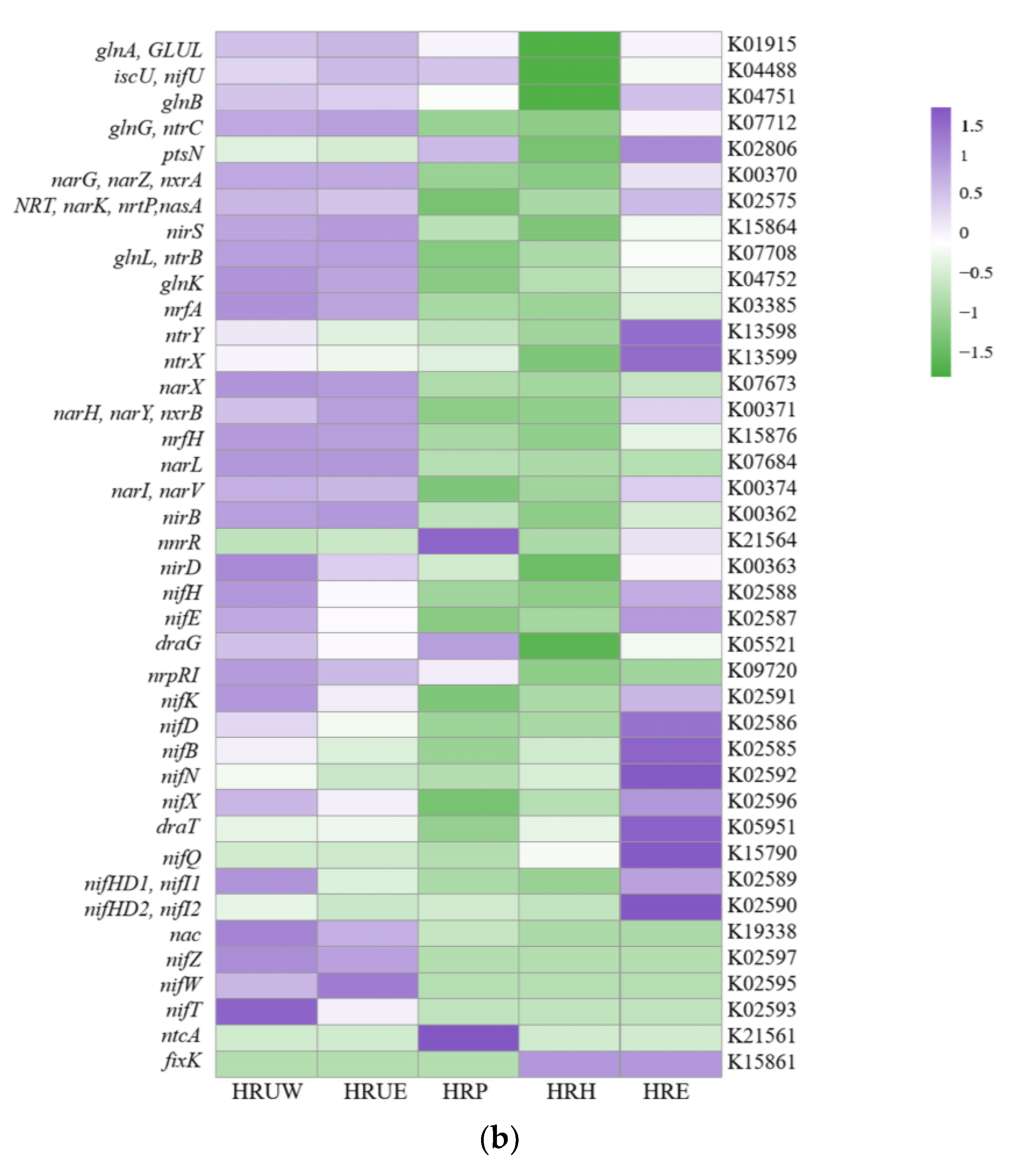
| Sample Name | Sampling Site | Location | Temp (°C) | Salinity (mg/kg) | DO (mg/L) | pH | NO2−-N (mg/kg) | NO3−-N (mg/kg) | NH4+-N (mg/kg) | TN (mg/kg) | TP (mg/kg) | S (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRUW | Urban West | 117.17 E39.1567 N | 11.00 | 1.67 × 103 ± 0.03 e | 8.70 | 7.42 | 0.41 ± 0.04 a | 6.62 ± 0.05 c | 209.30 ± 3.68 b | 3.42 × 103 ± 24.49 a | 1.66 × 103 ± 28.28 a | 5.07 ± 0.04 c |
| HRUE | Urban East | 117.19 E 39.1308 N | 9.50 | 5.04 × 103 ± 0.60 d | 8.11 | 7.28 | 0.17 ± 0.01 b | 7.86 ± 0.07 b | 266.70 ± 0.94 a | 3.37 × 103 ± 327.85 a | 1.09 × 103 ± 17.00 b | 6.52 ± 0.07 a |
| HRP | Pollution | 117.67 E 38.9975 N | 10.20 | 3.34 × 104 ± 1.47 a | 18.95 | 8.42 | 0.17 ± 0.00 b | 1.19 ± 0.04 e | 165.00 ± 3.56 c | 2.14 × 103 ± 91.77 b | 4.7 × 102 ± 3.09 d | 4.04 ± 0.04 e |
| HRH | Harbor | 117.72 E 38.9896 N | 10.10 | 2.07 × 104 ± 0.76 c | 9.83 | 7.57 | 0.15 ± 0.00 b | 1.84 ± 0.05 d | 6.90 ± 0.22 e | 5.50 × 102 ± 12.39 c | 2.6 × 102 ± 6.53 e | 4.38 ± 0.05 d |
| HRE | Estuary | 117.81 E 38.9605 N | 10.40 | 3.13 × 104 ± 0.48 b | 9.78 | 7.79 | 0.15 ± 0.00 b | 9.80 ± 0.10 a | 23.30 ± 0.34 d | 1.10 × 103 ± 28.67 d | 5.9 × 102 ± 5.73 c | 5.86 ± 0.10 b |
| Sample ID | NO. of Contigs | Total Len | N50 | N90 | Average Len | Max Len |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRUW1 | 372,582 | 297,816,176 | 760 | 532 | 799.3 | 19,500 |
| HRUW2 | 368,534 | 290,566,213 | 746 | 531 | 788.4 | 35,316 |
| HRUW3 | 367,011 | 283,507,046 | 732 | 530 | 772.5 | 30,185 |
| HRUE1 | 364,746 | 285,809,465 | 740 | 529 | 783.6 | 31,584 |
| HRUE2 | 321,303 | 257,675,979 | 758 | 531 | 802.0 | 46,219 |
| HRUE3 | 301,958 | 240,403,741 | 752 | 531 | 796.2 | 45,373 |
| HRP1 | 500,496 | 476,635,987 | 947 | 547 | 952.3 | 52,099 |
| HRP2 | 466,734 | 433,600,392 | 918 | 545 | 929.0 | 38,967 |
| HRP3 | 452,588 | 420,081,579 | 918 | 545 | 928.2 | 38,967 |
| HRH1 | 371,499 | 314,017,265 | 800 | 535 | 845.3 | 47,673 |
| HRH2 | 426,832 | 371,053,744 | 828 | 537 | 869.3 | 65,887 |
| HRH3 | 466,448 | 405,576,702 | 829 | 538 | 869.5 | 89,681 |
| HRE1 | 464,423 | 402,207,176 | 825 | 538 | 866.0 | 39,033 |
| HRE2 | 448,975 | 383,701,166 | 813 | 537 | 854.6 | 39,271 |
| HRE3 | 405,101 | 343,081,767 | 804 | 536 | 846.9 | 30,827 |
| Salinity | TP | S | TN | NH4+-N | NO3−-N | NO2−-N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salinity | 1 | −0.68 ** | −0.46 | −0.58 * | −0.48 | −0.24 | −0.59 * |
| TP | 1 | 0.59 * | 0.84 ** | 0.78 ** | 0.48 | 0.74 ** | |
| S | 1 | 0.37 | 0.48 | 0.88 ** | 0.10 | ||
| TN | 1 | 0.91 ** | 0.12 | 0.82 ** | |||
| NH4+-N | 1 | 0.19 | 0.72 ** | ||||
| NO3−-N | 1 | −0.15 | |||||
| NO2−-N | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Chen, T.; An, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, J. Effects of Different Types of Human Disturbance on Total and Nitrogen-Transforming Bacteria in Haihe River. Life 2022, 12, 2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122081
Li P, Chen T, An M, Zhang Y, Li Y, Li Y, Wang J. Effects of Different Types of Human Disturbance on Total and Nitrogen-Transforming Bacteria in Haihe River. Life. 2022; 12(12):2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122081
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Peiyang, Tingyu Chen, Miao An, Ying Zhang, Yanying Li, Yang Li, and Jing Wang. 2022. "Effects of Different Types of Human Disturbance on Total and Nitrogen-Transforming Bacteria in Haihe River" Life 12, no. 12: 2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122081
APA StyleLi, P., Chen, T., An, M., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Li, Y., & Wang, J. (2022). Effects of Different Types of Human Disturbance on Total and Nitrogen-Transforming Bacteria in Haihe River. Life, 12(12), 2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122081








