SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Responses in Various Populations, at the Time of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Virus Emergence: Evaluation of Two Surrogate Neutralization Assays in Front of Whole Virus Neutralization Test
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Populations Tested
2.2. Virus Neutralization Test
2.3. Neutralizing Antibodies Surrogate Lateral Flow Assay
2.4. Neutralizing Antibodies Surrogate ELISA Assay
2.5. Anti-Spike Antibodies EIA Quantitation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
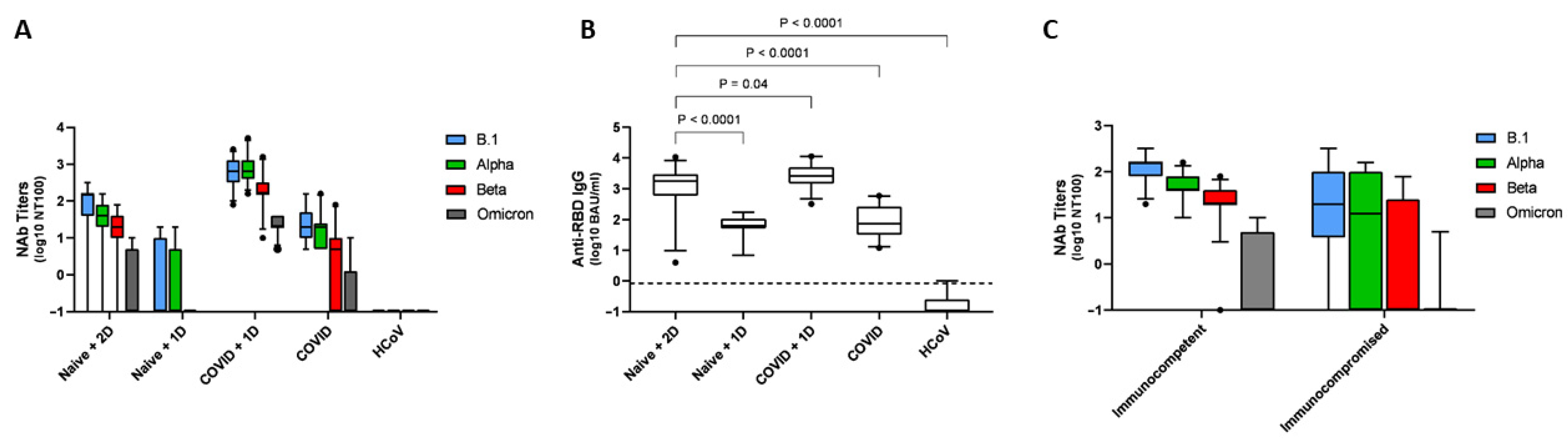
3.1. Anti-RBD IgG Antibody Levels and nAb Titers Assessed by the VNT Assays
3.2. Specificity of the Surrogate Assays
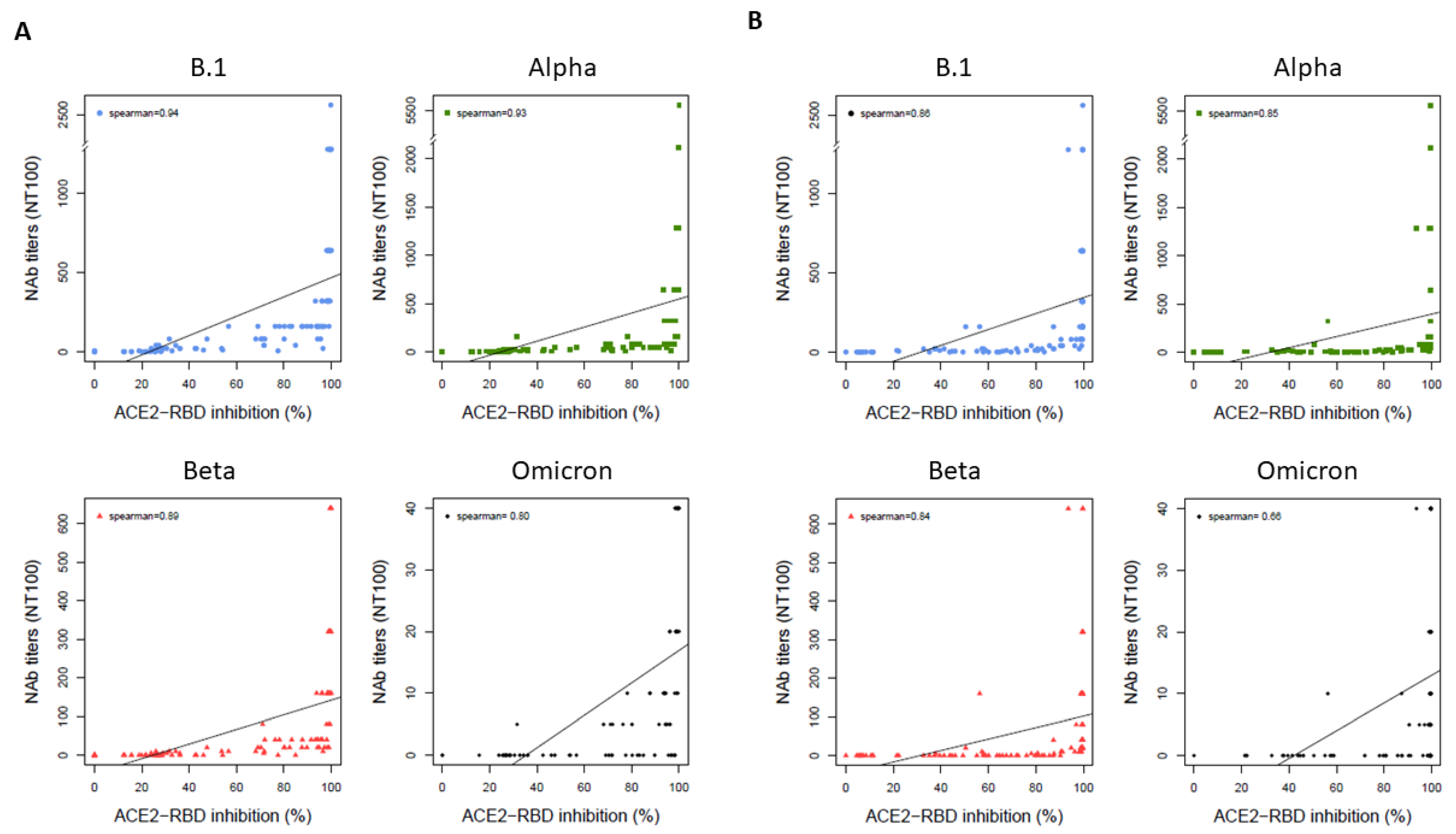
3.3. Correlations and Performances of the Surrogate Assays Compared to the VNT
3.4. Correlations between VNT and Quantitation of Anti-RBD Antibodies
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dispinseri, S.; Secchi, M.; Pirillo, M.F.; Tolazzi, M.; Borghi, M.; Brigatti, C.; De Angelis, M.L.; Baratella, M.; Bazzigaluppi, E.; Venturi, G.; et al. Neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in symptomatic COVID-19 is persistent and critical for survival. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, C.; Klein, J.; Sundaram, M.E.; Liu, F.; Wong, P.; Silva, J.; Mao, T.; Oh, J.E.; Mohanty, S.; Huang, J.; et al. Delayed production of neutralizing antibodies correlates with fatal COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergwerk, M.; Gonen, T.; Lustig, Y.; Amit, S.; Lipsitch, M.; Cohen, C.; Mandelboim, M.; Levin, E.G.; Rubin, C.; Indenbaum, V.; et al. COVID-19 Breakthrough Infections in Vaccinated Health Care Workers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchsinger, L.L.; Ransegnola, B.P.; Jin, D.K.; Muecksch, F.; Weisblum, Y.; Bao, W.; George, P.J.; Rodriguez, M.; Tricoche, N.; Schmidt, F.; et al. Serological Assays Estimate Highly Variable SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Activity in Recovered COVID-19 Patients. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e02005-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criscuolo, E.; Diotti, R.A.; Strollo, M.; Rolla, S.; Ambrosi, A.; Locatelli, M.; Burioni, R.; Mancini, N.; Clementi, M.; Clementi, N. Weak correlation between antibody titers and neutralizing activity in sera from SARS-CoV-2 infected subjects. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2160–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, D.; Bruel, T.; Grzelak, L.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Staropoli, I.; Porrot, F.; Planchais, C.; Buchrieser, J.; Rajah, M.M.; Bishop, E.; et al. Sensitivity of infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 variants to neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Lam, E.C.; St Denis, K.; Nitido, A.D.; Garcia, Z.H.; Hauser, B.M.; Feldman, J.; Pavlovic, M.N.; Gregory, D.J.; Poznansky, M.C.; et al. Multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants escape neutralization by vaccine-induced humoral immunity. Cell 2021, 184, 2372–2383.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marot, S.; Malet, I.; Leducq, V.; Abdi, B.; Teyssou, E.; Soulie, C.; Wirden, M.; Rodriguez, C.; Fourati, S.; Pawlotsky, J.-M.; et al. Neutralization Heterogeneity of UK and South African Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Variants in BNT162b2-Vaccinated or Convalescent Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Healthcare Workers. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 74, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planas, D.; Saunders, N.; Maes, P.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Planchais, C.; Buchrieser, J.; Bolland, W.H.; Porrot, F.; Staropoli, I.; Lemoine, F.; et al. Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to antibody neutralization. Nature 2022, 602, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marot, S.; Malet, I.; Leducq, V.; Zafilaza, K.; Sterlin, D.; Planas, D.; Gothland, A.; Jary, A.; Dorgham, K.; Bruel, T.; et al. Rapid decline of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 among infected healthcare workers. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.W.; Chia, W.N.; Qin, X.; Liu, P.; Chen, M.I.-C.; Tiu, C.; Hu, Z.; Chen, V.C.-W.; Young, B.E.; Sia, W.R.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test based on antibody-mediated blockage of ACE2–spike protein–protein interaction. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, W.N.; Zhu, F.; Ong, S.W.X.; Young, B.E.; Fong, S.-W.; Le Bert, N.; Tan, C.W.; Tiu, C.; Zhang, J.; Tan, S.Y.; et al. Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 neutralising antibody responses and duration of immunity: A longitudinal study. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e240–e249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegu, A.; O’Connell, S.E.; Schmidt, S.D.; O’Dell, S.; Talana, C.A.; Lai, L.; Albert, J.; Anderson, E.; Bennett, H.; Corbett, K.S.; et al. Durability of mRNA-1273 vaccine–induced antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Science 2021, 373, 1372–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lustig, Y.; Zuckerman, N.; Nemet, I.; Atari, N.; Kliker, L.; Regev-Yochay, G.; Sapir, E.; Mor, O.; Alroy-Preis, S.; Mendelson, E.; et al. Neutralising capacity against Delta (B.1.617.2) and other variants of concern following Comirnaty (BNT162b2, BioNTech/Pfizer) vaccination in health care workers, Israel. Eurosurveillance 2021, 26, 2100557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prendecki, M.; Clarke, C.; Brown, J.; Cox, A.; Gleeson, S.; Guckian, M.; Randell, P.; Pria, A.D.; Lightstone, L.; Xu, X.-N.; et al. Effect of previous SARS-CoV-2 infection on humoral and T-cell responses to single-dose BNT162b2 vaccine. Lancet 2021, 397, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, C.J.; Pade, C.; Gibbons, J.M.; Butler, D.K.; Otter, A.D.; Menacho, K.; Fontana, M.; Smit, A.; Sackville-West, J.E.; Cutino-Moguel, T.; et al. Prior SARS-CoV-2 infection rescues B and T cell responses to variants after first vaccine dose. Science 2021, 372, 1418–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, A.P.; Sølund, C.; Fernandez-Antunez, C.; Villadsen, S.L.; Winckelmann, A.A.; Bollerup, S.; Mikkelsen, L.S.; Sørensen, A.-L.; Feng, S.; Fahnøe, U.; et al. Neutralisation titres against SARS-CoV-2 are sustained 6 months after onset of symptoms in individuals with mild COVID-19. eBioMedicine 2021, 71, 103519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabidian, M.; Bocket, L.; Demaret, J.; Vuotto, F.; Rabat, A.; Faure, K.; Labalette, M.; Hober, D.; Lefevre, G.; Alidjinou, E.K. Evaluation of a rapid semiquantitative lateral flow assay for the prediction of serum neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 variants. J. Clin. Virol. 2022, 155, 105268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girl, P.; Zwirglmaier, K.; von Buttlar, H.; Wölfel, R.; Müller, K. Evaluation of Two Rapid Lateral Flow Tests and Two Surrogate ELISAs for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Specific Neutralizing Antibodies. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 820151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdivia, A.; Torres, I.; Latorre, V.; Francés-Gómez, C.; Ferrer, J.; Forqué, L.; Costa, R.; de la Asunción, C.S.; Huntley, D.; Gozalbo-Rovira, R.; et al. Suitability of two rapid lateral flow immunochromatographic assays for predicting SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing activity of sera. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2301–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, D.F.; Roeder, A.J.; Kaleta, E.; Jasbi, P.; Pfeffer, K.; Koelbela, C.; Periasamy, C.K.S.; Kuzmina, N.; Bukreyev, A.; Grys, T.E.; et al. Development of a rapid point-of-care test that measures neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 145, 105024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ge, X.; Fan, R.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; Ding, Y.; Osman, R.A.; et al. Dual-detection fluorescent immunochromatographic assay for quantitative detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD-ACE2 blocking neutralizing antibody. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 199, 113883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenwick, C.; Turelli, P.; Pellaton, C.; Farina, A.; Campos, J.; Raclot, C.; Pojer, F.; Cagno, V.; Nusslé, S.G.; D’Acremont, V.; et al. A high-throughput cell- and virus-free assay shows reduced neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants by COVID-19 convalescent plasma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, 8452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ren, C.; Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Liang, X.; Wang, P.; Ma, C. Palmitoylation of SARS-CoV-2 S protein is essential for viral infectivity. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bert, N.; Tan, A.T.; Kunasegaran, K.; Tham, C.Y.L.; Hafezi, M.; Chia, A.; Chng, M.H.Y.; Lin, M.; Tan, N.; Linster, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell immunity in cases of COVID-19 and SARS, and uninfected controls. Nature 2020, 584, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, G.E.; Edwards, E.S.J.; Aui, P.M.; Varese, N.; Stojanovic, S.; McMahon, J.; Peleg, A.Y.; Boo, I.; Drummer, H.E.; Hogarth, P.M.; et al. Rapid Generation of Durable B Cell Memory to SARS-CoV-2 Spike and Nucleocapsid Proteins in COVID-19 and Convalescence. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabf8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Global Population Characteristics | n = 105 |
|---|---|
| Male, n (%) | 46 (43.8%) |
| Age (years), median [IQR] | 50 [37–60] |
| Subpopulation characteristics | |
| Naive individuals vaccinated with two doses of vaccine: “Naive + 2D” | n = 35 |
| Male, n (%) | 10 (28.6%) |
| Age (years), median [IQR] | 58 [50–64.5] |
| Time between 2nd vaccine dose and serum sampling (days), median [IQR] | 7 [7–13.75] |
| Naive individuals vaccinated with 1 dose of vaccine: “Naive + 1D” | n = 14 |
| Male, n (%) | 4 (28.6%) |
| Age (years), median [IQR] | 32.5 [29.5–34.75] |
| Time between the vaccine dose and serum sampling (days), median [IQR] | 28 [27.25–28] |
| COVID-19 patients vaccinated with 1 dose of vaccine: “COVID-19 + 1D” | n = 24 |
| Male, n (%) | 16 (66.7%) |
| Age (years), median [IQR] | 44.5 [32.75–51.25] |
| Time between the vaccine dose and serum sampling (days), median [IQR] | 27 [20–28] |
| Individuals recovered from COVID-19: “COVID-19” | n = 22 |
| Male, n (%) | 9 (40.9%) |
| Age (years), median [IQR] | 47.5 [39.5–55.5] |
| Time between symptom’s onset and serum sampling (days), median [IQR] | 187 [182.5–238] |
| Patients recovered from other human coronavirus infection: “HCoV” | n = 10 |
| Male, n (%) | 7 (70%) |
| Age (years), median [IQR] | 57.5 [43–64] |
| Time between diagnostic and serum sampling (days), median [IQR] | 24.5 [16.75–32] |
| SARS-CoV-2 Strain | Optimal Cut-Off for Anti-RBD IgG (BAU/mL) | Nab Titer < 1:10 n (%) | Nab Titer ≥ 1:10 n (%) | Number of Patients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B.1 | <173.3 | 33 (79%) | 9 (21%) | 42 |
| ≥173.3 | 1 (2%) | 62 (98%) | 63 | |
| Alpha | <173.3 | 36 (86%) | 6 (14%) | 42 |
| ≥173.3 | 4 (6%) | 59 (94%) | 63 | |
| Beta | <731.7 | 53 (93%) | 4 (7%) | 57 |
| ≥731.7 | 2 (4%) | 46 (96%) | 48 | |
| Omicron | <1886.4 | 45 (94%) | 3 (6%) | 48 |
| ≥1886.4 | 16 (48%) | 17 (52%) | 33 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marot, S.; Bocar Fofana, D.; Flandre, P.; Malet, I.; Zafilaza, K.; Leducq, V.; Vivien, D.; Mrabet, S.; Poignon, C.; Calvez, V.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Responses in Various Populations, at the Time of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Virus Emergence: Evaluation of Two Surrogate Neutralization Assays in Front of Whole Virus Neutralization Test. Life 2022, 12, 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122064
Marot S, Bocar Fofana D, Flandre P, Malet I, Zafilaza K, Leducq V, Vivien D, Mrabet S, Poignon C, Calvez V, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Responses in Various Populations, at the Time of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Virus Emergence: Evaluation of Two Surrogate Neutralization Assays in Front of Whole Virus Neutralization Test. Life. 2022; 12(12):2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122064
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarot, Stephane, Djeneba Bocar Fofana, Philippe Flandre, Isabelle Malet, Karen Zafilaza, Valentin Leducq, Diane Vivien, Sarah Mrabet, Corentin Poignon, Vincent Calvez, and et al. 2022. "SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Responses in Various Populations, at the Time of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Virus Emergence: Evaluation of Two Surrogate Neutralization Assays in Front of Whole Virus Neutralization Test" Life 12, no. 12: 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122064
APA StyleMarot, S., Bocar Fofana, D., Flandre, P., Malet, I., Zafilaza, K., Leducq, V., Vivien, D., Mrabet, S., Poignon, C., Calvez, V., Morand-Joubert, L., Marcelin, A.-G., & Gozlan, J. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Responses in Various Populations, at the Time of SARS-CoV-2 Variant Virus Emergence: Evaluation of Two Surrogate Neutralization Assays in Front of Whole Virus Neutralization Test. Life, 12(12), 2064. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122064







