Effects of Pre-Pregnancy Overweight/Obesity on the Pattern of Association of Hypertension Susceptibility Genes with Preeclampsia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Subjects
2.2. DNA Isolation, Selection, and Genotyping SNPs
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. In Silico Bioinformatics Analysis of Functional SNPs
3. Results
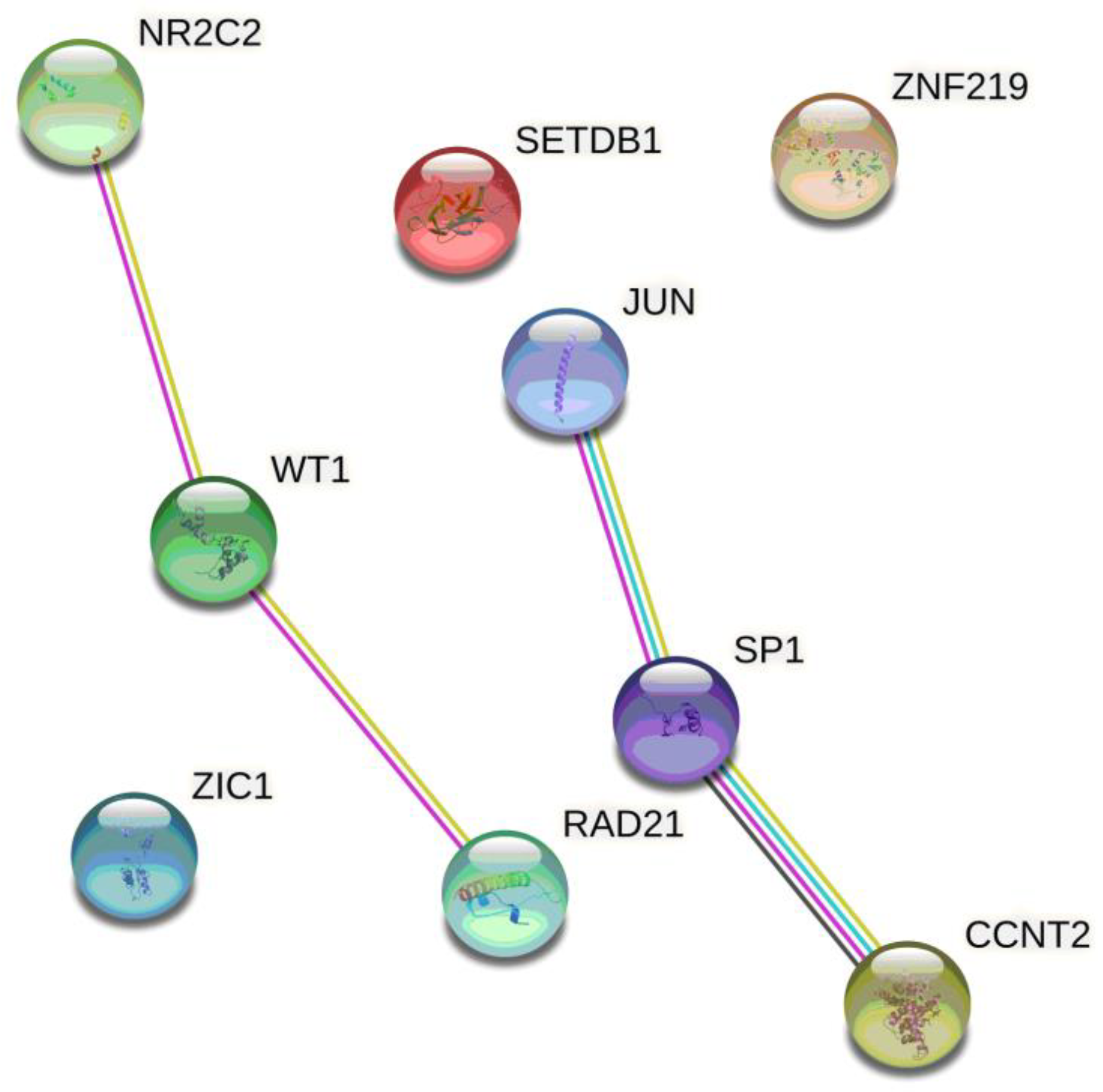
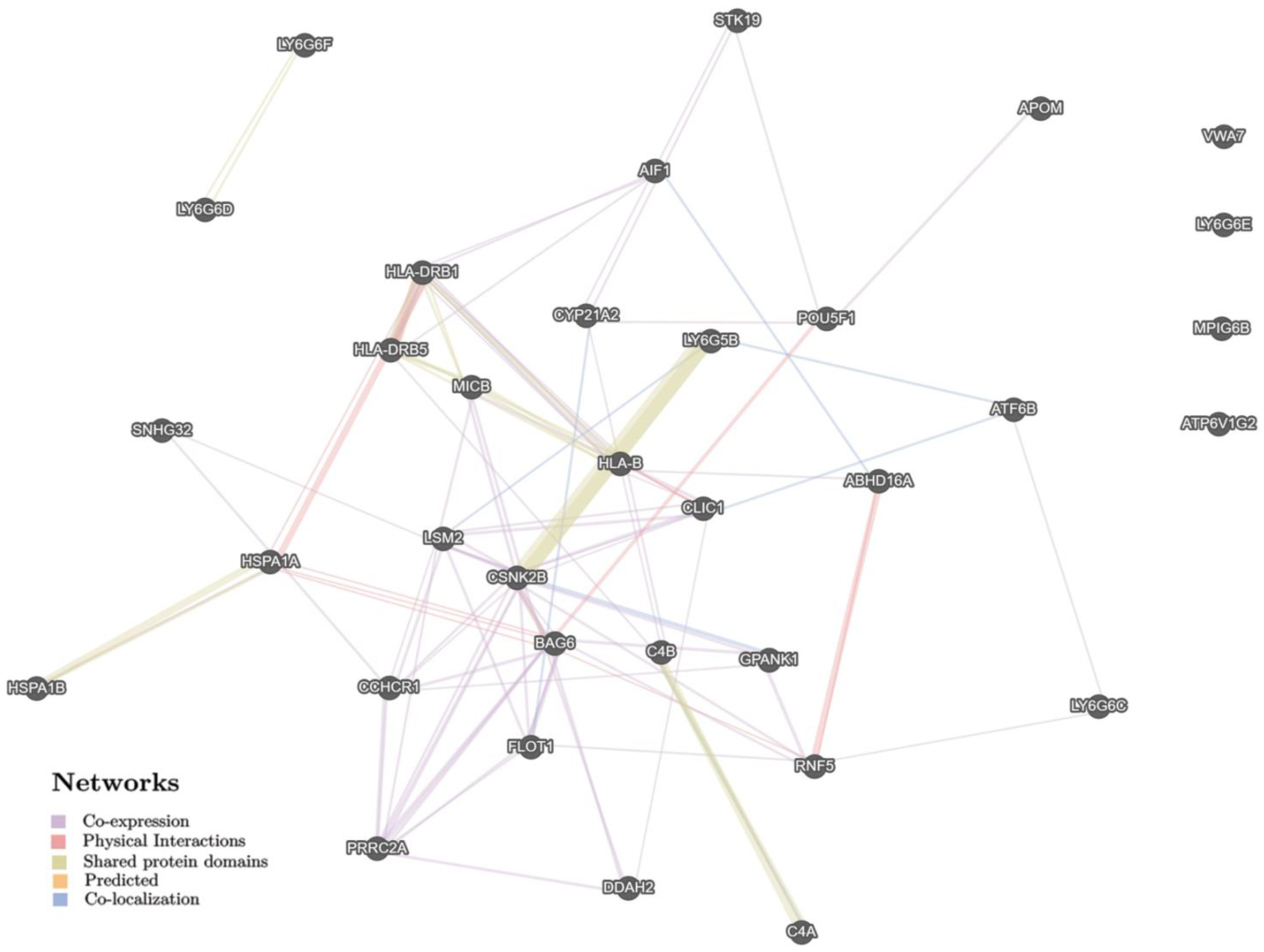
In Silico Data of Functional PE-Associated SNPs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poon, L.C.; Shennan, A.; Hyett, J.A.; Kapur, A.; Hadar, E.; Divakar, H.; McAuliffe, F.; da Silva Costa, F.; von Dadelszen, P.; McIntyre, H.D.; et al. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) initiative on pre-eclampsia: A pragmatic guide for first-trimester screening and prevention. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. Off. Organ Int. Fed. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2019, 145, S173–S211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.; Lemoine, E.; Granger, J.P.; Karumanchi, S.A. Preeclampsia: Pathophysiology, challenges, and perspectives. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1094–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opichka, M.A.; Rappelt, M.W.; Gutterman, D.D.; Grobe, J.L.; McIntosh, J.J. Vascular Dysfunction in Preeclampsia. Cells 2021, 10, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyabalan, A. Epidemiology of preeclampsia: Impact of obesity. Nutr. Rev. 2013, 71, S18–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodnar, L.M.; Catov, J.M.; Klebanoff, M.A.; Ness, R.B.; Roberts, J.M. Prepregnancy Body Mass Index and the Occurrence of Severe Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. Epidemiology 2007, 18, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.M.; Bodnar, L.M.; Patrick, T.E.; Powers, R.W. The role of obesity in preeclampsia. Pregnancy Hypertens. Int. J. Women’s Cardiovasc. Health 2010, 1, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, R.; Kitt, J.; Leeson, P.; Aye, C.Y.; Lewandowski, A.J. Preeclampsia: Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Management, and the Cardiovascular Impact on the Offspring. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cnattingius, S.; Reilly, M.; Pawitan, Y.; Lichtenstein, P. Maternal and fetal genetic factors account for most of familial aggregation of preeclampsia: A population-based Swedish cohort study. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2004, 130, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spradley, F.T.; Palei, A.C.; Granger, J.P. Increased risk for the development of preeclampsia in obese pregnancies: Weighing in on the mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 309, R1326–R1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spradley, F.T. Metabolic abnormalities and obesity’s impact on the risk for developing preeclampsia. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2017, 312, R5–R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivett, C.; Lees, Z.J.; Freeman, D.J. Adipose tissue function in healthy pregnancy, gestational diabetes mellitus and pre-eclampsia. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 75, 1745–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodnar, L.M.; Ness, R.B.; Markovic, N.; Roberts, J.M. The Risk of Preeclampsia Rises with Increasing Prepregnancy Body Mass Index. Ann. Epidemiol. 2005, 15, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funai, E.F.; Friedlander, Y.; Paltiel, O.; Tiram, E.; Xue, X.; Deutsch, L.; Harlap, S. Long-Term Mortality After Preeclampsia. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, S.S.; Ferreira, T.; Benonisdottir, S.; Rahmioglu, N.; Becker, C.M.; Granne, I.; Zondervan, K.T.; Holmes, M.V.; Lindgren, C.M.; Wittemans, L.B.L. Obesity and risk of female reproductive conditions: A Mendelian randomisation study. PLoS Med. 2022, 19, e1003679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durst, J.K.; Tuuli, M.G.; Stout, M.J.; Macones, G.A.; Cahill, A.G. Degree of obesity at delivery and risk of preeclampsia with severe features. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 214, 651.e1–651.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, F.; Calvani, R.; Picca, A.; Tosato, M.; Martone, A.M.; Ortolani, E.; Sisto, A.; D’Angelo, E.; Serafini, E.; Desideri, G.; et al. Body Mass Index is Strongly Associated with Hypertension: Results from the Longevity Check-Up 7+ Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, F.B.; Adhikary, G.; Chowdhury, A.B.; Shawon, S.R. Association between body mass index (BMI) and hypertension in south Asian population: Evidence from nationally-representative surveys. Clin. Hypertens. 2019, 25, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hounkpatin, O.I.; Amidou, S.A.; Houehanou, Y.C.; Lacroix, P.; Preux, P.M.; Houinato, D.S.; Bezanahary, H. Systematic review of observational studies of the impact of cardiovascular risk factors on preeclampsia in sub-saharan Africa. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2021, 21, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.P.; Brennecke, S.; East, C.; Göring, H.H.H.; Kent, J.; Dyer, T.D.; Said, J.; Roten, L.T.; Iversen, A.-C.; Abraham, L.J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Scan Identifies a Risk Locus for Preeclampsia on 2q14, Near the Inhibin, Beta B Gene. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshetnikov, E.A.; Akulova, L.Y.; Dobrodomova, I.S.; Dvornyk, V.Y.; Polonikov, A.V.; Churnosov, M.I. The insertion-deletion polymorphism of the ACE gene is associated with increased blood pressure in women at the end of pregnancy. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2013, 16, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serebrova, V.N.; Trifonova, E.A.; Stepanov, V.A. Evolutionary-genetic analysis of the role of regulatory regions in CORO2A gene in the development of hereditary predisposition to preeclampsia in Russian and Yakut ethnic groups. Res. Results Biomed. 2018, 4, 38–48. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakoordeen, S.; Moodley, J.; Naicker, T. Candidate Gene, Genome-Wide Association and Bioinformatic Studies in Pre-eclampsia: A Review. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshetnikov, E.; Ponomarenko, I.; Golovchenko, O.; Sorokina, I.; Batlutskaya, I.; Yakunchenko, T.; Dvornyk, V.; Polonikov, A.; Churnosov, M. The VNTR polymorphism of the endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene and blood pressure in women at the end of pregnancy. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 58, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, G.; Jahan, S.; Bibi, N.; Ullah, A.; Faryal, R.; Almajwal, A.; Afsar, T.; Al-Disi, D.; Abulmeaty, M.; Al Khuraif, A.A.; et al. Association of endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene variants with preeclampsia. Reprod. Health 2021, 18, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshetnikov, E.A. Polymorphism of genes associated with the age at menarche and the risk of complications of pregnancy in women in the Central Black Earth Region of Russia. Res. Results Biomed. 2021, 7, 132–142. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, K.J.; Kovacheva, V.P.; Mirzakhani, H.; Bjonnes, A.C.; Almoguera, B.; DeWan, A.T.; Triche, E.W.; Saftlas, A.F.; Hoh, J.; Bodian, D.L.; et al. Gene-Centric Analysis of Preeclampsia Identifies Maternal Association at PLEKHG1. Hypertension 2018, 72, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinthorsdottir, V.; FINNPEC Consortium; McGinnis, R.; Williams, N.O.; Stefansdottir, L.; Thorleifsson, G.; Shooter, S.; Fadista, J.; Sigurdsson, J.K.; Auro, K.M.; et al. Genetic predisposition to hypertension is associated with preeclampsia in European and Central Asian women. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, K.J.; Kovacheva, V.P.; Mirzakhani, H.; Bjonnes, A.C.; Almoguera, B.; Wilson, M.L.; Ingles, S.A.; Lockwood, C.J.; Hakonarson, H.; McElrath, T.F.; et al. Risk of pre-eclampsia in patients with a maternal genetic predisposition to common medical conditions: A case–control study. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2020, 128, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACOG Committee on Obstetric Practice. ACOG practice bulletin. Diagnosis and management of preeclampsia and eclampsia. Number 33, January 2002. Obs. Gynecol. 2002, 99, 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Efremova, O.A. Studying the role of interlocus interactions of folate cycle genes and matrix metalloproteinases in the formation of fetal growth retardation. Res. Results Biomed. 2022, 8, 36–55. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litovkina, O.; Nekipelova, E.; Dvornyk, V.; Polonikov, A.; Efremova, O.; Zhernakova, N.; Reshetnikov, E.; Churnosov, M. Genes involved in the regulation of vascular homeostasis determine renal survival rate in patients with chronic glomerulonephritis. Gene 2014, 546, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshetnikov, E.; Zarudskaya, O.; Polonikov, A.; Bushueva, O.; Orlova, V.; Krikun, E.; Dvornyk, V.; Churnosov, M. Genetic markers for inherited thrombophilia are associated with fetal growth retardation in the population of Central Russia. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2017, 43, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golovchenko, O.; Abramova, M.; Ponomarenko, I.; Reshetnikov, E.; Aristova, I.; Polonikov, A.; Dvornyk, V.; Churnosov, M. Functionally significant polymorphisms of ESR1and PGR and risk of intrauterine growth restriction in population of Central Russia. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2020, 253, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrema, D.; Lie, R.T.; Østbye, T.; Mahande, M.J.; Daltveit, A.K. The association between pre pregnancy body mass index and risk of preeclampsia: A registry based study from Tanzania. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2018, 18, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliseeva, N.; Ponomarenko, I.; Reshetnikov, E.; Dvornyk, V.; Churnosov, M. LOXL1 gene polymorphism candidates for exfoliation glaucoma are also associated with a risk for primary open-angle glaucoma in a Caucasian population from central Russia. Mol. Vis. 2021, 27, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ponomarenko, I.; Reshetnikov, E.; Polonikov, A.; Verzilina, I.; Sorokina, I.; Yermachenko, A.; Dvornyk, V.; Churnosov, M. Candidate Genes for Age at Menarche Are Associated With Uterine Leiomyoma. Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 512940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlova, N.; Demin, S.; Churnosov, M.; Reshetnikov, E.; Aristova, I.; Churnosova, M.; Ponomarenko, I. The Modifying Effect of Obesity on the Association of Matrix Metalloproteinase Gene Polymorphisms with Breast Cancer Risk. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.D.; Kellis, M. HaploReg v4: Systematic mining of putative causal variants, cell types, regulators and target genes for human complex traits and disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, D877–D881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikunova, E.; Ovtcharova, V.; Reshetnikov, E.; Dvornyk, V.; Polonikov, A.; Bushueva, O.; Churnosov, M. Genes of tumor necrosis factors and their receptors and the primary open angle glaucoma in the population of Central Russia. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 10, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskalenko, M.I.; Milanova, S.N.; Ponomarenko, I.V.; Polonikov, A.V.; Churnosov, M.I. Study of associations of polymorphism of matrix metalloproteinases genes with the development of arterial hypertension in men. Kardiologiia 2019, 59, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starikova, D.; Ponomarenko, I.; Reshetnikov, E.; Dvornyk, V.; Churnosov, M. Novel Data about Association of the Functionally Significant Polymorphisms of the MMP9 Gene with Exfoliation Glaucoma in the Caucasian Population of Central Russia. Ophthalmic Res. 2020, 64, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minyaylo, O.; Ponomarenko, I.; Reshetnikov, E.; Dvornyk, V.; Churnosov, M. Functionally significant polymorphisms of the MMP-9 gene are associated with peptic ulcer disease in the Caucasian population of Central Russia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlova, N.; Demin, S.; Churnosov, M.; Reshetnikov, E.; Aristova, I.; Churnosova, M.; Ponomarenko, I. Matrix Metalloproteinase Gene Polymorphisms Are Associated with Breast Cancer in the Caucasian Women of Russia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, R.; Jack, J.R.; Motsinger-Reif, A.A.; Brown, C.C. An adaptive permutation approach for genome-wide association study: Evaluation and recommendations for use. BioData Min. 2014, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, I.; Reshetnikov, E.; Polonikov, A.; Verzilina, I.; Sorokina, I.; Elgaeva, E.E.; Tsepilov, Y.A.; Yermachenko, A.; Dvornyk, V.; Churnosov, M. Candidate genes for age at menarche are associated with endometriosis. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2020, 41, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, I.; Reshetnikov, E.; Polonikov, A.; Sorokina, I.; Yermachenko, A.; Dvornyk, V.; Churnosov, M. Candidate genes for age at menarche are associated with endometrial hyperplasia. Gene 2020, 757, 144933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskalenko, M.; Ponomarenko, I.; Reshetnikov, E.; Dvornyk, V.; Churnosov, M. Polymorphisms of the matrix metalloproteinase genes are associated with essential hypertension in a Caucasian population of Central Russia. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churnosov, M.; Abramova, M.; Reshetnikov, E.; Lyashenko, I.V.; Efremova, O.; Churnosova, M.; Ponomarenko, I. Polymorphisms of hypertension susceptibility genes as a risk factors of preeclampsia in the Caucasian population of central Russia. Placenta 2022, 129, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovchenko, I.; Aizikovich, B.; Golovchenko, O.; Reshetnikov, E.; Churnosova, M.; Aristova, I.; Ponomarenko, I.; Churnosov, M. Sex Hormone Candidate Gene Polymorphisms Are Associated with Endometriosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Henikoff, S.; Ng, P.C. Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzhubei, I.; Jordan, D.M.; Sunyaev, S.R. Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using PolyPhen-2. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2013, 76, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GTEx Consortium. The GTEx Consortium atlas of genetic regulatory effects across human tissues. Science 2020, 369, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westra, H.-J.; Peters, M.J.; Esko, T.; Yaghootkar, H.; Schurmann, C.; Kettunen, J.; Christiansen, M.W.; Fairfax, B.P.; Schramm, K.; Powell, J.E.; et al. Systematic identification of trans eQTLs as putative drivers of known disease associations. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, M.; Rodriguez, H.; Lopes, C.; Zuberi, K.; Montojo, J.; Bader, G.D.; Morris, Q. GeneMANIA update 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W60–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene Ontology Consortium. The Gene Ontology resource: Enriching a GOld mine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D325–D334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein–protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauth, J.C.; Clifton, R.G.; Roberts, J.M.; Myatt, L.; Spong, C.Y.; Leveno, K.J.; Varner, M.; Wapner, R.J.; Thorp, J.M.; Mercer, B.M.; et al. Maternal insulin resistance and preeclampsia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 204, 327.e1–327.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.D.; Ness, R.B.; Olsen, J.; Hougaard, D.M.; Skogstrand, K.; Roberts, J.M.; Haggerty, C. Serum Leptin Measured in Early Pregnancy Is Higher in Women With Preeclampsia Compared With Normotensive Pregnant Women. Hypertension 2015, 65, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plowden, T.C.; Zarek, S.M.; Rafique, S.; Sjaarda, L.A.; Schisterman, E.F.; Silver, R.M.; Yeung, E.H.; Radin, R.; Hinkle, S.N.; Galai, N.; et al. Preconception leptin levels and pregnancy outcomes: A prospective cohort study. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2019, 6, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, F.; Schlüssel, M.M.; Vaz, J.; Franco-Sena, A.B.; Pinto, T.J.; Bastos, F.; Adegboye, A.R.A.; Kac, G. C-reactive protein and later preeclampsia: Systematic review and meta-analysis taking into account the weight status. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spracklen, C.N.; Smith, C.J.; Saftlas, A.F.; Robinson, J.G.; Ryckman, K.K. Maternal Hyperlipidemia and the Risk of Preeclampsia: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 180, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Barajas, J.; Rueda-Quijano, S.M.; Lopez-Lopez, C.; Felix, C. Obesity and Preeclampsia: Common Pathophysiological Mechanisms. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The International Consortium for Blood Pressure Genome-Wide Association Studies. Genetic variants in novel pathways influence blood pressure and cardiovascular disease risk. Nature 2011, 478, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, P.; Drenos, F.; Young, R.; Warren, H.; Cook, J.P.; Manning, A.K.; Grarup, N.; Sim, X.; Barnes, D.; Witkowska, K.; et al. Trans-ancestry meta-analyses identify rare and common variants associated with blood pressure and hypertension. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Kraja, A.T.; Smith, J.A.; Brody, J.A.; Franceschini, N.; Bis, J.C.; Rice, K.; Morrison, A.; Lu, Y.; Weiss, S.; et al. Meta-analysis identifies common and rare variants influencing blood pressure and overlapping with metabolic trait loci. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.J.; Ehret, G.B.; Nandakumar, P.; Ranatunga, D.; Schaefer, C.; Kwok, P.-Y.; Iribarren, C.; Chakravarti, A.; Risch, N. Genome-wide association analyses using electronic health records identify new loci influencing blood pressure variation. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.; Hellwege, J.N.; Keaton, J.M.; Park, J.; Qiu, C.X.; Warren, H.R.; Torstenson, E.S.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Sun, Y.V.; Wilson, O.D.; et al. Trans-ethnic association study of blood pressure determinants in over 750,000 individuals. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, C.A.; Sinsheimer, J.S.; Klimentidis, Y.C.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, J.J. Ordered multinomial regression for genetic association analysis of ordinal phenotypes at Biobank scale. Genet. Epidemiol. 2019, 44, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Jin, H.-S.; Kim, S.-S.; Shin, D. Identifying Interactions between Dietary Sodium, Potassium, Sodium–Potassium Ratios, and FGF5 rs16998073 Variants and Their Associated Risk for Hypertension in Korean Adults. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaue, S.; Kanai, M.; Tanigawa, Y.; Karjalainen, J.; Kurki, M.; Koshiba, S.; Narita, A.; Konuma, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Akiyama, M.; et al. A cross-population atlas of genetic associations for 220 human phenotypes. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comuzzie, A.G.; Cole, S.A.; Laston, S.L.; Voruganti, V.S.; Haack, K.; Gibbs, R.A.; Butte, N.F. Novel Genetic Loci Identified for the Pathophysiology of Childhood Obesity in the Hispanic Population. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschini, N.; Fox, E.; Zhang, Z.; Edwards, T.L.; Nalls, M.A.; Sung, Y.J.; Tayo, B.O.; Sun, Y.V.; Gottesman, O.; Adeyemo, A.; et al. Genome-wide Association Analysis of Blood-Pressure Traits in African-Ancestry Individuals Reveals Common Associated Genes in African and Non-African Populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelou, E.; Program, T.M.V.; Warren, H.R.; Mosen-Ansorena, D.; Mifsud, B.; Pazoki, R.; Gao, H.; Ntritsos, G.; Dimou, N.; Cabrera, C.P.; et al. Genetic analysis of over 1 million people identifies 535 new loci associated with blood pressure traits. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1412–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feitosa, M.F.; Kraja, A.T.; Chasman, D.I.; Sung, Y.J.; Winkler, T.W.; Ntalla, I.; Guo, X.; Franceschini, N.; Heng, C.K.; Sim, X.; et al. Novel genetic associations for blood pressure identified via gene-alcohol interaction in up to 570K individuals across multiple ancestries. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, Y.J.; Winkler, T.W.; Fuentes, L.D.L.; Bentley, A.R.; Brown, M.R.; Kraja, A.T.; Schwander, K.; Ntalla, I.; Guo, X.; Franceschini, N.; et al. A Large-Scale Multi-ancestry Genome-wide Study Accounting for Smoking Behavior Identifies Multiple Significant Loci for Blood Pressure. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 375–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frayling, T.M.; Timpson, N.J.; Weedon, M.N.; Zeggini, E.; Freathy, R.M.; Lindgren, C.M.; Perry, J.R.B.; Elliott, K.S.; Lango, H.; Rayner, N.W.; et al. A Common Variant in the FTO Gene Is Associated with Body Mass Index and Predisposes to Childhood and Adult Obesity. Science 2007, 316, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehret, G.B.; CHARGE-EchoGen Consortium; Ferreira, T.; Chasman, D.I.; Jackson, A.U.; Schmidt, E.; Johnson, T.; Thorleifsson, G.; Luan, J.; Donnelly, L.A.; et al. The genetics of blood pressure regulation and its target organs from association studies in 342,415 individuals. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1171–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, A.E.; Kahali, B.; Berndt, S.I.; Justice, A.E.; Pers, T.H.; Day, F.R.; Powell, C.; Vedantam, S.; Buchkovich, M.L.; Yang, J.; et al. Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature 2015, 518, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Than, N.G.; Romero, R.; Tarca, A.L.; Kekesi, K.A.; Xu, Y.; Xu, Z.; Juhasz, K.; Bhatti, G.; Leavitt, R.J.; Gelencser, Z.; et al. Integrated Systems Biology Approach Identifies Novel Maternal and Placental Pathways of Preeclampsia. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartiala, J.A.; Han, Y.; Jia, Q.; Hilser, J.R.; Huang, P.; Gukasyan, J.; Schwartzman, W.S.; Cai, Z.; Biswas, S.; Trégouët, D.A.; et al. Genome-wide analysis identifies novel susceptibility loci for myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart. J. 2021, 42, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, N.; Loh, M.; Takeuchi, F.; Verweij, N.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Kelly, T.N.; Saleheen, D.; Lehne, B.; Leach, I.M.; et al. Trans-ancestry genome-wide association study identifies 12 genetic loci influencing blood pressure and implicates a role for DNA methylation. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, S.; Ito, K.; Terao, C.; Akiyama, M.; Horikoshi, M.; Momozawa, Y.; Matsunaga, H.; Ieki, H.; Ozaki, K.; Onouchi, Y.; et al. Population-specific and trans-ancestry genome-wide analyses identify distinct and shared genetic risk loci for coronary artery disease. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.; Ehret, G.B.; Rice, K.; Verwoert, G.C.; Launer, L.J.; Dehghan, A.; Glazer, N.L.; Morrison, A.C.; Johnson, A.D.; Aspelund, T.; et al. Genome-wide association study of blood pressure and hypertension. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, C.P.; Goel, A.; Butterworth, A.S.; Kanoni, S.; Webb, T.R.; Marouli, E.; Zeng, L.; Ntalla, I.; Lai, F.Y.; Hopewell, J.C.; et al. Association analyses based on false discovery rate implicate new loci for coronary artery disease. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikpay, M.; Goel, A.; Won, H.H.; Hall, L.M.; Willenborg, C.; Kanoni, S.; Saleheen, D.; Kyriakou, T.; Nelson, C.P.; Hopewell, J.C.; et al. A comprehensive 1,000 Genomes-based genome-wide association meta-analysis of coronary artery disease. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shungin, D.; Winkler, T.W.; Croteau-Chonka, D.C.; Ferreira, T.; Locke, A.E.; Mägi, R.; Strawbridge, R.J.; Pers, T.H.; Fischer, K.; Justice, A.E.; et al. New genetic loci link adipose and insulin biology to body fat distribution. Nature 2015, 518, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachmazidou, I.; Süveges, D.; Min, J.L.; Ritchie, G.R.S.; Steinberg, J.; Walter, K.; Iotchkova, V.; Schwartzentruber, J.; Huang, J.; Memari, Y.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing Coupled to Imputation Discovers Genetic Signals for Anthropometric Traits. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 100, 865–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, F.; Akiyama, M.; Matoba, N.; Katsuya, T.; Nakatochi, M.; Tabara, Y.; Narita, A.; Saw, W.Y.; Moon, S.; Spracklen, C.N.; et al. Interethnic analyses of blood pressure loci in populations of East Asian and European descent. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wain, L.V.; Vaez, A.; Jansen, R.; Joehanes, R.; van der Most, P.J.; Erzurumluoglu, A.M.; O’Reilly, P.F.; Cabrera, C.P.; Warren, H.R.; Rose, L.M.; et al. Novel Blood Pressure Locus and Gene Discovery Using Genome-Wide Association Study and Expression Data Sets From Blood and the Kidney. Hypertension. 2017, 70, e4–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wain, L.V.; Verwoert, G.C.; O’Reilly, P.F.; Shi, G.; Johnson, T.; Johnson, A.D.; Bochud, M.; Rice, K.M.; Henneman, P.; Smith, A.V.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies six new loci influencing pulse pressure and mean arterial pressure. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Nielsen, J.B.; Fritsche, L.G.; Dey, R.; Gabrielsen, M.E.; Wolford, B.N.; LeFaive, J.; VandeHaar, P.; Gagliano, S.A.; Gifford, A.; et al. Efficiently controlling for case-control imbalance and sample relatedness in large-scale genetic association studies. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Lin, Y.; Shen, S.; Liu, C.L.; Hobbs, B.D.; Hasegawa, K.; Liang, L.; International COPD Genetics Consortium; et al. Genetic overlap of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cardiovascular disease-related traits: A large-scale genome-wide cross-trait analysis. Respir. Res. 2019, 20, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameters | PreBMI ≥ 25 | PreBMI < 25 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PE Patients | Controls | p | PE Patients | Controls | p | |
| N | 162 | 159 | - | 290 | 339 | - |
| Age, years(min–max) | 29.05 ± 5.09 (18–42) | 27.09 ± 5.31 (18–41) | 0.001 | 26.48 ± 4.83 (17–43) | 26.36 ± 4.77 (16–42) | 0.71 |
| Pre-pregnancy BMI, kg/m2 | 30.50 ± 4.51 | 27.82 ± 2.45 | 0.0001 | 21.71 ± 1.89 | 21.60 ± 2.02 | 0.39 |
| Family history of preeclampsia | 24.69 (40) | 13.84 (22) | 0.02 | 23.10 (67) | 11.50 (39) | 0.0008 |
| Smoker (yes) | 48.76 (79) | 52.83 (84) | 0.54 | 44.48 (129) | 52.80 (179) | 0.05 |
| Alcohol consumption (yes) | 77.78 (126) | 83.65 (133) | 0.23 | 74.14 (215) | 77.29 (262) | 0.41 |
| Pre-pregnancy blood pressure (BP) | ||||||
| Systolic BP, mm Hg | 113.82 ± 9.65 | 113.71 ± 6.54 | 0.78 | 111.95 ± 9.99 | 110.59 ± 9.26 | 0.08 |
| Diastolic BP, mm Hg | 72.30 ± 6.44 | 72.82 ± 6.30 | 0.54 | 71.68± 5.36 | 71.02 ± 4.24 | 0.56 |
| Mean BP, mm Hg | 86.14 ± 7.30 | 86.62 ± 6.33 | 0.22 | 85.24 ± 8.16 | 84.88 ± 7.65 | 0.13 |
| Pulse BP, mm Hg | 40.32 ± 4.91 | 39.99 ± 3.74 | 0.11 | 39.67 ± 4.36 | 38.57 ± 4.24 | 0.09 |
| Age at menarche and menstrual cycle | ||||||
| Age at menarche, years | 12.15 ± 1.17 | 12.39 ± 1.01 | 0.45 | 12.72 ± 0.93 | 12.67 ± 1.09 | 0.11 |
| Duration of menstrual bleeding (mean, days) | 4.85 ± 1.32 | 5.03 ± 0.76 | 0.16 | 4.93 ± 1.10 | 4.99 ± 0.75 | 0.48 |
| Menstrual cycle length (mean, days) | 27.41 ± 3.13 | 28.16 ± 1.16 | 0.13 | 28.14 ± 2.67 | 28.48 ± 1.87 | 0.59 |
| Reproductive status | ||||||
| First pregnancy | 35.80 (58) | 37.74 (60) | 0.81 | 41.38 (120) | 44.54 (151) | 0.47 |
| No. of gravidity (mean) | 2.14 ± 1.88 | 1.41 ± 1.67 | 0.03 | 1.10 ± 1.33 | 1.01 ± 1.33 | 0.36 |
| No. of births (mean) | 0.81 ± 0.89 | 0.79 ± 0.87 | 0.76 | 0.40 ± 0.54 | 0.41 ± 0.63 | 0.62 |
| No. of spontaneous abortions (mean) | 0.28 ± 0.52 | 0.12 ± 0.35 | 0.008 | 0.22 ± 0.47 | 0.16 ± 0.42 | 0.08 |
| No. of induced abortions (mean) | 0.98 ± 1.33 | 0.48 ± 0.88 | 0.003 | 0.45 ± 0.76 | 0.43 ± 0.82 | 0.38 |
| No. of stillbirths | 0.07 ± 0.25 | 0.02 ± 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.03 ± 0.18 | 0.01 ± 0.13 | 0.07 |
| Somatic pathologies | ||||||
| Cardiovascular | 17.90 (29) | 10.69 (17) | 0.09 | 11.38 (33) | 9.14 (31) | 0.42 |
| Kidney | 7.41 (12) | 5.03 (8) | 0.52 | 4.14 (12) | 2.95 (10) | 0.56 |
| Endocrine | 3.70 (6) | 3.77 (6) | 0.99 | 2.76 (8) | 0.88 (3) | 0.14 |
| Gastrointestinal | 3.09 (5) | 1.26 (2) | 0.46 | 1.72 (5) | 3.54 (12) | 0.25 |
| Obesity | 46.91 (76) | 20.13 (32) | 0.0001 | - | - | - |
| Chr | SNP | Minor Allele | n | Allelic Model | Additive Model | Dominant Model | Recessive Model | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95%CI | p | OR | 95%CI | p | OR | 95%CI | p | OR | 95%CI | p | ||||||||
| L95 | U95 | L95 | U95 | L95 | U95 | L95 | U95 | ||||||||||||
| female with preBMI < 25 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | rs1173771 | A | 609 | 0.83 | 0.66 | 1.05 | 0.113 | 0.83 | 0.65 | 1.04 | 0.107 | 0.78 | 0.55 | 1.10 | 0.154 | 0.78 | 0.51 | 1.18 | 0.241 |
| 6 | rs1799945 | G | 624 | 0.97 | 0.74 | 1.28 | 0.842 | 0.97 | 0.73 | 1.29 | 0.837 | 0.89 | 0.64 | 1.23 | 0.481 | 1.81 | 0.73 | 4.48 | 0.202 |
| 6 | rs805303 | A | 628 | 0.86 | 0.69 | 1.08 | 0.199 | 0.85 | 0.67 | 1.08 | 0.187 | 0.83 | 0.60 | 1.15 | 0.260 | 0.79 | 0.50 | 1.26 | 0.321 |
| 10 | rs932764 | A | 618 | 0.95 | 0.76 | 1.19 | 0.672 | 0.95 | 0.77 | 1.19 | 0.678 | 1.05 | 0.74 | 1.49 | 0.797 | 0.83 | 0.58 | 1.21 | 0.334 |
| 10 | rs4387287 | A | 587 | 0.90 | 0.67 | 1.20 | 0.468 | 0.90 | 0.67 | 1.20 | 0.465 | 0.87 | 0.62 | 1.22 | 0.420 | 0.95 | 0.39 | 2.33 | 0.915 |
| 11 | rs633185 | G | 620 | 1.02 | 0.80 | 1.30 | 0.891 | 1.02 | 0.79 | 1.32 | 0.885 | 1.07 | 0.78 | 1.46 | 0.696 | 0.87 | 0.45 | 1.66 | 0.665 |
| 12 | rs7302981 | A | 621 | 1.06 | 0.84 | 1.33 | 0.644 | 1.06 | 0.84 | 1.34 | 0.635 | 0.99 | 0.71 | 1.37 | 0.943 | 1.28 | 0.80 | 2.03 | 0.302 |
| 12 | rs2681472 | G | 625 | 1.16 | 0.84 | 1.60 | 0.360 | 1.16 | 0.84 | 1.61 | 0.356 | 1.13 | 0.79 | 1.61 | 0.500 | 2.06 | 0.60 | 7.11 | 0.253 |
| 17 | rs8068318 | C | 603 | 1.18 | 0.92 | 1.52 | 0.198 | 1.18 | 0.92 | 1.51 | 0.201 | 1.11 | 0.80 | 1.53 | 0.528 | 1.74 | 0.96 | 3.15 | 0.068 |
| 19 | rs167479 | G | 616 | 0.79 | 0.63 | 0.98 | 0.036 | 0.79 | 0.63 | 0.99 | 0.038 | 0.71 | 0.49 | 1.02 | 0.060 | 0.75 | 0.52 | 1.09 | 0.129 |
| female with preBMI ≥ 25 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | rs1173771 | A | 315 | 0.98 | 0.71 | 1.34 | 0.880 | 0.97 | 0.71 | 1.35 | 0.877 | 0.92 | 0.57 | 1.49 | 0.741 | 1.04 | 0.58 | 1.84 | 0.905 |
| 6 | rs1799945 | G | 319 | 1.15 | 0.77 | 1.70 | 0.494 | 1.14 | 0.78 | 1.67 | 0.507 | 1.00 | 0.63 | 1.59 | 0.998 | 2.82 | 0.88 | 9.06 | 0.081 |
| 6 | rs805303 | A | 318 | 0.66 | 0.48 | 0.92 | 0.014 | 0.68 | 0.49 | 0.93 | 0.018 | 0.73 | 0.47 | 1.15 | 0.173 | 0.36 | 0.18 | 0.74 | 0.005 |
| 10 | rs932764 | A | 318 | 1.02 | 0.74 | 1.39 | 0.927 | 1.01 | 0.74 | 1.38 | 0.927 | 1.22 | 0.75 | 1.98 | 0.418 | 0.82 | 0.48 | 1.40 | 0.460 |
| 10 | rs4387287 | A | 306 | 0.89 | 0.59 | 1.36 | 0.592 | 0.89 | 0.58 | 1.36 | 0.588 | 0.81 | 0.50 | 1.31 | 0.390 | 1.69 | 0.40 | 7.20 | 0.478 |
| 11 | rs633185 | G | 317 | 0.89 | 0.62 | 1.26 | 0.503 | 0.89 | 0.62 | 1.26 | 0.501 | 0.87 | 0.56 | 1.35 | 0.533 | 0.83 | 0.35 | 1.98 | 0.670 |
| 12 | rs7302981 | A | 316 | 0.80 | 0.58 | 1.11 | 0.184 | 0.79 | 0.56 | 1.11 | 0.172 | 0.81 | 0.52 | 1.27 | 0.358 | 0.60 | 0.30 | 1.22 | 0.160 |
| 12 | rs2681472 | G | 317 | 0.99 | 0.64 | 1.52 | 0.953 | 0.99 | 0.65 | 1.50 | 0.955 | 0.96 | 0.58 | 1.57 | 0.864 | 1.17 | 0.35 | 3.91 | 0.800 |
| 17 | rs8068318 | C | 314 | 0.87 | 0.61 | 1.23 | 0.420 | 0.87 | 0.62 | 1.23 | 0.430 | 0.84 | 0.54 | 1.30 | 0.428 | 0.85 | 0.38 | 1.89 | 0.682 |
| 19 | rs167479 | G | 317 | 1.34 | 0.98 | 1.83 | 0.067 | 1.36 | 0.99 | 1.88 | 0.062 | 1.86 | 1.11 | 3.11 | 0.019 | 1.19 | 0.70 | 2.02 | 0.520 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abramova, M.; Churnosova, M.; Efremova, O.; Aristova, I.; Reshetnikov, E.; Polonikov, A.; Churnosov, M.; Ponomarenko, I. Effects of Pre-Pregnancy Overweight/Obesity on the Pattern of Association of Hypertension Susceptibility Genes with Preeclampsia. Life 2022, 12, 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122018
Abramova M, Churnosova M, Efremova O, Aristova I, Reshetnikov E, Polonikov A, Churnosov M, Ponomarenko I. Effects of Pre-Pregnancy Overweight/Obesity on the Pattern of Association of Hypertension Susceptibility Genes with Preeclampsia. Life. 2022; 12(12):2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122018
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbramova, Maria, Maria Churnosova, Olesya Efremova, Inna Aristova, Evgeny Reshetnikov, Alexey Polonikov, Mikhail Churnosov, and Irina Ponomarenko. 2022. "Effects of Pre-Pregnancy Overweight/Obesity on the Pattern of Association of Hypertension Susceptibility Genes with Preeclampsia" Life 12, no. 12: 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122018
APA StyleAbramova, M., Churnosova, M., Efremova, O., Aristova, I., Reshetnikov, E., Polonikov, A., Churnosov, M., & Ponomarenko, I. (2022). Effects of Pre-Pregnancy Overweight/Obesity on the Pattern of Association of Hypertension Susceptibility Genes with Preeclampsia. Life, 12(12), 2018. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122018







