The Implementation of a Health Care Worker Screening Program Based on the Advanta RT-qPCR Saliva Assay in a Tertiary Care Referral Hospital in Northern Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participant Enrolment
2.2. Saliva Specimen Collection
2.3. Advanta Dx SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Assay (Standard Biotools Inc.)
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Griffin, K.M.; Karas, M.G.; Ivascu, N.S.; Lief, L. Hospital preparedness for COVID-19: A practical guide from a critical care perspective. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 201, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.H.; Drew, D.A.; Graham, M.S.; Joshi, A.D.; Guo, C.G.; Ma, W.; Mehta, R.S.; Warner, E.T.; Sikavi, D.R.; Lo, C.H.; et al. Risk of COVID-19 among front-line health-care workers and the general community: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e475–e483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Ochoa, S.A.; Franco, O.H.; Rojas, L.Z.; Raguindin, P.F.; Roa-Díaz, Z.M.; Wyssmann, B.M.; Guevara, S.L.R.; Echeverría, L.E.; Glisic, M.; Muka, T. COVID-19 in Health-Care Workers: A Living Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prevalence, Risk Factors, Clinical Characteristics, and Outcomes. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 190, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. The Impact of COVID-19 on Health and Care Workers: A Closer Look at Deaths; Working paper 1; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- McMichael, T.M.; Currie, D.W.; Clark, S.; Pogosjans, S.; Kay, M.; Schwartz, N.G.; Lewis, J.; Baer, A.; Kawakami, V.; Lukoff, M.D.; et al. Epidemiology of Covid-19 in a Long-Term Care Facility in King County, Washington. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2005–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arons, M.M.; Hatfield, K.M.; Reddy, S.C.; Kimball, A.; James, A.; Jacobs, J.R.; Taylor, J.; Spicer, K.; Bardossy, A.C.; Oakley, L.P.; et al. Presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infections and Transmission in a Skilled Nursing Facility. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, N.S.N.; Junghans, C.; Downes, R.; Sendall, C.; Lai, H.; McKirdy, A.; Elliott, P.; Howard, R.; Wingfield, D.; Priestman, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection, clinical features and outcome of COVID-19 in United Kingdom nursing homes. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; RobaloNunes, T.; Martischang, R.; Zingg, W.; Iten, A.; Pittet, D.; Harbarth, S. Nosocomial transmission and outbreaks of coronavirus disease 2019: The need to protect both patients and healthcare workers. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2021, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltansing, S.; Sikkema, R.S.; de Man, S.J.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; Oude Munnink, B.B.; de Man, P. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 among healthcare workers and patients in a teaching hospital in the Netherlands confirmed by whole-genome sequencing. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 110, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Piening, B.; Nouri-Pasovsky, P.A.; Krüger, A.C.; Gastmeier, P.; Aghdassi, S.J.S. SARS-Coronavirus-2 cases in healthcare workers may not regularly originate from patient care: Lessons from a university hospital on the underestimated risk of healthcare worker to healthcare worker transmission. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, E.; Price, D.A.; Murphy, E.; van der Loeff, I.S.; Baker, K.F.; Lendrem, D.; Lendrem, C.; Schmid, M.L.; Pareja-Cebrian, L.; Welch, A.; et al. First experience of COVID-19 screening of health-care workers in England. Lancet 2020, 395, e77–e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, A.J.; Evans, C.; Colton, H.; Ankcorn, M.; Cope, A.; State, A.; Bennett, T.; Giri, P.; de Silva, T.I.; Raza, M. Roll-out of SARS-CoV-2 testing for healthcare workers at a large NHS Foundation Trust in the United Kingdom, March 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Overview of Testing for SARS-CoV-2, the Virus That Causes COVID-19. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/testing-overview.html (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- World Health Organization. Recommendations for National SARS-CoV-2 Testing Strategies and Diagnostic Capacities. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-lab-testing-2021.1-eng (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Carrara, E.; Ong, D.S.Y.; Hussein, K.; Keske, S.; Johansson, A.F.; Presterl, E.; Tsioutis, C.; Tschudin-Sutter, S.; Tacconelli, E. ESCMID guidelines on testing for SARS-CoV-2 in asymptomatic individuals to prevent transmission in the health care setting. Clin.Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivett, L.; Sridhar, S.; Sparkes, D.; Routledge, M.; Jones, N.K.; Forrest, S.; Young, J.; Pereira-Dias, J.; Hamilton, W.L.; Ferris, M.; et al. Screening of healthcare workers for SARS-CoV-2 highlights the role of asymptomatic carriage in COVID-19 transmission. Elife 2020, 9, e58728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarnieri, V.; Moriondo, M.; Giovannini, M.; Lodi, L.; Ricci, S.; Pisano, L.; Barbacci, P.; Bini, C.; Indolfi, G.; Zanobini, A.; et al. Surveillance on Healthcare Workers During the First Wave of SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic in Italy: The Experience of a Tertiary Care Pediatric Hospital. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 644702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabs, J.M.; Schwabe, A.; Wollkopf, A.D.; Gebel, B.; Stadelmaier, J.; Erdmann, S.; Radicke, F.; Grundmann, H.; Kramer, A.; Monsef, I.; et al. The role of routine SARS-CoV-2 screening of healthcare-workers in acute care hospitals in 2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, Y.; Komazawa, H.; Oikawa, J.; Furuta, Y. Hospital-wide antigen screening for coronavirus disease in a tertiary reference center in Sapporo, Japan A single-center observational study. Medicine 2021, 100, E28398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, A.; Consonni, D.; Carugno, M.; Bozzi, G.; Mangioni, D.; Muscatello, A.; Castelli, V.; Palomba, E.; Cantù, A.P.; Ceriotti, F.; et al. Characteristics of 1573 healthcare workers who underwent nasopharyngeal swab testing for SARS-CoV-2 in Milan, Lombardy, Italy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1413.e9–1413.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanrath, A.T.; Schim van der Loeff, I.; Lendrem, D.W.; Baker, K.F.; Price, D.A.; McDowall, P.; McDowall, K.; Cook, S.; Towns, P.; Schwab, U.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Testing of 11,884 Healthcare Workers at an Acute NHS Hospital Trust in England: A Retrospective Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 636160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyllie, A.L.; Fournier, J.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Campbell, M.; Tokuyama, M.; Vijayakumar, P.; Geng, B.; Muenker, M.C.; Moore, A.; Vogels, C.; et al. Saliva or Nasopharyngeal Swab Specimens for Detection of SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standard Biotools Inc. Advanta Dx SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Assay. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/141541/download (accessed on 20 October 2022).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control Data on Testing for COVID-19 by Week and Country. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/covid-19-testing (accessed on 14 October 2022).
- Baggio, S.; Spechbach, H.; Vernaz, N.; Guessous, I.; Gétaz, L.; Kaiser, L.; Chappuis, F.; Salamun, J.; Jacquerioz, F. SARS-CoV-2 testing strategy: A comparison of restricted and extended strategies in a Swiss outpatient cohort from the community and hospital employees. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassly, N.C.; Pons-Salort, M.; Parker, E.P.K.; White, P.J.; Ferguson, N.M. Comparison of molecular testing strategies for COVID-19 control: A mathematical modelling study. LancetInfect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, J.R.M.; Bailey, C.; Przewrocka, J.; Dijkstra, K.K.; Swanton, C. COVID-19: The case for health-care worker screening to prevent hospital transmission. Lancet 2020, 395, 1418–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.; Wu, Y.; Mei, S.; Ye, C.; Zou, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wei, L.; Truelove, S.A.; Zhang, T.; et al. Epidemiology and transmission of COVID-19 in 391 cases and 1286 of their close contacts in Shenzhen, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, L.-M.; Wan, L.; Xiang, T.-X.; Le, A.; Liu, J.-M.; Peiris, M.; Poon, L.L.M.; Zhang, W. Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 656–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, L.; Wymant, C.; Kendall, M.; Zhao, L.; Nurtay, A.; Abeler-Dörner, L.; Parker, M.; Bonsall, D.; Fraser, C. Quantifying SARS-CoV-2 transmission suggests epidemic control with digital contact tracing. Science 2020, 368, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Lau, E.H.Y.; Wu, P.; Deng, X.; Wang, J.; Hao, X.; Lau, Y.C.; Wong, J.Y.; Guan, Y.; Tan, X.; et al. Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.A.; Quandelacy, T.M.; Kada, S.; Prasad, P.V.; Steele, M.; Brooks, J.T.; Slayton, R.B.; Biggerstaff, M.; Butler, J.C. SARS-CoV-2 Transmission from People without COVID-19 Symptoms. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.; Agnew, E.; Vynnycky, E.; Stimson, J.; Bhattacharya, A.; Rooney, C.; Warne, B.; Robotham, J. The impact of testing and infection prevention and control strategies on within-hospital transmission dynamics of COVID-19 in English hospitals. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 376, 20200268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treibel, T.A.; Manisty, C.; Burton, M.; McKnight, Á.; Lambourne, J.; Augusto, J.B.; Couto-Parada, X.; Cutino-Moguel, T.; Noursadeghi, M.; Moon, J.C. COVID-19: PCR screening of asymptomatic health-care workers at London hospital. Lancet 2020, 395, 1608–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennelly, K.; Whalen, C.C. Asymptomatic health-care worker screening during the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2020, 396, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Characteristics of Health Care Personnel with COVID-19—United States, February 12–April 9, 2020. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 477–481. [CrossRef]
- NPHO Daily report for COVID-19 surveillance until April 7th 2022. Available online: https://eody.gov.gr/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/covid-gr-daily-report-20220407.pdf (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Reid, R.J.; Rosella, L.; Milijasevic, N.; Small, L.N. Mass testing for asymptomatic COVID-19 infection among health care workers at a large canadian hospital. J. Assoc. Med. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Canada 2020, 5, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluytmans-van den Bergh, M.F.Q.; Buiting, A.G.M.; Pas, S.D.; Bentvelsen, R.G.; van den Bijllaardt, W.; van Oudheusden, A.J.G.; van Rijen, M.M.L.; Verweij, J.J.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; Kluytmans, J.A.J.W. Prevalence and Clinical Presentation of Health Care Workers With Symptoms of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 2 Dutch Hospitals During an Early Phase of the Pandemic. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e209673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, A.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Guo, H.; Hao, X.; Wang, Q.; Huang, J.; He, N.; Yu, H.; Lin, X.; et al. Association of Public Health Interventions with the Epidemiology of the COVID-19 Outbreak in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020, 323, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaska, S.; Pilalas, D.; Takardaki, A.; Koutra, P.; Parasidou, E.; Gkeka, I.; Tychala, A.; Meletis, G.; Fyntanidou, B.; Metallidis, S.; et al. Evaluation of the AdvantaDx SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR Assay, a High-Throughput Extraction-Free Diagnostic Test for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in Saliva: A Diagnostic Accuracy Study. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.H.; Allicock, O.; Armstrong-Hough, M.; Wyllie, A.L. Saliva as a gold-standard sample for SARS-CoV-2 detection. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.A.; Herigon, J.C.; Benedetti, A.; Pollock, N.R.; Denkinger, C.M.; Scholar, G. Performance of Saliva, Oropharyngeal Swabs, and Nasal Swabs. J. ClinMicrobiol. 2021, 59, e02881-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Taltavull, D.; Castelo-Szekely, V.; Murugan, S.; Hamley, J.I.D.; Rollenske, T.; Ganal-Vonarburg, S.C.; Büchi, I.; Keogh, A.; Li, H.; Salm, L.; et al. Regular testing of asymptomatic healthcare workers identifies cost-efficient SARS-CoV-2 preventive measures. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
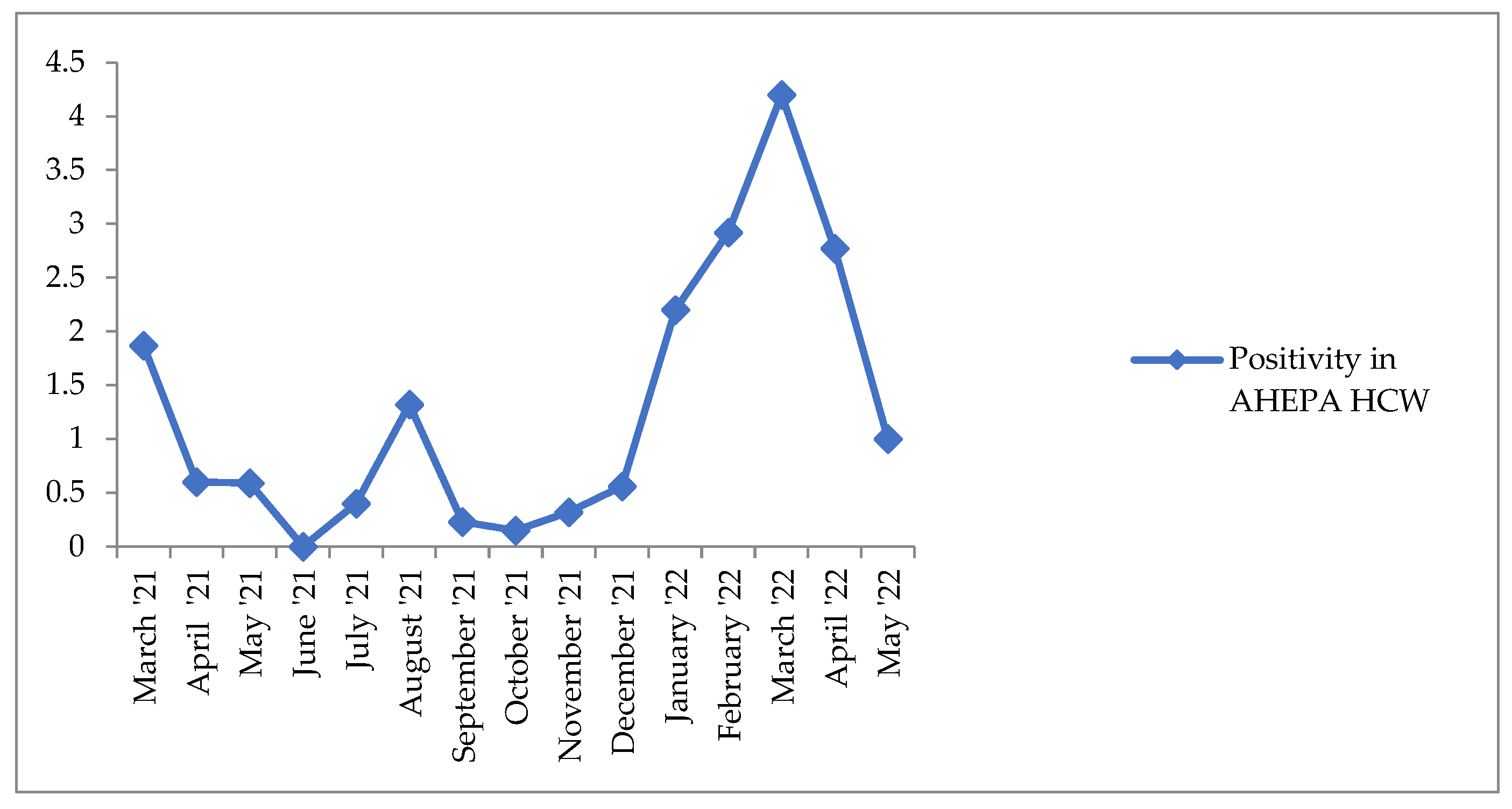
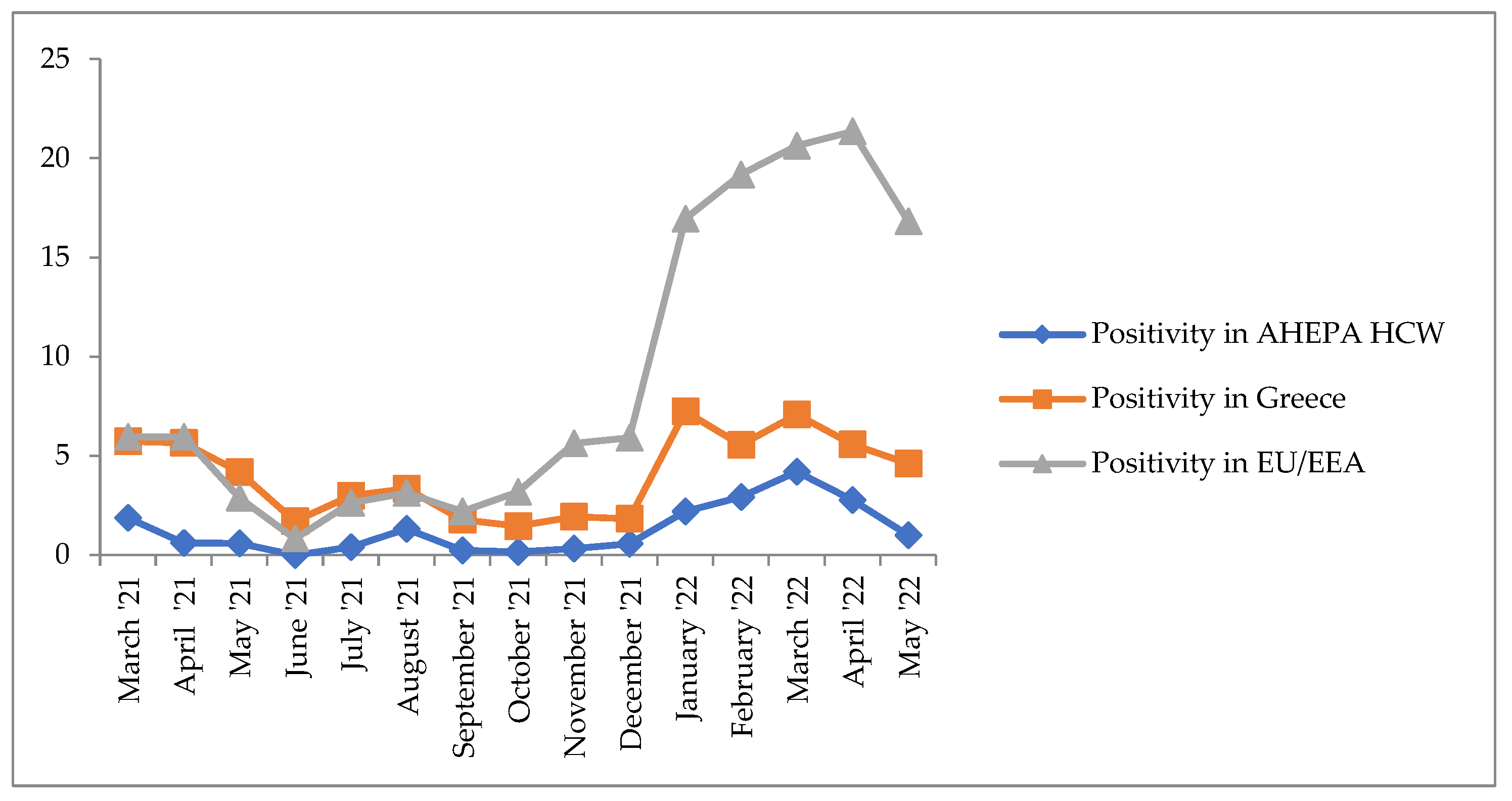
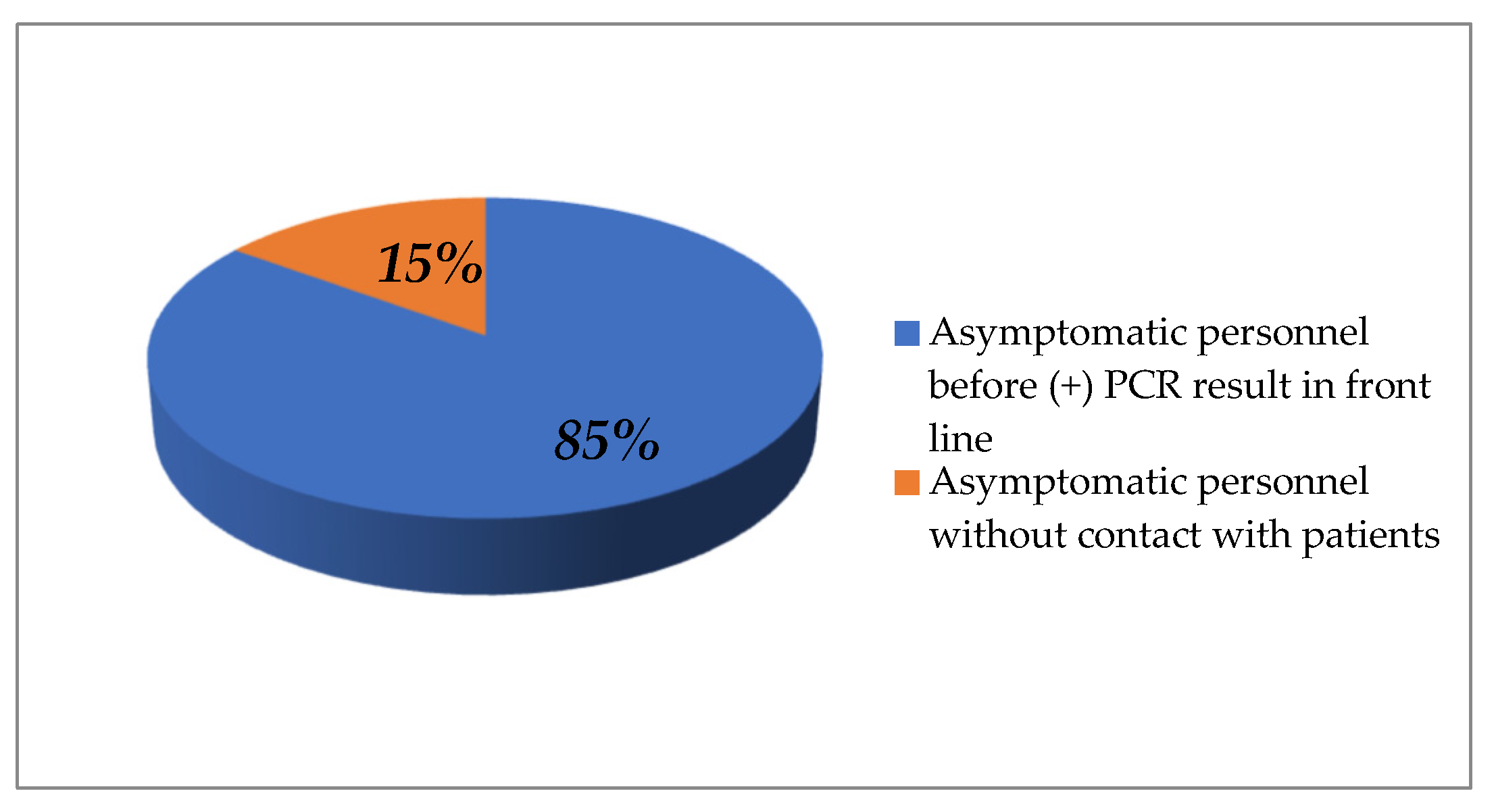
| Saliva Samples/Month | March 2021 | April 2021 | May 2021 | June 2021 | July 2021 | August 2021 | September 2021 | October 2021 | November 2021 | December 2021 | January 2022 | February 2022 | March 2022 | April 2022 | May 2022 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | 367 | 2611 | 1344 | 369 | 252 | 450 | 1292 | 3401 | 4966 | 4643 | 4699 | 4555 | 4765 | 3373 | 3468 | 40,555 |
| Positive | 7 | 16 | 8 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 16 | 26 | 107 | 137 | 209 | 96 | 35 | 672 |
| Total | 374 | 2627 | 1352 | 369 | 253 | 456 | 1295 | 3406 | 4982 | 4669 | 4806 | 4692 | 4974 | 3469 | 3493 | 41,217 |
| Saliva Samples/Month | March 2021 | April 2021 | May 2021 | June 2021 | July 2021 | August 2021 | September 2021 | October 2021 | November 2021 | December 2021 | January 2022 | February 2022 | March 2022 | April 2022 | May 2022 | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positivity Rate % | 1.87 | 0.6 | 0.59 | 0 | 0.4 | 1.32 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.32 | 0.56 | 2.20 | 2.92 | 4.20 | 2.77 | 1.00 | 1.28 |
| Reply | Front Line Personnel | Contact with Suspected or Positive Patient | Related COVID-19 Symptoms | Symptoms before Positive PCR Result | Contact with Positive Family Member | Contact with Positive Person at Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | 103 (80.5%) | 90 (70.3%) | 107 (83.6%) | 88 (69%) | 42 (32.8%) | 59 (46.1%) |
| No | 25 (19.5%) | 38 (29.7%) | 21 (16.4%) | 40 (31%) | 86 (67.2%) | 65 (52.4%) |
| Total | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 124 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Balaska, S.; Parasidou, E.; Takardaki, A.; Koutra, P.; Chrysafi, D.; Tychala, A.; Metallidis, S.; Meletis, G.; Skoura, L. The Implementation of a Health Care Worker Screening Program Based on the Advanta RT-qPCR Saliva Assay in a Tertiary Care Referral Hospital in Northern Greece. Life 2022, 12, 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122011
Balaska S, Parasidou E, Takardaki A, Koutra P, Chrysafi D, Tychala A, Metallidis S, Meletis G, Skoura L. The Implementation of a Health Care Worker Screening Program Based on the Advanta RT-qPCR Saliva Assay in a Tertiary Care Referral Hospital in Northern Greece. Life. 2022; 12(12):2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122011
Chicago/Turabian StyleBalaska, Sofia, Eleftheria Parasidou, Anna Takardaki, Paraskevoula Koutra, Dimitra Chrysafi, Areti Tychala, Simeon Metallidis, Georgios Meletis, and Lemonia Skoura. 2022. "The Implementation of a Health Care Worker Screening Program Based on the Advanta RT-qPCR Saliva Assay in a Tertiary Care Referral Hospital in Northern Greece" Life 12, no. 12: 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122011
APA StyleBalaska, S., Parasidou, E., Takardaki, A., Koutra, P., Chrysafi, D., Tychala, A., Metallidis, S., Meletis, G., & Skoura, L. (2022). The Implementation of a Health Care Worker Screening Program Based on the Advanta RT-qPCR Saliva Assay in a Tertiary Care Referral Hospital in Northern Greece. Life, 12(12), 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12122011









