Safety and Efficacy of Rivaroxaban as Extended-Phase Anticoagulation in Patients with Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism: A Preliminary Data Analysis from the Mac Project
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
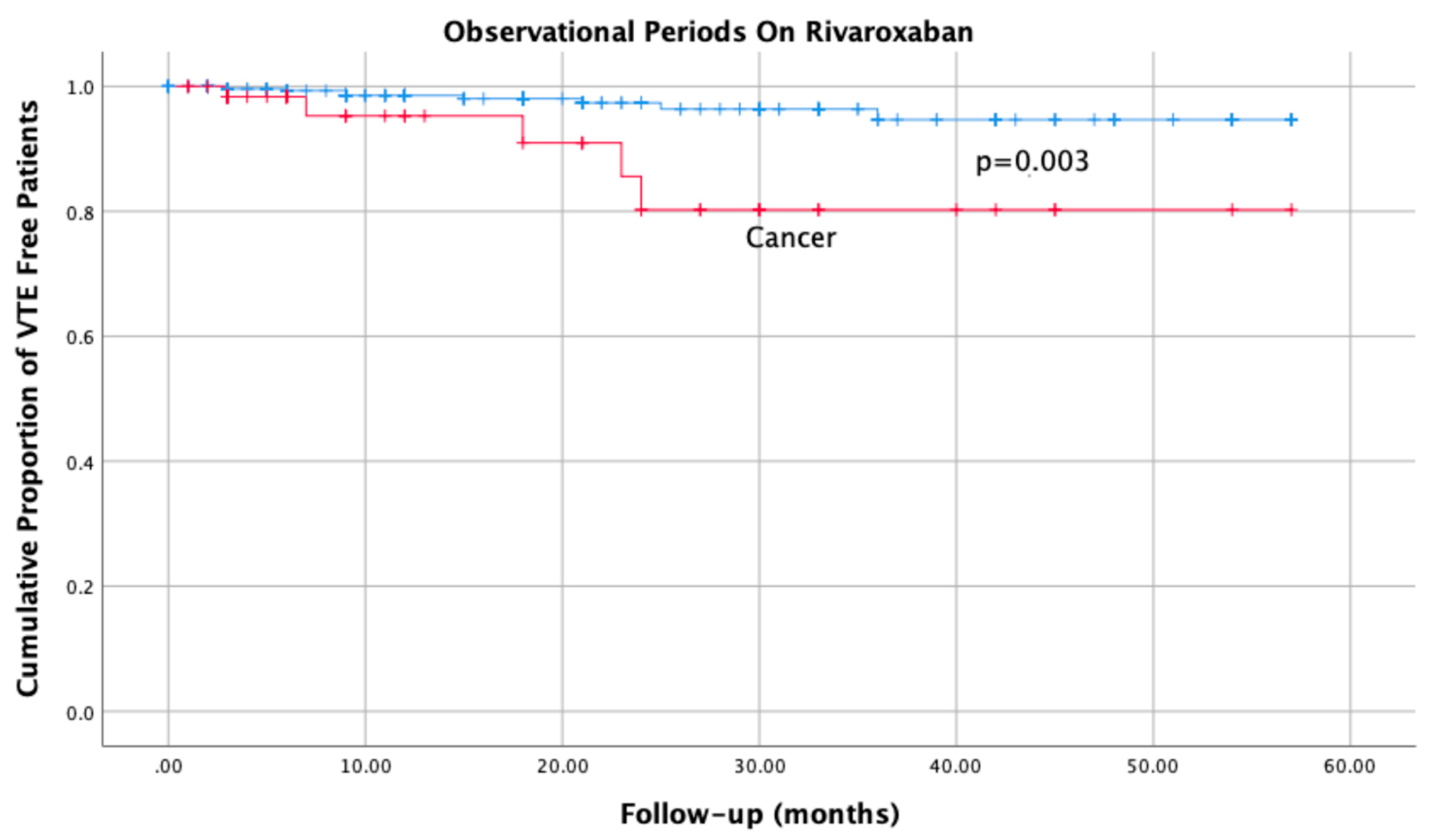
4.1. Primary Efficacy Outcome
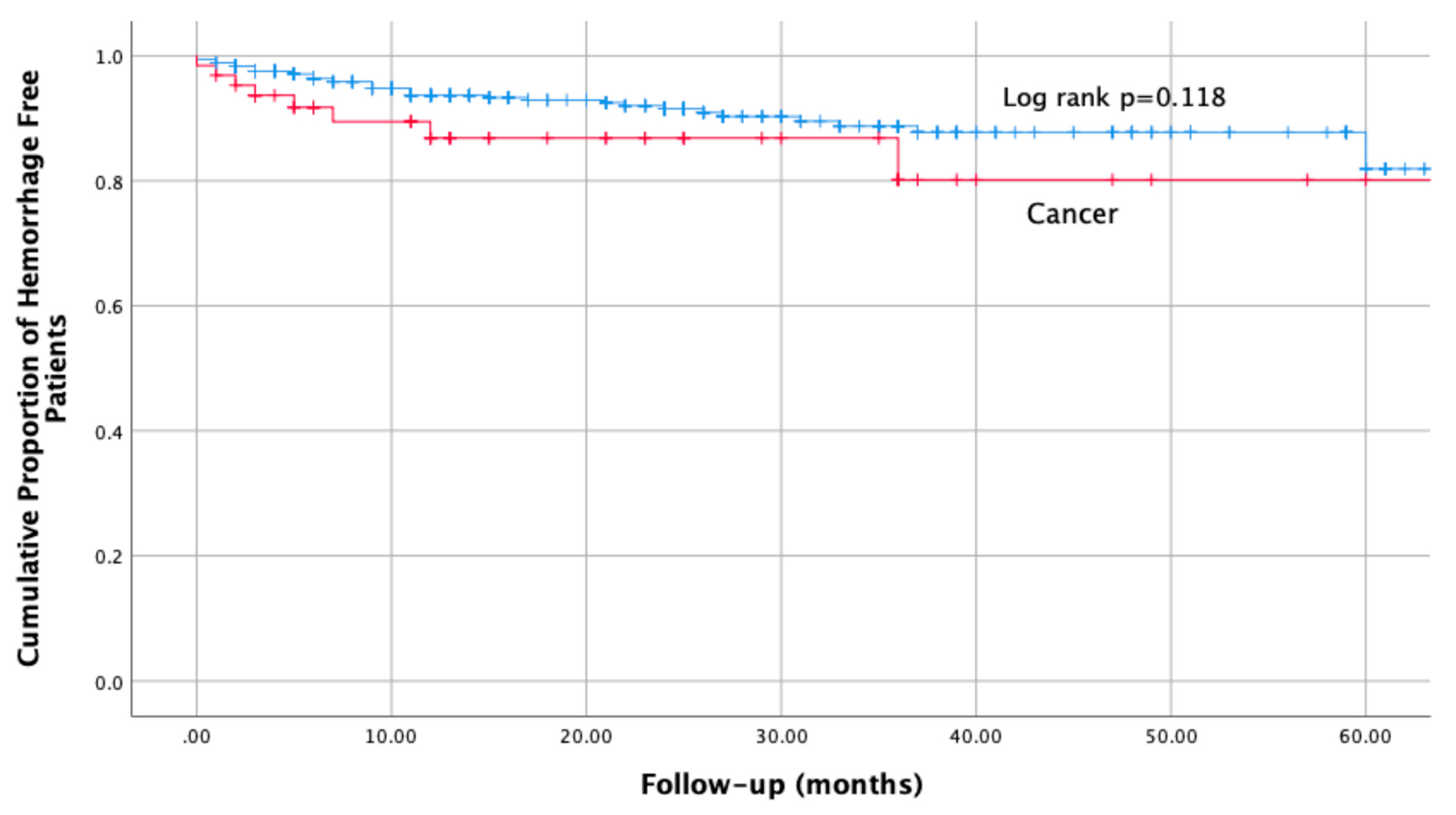
4.2. Primary Safety Outcome
4.3. Additional Observations
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prandoni, P.; Lensing, A.W.; Piccioli, A.; Bernardi, E.; Simioni, P.; Girolami, B.; Marchiori, A.; Sabbion, P.; Prins, M.H.; Noventa, F.; et al. Recurrent venous thromboembolism and bleeding complications during anticoagulant treatment in patients with cancer and venous thrombosis. Blood 2002, 100, 3484–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.Y.; Levine, M.N.; Baker, R.I.; Bowden, C.; Kakkar, A.K.; Prins, M.; Rickles, F.R.; Julian, J.A.; Haley, S.; Kovacs, M.J.; et al. Low-molecular-weight heparin versus a coumarin for the prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, R.D.; Pineo, G.F.; Brant, R.F.; Mah, A.F.; Burke, N.; Dear, R.; Wong, T.; Cook, R.; Solymoss, S.; Poon, M.C.; et al. Long-term low-molecular-weight heparin versus usual care in proximal-vein thrombosis patients with cancer. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahale, L.A.; Hakoum, M.B.; Tsolakian, I.G.; Matar, C.F.; Terrenato, I.; Sperati, F.; Barba, M.; Yosuico, V.E.; Schünemann, H.; Akl, E.A. Anticoagulation for the long-term treatment of venous thromboembolism in people with cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 6, CD006650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.; Hull, R.D.; Brant, R.; Pineo, G.F. Lower mortality in cancer patients treated with low-molecular-weight versus standard heparin. Lancet 1992, 339, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.Y.; Rickles, F.R.; Julian, J.A.; Gent, M.; Baker, R.I.; Bowden, C.; Kakkar, A.K.; Prins, M.; Levine, M.N. Randomized comparison of low molecular weight heparin and coumarin derivatives on the survival of patients with cancer and venous thromboembolism. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Garcia, D.A.; Lyman, G.H.; Carrier, M. Direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) versus low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) for treatment of cancer associated thrombosis (CAT): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb. Res. 2019, 173, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, A.A.; McCrae, K.R.; Milentijevic, D.; Fortier, J.; Nelson, W.W.; Laliberté, F.; Crivera, C.; Lefebvre, P.; Yannicelli, D.; Schein, J. Current practice patterns and patient persistence with anticoagulant treatments for cancer-associated thrombosis. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 1, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.M.; Marshall, A.; Thirlwall, J.; Chapman, O.; Lokare, A.; Hill, C.; Hale, D.; Dunn, J.A.; Lyman, G.H.; Hutchinson, C.; et al. Comparison of an Oral Factor Xa Inhibitor With Low Molecular Weight Heparin in Patients With Cancer With Venous Thromboembolism: Results of a Randomized Trial (SELECT-D). J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnelli, G.; Becattini, C.; Meyer, G.; Muñoz, A.; Huisman, M.V.; Connors, J.M.; Cohen, A.; Bauersachs, R.; Brenner, B.; Torbicki, A.; et al. Apixaban for the Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism Associated with Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1599–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskob, G.E.; van Es, N.; Verhamme, P.; Carrier, M.; Di Nisio, M.; Garcia, D.; Grosso, M.A.; Kakkar, A.K.; Kovacs, M.J.; Mercuri, M.F.; et al. Edoxaban for the Treatment of Cancer-Associated Venous Thromboembolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBane, R.D., 2nd; Wysokinski, W.E.; Le-Rademacher, J.G.; Zemla, T.; Ashrani, A.; Tafur, A.; Perepu, U.; Anderson, D.; Gundabolu, K.; Kuzma, C.; et al. Apixaban and dalteparin in active malignancy-associated venous thromboembolism: The ADAM VTE trial. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 18, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giustozzi, M.; Agnelli, G.; Del Toro-Cervera, J.; Klok, F.A.; Rosovsky, R.P.; Martin, A.C.; Herold, J.; Tzoran, I.; Szmit, S.; Bertoletti, L.; et al. Direct Oral Anticoagulants for the Treatment of Acute Venous Thromboembolism Associated with Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, F.I.; Bosch, F.T.M.; Young, A.M.; Marshall, A.; McBane, R.D.; Zemla, T.J.; Carrier, M.; Kamphuisen, P.W.; Bossuyt, P.M.M.; Büller, H.R.; et al. Direct oral anticoagulants for cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood 2020, 136, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyman, G.H.; Carrier, M.; Ay, C.; Di Nisio, M.; Hicks, L.K.; Khorana, A.A.; Leavitt, A.D.; Lee, A.Y.Y.; Macbeth, F.; Morgan, R.L.; et al. American Society of Hematology 2021 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: Prevention and treatment in patients with cancer. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 927–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camporese, G.; Bernardi, E.; Bortoluzzi, C.; Noventa, F.; Hong, N.V.; Callegari, E.; Villalta, S.; Tonello, C.; Nardin, M.; Campello, E.; et al. MAC Project-Monitoring Anticoagulant Therapy Observational Study: Rationale and Protocol. Front. Med. 2021, 7, 584459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prins, M.H.; Lensing, A.W.; Brighton, T.A.; Lyons, R.M.; Rehm, J.; Trajanovic, M.; Davidson, B.L.; Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Pap, Á.F.; Berkowitz, S.D.; et al. Oral rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin with vitamin K antagonist for the treatment of symptomatic venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer (EINSTEIN-DVT and EINSTEIN-PE): A pooled subgroup analysis of two randomized controlled trials. Lancet Haematol. 2014, 1, e37–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, S.M.; Woller, S.C.; Kreuziger, L.B.; Bounameaux, H.; Doerschug, K.; Geersing, G.J.; Huisman, M.V.; Kearon, C.; King, C.S.; Knighton, A.J.; et al. Antithrombotic Therapy for VTE Disease: Second Update of the CHEST Guideline and Expert Panel Report. Chest 2021, 160, e545–e608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søgaard, M.; Nielsen, P.B.; Skjøth, F.; Kjaeldgaard, J.N.; Larsen, T.B. Risk of recurrence and bleeding in patients with cancer-associated venous thromboembolism treated with rivaroxaban: A nationwide cohort study. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soff, G.A.; Mones, J.; Wilkins, C.; Devlin, S.; Haegler-Laube, E.; Wills, J.; Sarasohn, D.M.; Juluru, K.; Singer, M.; Miao, Y.; et al. Rivaroxaban treatment of cancer-associated venous thromboembolism: Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center institutional experience. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 3, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitz, J.I.; Lensing, A.W.A.; Prins, M.H.; Bauersachs, R.; Beyer-Westendorf, J.; Bounameaux, H.; Brighton, T.A.; Cohen, A.T.; Davidson, B.L.; Decousus, H.; et al. Rivaroxaban or Aspirin for Extended Treatment of Venous Thromboembolism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prins, M.H.; Lensing, A.W.; Bauersachs, R.; van Bellen, B.; Bounameaux, H.; Brighton, T.A.; Cohen, A.T.; Davidson, B.L.; Decousus, H.; Raskob, G.E.; et al. Oral rivaroxaban versus standard therapy for the treatment of symptomatic venous thromboembolism: A pooled analysis of the EINSTEIN-DVT and PE randomized studies. Thromb. J. 2013, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Cancer Status | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Variables at Baseline | Absent, n = 540 | Present, n = 64 | p |
| Age, years | 64.7 (16.4) | 71.3 (12.0) | 0.002 |
| Weight, kg | 74.9 (13.7) | 69.3 (14.8) | 0.002 |
| Sex (female) | 48.3% | 56.3% | NS |
| Previous venous thromboembolism | 39.6% | 31.3% | NS |
| Previous major haemorrhage A | 2% | 1.6% | NS |
| Heart failure | 1.7% | 0.0% | NS |
| COPD | 2.2% | 3.1% | NS |
| Diabetes | 8.2% | 9.4% | NS |
| Current smoker | 15.4% | 4.7% | 0.022 |
| Hormonal treatment B | 3.5% | 4.7% | NS |
| Antiplatelets / NSAIDS before inclusion | 12.3% | 12.7% | NS |
| Anticoagulation before inclusion C | 35.5% | 46.9% | 0.099 |
| Follow-up, months | 19.8 (16.2) | 18.8 (16.1) | NS |
| Creatinine clearance, mL/min | 79.1 (33.3) | 61.6 (25.1) | 0.001 |
| Haemoglobin levels, g/L | 136.9 (18.1) | 127.7 (15.9) | 0.001 |
| Hematocrit, % | 41.4 (4.7) | 38.4 (5.2) | 0.001 |
| Platelets, ×109/L | 236.9 (73.9) | 244.8 (92.2) | NS |
| Alanine Aminotransferase, U/L | 23.9 (18.9) | 23.1 (16.6) | NS |
| International normalised ratio | 1.2 (0.4) | 1.1 (0.4) | NS |
| APTT, seconds | 29.5 (11.8) | 24.9 (6.3) | 0.045 |
| Active Cancer at Baseline | ||
|---|---|---|
| Site of Bleeding, n. (%) | Yes, n = 64 | No, n = 540 |
| Intracranial | 2 (3.1) | 2 (0.4) |
| Intraocular | 0 | 1 (0.2) |
| Upper gastrointestinal | 2 (3.1) | 5 (0.9) |
| Lower gastrointestinal | 1 (1.6) | 7 (1.3) |
| Vaginal | 0 | 11 (2.0) |
| Urinary | 4 (6.2) | 2 (0.4) |
| Epistaxis | 0 | 3 (0.6) |
| Gingival | 0 | 2 (0.4) |
| Muscular | 1 (1.6) | 5 (0.9) |
| Other | 2 (3.1) | 2 (0.4) |
| Total A | 12 (18.7) | 40 (7.4) |
| Active Cancer | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 6-month outcome A | MAC study | Select-D [9] | Einstein pooled, cancer patients [17] |
| Recurrent VTE | 5.5 (0.0 to 11.6) | 3.9 (1.7 to 7.6) | 4.5 (2.6 to 7.2) |
| Major bleeding | 5.3 (0.0 to 11.2) | 2.9 (1.1 to 6.3) | 2.3 (0.9 to 4.4) |
| NMCRB B | 4.1 (0.0 to 9.8) | 3.5 (1.4 to 6.9) | 13.6 (10.2 to 17.6) |
| No Cancer | |||
| 6-month outcome A | MAC study | Einstein pooled, main study [22] | Einstein pooled, cancer patients [17] C |
| Recurrent VTE | 1.8 (0.6 to 3.0) | 2.1 (1.7 to 2.6) | 1.8 (1.4 to 2.3) |
| Major bleeding | 1.3 (0.3 to 2.3) | 2.3 (1.8 to 2.8) | 1.5 (0.1 to 1.9) |
| NMCRB B | 2.0 (0.8 to 3.2) | 7.2 (6.4 to 8.0) | 8.9 (7.9 to 9.8) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernardi, E.; Camporese, G.; Bortoluzzi, C.; Noventa, F.; Ceccato, D.; Tonello, C.; Vohong, S.; Campello, E.; Simion, C.; Imbalzano, E.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Rivaroxaban as Extended-Phase Anticoagulation in Patients with Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism: A Preliminary Data Analysis from the Mac Project. Life 2022, 12, 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12111725
Bernardi E, Camporese G, Bortoluzzi C, Noventa F, Ceccato D, Tonello C, Vohong S, Campello E, Simion C, Imbalzano E, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Rivaroxaban as Extended-Phase Anticoagulation in Patients with Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism: A Preliminary Data Analysis from the Mac Project. Life. 2022; 12(11):1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12111725
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernardi, Enrico, Giuseppe Camporese, Cristiano Bortoluzzi, Franco Noventa, Davide Ceccato, Chiara Tonello, Stefania Vohong, Elena Campello, Chiara Simion, Egidio Imbalzano, and et al. 2022. "Safety and Efficacy of Rivaroxaban as Extended-Phase Anticoagulation in Patients with Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism: A Preliminary Data Analysis from the Mac Project" Life 12, no. 11: 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12111725
APA StyleBernardi, E., Camporese, G., Bortoluzzi, C., Noventa, F., Ceccato, D., Tonello, C., Vohong, S., Campello, E., Simion, C., Imbalzano, E., Di Micco, P., Callegari, E., & Simioni, P. (2022). Safety and Efficacy of Rivaroxaban as Extended-Phase Anticoagulation in Patients with Cancer and Venous Thromboembolism: A Preliminary Data Analysis from the Mac Project. Life, 12(11), 1725. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12111725








